Griffin (processor) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 AMD Turion is the
AMD Turion is the
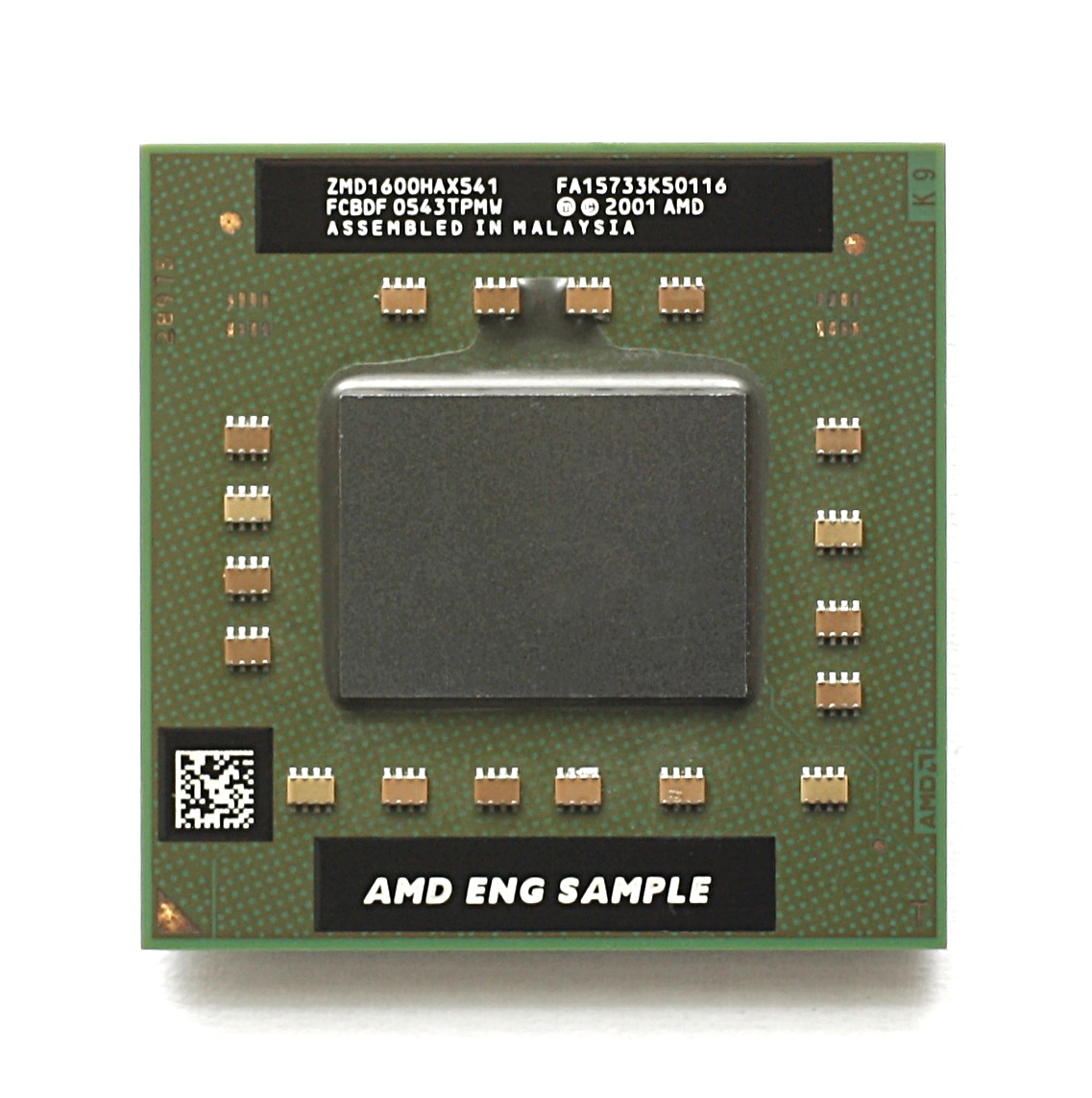 Turion 64 X2 is
Turion 64 X2 is
/ref> The Turion X2 Ultra processor, unlike earlier Turions, implements three voltage planes: one for the northbridge and one for each core. This, along with multiple
 * Dual
* Dual
AMD official website
Reuters news report on the announcement of the chips
PCworld Turion based notebooks review
Acer Aspire 5020 Series Review from www.notebookreview.com
Detailed review at www.anandtech.com
The Register : AMD, IBM "stress" silicon for 65nm process, by Tony Smith
Article from ExtremeTech: AMD Adds Second Core To Turion Notebook Chip
* http://support.amd.com/us/psearch/Pages/psearch.aspx?type=2.2%3b2.3&product=2.2.8&contentType=Tech+Doc+Embedded&ostype=&keywords=&items=20 {{AMD processors AMD x86 microprocessors Computer-related introductions in 2004
 AMD Turion is the
AMD Turion is the brand name
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's goods or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create and ...
AMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that de ...
applies to its x86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set architecture, instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new ope ...
low-power consumption mobile processor
A mobile processor is a microprocessor designed for mobile devices such as laptops and cell phones.
A CPU chip is designed for portable computers to run fanless, under 10 to 15W, which is cool enough without a fan. It is typically housed in a s ...
s codenamed ''K8L''. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel's mobile processors, initially the ''Pentium M
The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit single-core x86 microprocessors (with the modified Intel P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture) introduced in March 2003 and forming a part of the Intel Centrino#Carmel platform (2003), Carmel no ...
'' and the Intel Core
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors ...
and Intel Core 2
Intel Core 2 is a processor family encompassing a range of Intel's mainstream 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single- die, whereas the quad-co ...
processors.
Features
Turion 64
Earliest Turion 64 processors are plugged into AMD'sSocket 754
Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to supersede its Athlon XP platform ( Socket A, also referred to as Socket 462). Socket 754 was one of the first sockets developed by AMD to support their new 64-bit microprocessor family kn ...
. They are equipped with 512 or 1024 KiB of L2 cache, a 64-bit single channel on-die DDR-400 memory controller, and an 800 MHz HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
bus. Battery saving features, like ''PowerNow!
__NOTOC__
AMD PowerNow! is AMD's dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology for laptop processors. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduc ...
'', are central to the marketing and usefulness of these CPUs. The newer "Richmond" models are designed for AMD's Socket S1
Socket S1 is the CPU socket type used by AMD for their Turion 64, Athlon 64 Mobile, Phenom II Mobile and later Sempron processors, which debuted with the dual-core Turion 64 X2 CPUs on May 17, 2006.
Technical specifications
Socket S1 is a 638 p ...
and have a double-channel DDR2 controller.
Turion 64 X2
 Turion 64 X2 is
Turion 64 X2 is AMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that de ...
's 64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit central processing units (CPU) and arithmetic logic units (ALU) are those that are based on processor registers, a ...
dual-core
A multi-core processor (MCP) is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit (IC) with two or more separate central processing units (CPUs), called ''cores'' to emphasize their multiplicity (for example, ''dual-core'' or ''quad-core''). Ea ...
mobile CPU, intended to compete with Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
's Core
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (laboratory), a highly specialized shared research resource
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber ...
and Core 2
Intel Core 2 is a processor family encompassing a range of Intel's mainstream 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single- die, whereas the quad-c ...
CPUs. The Turion 64 X2 was launched on May 17, 2006, after several delays. These processors use Socket S1
Socket S1 is the CPU socket type used by AMD for their Turion 64, Athlon 64 Mobile, Phenom II Mobile and later Sempron processors, which debuted with the dual-core Turion 64 X2 CPUs on May 17, 2006.
Technical specifications
Socket S1 is a 638 p ...
and feature DDR2 memory. They also include AMD Virtualization Technology and more power-saving features.
The earlier 90 nm devices were codename
A code name, codename, call sign, or cryptonym is a code word or name used, sometimes clandestinely, to refer to another name, word, project, or person. Code names are often used for military purposes, or in espionage. They may also be used in ...
d Taylor and Trinidad, while the newer 65 nm cores have codename Tyler.
Turion X2 Ultra
Turion X2 Ultra (codenamed ''Griffin'') is the first processor family fromAMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that de ...
solely for the mobile platform, based on the Athlon 64
The Athlon 64 is a ninth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name ''Athlon'', and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. ...
(K8 Revision G) architecture with some specific architectural enhancements similar to current Phenom processors aimed at lower power consumption and longer battery life. The Turion Ultra processor was released as part of the "'' Puma''" mobile platform in June 2008.
The Turion X2 Ultra is a dual-core processor fabricated on 65 nm
The 65 nm process is an advanced lithographic node used in volume CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor fabrication. Printed linewidths (i.e. transistor gate lengths) can reach as low as 25 nm on a nominally 65 nm process, while the pitch bet ...
technology using 300 mm SOI wafers. It supports DDR2-800 SO-DIMM
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is a popular type of memory module used in computers. It is a printed circuit board with one or both sides (front and back) holding DRAM chips and pins. The vast majority of DIMMs are manufactured in compli ...
s and features a DRAM prefetcher to improve performance and a mobile-enhanced northbridge (memory controller, HyperTransport controller, and crossbar switch). Each processor core comes with 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
L2 cache for a total of 2 MiB L2 cache for the entire processor. This is double the L2 cache found on the Turion 64 X2 processor. Clock rates range from 2.0 GHz to 2.4 GHz, and thermal design power (TDP) range from 32 watts to 35 watts.AMD mobile CPU roadmap at Engadget/ref> The Turion X2 Ultra processor, unlike earlier Turions, implements three voltage planes: one for the northbridge and one for each core. This, along with multiple
phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and ou ...
s (PLL), allows one core to alter its voltage and operating frequency independently of the other core, and independently of the northbridge. Indeed, in a matter of microseconds, the processor can switch to one of 8 frequency levels and one of 5 voltage levels. By adjusting frequency and voltage during use, the processor can adapt to different workloads and help reduce power consumption. It can operate as low as 250 MHz to conserve power during light use.
Additionally, the processor features deep sleep state C3, deeper sleep state C4 (AltVID), and HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
3.0 up to 2.6 GHz, or up to 41.6 GB/s bandwidth per link at 16-bit link width and dynamic scaling of HT link width down to 0-bit ("disconnected") in both directions from and to the chipset
In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components on one or more integrated circuits that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. The chipset is usually found on the motherboard of computers. Chips ...
for four different usage scenarios. It also implements multiple on-die thermal sensors through integrated SMBUS (SB-TSI) interface (replaces and eliminates the thermal monitor circuit chip through SMBUS in its predecessors) with additional MEMHOT signal sent from embedded controller to the processor, and reduces memory temperature.
The Turion X2 Ultra processor uses the same socket S1 as its predecessor, Turion 64 X2
AMD Turion is the brand name AMD applies to its x86-64 low-power consumption mobile processors codenamed ''K8L''. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel Corporation, Intel's mobile processors, initially the ''Pentium ...
, but the pinout is different. It is designed to work with the RS780M chipset.
Given the above enhancements on the architecture, the cores were minimally modified and are based on the K8 instead of the K10 microarchitecture. AMD Fellow Maurice Steinman has said the cores are almost transistor-for-transistor identical to those found in the 65 nm Turion 64 X2 processors.
Turion II Ultra
Turion II Ultra (codenamed ''Caspian'') is the mobile version of the K10.5 architecture produced using 45 nm fabrication process, also known by its desktop variant ''Regor''. It is a dual core processor, and features clock speeds from 2.4 GHz to 2.7 GHz, 2 MB total L2 cache (1 MB per core), HyperTransport at 3.6 GT/s, and a 128 bit FPU. It maintains a TDP of 35W from its predecessor Turion X2 Ultra (codenamed ''Griffin'').Turion II
Turion II is identical to Turion II Ultra, except that the Turion II features only 1 MB of L2 cache (512 KB per core), and lower clock speeds ranging from 2.2 GHz to 2.6 GHz.Model naming methodology
The model naming scheme does not make it obvious how to compare one Turion with another, or even anAthlon 64
The Athlon 64 is a ninth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name ''Athlon'', and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. ...
. The model name is two letters, a dash, and a two digit number (for example, ML-34). The two letters together designate a processor class, while the number represents a performance rating
The PR (performance rating, P-rating, or Pentium rating) system was a figure of merit developed by AMD, Cyrix, IBM Microelectronics and SGS-Thomson in the mid-1990s as a method of comparing their x86 processors to those of rival Intel. The idea ...
(PR). The first letter is M for mono (single) core processors and T for twin (dual) core Turion 64 X2
AMD Turion is the brand name AMD applies to its x86-64 low-power consumption mobile processors codenamed ''K8L''. The Turion 64 and Turion 64 X2/Ultra processors compete with Intel Corporation, Intel's mobile processors, initially the ''Pentium ...
processors. The later in the alphabet that the second letter appears, the more the model has been designed for mobility (frugal power consumption). Take for instance, an MT-30 and an ML-34. Since the T in the MT-30 is later in the alphabet than the L in ML-34, the MT-30 consumes less power than the ML-34. But since 34 is greater than 30, the ML-34 is faster than the MT-30.
The release of the Turion II Ultra and Turion II lineups have simplified name methodology; all newly released Turions have the letter "M" followed by a number designating relative performance. The higher the number, the higher the clock speed. For example, the Turion II M500 has a clock speed of 2.2 GHz while the Turion II M520 has a clock speed of 2.3 GHz.
Cores
Lancaster (90 nm SOI)
* Stepping E5 * L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions) * L2 cache: 512 or 1024 KiB, full speed * MMX, Enhanced 3DNow!, SSE,SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
, SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
, AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
, PowerNow!
__NOTOC__
AMD PowerNow! is AMD's dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology for laptop processors. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduc ...
, NX Bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certai ...
* Socket 754
Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to supersede its Athlon XP platform ( Socket A, also referred to as Socket 462). Socket 754 was one of the first sockets developed by AMD to support their new 64-bit microprocessor family kn ...
, HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
(800 MHz, HT800)
* VCore:
**0.8 V - 1.2 V for MT chips
**0.8 V - 1.35 V for ML chips
* Power consumption ( TDP): 25/35 watt max
* First release: March 2005
* Clock rate: 1600, 1800, 2000, 2200, 2400 MHz
** 25W TDP:
*** MT-28: 1600 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base u ...
(512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-30: 1600 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base u ...
(1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-32: 1800 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base u ...
(512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-34: 1800 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base u ...
(1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-37: 2000 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base u ...
(1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MT-40: 2200 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base u ...
(1024 KiB L2-Cache)
** 35W TDP:
*** ML-28: 1600 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-30: 1600 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-32: 1800 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-34: 1800 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-37: 2000 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-40: 2200 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-42: 2400 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** ML-44: 2400 MHz (1024 KiB L2-Cache)
Richmond (90 nm SOI)
The models support the same features available in Lancaster, plusAMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware- ...
.
* L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions)
* L2 cache: 512 KiB, full speed
* MMX, Enhanced 3DNow!, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
, SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
, AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
, PowerNow!
__NOTOC__
AMD PowerNow! is AMD's dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology for laptop processors. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduc ...
, NX Bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certai ...
, AMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware- ...
* Socket S1
Socket S1 is the CPU socket type used by AMD for their Turion 64, Athlon 64 Mobile, Phenom II Mobile and later Sempron processors, which debuted with the dual-core Turion 64 X2 CPUs on May 17, 2006.
Technical specifications
Socket S1 is a 638 p ...
, HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
(800 MHz, HT800)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 31 watt max
* First release: September 1, 2006
* Clock rate: 2000, 2200 MHz
** 31W TDP:
*** MK-36: 2000 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
*** MK-38: 2200 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache)
Taylor & Trinidad (90 nm SOI)
 * Dual
* Dual AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
core
* Stepping F2
* L1 cache
Cache, caching, or caché may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cache (computing), a technique used in computer storage for easier data access
* Cache (biology) or hoarding, a food storing behavior of animals
* Cache (archaeology), artifacts p ...
: 64 + 64 KiB (data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
+ instructions) per core
* L2 cache: 256 KiB (''Taylor'') or 512 KiB (''Trinidad'') per core, full speed
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-667 MHz
* MMX, Extended 3DNow!
3DNow! is a deprecated extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It adds single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing of float ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
, SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
, AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
, PowerNow!
__NOTOC__
AMD PowerNow! is AMD's dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology for laptop processors. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduc ...
, NX bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certai ...
, AMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware- ...
* Socket S1
Socket S1 is the CPU socket type used by AMD for their Turion 64, Athlon 64 Mobile, Phenom II Mobile and later Sempron processors, which debuted with the dual-core Turion 64 X2 CPUs on May 17, 2006.
Technical specifications
Socket S1 is a 638 p ...
, HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
(800 MHz, 1600 MT/s, 10.7 GB/s CPU-RAM + 6.4 GB/s CPU-I/O transfer rate)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 31, 33, 35 watt max
* First release: May 17, 2006
* Clock rate: 1600, 1800, 2000, 2200 MHz
** 31W TDP:
*** TL-50: 1600 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-52: 1600 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
** 33W TDP:
*** TL-56: 1800 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
** 35W TDP:
*** TL-60: 2000 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-64: 2200 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
Tyler (65 nm SOI)
* Dual AMD64 core * Steppings G1, G2 * L1 cache: 64 + 64 KiB (data + instructions) per core * L2 cache: 256 KiB per core (All Athlon & Turion TL-50) or 512 KiB per core (All Others), full speed * Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-667 MHz (10.6 GB/s full-duplex CPU/RAM bandwidth) * 100 MHz granularity (Dynamic P-state Transitions) * MMX, Extended3DNow!
3DNow! is a deprecated extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It adds single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing of float ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
, SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
, AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
, PowerNow!
__NOTOC__
AMD PowerNow! is AMD's dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology for laptop processors. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduc ...
, NX Bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certai ...
, AMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware- ...
* Socket S1
Socket S1 is the CPU socket type used by AMD for their Turion 64, Athlon 64 Mobile, Phenom II Mobile and later Sempron processors, which debuted with the dual-core Turion 64 X2 CPUs on May 17, 2006.
Technical specifications
Socket S1 is a 638 p ...
, HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
(800 MHz / 1600 MT/s)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 31, 35 watt max.
* First release: 2007
* Clock rate: 1700, 1800, 1900, 2000, 2100, 2200, 2300, 2400 MHz
** 31W TDP:
*** TK-53 1700 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core) - ※Athlon 64 X2 Dual-Core for Notebooks
*** TK-55 1800 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core) - ※Athlon 64 X2 Dual-Core for Notebooks
*** TL-56 1800 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TK-57 1900 MHz (256 KiB L2-Cache per core) - ※Athlon 64 X2 Dual-Core for Notebooks
*** TL-58 1900 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-60 2000 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
** 35W TDP:
*** TL-62 2100 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-64 2200 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-66 2300 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
*** TL-68 2400 MHz (512 KiB L2-Cache per core)
Lion (65 nm SOI)
* DualAMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
core
* B1 Stepping
* L1 cache
Cache, caching, or caché may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cache (computing), a technique used in computer storage for easier data access
* Cache (biology) or hoarding, a food storing behavior of animals
* Cache (archaeology), artifacts p ...
: 64 + 64 KiB (data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
+ instructions) per core
** L2 cache: 512 KiB per core, full speed, or
** L2 cache: 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
per core, full speed
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-800 MHz
* MMX, Extended 3DNow!
3DNow! is a deprecated extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It adds single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing of float ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
, SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
, AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
, PowerNow!
__NOTOC__
AMD PowerNow! is AMD's dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology for laptop processors. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduc ...
, NX bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certai ...
, AMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware- ...
* Socket S1 (S1g2)
* HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
(1800 MHz, 3600 MT/s, 12.8 GB/s CPU-RAM + 14.4 GB/s CPU-I/O transfer rate)
* HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
(2200 MHz, 4400 MT/s on ZM-85 y ZM-87 only)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 32, 35 watt max
* First release: June 4, 2008
** Clock rate: 2000, 2100, 2200 MHz (RM-7x, L2 cache: 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
)
** Clock rate: 2100, 2200, 2300, 2400, 2500 MHz (ZM-8x, L2 cache: 2 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
)
** 31W TDP:
*** RM-70: 2000 MHz
** 32W TDP:
*** ZM-80: 2100 MHz
** 35W TDP:
*** RM-72: 2100 MHz
*** RM-74: 2200 MHz
*** ZM-82: 2200 MHz
*** ZM-84: 2300 MHz
*** ZM-85: 2300 MHz
*** ZM-86: 2400 MHz
*** ZM-87: 2400 MHz
*** ZM-88: 2500 MHz
Caspian (45 nm SOI)
* DualStars
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of ...
core
** L2 cache: 512 KiB per core, full speed (For Turion II, Athlon II and Sempron II), or
** L2 cache: 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
per core, full speed (For Turion II Ultra)
* Memory controller: dual channel DDR2-800 MHz
* MMX, Extended 3DNow!
3DNow! is a deprecated extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It adds single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing of float ...
, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
, SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
, SSE4a
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper;
, AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
, PowerNow!
__NOTOC__
AMD PowerNow! is AMD's dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology for laptop processors. The CPU's clock speed and VCore are automatically decreased when the computer is under low load or idle, to save battery power, reduc ...
, NX bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certai ...
, AMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware- ...
* Socket S1
Socket S1 is the CPU socket type used by AMD for their Turion 64, Athlon 64 Mobile, Phenom II Mobile and later Sempron processors, which debuted with the dual-core Turion 64 X2 CPUs on May 17, 2006.
Technical specifications
Socket S1 is a 638 p ...
g3
* HyperTransport
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer Processor (computing), processors. It is a bidirectional Serial communication, serial/Parallel communication, parallel high-Bandwi ...
(1800 MHz, 3600 MT/s on M6xx/M5xx models, 1600 MHz, 3200 MT/s for M3xx models)
* Power consumption ( TDP): 35 watt max
** Clock rate: 2000 (M1xx, L2 cache 512 KiB)
** Clock rate: 2000, 2100, 2200 MHz (M3xx, L2 cache: 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
)
** Clock rate: 2200, 2300, 2400 MHz (M5xx, L2 cache: 1 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
)
** Clock rate: 2400, 2500, 2600, 2700 MHz (M6xx, L2 cache: 2 MiB
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
)
** 25W TDP:
*** M100: 2000 MHz - Sempron II Single-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
*** M120: 2100 MHz - Sempron II Single-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
** 35W TDP:
*** M300: 2000 MHz – Athlon II Dual-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
*** M320: 2100 MHz – Athlon II Dual-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
*** M340: 2200 MHz – Athlon II Dual-Core (only 64 bit FPU)
*** M500: 2200 MHz – Turion II Dual-Core
*** M520: 2300 MHz – Turion II Dual-Core
*** M540: 2400 MHz – Turion II Dual-Core
*** M600: 2400 MHz – Turion II Ultra Dual-Core
*** M620: 2500 MHz – Turion II Ultra Dual-Core
*** M640: 2600 MHz – Turion II Ultra Dual-Core
*** M660: 2700 MHz – Turion II Ultra Dual-Core
Champlain (45 nm SOI)
* Based on the AMD K10 microarchitecture * All models support: '' MMX, SSE,SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. SSE2 instructions allow the use of ...
, SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revis ...
, SSE4a
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper;
, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit
The NX bit (no-execute bit) is a processor feature that separates areas of a virtual address space (the memory layout a program uses) into sections for storing data or program instructions. An operating system supporting the NX bit can mark certai ...
, AMD64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode an ...
, Cool'n'Quiet
AMD Cool'n'Quiet is a CPU dynamic frequency scaling and power saving technology introduced by AMD with its Athlon XP processor line. It works by reducing the processor's clock rate and voltage when the processor is idle. The aim of this techn ...
'', ''AMD-V
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU.
In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware- ...
''
* Memory support: DDR3 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth (" double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-spe ...
, DDR3L SDRAM
See also
*AMD mobile platform
The AMD mobile platform is an open platform for laptops from Advanced Micro Devices, AMD. Though little marketing was done on this platform, it has been competing with the Centrino platform in the segment to gain more marketshare. Each platform has ...
* List of AMD Turion microprocessors
Turion 64 is a family of CPUs designed by AMD for the mobile computing market.
Features overview
Single-core mobile processors
Turion 64
"Lancaster" ( 90 nm)
* All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, Enhanced 3DNow!, NX bit, AMD64, ...
* List of AMD Mobile Sempron microprocessors
References
External links
AMD official website
Reuters news report on the announcement of the chips
PCworld Turion based notebooks review
Acer Aspire 5020 Series Review from www.notebookreview.com
Detailed review at www.anandtech.com
The Register : AMD, IBM "stress" silicon for 65nm process, by Tony Smith
Article from ExtremeTech: AMD Adds Second Core To Turion Notebook Chip
* http://support.amd.com/us/psearch/Pages/psearch.aspx?type=2.2%3b2.3&product=2.2.8&contentType=Tech+Doc+Embedded&ostype=&keywords=&items=20 {{AMD processors AMD x86 microprocessors Computer-related introductions in 2004