foehn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a
A Foehn, or Föhn (, , , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm downslope wind in the lee of a
 There are four known causes of the Foehn warming and drying effect. These mechanisms often act together, with their contributions varying depending on the size and shape of the mountain barrier and on the meteorological conditions, such as the upstream wind speed, temperature and humidity.
There are four known causes of the Foehn warming and drying effect. These mechanisms often act together, with their contributions varying depending on the size and shape of the mountain barrier and on the meteorological conditions, such as the upstream wind speed, temperature and humidity.


 * Favonio in
* Favonio in

mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have aris ...
. It is a rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and larg ...
wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point ...
slopes (see orographic lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and cr ...
). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rate
The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. ''Lapse rate'' arises from the word ''lapse'' (in its "becoming less" sense, not its "interruption" sense). In dry air, ...
s of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevation
The elevation of a geographic location (geography), ''location'' is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational equipotenti ...
s on the windward slopes.
Foehn winds can raise temperatures
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a subst ...
by as much as in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany, and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
blow over the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
.
Etymology
The name ''Foehn'' (, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin , a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by or just , the term was adopted as . In the Southern Alps, the phenomenon is known as but also and inSerbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually i ...
and Slovene. The German word (pronounced the same way) also means 'hairdryer', while the word is a genericized trademark
A generic trademark, also known as a genericized trademark or proprietary eponym, is a trademark or brand name that, because of its popularity or significance, has become the generic term for, or synonymous with, a general class of products or ...
today owned by AEG The initials AEG are used for or may refer to:
Common meanings
* AEG (German company)
; AEG) was a German producer of electrical equipment. It was established in 1883 by Emil Rathenau as the ''Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte El ...
. The form ''phon'' is used in French-speaking parts of Switzerland as well as in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
.
The name was originally used to refer to the south wind which blows during the winter months and brings thaw conditions to the northern side of the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
. Because Föhn later became a generic term that was extended to other mountain ranges around the world that experience similar phenomena, the name "Alpine föhn
The Alpine föhn () is the name given to the föhn wind in the Alps, Alpine region. The name ''föhn'' was originally used to refer to the south wind which blows during the winter months and brings thaw conditions to the northern side of the Alps. ...
" () was coined for the Föhns of the Alpine region.''Der Brockhaus. Wetter und Klima.'' Seite 101, Brockhaus, Leipzig/Mannheim, 2009,
Causes
 There are four known causes of the Foehn warming and drying effect. These mechanisms often act together, with their contributions varying depending on the size and shape of the mountain barrier and on the meteorological conditions, such as the upstream wind speed, temperature and humidity.
There are four known causes of the Foehn warming and drying effect. These mechanisms often act together, with their contributions varying depending on the size and shape of the mountain barrier and on the meteorological conditions, such as the upstream wind speed, temperature and humidity.
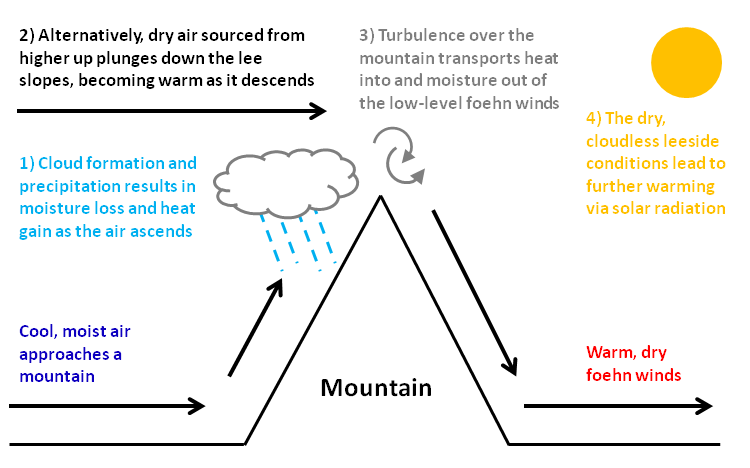
Condensation and precipitation
When winds blow over elevated terrain, air forced upwards expands and cools due to the decrease in pressure with height. Since colder air can hold less water vapor, moisture condenses to form clouds and precipitates as rain or snow on the mountain's upwind slopes. The change of state from vapor to liquid water releaseslatent heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation. ...
energy which heats the air, partially countering the cooling that occurs as the air rises. The subsequent removal of moisture as precipitation renders this heat gain by the air irreversible, leading to the warm, dry, Foehn conditions as the air descends in the mountain's lee. This mechanism has become a popular textbook example of atmospheric thermodynamics. However, the common occurrence of 'dry' Foehn events, where there is no precipitation, implies there must be other mechanisms.

Isentropic draw-down
Isentropic draw-down is the draw-down of warmer, drier air from aloft. When the approaching winds are insufficiently strong to propel the low-level air up and over the mountain barrier, the airflow is said to be 'blocked' by the mountain and only air higher up near mountain-top level is able to pass over and down the lee slopes as Foehn winds. These higher source regions provide Foehn air that becomes warmer and drier on the leeside after it is compressed with descent due to the increase in pressure towards the surface.Mechanical mixing
When river water passes over rocks, turbulence is generated in the form of rapids, and white water reveals the turbulent mixing of the water with the air above. Similarly, as air passes over mountains, turbulence occurs and the atmosphere is mixed in the vertical. This mixing generally leads to a downward warming and upward moistening of the cross-mountain airflow, and consequently to warmer, drier Foehn winds in the valleys downwind.Radiative warming
Dry Foehn conditions are responsible for the occurrence of rain shadows in the lee of mountains, where clear, sunny conditions prevail. This often leads to greater daytime radiative (solar) warming under Foehn conditions. This type of warming is particularly important in cold regions where snow or ice melt is a concern or where avalanches are a risk.Effects
Winds of this type are also called "snow-eaters" for their ability to make snow and ice melt or sublimate rapidly. This is a result not only of the warmth of Foehn air, but also its low relativehumidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
. Accordingly, Foehn winds are known to contribute to the disintegration of ice shelves in the polar regions.
Foehn winds are notorious among mountaineers in the Alps, especially those climbing the Eiger
The Eiger () is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, overlooking Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen in the Bernese Oberland of Switzerland, just north of the main watershed and border with Valais. It is the easternmost peak of a ridge crest that extends ...
, for whom the winds add further difficulty in ascending an already difficult peak.
They are also associated with the rapid spread of wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
s, making some regions which experience these winds particularly fire-prone.
Purported physiological effects
Anecdotally, residents in areas of frequent Foehn winds have reported experiencing a variety of illnesses ranging frommigraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
s to psychosis
In psychopathology, psychosis is a condition in which a person is unable to distinguish, in their experience of life, between what is and is not real. Examples of psychotic symptoms are delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized or inco ...
. The first clinical review of these effects was published by the Austrian physician Anton Czermak in the 19th century. A study by the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich, LMU or LMU Munich; ) is a public university, public research university in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. Originally established as the University of Ingolstadt in 1472 by Duke ...
found that suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
and accidents increased by 10 percent during Foehn winds in Central Europe. The causation of '' Föhnkrankheit'' (English: Foehn-sickness) is unproven. Labels for preparations of aspirin combined with caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
, codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
and the like will sometimes include ''Föhnkrankheit'' among the indications. Evidence for effects from Chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
s remains anecdotal, as it does for New Zealand's Nor'wester.
In some regions, Foehn winds are associated with causing circulatory problems, headaches, or similar ailments. Researchers have found, however, the Foehn wind's warm temperature to be beneficial to humans in most situations, and have theorized that the reported negative effects may be a result of secondary factors, such as changes in the electrical field or in the ion state of the atmosphere, the wind's relatively low humidity, or the generally unpleasant sensation of being in an environment with strong and gusty winds.
Local examples
Regionally, these winds are known by many different names. These include: ;in Africa *Bergwind
Berg wind (from Afrikaans ''berg'' "mountain" + ''wind'' "wind", i.e. a mountain wind) is the South African English, South African name for a katabatic wind: a hot dry wind blowing down the Great Escarpment, Southern Africa, Great Escarpment fro ...
in South Africa
;in the Americas
*The Brookings Effect on the southwestern coast of Oregon, also known as the Chetco Effect.
* Chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
s east of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
and the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington (state), Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as m ...
in the United States and Canada, and north, east and west of the Chugach Mountains
The Chugach Mountains of southern Alaska are the northernmost of the several mountain ranges that make up the Pacific Coast Ranges of the western edge of North America. The range is about long and wide, and extends from the Knik and Turnag ...
of Alaska, United States
* Foehn winds in the foothills of the southern Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
, which can be unusual compared to other Foehn winds in that the relative humidity typically changes little due to the increased moisture in the source air mass
* Mono winds in the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
.
*The Santa Ana winds of southern California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, including the Sundowner winds of Santa Barbara, are in some ways similar to the Föhn, but originate in dry deserts as a katabatic wind
A katabatic wind (named ) is a downslope wind caused by the flow of an elevated, high-density air mass into a lower-density air mass below under the force of gravity. The spelling catabatic is also used. Since air density is strongly dependent o ...
. However, traditional Föhn conditions frequently prevail along the Santa Monica
Santa Monica (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Santa Mónica'') is a city in Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County, situated along Santa Monica Bay on California's South Coast (California), South Coast. Santa Monica's 2020 United Sta ...
and Santa Ana Mountains and their respective leeward valleys, the San Fernando Valley
The San Fernando Valley, known locally as the Valley, is an urbanized valley in Los Angeles County, Los Angeles County, California. Situated to the north of the Los Angeles Basin, it comprises a large portion of Los Angeles, the Municipal corpo ...
and the Riverside County portion of the Inland Empire
The Inland Empire (commonly abbreviated as the IE) is a metropolitan area and region inland of and adjacent to coastal Southern California, centering around the cities of San Bernardino and Riverside, and bordering Los Angeles County and Or ...
region.
* Puelche wind in Chile
*Suêtes
Suetes, ''suêtes'', ''les suêtes'', are strong south-east foehn winds on the west coast of Cape Breton Island.
The term "suête" originates from the Acadian French inhabitants of the Chéticamp area as a contraction of "sud est" (south-east).
...
on the west coast of Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although ...
, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
* Wreckhouse winds in the southwest corner of the island of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the populatio ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
* Zonda winds in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
;in Antarctica
* Föhn wall on Signy Island, South Orkneys
;in Asia
* Garmesh, Garmij, Garmbaad (): (, ) in Gilan
Gilan Province () is one of the 31 provinces of Iran, in the northwest of the country and southwest of the Caspian Sea. Its capital is the city of Rasht. The province lies along the Caspian Sea, in Iran's Region 3, west of the province of ...
region (near the Alborz
The Alborz ( ) range, also spelled as Alburz, Elburz or Elborz, is a mountain range in northern Iran that stretches from the border of Azerbaijan along the western and entire southern coast of the Caspian Sea and finally runs northeast and merge ...
) in the south west of Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
.
* In winter, a Foehn effect occurs in the West Azerbaijan province
West Azerbaijan province () is one of the 31 provinces of Iran, whose capital and largest city is Urmia.
It is in the northwest of the country, bordered by Turkey ( Ağrı, Hakkâri, Iğdır and Van Provinces), Iraq ( Erbil and Sula ...
, Iran (around Lake Urmia
Lake Urmia is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is located between the provinces of East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan in Iran, and west of the southern portion of the Caspian Sea. At its greatest extent, it was the largest lake in th ...
) as manifested by the province's dry winters relative to those in the windward part of the region (Northern Iraq or Kurdistan Region
Kurdistan Region (KRI) is a semi-autonomous Federal regions of Iraq, federal region of the Iraq, Republic of Iraq. It comprises four Kurds, Kurdish-majority governorates of Arabs, Arab-majority Iraq: Erbil Governorate, Sulaymaniyah Governorate ...
and Hakkâri Province
Hakkâri Province (, ; ), is a province in the southeast of Turkey. The administrative centre is the city of Hakkâri. Its area is 7,095 km2, and its population is 287,625 (2023). The current Governor is Ali Çelik. The province encompasses ...
in Turkey). For example, the winter rainfall of Urmia
Urmia (; ) is the largest city in West Azerbaijan Province of Iran. In the Central District of Urmia County, it is capital of the province, the county, and the district. The city is situated near the borders of Iran with Turkey and Iraq.
...
and Salmas
Salmas () is a city in the Central District of Salmas County, West Azerbaijan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. It is northwest of Lake Urmia, near Turkey.
Etymology
The original name of Salmas was ...
in Iranian Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan or Azarbaijan (, , ), also known as Iranian Azerbaijan, is a historical region in northwestern Iran that borders Iraq and Turkey to the west and Armenia, Azerbaijan, and the Azerbaijani exclave of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republ ...
is much lower than Batifa and Soran in Iraqi Kurdistan, and Hakkâri Hakkari or Hakkâri may refer to:
* Hakkari (historical region), a historical region in modern-day Turkey and Iraq
*Hakkâri (city), a city and the capital of Hakkâri Province, Turkey
*Hakkâri Province
Hakkâri Province (, ; ), is a province ...
in the Hakkâri Province, which are roughly on the same latitude but are on the windward side of the Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of s ...
.
* Loo in Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, easte ...
* Warm Braw in the Schouten Islands
The Biak Islands (, also Schouten Islands or Geelvink Islands) are an island group of Southwest Papua province, eastern Indonesia in the Cenderawasih Bay (or Geelvink Bay) 50 km off the north-western coast of the island of New Guinea. Th ...
north of West Papua, Indonesia.
*Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National cent ...
in China is famously known as one of the Three Furnaces on account of its extremely hot weather in summer resulting from the adiabatic warming effect created by mountains further south.
*Laos wind (), hot-dry west wind () in northern and central Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
.
;in Europe

 * Favonio in
* Favonio in Ticino
Ticino ( ), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts ...
and north-western Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
due to western and northern winds crossing the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
(mostly in winter)
*Garbino in the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
coast of Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
due to south-western winds crossing the Apennine Mountains
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains ( ; or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; or – a singular with plural meaning; )Latin ''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which would be segmented ''Apenn-inus'', often used with nouns s ...
(mostly in fall and winter)
* Fen in northwest Slovenia
* Fønvind in South Norway, in particular Central Norway
Central Norway (, ) is an informal, unclearly defined region of Norway. In its most limited usage, the term "Central Norway" may refer only to Trøndelag county; however, it may also be understood to include all or parts of the county of Møre og ...
, resulting in extreme winter warming, including Scandinavia's warmest winter temperature in Sunndalsøra
is the administrative centre of Sunndal Municipality in Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. The village of Sunndalsøra lies at the mouth of the river Driva at the beginning of the Sunndalsfjord. Sunndalsøra is surrounded by steep mountains, su ...
.
* Fogony in the Catalan Pyrenees
The Pyrenees are a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. They extend nearly from their union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean coast, reaching a maximum elevation of at the peak of Aneto. ...
* Föhn or Foehn in Austria, southern Germany, Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
*Föhn in Ostrobothnia and Western Lapland in Finland as moist air crosses Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway, whereas to th ...
and dries up.
* Halny in the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
, southern Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and northern Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
*The Helm Wind, on the Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of highland, uplands mainly located in Northern England. Commonly described as the "Vertebral column, backbone of England" because of its length and position, the ra ...
in the Eden Valley, Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders the Scottish council areas of Dumfries and Galloway and Scottish Borders to the north, Northumberland and County Durham to the east, North Yorkshire to the south-east, Lancash ...
, England
*Hnjúkaþeyr in Icelandic
* Lodos wind, causing warm temperatures in the leeward side of mountains in the mild-winter climate of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
and western Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, as well as unusually mild temperatures in the cool or moderately cold winter climates north of the Marmara Sea
The Sea of Marmara, also known as the Sea of Marmora or the Marmara Sea, is a small inland sea entirely within the borders of Turkey. It links the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea via the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits, separating Turkey's E ...
, such as Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
, Adapazarı
Adapazarı () is a municipality and the capital Districts of Turkey, district of Sakarya Province, Turkey. Its area is 324 km2, and its population 281,489 (2022). It covers the central and northern part of the agglomeration of Adapazarı and t ...
and Zonguldak
Zonguldak () is a List of cities in Turkey, city of about 100 thousand people in the Black Sea region of Turkey. It is the seat of Zonguldak Province and Zonguldak District.Košava (Koshava) wind in Serbia that blows along the river
The Canterbury nor'wester
" ''New Zealand Geographic''. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
File:Pájara Morro Jable - Carretera Punta de Jandía - cemetery + foehn 01 ies.jpg, Foehn over Carretera Punta de Jandía in
Photo of Föhnmauer
The strong clouds at the mountain ridges where the Föhn winds form are called ''Föhnmauer'' (Föhn wall).
Illustration
Movie of a Föhn situation in the Swiss Alps
East Scotland warmth due to Foehn Effect
{{Authority control Föhn effect Mountain meteorology Weather and health Wind Winds cs:Místní názvy větrů#Fén
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
*Nortada in Cascais
Cascais () is a town and municipality in the Lisbon District of Portugal, located on the Portuguese Riviera, Estoril Coast. The municipality has a total of 214,158 inhabitants in an area of 97.40 km2. Cascais is an important tourism in Port ...
, and most notoriously in Guincho Beach, making it one of the best windsurfing spots in Europe
*Ponentà in Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
(eastern Spain)
*Terral in Málaga
Málaga (; ) is a Municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 591,637 in 2024, it is the second-most populo ...
(southern Spain)
*Viento del Sur (Southern Wind) or Hego haizea in Basque in the Cantabrian region (northern Spain)
;in Oceania
*The Great Dividing foehn in southeast Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, leeward of the Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills. It runs roughl ...
, observed in the coastal plains of New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
, and also in eastern Victoria and eastern Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
.
*The Nor'wester in Hawkes Bay, Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, in the county of Kent, England; it was a county borough until 1974. It lies on the River Stour, Kent, River Stour. The city has a mild oceanic climat ...
, and Otago
Otago (, ; ) is a regions of New Zealand, region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island and administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local go ...
, New ZealandRelph, D.The Canterbury nor'wester
" ''New Zealand Geographic''. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
Gallery
Morro Jable
Morro Jable is a locality belonging of the municipality of Pájara, in the island of Fuerteventura, Canary Islands, Spain. With around 7,000 inhabitants as of 2020, it is the most populated settlement in the municipality. It was founded by Cirilo ...
, Pájara
Pájara is a municipality in the southwestern portion of the island of Fuerteventura in the Province of Las Palmas in the Canary Islands as well as the name of its largest town. Its population is 20,931 (2013),Fuerteventura
Fuerteventura () is one of the Canary Islands, in the Atlantic Ocean, geographically part of Macaronesia, and politically part of Spain. It is located away from the coast of North Africa. The island was declared a biosphere reserve by UNESCO i ...
, Canary Islands
File:La Palma - El Paso - Cumbre Nueva+Foehn (Mirador Llano del Jable) 01 ies.jpg, Dissolving clouds from Foehn wind over the Cumbre Nueva in El Paso, La Palma, Canary Island
File:Wolkenwasserfall ms1408101.jpg, Foehn over Llano del Jable
File:Storm Oratia 30 Oct 2000.jpg, Foehn can be initiated when deep low-pressure systems move into Europe, drawing moist Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
air over the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
.
See also
*Alpine climate
Alpine climate is the typical climate for elevations above the tree line, where trees fail to grow due to cold. This climate is also referred to as a mountain climate or highland climate.
Definition
There are multiple definitions of alpine cli ...
* Anabatic wind
* Chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
* Föhn cloud
* Katabatic wind
A katabatic wind (named ) is a downslope wind caused by the flow of an elevated, high-density air mass into a lower-density air mass below under the force of gravity. The spelling catabatic is also used. Since air density is strongly dependent o ...
s
* Lee wave
* Meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...
References
* McKnight, TL & Hess, Darrel (2000). "Foehn/Chinook Winds". In ''Physical Geography: A Landscape Appreciation'', p. 132. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. .Footnotes
External links
Photo of Föhnmauer
The strong clouds at the mountain ridges where the Föhn winds form are called ''Föhnmauer'' (Föhn wall).
Illustration
Movie of a Föhn situation in the Swiss Alps
East Scotland warmth due to Foehn Effect
{{Authority control Föhn effect Mountain meteorology Weather and health Wind Winds cs:Místní názvy větrů#Fén