Gangut-class battleship on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''Gangut'' class, also known as the ''Sevastopol'' class, were the first
 After the end of the
After the end of the
 The main armament consisted of a dozen 52-
The main armament consisted of a dozen 52-
Battleship "Sevastopol" from Russian/Soviet Black Sea fleet (with photos)Article in Russian
{{Good article Battleship classes Gangut class battleship Gangut class battleship Gangut class battleship
dreadnought
The dreadnought was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an effect when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her were referred to as "dreadnoughts", ...
s built for the Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until being dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution and the declaration of ...
before World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. They had a convoluted design history involving several British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
companies, evolving requirements, an international design competition, and foreign protests. Four ships were ordered in 1909, , , , and . Construction was delayed by financing problems until the Duma
A duma () is a Russian assembly with advisory or legislative functions.
The term ''boyar duma'' is used to refer to advisory councils in Russia from the 10th to 17th centuries. Starting in the 18th century, city dumas were formed across Russia ...
formally authorized the ships in 1911. They were delivered from December 1914 through January 1915, although they still needed work on the gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
s and fire-control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a hum ...
s until mid-1915. Their role was to defend the mouth of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. ...
against the Germans, who never tried to enter, so the ships spent their time training and providing cover for minelaying operations. Their crews participated in the general mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military or a crew) to oppose, change, or remove superiors or their orders. The term is commonly used for insubordination by members of the military against an officer or superior, ...
of the Baltic Fleet
The Baltic Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Baltic Sea.
Established 18 May 1703, under Tsar Peter the Great as part of the Imperial Russian Navy, the Baltic Fleet is the oldest Russian fleet. In 1918, the fleet w ...
after the February Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
in 1917, and joined the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
s the following year.
All of the dreadnoughts except for ''Petropavlovsk'' were laid up in late 1918 for lack of manpower and ''Poltava'' was severely damaged by a fire while laid up. ''Petropavlovsk'' was retained in commission to defend Kronstadt
Kronstadt (, ) is a Russian administrative divisions of Saint Petersburg, port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Saint Petersburg, located on Kotlin Island, west of Saint Petersburg, near the head ...
and Leningrad against the British forces supporting the White Russians although she also helped to suppress a mutiny by the garrison of Fort Krasnaya Gorka in 1919. Her crew, and that of ''Sevastopol'', joined the Kronstadt rebellion
The Kronstadt rebellion () was a 1921 insurrection of Soviet sailors, Marines, naval infantry, and civilians against the Bolsheviks, Bolshevik government in the Russian port city of Kronstadt. Located on Kotlin Island in the Gulf of Finland, ...
of March 1921. After the revolt was violently quashed, the two ships were given 'revolutionary' names, with ''Petropavlovsk'' being renamed ''Marat'' and ''Sevastopol'' renamed to ''Parizhskaya Kommuna''. The other two serviceable vessels were recommissioned and renamed in 1925–1926. ''Gangut'' was renamed ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' and ''Poltava'' was renamed ''Frunze''. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' was modified in 1928 to improve her sea-keeping abilities so that she could be transferred to the Black Sea Fleet
The Black Sea Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Black Sea, the Sea of Azov and the Mediterranean Sea. The Black Sea Fleet, along with other Russian ground and air forces on the Crimea, Crimean Peninsula, are subordin ...
. This proved to be the first of a series of modernizations where each ship of the class was progressively reconstructed and improved, with the exception of ''Frunze''. A number of proposals were made in the 1930s to rebuild ''Frunze'', but these came to naught and she was hulk
The Hulk is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer Stan Lee and artist Jack Kirby, the character first appeared in the debut issue of ''The Incredible Hulk (comic book), The Incredible Hulk ...
ed preparatory to scrapping.
The two ships of the Baltic Fleet did not play a prominent role in the Winter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
, but did have their anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) is the counter to aerial warfare and includes "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It encompasses surface-based, subsurface ( submarine-launched), and air-ba ...
guns significantly increased before Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along ...
in 1941. ''Marat'' had her bow blown off and ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' was badly damaged by multiple bomb hits in September. The former was sunk, but later raised and became a floating battery for the duration of the Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad was a Siege, military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) in the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 1941 t ...
while the latter spent over a year under repair. Both ships bombarded German troops so long as they remained within reach, but ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' did not venture away from Kronstadt for the duration of the war. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' remained in Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
until forced to evacuate by advancing German troops. She made one trip to besieged Sevastopol in December 1941 and made a number of bombardments in support of the Kerch Offensive during January–March 1942. She was withdrawn from combat in April as German aerial supremacy had made it too dangerous to risk such a large target.
''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' and ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' remained on the active list after the end of the war although little is known of their activities. Both were reclassified as 'school battleships' (''uchebnyi lineinyi korabl'') in 1954 and stricken in 1956 after which they were slowly scrapped. There were several plans to reconstruct ''Petropavlovsk'' using the bow of ''Frunze'', but they were not accepted and were formally cancelled on 29 June 1948. She was renamed ''Volkhov'' in 1950 and served as a stationary training ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house class ...
until stricken in 1953 and subsequently broken up. ''Frunze'' was finally scrapped beginning in 1949.
Design and development
 After the end of the
After the end of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the ...
the Imperial Russian Navy was in a state of confusion. Its leadership, tactics and ship designs had all been cast into disrepute by its repeated defeats by the Japanese at the Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima (, ''Tsusimskoye srazheniye''), also known in Japan as the , was the final naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 27–28 May 1905 in the Tsushima Strait. A devastating defeat for the Imperial Russian Navy, the ...
, Battle off Ulsan
The naval Battle of Ulsan (Japanese: 蔚山沖海戦 ''Urusan'oki kaisen''; Russian: Бой в Корейском проливе, ''Boi v Koreiskom prolive''), also known as the Battle of the Japanese Sea or Battle of the Korean Strait, took pl ...
and the Battle of the Yellow Sea
The Battle of the Yellow Sea (; ) was a naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 10 August 1904. In the Russian Navy, it was referred to as the Battle of 10 August. The battle foiled an attempt by the Russian fleet at Lüshunkou (Port ...
. The Navy took quite some time to absorb the design lessons from the war while the government reformed the Naval Ministry and forced many of its more conservative officers to retire. It conducted a design contest for a dreadnought in 1906, but the Duma
A duma () is a Russian assembly with advisory or legislative functions.
The term ''boyar duma'' is used to refer to advisory councils in Russia from the 10th to 17th centuries. Starting in the 18th century, city dumas were formed across Russia ...
refused to authorize it, preferring to spend the money on rebuilding the Army.
The requirements for a new class of dreadnoughts were in a state of flux during 1907, but Vickers Ltd submitted a design that met the latest specifications and was very nearly accepted by the Navy for a ship with twelve guns in triple superimposed turrets. However rumors of a contract with Vickers raised a public outcry as they had some problems with the armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a pre-dreadnought battles ...
then building in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
. The Naval Ministry defused the situation on 30 December 1907All dates used in this article are New Style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, they refer to the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various Europe, European countrie ...
by announcing an international design contest with the ship built in Russia regardless of the nationality of the winning firm. By the deadline of 12 March 1908 a total of 51 designs had been submitted by 13 different shipyards. The winner of the competition was a design from the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
firm of Blohm & Voss
Blohm+Voss (B+V), also written historically as Blohm & Voss, Blohm und Voß etc., is a German shipbuilding and engineering company. Founded in Hamburg in 1877 to specialise in steel-hulled ships, its most famous product was the World War II battle ...
, but the French protested that they did not want to see any of the money that they had loaned Russia to build up its defenses in German pockets. The Russians bought the design for 250,000 ruble
The ruble or rouble (; rus, рубль, p=rublʲ) is a currency unit. Currently, currencies named ''ruble'' in circulation include the Russian ruble (RUB, ₽) in Russia and the Belarusian ruble (BYN, Rbl) in Belarus. These currencies are s ...
s and shelved it to placate both sides. A design by the Baltic Works had been the runner-up and was revised for the Navy's updated requirements with a complete design to be presented by 22 March 1909. This was extended by a month to allow the Baltic Works to finalize its contract with the British firm of John Brown & Company
John Brown and Company of Clydebank was a Scottish Naval architecture, marine engineering and shipbuilding firm. It built many notable and world-famous ships including , , , , , and ''Queen Elizabeth 2 (ship), Queen Elizabeth 2''.
At its heig ...
for design assistance with the hull form and machinery.
The Naval General Staff believed that a speed advantage over the German battle fleet would prove very useful in battle, as demonstrated at the Battle of Tsushima, but use of the heavy and bulky Belleville Water-tube boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generat ...
s, as insisted upon by the Engineering Section of the Naval Technical Committee, would prevent the new design from exceeding 21.25 knots itself. However, after John Brown indicated that the ship's turbines could deliver if supplied with enough steam and that the hull form could reach with that amount of power, the Naval General Staff took the opportunity to get the speed it desired by using small-tube boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, centra ...
s. It convened a meeting of the Naval Technical Committee to discuss the issue, but packed it with engineers from the fleet who were in favor of small-tube boilers and the Engineering Section was outvoted. The Yarrow
''Achillea millefolium'', commonly known as yarrow () or common yarrow, is a flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. Growing to tall, it is characterized by small whitish flowers, a tall stem of fernlike leaves, and a pungent odor.
The plan ...
small-tube boiler was significantly smaller and lighter than Belleville large-tube boiler, but required more frequent cleaning and repair and their horsepower dropped off more rapidly with use.
The Russians did not believe that superfiring
Superfiring armament is a naval design technique in which two or more turrets are located one behind the other, with the rear turret located above ("super") the one in front so that it can fire over the first. This configuration meant that both ...
turrets offered any advantage as they discounted the value of axial fire, believed that broadside fire was much more important and also believed that super firing turrets could not fire while over the lower turret because of muzzle blast
A muzzle blast is an explosive shockwave created at the muzzle of a firearm during shooting. Before a projectile leaves the gun barrel, it obturates the bore and "plugs up" the pressurized gaseous products of the propellant combustion behind ...
interfering with the open sighting hoods in the lower turret's roof. They therefore designed the ships with a 'linear' arrangement (''lineinoe raspolozhenie'') of turrets distributed over the length of the ship. This arrangement had several advantages because it reduced the stress on the ends of the ship since the turrets were not concentrated at the end of the ship, increased stability because the lack of elevated turrets and their barbettes, improved the survivability of the ship because the magazines
A magazine is a periodical literature, periodical publication, print or digital, produced on a regular schedule, that contains any of a variety of subject-oriented textual and visual content (media), content forms. Magazines are generally fin ...
were separated from each other and gave a lower silhouette. Disadvantages were that the magazines had to be put in the middle of all the machinery, which required steam pipes to be run through or around them and the lack of deck space free from blast. This greatly complicated the placement of the anti-torpedo boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of ...
guns which ultimately had to be mounted in the hull, closer to the water than was desirable.
General characteristics
The ''Gangut''s were long at the waterline and long overall. They had a beam of and adraft
Draft, the draft, or draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a v ...
of , more than designed. They were overweight and their displacement
Displacement may refer to:
Physical sciences
Mathematics and physics
*Displacement (geometry), is the difference between the final and initial position of a point trajectory (for instance, the center of mass of a moving object). The actual path ...
was at load, over more than their designed displacement of . This reduced their freeboard by about and gave them a slight bow trim that made them very wet ships.
High-tensile steel was used throughout the longitudinally framed hull with mild steel used only in areas that did not contribute to structural strength. This, plus refinements in the design process, meant that the hull was 19% lighter than that of the preceding pre-dreadnoughts. The hull was subdivided by 13 transverse watertight bulkheads and had a double bottom
A double hull is a ship hull design and construction method where the bottom and sides of the ship have two complete layers of watertight hull surface: one outer layer forming the normal hull of the ship, and a second inner hull which is some di ...
. The engine and condenser rooms were divided by two longitudinal bulkheads. They had two electrically driven rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually air or water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw ...
s on the centerline, the main rudder abaft the smaller auxiliary rudder. Their designed metacentric height
The metacentric height (GM) is a measurement of the initial static stability of a floating body. It is calculated as the distance between the centre of gravity of a ship and its '' metacentre''. A larger metacentric height implies greater initial ...
was .
Propulsion
Two Parsons-typesteam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
sets drove the four propellers. The engine rooms were located between turrets three and four in three transverse compartments. The outer compartments each had a high-pressure ahead and reverse turbine for each wing propeller shaft. The central engine room had two each low-pressure ahead and astern turbines as well as two cruising turbines driving the two center shafts. The engines had a total designed output of , but they produced during 's full-speed trials on 21 November 1915 and gave a top speed of . Twenty-five Yarrow boiler
Yarrow boilers are an important class of high-pressure water-tube boilers. They were developed by
Yarrow Shipbuilders, Yarrow & Co. (London), Shipbuilders and Engineers and were widely used on ships, particularly warships.
The Yarrow boiler desi ...
s provided steam to the engines at a designed working pressure of . Each boiler was fitted with Thornycroft
Thornycroft was an English vehicle manufacturer which built coaches, buses, and trucks from 1896 until 1977.
History
In 1896, naval engineer John Isaac Thornycroft formed the Thornycroft Steam Carriage and Van Company which built its f ...
oil sprayers for mixed oil/coal burning. They were arranged in two groups. The forward group consisted of two boiler rooms in front of the second turret, the foremost of which had three boilers while the second one had six. The rear group was between the second and third turrets and comprised two compartments, each with eight boilers. At full load they carried of coal and of fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil (bunker fuel), marine f ...
and that provided them a range of at a speed of .
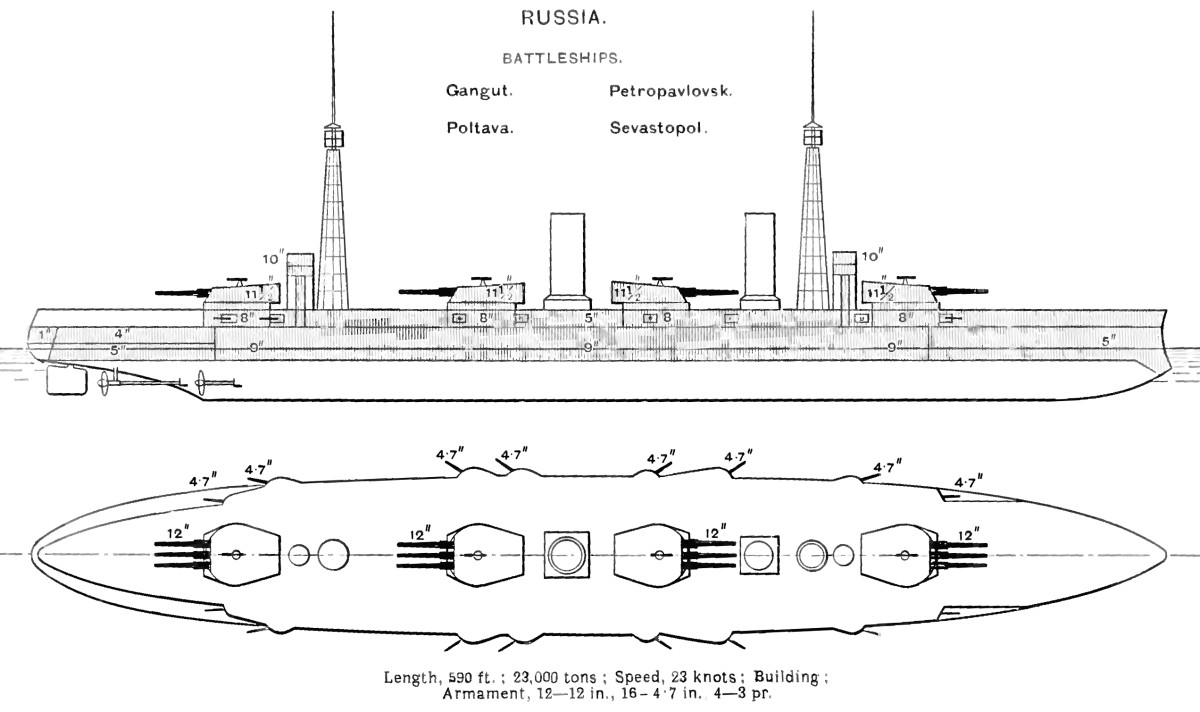
Armament
 The main armament consisted of a dozen 52-
The main armament consisted of a dozen 52-caliber
In guns, particularly firearms, but not #As a measurement of length, artillery, where a different definition may apply, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel Gauge ( ...
Obukhovskii 12-inch (305 mm) Pattern 1907 guns mounted in four electrically powered triple-gun turrets. The guns could be depressed to −5° and elevated to 25°. They could be loaded at any angle between −5° and +15°; their rate of fire was one round every 30 to 40 seconds up to 15° of elevation and one round per minute above that. The forward turret had an arc of fire
The field of fire or zone of fire (ZF) of a weapon, or group of weapons, is the area around it that can easily and effectively be reached by projectiles from a given position.
Field of fire
The term originally came from the ''field of fire'' in f ...
of 330°, the second turret had a total of 280°, the third turret 310° and the aft turret 300°. They could elevate at 3–4° per second and traverse at a rate of 3.2° per second. 100 rounds per gun were carried at full load. The guns fired projectiles at a muzzle velocity
Muzzle velocity is the speed of a projectile (bullet, pellet, slug, ball/ shots or shell) with respect to the muzzle at the moment it leaves the end of a gun's barrel (i.e. the muzzle). Firearm muzzle velocities range from approximately t ...
of ; this provided a maximum range of .
Sixteen manually operated 50-caliber 4.7-inch (120 mm) Pattern 1905 guns were mounted in the hull in casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armoured structure from which guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to antiquity, the term "casemate wall" ...
s as the secondary battery intended to defend the ship against torpedo boats.McLaughlin, p. 207 Because of the lack of freeboard and a bow-heavy trim the forward casemates were often washed out in even moderate seas. All guns had a firing arc of 125°–30° and at least four could bear on any part of the horizon. Their maximum elevation was +25° and they could elevate at 3.5° per second. They could traverse at six to eight degrees per second. 300 rounds per gun were provided which was increased from 245 rounds during construction. As designed they were above the waterline, but this was reduced in service as the ships were overweight. The guns had a rate of fire of seven rounds per minute and a maximum range of about at 25° elevation with a semi-armor-piercing
Armour-piercing ammunition (AP) is a type of projectile designed to penetrate armour protection, most often including naval armour, body armour, and vehicle armour.
The first, major application of armour-piercing projectiles was to defeat the ...
Model 1911 shell at a muzzle velocity of .
The ''Gangut''-class ships were completed with only a single 30-caliber ''Lender'' anti-aircraft (AA) gun mounted on the quarterdeck.McLaughlin, p. 221 This had a maximum depression of -5° and a maximum elevation of +65°. It fired a shell at a muzzle velocity of . It had a rate of fire of 10–12 rounds per minute and had a maximum ceiling of . Other AA guns were probably added during the course of World War I, but details are lacking, although Conway's says that four guns were added to the roofs of the end turrets during the war. Four submerged torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s were fitted with three torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such ...
es for each tube.
Fire control
Two Zeissrangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to Length measurement, measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, suc ...
s were fitted on the conning towers and there was also a Barr & Stroud
Barr & Stroud Limited was a pioneering Glasgow optical engineering firm. They played a leading role in developing modern optics, including rangefinders, for the Royal Navy and other branches of British Armed Forces during the 20th century. There ...
instrument, possibly for precise stationkeeping on the master ship when concentrating fire. Two Krylov stadimeters were situated in the lower level of the forward conning tower. These would provide data for the central artillery post to calculate with its imported Pollen Argo Mark V Clock, a mechanical fire-control computer, and then transmit the gun commands via the Geisler transmission system for the gun crew to follow. During the winter of 1915–1916 the Zeiss rangefinders were transferred to armored hoods on the rear of the fore and aft turrets and, at some point, Barr & Stroud rangefinders were added to the roofs of the middle turrets. received a Pollen rangefinder in the spring of 1916.
Protection
The armor protection of the ''Gangut''-class ships had to protect against two different threats as revealed during the Russo-Japanese War. Japanesehigh explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An exp ...
shells had riddled the unarmored portions of Russian ships and had even sunk several ships with their heavy armor belts unpenetrated. The Russians decided that the entire side of the ship needed to be armored, even though this would limit the thickness of the main belt. They developed a system where the outer armor would break up or at least slow shells down and burst immediately behind the outer armor and an inboard armor bulkhead would stop the splinters and shell fragments from reaching the vitals. This system likely would have worked against the British armor-piercing shells that performed so badly at the Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland () was a naval battle between Britain's Royal Navy Grand Fleet, under Admiral John Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, Sir John Jellicoe, and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet, under Vice-Admiral Reinhard Scheer, durin ...
, but would have failed against the improved shells introduced afterwards with their redesigned fuses. A related weakness was that the turrets and conning towers lacked the inboard splinter bulkhead even though they used armor thickness roughly equivalent to that of the main belt.
The waterline belt, made of Krupp cemented armor (KCA), had a maximum thickness of , but tapered to about on its bottom edge. It was long and had a total height of , of which was above the design waterline and below. However, the ship's draft was almost deeper than intended, which meant that much less was above water. The remaining portion of the waterline was protected by plates. The upper belt, which protected the casemates, was 125 mm of KCA over the citadel and high. It thinned to a thickness of 75 millimeters forward of the citadel. The area aft of the citadel was the only unprotected section of the hull. inboard of the side was a longitudinal splinter bulkhead made of Krupp non-cemented armor (KNC). It was thick at the level of the main belt, but thinned to behind the upper belt. The main deck sloped from the bulkhead to the lower edge of the waterline belt and consisted of a 50-millimeter KNC plate on a mild steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:
* no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt ...
plate. This space was used as a coal bunker, which added extra protection. The main belt was closed off by transverse bulkheads fore and aft and the steering gear was protected by armor 100–125 mm thick.
The main gun turrets had a KCA face and sides thick with a 100 mm roof. The guns had 3-inch gun shields to protect against splinters entering the embrasures and they were separated by splinter bulkheads. The barbettes were 150 mm thick above the upper deck, but reduced to 75 mm behind other armor, except for the fore and aft barbettes which only thinned to 125 mm. The conning tower sides were thick with a 100 mm roof. The 120 mm guns had their own individual 3-inch gun shield
A U.S. Marine manning an M240 machine gun equipped with a gun shield
A gun shield is a flat (or sometimes curved) piece of armor designed to be mounted on a crew-served weapon such as a machine gun, automatic grenade launcher, or artillery pie ...
s. The funnel uptakes were protected by of armor. The upper deck was of nickel-chrome steel and the middle deck was of nickel-chrome steel between the longitudinal splinter bulkheads, but thinned to outside them. The lower deck was of mild steel.
Underwater protection was minimal as there was only a single watertight bulkhead, presumably of high-tensile steel, behind the upwards extension of the double bottom. This was an extension of the splinter bulkhead and was also 3.4 meters inboard. A more comprehensive system was considered early in the design process but rejected because it would have cost some .
The armor scheme of the ''Gangut''-class ships had some significant weaknesses. The rear transverse bulkhead was unprotected by any other armor but was the same thickness as the forward bulkhead which was defended by the upper belt armor. The thinness of the barbette armor was a serious defect which could have proved fatal in a battle. And the lack of a splinter bulkhead behind the armor of the turrets, barbettes and conning towers left all of those locations vulnerable to main gun hits. But the biggest weakness was the lack of an anti-torpedo bulkhead, which made the ships highly vulnerable to mines or torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such ...
es.
Ships
All four ships were laid down on 16 June 1909, but this was just a ceremonial event as actual work did not begin until September–October. One major complication was that the design for the turrets and their magazines was not completed when construction began so their weights and dimensions had to be estimated.McLaughlin, p. 214 The machinery for these ships was built by either the Baltic Works or the Franco-Russian Works as the New Admiralty Shipyard lacked its own engine shop. Construction was initially very slow because the Duma did not allocate any money for these ships until May 1911. Initial funding was taken from other budget items or the emperor's discretionary fund and the shipyards had to use their own money to keep the work going. They were enormously expensive with their cost estimated at 29.4 million rubles each, including armament. By way of comparison the preceding class of pre-dreadnoughts had only cost 11 million rubles each. Once the Duma provided the funding the pace of work accelerated and the ships were launched later that year, although delays in the delivery of engines and turrets hindered their completion. All of the ships completed abbreviated trials by the end of 1914 and reached the fleet in December 1914 – January 1915.Service
World War I
All four of the ''Gangut''s were assigned to the First Battleship Brigade of theBaltic Fleet
The Baltic Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Baltic Sea.
Established 18 May 1703, under Tsar Peter the Great as part of the Imperial Russian Navy, the Baltic Fleet is the oldest Russian fleet. In 1918, the fleet w ...
in December 1914 – January 1915 when they reached Helsingfors
Helsinki () is the capital and most populous city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipality, with million in the capital region and ...
. Their turrets and fire-control systems, however, were still being adjusted and fine-tuned through the next spring. Their role was to defend the mouth of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. ...
against the Germans, who never tried to enter, so they spent their time training with occasional sorties into the Baltic. Several ships ran aground in 1915 and 1916, often while providing cover for minelaying operations, but only ''Sevastopol'' suffered any significant damage. A minor mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military or a crew) to oppose, change, or remove superiors or their orders. The term is commonly used for insubordination by members of the military against an officer or superior, ...
broke out on 1 November on board ''Gangut'' when the executive officer refused to feed the crew the traditional meal of meat and macaroni after coaling. The crews of the battleships joined the general mutiny of the Baltic Fleet on 16 March 1917, after the idle sailors received word of the February Revolution
The February Revolution (), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and sometimes as the March Revolution or February Coup was the first of Russian Revolution, two revolutions which took place in Russia ...
in Saint Petersburg. The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, whi ...
required the Soviets to evacuate their base at Helsinki in March 1918 or have them interned by newly independent Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
even though the Gulf of Finland was still frozen over. ''Gangut'' and her sisters led the first group of ships on 12 March and reached Kronstadt
Kronstadt (, ) is a Russian administrative divisions of Saint Petersburg, port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Saint Petersburg, located on Kotlin Island, west of Saint Petersburg, near the head ...
five days later in what became known as the 'Ice Voyage'.
Russian Civil War and interwar period
All of the dreadnoughts except for ''Petropavlovsk'' were laid up in October–November 1918 for lack of manpower. She bombarded the rebellious garrison of Fort Krasnaya Gorka in 1919 and supportedBolshevik
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ...
light forces operating against British ships supporting the White Russians in the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland (; ; ; ) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and Estonia to the south, to Saint Petersburg—the second largest city of Russia—to the east, where the river Neva drains into it. ...
. On 17 August 1919 ''Petropavlovsk'' was claimed as torpedoed and put out of action by the British Coastal Motor Boat ''CMB 88'' in Kronstadt harbor, but was, in fact, not damaged at all. On 24 November 1919 a fire broke out in ''Poltava''s forward boiler room and gutted much of her interior; she was never repaired although numerous proposals were made to reconstruct her. The crews of ''Sevastopol'' and ''Petropavlovsk'' joined the Kronstadt rebellion
The Kronstadt rebellion () was a 1921 insurrection of Soviet sailors, Marines, naval infantry, and civilians against the Bolsheviks, Bolshevik government in the Russian port city of Kronstadt. Located on Kotlin Island in the Gulf of Finland, ...
of 1921 and they were renamed ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' and ''Marat'' respectively after the rebellion was crushed to commemorate the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (, ) was a French revolutionary government that seized power in Paris on 18 March 1871 and controlled parts of the city until 28 May 1871. During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard (France), Nation ...
and to erase their 'betrayal' of the Communist Party. The two undamaged ships were recommissioned in 1925–1926 and all the ships were given proper revolutionary names.
The initial attempts to return ''Frunze'' to service were to restore her to the original design, but money ran out before she was even half completed. Subsequent plans that focused on reconstructing her as a modernized equivalent to her sisters or even as a battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of att ...
, with one turret deleted to save weight, were considered, but finally abandoned on 23 January 1935 when all work was stopped.McLaughlin, pp. 227, 348–354
''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' was refitted in 1928 in preparation for her transfer to the Black Sea Fleet the next year and she was given an open-topped false bow to improve her sea-keeping ability. However, while en route through the Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay ( ) is a gulf of the northeast Atlantic Ocean located south of the Celtic Sea. It lies along the western coast of France from Point Penmarc'h to the Spanish border, and along the northern coast of Spain, extending westward ...
, she was caught in a heavy storm that damaged the bow and she was forced to put into Brest for repairs. ''Marat'' was the first of the class to be reconstructed between 1928 and 8 April 1931. Her superstructure was enlarged, her guns were replaced, the turrets overhauled, the anti-aircraft armament augmented and the fire-control equipment modernized. Her boilers were converted to burn only fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil (bunker fuel), marine f ...
and this produced enough steam that the forward three boilers could be removed and the boiler room was turned into anti-aircraft magazine
A magazine is a periodical literature, periodical publication, print or digital, produced on a regular schedule, that contains any of a variety of subject-oriented textual and visual content (media), content forms. Magazines are generally fin ...
s and control spaces. The forward funnel was angled to the rear and extended to try to keep the exhaust out of the gunnery spaces and the bridge. She was also given a false bow, but hers had a solid top that turned it into a forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck (ship), deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is t ...
. ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' was the next ship to be rebuilt and profited from the experiences of her sister's modernization between 1931 and 1934. All twenty-five of her old boilers were replaced by a dozen oil-fired boilers originally intended for the ''Izmail''. The space saved was used to add another inboard longitudinal watertight bulkhead that greatly improved her underwater protection. The rest of her modernization was along the same lines as ''Marat''s, except that the latter's tubular foremast was replaced by a sturdier semi-conical mast, a new aft structure was built in front of the rear conning tower which caused the mainmast to be moved forward, her forward funnel was curved to the rear to better keep the bridge clear of exhaust gases and the thickness of her turret roofs was increased to . ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' began her two-stage reconstruction in 1933 along the lines of ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya''s modernization. Major differences were that her guns and turrets were improved to increase their rate of fire to about two rounds per minute and to extend their range, she was the first ship of the class to receive light anti-aircraft guns and her forward funnel was given a more sinuous curve to direct its exhaust gases away from the forward superstructure. She completed these alterations in 1938, but was returned to the dockyard from December 1939 through July 1940 to receive a new armored deck and anti-torpedo bulges which cured her stability problems and greatly increased her underwater protection at a modest cost in speed.
World War II
Baltic Fleet
The participation of ''Marat'' and ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' in theWinter War
The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peac ...
was limited to a bombardment of Finnish coastal artillery
Coastal artillery is the branch of the armed forces concerned with operating anti-ship artillery or fixed gun batteries in coastal fortifications.
From the Middle Ages until World War II, coastal artillery and naval artillery in the form of ...
in December 1939 at Saarenpää in the Beryozovye Islands
Beryozovye Islands (; ; , "Birch Island"), alternatively spelled Berezovye Islands, is an island group in Leningrad Oblast, Russia.
Geography
The islands are situated at the head of the Gulf of Finland, just outside the town of Primorsk on th ...
before the Gulf of Finland iced over. They failed to inflict any permanent damage before being driven off by near misses. Both ships had their anti-aircraft armament modernized and reinforced over the winter of 1939–40 and were transferred to Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Estonia, most populous city of Estonia. Situated on a Tallinn Bay, bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, it has a population of (as of 2025) and ...
shortly after the Soviets occupied Estonia in 1940. ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' received more AA guns in February–March 1941. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' received a more modest number of AA guns while she was receiving her bulges, but landed four 120-mm guns right before the Germans invaded.
On 22 June 1941, the Germans attacked the Soviet Union under the codename of Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along ...
; on that date ''Marat'' was in Kronstadt and ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' was in Tallinn. The latter was soon forced to fall back to Kronstadt by the speed of the German advance and neither of the Baltic Fleet dreadnoughts participated in combat until 8 September when they fired on troops of the German 18th Army from positions near Kronstadt and Leningrad. ''Marat'' was lightly damaged by German guns on 16 September and had her bow blown off on 23 September by two bomb hits, one of which was claimed by Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a Junior officer, junior commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations, as well as fire services, emergency medical services, Security agency, security services ...
Hans-Ulrich Rudel of III./ StG 2 flying a Junkers Ju 87
The Junkers Ju 87, popularly known as the "Stuka", is a German dive bomber and ground-attack aircraft. Designed by Hermann Pohlmann, it first flew in 1935. The Ju 87 made its combat debut in 1937 with the Luftwaffe's Condor Legion during the ...
B 'Stuka', that detonated her forward magazine. She sank in the shallow water from progressive flooding, but was raised and used as a floating artillery battery for the rest of the war using two, and later, three of her gun turrets. ''Marat'' reverted to her original name on 31 May 1943. ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' was badly damaged on 21 September 1941 by three bomb hits on her bow that knocked out two of her turrets. She was sent for repairs at the Ordzhonikidze Yard
The OJSC Baltic Shipyard (''Baltiysky Zavod'', formerly Shipyard 189 named after Grigoriy Ordzhonikidze) () is one of the oldest shipyards in Russia and is part of United Shipbuilding Corporation today.
It is located in Saint Petersburg in th ...
on 23 October, although she was hit by more bombs on two different occasions while under repair until November 1942. Her AA armament was further reinforced during this period and ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' returned to her mission of providing fire support during the Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad was a Siege, military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) in the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 1941 t ...
, the Leningrad–Novgorod Offensive in January 1944 and the Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive
The Vyborg–Petrozavodsk offensive or Karelian offensive was a strategic operation by the Soviet Leningrad and Karelian Fronts against Finland on the Karelian Isthmus and East Karelia fronts of the Continuation War, on the Eastern Front of Wor ...
in June 1944. She was the last Soviet battleship to fire shots in anger on 9 June 1944 during the latter offensive.McLaughlin, p. 402 On 22 July 1944, the ship was awarded the Order of the Red Banner
The Order of the Red Banner () was the first Soviet military decoration. The Order was established on 16 September 1918, during the Russian Civil War by decree of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee. It was the highest award of S ...
. ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' received a Lend-Lease
Lend-Lease, formally the Lend-Lease Act and introduced as An Act to Promote the Defense of the United States (),3,000 Hurricanes and >4,000 other aircraft)
* 28 naval vessels:
** 1 Battleship. (HMS Royal Sovereign (05), HMS Royal Sovereign)
* ...
British Type 279 air-warning radar sometime during 1944.
During the late 1930s ''Frunze'' was used as a barracks hulk
The Hulk is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer Stan Lee and artist Jack Kirby, the character first appeared in the debut issue of ''The Incredible Hulk (comic book), The Incredible Hulk ...
while she was stripped for parts, until she was formally discarded 1 December 1940, after scrapping had already begun at a leisurely pace. After the German invasion she was towed to Kronstadt and run aground in late July 1941 near the Leningrad Sea Canal. During the Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad was a Siege, military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) in the Soviet Union on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 1941 t ...
her hull was used as a base for small ships. ''Frunze'' raised on 31 May 1944, towed to Leningrad
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the Neva, River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland ...
and scrapped beginning in 1949.
Black Sea Fleet
''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' was in Sevastopol and remained until 30 October 1941 when she was evacuated toNovorossiysk
Novorossiysk (, ; ) is a city in Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It is one of the largest ports on the Black Sea. It is one of the few cities designated by the Soviet Union as a Hero City. The population was
History
In antiquity, the shores of the ...
after the Germans had breached Soviet defensive lines near the Perekop Isthmus. The ship fired her first shots of the war on 28–29 November when she bombarded German and Romanian troops south of Sevastopol. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' made one evacuation run to Sevastopol on 29 December, bombarding German troops on her arrival, but spent most of her time supporting troops during the Kerch Offensive in January–March 1942. She fired her last shots of the war at targets near Feodosiya
Feodosia (, ''Feodosiia, Teodosiia''; , ''Feodosiya''), also called in English Theodosia (from ), is a city on the Crimean coast of the Black Sea. Feodosia serves as the administrative center of Feodosia Municipality, one of the regions into w ...
during the nights of 20–22 March 1942 before returning to Poti
Poti ( ka, ფოთი ; Mingrelian language, Mingrelian: ფუთი; Laz language, Laz: ჶაში/Faşi or ფაში/Paşi) is a port city in Georgia (country), Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the mkhare, region of ...
to have her worn-out 12-inch guns relined. By the time this was finished the Soviets were unwilling to expose such a prominent ship to German air attacks, which had already sunk a number of cruisers and destroyers. She returned to her original name on 31 May 1943, but remained in Poti
Poti ( ka, ფოთი ; Mingrelian language, Mingrelian: ფუთი; Laz language, Laz: ჶაში/Faşi or ფაში/Paşi) is a port city in Georgia (country), Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the mkhare, region of ...
until late 1944 when she led the surviving major units of the Black Sea Fleet
The Black Sea Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Black Sea, the Sea of Azov and the Mediterranean Sea. The Black Sea Fleet, along with other Russian ground and air forces on the Crimea, Crimean Peninsula, are subordin ...
back to Sevastopol on 5 November. British Type 290 and Type 291 air-warning radars were fitted during the war. ''Sevastopol'' was awarded the Order of the Red Banner on 8 July 1945.
Postwar
''Sevastopol'' and ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' remained on the active list after the end of the war although little is known of their activities. Both were reclassified as 'school battleships' (''uchebnyi lineinyi korabl'') on 24 July 1954 and stricken on 17 February 1956. Theirscrap
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap can have monetary value, especially recover ...
ping began that same year although ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya''s hulk was still in existence in May 1958.
After the war there were several plans, known as ''Project 27'', to reconstruct ''Petropavlovsk'' (ex-Marat), using the bow of ''Frunze'' and moving her third turret to replace the first, but they were not accepted and were formally cancelled on 29 June 1948. She was renamed ''Volkhov'', after the nearby river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
, on 28 November 1950 and served as a stationary training ship until stricken on 4 September 1953 and broken up afterwards.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
two of ''Frunze''s turrets and their guns were used to rebuild the destroyed Coastal Defense Battery 30 (Maxim Gorky I) in Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
. It remained in service with the Soviet Navy
The Soviet Navy was the naval warfare Military, uniform service branch of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy made up a large part of the Soviet Union's strategic planning in the event of a conflict with t ...
and the Russian Navy
The Russian Navy is the Navy, naval arm of the Russian Armed Forces. It has existed in various forms since 1696. Its present iteration was formed in January 1992 when it succeeded the Navy of the Commonwealth of Independent States (which had i ...
until 1997.Wernet, pp. 22–34
See also
* Vladimir YourkevitchNotes
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
Battleship "Sevastopol" from Russian/Soviet Black Sea fleet (with photos)
{{Good article Battleship classes Gangut class battleship Gangut class battleship Gangut class battleship