First Battle of Panipat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The first Battle of Panipat, on 20 April 1526, was fought between the invading forces of 
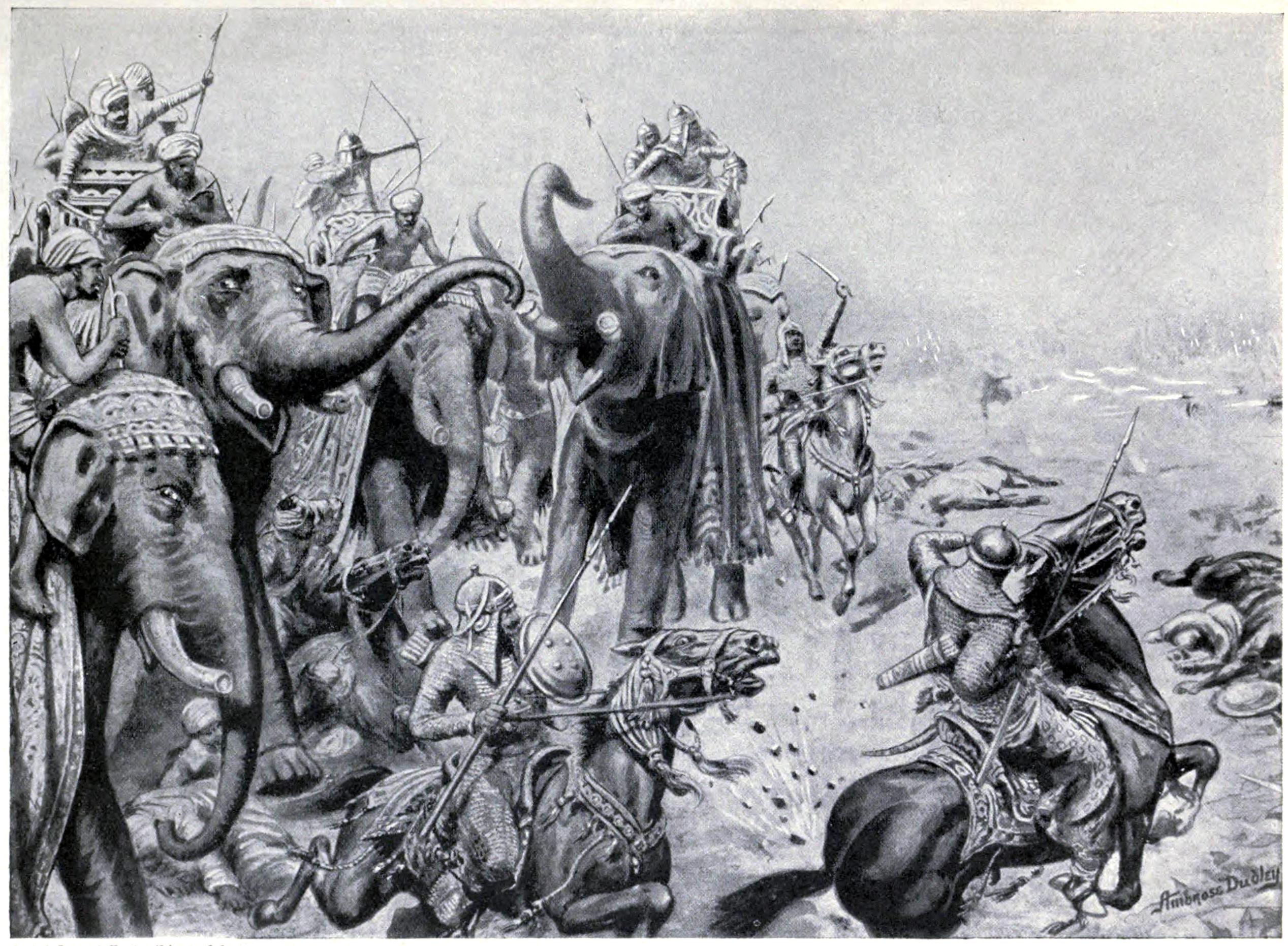 Tactics used by Babur were the ''tulguhma'' and the ''araba''. ''Tulguhma'' meant dividing the whole army into various units, viz. the Left, the Right, and the Centre. The Left and Right divisions were further subdivided into Forward and Rear divisions. Through this, a small army could be used to surround the enemy from all sides. The Centre Forward division was then provided with carts (''araba'') which were placed in rows facing the enemy and tied to each other with animal hide ropes. Behind them were placed cannons protected and supported by mantlets that could be used to easily manoeuvre the cannons. These two tactics made Babur's artillery lethal. The cannons could be fired without any fear of being hit, as they were shielded by the bullock carts held in place by hiding ropes. The heavy cannons could also be easily traversed onto new targets, as they could be manoeuvred by the mantlets which were on wheels.
Tactics used by Babur were the ''tulguhma'' and the ''araba''. ''Tulguhma'' meant dividing the whole army into various units, viz. the Left, the Right, and the Centre. The Left and Right divisions were further subdivided into Forward and Rear divisions. Through this, a small army could be used to surround the enemy from all sides. The Centre Forward division was then provided with carts (''araba'') which were placed in rows facing the enemy and tied to each other with animal hide ropes. Behind them were placed cannons protected and supported by mantlets that could be used to easily manoeuvre the cannons. These two tactics made Babur's artillery lethal. The cannons could be fired without any fear of being hit, as they were shielded by the bullock carts held in place by hiding ropes. The heavy cannons could also be easily traversed onto new targets, as they could be manoeuvred by the mantlets which were on wheels.
Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through hi ...
and the Lodi dynasty. It took place in North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Cen ...
and marked the beginning of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
and the end of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
. This was one of the earliest battles involving gunpowder firearms and field artillery in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
which were introduced by Mughals in this battle.

Background
After losingSamarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
for the second time, Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through hi ...
gave attention to conquer Hindustan
''Hindūstān'' ( , from '' Hindū'' and ''-stān''), also sometimes spelt as Hindōstān ( ''Indo-land''), along with its shortened form ''Hind'' (), is the Persian-language name for the Indian subcontinent that later became commonly used b ...
as he reached the banks of the Chenab in 1519. Until 1524, his aim was to only expand his rule to Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
, mainly to fulfil his ancestor Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kü ...
's legacy, since it used to be part of his empire. At that time, most of North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Cen ...
was under the rule of Ibrahim Lodi of the Lodi dynasty, but the empire was crumbling and there were many defectors. He received invitations from Daulat Khan Lodi, Governor of Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
and Ala-ud-Din, uncle of Ibrahim. He sent an ambassador to Ibrahim, claiming himself the rightful heir to the throne of the country, however the ambassador was detained at Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second List of cities in Pakistan by population, most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th List of largest cities, most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is th ...
and released months later.
Babur started for Lahore, Punjab, in 1524 but found that Daulat Khan Lodi had been driven out by forces sent by Ibrahim Lodi. When Babur arrived at Lahore, the Lodi army marched out and was routed. In response, Babur burned Lahore for two days, then marched to Dipalpur
Dipalpur ( pa, ; ur, ), also spelt Depalpur, is a city in the Okara District of Pakistani province of Punjab that served as headquarters of Depalpur Tehsil, the largest Tehsil of Pakistan. It is situated 25 kilometres from the district capit ...
, placing Alam Khan, another rebel uncle of Lodi's, as governor. Alam Khan was quickly overthrown and fled to Kabul. In response, Babur supplied Alam Khan with troops who later joined up with Daulat Khan Lodi and together with about 30,000 troops, they besieged Ibrahim Lodi at Delhi. He defeated them and drove Alam's army off; and Babur realised Lodi would not allow him to occupy the Punjab.
Battle
Hearing of the size of Ibrahim's army, Babur secured his right flank against the city of Panipat, while digging a trench covered with tree branches to secure his left flank. In the centre, he placed 700 carts tied together with ropes. Between every two carts, there were breastworks for his matchlock men. Babur also ensured that there was enough space for his soldiers to rest their guns and fire. Babur referred to this method as the "Ottoman device" due to its previous use by the Ottomans during the Battle of Chaldiran. When Ibrahim's army arrived, he found the approach to Babur's army too narrow to attack. While Ibrahim redeployed his forces to allow for the narrower front, Babur quickly took advantage of the situation to flank (''tulghuma'') the Lodi army. Many of Ibrahim's troops were unable to get into action and fled when the battle turned against them. Ibrahim Lodi was killed while trying to retreat and beheaded. 20,000 Lodi soldiers were killed in battle.Advantage of cannons in the battle
Babur's guns proved decisive in battle, firstly because Ibrahim lacked any field artillery, but also because the sound of the cannon frightened Ibrahim's elephants, causing them to trample his men.Tactics
 Tactics used by Babur were the ''tulguhma'' and the ''araba''. ''Tulguhma'' meant dividing the whole army into various units, viz. the Left, the Right, and the Centre. The Left and Right divisions were further subdivided into Forward and Rear divisions. Through this, a small army could be used to surround the enemy from all sides. The Centre Forward division was then provided with carts (''araba'') which were placed in rows facing the enemy and tied to each other with animal hide ropes. Behind them were placed cannons protected and supported by mantlets that could be used to easily manoeuvre the cannons. These two tactics made Babur's artillery lethal. The cannons could be fired without any fear of being hit, as they were shielded by the bullock carts held in place by hiding ropes. The heavy cannons could also be easily traversed onto new targets, as they could be manoeuvred by the mantlets which were on wheels.
Tactics used by Babur were the ''tulguhma'' and the ''araba''. ''Tulguhma'' meant dividing the whole army into various units, viz. the Left, the Right, and the Centre. The Left and Right divisions were further subdivided into Forward and Rear divisions. Through this, a small army could be used to surround the enemy from all sides. The Centre Forward division was then provided with carts (''araba'') which were placed in rows facing the enemy and tied to each other with animal hide ropes. Behind them were placed cannons protected and supported by mantlets that could be used to easily manoeuvre the cannons. These two tactics made Babur's artillery lethal. The cannons could be fired without any fear of being hit, as they were shielded by the bullock carts held in place by hiding ropes. The heavy cannons could also be easily traversed onto new targets, as they could be manoeuvred by the mantlets which were on wheels.
After Ibrahim Lodi died
Ibrahim Lodi died on the field of battle along with 20,000 of his troops. The battle of Panipat was militarily a decisive victory for the Timurids. Politically it gained Babur new lands, and initiated a new phase of his establishment of the long-lastingMughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
in the heart of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
.
See also
*Battle of Hisar Firoza
The Battle of Hisar Firoza took place in Hisar, in the state of Haryana, India between Zahir-ud-din Muhammad Babur and Hamid Khan on February 26, 1526. Babur with his son Humayun clashed against the Afghan under the command of Hamid Khan. It was ...
* Battle of Khanwa
* Second Battle of Panipat
* Third Battle of Panipat
* Battle of Ghaghra
The Battle of Ghaghra, fought in 1529, was a great battle for the conquest of India by the Mughal Empire. It followed the first Battle of Panipat in 1526 and the Battle of Khanwa in 1527. The forces of Mughal Emperor Babur of the emerging Mughal ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Battle of Panipat (1526) Panipat 1st Battle 1526 Panipat Panipat Lodi dynasty B History of Haryana 1526 in India Panipat 16th century in Delhi