Famatinian Orogeny on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Famatinian orogeny ( es, Orogenia de Famatina) is an
The Famatinian orogeny ( es, Orogenia de Famatina) is an
Animation of world plate tectonics
note Cuyania's (red) trajectory from 0:20 onwards. Orogenies of South America Geology of Argentina Geology of Bolivia Geology of Chile Geology of Peru Cambrian orogenies Ordovician orogenies Silurian orogenies Devonian orogenies Carboniferous orogenies Cambrian South America Ordovician South America Silurian South America Devonian South America Carboniferous South America Sierras Pampeanas
 The Famatinian orogeny ( es, Orogenia de Famatina) is an
The Famatinian orogeny ( es, Orogenia de Famatina) is an orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted ...
that predates the rise of the Andes and that took place in what is now western South America during the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and '' ...
, leading to the formation of the Famatinian orogen also known as the Famatinian belt. The Famatinian orogeny lasted from the Late Cambrian
Late may refer to:
* LATE, an acronym which could stand for:
** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia
** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law
** Local average treatment effect, ...
to at least the Late Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wher ...
and possibly the Early Carboniferous
Early may refer to:
History
* The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.:
** Early Christianity
** Early modern Europe
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa
* Early, Texas
* Early ...
, with orogenic activity peaking about 490 to 460 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
. The orogeny involved metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chem ...
and deformation
Deformation can refer to:
* Deformation (engineering), changes in an object's shape or form due to the application of a force or forces.
** Deformation (physics), such changes considered and analyzed as displacements of continuum bodies.
* Defo ...
in the crust and the eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra ( ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often ...
and intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
of magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural s ...
along a Famatinian magmatic arc that formed a chain of volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
es. The igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
s of the Famatinian magmatic arc are of calc-alkaline
The calc-alkaline magma series is one of two main subdivisions of the subalkaline magma series, the other subalkaline magma series being the tholeiitic series. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic ma ...
character and include gabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is ch ...
s, tonalite
Tonalite is an igneous, plutonic ( intrusive) rock, of felsic composition, with phaneritic (coarse-grained) texture. Feldspar is present as plagioclase (typically oligoclase or andesine) with alkali feldspar making up less than 10% of the total f ...
s and granodiorite
Granodiorite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock similar to granite, but containing more plagioclase feldspar than orthoclase feldspar.
The term banatite is sometimes used informally for various rocks ranging from gr ...
s. The youngest igneous rocks of the arc are granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underg ...
s.
The relationship of the orogeny with the Achala and Cerro Aspero batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, such ...
s of central Argentina is not fully understood. These Devonian batholiths are possibly of post-orogenic character.
Outcrops and sediments
The Famatinian orogen's mainoutcrops
An outcrop or rocky outcrop is a visible exposure of bedrock or ancient superficial deposits on the surface of the Earth.
Features
Outcrops do not cover the majority of the Earth's land surface because in most places the bedrock or superficia ...
lie in Sierras Pampeanas in northwestern Argentina. Only the western part of Sierras Pampeanas bears evidence of the Famatinian orogeny; the eastern parts appear to have been largely unaffected. In northern Chile the Belén Metamorphic Complex is believed to be part of the orogen as it was subject to metamorphism in the early Paleozoic. To the south in La Pampa Province
La Pampa () is a sparsely populated province of Argentina, located in the Pampas in the center of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the north clockwise San Luis, Córdoba, Buenos Aires, Río Negro, Neuquén and Mendoza.
History
In ...
, outcrops associated with the orogeny are scarce since most of that region has become blanketed by much more recent Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand a ...
s.
In Peru's Cordillera Oriental a "Famatinian" orogeny exists which is coeval with the classical Famatinian orogeny found further south. In the time-span from 480 Ma to 435 Ma (Late Cambrian to Silurian) rocks of Cordillera Oriental were deformed and a magmatic arc developed.
Towards what is now the east of the Famatinian magmatic arc a Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the P ...
sedimentary basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock. They form when long-term subsidence ...
developed into a back-arc basin
A back-arc basin is a type of geologic basin, found at some convergent plate boundaries. Presently all back-arc basins are submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones, with many found in the western Pacific Ocean. Most of ...
during the Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya.
The ...
. This basin went from Peru, through Bolivia to northwestern Argentina. The basin collected sediments from the Famatinian orogen and arc and while it did not contain oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic c ...
it was a marine basin.
Plutonic rock
Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form '' intrusions'', such as batholiths, dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.Intrusive RocksIntrusive rocks accessdate: March 2 ...
s cropping out in Cordón de Lila and Sierra de Almeida south of Salar de Atacama
Salar de Atacama is the largest salt flat in Chile. It is located south of San Pedro de Atacama, is surrounded by mountains, and has no drainage outlets. In the east it is enclosed by the main chain of the Andes, while to the west lies a seconda ...
in Chile formed in the Cambrian and Ordovician in association with the orogeny. The compositions of the plutonic rocks are granodiorite
Granodiorite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock similar to granite, but containing more plagioclase feldspar than orthoclase feldspar.
The term banatite is sometimes used informally for various rocks ranging from gr ...
and monzogranite
Monzogranites are biotite granite rocks that are considered to be the final fractionation product of magma. Monzogranites are characteristically felsic (SiO2 > 73%, and FeO + MgO + TiO2 < 2.4), weakly metaluminous Metaluminous rocks are igneous rocks that have a molar proportion of aluminium oxide lower than the combination of calcium oxide, sodium oxide and potassium oxide. This contrasts with peraluminous rocks in which the aluminium oxide concentration i ...
or peraluminous
Peraluminous rocks are igneous rocks that have a molecular proportion of aluminium oxide higher than the combination of sodium oxide, potassium oxide and calcium oxide.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy, ''Petrology,'' Freeman, 2nd ed., 1995, p. ...
. These rocks are remnants of the magmatism along the western rim of the Famatinian orogeny.
Plate tectonic setting
Famatinian arcmagmatism
Magmatism is the emplacement of magma within and at the surface of the outer layers of a terrestrial planet, which solidifies as igneous rocks. It does so through magmatic activity or igneous activity, the production, intrusion and extrusion of ...
was caused by the subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, ...
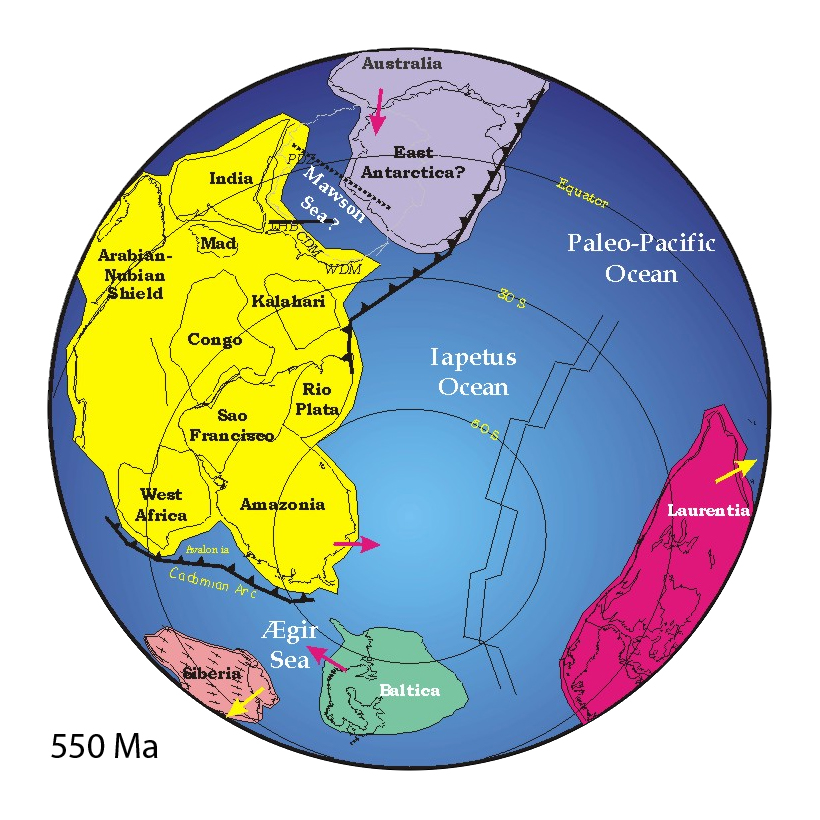
of Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean (; ) was an ocean that existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale (between 600 and 400 million years ago). The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleoco ...
lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years o ...
beneath Gondwana. As subduction went on, the peak of the orogeny resulted from the collision
In physics, a collision is any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time. Although the most common use of the word ''collision'' refers to incidents in which two or more objects collide with great fo ...
of the Cuyania terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own ...
with Pampia in the Ordovician.
It has been suggested that the coeval Appalachian Taconic orogeny
The Taconic orogeny was a mountain building period that ended 440 million years ago and affected most of modern-day New England. A great mountain chain formed from eastern Canada down through what is now the Piedmont of the East coast of the Uni ...
is the "northward" continuation of the Famatinian orogeny. This has been explained by adding that the continent Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although ...
could have collided with Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
(at what is today western South America) in early Paleozoic times due to the closure of the Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean (; ) was an ocean that existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale (between 600 and 400 million years ago). The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleoco ...
. Supporting this hypothesis is the suggestion that the orogens have "truncated ends" that can be matched and that both share the commonality of having carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ...
platform
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand a ...
s at what is today their western side. Further, in the mentioned sediments both orogens host similar Olenellid trilobite faunas, something that is not expected to be unless both orogens had some sort of contact. This is because trilobites are unable to cross deep ocean basins. According to this view the Cuyania terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own ...
would be an allochthon
upright=1.6, Schematic overview of a thrust system. The hanging wall block is (when it has reasonable proportions) called a nappe. If an erosional hole is created in the nappe that is called a window (geology)">window. A klippe is a solitary ou ...
ous block of Laurentian origin that was left in Gondwana after the continents went apart. But such views are not unchallenged since Cuyania is alternatively suggested to have drifted across Iapetus Ocean as a microcontinent
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin.
Caus ...
starting in Laurentia and accreting then to Gondwana. Further a third model claims Cuyania is para-autochthonous and arrived at its current place by strike-slip fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tecton ...
movements starting not from Laurentia but from another region of Gondwana. The fact that Precordillera terrane has many trilobite genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomencl ...
in common with Laurentia but many species are endemic have led to some differing interpretations on what paleogeographic and tectonic history conditions are plausible explanations for this biogeography.
Notes
References
{{Major South American geological formationsExternal links
Animation of world plate tectonics
note Cuyania's (red) trajectory from 0:20 onwards. Orogenies of South America Geology of Argentina Geology of Bolivia Geology of Chile Geology of Peru Cambrian orogenies Ordovician orogenies Silurian orogenies Devonian orogenies Carboniferous orogenies Cambrian South America Ordovician South America Silurian South America Devonian South America Carboniferous South America Sierras Pampeanas