FGF21 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) is a
 FGF21 is specifically induced by mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (HMGCS2) activity. The oxidized form of ketone bodies (acetoacetate) in a cultured medium also induced FGF21, possibly via a sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-dependent mechanism. HMGCS2 activity has also been shown to be increased by deacetylation of lysines 310, 447, and 473 via SIRT3 in the mitochondria.
While FGF21 is expressed in numerous tissues, including liver,
FGF21 is specifically induced by mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (HMGCS2) activity. The oxidized form of ketone bodies (acetoacetate) in a cultured medium also induced FGF21, possibly via a sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-dependent mechanism. HMGCS2 activity has also been shown to be increased by deacetylation of lysines 310, 447, and 473 via SIRT3 in the mitochondria.
While FGF21 is expressed in numerous tissues, including liver,
Got a sweet tooth? Blame your liver
Phys.org, 2017 {{Growth factor receptor modulators Aging-related proteins Anti-aging substances
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
that in mammals is encoded by the ''FGF21'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
. The protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by the macrophages. They are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in ...
(FGF) family and specifically a member of the endocrine subfamily which includes FGF23 and FGF15/19. FGF21 is the primary endogenous agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
of the FGF21 receptor, which is composed of the co-receptor
A co-receptor is a cell surface receptor that binds a signalling molecule in addition to a primary receptor in order to facilitate Ligand (biochemistry), ligand recognition and initiate biological processes, such as entry of a pathogen into a host ...
s FGF receptor 1 and β-Klotho.
FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities and are involved in a variety of biological processes including embryonic development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermat ...
, cell growth, morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGFs act through a family of four FGF receptors. Binding is complicated and requires both interaction of the FGF molecule with an FGF receptor and binding to heparin through a heparin binding domain. Endocrine FGFs lack a heparin binding domain and thus can be released into the circulation.
FGF21 is a hepatokine
Hepatokines (Greek ''heapto-'', liver; and ''-kinos'', movement) are proteins produced by liver cells (hepatocytes) that are Secretion, secreted into the Circulatory system, circulation and function as hormones across the organism. Research is most ...
– i.e., a hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
secreted by the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
– that regulates simple sugar
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units ( monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
Chemically, monosaccharides are poly ...
intake and preferences for sweet foods via signaling through FGF21 receptors in the paraventricular nucleus
The paraventricular nucleus (PVN) is a nucleus in the hypothalamus, located next to the third ventricle. Many of its neurons project to the posterior pituitary where they secrete oxytocin, and a smaller amount of vasopressin. Other secretions ...
of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
and correlates with reduced dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
neurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron ...
within the nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for ' nucleus adjacent to the septum') is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypo ...
.
A single-nucleotide polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a ...
of the FGF21 gene – the FGF21 rs838133 variant (frequency 44.7%) – has been identified as a genetic mechanism responsible for the sweet tooth behavioral phenotype, a trait associated with cravings for sweets and high sugar consumption, in both humans and mice.
Regulation
 FGF21 is specifically induced by mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (HMGCS2) activity. The oxidized form of ketone bodies (acetoacetate) in a cultured medium also induced FGF21, possibly via a sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-dependent mechanism. HMGCS2 activity has also been shown to be increased by deacetylation of lysines 310, 447, and 473 via SIRT3 in the mitochondria.
While FGF21 is expressed in numerous tissues, including liver,
FGF21 is specifically induced by mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2 (HMGCS2) activity. The oxidized form of ketone bodies (acetoacetate) in a cultured medium also induced FGF21, possibly via a sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-dependent mechanism. HMGCS2 activity has also been shown to be increased by deacetylation of lysines 310, 447, and 473 via SIRT3 in the mitochondria.
While FGF21 is expressed in numerous tissues, including liver, brown adipose tissue
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) or brown fat makes up the adipose organ together with white adipose tissue (or white fat). Brown adipose tissue is found in almost all mammals.
Classification of brown fat refers to two distinct cell populations with si ...
, white adipose tissue
White adipose tissue or white fat is one of the two types of adipose tissue found in mammals. The other kind is brown adipose tissue. White adipose tissue is composed of monolocular Adipocyte, adipocytes.
In humans, the healthy body fat percent ...
(WAT) and pancreas, circulating levels of FGF21 are derived specifically from the liver in mice. In liver FGF21 expression is regulated by PPARα and levels rise substantially with both fasting and consumption of ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate diet, low-carbohydrate dietary therapy that in conventional medicine is used mainly to treat hard-to-control (refractory) epilepsy in children. The diet forces the body to b ...
s.
Liver X receptor
The liver X receptor (LXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors and is closely related to nuclear receptors such as the PPARs, FXR and RXR. Liver X receptors (LXRs) are important regulators of cholesterol, fatt ...
(LXR) represses FGF21 in humans via an LXR response element located from -37 to -22 bp on the human FGF21 promoter.
Function
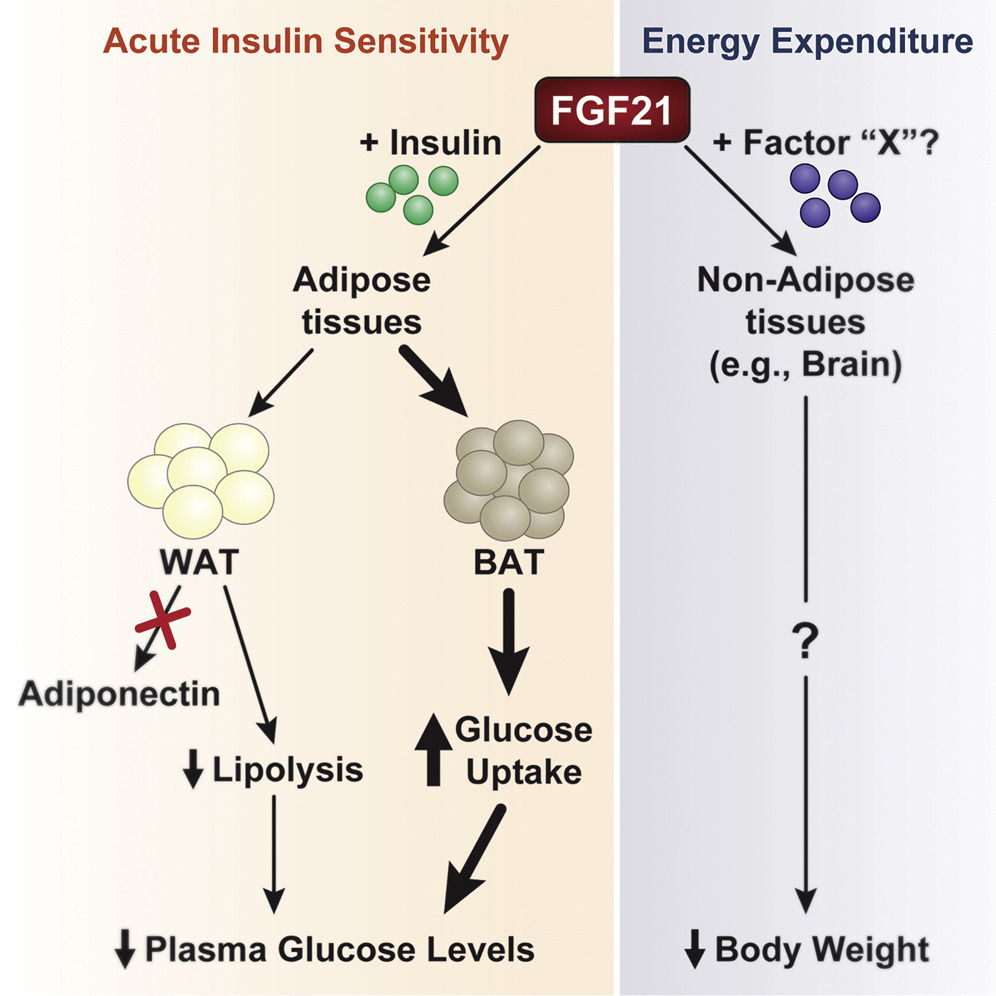
FGF21 stimulatesglucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
uptake in adipocyte
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cell (biology), cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through ...
s but not in other cell types. This effect is additive to the activity of insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
. FGF21 treatment of adipocytes is associated with phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
of FRS2, a protein linking FGF receptors to the Ras/MAP kinase pathway. FGF21 injection in ob/ob mice results in an increase in Glut1
Glucose transporter 1 (or GLUT1), also known as solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 (SLC2A1), is a uniporter protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC2A1'' gene. GLUT1 facilitates the transport of glucose acro ...
in adipose
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
tissue. FGF21 also protects animals from diet-induced obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
when overexpressed in transgenic
A transgene is a gene that has been transferred naturally, or by any of a number of genetic engineering techniques, from one organism to another. The introduction of a transgene, in a process known as transgenesis, has the potential to change the ...
mice and lowers blood glucose and triglyceride
A triglyceride (from '' tri-'' and '' glyceride''; also TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids.
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates ...
levels when administered to diabetic
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
rodents. Treatment of animals with FGF21 results in increased energy expenditure, fat utilization and lipid excretion.
β-Klotho () functions as a cofactor essential for FGF21 activity.
In cows plasma FGF21 was nearly undetectable in late pregnancy (LP), peaked at parturition, and then stabilized at lower, chronically elevated concentrations during early lactation (EL). Plasma FGF21 was similarly increased in the absence of parturition when an energy-deficit state was induced by feed restricting late-lactating dairy cows, implicating energy insufficiency as a cause of chronically elevated FGF21 in EL. The liver was the major source of plasma FGF21 in early lactation with little or no contribution by WAT
A wat (, ; , ; , ; ; , ) is a type of Buddhist and Hindu temple in Cambodia, Laos, East Shan State (Myanmar), Yunnan (China), the Southern Province of Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
Etymology
The word ''wat'' is borrowed from the Sanskrit ''v ...
, skeletal muscle, and mammary gland. Meaningful expression of the FGF21 coreceptor β-Klotho was restricted to liver and WAT in a survey of 15 tissues that included the mammary gland. Expression of β-Klotho and its subset of interacting FGF receptors was modestly affected by the transition from LP to EL in liver but not in WAT.
Clinical significance
Serum FGF-21 levels were significantly increased in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) which may indicate a role in the pathogenesis of T2DM. Elevated levels also correlate with liver fat content in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and positively correlate with BMI in humans suggesting obesity as a FGF21-resistant state. Asingle-nucleotide polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a ...
(SNP) of the FGF21 gene – the FGF21 rs838133 variant (frequency 44.7%) – has been identified as a genetic mechanism responsible for the sweet tooth behavioral phenotype, a trait associated with cravings for sweets and high sugar consumption, in both humans and mice.
Animal studies
Mice lacking FGF21 fail to fully induce PGC-1α expression in response to a prolonged fast and have impairedgluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
and ketogenesis.
FGF21 stimulates phosphorylation of fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 and ERK1/2 in the liver. Acute FGF21 treatment induced hepatic expression of key regulators of gluconeogenesis, lipid metabolism, and ketogenesis including glucose-6-phosphatase, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase, 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase type 1, and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1α. In addition, injection of FGF21 was associated with decreased circulating insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
and free fatty acid levels. FGF21 treatment induced mRNA and protein expression of PGC-1α, but in mice PGC-1α expression was not necessary for the effect of FGF21 on glucose metabolism.
In mice FGF21 is strongly induced in liver by prolonged fasting via PPAR-alpha and in turn induces the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α and stimulates hepatic gluconeogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, and ketogenesis. FGF21 also blocks somatic growth and sensitizes mice to a hibernation-like state of torpor, playing a key role in eliciting and coordinating the adaptive starvation response. FGF21 expression is also induced in white adipose tissue by PPAR-gamma, which may indicate it also regulates metabolism in the fed state. FGF21 is induced in both rodents and humans consuming a low protein diet. FGF21 expression is also induced by diets with reduced levels of the essential dietary amino acids methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans.
As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine play ...
or threonine, or with reduced levels of branched-chain amino acids.
Activation of AMPK and SIRT1 by FGF21 in adipocytes enhanced mitochondrial oxidative capacity as demonstrated by increases in oxygen consumption, citrate synthase activity, and induction of key metabolic genes. The effects of FGF21 on mitochondrial function require serine/threonine kinase 11 (STK11/LKB1), which activates AMPK. Inhibition of AMPK, SIRT1, and PGC-1α activities attenuated the effects of FGF21 on oxygen consumption and gene expression, indicating that FGF21 regulates mitochondrial activity and enhances oxidative capacity through an LKB1-AMPK-SIRT1-PGC-1α-dependent mechanism in adipocytes, resulting in increased phosphorylation of AMPK, increased cellular NAD+ levels and activation of SIRT1 and deacetylation of SIRT1 targets PGC-1α and histone 3.
Acutely, the rise in FGF21 in response to alcohol consumption inhibits further drinking. Chronically, the rise in FGF21 expression in the liver may protect against liver damage.
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
* * *Got a sweet tooth? Blame your liver
Phys.org, 2017 {{Growth factor receptor modulators Aging-related proteins Anti-aging substances