Fintech on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Financial technology (abbreviated as fintech) refers to the application of innovative technologies to products and services in the financial industry. This broad term encompasses a wide array of technological advancements in financial services, including mobile banking, online lending platforms, digital payment systems, robo-advisors, and
Financial technology (abbreviated as fintech) refers to the application of innovative technologies to products and services in the financial industry. This broad term encompasses a wide array of technological advancements in financial services, including mobile banking, online lending platforms, digital payment systems, robo-advisors, and
 The 1980s and 1990s witnessed significant developments in financial technology, with the rise of digital financial services and the early stages of online banking. A major breakthrough came when Michael Bloomberg founded Innovative Market Systems (later Bloomberg L.P.) and introduced the Bloomberg Terminal. This innovation revolutionized how financial professionals accessed and analyzed market data, providing real-time financial market data, analytics, and news to financial institutions worldwide.
Online banking emerged in the early 1980s, with the Bank of Scotland offering the first UK online banking service called Homelink. This service allowed customers to view statements, transfer money, and pay bills using their
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed significant developments in financial technology, with the rise of digital financial services and the early stages of online banking. A major breakthrough came when Michael Bloomberg founded Innovative Market Systems (later Bloomberg L.P.) and introduced the Bloomberg Terminal. This innovation revolutionized how financial professionals accessed and analyzed market data, providing real-time financial market data, analytics, and news to financial institutions worldwide.
Online banking emerged in the early 1980s, with the Bank of Scotland offering the first UK online banking service called Homelink. This service allowed customers to view statements, transfer money, and pay bills using their
 Subscription and freemium models allow companies to offer basic services at no cost while charging for advanced features or premium tiers. This approach is common among digital banks and financial management platforms. In the business-to-business (B2B) sector, usage-based pricing is prevalent, especially for API services. Financial technology infrastructure providers often charge based on the volume of API calls or transactions processed, enabling other businesses to access specialized financial services without developing them internally.
Interest-based revenue is crucial for many financial technology companies, particularly in the banking and lending sectors. Digital banks and investment platforms typically earn interest on customer deposits and cash balances. Lending platforms often combine interest revenue with loan sales, selling portions of their loan portfolios to other institutions or investors.
Data-driven revenue models, while potentially lucrative, have faced increasing scrutiny and regulation. Some firms engage in data monetization, selling aggregated or anonymized user data to third parties. However, this practice has raised privacy concerns and regulatory challenges. A less controversial approach involves leveraging user data for targeted advertising and lead generation, earning revenue through product recommendations and referral fees while providing free services to users.
Some revenue models, such as payment for order flow (PFOF) used by certain brokerage firms, occupy a regulatory gray area. While PFOF allows for commission-free trades, potentially benefiting retail investors, it has faced scrutiny due to concerns about conflicts of interest and best execution practices.
Subscription and freemium models allow companies to offer basic services at no cost while charging for advanced features or premium tiers. This approach is common among digital banks and financial management platforms. In the business-to-business (B2B) sector, usage-based pricing is prevalent, especially for API services. Financial technology infrastructure providers often charge based on the volume of API calls or transactions processed, enabling other businesses to access specialized financial services without developing them internally.
Interest-based revenue is crucial for many financial technology companies, particularly in the banking and lending sectors. Digital banks and investment platforms typically earn interest on customer deposits and cash balances. Lending platforms often combine interest revenue with loan sales, selling portions of their loan portfolios to other institutions or investors.
Data-driven revenue models, while potentially lucrative, have faced increasing scrutiny and regulation. Some firms engage in data monetization, selling aggregated or anonymized user data to third parties. However, this practice has raised privacy concerns and regulatory challenges. A less controversial approach involves leveraging user data for targeted advertising and lead generation, earning revenue through product recommendations and referral fees while providing free services to users.
Some revenue models, such as payment for order flow (PFOF) used by certain brokerage firms, occupy a regulatory gray area. While PFOF allows for commission-free trades, potentially benefiting retail investors, it has faced scrutiny due to concerns about conflicts of interest and best execution practices.
 Financial technology (abbreviated as fintech) refers to the application of innovative technologies to products and services in the financial industry. This broad term encompasses a wide array of technological advancements in financial services, including mobile banking, online lending platforms, digital payment systems, robo-advisors, and
Financial technology (abbreviated as fintech) refers to the application of innovative technologies to products and services in the financial industry. This broad term encompasses a wide array of technological advancements in financial services, including mobile banking, online lending platforms, digital payment systems, robo-advisors, and blockchain
The blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of Record (computer science), records (''blocks'') that are securely linked together via Cryptographic hash function, cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of th ...
-based applications such as cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency (colloquially crypto) is a digital currency designed to work through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Individual coin ownership records ...
. Financial technology companies include both startups
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an Entrepreneurship, entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship includes all new businesses including self-employment and businesses tha ...
and established technology and financial firms that aim to improve, complement, or replace traditional financial services.
Evolution
The evolution of financial technology spans over a century, marked by significant technological innovations that have revolutionized the financial industry. While the application of technology to finance has deep historical roots, the term "financial technology" emerged in the late 20th century and gained prominence in the 1990s. The earliest documented use of the term dates back to 1967, appearing in an article in ''The Boston Globe
''The Boston Globe,'' also known locally as ''the Globe'', is an American daily newspaper founded and based in Boston, Massachusetts. The newspaper has won a total of 27 Pulitzer Prizes. ''The Boston Globe'' is the oldest and largest daily new ...
'' titled "Fin-Tech New Source of Seed Money." This piece reported on a startup investment company established by former executives of Computer Control Company, aimed at providing venture capital and industry expertise to startups in the financial technology industry.
However, the term didn't gain popularity until the early 1990s when Citicorp Chairman John Reed used it to describe the Financial Services Technology Consortium. This project, initiated by Citigroup, was designed to promote technological cooperation in the financial sector, marking a pivotal moment in the industry's collaborative approach to innovation.
The financial technology ecosystem includes various types of companies. While startups developing new financial technologies or services are often associated with financial technology, the sector also encompasses established technology companies expanding into financial services and traditional financial institution
A financial institution, sometimes called a banking institution, is a business entity that provides service as an intermediary for different types of financial monetary transactions. Broadly speaking, there are three major types of financial ins ...
s adopting new technologies. This diverse landscape has led to innovations across multiple financial sectors, including banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
, insurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to protect ...
, investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broade ...
, and payment system
A payment system is any system used to settle financial transactions through the transfer of monetary value. This includes the institutions, payment instruments such as payment cards, people, rules, procedures, standards, and technologies that ...
s.
Financial technology applications span a wide range of financial services. These include digital banking, mobile payments and digital wallets, peer-to-peer lending
Peer-to-peer lending, also abbreviated as P2P lending, is the practice of loan, lending money to individuals or businesses through online services that match lenders with borrowers. Peer-to-peer lending companies often offer their services online ...
platforms, robo-advisors and algorithmic trading, insurtech, blockchain
The blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of Record (computer science), records (''blocks'') that are securely linked together via Cryptographic hash function, cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of th ...
and cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency (colloquially crypto) is a digital currency designed to work through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Individual coin ownership record ...
, regulatory technology, and crowdfunding
Crowdfunding is the practice of funding a project or venture by raising money from a large number of people, typically via the internet. Crowdfunding is a form of crowdsourcing and Alternative Finance, alternative finance, to fund projects "withou ...
platforms.
History
Foundations
The late 19th century laid the groundwork for early financial technology with the development of thetelegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
and transatlantic cable systems. These innovations transformed the transmission of financial information across borders, enabling faster and more efficient communication between financial institutions.
A significant milestone in electronic money movement came with the establishment of the Fedwire Funds Service by the Federal Reserve Banks in 1918. This early electronic funds transfer system used telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
lines to facilitate secure transfers between member banks, marking one of the first instances of electronic money movement.
The 1950s ushered in a new era of consumer financial services. Diners Club International introduced the first universal credit card in 1950, a pivotal moment that would reshape consumer spending and credit. This innovation paved the way for the launch of American Express
American Express Company or Amex is an American bank holding company and multinational financial services corporation that specializes in payment card industry, payment cards. It is headquartered at 200 Vesey Street, also known as American Expr ...
cards in 1958 and the BankAmericard (later Visa) in 1959, further expanding the credit card industry.
Digital revolution
The 1960s and 1970s marked the beginning of the shift from analog to digital finance, with several groundbreaking developments shaping the future of financial technology. In 1967, Barclays introduced the world's first ATM inLondon
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, revolutionizing access to cash and basic banking services. Inspired by vending machine
A vending machine is an automated machine that dispenses items such as snacks, beverages, cigarettes, and lottery tickets to consumers after cash, a credit card, or other forms of payment are inserted into the machine or payment is otherwise m ...
s, the ATM marked a significant step towards self-service banking.
Financial technology infrastructure continued to evolve with the establishment of the Inter-bank Computer Bureau in the UK in 1968. This development laid the groundwork for the country's first automated clearing house system, eventually evolving into BACS (Bankers' Automated Clearing Services) to facilitate electronic funds transfers between banks.
The world of securities trading was transformed in 1971 with the establishment of NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market (; National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the U.S. by volume, and ranked second on the list ...
, the world's first digital stock exchange
A stock exchange, securities exchange, or bourse is an exchange where stockbrokers and traders can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock, bonds and other financial instruments. Stock exchanges may also provide facilities for ...
. NASDAQ's electronic quotation system represented a significant leap forward from the traditional open outcry system used in stock exchanges.
Two years later, the founding of the SWIFT
Swift or SWIFT most commonly refers to:
* SWIFT, an international organization facilitating transactions between banks
** SWIFT code
* Swift (programming language)
* Swift (bird), a family of birds
It may also refer to:
Organizations
* SWIF ...
(Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) standardized and secured communication between financial institutions globally. SWIFT's messaging system became the global standard for international money and security transfers.
The introduction of electronic fund transfer systems, such as the ACH (Automated Clearing House) in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, facilitated faster and more efficient money transfers. The ACH network allowed for direct deposits, payroll payments, and electronic bill payments, significantly reducing the need for paper checks.
Rise of digital financial services
 The 1980s and 1990s witnessed significant developments in financial technology, with the rise of digital financial services and the early stages of online banking. A major breakthrough came when Michael Bloomberg founded Innovative Market Systems (later Bloomberg L.P.) and introduced the Bloomberg Terminal. This innovation revolutionized how financial professionals accessed and analyzed market data, providing real-time financial market data, analytics, and news to financial institutions worldwide.
Online banking emerged in the early 1980s, with the Bank of Scotland offering the first UK online banking service called Homelink. This service allowed customers to view statements, transfer money, and pay bills using their
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed significant developments in financial technology, with the rise of digital financial services and the early stages of online banking. A major breakthrough came when Michael Bloomberg founded Innovative Market Systems (later Bloomberg L.P.) and introduced the Bloomberg Terminal. This innovation revolutionized how financial professionals accessed and analyzed market data, providing real-time financial market data, analytics, and news to financial institutions worldwide.
Online banking emerged in the early 1980s, with the Bank of Scotland offering the first UK online banking service called Homelink. This service allowed customers to view statements, transfer money, and pay bills using their television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
s and telephone
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most ...
s.
The late 1980s saw the development of EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) standards, allowing businesses to exchange financial documents electronically and streamlining B2B (business-to-business) transactions.
A significant milestone in consumer digital banking came in 1994 when Stanford Federal Credit Union launched the first Internet banking website. This service initially allowed members to check account balances online, with bill pay functionality added in 1997. However, it was not until 1999 that the first state-chartered, FDIC-insured institution operating primarily online was established. First Internet Bank, founded by David Becker, marked a new era in online-only banking.
Dot-com era
The late 1990s and early 2000s marked a significant turning point in the evolution of financial technology, as numerous innovations emerged during the dot-com boom. One notable development was the rise of online trading platforms, with E-Trade, founded in 1982, leading the charge. In 1992, E-Trade became one of the first financial services companies to offer online trading to consumers, revolutionizing the way individuals interacted with thestock market
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks (also called shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include ''securities'' listed on a public stock exchange a ...
.
Another pivotal moment was the founding of PayPal
PayPal Holdings, Inc. is an American multinational financial technology company operating an online payments system in the majority of countries that support E-commerce payment system, online money transfers; it serves as an electronic alter ...
in 1998. PayPal's success in creating a secure and user-friendly online payment system demonstrated the viability of digital payment solutions and paved the way for numerous subsequent financial technology startups.
The early 2000s also saw the emergence of innovative business models in the financial services industry. WebBank, established in 1997, began offering a "rent-a-charter" model in 2005, providing the necessary banking infrastructure and regulatory compliance for financial technology startups to offer banking services without obtaining their own charters. This model would later prove crucial in enabling the growth of numerous financial technology companies.
Post-2008 financial crisis
The2008 financial crisis
The 2008 financial crisis, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a major worldwide financial crisis centered in the United States. The causes of the 2008 crisis included excessive speculation on housing values by both homeowners ...
served as a catalyst for the rapid growth of the financial technology industry, as declining trust in traditional financial institutions created opportunities for innovative, technology-driven solutions. The early days of the post-crisis era saw the emergence of digital currencies, with e-Gold
E-gold or eGold was a digital gold currency operated by Gold & Silver Reserve Inc. (G&SR) that allowed users to make payments, which it called "spends", in grams of gold, silver, and other precious metals. E-gold was launched in 1996 and grew to ...
serving as a precursor to the development of Bitcoin
Bitcoin (abbreviation: BTC; Currency symbol, sign: ₿) is the first Decentralized application, decentralized cryptocurrency. Based on a free-market ideology, bitcoin was invented in 2008 when an unknown entity published a white paper under ...
. While e-Gold, which allowed users to create accounts denominated in grams of gold and enable instant transfers, ultimately faced legal challenges and closure, it laid the foundation for future digital currencies.
The invention of Bitcoin in 2008 by an anonymous creator using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto marked a turning point in the evolution of digital currencies and decentralized finance. Bitcoin's innovative use of blockchain
The blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of Record (computer science), records (''blocks'') that are securely linked together via Cryptographic hash function, cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of th ...
technology sparked a wave of development in the field of cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency (colloquially crypto) is a digital currency designed to work through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Individual coin ownership records ...
, opening up new possibilities for secure, transparent, and decentralized financial systems.
As the financial technology landscape continued to evolve, new payment processing companies entered the market, offering developer-friendly API
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build ...
s that dramatically simplified online payment integration. By lowering the barriers to entry for e-commerce
E-commerce (electronic commerce) refers to commercial activities including the electronic buying or selling products and services which are conducted on online platforms or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile co ...
and online financial services, these companies played a crucial role in enabling the growth of new financial technology startups and driving innovation in the sector.
The partner banking model, which emerged in the early 2000s, gained significant traction in the post-crisis era. This model expanded beyond its initial "rent-a-charter" concept, evolving into more comprehensive partnerships between traditional banks and financial technology companies. These collaborations allowed for rapid innovation and market entry, as financial technologys leveraged the regulatory compliance and infrastructure of established banks while bringing their own technological expertise and customer-centric approaches. This further accelerated the growth of the financial technology sector, enabling the proliferation of digital-first financial services. The maturation of this model paved the way for the rise of neobanks, which challenged traditional banking paradigms by offering fully digital experiences, redefining customer expectations in the banking sector.
The increasing adoption of smartphone
A smartphone is a mobile phone with advanced computing capabilities. It typically has a touchscreen interface, allowing users to access a wide range of applications and services, such as web browsing, email, and social media, as well as multi ...
s drove the development of mobile-first financial technology solutions. Square's introduction of a mobile card reader in 2009 enabled small businesses to accept credit card payments using smartphones, democratizing access to payment processing and highlighting the transformative potential of mobile technology in the financial services industry.
The evolution of mobile payment systems continued with the launch of Google Wallet in 2011 and Apple Pay in 2014, which further popularized mobile payments and demonstrated the growing consumer demand for convenient, secure, and user-friendly payment solutions.
This period also saw the rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) payment applications. These platforms revolutionized how individuals transfer money, enabling quick and easy transactions between users. By allowing fast, direct transfers through mobile devices, P2P payment apps significantly reduced the friction in personal financial transactions, making it simpler for people to split bills, share costs, or send money to friends and family.
Accelerated growth of digital finance
The globalCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, which began in early 2020, had a profound impact on the financial technology industry, accelerating the adoption of digital financial services and highlighting the importance of technology in ensuring the resilience and accessibility of financial systems. As lockdowns and social distancing measures forced businesses and consumers to rely more heavily on digital channels, financial technology solutions experienced a surge in demand.
Mobile-first financial technology applications saw unprecedented growth during this period. Many trading platforms reported significant increases in new user accounts, with some seeing millions of new funded accounts added in the early months of the pandemic. Similarly, payment and money transfer apps experienced substantial user growth, with some platforms more than doubling their monthly active users over a three-year period, indicating a massive shift towards digital financial services.
The events of 2020 also exposed the limitations of traditional financial institutions in meeting the needs of consumers and businesses in times of crisis. financial technology companies, with their agile and technology-driven business models, were better positioned to respond to the challenges posed by the rapidly changing environment, offering innovative solutions for remote banking, contactless payments, and digital lending.
During this period, venture capital
Venture capital (VC) is a form of private equity financing provided by firms or funds to start-up company, startup, early-stage, and emerging companies, that have been deemed to have high growth potential or that have demonstrated high growth in ...
valuations for financial technology companies soared, driven by low interest rates and a booming stock market
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks (also called shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include ''securities'' listed on a public stock exchange a ...
. The surge in financial technology investments was marked by significant capital inflows, leading to higher valuations and more frequent exits via IPOs and SPACs. Several prominent financial technology companies achieved record-breaking valuations, further underscoring the sector's growth and investor confidence.
The shift towards digital financial services during this period also accelerated the adoption of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies. As central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
s around the world explored the possibility of issuing digital currencies, the interest in decentralized finance and non-fungible tokens grew, opening up new avenues for innovation in the financial technology sector.
The financial technology landscape in Africa is on the rise, with active companies reaching 1,263 in 2024, a significant increase from 1,049 in 2022 and 450 in 2020. Nigeria leads the financial technology sector, accounting for 28% of all financial technology companies on the continent.
Industry landscape
The financial technology industry includes a diverse range of financial services and technologies, categorized into several key areas. Many companies operate across multiple areas or create new niches that blur these distinctions.Revenue models
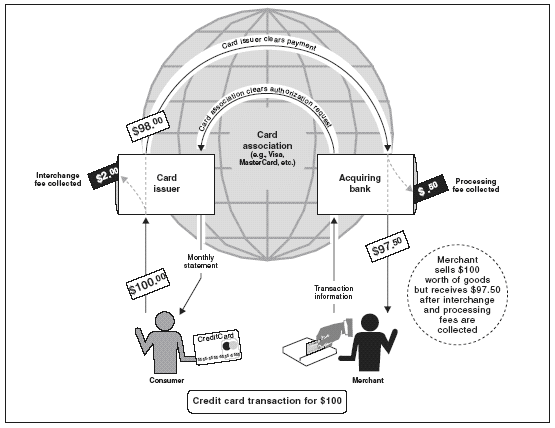
Financial technology companies utilize various revenue models, often combining multiple approaches to diversify income streams. Transaction fees form a primary source of income for many financial technology businesses, particularly payment processors and cryptocurrency exchanges. These companies typically charge a percentage of each processed transaction. Some companies have expanded this model to include premium fees for services like instant payouts, catering to merchants who require immediate access to funds. Interchange fees represent another significant revenue stream, particularly for firms offering payment cards. Subscription and freemium models allow companies to offer basic services at no cost while charging for advanced features or premium tiers. This approach is common among digital banks and financial management platforms. In the business-to-business (B2B) sector, usage-based pricing is prevalent, especially for API services. Financial technology infrastructure providers often charge based on the volume of API calls or transactions processed, enabling other businesses to access specialized financial services without developing them internally.
Interest-based revenue is crucial for many financial technology companies, particularly in the banking and lending sectors. Digital banks and investment platforms typically earn interest on customer deposits and cash balances. Lending platforms often combine interest revenue with loan sales, selling portions of their loan portfolios to other institutions or investors.
Data-driven revenue models, while potentially lucrative, have faced increasing scrutiny and regulation. Some firms engage in data monetization, selling aggregated or anonymized user data to third parties. However, this practice has raised privacy concerns and regulatory challenges. A less controversial approach involves leveraging user data for targeted advertising and lead generation, earning revenue through product recommendations and referral fees while providing free services to users.
Some revenue models, such as payment for order flow (PFOF) used by certain brokerage firms, occupy a regulatory gray area. While PFOF allows for commission-free trades, potentially benefiting retail investors, it has faced scrutiny due to concerns about conflicts of interest and best execution practices.
Subscription and freemium models allow companies to offer basic services at no cost while charging for advanced features or premium tiers. This approach is common among digital banks and financial management platforms. In the business-to-business (B2B) sector, usage-based pricing is prevalent, especially for API services. Financial technology infrastructure providers often charge based on the volume of API calls or transactions processed, enabling other businesses to access specialized financial services without developing them internally.
Interest-based revenue is crucial for many financial technology companies, particularly in the banking and lending sectors. Digital banks and investment platforms typically earn interest on customer deposits and cash balances. Lending platforms often combine interest revenue with loan sales, selling portions of their loan portfolios to other institutions or investors.
Data-driven revenue models, while potentially lucrative, have faced increasing scrutiny and regulation. Some firms engage in data monetization, selling aggregated or anonymized user data to third parties. However, this practice has raised privacy concerns and regulatory challenges. A less controversial approach involves leveraging user data for targeted advertising and lead generation, earning revenue through product recommendations and referral fees while providing free services to users.
Some revenue models, such as payment for order flow (PFOF) used by certain brokerage firms, occupy a regulatory gray area. While PFOF allows for commission-free trades, potentially benefiting retail investors, it has faced scrutiny due to concerns about conflicts of interest and best execution practices.
Controversies
As financial technology companies seek to disrupt traditionalfinancial services
Financial services are service (economics), economic services tied to finance provided by financial institutions. Financial services encompass a broad range of tertiary sector of the economy, service sector activities, especially as concerns finan ...
, some have been criticized for prioritizing growth over compliance, security, and consumer protection
Consumer protection is the practice of safeguarding buyers of goods and services, and the public, against unfair practices in the marketplace. Consumer protection measures are often established by law. Such laws are intended to prevent business ...
.
In a notable controversy, cryptocurrency exchange FTX collapsed in November 2022, facing accusations of deceptive practices, improper handling of client assets, and insufficient risk controls.
Sam Bankman-Fried, FTX's founder and CEO, was later convicted of wire fraud, conspiracy
A conspiracy, also known as a plot, ploy, or scheme, is a secret plan or agreement between people (called conspirers or conspirators) for an unlawful or harmful purpose, such as murder, treason, or corruption, especially with a political motivat ...
, and money laundering
Money laundering is the process of illegally concealing the origin of money obtained from illicit activities (often known as dirty money) such as drug trafficking, sex work, terrorism, corruption, and embezzlement, and converting the funds i ...
.
See also
* Artificial intelligence in finance * Financial technology in Australia * Smart contract * Trade finance technologyReferences and notes
Further reading
* *External links
* {{authority control Financial markets Financial services Technology in society