Event Horizon Telescope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a large telescope array consisting of a global network of
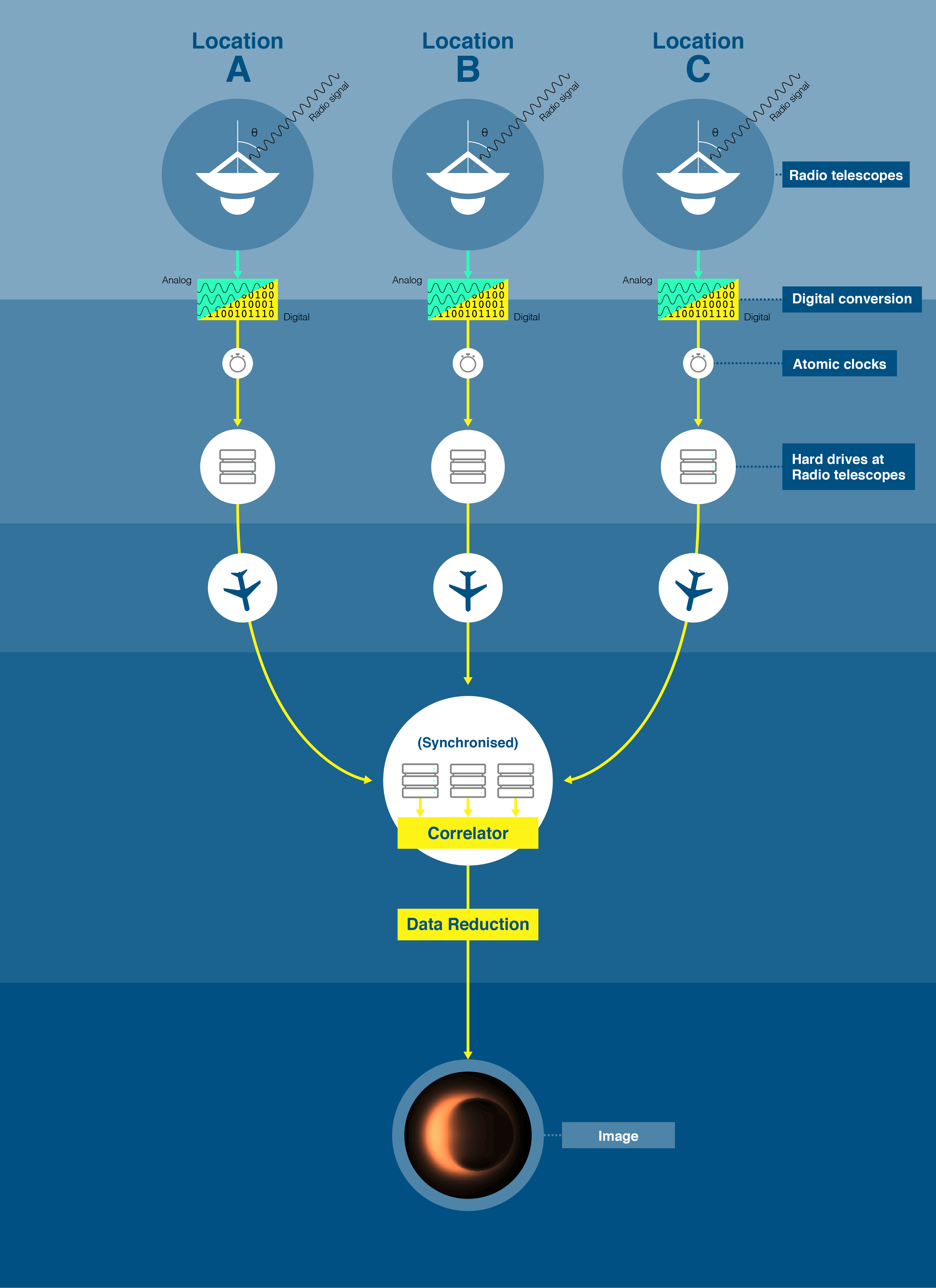 The EHT is composed of many radio observatories or radio-telescope facilities around the world, working together to produce a high-sensitivity, high-angular-resolution telescope. Through the technique of
The EHT is composed of many radio observatories or radio-telescope facilities around the world, working together to produce a high-sensitivity, high-angular-resolution telescope. Through the technique of
 The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration announced its first results in six simultaneous press conferences worldwide on April 10, 2019. The announcement featured the first direct image of a black hole, which showed the
The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration announced its first results in six simultaneous press conferences worldwide on April 10, 2019. The announcement featured the first direct image of a black hole, which showed the
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2020): p. 1 The image provided a test for
Seitz, Schneider, and Bartelmann (1998) Entropy-regularized maximum-likelihood cluster mass reconstruction
cites Narayan and Nityananda 1986. for astronomy such as the CHIRP algorithm created by Katherine Bouman and others. The algorithms that were ultimately used were a regularized
p. 127–170. algorithm and the CLEAN algorithm. In March 2020, astronomers proposed an improved way of seeing more of the rings in the first black hole image. In March 2021, a new photo was revealed, showing how the M87 black hole looks in polarised light. This is the first time astronomers have been able to measure polarisation so close to the edge of a black hole. The lines on the photo mark the orientation of polarisation, which is related to the magnetic field around the shadow of the black hole. In August 2022, a team led by
 In April 2020, the EHT released the first 20 microarcsecond resolution images of the archetypal
In April 2020, the EHT released the first 20 microarcsecond resolution images of the archetypal
 In July 2021, high resolution images of the jet produced by black hole sitting at the center of Centaurus A were released. With a mass around , the black hole is not big enough to observe its ring as with Messier M87*, but its jet extends even beyond its host galaxy while staying as a highly collimated beam which is a point of study. Edge-brightening of the jet was also observed which would exclude models of particle acceleration that are unable to reproduce this effect. The image was 16 times sharper than previous observations and utilized a 1.3 mm wavelength.
In July 2021, high resolution images of the jet produced by black hole sitting at the center of Centaurus A were released. With a mass around , the black hole is not big enough to observe its ring as with Messier M87*, but its jet extends even beyond its host galaxy while staying as a highly collimated beam which is a point of study. Edge-brightening of the jet was also observed which would exclude models of particle acceleration that are unable to reproduce this effect. The image was 16 times sharper than previous observations and utilized a 1.3 mm wavelength.
 In August 2022, the EHT together with Global Millimeter VLBI Array and the
In August 2022, the EHT together with Global Millimeter VLBI Array and the
EHT "Ask Me Anything" (AMA) serie
on
The Next Generation Event Horizon Telescope
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Interferometric telescopes
radio telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency ...
s. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry
Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. Th ...
(VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolut ...
sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ob ...
's event horizon
In astrophysics, an event horizon is a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an observer. Wolfgang Rindler coined the term in the 1950s.
In 1784, John Michell proposed that gravity can be strong enough in the vicinity of massive compact ob ...
. The project's observational targets include the two black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can def ...
s with the largest angular diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular distance describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the visual angle, and in optics, it ...
as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperature range of supergiant stars spa ...
elliptical galaxy
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the four main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work ''The Real ...
Messier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy with several trillion stars in the constellation Virgo. One of the largest and most massive galaxies in the local ...
(M87*, pronounced "M87-Star"), and Sagittarius A*
Sagittarius A* ( ), abbreviated Sgr A* ( ), is the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center of the Milky Way. It is located near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius, about 5.6° south of the ecliptic, ...
(Sgr A*, pronounced "Sagittarius A-Star") at the center
The Center () is the fifth tallest skyscraper in Hong Kong, after International Commerce Centre, Two International Finance Centre (88 storeys), Central Plaza and Bank of China Tower. With a height of , it comprises 73 storeys. The center is ...
of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
.
The Event Horizon Telescope project is an international collaboration that was launched in 2009 after a long period of theoretical and technical developments. On the theory side, work on the photon orbit and first simulations of what a black hole would look like progressed to predictions of VLBI imaging for the Galactic Center black hole, Sgr A*. Technical advances in radio observing moved from the first detection of Sgr A*, through VLBI at progressively shorter wavelengths, ultimately leading to detection of horizon scale structure in both Sgr A* and M87. The collaboration now comprises over 300 members, 60 institutions, working in over 20 countries and regions.
The first image of a black hole, at the center of galaxy Messier 87, was published by the EHT Collaboration on April 10, 2019, in a series of six scientific publications. The array made this observation at a wavelength of 1.3 mm and with a theoretical diffraction-limited resolution of . In March 2021, the Collaboration presented, for the first time, a polarized-based image of the black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can def ...
which may help better reveal the forces giving rise to quasar
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is pronounced , and sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. This emission from a galaxy nucleus is powered by a supermassive black hole with a mass rangi ...
s. Future plans involve improving the array's resolution by adding new telescopes and by taking shorter-wavelength observations. On 12 May 2022, astronomers unveiled the first image of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
, Sagittarius A*
Sagittarius A* ( ), abbreviated Sgr A* ( ), is the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center of the Milky Way. It is located near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius, about 5.6° south of the ecliptic, ...
.
Telescope array
 The EHT is composed of many radio observatories or radio-telescope facilities around the world, working together to produce a high-sensitivity, high-angular-resolution telescope. Through the technique of
The EHT is composed of many radio observatories or radio-telescope facilities around the world, working together to produce a high-sensitivity, high-angular-resolution telescope. Through the technique of very-long-baseline interferometry
Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. Th ...
(VLBI), many independent radio antennas separated by hundreds or thousands of kilometres can act as a phased array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving th ...
, a virtual telescope which can be pointed electronically, with an effective aperture
In electromagnetics and antenna theory, the aperture of an antenna is defined as "A surface, near or on an antenna, on which it is convenient to make
assumptions regarding the field values for the purpose of computing fields at external points. T ...
which is the diameter of the entire planet, substantially improving its angular resolution. The effort includes development and deployment of submillimeter dual polarization receivers, highly stable frequency standards to enable very-long-baseline interferometry at 230–450 GHz, higher-bandwidth VLBI backends and recorders, as well as commissioning of new submillimeter VLBI sites.
Each year since its first data capture in 2006, the EHT array has moved to add more observatories to its global network of radio telescopes. The first image of the Milky Way's supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A*, was expected to be produced from data taken in April 2017, but because there are no flights in or out of the South Pole during austral winter (April to October), the full data set could not be processed until December 2017, when the shipment of data from the South Pole Telescope
The South Pole Telescope (SPT) is a diameter telescope located at the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station, Antarctica. The telescope is designed for observations in the microwave, millimeter-wave, and submillimeter-wave regions of the electroma ...
arrived.
Data collected on hard drives are transported by commercial freight airplanes (a so-called sneakernet) from the various telescopes to the MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
Haystack Observatory and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy
The Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (MPIfRA) (German: ''Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie'') is located in Bonn, Germany. It is one of 80 institutes in the Max Planck Society (German: Max-Planck-Gesellschaft).
History
By com ...
, where the data are cross-correlated and analyzed on a grid computer made from about 800 CPUs all connected through a network.
Because of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, weather patterns, and celestial mechanics, the 2020 observational campaign was postponed to March 2021.
Messier 87*
 The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration announced its first results in six simultaneous press conferences worldwide on April 10, 2019. The announcement featured the first direct image of a black hole, which showed the
The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration announced its first results in six simultaneous press conferences worldwide on April 10, 2019. The announcement featured the first direct image of a black hole, which showed the supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ob ...
at the center of Messier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy with several trillion stars in the constellation Virgo. One of the largest and most massive galaxies in the local ...
, designated M87*. The scientific results were presented in a series of six papers published in ''The Astrophysical Journal Letters
''The Astrophysical Journal'', often abbreviated ''ApJ'' (pronounced "ap jay") in references and speech, is a Peer review, peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery H ...
''. Clockwise rotating black hole
A rotating black hole is a black hole that possesses angular momentum. In particular, it rotates about one of its axes of symmetry.
All celestial objects – planets, stars (Sun), galaxies, black holes – spin.
Types of black holes
Ther ...
was observed in the 6σ region.Fabrizio Tamburini, Bo Thide´, Massimo Della Valle. Measurement of the spin of the M87 black hole from its observed twisted light.Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2020): p. 1 The image provided a test for
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
's general theory of relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric scientific theory, theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current descr ...
under extreme conditions. Studies have previously tested general relativity by looking at the motions of stars and gas clouds near the edge of a black hole. However, an image of a black hole brings observations even closer to the event horizon. Relativity predicts a dark shadow-like region, caused by gravitational bending and capture of light, which matches the observed image. The published paper states: "Overall, the observed image is consistent with expectations for the shadow of a spinning Kerr black hole as predicted by general relativity." Paul T.P. Ho, EHT Board member, said: "Once we were sure we had imaged the shadow, we could compare our observations to extensive computer models that include the physics of warped space, superheated matter, and strong magnetic fields. Many of the features of the observed image match our theoretical understanding surprisingly well."
The image also provided new measurements for the mass and diameter of M87*. EHT measured the black hole's mass to be and measured the diameter of its event horizon to be approximately , roughly 2.5 times smaller than the shadow that it casts, seen at the center of the image. Previous observations of M87 showed that the large-scale jet is inclined at an angle of 17° relative to the observer's line of sight and oriented on the plane of the sky at a position angle
In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the north celestial pole (NCP), turning positive into the ...
of −72°. From the enhanced brightness of the southern part of the ring due to relativistic beaming
Relativistic beaming (also known as Doppler beaming, Doppler boosting, or the headlight effect) is the process by which relativistic effects modify the apparent luminosity of emitting matter that is moving at speeds close to the speed of ligh ...
of approaching funnel wall jet emission, EHT concluded the black hole, which anchors the jet, spins clockwise, as seen from Earth. EHT simulations allow for both prograde and retrograde inner disk rotation with respect to the black hole, while excluding zero black hole spin using a conservative minimum jet power of 1042 erg/s via the Blandford–Znajek process.
Producing an image from data from an array of radio telescopes requires much mathematical work. Four independent teams created images to assess the reliability of the results. These methods included both an established algorithm in radio astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation comin ...
for image reconstruction
Iterative reconstruction refers to iterative algorithms used to reconstruct 2D and 3D images in certain imaging techniques.
For example, in computed tomography an image must be reconstructed from projections of an object. Here, iterative recon ...
known as CLEAN, invented by Jan Högbom, as well as self-calibrating image processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensio ...
methodsSAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS)Seitz, Schneider, and Bartelmann (1998) Entropy-regularized maximum-likelihood cluster mass reconstruction
cites Narayan and Nityananda 1986. for astronomy such as the CHIRP algorithm created by Katherine Bouman and others. The algorithms that were ultimately used were a regularized
maximum likelihood
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimating the parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed stat ...
(RML)Narayan, Ramesh and Nityananda, Rajaram (1986) "Maximum entropy image restoration in astronomy" ''Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics'' Volume 24 (A87-26730 10–90). Palo Alto, CA, Annual Reviews, Inc.p. 127–170. algorithm and the CLEAN algorithm. In March 2020, astronomers proposed an improved way of seeing more of the rings in the first black hole image. In March 2021, a new photo was revealed, showing how the M87 black hole looks in polarised light. This is the first time astronomers have been able to measure polarisation so close to the edge of a black hole. The lines on the photo mark the orientation of polarisation, which is related to the magnetic field around the shadow of the black hole. In August 2022, a team led by
University of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo (UWaterloo, UW, or Waterloo) is a public research university with a main campus in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on of land adjacent to "Uptown" Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university also operates ...
researcher Avery Broderick released a "remaster d version of original image generated from the data collected by the EHT. This image "resolve a fundamental signature of gravity around a black hole," with it showing a displaying photon ring around M87*.The claim has been subsequently disputed
3C 279
 In April 2020, the EHT released the first 20 microarcsecond resolution images of the archetypal
In April 2020, the EHT released the first 20 microarcsecond resolution images of the archetypal blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from t ...
3C 279 it observed in April 2017. These images, generated from observations over 4 nights in April 2017, reveal bright components of a jet whose projection on the observer plane exhibit apparent superluminal motion
In astronomy, superluminal motion is the apparently faster-than-light motion seen in some
radio galaxies, BL Lac objects, quasars, blazars and recently also in some galactic sources called microquasars. Bursts of energy moving out along the re ...
s with speeds up to 20 c. Such apparent superluminal motion from relativistic emitters such as an approaching jet is explained by emission originating closer to the observer (downstream along the jet) catching up with emission originating further from the observer (at the jet base) as the jet propagates close to the speed of light at small angles to the line of sight.
Centaurus A
 In July 2021, high resolution images of the jet produced by black hole sitting at the center of Centaurus A were released. With a mass around , the black hole is not big enough to observe its ring as with Messier M87*, but its jet extends even beyond its host galaxy while staying as a highly collimated beam which is a point of study. Edge-brightening of the jet was also observed which would exclude models of particle acceleration that are unable to reproduce this effect. The image was 16 times sharper than previous observations and utilized a 1.3 mm wavelength.
In July 2021, high resolution images of the jet produced by black hole sitting at the center of Centaurus A were released. With a mass around , the black hole is not big enough to observe its ring as with Messier M87*, but its jet extends even beyond its host galaxy while staying as a highly collimated beam which is a point of study. Edge-brightening of the jet was also observed which would exclude models of particle acceleration that are unable to reproduce this effect. The image was 16 times sharper than previous observations and utilized a 1.3 mm wavelength.
Sagittarius A*
On May 12, 2022, the EHT Collaboration revealed an image ofSagittarius A*
Sagittarius A* ( ), abbreviated Sgr A* ( ), is the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center of the Milky Way. It is located near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius, about 5.6° south of the ecliptic, ...
, the supermassive black hole at the center
Center or centre may refer to:
Mathematics
*Center (geometry), the middle of an object
* Center (algebra), used in various contexts
** Center (group theory)
** Center (ring theory)
* Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentrici ...
of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System ...
. The black hole is 27,000 light-years away from Earth; it is thousands of times smaller than M87*. Sera Markoff, Co-Chair of the EHT Science Council, said: "We have two completely different types of galaxies and two very different black hole masses, but close to the edge of these black holes they look amazingly similar. This tells us that General Relativity governs these objects up close, and any differences we see further away must be due to differences in the material that surrounds the black holes."
J1924-2914
 In August 2022, the EHT together with Global Millimeter VLBI Array and the
In August 2022, the EHT together with Global Millimeter VLBI Array and the Very Long Baseline Array
The Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) is a system of ten radio telescopes which are operated remotely from their Array Operations Center located in Socorro, New Mexico, as a part of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO). These ten radi ...
imaged the distant blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from t ...
J1924-2914. They operated at 230 GHz, 86 GHz and 2.3+8.7 GHz, respectively, the highest angular resolution images of polarized emission from a quasar ever obtained. Observations reveal a helically bent jet and the polarization of its emission suggest a toroidal magnetic field structure. The object is used as calibrator for Sagittarius A* sharing strong optical variability and polarization with it.
Collaborating institutes
The EHT Collaboration consists of 13 stakeholder institutes: * theAcademia Sinica
Academia Sinica (AS, la, 1=Academia Sinica, 3=Chinese Academy; ), headquartered in Nangang, Taipei, is the national academy of Taiwan. Founded in Nanking, the academy supports research activities in a wide variety of disciplines, ranging fro ...
Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics
* the University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first ...
* the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the b ...
* the East Asian Observatory
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
* Goethe University Frankfurt
Goethe University (german: link=no, Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main) is a university located in Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It was founded in 1914 as a citizens' university, which means it was founded and funded by the wealt ...
* Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) is a research institute of the Smithsonian Institution, concentrating on astrophysical studies including galactic and extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, solar, earth and planetary sciences, the ...
(part of the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian)
* Institut de radioastronomie millimétrique
Institut de Radioastronomie Millimetrique (IRAM) is an international research institute and Europe's leading center for radio astronomy at millimeter wavelengths. Its mission is to explore the universe, study its origins and its evolution with two ...
(IRAM, itself a collaboration between the French CNRS
The French National Centre for Scientific Research (french: link=no, Centre national de la recherche scientifique, CNRS) is the French state research organisation and is the largest fundamental science agency in Europe.
In 2016, it employed 31,63 ...
, the German Max Planck Society
The Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science (german: Max-Planck-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften e. V.; abbreviated MPG) is a formally independent non-governmental and non-profit association of German research institutes. ...
, and the Spanish Instituto Geográfico Nacional),
* Large Millimeter Telescope Alfonso Serrano
* Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy
The Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (MPIfRA) (German: ''Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie'') is located in Bonn, Germany. It is one of 80 institutes in the Max Planck Society (German: Max-Planck-Gesellschaft).
History
By com ...
* MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
Haystack Observatory
* National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
The (NAOJ) is an astronomical research organisation comprising several facilities in Japan, as well as an observatory in Hawaii and Chile. It was established in 1988 as an amalgamation of three existing research organizations - the Tokyo Astro ...
* Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics
Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics (PI, Perimeter, PITP) is an independent research centre in foundational theoretical physics located in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. It was founded in 1999. The institute's founding and major benefactor ...
* Radboud University
Institutions affiliated with the EHT include:
* Aalto University
Aalto University ( fi, Aalto-yliopisto; sv, Aalto-universitetet) is a public research university located in Espoo, Finland. It was established in 2010 as a merger of three major Finnish universities: the Helsinki University of Technology, the ...
* Boston University
Boston University (BU) is a private research university in Boston, Massachusetts. The university is nonsectarian, but has a historical affiliation with the United Methodist Church. It was founded in 1839 by Methodists with its original cam ...
* Brandeis University
, mottoeng = "Truth even unto its innermost parts"
, established =
, type = Private research university
, accreditation = NECHE
, president = Ronald D. Liebowitz
, p ...
* California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasional ...
* Canadian Institute for Advanced Research
The Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) is a Canadian-based global research organization that brings together teams of top researchers from around the world to address important and complex questions. It was founded in 1982 and is s ...
* Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics
* Chalmers University of Technology
Chalmers University of Technology ( sv, Chalmers tekniska högskola, often shortened to Chalmers) is a Swedish university located in Gothenburg that conducts research and education in technology and natural sciences at a high international le ...
, Onsala Space Observatory
Onsala Space Observatory (OSO), the Swedish National Facility for Radio Astronomy, provides scientists with equipment to study the Earth and the rest of the Universe. The observatory operates two radio telescopes in Onsala, 45 km south of Got ...
* Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS); ), known by Academia Sinica in English until the 1980s, is the national academy of the People's Republic of China for natural sciences. It has historical origins in the Academia Sinica during the Republi ...
* Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología
Consejo is a village in the north of Corozal District, Belize. Consejo is located on a point of land where the bays of Corozal and Chetumal meet. Consejo is about 8 miles (12.9 km) from the district capital of Corozal Town, and across the wate ...
* Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to tea ...
, Center for Astrophysics and Planetary Science
* European Research Council
The European Research Council (ERC) is a public body for funding of scientific and technological research conducted within the European Union (EU). Established by the European Commission in 2007, the ERC is composed of an independent Scientific ...
* Google Research
* The Graduate University for Advanced Studies (SOKENDAI), Department of Statistical Science / Department of Astronomical Science
* Hiroshima University, Hiroshima Astrophysical Science Center
* Huazhong University of Science and Technology
The Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST; ) is a public research university located in Guanshan Subdistrict, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei province, China. As a national key university directly affiliated to the Ministry of ...
, School of Physics
* Institute of Statistical Mathematics
An institute is an organisational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations (research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body.
In some countries, institutes can ...
* Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía
The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia ( es, Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, IAA-CSIC) is a research institute funded by the High Council of Scientific Research of the Spanish government Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científ ...
, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas
* Instituto Geográfico Nacional
* Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Óptica y Electrónica
* Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica
The National Institute for Astrophysics ( it, Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica, or INAF) is an Italian research institute in astronomy and astrophysics, founded in 1999. INAF funds and operates twenty separate research facilities, which in turn e ...
(INAF) – Istituto di Radioastronomia, Italian ALMA Regional Centre
* Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare
The Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN; "National Institute for Nuclear Physics") is the coordinating institution for nuclear, particle, theoretical and astroparticle physics in Italy.
History
INFN was founded on 8 August 1951, to furt ...
, Sezione di Napoli
* Joint Institute for VLBI in Europe
* Kogakuin University of Technology Engineering
* Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute
The Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI) is the national research institute in astronomy and space science of South Korea funded by the South Korean Government. Its headquarters are located in Daejeon, in the Daedeok Science Town. ...
* Leiden University
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; nl, Universiteit Leiden) is a public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city o ...
, Leiden Observatory
Leiden Observatory ( nl, Sterrewacht Leiden) is an astronomical institute of Leiden University, in the Netherlands. Established in 1633 to house the quadrant of Rudolph Snellius, it is the oldest operating university observatory in the world, wit ...
* Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, ...
* Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik
The Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics is a Max Planck Institute, located in Garching, near Munich, Germany.
In 1991 the Max Planck Institute for Physics and Astrophysics split up into the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Ph ...
* Nanjing University
Nanjing University (NJU; ) is a national public research university in Nanjing, Jiangsu. It is a member of C9 League and a Class A Double First Class University designated by the Chinese central government. NJU has two main campuses: the Xian ...
, Key Laboratory of Modern Astronomy and Astrophysics / School of Astronomy and Space Science
* National Optical Astronomy Observatory
The National Optical Astronomy Observatory (NOAO) was the United States national observatory for ground-based nighttime ultraviolet- optical-infrared (OUVIR) astronomy. The National Science Foundation (NSF) funded NOAO to provide forefront astrono ...
* National Radio Astronomy Observatory
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a federally funded research and development center of the United States National Science Foundation operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc. for the purpose of radio a ...
* National Sun Yat-Sen University
National Sun Yat-sen University (NSYSU; ) is a public research-intensive university renowned as an official think tank scholars' community, located in Sizihwan, Kaohsiung, Taiwan. NSYSU is listed as one of six national research universiti ...
, Physics Department
* National Taiwan University
National Taiwan University (NTU; ) is a public research university in Taipei, Taiwan.
The university was founded in 1928 during Japanese rule as the seventh of the Imperial Universities. It was named Taihoku Imperial University and served d ...
, Department of Physics
* Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research
* Peking University
Peking University (PKU; ) is a public research university in Beijing, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education.
Peking University was established as the Imperial University of Peking in 1898 when it received its royal charte ...
, Department of Astronomy, School of Physics / Kavli Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics
* Rhodes University
Rhodes University is a public research university located in Makhanda (Grahamstown) in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. It is one of four universities in the province. Established in 1904, Rhodes University is the province's oldest ...
, Centre for Radio Astronomy Techniques and Technologies, Department of Physics and Electronics
* Seoul National University
Seoul National University (SNU; ) is a national public research university located in Seoul, South Korea. Founded in 1946, Seoul National University is largely considered the most prestigious university in South Korea; it is one of the three " ...
, Department of Physics and Astronomy
* Tohoku University
, or is a Japanese national university located in Sendai, Miyagi in the Tōhoku Region, Japan. It is informally referred to as . Established in 1907, it was the third Imperial University in Japan and among the first three Designated Natio ...
, Astronomy Institute / Frontier Research Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences
* Universidad de Concepción
Universidad (Spanish for "university") may refer to:
Places
* Universidad, San Juan, Puerto Rico
* Universidad (Madrid)
Football clubs
* Universidad SC, a Guatemalan football club that represents the Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala
...
, Astronomy Department
* Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México
The National Autonomous University of Mexico ( es, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, UNAM) is a public research university in Mexico. It is consistently ranked as one of the best universities in Latin America, where it's also the bigges ...
, Instituto de Astronomía / Instituto de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica
* Universitat de València, Departament d'Astronomia i Astrofísica / Observatori Astronòmic
* University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
, Mullard Space Science Laboratory
The UCL Mullard Space Science Laboratory (MSSL) is the United Kingdom's largest university space research group. MSSL is part of the Department of Space and Climate Physics at University College London (UCL), one of the first universities in the ...
* University of Amsterdam
The University of Amsterdam (abbreviated as UvA, nl, Universiteit van Amsterdam) is a public research university located in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The UvA is one of two large, publicly funded research universities in the city, the other being ...
, Anton Pannekoek Institute & GRAPPA
* University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first ...
* University of California Berkeley
* University of California Santa Barbara
* University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, School of Astronomy and Space Sciences
* University of Illinois
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the Uni ...
, Department of Astronomy / Department of Physics
* University of Massachusetts Amherst
The University of Massachusetts Amherst (UMass Amherst, UMass) is a public research university in Amherst, Massachusetts and the sole public land-grant university in Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Founded in 1863 as an agricultural college, ...
, Department of Astronomy
* University of Pretoria
The University of Pretoria ( af, Universiteit van Pretoria, nso, Yunibesithi ya Pretoria) is a multi-campus public research university in Pretoria, the administrative and de facto capital of South Africa. The university was established in 1908 ...
, Department of Physics
* University of Science and Technology
* University of Science and Technology of China
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degree
An academic degree is a qualification awarded to students upon successful completion of a course of study in higher education, usua ...
, Astronomy Department
* University of St. Petersburg, Astronomy Institute
* University of Tokyo
, abbreviated as or UTokyo, is a public research university located in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Established in 1877, the university was the first Imperial University and is currently a Top Type university of the Top Global University Project b ...
, Graduate School of Science, Department of Astronomy / Kavli Institute for Physics & Mathematics of the Universe
* University of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution ...
, Dunlap Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics
* University of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo (UWaterloo, UW, or Waterloo) is a public research university with a main campus in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on of land adjacent to "Uptown" Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university also operates ...
, Waterloo Center for Astrophysics / Department of Physics and Astronomy
* Yonsei University
Yonsei University (; ) is a private research university in Seoul, South Korea. As a member of the " SKY" universities, Yonsei University is deemed one of the three most prestigious institutions in the country. It is particularly respected in th ...
, Department of Astronomy
References
External links
* * * *EHT "Ask Me Anything" (AMA) serie
on
reddit
Reddit (; stylized in all lowercase as reddit) is an American social news aggregation, content rating, and discussion website. Registered users (commonly referred to as "Redditors") submit content to the site such as links, text posts, imag ...
The Next Generation Event Horizon Telescope
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System Interferometric telescopes