Franz Joseph Haydn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of
Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of
 Joseph Haydn was born in Rohrau, Austria, a village that at that time stood on the border with Hungary. His father was
Joseph Haydn was born in Rohrau, Austria, a village that at that time stood on the border with Hungary. His father was 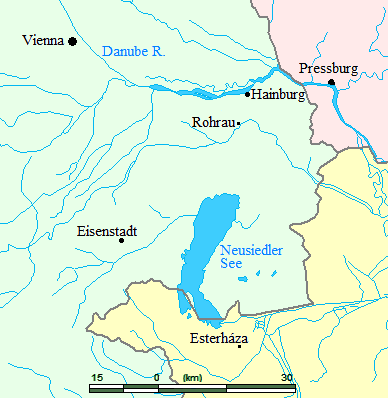
 In 1760, with the security of a Kapellmeister position, Haydn married. His wife was the former Maria Anna Theresia Keller (1729–1800), the sister of Therese (b. 1733), with whom Haydn had previously been in love. Haydn and his wife had an unhappy marriage, from which the laws of the time permitted no escape. They produced no children, and both took lovers.
In 1760, with the security of a Kapellmeister position, Haydn married. His wife was the former Maria Anna Theresia Keller (1729–1800), the sister of Therese (b. 1733), with whom Haydn had previously been in love. Haydn and his wife had an unhappy marriage, from which the laws of the time permitted no escape. They produced no children, and both took lovers.
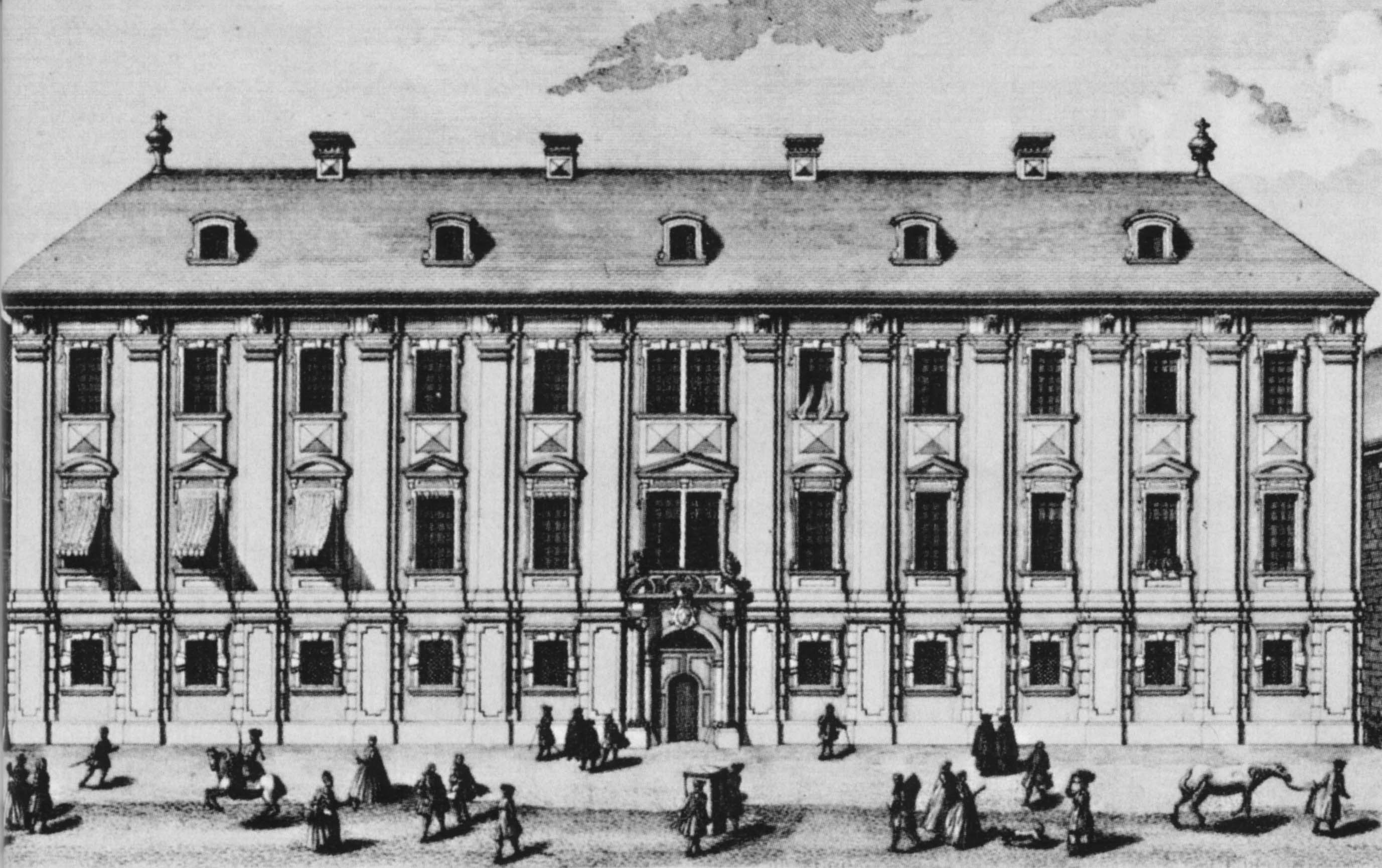

 Count Morzin soon suffered financial reverses that forced him to dismiss his musical establishment, but Haydn was quickly offered a similar job (1761) by Prince Paul Anton, head of the immensely wealthy
Count Morzin soon suffered financial reverses that forced him to dismiss his musical establishment, but Haydn was quickly offered a similar job (1761) by Prince Paul Anton, head of the immensely wealthy  As a "house officer" in the Esterházy establishment, Haydn wore
As a "house officer" in the Esterházy establishment, Haydn wore
 In 1790, Prince Nikolaus died and was succeeded as prince by his son Anton. Following a trend of the time, Anton sought to economize by dismissing most of the court musicians. Haydn retained a nominal appointment with Anton, at a reduced salary of 400 florins, as well as a 1000-florin pension from Nikolaus. Since Anton had little need of Haydn's services, he was willing to let him travel, and the composer accepted a lucrative offer from
In 1790, Prince Nikolaus died and was succeeded as prince by his son Anton. Following a trend of the time, Anton sought to economize by dismissing most of the court musicians. Haydn retained a nominal appointment with Anton, at a reduced salary of 400 florins, as well as a 1000-florin pension from Nikolaus. Since Anton had little need of Haydn's services, he was willing to let him travel, and the composer accepted a lucrative offer from  Musically, Haydn's visits to England generated some of his best-known work, including the '' Surprise'', ''
Musically, Haydn's visits to England generated some of his best-known work, including the '' Surprise'', ''
 By this time Haydn had become a public figure in Vienna. He spent most of his time in his home, a large house in the suburb of Windmühle, and wrote works for public performance. In collaboration with his librettist and mentor Gottfried van Swieten, and with funding from van Swieten's Gesellschaft der Associierten, he composed his two great oratorios, ''The Creation (Haydn), The Creation'' (1798) and ''The Seasons (Haydn), The Seasons'' (1801). Both were enthusiastically received. Haydn frequently appeared before the public, often leading performances of ''The Creation'' and ''The Seasons'' for charity benefits, including Tonkünstler-Societät programs with massed musical forces. He also composed instrumental music: the popular ''Trumpet Concerto (Haydn), Trumpet Concerto'', and the last nine in his long series of string quartets, including the ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 2 ("Fifths"), Fifths'', ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 3 ("Emperor"), Emperor'', and ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 4 ("Sunrise"), Sunrise''. Directly inspired by hearing audiences sing God Save the King in London, in 1797 Haydn wrote a patriotic "Emperor's Hymn" "", ("God Save Emperor Francis"). This achieved great success and became "the enduring emblem of Austrian identity right up to the First World War" (Jones). The melody was used for von Fallersleben's (1841), whose third stanza is today the national anthem of Germany.
During the later years of this successful period, Haydn faced incipient old age and fluctuating health, and he had to struggle to complete his final works. His last major work, from 1802, was the sixth mass for the Esterházys, the ''Harmoniemesse''.
By this time Haydn had become a public figure in Vienna. He spent most of his time in his home, a large house in the suburb of Windmühle, and wrote works for public performance. In collaboration with his librettist and mentor Gottfried van Swieten, and with funding from van Swieten's Gesellschaft der Associierten, he composed his two great oratorios, ''The Creation (Haydn), The Creation'' (1798) and ''The Seasons (Haydn), The Seasons'' (1801). Both were enthusiastically received. Haydn frequently appeared before the public, often leading performances of ''The Creation'' and ''The Seasons'' for charity benefits, including Tonkünstler-Societät programs with massed musical forces. He also composed instrumental music: the popular ''Trumpet Concerto (Haydn), Trumpet Concerto'', and the last nine in his long series of string quartets, including the ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 2 ("Fifths"), Fifths'', ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 3 ("Emperor"), Emperor'', and ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 4 ("Sunrise"), Sunrise''. Directly inspired by hearing audiences sing God Save the King in London, in 1797 Haydn wrote a patriotic "Emperor's Hymn" "", ("God Save Emperor Francis"). This achieved great success and became "the enduring emblem of Austrian identity right up to the First World War" (Jones). The melody was used for von Fallersleben's (1841), whose third stanza is today the national anthem of Germany.
During the later years of this successful period, Haydn faced incipient old age and fluctuating health, and he had to struggle to complete his final works. His last major work, from 1802, was the sixth mass for the Esterházys, the ''Harmoniemesse''.
 The winding down of Haydn's career was gradual. The Esterházy family kept him on as Kapellmeister to the very end (much as they had with his predecessor Werner long before), but they appointed new staff to lead their musical establishment: Johann Michael Fuchs in 1802 as Vice-Kapellmeister. and Johann Nepomuk Hummel as Konzertmeister in 1804. Haydn's last summer in Eisenstadt was in 1803, and his last appearance before the public as a conductor was a charity performance of ''The Seven Last Words'' on 26 December 1803. As debility set in, he made largely futile efforts at composition, attempting to revise a rediscovered Missa brevis (Haydn), Missa brevis from his teenage years and complete his List of string quartets by Joseph Haydn#Opus 103, final string quartet. The former project was abandoned for good in 1805, and the quartet was published with just two movements.
Haydn was well cared for by his servants, and he received many visitors and public honours during his last years, but they could not have been very happy years for him. During his illness, Haydn often found solace by sitting at the piano and playing his "Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser, Emperor's Hymn". A final triumph occurred on 27 March 1808 when a performance of ''The Creation'' was organized in his honour. The very frail composer was brought into the hall on an armchair to the sound of trumpets and drums and was greeted by Beethoven, Antonio Salieri, Salieri (who led the performance) and by other musicians and members of the aristocracy. Haydn was both moved and exhausted by the experience and had to depart at intermission.
The winding down of Haydn's career was gradual. The Esterházy family kept him on as Kapellmeister to the very end (much as they had with his predecessor Werner long before), but they appointed new staff to lead their musical establishment: Johann Michael Fuchs in 1802 as Vice-Kapellmeister. and Johann Nepomuk Hummel as Konzertmeister in 1804. Haydn's last summer in Eisenstadt was in 1803, and his last appearance before the public as a conductor was a charity performance of ''The Seven Last Words'' on 26 December 1803. As debility set in, he made largely futile efforts at composition, attempting to revise a rediscovered Missa brevis (Haydn), Missa brevis from his teenage years and complete his List of string quartets by Joseph Haydn#Opus 103, final string quartet. The former project was abandoned for good in 1805, and the quartet was published with just two movements.
Haydn was well cared for by his servants, and he received many visitors and public honours during his last years, but they could not have been very happy years for him. During his illness, Haydn often found solace by sitting at the piano and playing his "Gott erhalte Franz den Kaiser, Emperor's Hymn". A final triumph occurred on 27 March 1808 when a performance of ''The Creation'' was organized in his honour. The very frail composer was brought into the hall on an armchair to the sound of trumpets and drums and was greeted by Beethoven, Antonio Salieri, Salieri (who led the performance) and by other musicians and members of the aristocracy. Haydn was both moved and exhausted by the experience and had to depart at intermission.
 Haydn lived on for 14 more months. His final days were hardly serene, as in May 1809 the French army under Napoleon launched an attack on Vienna and on 10 May bombarded his neighbourhood. According to Griesinger, "Four case shots fell, rattling the windows and doors of his house. He called out in a loud voice to his alarmed and frightened people, 'Don't be afraid, children, where Haydn is, no harm can reach you!'. But the spirit was stronger than the flesh, for he had hardly uttered the brave words when his whole body began to tremble.". More bombardments followed until the city fell to the French on 13 May. Haydn, was, however, deeply moved and appreciative when on 17 May a French cavalry officer named Sulémy came to pay his respects and sang, skillfully, an aria from ''The Creation''.
On 26 May Haydn played his "Emperor's Hymn" with unusual gusto three times; the same evening he collapsed and was taken to what proved to be his deathbed. He died peacefully in his own home at 12:40 a.m. on 31 May 1809, aged 77. On 15 June, a memorial service was held in the Schottenkirche, Vienna, Schottenkirche at which Mozart's Requiem (Mozart), Requiem was performed. Haydn's remains were interred in the local Haydnpark, Hundsturm cemetery until 1820 when they were moved to Eisenstadt by Prince Nikolaus. His head took a different journey; Haydn's head, it was stolen by phrenology, phrenologists shortly after burial, and the skull was reunited with the other remains only in 1954, now interred in a tomb in the north tower of the Bergkirche (Eisenstadt), Bergkirche.
Haydn lived on for 14 more months. His final days were hardly serene, as in May 1809 the French army under Napoleon launched an attack on Vienna and on 10 May bombarded his neighbourhood. According to Griesinger, "Four case shots fell, rattling the windows and doors of his house. He called out in a loud voice to his alarmed and frightened people, 'Don't be afraid, children, where Haydn is, no harm can reach you!'. But the spirit was stronger than the flesh, for he had hardly uttered the brave words when his whole body began to tremble.". More bombardments followed until the city fell to the French on 13 May. Haydn, was, however, deeply moved and appreciative when on 17 May a French cavalry officer named Sulémy came to pay his respects and sang, skillfully, an aria from ''The Creation''.
On 26 May Haydn played his "Emperor's Hymn" with unusual gusto three times; the same evening he collapsed and was taken to what proved to be his deathbed. He died peacefully in his own home at 12:40 a.m. on 31 May 1809, aged 77. On 15 June, a memorial service was held in the Schottenkirche, Vienna, Schottenkirche at which Mozart's Requiem (Mozart), Requiem was performed. Haydn's remains were interred in the local Haydnpark, Hundsturm cemetery until 1820 when they were moved to Eisenstadt by Prince Nikolaus. His head took a different journey; Haydn's head, it was stolen by phrenology, phrenologists shortly after burial, and the skull was reunited with the other remains only in 1954, now interred in a tomb in the north tower of the Bergkirche (Eisenstadt), Bergkirche.
 James Webster (musicologist), James Webster writes of Haydn's public character thus: "Haydn's public life exemplified the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment ideal of the ''honnête homme'' (''honest man''): the man whose good character and worldly success enable and justify each other. His modesty and probity were everywhere acknowledged. These traits were not only prerequisites to his success as
James Webster (musicologist), James Webster writes of Haydn's public character thus: "Haydn's public life exemplified the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment ideal of the ''honnête homme'' (''honest man''): the man whose good character and worldly success enable and justify each other. His modesty and probity were everywhere acknowledged. These traits were not only prerequisites to his success as
 A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical Motif (music), motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly. W. Dean Sutcliffe mentions this in a criticism of contemporary Haydn performance practice:
A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical Motif (music), motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly. W. Dean Sutcliffe mentions this in a criticism of contemporary Haydn performance practice:
"Joseph Haydn"
by Karl Geiringer, Raymond L. Knapp, H. C. Robbins Landon, ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' * *
Joseph Haydn-Institut
(in German)
The Haydn Society of North America
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Haydn, Joseph Joseph Haydn, 1732 births 1809 deaths 18th-century Austrian people 18th-century Austrian classical composers 18th-century Austrian male musicians 19th-century Austrian male musicians Age of Enlightenment Austrian classical pianists Austrian Classical-period composers Austrian expatriates in Hungary Austrian Freemasons Austrian opera composers Austrian Roman Catholics Catholic liturgical composers Classical composers of church music Composers for piano Composers from Vienna Esterházy family Harrach family Austrian male classical pianists Austrian male opera composers National anthem writers Oratorio composers People from Bruck an der Leitha District Musicians from Lower Austria Pupils of Nicola Porpora Austrian string quartet composers
 Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of
Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music
Chamber music is a form of classical music that is composed for a small group of Musical instrument, instruments—traditionally a group that could fit in a Great chamber, palace chamber or a large room. Most broadly, it includes any art music ...
such as the string quartet
The term string quartet refers to either a type of musical composition or a group of four people who play them. Many composers from the mid-18th century onwards wrote string quartets. The associated musical ensemble consists of two Violin, violini ...
and piano trio
A piano trio is a group of piano and two other instruments, usually a violin and a cello, or a piece of music written for such a group. It is one of the most common forms found in European classical music, classical chamber music. The term can also ...
. His contributions to musical form
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or musical improvisation, performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a ...
have led him to be called "Father of the Symphony
A symphony is an extended musical composition in Western classical music, most often for orchestra. Although the term has had many meanings from its origins in the ancient Greek era, by the late 18th century the word had taken on the meaning c ...
" and "Father of the String quartet".
Haydn arose from humble origins, the child of working people in a rural village. He established his career first by serving as a chorister at St. Stephen's Cathedral, Vienna, then through an arduous period as a freelance musician. Eventually he found career success, spending much of his working life as music director
A music director, musical director or director of music is a person responsible for the musical aspects of a performance, production, or organization. This would include the artistic director and usually chief conductor of an orchestra or concert ...
for the wealthy Esterházy
The House of Esterházy, also spelled Eszterházy (), is a Hungarian nobility, Hungarian noble family with origins in the Middle Ages. From the 17th century, the Esterházys were the greatest landowner magnates of the Kingdom of Hungary, durin ...
family at their palace of Eszterháza
Eszterháza is a palace in Fertőd, Hungary, built by Prince Nikolaus I, Prince Esterházy, Nikolaus Esterházy. Sometimes called the "Hungarian Palace of Versailles, Versailles", it is Hungary's grandest Rococo edifice. It was the home of Josep ...
in rural Hungary. Though he had his own orchestra there, it isolated him from other composers and trends in music so that he was, as he put it, "forced to become original". During this period his music circulated widely in publication, eventually making him the most celebrated composer in Europe. With the death of his primary patron Nikolaus Esterházy in 1790, Haydn was free to travel, and augmented his fame—now as a performer before the public—in both London and Vienna. The last years of his life (1803–1809) were spent in a state of debility, unable to compose due to poor health. He died in Vienna in 1809 at the age of 77.
Haydn was a friend and mentor of Mozart, a teacher of Beethoven, and the elder brother of composer Michael Haydn
Johann Michael Haydn (; 14 September 1737 – 10 August 1806) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period, the younger brother of Joseph Haydn.
Life
Michael Haydn was born in 1737 in the Austrian village of Rohra ...
.
Life and career
Early life
 Joseph Haydn was born in Rohrau, Austria, a village that at that time stood on the border with Hungary. His father was
Joseph Haydn was born in Rohrau, Austria, a village that at that time stood on the border with Hungary. His father was Mathias Haydn
Mathias Haydn (31 January 1699 – 12 September 1763) was the father of two famous composers, Joseph and Michael Haydn. He worked as a wheelwright in the Austrian village of Rohrau, where he also served as ''Marktrichter'', an office akin to villa ...
, a wheelwright
A wheelwright is a Artisan, craftsman who builds or repairs wooden wheels. The word is the combination of "wheel" and the word "wright" (which comes from the Old English word "''wryhta''", meaning a worker - as also in shipbuilding, shipwright ...
who also served as "Marktrichter", or marketplace supervisor. Haydn's mother Maria, née Koller, had worked as a cook in the palace of Count Harrach, the presiding aristocrat of Rohrau. Neither parent could read music; however, Mathias was an enthusiastic folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes #Traditional folk music, traditional folk music and the Contemporary folk music, contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be ca ...
ian, who during the journeyman
A journeyman is a worker, skilled in a given building trade or craft, who has successfully completed an official apprenticeship qualification. Journeymen are considered competent and authorized to work in that field as a fully qualified employee ...
period of his career had taught himself to play the harp. According to Haydn's later reminiscences, his family was extremely musical, and they frequently sang together and with their neighbours.
Haydn's parents had noticed that their son was musically gifted and knew that in Rohrau he would have no chance to obtain serious musical training. It was for this reason that, around the time Haydn turned six, they accepted a proposal from their relative Johann Matthias Frankh, the schoolmaster and choirmaster in Hainburg, that Haydn be apprenticed to Frankh in his home to train as a musician. Haydn therefore went off with Frankh to Hainburg and he never again lived with his parents.
Life in the Frankh household was not easy for Haydn, who later remembered being frequently hungry and humiliated by the filthy state of his clothing. He began his musical training there, and could soon play both harpsichord
A harpsichord is a musical instrument played by means of a musical keyboard, keyboard. Depressing a key raises its back end within the instrument, which in turn raises a mechanism with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic that plucks one ...
and violin
The violin, sometimes referred to as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone, and is the smallest, and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in regular use in the violin family. Smaller violin-type instruments exist, including the violino picc ...
. He also sang treble parts in the church choir.
There is reason to think that Haydn's singing impressed those who heard him, because in 1739 he was brought to the attention of Georg Reutter the Younger, the director of music in St. Stephen's Cathedral in Vienna, who happened to be visiting Hainburg and was looking for new choirboys. Haydn passed his audition with Reutter, and after several months of further training moved to Vienna (1740), where he worked for the next nine years as a chorister.
Haydn lived in the Kapellhaus next to the cathedral, along with Reutter, Reutter's family, and the other four choirboys, which after 1745 included his younger brother Michael
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* he He ..., a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name
* Michael (bishop elect)">Michael (surname)">he He ..., a given nam ...
. The choirboys were instructed in Latin and other school subjects as well as voice, violin, and keyboard. Reutter was of little help to Haydn in the areas of music theory
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "Elements of music, ...
and composition, giving him only two lessons in his entire time as a chorister. However, since St. Stephen's was one of the leading musical centres in Europe, Haydn learned a great deal simply by serving as a professional musician there.
Like Frankh before him, Reutter did not always bother to make sure Haydn was properly fed. As he later told his biographer Albert Christoph Dies, Haydn was motivated to sing well, in hopes of gaining more invitations to perform before aristocratic audiences, where the singers were usually served refreshments.
Struggles as a freelancer
By 1749, Haydn had matured physically to the point that he was no longer able to sing high choral parts. EmpressMaria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the ...
herself complained to Reutter about his singing, calling it "crowing". One day, Haydn carried out a prank, snipping off the pigtail of a fellow chorister. This was enough for Reutter: Haydn was first caned, then summarily dismissed and sent into the streets. He had the good fortune to be taken in by a friend, Johann Michael Spangler, who shared his family's crowded garret room with Haydn for a few months. Haydn immediately began his pursuit of a career as a freelance musician.
Haydn struggled at first, working at many different jobs: as a music teacher, as a street serenader, and eventually, in 1752, as valet-accompanist for the Italian composer Nicola Porpora
Nicola (or Niccolò) Antonio Giacinto Porpora (17 August 16863 March 1768) was an Italian composer and teacher of singing of the Baroque era, whose most famous singing students were the castrati Farinelli and Caffarelli. Other students include ...
, from whom he later said he learned "the true fundamentals of composition". He was also briefly in Count Friedrich Wilhelm von Haugwitz
Friedrich Wilhelm Graf von Haugwitz (), ; 11 December 1702, Electorate of Saxony, Saxony – 30 August 1765, Miroslavské Knínice, Deutsch Knönitz (), Habsburg Moravia) was Supreme Chancellor of the United Court Chancery and the head of ''Di ...
's employ, playing the organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
in the Bohemian Chancellery chapel at the Judenplatz.
While a chorister, Haydn had not received any systematic training in music theory and composition. As a remedy, he worked his way through the counterpoint
In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous musical lines (also called voices) that are harmonically dependent on each other, yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. The term originates from the Latin ...
exercises in the text '' Gradus ad Parnassum'' by Johann Joseph Fux
Johann Joseph Fux (; – 13 February 1741) was an Austrian composer, music theorist and pedagogue of the late Baroque era. His most enduring work is not a musical composition but his treatise on counterpoint, '' Gradus ad Parnassum'', which ha ...
and carefully studied the work of Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach
Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach (8 March 1714 – 14 December 1788), also formerly spelled Karl Philipp Emmanuel Bach, and commonly abbreviated C. P. E. Bach, was a German composer and musician of the Baroque and Classical period. He was the fifth ch ...
, whom he later acknowledged as an important influence. He said of CPE Bach's first six keyboard sonatas, "I did not leave my clavier till I played them through, and whoever knows me thoroughly must discover that I owe a great deal to Emanuel Bach, that I understood him and have studied him with diligence." According to Griesinger and Dies, in the 1750s Haydn studied an encyclopedic treatise by Johann Mattheson
Johann Mattheson (28 September 1681 – 17 April 1764) was a German composer, critic, lexicographer and music theorist. His writings on the late Baroque and early Classical period were highly influential, specifically, "his biographical and the ...
, a German composer.
As his skills increased, Haydn began to acquire a public reputation, first as the composer of an opera, '' Der krumme Teufel'', "The Limping Devil", written for the comic actor Joseph Felix von Kurz, whose stage name was "Bernardon". The work was premiered successfully in 1753, but was soon closed down by the censors due to "offensive remarks". Haydn also noticed, apparently without annoyance, that works he had simply given away were being published and sold in local music shops. Between 1754 and 1756 Haydn also worked freelance for the court in Vienna. He was among several musicians who were paid for services as supplementary musicians at balls given for the imperial children during carnival season, and as supplementary singers in the imperial chapel (the '' Hofkapelle'') in Lent and Holy Week.
With the increase in his reputation, Haydn eventually obtained aristocratic patronage, crucial for the career of a composer in his day. Countess Thun, having seen one of Haydn's compositions, summoned him and engaged him as her singing and keyboard teacher. In 1756, Baron Carl Josef Fürnberg employed Haydn at his country estate, Weinzierl, where the composer wrote his first string quartets. Their enthusiastic reception encouraged Haydn to write more. Fürnberg later recommended Haydn to Count Morzin, who, in 1757, became his first full-time employer.
Years as Kapellmeister
Haydn's job title under Count Morzin was ''Kapellmeister
( , , ), from German (chapel) and (master), literally "master of the chapel choir", designates the leader of an ensemble of musicians. Originally used to refer to somebody in charge of music in a chapel, the term has evolved considerably in i ...
'', that is, music director. Like many aristocrats of the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
at the time, the Count kept his own small orchestra, which Haydn led and composed for. His salary was a respectable 200 florins a year, plus free board and lodging. The Count lived the typical aristocractic lifestyle: winters in fashionable Vienna, but in summer escaping the heat and dust of the city for the ancestral estate in the country; this was at Unterlukawitz, now in the Czech Republic. Haydn and his musicians served their employer wherever he happened to be living. For Count Morzin Haydn wrote his first symphonies (perhaps about 10-20; the number is unknown). Philip Downs comments on these first symphonies: "the seeds of the future are there, his works already exhibit a richness and profusion of material, and a disciplined yet varied expression."
 In 1760, with the security of a Kapellmeister position, Haydn married. His wife was the former Maria Anna Theresia Keller (1729–1800), the sister of Therese (b. 1733), with whom Haydn had previously been in love. Haydn and his wife had an unhappy marriage, from which the laws of the time permitted no escape. They produced no children, and both took lovers.
In 1760, with the security of a Kapellmeister position, Haydn married. His wife was the former Maria Anna Theresia Keller (1729–1800), the sister of Therese (b. 1733), with whom Haydn had previously been in love. Haydn and his wife had an unhappy marriage, from which the laws of the time permitted no escape. They produced no children, and both took lovers.

Esterházy family
The House of Esterházy, also spelled Eszterházy (), is a Hungarian nobility, Hungarian noble family with origins in the Middle Ages. From the 17th century, the Esterházys were the greatest landowner magnates of the Kingdom of Hungary, durin ...
. Haydn's job title was only Vice-Kapellmeister, but he was immediately placed in charge of most of the Esterházy musical establishment, with the old Kapellmeister Gregor Werner retaining authority only for church music. When Werner died in 1766, Haydn was elevated to full Kapellmeister.
 As a "house officer" in the Esterházy establishment, Haydn wore
As a "house officer" in the Esterházy establishment, Haydn wore livery
A livery is an identifying design, such as a uniform, ornament, symbol, or insignia that designates ownership or affiliation, often found on an individual or vehicle. Livery often includes elements of the heraldry relating to the individual or ...
and followed the family as they moved among their various palaces, most importantly the family's ancestral seat Schloss Esterházy
Schloss Esterházy () is a palace in Eisenstadt, Austria, the capital of the Burgenland state. It was constructed in the late 13th century, and came under ownership of the Hungarian Esterházy family in 1622. Under Paul I, 1st Prince Esterhá ...
in Eisenstadt
Eisenstadt (; ; ; or ; ) is the capital city of the Provinces of Austria, Austrian state of Burgenland. With a population of 15,074 (as of 2023), it is the smallest state capital and the 38th-largest city in Austria overall. It lies at the foot o ...
and later on Esterháza, a grand new palace built in rural Hungary in the 1760s. Haydn had a huge range of responsibilities, including composition, running the orchestra, playing chamber music
Chamber music is a form of classical music that is composed for a small group of Musical instrument, instruments—traditionally a group that could fit in a Great chamber, palace chamber or a large room. Most broadly, it includes any art music ...
for and with his patrons, and eventually the mounting of operatic productions. Despite this backbreaking workload, the job was in artistic terms a superb opportunity for Haydn. The Esterházy princes (Paul Anton, then from 1762 to 1790 Nikolaus I) were musical connoisseurs who appreciated his work and gave him daily access to his own small orchestra. During the nearly thirty years that Haydn worked at the Esterházy court, he produced a flood of compositions, and his musical style continued to develop.
Much of Haydn's activity at the time followed the musical taste of his patron Prince Nikolaus. In about 1765, the prince obtained and began to learn to play the baryton
The baryton is a bowed string instrument similar to the viol, but distinguished by an extra set of sympathetic but also pluckable strings. It was in regular use in Europe until the end of the 18th century.
Design
The baryton can be viewed as a ...
, an uncommon musical instrument similar to the bass viol
The viola da gamba (), or viol, or informally gamba, is a bowed and fretted string instrument that is played (i.e. "on the leg"). It is distinct from the later violin family, violin, or ; and it is any one of the earlier viol family of bow (m ...
, but with a set of plucked sympathetic strings. Haydn was commanded to provide music for the prince to play, and over the next ten years produced about 200 works for this instrument in various ensembles, the most notable of which are the 126 baryton trios. Around 1775, the prince abandoned the baryton and took up a new hobby: opera productions, previously a sporadic event for special occasions, became the focus of musical life at court, and the opera theatre the prince had built at Esterháza came to host a major season, with (per Jones) "a schedule that soon rivalled any private or public opera house in Europe." Haydn served as ''de facto'' company director, recruiting and training the singers and preparing and leading the performances. He wrote several of the operas performed and wrote substitution aria
In music, an aria (, ; : , ; ''arias'' in common usage; diminutive form: arietta, ; : ariette; in English simply air (music), air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrument (music), instrumental or orchestral accompan ...
s to insert into the operas of other composers.
1779 was a watershed year for Haydn, as his contract was renegotiated: whereas previously all his compositions were the property of the Esterházy family, he now was permitted to write for others and sell his work to publishers. Haydn soon shifted his emphasis in composition to reflect this (fewer operas, and more quartets and symphonies) and he negotiated with multiple publishers, both Austrian and foreign. His new employment contract "acted as a catalyst in the next stage in Haydn's career, the achievement of international popularity. By 1790 Haydn was in the paradoxical position ... of being Europe's leading composer, but someone who spent his time as a duty-bound Kapellmeister in a remote palace in the Hungarian countryside." The new publication campaign resulted in the composition of a great number of new string quartets (the six-quartet sets of Op. 33, 50, 54/55, and 64). Haydn also composed in response to commissions from abroad: the Paris symphonies (1785–1786) and the original orchestral version of '' The Seven Last Words of Christ'' (1786), a commission from Cádiz
Cádiz ( , , ) is a city in Spain and the capital of the Province of Cádiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. It is located in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula off the Atlantic Ocean separated fr ...
, Spain.
The remoteness of Eszterháza
Eszterháza is a palace in Fertőd, Hungary, built by Prince Nikolaus I, Prince Esterházy, Nikolaus Esterházy. Sometimes called the "Hungarian Palace of Versailles, Versailles", it is Hungary's grandest Rococo edifice. It was the home of Josep ...
, which was farther from Vienna than Eisenstadt, led Haydn gradually to feel more isolated and lonely. He longed to visit Vienna because of his friendships there. Of these, a particularly important one was with Maria Anna von Genzinger (1754–1793), the wife of Prince Nikolaus's personal physician in Vienna, who began a close, platonic relationship with the composer in 1789. Haydn wrote to Mrs. Genzinger often, expressing his loneliness at Esterháza and his happiness for the few occasions on which he was able to visit her in Vienna. Later on, Haydn wrote to her frequently from London. Her premature death in 1793 was a blow to Haydn, and his F minor variations for piano, Hob. XVII:6, may have been written in response to her death.
Another friend in Vienna was Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
, whom Haydn had met sometime around 1784. According to later testimony by Michael Kelly and others, the two composers occasionally played in string quartet
The term string quartet refers to either a type of musical composition or a group of four people who play them. Many composers from the mid-18th century onwards wrote string quartets. The associated musical ensemble consists of two Violin, violini ...
s with Carl Ditters von Dittersdorf
Carl Ditters von Dittersdorf (2 November 1739 – 24 October 1799) was an Austrian composer and violinist. He was a friend of both Haydn and Mozart.
(webpage has a translation button)
His best-known works include the German singspiel '' Doktor un ...
(second violin) and Johann Baptist Wanhal
Johann Baptist Wanhal (12 May 1739 – 20 August 1813) was a Czech composer of the Classical period. He was born in Nechanice, Bohemia, and died in Vienna. His music was well respected by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Joseph Haydn, Ludwig van Beetho ...
(cello) for small gatherings attended by Giovanni Paisiello
Giovanni Paisiello (or Paesiello; 9 May 1740 – 5 June 1816) was an Italian composer of the Classical era, and was the most popular opera composer of the late 1700s. His operatic style influenced Mozart and Rossini.
Life
Paisiello was born i ...
and Giovanni Battista Casti. Impressed by Mozart's work, Haydn praised it unstintingly to others. Mozart returned the esteem in his "Haydn" quartets. In 1785 Haydn was admitted to the same Masonic lodge
A Masonic lodge (also called Freemasons' lodge, or private lodge or constituent lodge) is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry.
It is also a commonly used term for a building where Freemasons meet and hold their meetings. Every new l ...
as Mozart, the "''Zur wahren Eintracht''" in Vienna.
London journeys
 In 1790, Prince Nikolaus died and was succeeded as prince by his son Anton. Following a trend of the time, Anton sought to economize by dismissing most of the court musicians. Haydn retained a nominal appointment with Anton, at a reduced salary of 400 florins, as well as a 1000-florin pension from Nikolaus. Since Anton had little need of Haydn's services, he was willing to let him travel, and the composer accepted a lucrative offer from
In 1790, Prince Nikolaus died and was succeeded as prince by his son Anton. Following a trend of the time, Anton sought to economize by dismissing most of the court musicians. Haydn retained a nominal appointment with Anton, at a reduced salary of 400 florins, as well as a 1000-florin pension from Nikolaus. Since Anton had little need of Haydn's services, he was willing to let him travel, and the composer accepted a lucrative offer from Johann Peter Salomon
Johann Peter Salomon (20 February 1745 aptized– 25 November 1815) was a German violinist, composer, conducting, conductor and musical impresario. Although an accomplished violinist, he is best known for bringing Joseph Haydn to London a ...
, a German violinist and impresario
An impresario (from Italian ''impresa'', 'an enterprise or undertaking') is a person who organizes and often finances concerts, Play (theatre), plays, or operas, performing a role in stage arts that is similar to that of a film producer, film or ...
, to visit England and conduct new symphonies with a large orchestra.
The choice was a sensible one because Haydn was already a very popular composer there. Since the death of Johann Christian Bach
Johann Christian Bach (5 September 1735 – 1 January 1782) was a German composer of the Classical era, the youngest son of Johann Sebastian Bach. He received his early musical training from his father, and later from his half-brother, Carl ...
in 1782, Haydn's music had dominated the concert scene in London; "hardly a concert did not feature a work by him".. Haydn's work was widely distributed by publishers in London, including Forster (who had their own contract with Haydn) and Longman & Broderip (who served as an agent in England for Haydn's Vienna publisher Artaria). Efforts to bring Haydn to London had been made since 1782, though Haydn's loyalty to Prince Nikolaus had prevented him from accepting.
After fond farewells from Mozart and other friends, Haydn departed from Vienna with Salomon on 15 December 1790, arriving in Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a French port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Calais is the largest city in Pas-de-Calais. The population of the city proper is 67,544; that of the urban area is 144,6 ...
in time to cross the English Channel on New Year's Day of 1791. It was the first time that the 58-year-old composer had seen the sea. Arriving in London, Haydn stayed with Salomon in Great Pulteney Street (London, near Piccadilly Circus
Piccadilly Circus is a road junction and public space of London's West End of London, West End in the City of Westminster. It was built in 1819 to connect Regent Street with Piccadilly. In this context, a ''List of road junctions in the Unite ...
) working in a borrowed studio at the Broadwood piano firm nearby.
It was the start of a very auspicious period for Haydn: both the 1791–1792 journey, along with a repeat visit in 1794–1795, were greatly successful. Audiences flocked to Haydn's concerts; he augmented his fame and made large profits, thus becoming financially secure. Charles Burney
Charles Burney (7 April 1726 – 12 April 1814) was an English music historian, composer and musician. He was the father of the writers Frances Burney and Sarah Burney, of the explorer James Burney, and of Charles Burney, a classicis ...
reviewed the first concert thus: "Haydn himself presided at the piano-forte; and the sight of that renowned composer so electrified the audience, as to excite an attention and a pleasure superior to any that had ever been caused by instrumental music in England." Haydn made many new friends and, for a time, was involved in a romantic relationship with Rebecca Schroeter.
 Musically, Haydn's visits to England generated some of his best-known work, including the '' Surprise'', ''
Musically, Haydn's visits to England generated some of his best-known work, including the '' Surprise'', ''Military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
'', '' Drumroll'' and ''London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
'' symphonies; the ''Rider'' quartet; and the "Gypsy Rondo" piano trio. The great success of the overall enterprise does not mean that the journeys were free of trouble. Notably, his first project, the commissioned opera '' L'anima del filosofo'' was duly written during the early stages of the trip, but the opera's impresario John Gallini was unable to obtain a license to permit opera performances in the theatre he directed, the King's Theatre. Haydn was well paid for the opera (£300) but much time was wasted. Thus only two new symphonies, No. 95 and No. 96 ''Miracle'', could be premiered in the 12 concerts of Salomon's spring concert series in 1791. Another problem arose from the jealously competitive efforts of a senior, rival orchestra, the Professional Concerts, who recruited Haydn's old pupil Ignaz Pleyel as a rival visiting composer; the two composers, refusing to play along with the concocted rivalry, dined together and put each other's symphonies on their concert programs.
The end of Salomon's series in June gave Haydn a rare period of relative leisure. He spent some of the time in the country ( Hertingfordbury), but also had time to travel, notably to Oxford, where he was awarded an honorary doctorate by the university. The symphony performed for the occasion, No. 92 has since come to be known as the ''Oxford Symphony'', although it had been written two years before, in 1789. Four further new symphonies (Nos. 93, 94, 97 and 98) were performed in early 1792.
While travelling to London in 1790, Haydn met the young Ludwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire ...
in his native city of Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This ...
. On Haydn's return, Beethoven came to Vienna and was Haydn's pupil up until the second London journey. Haydn took Beethoven with him to Eisenstadt
Eisenstadt (; ; ; or ; ) is the capital city of the Provinces of Austria, Austrian state of Burgenland. With a population of 15,074 (as of 2023), it is the smallest state capital and the 38th-largest city in Austria overall. It lies at the foot o ...
for the summer, where Haydn had little to do, and taught Beethoven some counterpoint
In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous musical lines (also called voices) that are harmonically dependent on each other, yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. The term originates from the Latin ...
. While in Vienna, Haydn purchased a house for himself and his wife in the suburbs and started remodelling it. He also arranged for the performance of some of his London symphonies in local concerts.
By the time he arrived on his second journey to England (1794–1795), Haydn had become a familiar figure on the London concert scene. The 1794 season was dominated by Salomon's ensemble, as the Professional Concerts had abandoned their efforts. The concerts included the premieres of the 99th, 100th, and 101st symphonies. In 1795, Salomon had abandoned his own series, citing difficulty in obtaining "vocal performers of the first rank from abroad", and Haydn joined forces with the Opera Concerts, headed by the violinist Giovanni Battista Viotti
Giovanni Battista Viotti (12 May 1755 – 3 March 1824) was an Italian violinist whose virtuosity was famed and whose work as a composer featured a prominent violin and an appealing lyrical tunefulness. He was also a director of French and Italia ...
. The location of the concerts was shifted from the Hanover Square Rooms, seating an audience of 500, to a new hall in the King's Theatre, seating 800. At these concerts were premiered Haydn's final three symphonies, Symphony No. 102 (Haydn), 102, Symphony No. 103 (Haydn), 103, and Symphony No. 104 (Haydn), 104. The final benefit concert for Haydn ("Dr. Haydn's night"), at the end of the 1795 season, was a great success and was perhaps the peak of his English career. Haydn's biographer Griesinger wrote that Haydn "considered the days spent in England the happiest of his life. He was everywhere appreciated there; it opened a new world to him".
Years of celebrity in Vienna
Haydn returned to Vienna in 1795. Prince Anton had died, and his successor Nikolaus II, Prince Esterházy, Nikolaus II proposed that the Esterházy musical establishment be revived with Haydn serving again as Kapellmeister. Haydn took up the position on a part-time basis. He spent his summers with the Esterházys in Eisenstadt, and over the course of several years wrote six List of masses by Joseph Haydn, masses for them including the Lord Nelson mass in 1798. By this time Haydn had become a public figure in Vienna. He spent most of his time in his home, a large house in the suburb of Windmühle, and wrote works for public performance. In collaboration with his librettist and mentor Gottfried van Swieten, and with funding from van Swieten's Gesellschaft der Associierten, he composed his two great oratorios, ''The Creation (Haydn), The Creation'' (1798) and ''The Seasons (Haydn), The Seasons'' (1801). Both were enthusiastically received. Haydn frequently appeared before the public, often leading performances of ''The Creation'' and ''The Seasons'' for charity benefits, including Tonkünstler-Societät programs with massed musical forces. He also composed instrumental music: the popular ''Trumpet Concerto (Haydn), Trumpet Concerto'', and the last nine in his long series of string quartets, including the ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 2 ("Fifths"), Fifths'', ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 3 ("Emperor"), Emperor'', and ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 4 ("Sunrise"), Sunrise''. Directly inspired by hearing audiences sing God Save the King in London, in 1797 Haydn wrote a patriotic "Emperor's Hymn" "", ("God Save Emperor Francis"). This achieved great success and became "the enduring emblem of Austrian identity right up to the First World War" (Jones). The melody was used for von Fallersleben's (1841), whose third stanza is today the national anthem of Germany.
During the later years of this successful period, Haydn faced incipient old age and fluctuating health, and he had to struggle to complete his final works. His last major work, from 1802, was the sixth mass for the Esterházys, the ''Harmoniemesse''.
By this time Haydn had become a public figure in Vienna. He spent most of his time in his home, a large house in the suburb of Windmühle, and wrote works for public performance. In collaboration with his librettist and mentor Gottfried van Swieten, and with funding from van Swieten's Gesellschaft der Associierten, he composed his two great oratorios, ''The Creation (Haydn), The Creation'' (1798) and ''The Seasons (Haydn), The Seasons'' (1801). Both were enthusiastically received. Haydn frequently appeared before the public, often leading performances of ''The Creation'' and ''The Seasons'' for charity benefits, including Tonkünstler-Societät programs with massed musical forces. He also composed instrumental music: the popular ''Trumpet Concerto (Haydn), Trumpet Concerto'', and the last nine in his long series of string quartets, including the ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 2 ("Fifths"), Fifths'', ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 3 ("Emperor"), Emperor'', and ''String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 4 ("Sunrise"), Sunrise''. Directly inspired by hearing audiences sing God Save the King in London, in 1797 Haydn wrote a patriotic "Emperor's Hymn" "", ("God Save Emperor Francis"). This achieved great success and became "the enduring emblem of Austrian identity right up to the First World War" (Jones). The melody was used for von Fallersleben's (1841), whose third stanza is today the national anthem of Germany.
During the later years of this successful period, Haydn faced incipient old age and fluctuating health, and he had to struggle to complete his final works. His last major work, from 1802, was the sixth mass for the Esterházys, the ''Harmoniemesse''.
Retirement, illness, and death
By the end of 1803, Haydn's condition had declined to the point that he became physically unable to compose. He suffered from weakness, dizziness, inability to concentrate and painfully swollen legs. Since diagnosis was uncertain in Haydn's time, it is unlikely that the precise illness can ever be identified, though Jones suggests arteriosclerosis. The illness was especially hard for Haydn because the flow of fresh musical ideas continued unabated, although he could no longer work them out as compositions. His biographer Dies reported Haydn saying in 1806: Haydn lived on for 14 more months. His final days were hardly serene, as in May 1809 the French army under Napoleon launched an attack on Vienna and on 10 May bombarded his neighbourhood. According to Griesinger, "Four case shots fell, rattling the windows and doors of his house. He called out in a loud voice to his alarmed and frightened people, 'Don't be afraid, children, where Haydn is, no harm can reach you!'. But the spirit was stronger than the flesh, for he had hardly uttered the brave words when his whole body began to tremble.". More bombardments followed until the city fell to the French on 13 May. Haydn, was, however, deeply moved and appreciative when on 17 May a French cavalry officer named Sulémy came to pay his respects and sang, skillfully, an aria from ''The Creation''.
On 26 May Haydn played his "Emperor's Hymn" with unusual gusto three times; the same evening he collapsed and was taken to what proved to be his deathbed. He died peacefully in his own home at 12:40 a.m. on 31 May 1809, aged 77. On 15 June, a memorial service was held in the Schottenkirche, Vienna, Schottenkirche at which Mozart's Requiem (Mozart), Requiem was performed. Haydn's remains were interred in the local Haydnpark, Hundsturm cemetery until 1820 when they were moved to Eisenstadt by Prince Nikolaus. His head took a different journey; Haydn's head, it was stolen by phrenology, phrenologists shortly after burial, and the skull was reunited with the other remains only in 1954, now interred in a tomb in the north tower of the Bergkirche (Eisenstadt), Bergkirche.
Haydn lived on for 14 more months. His final days were hardly serene, as in May 1809 the French army under Napoleon launched an attack on Vienna and on 10 May bombarded his neighbourhood. According to Griesinger, "Four case shots fell, rattling the windows and doors of his house. He called out in a loud voice to his alarmed and frightened people, 'Don't be afraid, children, where Haydn is, no harm can reach you!'. But the spirit was stronger than the flesh, for he had hardly uttered the brave words when his whole body began to tremble.". More bombardments followed until the city fell to the French on 13 May. Haydn, was, however, deeply moved and appreciative when on 17 May a French cavalry officer named Sulémy came to pay his respects and sang, skillfully, an aria from ''The Creation''.
On 26 May Haydn played his "Emperor's Hymn" with unusual gusto three times; the same evening he collapsed and was taken to what proved to be his deathbed. He died peacefully in his own home at 12:40 a.m. on 31 May 1809, aged 77. On 15 June, a memorial service was held in the Schottenkirche, Vienna, Schottenkirche at which Mozart's Requiem (Mozart), Requiem was performed. Haydn's remains were interred in the local Haydnpark, Hundsturm cemetery until 1820 when they were moved to Eisenstadt by Prince Nikolaus. His head took a different journey; Haydn's head, it was stolen by phrenology, phrenologists shortly after burial, and the skull was reunited with the other remains only in 1954, now interred in a tomb in the north tower of the Bergkirche (Eisenstadt), Bergkirche.
Character and appearance
Kapellmeister
( , , ), from German (chapel) and (master), literally "master of the chapel choir", designates the leader of an ensemble of musicians. Originally used to refer to somebody in charge of music in a chapel, the term has evolved considerably in i ...
, entrepreneur and public figure, but also aided the favourable reception of his music." Haydn was especially respected by the Esterházy court musicians whom he supervised, as he maintained a cordial working atmosphere and effectively represented the musicians' interests with their employer; see Papa Haydn and the tale of the Symphony No. 45 (Haydn), "Farewell" Symphony. Haydn had a robust sense of humour, evident in his love of practical jokes and often apparent in his music, and he had many friends. For much of his life he benefited from a "happy and naturally cheerful temperament", but in his later life, there is evidence for periods of depression, notably in the correspondence with Maria Anna von Genzinger, Mrs. Genzinger and in Dies's biography, based on visits made in Haydn's old age.
Haydn was a devout Catholic who often turned to his rosary when he had trouble composing, a practice that he usually found to be effective. He normally began the manuscript of each composition with [in the name of the Lord] and ended with [praise be to God]. He retained this practice even in his secular works; he frequently only uses the initials "L. D.", "S. D. G." , or and sometimes adds, "et om si ( – and all saints)
Haydn's early years of poverty and awareness of the financial precariousness of musical life made him astute and even sharp in his business dealings. Some contemporaries (usually, it has to be said, wealthy ones) were surprised and even shocked at this. Webster writes: "As regards money, Haydn…always attempted to maximize his income, whether by negotiating the right to sell his music outside the Esterházy court, driving hard bargains with publishers or selling his works three and four times over [to publishers in different countries]; he regularly engaged in 'sharp practice'" which nowadays might be regarded as plain fraud. But those were days when copyright was in its infancy, and the pirating of musical works was common. Publishers had few qualms about attaching Haydn's name to popular works by lesser composers, an arrangement that effectively robbed the lesser musician of livelihood. Webster notes that Haydn's ruthlessness in business might be viewed more sympathetically in light of his struggles with poverty during his years as a freelancer—and that outside the world of business, in his dealings, for example, with relatives, musicians and servants, and in volunteering his services for charitable concerts, Haydn was a generous man – e.g., offering to teach the two infant sons of Mozart for free after their father's death. When Haydn died he was certainly comfortably off, but by middle class rather than aristocratic standards.
Haydn was short in stature, perhaps as a result of having been underfed throughout most of his youth. He was not handsome, and like many in his day he was a survivor of smallpox; his face was pitted with the scars of this disease. His biographer Albert Christoph Dies, Dies wrote: "he couldn't understand how it happened that in his life he had been loved by many a pretty woman. 'They couldn't have been led to it by my beauty.
Haydn generally enjoyed good health, but he suffered from nasal polyps during much of his adult life, an agonizing and debilitating condition that at times prevented him from writing music.
Music
James Webster summarizes Haydn's role in the history of classical music as follows:Structure
 A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical Motif (music), motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly. W. Dean Sutcliffe mentions this in a criticism of contemporary Haydn performance practice:
A central characteristic of Haydn's music is the development of larger structures out of very short, simple musical Motif (music), motifs, often derived from standard accompanying figures. The music is often quite formally concentrated, and the important musical events of a movement can unfold rather quickly. W. Dean Sutcliffe mentions this in a criticism of contemporary Haydn performance practice:
[Haydn's] music sometime seems to 'live on its nerves' ... It is above all in this respect that Haydn performances often fail, whereby most interpreters lack the mental agility to deal with the ever-changing 'physiognomy' of Haydn's music, subsiding instead into an ease of manner and a concern for broader effects that they have acquired in their playing of Mozart.Haydn's work was central to the development of what came to be called sonata form. His practice, however, differed in some ways from that of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Mozart and Ludwig van Beethoven, Beethoven, his younger contemporaries who likewise excelled in this form of composition. Haydn was particularly fond of the so-called Sonata form#Monothematic expositions, monothematic exposition, in which the music that establishes the dominant key is similar or identical to the opening theme. Haydn also differs from Mozart and Beethoven in his Recapitulation (music), recapitulation sections, where he often rearranges the order of themes compared to the exposition and uses extensive thematic development. Of these "rearranged recapitulations", Rosemary Hughes writes
Having begun to 'develop', he could not stop; his recapitulations begin to take on irregular contours, sometimes sharply condensed, sometimes surprisingly expanded, losing their first tame symmetry to regain a balance of a far higher and more satisfying order.Haydn's formal inventiveness also led him to integrate the fugue into the classical style and to enrich the rondo form with more cohesive tonal logic (see sonata rondo form). Haydn was also the principal exponent of the double variation form—variations on two alternating themes, which are often major- and minor-mode versions of each other.
Character
The Haydn scholar Karl Geiringer has emphasized the sheer joyfulness of much of Haydn's music:Out of Haydn's love for the beauties of our world grew the gaiety and affirmative spirit apparent throughout all his creative periods ... Even in his advanced age, this gaiety did not entirely desert him. Nurtured by ... a victorious optimism maintained through all the vicissitudes of a long and arduous life, this radiant joyfulness again and again manifested itself, and Haydn considered it his mission to let his fellow beings share in this unique gift.The sense of bliss often evident in Haydn's music was also noticed by Charles Rosen, who (describing a theme in the piano trio Hoboken catalog, Hob. XV:13), wrote of
Haydn's ability to create an emotion that was completely his own and that no other composer could duplicate -- a feeling of ecstasy that is completely unsensual, almost amiable. There is no recipe for producing this effect ...A modest number of Haydn's works are striking exceptions to this upbeat character. Some excursions into emotional darkness include The Seven Last Words of Christ, the ''largo'' movement of the string quartet String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn), Op. 76 no. 5, which Haydn marked "mesto" (sorrowful), and the widely admired coda section of his Variations in F minor for piano. Perhaps more than any other composer's, Haydn's music is known for its humour; specifically, incongruous musical passages heard as jokes. The most famous example is the sudden loud chord in the slow movement of his Symphony No. 94 (Haydn), "Surprise" symphony; Haydn's many other musical jokes include numerous False ending#Music, false endings (e.g., in the quartets String Quartets, Op. 33 (Haydn), Op. 33 No. 2 and String Quartets, Op. 50 (Haydn), Op. 50 No. 3), and the remarkable rhythmic illusion placed in the trio section of the third movement of String Quartets, Op. 50 (Haydn)#Opus 50, No. 1, Op. 50 No. 1. Haydn's fast movements tend to be rhythmically propulsive and often impart a great sense of energy, especially in the finales. Some characteristic examples of Haydn's "rollicking" finale type are found in the Symphony No. 104 (Haydn), "London" Symphony No. 104, the String Quartet Op. 50 No. 1, and the Piano Trio Hob XV: 27. Haydn's early slow movements are usually not too slow in tempo, relaxed, and reflective. Later on, the emotional range of the slow movements increases, notably in the deeply felt slow movements of the quartets String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn), Op. 76 Nos. 3 and 5, the Symphony No. 98 (Haydn), Symphonies No. 98 and Symphony No. 102 (Haydn), 102, and the Piano Trio Hob XV: 23. The minuets tend to have a strong downbeat and a clearly popular character. Over time, Haydn turned some of his minuets into "Scherzo, scherzi" which are much faster, at one beat to the bar.
Evolution of Haydn's style
Haydn's lifetime overlapped substantially with those of the most celebrated masters of Baroque music: he was born 18 years before the death of Johann Sebastian Bach, J. S. Bach and 27 years before that of George Frideric Handel, Handel. Yet the models that influenced him, according to Karl Geiringer, were not at all these composers, but rather the leaders in the earliest development of the emerging Classical period (music), Classical style, particularly in Vienna: his employer Johann Georg Reutter, Georg Christoph Wagenseil, and Georg Matthias Monn -- none of whom wrote music that is widely played today. This was a period of exploration and uncertainty, and Haydn was himself one of the musical explorers of this time. Fairly early in his career Haydn discovered, and quickly came to revere, the music of a composer from outside Vienna, J. S. Bach's sonCarl Philipp Emanuel Bach
Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach (8 March 1714 – 14 December 1788), also formerly spelled Karl Philipp Emmanuel Bach, and commonly abbreviated C. P. E. Bach, was a German composer and musician of the Baroque and Classical period. He was the fifth ch ...
. Geiringer emphasizes how Haydn was struck by the emotional depth of Bach's work: "Up to then he had been familiar with the gay and superficial idiom of the musical rococo; here he found compositions that deeply stirred and excited him.".
Tracing Haydn's subsequent work over the six decades in which it was produced (he composed from about 1749 to 1802), one finds a gradual but steady increase in complexity and musical sophistication, which developed as Haydn learned from his own experience and that of his colleagues. Several important landmarks have been observed in the evolution of Haydn's musical style.
In the late 1760s and early 1770s, Haydn entered a stylistic period known as "Sturm und Drang" ("storm and stress"). This term is taken from Sturm und Drang, a literary movement of about the same time, though it appears that the musical development actually preceded the literary one by a few years. The musical language of this period is similar to what went before, but it is deployed in work that is more intensely expressive, especially in the works in minor keys. James Webster describes the works of this period as "longer, more passionate, and more daring". Some of the most famous compositions of this time are the Symphony No. 44 (Haydn), "Trauer" (Mourning) Symphony No. 44, Symphony No. 45 (Haydn), "Farewell" Symphony No. 45, the Piano Sonata in C minor (Hob. XVI/20, L. 33), and the String Quartets, Op. 20 (Haydn), six "Sun" Quartets Op. 20, all from c. 1771–72. It was also around this time that Haydn became interested in writing fugues in the Baroque style, and three of the Op. 20 quartets end with a fugue.
Following the climax of the "Sturm und Drang", Haydn returned to a lighter, more overtly entertaining style. There are no quartets from this period, and the symphonies take on new features: the scoring often includes trumpets and timpani. These changes are often related to a major shift in Haydn's professional duties, which moved him away from instrumental music and toward the production of Opera buffa, comic operas. Several of the operas were Haydn's own work (see List of operas by Joseph Haydn); these are seldom performed today. Haydn sometimes recycled his opera music in symphonic works, which helped him continue his career as a symphonist during this hectic decade.
In 1779, an important change in Haydn's contract permitted him to publish his compositions without prior authorization from his employer. This may have encouraged Haydn to rekindle his career as a composer of instrumental music. The change made itself felt most dramatically in 1781, when Haydn published the String Quartets, Op. 33 (Haydn), six Op. 33 String Quartets, announcing (in a letter to potential purchasers) that they were written in "a new and completely special way". Charles Rosen has argued that this assertion on Haydn's part was not just sales talk but meant quite seriously, and he points out a number of important advances in Haydn's compositional technique that appear in these quartets, advances that mark the advent of the Classical music era, Classical style in full flower. These include a fluid form of phrasing, in which each motif emerges from the previous one without interruption, the practice of letting accompanying material evolve into melodic material, and a kind of "Classical counterpoint
In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous musical lines (also called voices) that are harmonically dependent on each other, yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. The term originates from the Latin ...
" in which each instrumental part maintains its own integrity. These traits continue in the many quartets that Haydn wrote after Op. 33.
In the 1790s, stimulated by his England journeys, Haydn developed what Rosen calls his "popular style", a method of composition that, with unprecedented success, created music having great popular appeal but retaining a learned and rigorous musical structure. An important element of the popular style was the frequent use of folk music, folk or folk-like material (see Haydn and folk music). Haydn took care to deploy this material in appropriate locations, such as the endings of sonata expositions or the opening themes of finales. In such locations, the folk material serves as an element of stability, helping to anchor the larger structure. Haydn's popular style can be heard in virtually all of his later work, including the twelve London symphonies, "London" symphonies, the late quartets and piano trios, and the two late oratorios.
The return to Vienna in 1795 marked the last turning point in Haydn's career. Although his musical style evolved little, his intentions as a composer changed. While he had been a servant, and later a busy entrepreneur, Haydn wrote his works quickly and in profusion, with frequent deadlines. As a rich man, Haydn now felt that he had the privilege of taking his time and writing for posterity. This is reflected in the subject matter of ''The Creation (Haydn), The Creation'' (1798) and ''The Seasons (Haydn), The Seasons'' (1801), which address such weighty topics as the meaning of life and the purpose of humankind and represent an attempt to render the sublime in music. Haydn's new intentions also meant that he was willing to spend much time on a single work: both oratorios took him over a year to complete. Haydn once remarked that he had worked on ''The Creation'' so long because he wanted it to last.
The change in Haydn's approach was important in the history of classical music, as other composers were soon following his lead. Notably, Beethoven adopted the practice of taking his time and aiming high.
Catalogues
Anthony van Hoboken prepared a comprehensive catalogue of Haydn's works. The Hoboken catalogue assigns a catalogue number to each work, called its Hoboken number (abbreviated H. or Hob.). These Hoboken numbers are often used in identifying Haydn's compositions. Haydn's string quartets also have Hoboken numbers, but they are usually identified instead by their opus numbers, which have the advantage of indicating the groups of six quartets that Haydn published together. For example, the string quartet String Quartets, Op. 76 (Haydn)#Opus 76 No. 3 ("Emperor"), Opus 76, No. 3 is the third of the six quartets published in 1799 as Opus 76.Instruments
An "Anton Walter in Wien" fortepiano used by the composer is now on display in the ''Haydn-Haus Eisenstadt''. In Vienna in 1788 Haydn bought himself a fortepiano made by Wenzel Schantz. When the composer was visiting London for the first time, an English piano builder, John Broadwood, supplied him with a concert grand.See also
* List of compositions by Joseph Haydn * List of concertos by Joseph Haydn * List of masses by Joseph Haydn * List of operas by Joseph Haydn * List of piano trios by Joseph Haydn * List of solo piano compositions by Joseph Haydn * List of string quartets by Joseph Haydn * List of symphonies by Joseph Haydn * Joseph Haydn's ethnicity * Haydn's birthplace * List of residences of Joseph Haydn, List of Haydn's residencesReferences
Informational notes Citations Bibliography Biographical sources * * English translation in: One of the first biographies of Haydn, written on the basis of 30 interviews carried out during the composer's old age. * Highly detailed discussion of life and work; in German. * The first edition was published in 1946 with Karl Geiringer as the sole author. * A translation from the original German: . Like Dies's, a biography produced from interviews with the elderly Haydn. * Reissued 2010 by Cambridge University Press. * Originally published in 1950. Gives a sympathetic and witty account of Haydn's life, along with a survey of the music. * Focuses on biography rather than musical works; an up-to-date study benefiting from recent scholarly research on Haydn's life and times. * A comprehensive one-volume collection of detailed contributions by Haydn scholars. * An extensive compilation of original sources in five volumes. * Biography chapters by Robbins Landon, excerpted from and rich in original source documents. Analysis and appreciation of the works by Jones. * Published separately as * * Published separately as a book: Careful scholarship with little subjective interpretation; covers both life and music, and includes a very detailed list of works. The biography section is by Webster, the extensive list of works by Feder. Criticism and analysis * On jokes in Haydn and Beethoven. * * * Surveys the decline in Haydn's reputation in the nineteenth century before examining the factors that led to a resurgence in the twentieth. * First edition published in 1971. Covers much of Haydn's output and seeks to explicate Haydn's central role in the creation of the classical style. The work has been influential, provoking both positive citation and work (e.g., ) written in reaction. * . Further discussion of Haydn's style and technique as it relates to sonata form. * * * This book focuses on a single work, but contains many observations and opinions about Haydn in general.Further reading
* On the sublime in Haydn's later works; in German. * Covers each of the genres Haydn composed in as well as stylistic and interpretive contexts and performance and reception. * Sixty-seven scholars contribute over eighty entries as well as seven longer thematic essays on biography and identity, ideas, institutions, musical materials, people and networks, performance, and place. * * A brief (55-page) introduction to Haydn's string quartets. * * Covers not just Op. 50 but also its relevance to Haydn's other output as well as his earlier quartets.External links
"Joseph Haydn"
by Karl Geiringer, Raymond L. Knapp, H. C. Robbins Landon, ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' * *
Joseph Haydn-Institut
(in German)
The Haydn Society of North America
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Haydn, Joseph Joseph Haydn, 1732 births 1809 deaths 18th-century Austrian people 18th-century Austrian classical composers 18th-century Austrian male musicians 19th-century Austrian male musicians Age of Enlightenment Austrian classical pianists Austrian Classical-period composers Austrian expatriates in Hungary Austrian Freemasons Austrian opera composers Austrian Roman Catholics Catholic liturgical composers Classical composers of church music Composers for piano Composers from Vienna Esterházy family Harrach family Austrian male classical pianists Austrian male opera composers National anthem writers Oratorio composers People from Bruck an der Leitha District Musicians from Lower Austria Pupils of Nicola Porpora Austrian string quartet composers