Freemasons' Tavern on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
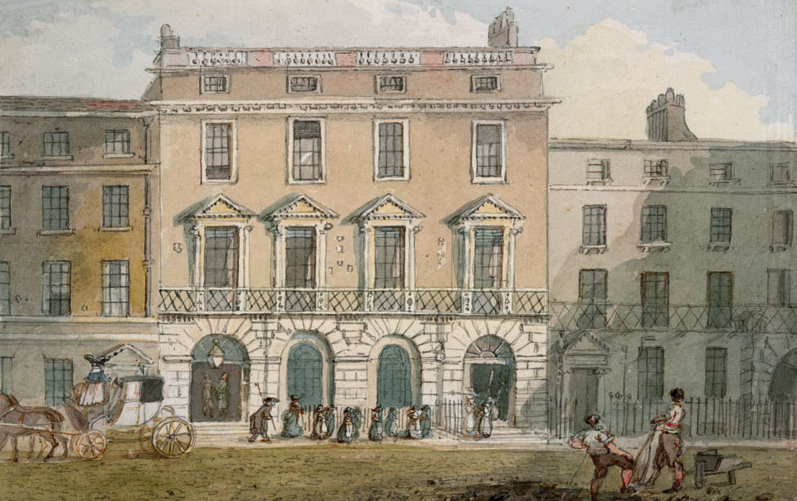 The Freemasons' Tavern was established in 1775 at 61-65 Great Queen Street in the West End of
The Freemasons' Tavern was established in 1775 at 61-65 Great Queen Street in the West End of
 In 1769, the
In 1769, the
 In 1909 the Grand Lodge demolished most of the Freemasons' Tavern and replaced it over succeeding decades with a new building designed by H. V. Ashley and Winton Newman, who also designed the adjoining Freemasons' Hall. The new building, costing £30,000, was named the Connaught Rooms after the Lodge's Grand Master,
In 1909 the Grand Lodge demolished most of the Freemasons' Tavern and replaced it over succeeding decades with a new building designed by H. V. Ashley and Winton Newman, who also designed the adjoining Freemasons' Hall. The new building, costing £30,000, was named the Connaught Rooms after the Lodge's Grand Master,
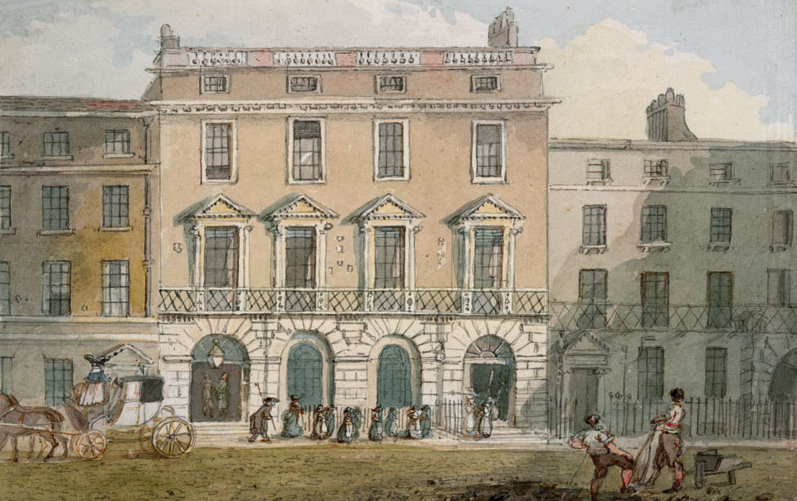 The Freemasons' Tavern was established in 1775 at 61-65 Great Queen Street in the West End of
The Freemasons' Tavern was established in 1775 at 61-65 Great Queen Street in the West End of London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
. It served as a meeting place for a variety of notable organisations from the 18th century until it was demolished in 1909 to make way for the Connaught Rooms.
History
 In 1769, the
In 1769, the Premier Grand Lodge of England
The organisation now known as the Premier Grand Lodge of England was founded on 24 June 1717 as the Grand Lodge of London and Westminster. Originally concerned with the practice of Freemasonry in London and Westminster, it soon became known as ...
decided to build a Central Hall. A building was purchased in Great Queen Street in 1775 and Thomas Sandby
Thomas Sandby (1721 – 25 June 1798) was an English draughtsman, watercolour artist, architect and teacher. In 1743 he was appointed private secretary to the Duke of Cumberland, who later appointed him Deputy Ranger of Windsor Great Park, wh ...
was tasked with building a hall in the garden. The original house became the tavern with a second house providing office space for the Freemasons
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
. In 1813 the Premier Grand Lodge and rival Ancient Grand Lodge of England merged to form the United Grand Lodge of England
The United Grand Lodge of England (UGLE) is the governing Masonic lodge for the majority of freemasons in England, Wales and the Commonwealth of Nations. Claiming descent from the Masonic grand lodge formed 24 June 1717 at the Goose & Gridiron ...
.
The hall was not only used for Masonic purposes, but also became an important venue in London for a variety of meetings and concerts. Organisations using the hall included:
* Political Economy Club
The Political Economy Club is the world's oldest economics association founded by James Mill and a circle of friends in 1821 in London, for the purpose of coming to an agreement on the fundamental principles of political economy. David Ricardo, ...
* African Institution
The African Institution was founded in 1807 after British abolitionists succeeded in ending the slave trade based in the United Kingdom. The Institution was formed to succeed where the former Sierra Leone Company had failed—to create a viab ...
* British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, for the World Anti-Slavery Convention
The World Anti-Slavery Convention met for the first time at Exeter Hall in London, on 12–23 June 1840. It was organised by the British and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society, largely on the initiative of the English Quaker Joseph Sturge. The exc ...
in 1840
* British and Foreign Bible Society
The British and Foreign Bible Society, often known in England and Wales as simply the Bible Society, is a non-denominational Christian Bible society with charity status whose purpose is to make the Bible available throughout the world.
The So ...
* Highland and Island Emigration Society
The Highland and Island Emigration Society was a charitable society formed to promote and assist emigration as a solution to the Highland Potato Famine.
Between 1852 and 1857, it assisted the passage of around 5,000 emigrants from Scotland to Au ...
* The Football Association
The Football Association (also known as The FA) is the governing body of association football in England and the Crown Dependencies of Jersey, Guernsey and the Isle of Man. Formed in 1863, it is the oldest football association in the world a ...
(FA) held its first meeting here on 26 October 1863
Connaught Rooms
 In 1909 the Grand Lodge demolished most of the Freemasons' Tavern and replaced it over succeeding decades with a new building designed by H. V. Ashley and Winton Newman, who also designed the adjoining Freemasons' Hall. The new building, costing £30,000, was named the Connaught Rooms after the Lodge's Grand Master,
In 1909 the Grand Lodge demolished most of the Freemasons' Tavern and replaced it over succeeding decades with a new building designed by H. V. Ashley and Winton Newman, who also designed the adjoining Freemasons' Hall. The new building, costing £30,000, was named the Connaught Rooms after the Lodge's Grand Master, Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn
Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught and Strathearn (Arthur William Patrick Albert; 1 May 185016 January 1942), was the seventh child and third son of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. He served as G ...
.
After a further renovation by Friendly Hotels (later the Real Hotel Company) in the 1980s it reopened as the New Connaught Rooms, a hotel and conference centre
A convention center (American English; or conference centre in British English) is a large building that is designed to hold a convention, where individuals and groups gather to promote and share common interests. Convention centers typica ...
. The art deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unit ...
Grand Hall can seat 800 conference delegates. When the Real Hotel Company collapsed in 2009, Principal Hayley Group bought the venue, renamed it the Grand Connaught Rooms, and in 2016 placed it in its De Vere brand. In 2010 it became the first art deco building to be Grade II* listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern I ...
.
References
External sites
* {{coord, 51.5156, -0.1205, type:landmark_region:GB, display=title Freemasonry Covent Garden Demolished buildings and structures in London Buildings and structures demolished in 1909