Galactic coordinate system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The galactic coordinate system is a
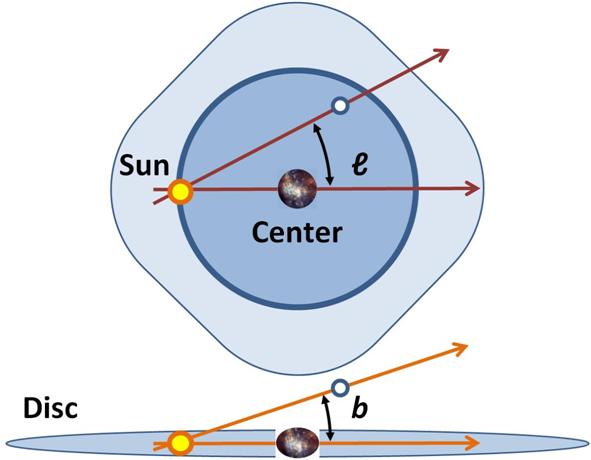 Longitude (symbol ) measures the
Longitude (symbol ) measures the
 The IAU recommended that during the transition period from the old, pre-1958 system to the new, the old longitude and latitude should be designated and while the new should be designated and . This convention is occasionally seen.
Radio source
The IAU recommended that during the transition period from the old, pre-1958 system to the new, the old longitude and latitude should be designated and while the new should be designated and . This convention is occasionally seen.
Radio source
Universal coordinate converter
Galactic Coordinate System - Wolfram Demonstration
The
Positional Astronomy: Galactic coordinates
,
An Atlas of the Universe
{{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Astronomical coordinate systems Milky Way Orientation (geometry)
celestial coordinate system
In astronomy, coordinate systems are used for specifying positions of celestial objects (satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, etc.) relative to a given reference frame, based on physical reference points available to a situated observer (e. ...
in spherical coordinates
In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system specifies a given point in three-dimensional space by using a distance and two angles as its three coordinates. These are
* the radial distance along the line connecting the point to a fixed point ...
, with the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
as its center, the primary direction aligned with the approximate center of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
Galaxy
A galaxy is a Physical system, system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar medium, interstellar gas, cosmic dust, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ' (), literally 'milky', ...
, and the fundamental plane parallel to an approximation of the galactic plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galac ...
but offset to its north. It uses the right-handed convention, meaning that coordinates are positive toward the north and toward the east in the fundamental plane.
Spherical coordinates
Galactic longitude
angular distance
Angular distance or angular separation is the measure of the angle between the orientation (geometry), orientation of two straight lines, ray (geometry), rays, or vector (geometry), vectors in three-dimensional space, or the central angle subtende ...
of an object eastward along the galactic equator from the Galactic Center. Analogous to terrestrial longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
, galactic longitude is usually measured in degrees (°).
Galactic latitude
Latitude (symbol ) measures theangle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two R ...
of an object northward of the galactic equator (or midplane) as viewed from Earth. Analogous to terrestrial latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
, galactic latitude is usually measured in degrees (°).
Definition
The first galactic coordinate system was used byWilliam Herschel
Frederick William Herschel ( ; ; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel. Born in the Electorate of Hanover ...
in 1785. A number of different coordinate systems, each differing by a few degrees, were used until 1932, when Lund Observatory assembled a set of conversion tables that defined a standard galactic coordinate system based on a galactic north pole at RA , dec +28° (in the B1900.0 epoch convention) and a 0° longitude at the point where the galactic plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galac ...
and equatorial plane
The celestial equator is the great circle of the imaginary celestial sphere on the same plane as the equator of Earth. By extension, it is also a plane of reference in the equatorial coordinate system. Due to Earth's axial tilt, the celestial e ...
intersected.
In 1958, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
(IAU) defined the galactic coordinate system in reference to radio observations of galactic neutral hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
through the hydrogen line
The hydrogen line, 21 centimeter line, or H I line is a spectral line that is created by a change in the energy state of solitary, electrically neutral hydrogen atoms. It is produced by a spin-flip transition, which means the dire ...
, changing the definition of the Galactic longitude by 32° and the latitude by 1.5°. In the equatorial coordinate system
The equatorial coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system widely used to specify the positions of astronomical object, celestial objects. It may be implemented in spherical coordinate system, spherical or Cartesian coordinate system, rect ...
, for equinox and equator of 1950.0, the north galactic pole is defined at right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in questio ...
, declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
+27.4°, in the constellation Coma Berenices
Coma Berenices is an ancient asterism in the northern sky, which has been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is in the direction of the fourth galactic quadrant, between Leo and Boötes, and it is visible in both hemispher ...
, with a probable error of ±0.1°. Longitude 0° is the great semicircle that originates from this point along the line in position angle
In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the Celestial pole, north celestial pole (NCP), turning pos ...
123° with respect to the equatorial pole. The galactic longitude increases in the same direction as right ascension. Galactic latitude is positive towards the north galactic pole, with a plane passing through the Sun and parallel to the galactic equator being 0°, whilst the poles are ±90°. Based on this definition, the galactic poles and equator can be found from spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the edge (geometry), sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, ge ...
and can be precessed to other epochs
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
; see the table.
 The IAU recommended that during the transition period from the old, pre-1958 system to the new, the old longitude and latitude should be designated and while the new should be designated and . This convention is occasionally seen.
Radio source
The IAU recommended that during the transition period from the old, pre-1958 system to the new, the old longitude and latitude should be designated and while the new should be designated and . This convention is occasionally seen.
Radio source Sagittarius A*
Sagittarius A*, abbreviated as Sgr A* ( ), is the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center of the Milky Way. Viewed from Earth, it is located near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius, about 5.6° south o ...
, which is the best physical marker of the true Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a ...
, is located at , (J2000). Rounded to the same number of digits as the table, , −29.01° (J2000), there is an offset of about 0.07° from the defined coordinate center, well within the 1958 error estimate of ±0.1°. Due to the Sun's position, which currently lies north of the midplane, and the heliocentric definition adopted by the IAU, the galactic coordinates of Sgr A* are latitude south, longitude . Since as defined the galactic coordinate system does not rotate with time, Sgr A* is actually decreasing in longitude at the rate of galactic rotation at the sun, , approximately 5.7 milliarcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of Angular unit, angular measurement equal to of a Degree (angle), degree. Since one degree is of a turn (geometry), turn, or ...
s per year (see Oort constants).
Conversion between equatorial and galactic coordinates
An object's location expressed in theequatorial coordinate system
The equatorial coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system widely used to specify the positions of astronomical object, celestial objects. It may be implemented in spherical coordinate system, spherical or Cartesian coordinate system, rect ...
can be transformed into the galactic coordinate system. In these equations, is right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in questio ...
, is declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or ...
. NGP refers to the coordinate values of the north galactic pole and NCP to those of the north celestial pole.
:
The reverse (galactic to equatorial) can also be accomplished with the following conversion formulas.
:
Where:
:
Rectangular coordinates
In some applications use is made of rectangular coordinates based on galactic longitude and latitude and distance. In some work regarding the distant past or future the galactic coordinate system is taken as rotating so that the -axis always goes to the centre of the galaxy.For example There are two majorrectangular
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a rectilinear convex polygon or a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90 ...
variations of galactic coordinates, commonly used for computing space velocities of galactic objects. In these systems the -axes are designated , but the definitions vary by author. In one system, the axis is directed toward the Galactic Center ( = 0°), and it is a right-handed
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to and causing it to be stronger, faster or more Fine motor skill, dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dext ...
system (positive towards the east and towards the north galactic pole); in the other, the axis is directed toward the galactic anticenter ( = 180°), and it is a left-handed system (positive towards the east and towards the north galactic pole).
In the constellations
The galactic equator runs through the followingconstellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
s:
* Sagittarius
*Serpens
Serpens () is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union. It ...
* Scutum
* Aquila
*Sagitta
Sagitta is a dim but distinctive constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'arrow', not to be confused with the significantly larger constellation Sagittarius 'the archer'. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by t ...
*Vulpecula
Vulpecula is a faint constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "little fox", although it is commonly known simply as the fox. It was identified in the seventeenth century, and is located in the middle of the Summer Triangle (an ...
* Cygnus
* Cepheus
*Cassiopeia
Cassiopeia or Cassiopea may refer to:
Greek mythology
* Cassiopeia (mother of Andromeda), queen of Aethiopia and mother of Andromeda
* Cassiopeia (wife of Phoenix), wife of Phoenix, king of Phoenicia
* Cassiopeia, wife of Epaphus, king of Egy ...
*Camelopardalis
Camelopardalis is a large but faint constellation of the northern sky representing a giraffe. The constellation was introduced in 1612 or 1613 by Petrus Plancius. Some older astronomy books give Camelopardalus or Camelopardus as alternative form ...
*Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (, ; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of ...
* Auriga
* Taurus
* Gemini
* Orion
*Monoceros
Monoceros ( Greek: , "unicorn") is a faint constellation on the celestial equator. Its definition is attributed to the 17th-century cartographer Petrus Plancius. It is bordered by Orion to the west, Gemini to the north, Canis Major to the s ...
*Canis Major
Canis Major is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for "greater dog" in contrast to C ...
*Puppis
Puppis ("poop deck, stern") is a constellation in the southern sky. It was originally part of the Former constellations, traditional constellation of Argo Navis (the ship of Jason and the Argonauts), which was divided into three parts, the other ...
* Vela
*Carina
Carina may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Carina, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina Heights, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina, Victoria, a locality in Mildura
Serbia
* Carina, Osečina, a village in the Kolubara District
...
*Crux
CRUX is a lightweight x86-64 Linux distribution targeted at experienced Linux users and delivered by a tar.gz-based package system with BSD-style initscripts. It is not based on any other Linux distribution. It also utilizes a ports system ...
*Centaurus
Centaurus () is a bright constellation in the southern sky. One of the 88 modern constellations by area, largest constellations, Centaurus was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one ...
* Circinus
*Norma Norma may refer to:
* Norma (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name)
** Norma Lizbeth Ramos, a Mexican bullying victim
Astronomy
*Norma (constellation)
* 555 Norma, a minor asteroid
* Cygnus Arm or Norma Arm, a spiral ...
* Ara
*Scorpius
Scorpius is a zodiac constellation located in the Southern celestial hemisphere, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way, between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation whose recognition pred ...
*Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellati ...
See also
* * * * *References
External links
Universal coordinate converter
Galactic Coordinate System - Wolfram Demonstration
The
Internet Encyclopedia of Science
David Darling (born 29 July 1953 in Glossop, Derbyshire) is an England, English astronomer, freelance science writer, and musician. Darling has published numerous popular science works, including ''Life Everywhere: The Maverick Science of As ...
* Fiona VincentPositional Astronomy: Galactic coordinates
,
University of St Andrews
The University of St Andrews (, ; abbreviated as St And in post-nominals) is a public university in St Andrews, Scotland. It is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest of the four ancient universities of Scotland and, f ...
An Atlas of the Universe
{{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Astronomical coordinate systems Milky Way Orientation (geometry)