Flemings on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to
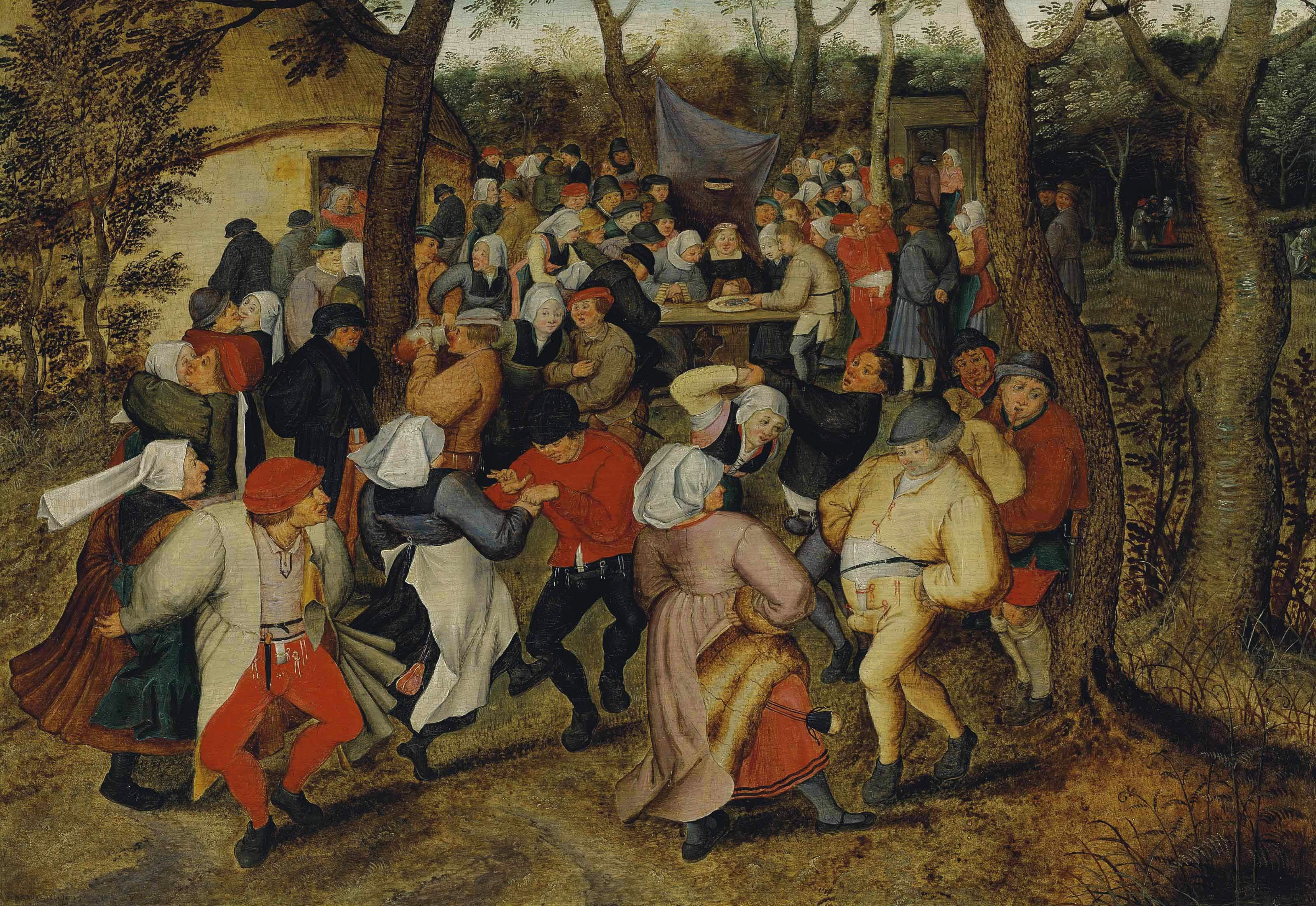 In 1830, the southern provinces of the United Netherlands proclaimed their independence. French-dialect speaking population, as well as the administration and elites, feared the loss of their status and autonomy under Dutch rule while the rapid industrialization in the south highlighted economic differences between the two. Under French rule (1794–1815), French was enforced as the only official language in public life, resulting in a Frenchification of the elites and, to a lesser extent, the middle classes. The Dutch king allowed the use of both Dutch and French dialects as administrative languages in the Flemish provinces. He also enacted laws to reestablish Dutch in schools. The language policy was not the only cause of the secession; the
In 1830, the southern provinces of the United Netherlands proclaimed their independence. French-dialect speaking population, as well as the administration and elites, feared the loss of their status and autonomy under Dutch rule while the rapid industrialization in the south highlighted economic differences between the two. Under French rule (1794–1815), French was enforced as the only official language in public life, resulting in a Frenchification of the elites and, to a lesser extent, the middle classes. The Dutch king allowed the use of both Dutch and French dialects as administrative languages in the Flemish provinces. He also enacted laws to reestablish Dutch in schools. The language policy was not the only cause of the secession; the
 Within Belgium, Flemings form a clearly distinguishable group set apart by their language and customs. However, when compared to the Netherlands most of these cultural and linguistic differences quickly fade, as the Flemish share the same language, similar or identical customs and (though chiefly with the southern part of today's Netherlands) traditional religion with the Dutch. However, the popular perception of being a single polity varies greatly, depending on subject matter, locality and personal background. Generally, Flemings will not identify themselves as being Dutch and vice versa, especially on a national level.
This is partly caused by the popular stereotypes in the Netherlands as well as Flanders which are mostly based on the 'cultural extremes' of both Northern and Southern culture. But also in great part because of the history of emancipation of their culture in Belgium, which has left many Flemings with a high degree of national consciousness, which can be very marked among some Dutch-speaking Belgians. Alongside this overarching political and social affiliation, there also exists a strong tendency towards regionalism, in which individuals greatly identify themselves culturally through their native province, city, region or dialect they speak.
Within Belgium, Flemings form a clearly distinguishable group set apart by their language and customs. However, when compared to the Netherlands most of these cultural and linguistic differences quickly fade, as the Flemish share the same language, similar or identical customs and (though chiefly with the southern part of today's Netherlands) traditional religion with the Dutch. However, the popular perception of being a single polity varies greatly, depending on subject matter, locality and personal background. Generally, Flemings will not identify themselves as being Dutch and vice versa, especially on a national level.
This is partly caused by the popular stereotypes in the Netherlands as well as Flanders which are mostly based on the 'cultural extremes' of both Northern and Southern culture. But also in great part because of the history of emancipation of their culture in Belgium, which has left many Flemings with a high degree of national consciousness, which can be very marked among some Dutch-speaking Belgians. Alongside this overarching political and social affiliation, there also exists a strong tendency towards regionalism, in which individuals greatly identify themselves culturally through their native province, city, region or dialect they speak.
''The Flemish In Wisconsin'', Jeanne and Les Rentmeester, 1985. The small town of Belgique, Missouri, Belgique was settled almost entirely by Flemish immigrants, although a significant number of its residents left after the Great Flood of 1993.
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.
"''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all inhabitants of the medieval County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges a ...
in modern-day Belgium, France, and the Netherlands were referred to as "Flemings", irrespective of their ethnicity or language. The contemporary region of Flanders comprises a part of this historical county, as well as parts of the medieval duchy of Brabant and the medieval county of Loon, where the modern national identity and culture gradually formed.
History
The sense of "Flemish" identity increased significantly after the Belgian Revolution. Prior to this, the term "Vlamingen" in the Dutch language was in first place used for the inhabitants of the former County of Flanders. Flemish, however, had been used since the 14th century to refer to the language and dialects of both the peoples of Flanders and the Duchy of Brabant. The modern Belgian province of Limburg was not part of the Treaty of London that followed the Belgian Revolution, and only came to be considered "Flemish" in the 19th century. In 1830, the southern provinces of the United Netherlands proclaimed their independence. French-dialect speaking population, as well as the administration and elites, feared the loss of their status and autonomy under Dutch rule while the rapid industrialization in the south highlighted economic differences between the two. Under French rule (1794–1815), French was enforced as the only official language in public life, resulting in a Frenchification of the elites and, to a lesser extent, the middle classes. The Dutch king allowed the use of both Dutch and French dialects as administrative languages in the Flemish provinces. He also enacted laws to reestablish Dutch in schools. The language policy was not the only cause of the secession; the
In 1830, the southern provinces of the United Netherlands proclaimed their independence. French-dialect speaking population, as well as the administration and elites, feared the loss of their status and autonomy under Dutch rule while the rapid industrialization in the south highlighted economic differences between the two. Under French rule (1794–1815), French was enforced as the only official language in public life, resulting in a Frenchification of the elites and, to a lesser extent, the middle classes. The Dutch king allowed the use of both Dutch and French dialects as administrative languages in the Flemish provinces. He also enacted laws to reestablish Dutch in schools. The language policy was not the only cause of the secession; the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
majority viewed the sovereign, the Protestant William I, with suspicion and were heavily stirred by the Roman Catholic Church which suspected William of wanting to enforce Protestantism. Lastly, Belgian liberals were dissatisfied with William for his allegedly despotic behaviour.
Following the revolt, the language reforms of 1823 were the first Dutch laws to be abolished and the subsequent years would see a number of laws restricting the use of the Dutch language. This policy led to the gradual emergence of the Flemish Movement, that was built on earlier anti-French feelings of injustice, as expressed in writings (for example by the late 18th-century writer, Jan Verlooy) which criticized the Southern Francophile elites. The efforts of this movement during the following 150 years, have to no small extent facilitated the creation of the '' de jure'' social, political and linguistic equality of Dutch from the end of the 19th century.
After the Hundred Years War many Flemings migrated to the Azores. By 1490 there were 2,000 Flemings living in the Azores. Willem van der Haegen was the original sea captain who brought settlers from Flanders to the Azores. Today many Azoreans trace their genealogy from present day Flanders. Many of their customs and traditions are distinctively Flemish in nature such as windmills used for grain, São Jorge cheese and several religious events such as the imperios and the feast of the Cult of the Holy Spirit.
Identity and culture
 Within Belgium, Flemings form a clearly distinguishable group set apart by their language and customs. However, when compared to the Netherlands most of these cultural and linguistic differences quickly fade, as the Flemish share the same language, similar or identical customs and (though chiefly with the southern part of today's Netherlands) traditional religion with the Dutch. However, the popular perception of being a single polity varies greatly, depending on subject matter, locality and personal background. Generally, Flemings will not identify themselves as being Dutch and vice versa, especially on a national level.
This is partly caused by the popular stereotypes in the Netherlands as well as Flanders which are mostly based on the 'cultural extremes' of both Northern and Southern culture. But also in great part because of the history of emancipation of their culture in Belgium, which has left many Flemings with a high degree of national consciousness, which can be very marked among some Dutch-speaking Belgians. Alongside this overarching political and social affiliation, there also exists a strong tendency towards regionalism, in which individuals greatly identify themselves culturally through their native province, city, region or dialect they speak.
Within Belgium, Flemings form a clearly distinguishable group set apart by their language and customs. However, when compared to the Netherlands most of these cultural and linguistic differences quickly fade, as the Flemish share the same language, similar or identical customs and (though chiefly with the southern part of today's Netherlands) traditional religion with the Dutch. However, the popular perception of being a single polity varies greatly, depending on subject matter, locality and personal background. Generally, Flemings will not identify themselves as being Dutch and vice versa, especially on a national level.
This is partly caused by the popular stereotypes in the Netherlands as well as Flanders which are mostly based on the 'cultural extremes' of both Northern and Southern culture. But also in great part because of the history of emancipation of their culture in Belgium, which has left many Flemings with a high degree of national consciousness, which can be very marked among some Dutch-speaking Belgians. Alongside this overarching political and social affiliation, there also exists a strong tendency towards regionalism, in which individuals greatly identify themselves culturally through their native province, city, region or dialect they speak.
Language
Flemings speak Dutch (specifically its southern variant, which is often colloquially called ' Flemish'). It is the majority language in Belgium, being spoken natively by three-fifths of the population. Its various dialects contain a number of lexical and a few grammatical features which distinguish them from the standard language. As in the Netherlands, the pronunciation of Standard Dutch is affected by the native dialect of the speaker. At the same time East Flemish forms a continuum with both Brabantic and West Flemish. Standard Dutch is primarily based on the Hollandic dialect (spoken in the northwestern Netherlands) and to a lesser extent on Brabantic, which is the most dominant Dutch dialect of the Southern Netherlands andFlanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
.
Religion
Approximately 75% of the Flemish people are by baptism assumedRoman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
, though a still diminishing minority of less than 8% attends Mass on a regular basis and nearly half of the inhabitants of Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
are agnostic or atheist. A 2006 inquiry in Flanders showed 55% chose to call themselves religious and 36% believe that God created the universe.
National symbols
The official flag and coat of arms of the Flemish Community represents a black lion with red claws and tongue on a yellow field ('' or a lion rampant sable armed and langued gules''). A flag with a completely black lion had been in wide use before 1991 when the current version was officially adopted by the Flemish Community. That older flag was at times recognized by government sources (alongside the version with red claws and tongue). Today, only the flag bearing a lion with red claws and tongue is recognized by Belgian law, while the flag with the all black lion is mostly used by Flemish separatist movements. The Flemish authorities also use two logos of a highly stylized black lion which show the claws and tongue in either red or black. The first documented use of the Flemish lion was on the seal of Philip d'Alsace, count of Flanders of 1162. As of that date the use of the Flemish coat of arms (''or a lion rampant sable'') remained in use throughout the reigns of the d'Alsace, Flanders (2nd) and Dampierre dynasties of counts. The motto "Vlaanderen de Leeuw" (Flanders the lion) was allegedly present on the arms of Pieter de Coninck at the Battle of the Golden Spurs on July 11, 1302. After the acquisition of Flanders by the Burgundian dukes the lion was only used in escutcheons. It was only after the creation of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands that the coat of arms (surmounted by a chief bearing the Royal Arms of the Netherlands) once again became the official symbol of the new province East Flanders.Diaspora
Brazil
Canada
The first sizeable wave of Flemish migration toCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
occurred in the 1870s, when Saint Boniface proved a popular destination for work in local flour mills, brick yards and railway yards. Similarly, Flemish were drawn to smaller villages in Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
, where jobs in farming were available. In the early 20th century, Flemish settled in significant numbers across Ontario, particularly attracted by the tobacco-growing industry, in the towns of Chatham, Leamington, Tillsonburg
Tillsonburg is a town in Oxford County, Ontario, Canada with a population of 18,615 located about 50 kilometres southeast of London, on Highway 3 at the junction of Highway 19.
History
Prior to European settlement, the present site of Tills ...
, Wallaceburg, Simcoe Simcoe may refer to:
Geography Canada
* Simcoe, Ontario, a town in southwestern Ontario, near Lake Erie, Canada
* Simcoe County, a county in central Ontario, Canada
* Lake Simcoe, a lake in central Ontario, Canada
* Simcoe North, a federal and pr ...
, Sarnia and Port Hope.
France and the Netherlands
The original County of Flanders encompassed areas which today belong toFrance
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, but are still host to people of Flemish descent and some continued use of Flemish Dutch. Namely, these are Zeelandic Flanders and the Arrondissement of Dunkirk
The arrondissement of Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque, nl, Duinkerke) is an arrondissement of France in the Nord department in the Hauts-de-France region. It has 111 communes. Its population is 377,294 (2016), and its area is .
It roughly correspond ...
(historically known as French Westhoek). The people of North Brabant
North Brabant ( nl, Noord-Brabant ; Brabantian: ; ), also unofficially called Brabant, is a province in the south of the Netherlands. It borders the provinces of South Holland and Gelderland to the north, Limburg to the east, Zeeland to t ...
also share related ancestry.
South Africa
United Kingdom
Prior to the 1600s, there were several substantial waves of Flemish migration to theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
. Today, numerous towns in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
boast large or majority populations with Flemish ancestry as a result. The first wave fled to England in the early 12th Century, escaping damages from a storm across the coast of Flanders, where they were largely resettled in Pembrokeshire by Henry I Henry I may refer to:
876–1366
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876–936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008–1060)
* Henry I the Long, Margrave of the N ...
. They changed the culture and accent in south Pembrokeshire to such an extent, that it led to the area receiving the name Little England beyond Wales
Little England beyond Wales is a name that has been applied to an area of southern Pembrokeshire and southwestern Carmarthenshire in Wales, which has been English in language and culture for many centuries despite its remoteness from England. ...
. Haverfordwest and Tenby
Tenby ( cy, Dinbych-y-pysgod, lit=fortlet of the fish) is both a walled seaside town in Pembrokeshire, Wales, on the western side of Carmarthen Bay, and a local government community.
Notable features include of sandy beaches and the Pembroke ...
consequently grew as important settlements for the Flemish settlers.
In the 14th Century, encouraged by King Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
and perhaps in part due to his marriage to Philippa of Hainault, another wave of migration to England occurred when skilled cloth weavers from Flanders were granted permission to settle there and contribute to the then booming cloth and woollen industries. These migrants particularly settled in the growing Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancas ...
and Yorkshire textile towns of Manchester, Bolton, Blackburn, Liversedge, Bury, Halifax and Wakefield.
Demand for Flemish weavers in England occurred again in both the 15th and 16th Centuries, but this time particularly focused on towns close to the coastline of East Anglia and South East England. Many from this generation of weavers went to Colchester, Sandwich and Braintree. In 1582, it was estimated that there could have been around 1600 Flemish in Sandwich, today almost half of its total population. London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. Norwich is by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of ...
and North Walsham, however, were the most popular destinations, and the nickname for Norwich City F.C. fans, Canaries, is derived from the fact that many of the Norfolk weavers kept pet canaries. The town of Whitefield, near Bury, also claims to owe its name to Flemish cloth weavers that settled in the area during this era, who would lay their cloths out in the sun to bleach them.
These waves of settlement are also evidenced by the common surnames Fleming, Flemings, Flemming and Flemmings.
United States
In theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, the cities of De Pere and Green Bay in Wisconsin attracted many Flemish and Walloon immigrants during the 19th Century.''The Flemish In Wisconsin'', Jeanne and Les Rentmeester, 1985. The small town of Belgique, Missouri, Belgique was settled almost entirely by Flemish immigrants, although a significant number of its residents left after the Great Flood of 1993.
See also
*De Vlaamse Leeuw
"" (; The Flemish Lion) is the official anthem of Flanders, a region and community in Belgium.
Composition
The words of this anthem were written in July 1847 by Hippoliet Van Peene (1811–1864) who was clearly inspired by the song ''Sie ...
* Greater Netherlands
* Flemish Movement
* Flemish Region
* French Flemish
Notes and references
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Flemish People Flanders Germanic ethnic groups Ethnic groups in Belgium