European ethnic groups on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Europeans are the focus of European
Minderheitenrechte in Europa. Handbuch der europäischen Volksgruppen
', Braumüller, (Google Books, snippet view). Als
2006 reprint by Springer
(Amazon, no preview) . The
ethnology
Ethnology (from the grc-gre, ἔθνος, meaning 'nation') is an academic field that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology) ...
, the field of anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
related to the various ethnic groups
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history ...
that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) count 87 distinct "''peoples of Europe''", of which 33 form the majority population in at least one sovereign state, while the remaining 54 constitute ethnic minorities
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
. The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of 770 million Europeans.Christoph Pan, Beate Sibylle Pfeil (2002), Minderheitenrechte in Europa. Handbuch der europäischen Volksgruppen
', Braumüller, (Google Books, snippet view). Als
2006 reprint by Springer
(Amazon, no preview) . The
Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
are the most populous among Europeans, with a population of roughly 120 million. There are no universally accepted and precise definitions of the terms " ethnic group" and "nationality
Nationality is a legal identification of a person in international law, establishing the person as a subject, a ''national'', of a sovereign state. It affords the state jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is th ...
". In the context of European ethnography in particular, the terms ''ethnic group'', ''people'', ''nationality'' and ''ethno-linguistic group'', are used as mostly synonymous, although preference may vary in usage with respect to the situation specific to the individual countries of Europe.
Overview
About 20–25 million residents (3%) are members of diasporas of non-European origin. The population of the European Union, with some 450 million residents, accounts for two thirds of the current European population. BothSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
are special cases, in that the designation of nationality
Nationality is a legal identification of a person in international law, establishing the person as a subject, a ''national'', of a sovereign state. It affords the state jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is th ...
, Spanish and British, may controversially take ethnic aspects, subsuming various regional ethnic groups (see nationalisms and regionalisms of Spain
Both the perceived nationhood of Spain, and the perceived distinctions between different parts of its territory derive from historical, geographical, linguistic, economic, political, ethnic and social factors.
Present-day Spain was formed in the ...
and native populations of the United Kingdom).
Switzerland is a similar case, but the linguistic subgroups of the Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
*Swiss, North Carolina
* Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
* Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internati ...
are discussed in terms of both ethnicity and language affiliations.
Linguistic classifications
Of the total population of Europe of some 740 million (as of 2010), close to 90% (or some 650 million) fall within three large branches ofIndo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
, these being;
* Romance, including Aromanian, Arpitan, Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid ...
, Corsican, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and other Langues d'oïl, Friulian, Galician, Istro-Romanian, Italian, Ligurian, Ladino, Megleno-Romanian, Occitan, Portuguese, Romanian, Romansh, Sardinian and Spanish.
* Germanic, including Danish, Dutch, English, Faroese, Frisian, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, Icelandic, Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg and in the neig ...
, Low Saxon, Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish ( ; also ''Luxemburgish'', ''Luxembourgian'', ''Letzebu(e)rgesch''; Luxembourgish: ) is a West Germanic language that is spoken mainly in Luxembourg. About 400,000 people speak Luxembourgish worldwide.
As a standard form of t ...
, Norwegian, Scots
Scots usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
* Scots language, a language of the West Germanic language family native to Scotland
* Scots people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland
* Scoti, a Latin na ...
, Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
, and Yiddish. Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans g ...
, a daughter language of Dutch, is spoken by some South African and Namibian migrant populations.
* Slavic, including Belarusian
Belarusian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Belarus
* Belarusians, people from Belarus, or of Belarusian descent
* A citizen of Belarus, see Demographics of Belarus
* Belarusian language
* Belarusian culture
* Belarusian cuisine
* Byelor ...
, Bulgarian, Czech, Kashubian Kashubian can refer to:
* Pertaining to Kashubia, a region of north-central Poland
* Kashubians, an ethnic group of north-central Poland
* Kashubian language
See also
*Kashubian alphabet
The Kashubian or Cassubian alphabet (''kaszëbsczi alf ...
, Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
, Polish, Russian, Rusyn, Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia an ...
, Slovak, Slovenian, Sorbian and Ukrainian.
Three stand-alone Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
languages do not fall within larger sub-groups and are not closely related to those larger language families;
* Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(about 12 million)
* Albanian (about 9 million)
* Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
(about 3.5 million)
In addition, there are also smaller sub-groups within the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
languages of Europe, including;
* Baltic, including Latvian, Lithuanian
Lithuanian may refer to:
* Lithuanians
* Lithuanian language
* The country of Lithuania
* Grand Duchy of Lithuania
* Culture of Lithuania
* Lithuanian cuisine
* Lithuanian Jews as often called "Lithuanians" (''Lita'im'' or ''Litvaks'') by other Jew ...
, Samogitian and Latgalian.
* Celtic languages
The Celtic languages (usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
, including Breton, Cornish, Irish, Manx
Manx (; formerly sometimes spelled Manks) is an adjective (and derived noun) describing things or people related to the Isle of Man:
* Manx people
**Manx surnames
* Isle of Man
It may also refer to:
Languages
* Manx language, also known as Manx ...
, Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
, and Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well a ...
.
* Iranic, mainly Ossetian in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
.
* Indo-Aryan is represented by the Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
language spoken by Roma people of eastern Europe, and is at root related to the Indo-Aryan languages of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
.
Besides the Indo-European languages, there are other language families
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in his ...
on the European continent which are considered unrelated to Indo-European:
* Uralic languages
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (w ...
, including Estonian, Finnish, Hungarian, Komi, Livonian, Mari, Mordvin, Sámi
The Sámi ( ; also spelled Sami or Saami) are a Finno-Ugric-speaking people inhabiting the region of Sápmi (formerly known as Lapland), which today encompasses large northern parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and of the Murmansk Oblast, R ...
, Samoyedic, and Udmurt.
* Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic l ...
, including Azeri
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most numer ...
, Bashkir, Chuvash, Gagauz, Kazakh
Kazakh, Qazaq or Kazakhstani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Kazakhstan
*Kazakhs, an ethnic group
*Kazakh language
*The Kazakh Khanate
* Kazakh cuisine
* Qazakh Rayon, Azerbaijan
*Qazax, Azerbaijan
*Kazakh Uyezd, administrative dis ...
, Nogai, Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different , and
 The
The


 Ethno-linguistic groups that arrived from outside Europe during historical times are:
*
Ethno-linguistic groups that arrived from outside Europe during historical times are:
*
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different , and
Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
.
* Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant a ...
, including: Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
Suret ( syr, ܣܘܪܝܬ) ( �su:rɪtʰor �su:rɪθ, also known as Assyrian or Chaldean, refers to the varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic (NENA) spoken by ethnic Assyrians, including those identifying as religious groups rather than ethn ...
(spoken in parts of eastern Turkey and the Caucasus by Assyrian Christians), Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
(spoken by some Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
populations), and Maltese
Maltese may refer to:
* Someone or something of, from, or related to Malta
* Maltese alphabet
* Maltese cuisine
* Maltese culture
* Maltese language, the Semitic language spoken by Maltese people
* Maltese people, people from Malta or of Malte ...
. Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
is spoken by some migrant communities from the Middle East and North Africa.
* Kartvelian languages
The Kartvelian languages (; ka, ქართველური ენები, tr; also known as South Caucasian, Kartvelic, and Iberian languagesBoeder (2002), p. 3) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primari ...
(also known as South Caucasian languages
The Kartvelian languages (; ka, ქართველური ენები, tr; also known as South Caucasian, Kartvelic, and Iberian languagesBoeder (2002), p. 3) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primari ...
), including Georgian, Laz, Mingrelian, Svan, and Zan.
* Northwest Caucasian languages, including Abkhaz, Abaza, Adyghe, Circassian, Kabardian, and Ubykh.
* Northeast Caucasian languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages, also called East Caucasian, Nakh-Daghestani or ''Vainakh-Daghestani'', is a family of languages spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya and Ingushetia and in Northern Azerbaijan as well as ...
, including Avar, Chechen, Dargin, Ingush Ingush may refer to:
* Ingush language
* Ingush people
The Ingush (, inh, ГIалгIай, translit=Ghalghaj, pronounced ) per Oxford dictionary "a member of a people living mainly in Ingushetia in the central Caucasus." Ingushetia is a federa ...
, Lak, and Lezgian.
* Language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
s: Basque, spoken in the Basque regions of Spain and France, is an isolate language, the only one in Europe, and is believed to be unrelated to any other language, living or extinct.
* Mongolic languages
The Mongolic languages are a language family spoken by the Mongolic peoples in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, North Asia and East Asia, mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas and in Kalmykia and Buryatia. The best-known member of this language ...
exist in the form of Kalmyk, spoken in the South region of Russia.
History
Prehistoric populations
 The
The Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Bas ...
have been found to descend from the population of the late Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
or early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
directly.
By contrast, Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
groups of Europe (the Centum, Balto-Slavic, and Albanian groups) migrated throughout most of Europe from the Pontic steppe. They are assumed to have developed ''in situ'' through admixture of earlier Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
and Neolithic populations with Bronze Age, proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
s.
The Finnic peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples, sometimes simply called Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finnic (now commonly ''Finno-Permic'') language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of ...
are assumed to also be descended from Proto-Uralic populations further to the east, nearer to the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, that had migrated to their historical homelands in Europe by about 3,000 years ago.
Reconstructed languages of Iron Age Europe
In Europe, the Iron Age is the last stage of the prehistoric period and the first of the protohistoric periods,The Junior Encyclopædia Britannica: A reference library of general knowledge. (1897). Chicago: E.G. Melvin. (seriously? 1897 "Junior ...
include Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celt ...
, Proto-Italic
The Proto-Italic language is the ancestor of the Italic languages, most notably Latin and its descendants, the Romance languages. It is not directly attested in writing, but has been reconstructed to some degree through the comparative method. ...
and Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic bran ...
, all of these Indo-European languages of the centum group, and Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the Attested language, unattested, linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately ...
and Proto-Baltic, of the satem group. A group of Tyrrhenian languages appears to have included Etruscan, Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age of the Triassic Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage of the Triassic System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest ...
, Lemnian, and perhaps Camunic. A pre-Roman stage of Proto-Basque can only be reconstructed with great uncertainty.
Regarding the European Bronze Age
The European Bronze Age is characterized by bronze artifacts and the use of bronze implements. The regional Bronze Age succeeds the Neolithic and Copper Age and is followed by the Iron Age. It starts with the Aegean Bronze Age in 3200 BC
(succee ...
, the only relatively likely reconstruction is that of Proto-Greek
The Proto-Greek language (also known as Proto-Hellenic) is the Indo-European language which was the last common ancestor of all varieties of Greek, including Mycenaean Greek, the subsequent ancient Greek dialects (i.e., Attic, Ionic, Ae ...
(ca. 2000 BC). A Proto-Italo-Celtic ancestor of both Italic and Celtic (assumed for the Bell beaker period), and a Proto-Balto-Slavic language (assumed for roughly the Corded Ware horizon) has been postulated with less confidence. Old European hydronymy has been taken as indicating an early (Bronze Age) Indo-European predecessor of the later centum languages.
According to geneticist David Reich, based on ancient human genomes that his laboratory sequenced in 2016, Europeans descend from a mixture of four distinct ancestral components.
Historical populations
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
(pre-Great Migrations
''Great Migrations'' is a seven-episode nature documentary television miniseries that airs on the National Geographic Channel, featuring the great migrations of animals around the globe. The seven-part show is the largest programming event in th ...
) populations of Europe known from Greco-Roman historiography
Hellenic historiography (or Greek historiography) involves efforts made by Greeks to track and record historical events. By the 5th century BC, it became an integral part of ancient Greek literature and held a prestigious place in later Roman hist ...
, notably Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for ...
, Pliny, Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
and Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
:
* Aegean: the Greek tribes, Pelasgians
The name Pelasgians ( grc, Πελασγοί, ''Pelasgoí'', singular: Πελασγός, ''Pelasgós'') was used by classical Greek writers to refer either to the predecessors of the Greeks, or to all the inhabitants of Greece before the emergen ...
, and Anatolians
The Anatolians were Indo-European-speaking peoples of the Anatolian Peninsula in present-day Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental cou ...
.
*Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
: the Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, a ...
( List of ancient tribes in Illyria), Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often cons ...
, and Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
.
* Italian peninsula: the Camunni, Rhaetians, Lepontii, Adriatic Veneti, Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They s ...
, Ligurians, Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roug ...
, Italic peoples
The Italic peoples were an ethnolinguistic group identified by their use of Italic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
The Italic peoples are descended from the Indo-European speaking peoples who inhabited Italy from at lea ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Phoenician colonies in its neighboring Italian islands.
*Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
* Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that i ...
/Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ...
: the Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
( list of peoples of Gaul, List of Celtic tribes
This is a list of Celtic tribes, organized in order of the likely ethnolinguistic kinship of the peoples and tribes.
In Classical antiquity, Celts were a large number and a significant part of the population in many regions of Western Europe ...
), Rhaetians and Swabians, Vistula Veneti, Lugii and Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages.
One of the features of Baltic languages is the numbe ...
.
*Iberian peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
and Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
: the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
This is a list of the pre- Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania, i. e., modern Portugal, Spain and Andorra). Some closely fit the concept of a people, ethnic group or tribe. Others are confederations or even unions of t ...
(Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (amo ...
, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
, Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BCE. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strab ...
, Lusitani, Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Bas ...
, Turdetani
The Turdetani were an ancient pre-Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula, living in the valley of the Guadalquivir (the river that the Turdetani called by two names: ''Kertis'' and ''Rérkēs'' (Ῥέρκης); Romans would call the river by ...
), of the Pyrenean piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
( Aquitani) between the Pyrenees and the Atlantic ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
, and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Phoenician coastal Mediterranean colonies.
*Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label= Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, af ...
and Corsica: the ancient Sardinians
The Sardinians, or Sards ( sc, Sardos or ; Italian and Sassarese: ''Sardi''; Gallurese: ''Saldi''), are a Romance language-speaking ethnic group native to Sardinia, from which the western Mediterranean island and autonomous region of Italy ...
and Corsicans
The Corsicans ( Corsican, Italian and Ligurian: ''Corsi''; French: ''Corses'') are a Romance ethnic group. They are native to Corsica, a Mediterranean island and a territorial collectivity of France.
Origin
The island was populated sinc ...
(also known as Nuragic
The nuraghe (, ; plural: Logudorese Sardinian , Campidanese Sardinian , Italian ), or also nurhag in English, is the main type of ancient megalithic edifice found in Sardinia, developed during the Nuragic Age between 1900 and 730 B.C. To ...
and Torrean peoples), comprising the '' Corsi'', '' Balares'', '' Ilienses'' tribes and Phoenician colonies.
*British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles (O ...
: the Celtic tribes in Britain and Ireland
This is a list of Celtic tribes, organized in order of the likely ethnolinguistic kinship of the peoples and tribes.
In Classical antiquity, Celts were a large number and a significant part of the population in many regions of Western Europe, ...
and Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
/ Priteni.
* Northern Europe: the Baltic Finns, Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
(list of Germanic peoples
This list of ancient Germanic peoples is an inventory of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groupings and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilisations in ancient times. The information comes from various ancient historical documents, begin ...
) and Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. T ...
.
*Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
: the Italic Sicels
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the name it has held since antiquity, b ...
and Morgetes, the Sicani
The Sicani (Ancient Greek Σῐκᾱνοί ''Sikānoí'') or Sicanians were one of three Ancient Italic people, ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greeks, Greek Colonies in antiquity, colonization. The Sicani dwelt ea ...
, Elymians and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Phoenician colonies.
*Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
: the Veneti (Early Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central and Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the Sla ...
), Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
and Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th ...
.
* Armenian Highlands/Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
: the Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
.
Historical immigration

 Ethno-linguistic groups that arrived from outside Europe during historical times are:
*
Ethno-linguistic groups that arrived from outside Europe during historical times are:
*Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
n colonies in the Mediterranean (including regions in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label= Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, af ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
and the Aegean), from about 1200 BC to the fall of Carthage after the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War (149–146 BC) was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in modern northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 ...
in 146 BC.
*Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the As ...
n conquest of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
, Southern Caucasus (including parts of modern Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
and Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
) and Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian language, Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from th ...
during the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew ...
(911–605 BC).
*Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
influence: Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
control of Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
(512–343 BC) and the Bosporan Kingdom
The Bosporan Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus (, ''Vasíleio toú Kimmerikoú Vospórou''), was an ancient Greco-Scythian state located in eastern Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Cimmerian Bosporu ...
, Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
(possible Iranians), Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
, Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th ...
, Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the ...
, Ossetes.
*The Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of ...
reached Europe in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
period, the Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
community in Italy dating to around AD 70 and records of Jews settling Central Europe (Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
) from the 5th century (see History of the Jews in Europe
The history of the Jews in Europe spans a period of over two thousand years. Some Jews, a Judaean tribe from the Levant, Natural History 102:11 (November 1993): 12–19. migrated to Europe just before the rise of the Roman Empire. A notable ea ...
).
*The Hunnic Empire
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
(5th century AD), converged with the Barbarian invasions, contributing to the formation of the First Bulgarian Empire.
*The Slavic migrations (6th century AD), and the subsequent split into Eastern Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert Hud ...
, Western Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the early Slavs, common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West ...
and Southern Slavs.
*Avar Khaganate
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars ...
(c. 560s–800).
*The Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ...
(or Proto-Bulgarians), a semi-nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ic Turkic people, originally from Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
, eventually absorbed by the Slavs.
*The Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ural ...
(Hungarians), an Uralic-speaking people, and the Turkic Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პაჭ ...
and Khazars, arrived in Europe in about the 8th century (see Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin).
*The Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
conquered Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
, Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cypru ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
(establishing the Emirate of Sicily
The Emirate of Sicily ( ar, إِمَارَة صِقِلِّيَة, ʾImārat Ṣiqilliya) was an Islamic kingdom that ruled the island of Sicily from 831 to 1091. Its capital was Palermo (Arabic: ''Balarm''), which during this period became a ...
in 831, from which they would be expelled in 1224), some places along the coast of southern Italy, Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, Greek Empire and most of Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a la ...
(founding a polity
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of p ...
known as Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Mus ...
in 711, ruled also by Berber dynasties of the Almoravides and the Almohads
The Almohad Caliphate (; ar, خِلَافَةُ ٱلْمُوَحِّدِينَ or or from ar, ٱلْمُوَحِّدُونَ, translit=al-Muwaḥḥidūn, lit=those who profess the unity of God) was a North African Berber Muslim empire fo ...
, from whose domain they would be expelled in 1492).
*Exodus of Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
Christians.
*The western Kipchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the Sec ...
known as Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
entered the lands of present-day Ukraine in the 11th century.
*The Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
/ Tatar invasions (1223–1480), and Ottoman control of the Balkans (1389–1878). These medieval incursions account for the presence of European Turks and Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different . *The

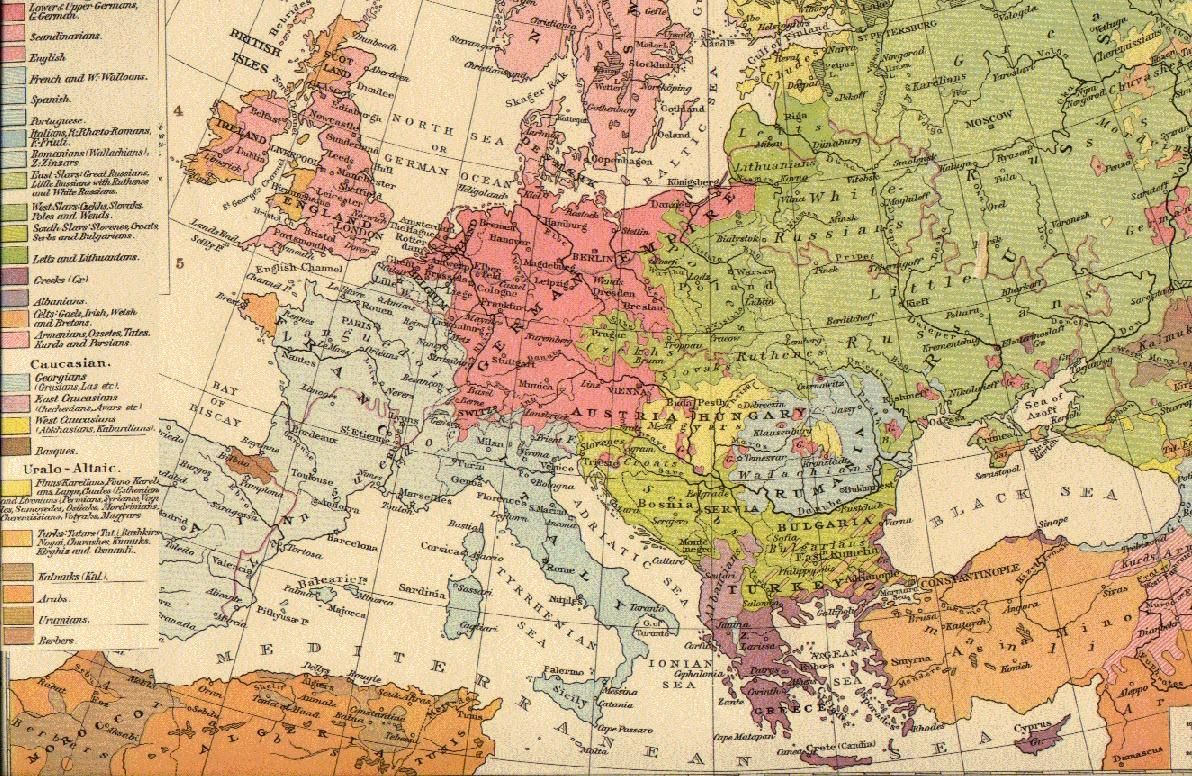 The earliest accounts of European ethnography date from
The earliest accounts of European ethnography date from
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different . *The
Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sig ...
arrived during the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
.
*The Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
Kalmyks arrived in Kalmykia
he official languages of the Republic of Kalmykia are the Kalmyk and Russian languages./ref>
, official_lang_list= Kalmyk
, official_lang_ref=Steppe Code (Constitution) of the Republic of Kalmykia, Article 17: he official languages of the R ...
in the 17th century.
History of European ethnography

 The earliest accounts of European ethnography date from
The earliest accounts of European ethnography date from Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
. Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for ...
described the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
and Thraco-Illyrians. Dicaearchus gave a description of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
itself, besides accounts of western and northern Europe. His work survives only fragmentarily, but was received by Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
and others.
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
period authors include Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which ...
, Strabo and Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
. Julius Caesar gives an account of the Celtic tribes
This is a list of Celtic tribes, organized in order of the likely ethnolinguistic kinship of the peoples and tribes.
In Classical antiquity, Celts were a large number and a significant part of the population in many regions of Western Europe, ...
of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
, while Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
describes the Germanic tribes of Magna Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north-c ...
. A number of authors like Diodorus Siculus, Pausanias and Sallust
Gaius Sallustius Crispus, usually anglicised as Sallust (; 86 – ), was a Roman historian and politician from an Italian plebeian family. Probably born at Amiternum in the country of the Sabines, Sallust became during the 50s BC a partisan ...
depict the ancient Sardinian and Corsican peoples.
The 4th century Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire.
The map is a 13th-ce ...
records the names of numerous peoples and tribes.
Ethnographers of Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has ...
such as Agathias of Myrina Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). His work, known as the ''Res Gestae' ...
, Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') a ...
and Theophylact Simocatta
Theophylact Simocatta (Byzantine Greek: Θεοφύλακτος Σιμοκάτ(τ)ης ''Theophýlaktos Simokát(t)ēs''; la, Theophylactus Simocatta) was an early seventh-century Byzantine historiographer, arguably ranking as the last historian o ...
give early accounts of the Slavs, the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, the Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pr ...
and the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
.
Book IX of Isidore's '' Etymologiae'' (7th century) treats ''de linguis, gentibus, regnis, militia, civibus'' (concerning languages, peoples, realms, war and cities).
Ahmad ibn Fadlan
Aḥmad ibn Faḍlān ibn al-ʿAbbās ibn Rāšid ibn Ḥammād, ( ar, أحمد بن فضلان بن العباس بن راشد بن حماد; ) commonly known as Ahmad ibn Fadlan, was a 10th-century Muslim traveler, famous for his account of hi ...
in the 10th century gives an account of the Bolghar
Bolghar ( tt-Cyrl, Болгар, cv, Пăлхар) was intermittently the capital of Volga Bulgaria from the 8th to the 15th centuries, along with Bilyar and Nur-Suvar. It was situated on the bank of the Volga River, about 30 km downstre ...
and the Rus' people
The Rusʹ ( Old East Slavic: Рѹсь; Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian: Русь; Old Norse: '' Garðar''; Greek: Ῥῶς, ''Rhos'') were a people in early medieval eastern Europe. The scholarly consensus holds that they were or ...
s.
William Rubruck, while most notable for his account of the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
, in his account of his journey to Asia also gives accounts of the Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different and the

 The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of Europeans.
The member states of the Council of Europe in 1995 signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. The broad aims of the convention are to ensure that the signatory states respect the rights of national minorities, undertaking to combat discrimination, promote equality, preserve and develop the culture and identity of national minorities, guarantee certain freedoms in relation to access to the media, minority languages and education and encourage the participation of national minorities in public life. The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities defines a national minority implicitly to include minorities possessing a territorial identity and a distinct cultural heritage. By 2008, 39 member states had signed and ratified the convention, with the notable exception of
The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of Europeans.
The member states of the Council of Europe in 1995 signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. The broad aims of the convention are to ensure that the signatory states respect the rights of national minorities, undertaking to combat discrimination, promote equality, preserve and develop the culture and identity of national minorities, guarantee certain freedoms in relation to access to the media, minority languages and education and encourage the participation of national minorities in public life. The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities defines a national minority implicitly to include minorities possessing a territorial identity and a distinct cultural heritage. By 2008, 39 member states had signed and ratified the convention, with the notable exception of
 Many non-European ethnic groups and nationalities have migrated to Europe over the centuries. Some arrived centuries ago. However, the vast majority arrived more recently, mostly in the 20th and 21st centuries. Often, they come from former colonies of the British, Dutch, French, Portuguese and Spanish empires.
* Western Asians
** Turks: There were 10 million Turks living in
Many non-European ethnic groups and nationalities have migrated to Europe over the centuries. Some arrived centuries ago. However, the vast majority arrived more recently, mostly in the 20th and 21st centuries. Often, they come from former colonies of the British, Dutch, French, Portuguese and Spanish empires.
* Western Asians
** Turks: There were 10 million Turks living in  **
**
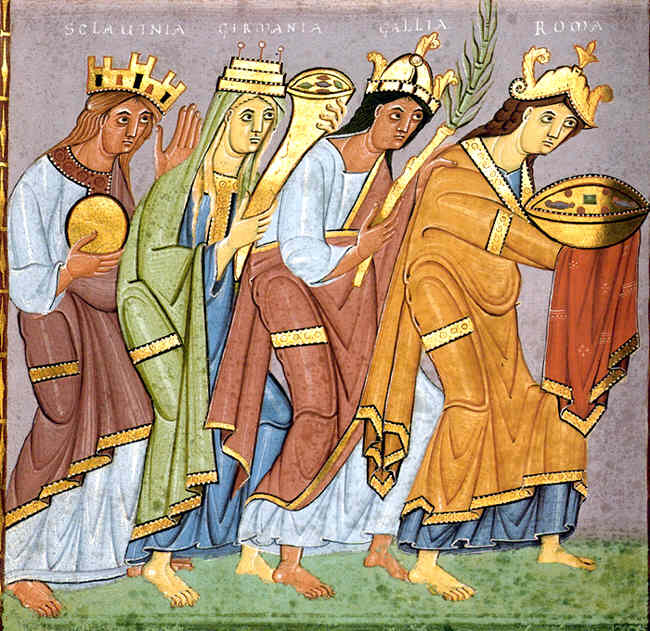 Medieval notions of a relation of the peoples of Europe are expressed in terms of
Medieval notions of a relation of the peoples of Europe are expressed in terms of
 Since the
Since the
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different and the
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the ...
.
Saxo Grammaticus
Saxo Grammaticus (c. 1150 – c. 1220), also known as Saxo cognomine Longus, was a Danish historian, theologian and author. He is thought to have been a clerk or secretary to Absalon, Archbishop of Lund, the main advisor to Valdemar I of Denma ...
and Adam of Bremen
Adam of Bremen ( la, Adamus Bremensis; german: Adam von Bremen) (before 1050 – 12 October 1081/1085) was a German medieval chronicler. He lived and worked in the second half of the eleventh century. Adam is most famous for his chronicle '' Ges ...
give an account of pre-Christian Scandinavia. The '' Chronicon Slavorum'' (12th century) gives an account of the northwestern Slavic tribes.
Gottfried Hensel in his 1741 ''Synopsis Universae Philologiae
''Synopsis Universae Philologiae'' is an early work on comparative linguistics by Gottfried Hensel (''Godofredus Henselius''; 1687–1767), a rector in Hirschberg (Jelenia Góra), Lower Silesia.
Its full title reads: ''Synopsis universae phil ...
'' published one of the earliest ethno-linguistic map of Europe, showing the beginning of the '' pater noster'' in the various European languages and scripts.
In the 19th century, ethnicity was discussed in terms of scientific racism
Scientific racism, sometimes termed biological racism, is the pseudoscientific belief that empirical evidence exists to support or justify racism ( racial discrimination), racial inferiority, or racial superiority.. "Few tragedies can be more ...
, and the ethnic groups of Europe were grouped into a number of " races", Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
, Alpine and Nordic, all part of a larger "Caucasian
Caucasian may refer to:
Anthropology
*Anything from the Caucasus region
**
**
** ''Caucasian Exarchate'' (1917–1920), an ecclesiastical exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church in the Caucasus region
*
*
*
Languages
* Northwest Caucasian l ...
" group.
The beginnings of ethnic geography as an academic subdiscipline lie in the period following World War I, in the context of nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
, and in the 1930s exploitation for the purposes of fascist
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the ...
and Nazi propaganda
The propaganda used by the German Nazi Party in the years leading up to and during Adolf Hitler's dictatorship of Germany from 1933 to 1945 was a crucial instrument for acquiring and maintaining power, and for the implementation of Nazi polici ...
, so that it was only in the 1960s that ethnic geography began to thrive as a ''bona fide'' academic subdiscipline.
The origins of modern ethnography are often traced to the work of Bronisław Malinowski
Bronisław Kasper Malinowski (; 7 April 1884 – 16 May 1942) was a Polish-British anthropologist and ethnologist whose writings on ethnography, social theory, and field research have exerted a lasting influence on the discipline of anthropol ...
, who emphasized the importance of fieldwork.
The emergence of population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and pop ...
further undermined the categorisation of Europeans into clearly defined racial groups. A 2007 study on the genetic history of Europe found that the most important genetic differentiation in Europe occurs on a line from the north to the south-east (northern Europe to the Balkans), with another east–west axis of differentiation across Europe, separating the indigenous Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Bas ...
, Sardinians
The Sardinians, or Sards ( sc, Sardos or ; Italian and Sassarese: ''Sardi''; Gallurese: ''Saldi''), are a Romance language-speaking ethnic group native to Sardinia, from which the western Mediterranean island and autonomous region of Italy ...
and Sami
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise net ...
from other European populations.
Despite these stratifications it noted the unusually high degree of European homogeneity: "there is low apparent diversity in Europe with the entire continent-wide samples only marginally more dispersed than single population samples elsewhere in the world."
Minorities

 The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of Europeans.
The member states of the Council of Europe in 1995 signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. The broad aims of the convention are to ensure that the signatory states respect the rights of national minorities, undertaking to combat discrimination, promote equality, preserve and develop the culture and identity of national minorities, guarantee certain freedoms in relation to access to the media, minority languages and education and encourage the participation of national minorities in public life. The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities defines a national minority implicitly to include minorities possessing a territorial identity and a distinct cultural heritage. By 2008, 39 member states had signed and ratified the convention, with the notable exception of
The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of Europeans.
The member states of the Council of Europe in 1995 signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities. The broad aims of the convention are to ensure that the signatory states respect the rights of national minorities, undertaking to combat discrimination, promote equality, preserve and develop the culture and identity of national minorities, guarantee certain freedoms in relation to access to the media, minority languages and education and encourage the participation of national minorities in public life. The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities defines a national minority implicitly to include minorities possessing a territorial identity and a distinct cultural heritage. By 2008, 39 member states had signed and ratified the convention, with the notable exception of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
.
Indigenous minorities
Notable indigenous minority populations in Europe that are recognized by the UN include the Uralic Nenets, Samoyed, and Komi peoples of northern Russia;Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
of southern Russia and the North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, ( ady, Темыр Къафкъас, Temır Qafqas; kbd, Ишхъэрэ Къаукъаз, İṩxhərə Qauqaz; ce, Къилбаседа Кавказ, Q̇ilbaseda Kavkaz; , os, Цӕгат Кавказ, Cægat Kavkaz, inh, ...
; Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
, Krymchaks
The Krymchaks ( Krymchak: , , , ) are Jewish ethno-religious communities of Crimea derived from Turkic-speaking adherents of Rabbinic Judaism.Crimean Karaites
The Crimean Karaites or Krymkaraylar (Crimean Karaim: Кърымкъарайлар, ''Qrımqaraylar'', singular къарай, ''qaray''; Trakai dialect: ''karajlar'', singular ''karaj''; he, קראי מזרח אירופה; crh, Qaraylar; ), a ...
of Crimea (Ukraine); Sámi
The Sámi ( ; also spelled Sami or Saami) are a Finno-Ugric-speaking people inhabiting the region of Sápmi (formerly known as Lapland), which today encompasses large northern parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and of the Murmansk Oblast, R ...
peoples of northern Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
, Sweden, and Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
and northwestern Russia (in an area also referred to as Sápmi
(, smj, Sábme / Sámeednam, sma, Saepmie, sju, Sábmie, , , sjd, Са̄мь е̄ммьне, Saam' jiemm'n'e) is the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Sámi people. Sápmi is in Northern and Eastern Europe and includes th ...
); Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Bas ...
of Basque Country
Basque Country may refer to:
* Basque Country (autonomous community), as used in Spain ( es, País Vasco, link=no), also called , an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain (shown in pink on the map)
* French Basque Country o ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and southern France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
; and the Sorbian people of Germany and Poland.
Non-indigenous minorities
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
and the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
in 1997 (excluding Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, isl ...
and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
). By 2010 there was up to 15 million Turks living in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
(i.e. excluding Turkish communities in Turkey as well as several Balkan countries and former USSR countries which are not in the EU). According to Dr Araks Pashayan 10 million " Euro-Turks" alone were living in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
in 2012. In addition, there is 500,000 Turks in the UK (2011 estimate), 500,000 in Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
(2011 estimate) 150,000 in Sweden, 120,000 in Switzerland, 70,000 in Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
(2008 estimate), as well as growing communities in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Lichtenstein, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
. In addition, over one million Turks were living in the Balkans in 2019 (especially in Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
, Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Eur ...
, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Feder ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
), and approximately 400,000 Meskhetian Turks were living in the Eastern European regions of the Post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics and in Russia as the near abroad (russian: links=no, ближнее зарубежье, blizhneye zarubezhye), are the 15 sovereign states that wer ...
(i.e. Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
) in 2014.
**Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
: approx. 2.0 million, mostly in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, the UK, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
. They are descended from the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
of the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
(Southwest Asia), originating from the historical kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Natural History 102:11 (November 1993): 12–19.
***Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
: approx. 1.4 million, mostly in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
. They are believed by scholars to have arrived from Israel via southern Europe in the Roman era and settled in France and Germany towards the end of the first millennium. The Nazi Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
wiped out the vast majority during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and forced most to flee, with many of them going to Israel.
***Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), ...
: approx. 0.3 million, mostly in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
. They arrived via Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
in the pre- Roman and Roman eras, and were forcibly converted or expelled in the 15th and 16th centuries.
***Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews ( he, יהודי המִזְרָח), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () or ''Mizrachi'' () and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are a grouping of Jewish communities comprising those who remained i ...
: approx. 0.3 million, mostly in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, via Islamic-majority countries of the Middle East.
***Italqim
Italian Jews ( it, Ebrei Italiani, he, יהודים איטלקים ''Yehudim Italkim'') or Roman Jews ( it, Ebrei Romani, he, יהודים רומים ''Yehudim Romim'') can be used in a broad sense to mean all Jews living in or with roots in I ...
: approx. 50,000, mostly in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, since the 2nd century BC.
***Romaniotes
The Romaniote Jews or the Romaniotes ( el, Ῥωμανιῶτες, ''Rhomaniótes''; he, רומניוטים, Romanyotim) are a Greek-speaking ethnic Jewish community native to the Eastern Mediterranean. They are one of the oldest Jewish comm ...
: approx. 6,000, mostly in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
, with communities dating at least from the 1st century AD.
***Crimean Karaites
The Crimean Karaites or Krymkaraylar (Crimean Karaim: Кърымкъарайлар, ''Qrımqaraylar'', singular къарай, ''qaray''; Trakai dialect: ''karajlar'', singular ''karaj''; he, קראי מזרח אירופה; crh, Qaraylar; ), a ...
(Karaim): less than 4,000, mostly in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
and Lithuania. They arrived in Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.
**Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
: mostly in Sweden and Germany, as well as in Russia, Armenia, Denmark and Great Britain (see Assyrian diaspora
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assy ...
). Assyrians have been present in Eastern Turkey since the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
(circa 2000 BCE).
**Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Ir ...
: approx. 2.5 million, mostly in the UK, Germany, Sweden and Turkey.
** Iraqi diaspora: mostly in the UK, Germany and Sweden, and can be of varying ethnic origin, including Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
, Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Ir ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, Shabaks
Shabaks ( ar, الشبك; ku, شەبەک, translit=Şebek) are a group with a disputed ethnic origin. Some Shabaks identify themselves as a distinct ethnic group and others as ethnic Kurds. They live east of Mosul in Iraq. However their cultural ...
, Mandeans, Turks, Kawliya and Yezidis.
**Lebanese diaspora
Lebanese diaspora refers to Lebanese migrants and their descendants who emigrated from Lebanon and now reside in other countries. There are more Lebanese living outside Lebanon (over 4 million), than within the country (4 million citizens). T ...
: especially in France, Netherlands, Germany, Cyprus and the UK.
** Syrian diaspora: Largest number of Syrians live in Germany, the Netherlands and Sweden and can be of varying ethnic origin, including; Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
, Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Ir ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, Arameans
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean ...
, Turks, Mhallami and Yezidis.
*Africans
African or Africans may refer to:
* Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa:
** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa
*** Ethn ...
** North Africans ( North African Arabs, Egyptian Copts, and Berbers): approx. 5 million, mostly in France, Spain, Italy, the Netherlands and Sweden. The bulk of North African migrants are Moroccans
Moroccans (, ) are the citizens and nationals of the Kingdom of Morocco. The country's population is predominantly composed of Arabs and Berbers (Amazigh). The term also applies more broadly to any people who are of Moroccan nationality, s ...
, although France also has a large number of Algerians, and others may be from Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
(including Copts
Copts ( cop, ⲛⲓⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ ; ar, الْقِبْط ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group indigenous to North Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt and Sudan since antiquity. Most ethnic Copts are ...
), Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Su ...
and Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
.
** Horn Africans (Somalis
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic Somali language is the shared mo ...
, Ethiopians
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
, Eritreans, Djiboutians, and the Northern Sudanese): approx. 700,000, mostly in Scandinavia, the UK, the Netherlands, Germany, Switzerland, Austria, Finland, and Italy. Majority arrived to Europe as refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
s. Proportionally few live in Italy despite former colonial ties, most live in the Nordic countries.
**Sub-Saharan Africans
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the African co ...
(many ethnicities including Afro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
s, African-Americans, Afro-Latinos and others by descent): approx. 5 million, mostly in the UK and France, with smaller numbers in the Netherlands, Germany, Italy, Spain, Portugal and elsewhere.
*Latin Americans
Latin Americans ( es, Latinoamericanos; pt, Latino-americanos; ) are the citizens of Latin American countries (or people with cultural, ancestral or national origins in Latin America). Latin American countries and their diasporas are multi-et ...
: approx. 2.2 million, mainly in Spain and to a lesser extent Italy and the UK. See also Latin American Britons (80,000 Latin American born in 2001).
**Brazilians
Brazilians ( pt, Brasileiros, ) are the citizens of Brazil. A Brazilian can also be a person born abroad to a Brazilian parent or legal guardian as well as a person who acquired Brazilian citizenship. Brazil is a multiethnic society, which me ...
: around 280,000 in Portugal, and 50,000 in Italy and Germany each (mainly German-Brazilians).
** Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
an refugees escaping the Augusto Pinochet
Augusto José Ramón Pinochet Ugarte (, , , ; 25 November 1915 – 10 December 2006) was a Chilean general who ruled Chile from 1973 to 1990, first as the leader of the Military Junta of Chile from 1973 to 1981, being declared President of ...
regime of the 1970s formed communities in France, Sweden, the UK, former East Germany and the Netherlands.
**Mexicans
Mexicans ( es, mexicanos) are the citizens of the United Mexican States.
The most spoken language by Mexicans is Spanish, but some may also speak languages from 68 different Indigenous linguistic groups and other languages brought to Mexi ...
: about 21,000 in Spain and 14,000 in Germany
**Venezuelans
Venezuelans ( Spanish: ''venezolanos'') are the citizens identified with the country of Venezuela. This connection may be through citizenship, descent or cultural. For most Venezuelans, many or all of these connections exist and are the source o ...
: around 520,000 mostly in Spain (200,000), Portugal (100,000), France (30,000), Germany (20,000), UK (15,000), Ireland (5,000), Italy (5,000) and the Netherlands (1,000).
* South Asians: approx. 3–4 million, mostly in the UK but reside in smaller numbers in Germany and France. **
**Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
(Gypsies): approx. 4 or 10 million (although estimates vary widely), dispersed throughout Europe but with large numbers concentrated in the Balkans area, they are of ancestral South Asian and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
an descent, originating from the northern regions of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
.
**Indians
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
: approx. 2 million, mostly in the UK, also in Netherlands, Italy, in Germany and France.
** Pakistanis: approx. 1,000,000, mostly in the UK, but also in France, Spain, Germany and Italy.
**Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million pe ...
i residing in Europe estimated at over 500,000, mostly in the UK.
**Sri Lankans
This is a demography of the population of Sri Lanka including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Sri Lanka is an island in the ...
: approx. 200,000, mainly in the UK.
** Nepalese: approx. 50,000 in the UK.
**Afghans
Afghans ( ps, افغانان, translit=afghanan; Persian/ prs, افغان ها, translit=afghānhā; Persian: افغانستانی, romanized: ''Afghanistani'') or Afghan people are nationals or citizens of Afghanistan, or people with ancestry ...
, about 100,000 to 200,000, most happen to live in the UK, but Germany and Sweden are destinations for Afghan immigrants since the 1960s.
* Southeast Asians
**Filipinos
Filipinos ( tl, Mga Pilipino) are the people who are citizens of or native to the Philippines. The majority of Filipinos today come from various Austronesian ethnolinguistic groups, all typically speaking either Filipino, English and/or oth ...
: above 1 million, mostly in Italy, the UK, France, Germany, and Spain.
**Others of multiple nationalities, ca. total 1 million, such as Indonesians
Indonesians (Indonesian: ''orang Indonesia'') are citizens or people originally from Indonesia, regardless of their ethnic or religious background. There are more than 1,300 ethnicities in Indonesia, making it a multicultural archipelagic coun ...
in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Thais in the UK and Sweden, Vietnamese in France and former East Germany, and Cambodians in France, together with Burmese
Burmese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Myanmar, a country in Southeast Asia
* Burmese people
* Burmese language
* Burmese alphabet
* Burmese cuisine
* Burmese culture
Animals
* Burmese cat
* Burmese chicken
* Burmese (hor ...
, Malaysian
Malaysian may refer to:
* Something from or related to Malaysia, a country in Southeast Asia
* Malaysian Malay, a dialect of Malay language spoken mainly in Malaysia
* Malaysian people, people who are identified with the country of Malaysia regar ...
, Singaporean, Timorese
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor on the eastern part and Indonesia on the western part. The Indonesian part, also ...
and Laotian migrants. See also Vietnamese people in the Czech Republic.
* East Asians
** Chinese: approx. 1.7 million, mostly in France, Russia, the UK, Spain, Italy and the Netherlands.
** Japanese: mostly in the UK and a sizable community in Düsseldorf, Germany.
**Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
: 100,000 estimated (excludes a possible 100,000 more in Russia), mainly in the UK, France and Germany. See also Koryo-saram
Koryo-saram ( ko, 고려사람; russian: Корё сарам; uk, Корьо-сарам) is the name which ethnic Koreans in the post-Soviet states use to refer to themselves. The term is composed of two Korean words: "", a historical name for ...
.
**Mongolians
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
in Germany.
*North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Ca ...
s
**U.S. and Canadian expatriates: American British and Canadian British
Canadians in the United Kingdom, or Canadian Britons, are people from Canada living in the United Kingdom and their descendants. In 2001 some 72,518 people born in Canada were living in the UK according to the UK census. Of the ten census tracts ...
, Canadiens and Acadians
The Acadians (french: Acadiens , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the ...
in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, as well as Americans/Canadians of European ancestry residing elsewhere in Europe.
*** African Americans (i.e. African American British) who are Americans of black/African ancestry reside in other countries. In the 1920s, African-American entertainers established a colony in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
( African American French) and descendants of World War II/Cold War-era black American soldiers stationed in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
are well known.
*Others
** European diaspora – Australians
Australians, colloquially known as Aussies, are the citizens
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the con ...
, New Zealanders
New Zealanders ( mi, Tāngata Aotearoa), colloquially known as Kiwis (), are people associated with New Zealand, sharing a common history, culture, and language (New Zealand English). People of various ethnicities and national origins are citiz ...
, South Africans (mostly White South Africans
White South Africans generally refers to South Africans of European descent. In linguistic, cultural, and historical terms, they are generally divided into the Afrikaans-speaking descendants of the Dutch East India Company's original settl ...
of Afrikaner
Afrikaners () are a South African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch settlers first arriving at the Cape of Good Hope in the 17th and 18th centuries.Entry: Cape Colony. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Volume 4 Part 2: Brain to Cas ...
and British descent), and white Namibians, Zimbabweans, Kenyans, Malawians and Zambians mainly in the UK, together with white Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
ns and Mozambicans, mainly of Portuguese descent.
**Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Ocea ...
s: A small population of Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Aust ...
ans of Polynesian origin in mainland France, Fijians in the United Kingdom from Fiji and Māori in the United Kingdom
New Zealanders in the United Kingdom are citizens or residents of the United Kingdom who originate from New Zealand.
Population
According to the 2001 UK Census, 58,286 New Zealand-born people were residing in the United Kingdom. The 2011 cens ...
of the Māori people
The Māori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over severa ...
of New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
, a small number of Tongans
Tongans, a Polynesian group, represent more than 98% of the inhabitants of Tonga. The rest are European (the majority are British), mixed European, and other Pacific Islanders. There also are several hundred Chinese. Almost two-thirds of the p ...
and Samoans
Samoans or Samoan people ( sm, tagata Sāmoa) are the indigenous Polynesian people of the Samoan Islands, an archipelago in Polynesia, who speak the Samoan language. The group's home islands are politically and geographically divided between ...
, also in the United Kingdom.
**Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
, a scant few in the European continent of American Indian ancestry (often Latin Americans in Spain, France and the UK; Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, ...
in Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
), but most may be children or grandchildren of U.S. soldiers from American Indian tribes by intermarriage with local European women.
European identity
Historical
 Medieval notions of a relation of the peoples of Europe are expressed in terms of
Medieval notions of a relation of the peoples of Europe are expressed in terms of genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kins ...
of mythical founders of the individual groups.
The Europeans were considered the descendants of Japheth
Japheth ( he, יֶפֶת ''Yép̄eṯ'', in pausa ''Yā́p̄eṯ''; el, Ἰάφεθ '; la, Iafeth, Iapheth, Iaphethus, Iapetus) is one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis, in which he plays a role in the story of Noah's drunk ...
from early times, corresponding to the division of the known world into three continents, the descendants of Shem
Shem (; he, שֵׁם ''Šēm''; ar, سَام, Sām) ''Sḗm''; Ge'ez: ሴም, ''Sēm'' was one of the sons of Noah in the book of Genesis and in the book of Chronicles, and the Quran.
The children of Shem were Elam, Ashur, Arphaxad, L ...
peopling Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an ...
and those of Ham peopling Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. Identification of Europeans as " Japhetites" is also reflected in early suggestions for terming the Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, ...
"Japhetic".
In this tradition, the ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British ( Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia B ...
'' (9th century) introduces a genealogy of the peoples of the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
based on the sixth-century Frankish Table of Nations
The Frankish Table of Nations (german: fränkische Völkertafel) is a brief early medieval genealogical text in Latin giving the supposed relationship between thirteen nations descended from three brothers. The nations are the Ostrogoths, Visigot ...
as follows,
:''The first man that dwelt in Europe was Alanus, with his three sons, Hisicion, Armenon, and Neugio. Hisicion had four sons, Francus, Romanus, Alamanus, and Bruttus. Armenon had five sons, Gothus, Valagothus, Cibidus, Burgundus, and Longobardus. Neugio had three sons, Vandalus, Saxo, and Boganus.''
:''From Hisicion arose four nations—the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, the Latins
The Latins were originally an Italic tribe in ancient central Italy from Latium. As Roman power and colonization spread Latin culture during the Roman Republic.
Latins culturally "Romanized" or "Latinized" the rest of Italy, and the word Latin ...
, the Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, and Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs m ...
; from Armenon, the Gothi, Valagothi
The Frankish Table of Nations (german: fränkische Völkertafel) is a brief early medieval genealogical text in Latin giving the supposed relationship between thirteen nations descended from three brothers. The nations are the Ostrogoths, Visi ...
, Cibidi, Burgundi, and Longobardi; from Neugio, the Bogari
The Baiuvarii or Bavarians (german: Bajuwaren) were a Germanic people. The Baiuvarii had settled modern-day Bavaria (which is named after them), Austria, and South Tyrol by the 6th century AD, and are considered the ancestors of modern-day Bavar ...
, Vandali, Saxones, and Tarincgi. The whole of Europe was subdivided into these tribes.''
The text goes then on to list the genealogy of Alanus, connecting him to Japheth via eighteen generations.
European culture
European culture is largely rooted in what is often referred to as its "common cultural heritage". Due to the great number of perspectives which can be taken on the subject, it is impossible to form a single, all-embracing conception of European culture. Nonetheless, there are core elements which are generally agreed upon as forming the cultural foundation of modern Europe. One list of these elements given by K. Bochmann includes: *A common cultural and spiritual heritage derived fromGreco-Roman
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were dir ...
antiquity, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
, the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
and its Humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
, the political thinking of the Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
, and the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
, and the developments of Modernity
Modernity, a topic in the humanities and social sciences, is both a historical period (the modern era) and the ensemble of particular socio-cultural norms, attitudes and practices that arose in the wake of the Renaissancein the "Age of Reas ...
, including all types of socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
;
*A rich and dynamic material culture that has been extended to the other continents as the result of industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econ ...
and colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their rel ...
during the " Great Divergence";
*A specific conception of the individual expressed by the existence of, and respect for, a legality that guarantees human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
and the liberty of the individual;
*A plurality of states with different political orders, which are condemned to live together in one way or another;
*Respect for peoples, states and nations outside Europe.
Berting says that these points fit with "Europe's most positive realisations".
The concept of European culture is generally linked to the classical definition of the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
. In this definition, Western culture is the set of literary
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to includ ...
, scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
, political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studi ...
, artistic and philosophical
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Som ...
principles which set it apart from other civilizations. Much of this set of traditions and knowledge is collected in the Western canon
The Western canon is the body of high culture literature, music, philosophy, and works of art that are highly valued in the West; works that have achieved the status of classics. However, not all these works originate in the Western world, ...
. The term has come to apply to countries whose history has been strongly marked by European immigration or settlement during the 18th and 19th centuries, such as the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, and Australasia
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecolo ...
, and is not restricted to Europe.
Religion
 Since the
Since the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD ...
, most of Europe has been dominated by Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesu ...
. There are three major denominations: Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
, Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
and Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canoni ...
, with Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
restricted mostly to Northern Europe, and Orthodoxy to East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
and South Slavic regions, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnist ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
, and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
. The Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
, part of the Oriental Church, is also in Europe – another branch of Christianity (world's oldest National Church). Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, while typically centered in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, also has a very significant following in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ...
(especially among the Germanic, Western Slavic and Hungarian peoples/regions) as well as in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
(with some in Great Britain).
Christianity has been the dominant religion shaping European culture for at least the last 1700 years.Cambridge University Historical Series, ''An Essay on Western Civilization in Its Economic Aspects'', p.40: Hebraism, like Hellenism, has been an all-important factor in the development of Western Civilization; Judaism, as the precursor of Christianity, has indirectly had had much to do with shaping the ideals and morality of western nations since the christian era.Caltron J.H Hayas, ''Christianity and Western Civilization'' (1953), Stanford University Press, p.2: That certain distinctive features of our Western civilization — the civilization of western Europe and of America— have been shaped chiefly by Judaeo – Graeco – Christianity, Catholic and Protestant.Horst Hutter, University of New York, ''Shaping the Future: Nietzsche's New Regime of the Soul And Its Ascetic Practices'' (2004), p.111:three mighty founders of Western culture, namely Socrates, Jesus, and Plato.Fred Reinhard Dallmayr, ''Dialogue Among Civilizations: Some Exemplary Voices'' (2004), p.22: Western civilization is also sometimes described as "Christian" or "Judaeo- Christian" civilization. Modern philosophical thought has very much been influenced by Christian philosophers such as St Thomas Aquinas and Erasmus, and throughout most of its history, Europe has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture. The Christian culture was the predominant force in western civilization, guiding the course of philosophy, art, and science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
. The notion of "Europe" and the "Western World" has been intimately connected with the concept of " Christianity and Christendom" many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.
Christianity is still the largest religion in Europe; according to a 2011 survey, 76.2% of Europeans considered themselves Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
. Also according to a study on Religiosity in the European Union in 2012, by Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer is a series of public opinion surveys conducted regularly on behalf of the European Commission and other EU Institutions since 1973. These surveys address a wide variety of topical issues relating to the European Union throughout ...
, Christianity is the largest religion in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
, accounting for 72% of the EU's population. As of 2010 Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
were the largest Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
group in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
, accounting for more than 48% of European Christians. The second-largest Christian group in Europe were the Orthodox, who made up 32% of European Christians. About 19% of European Christians were part of the Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
tradition. Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
is the largest Christian country in Europe by population, followed by Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
.
Islam has some tradition in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
and the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
due to conquest and colonization from the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in the 16th to 19th centuries, as well as earlier though discontinued long-term presence in much of Iberia as well as Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
. Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abra ...
account for the majority of the populations in Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
, Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Eur ...
, Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, isl ...
(controlled by Turks), and Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
. Significant minorities are present in the rest of Europe. Russia also has one of the largest Muslim communities in Europe, including the Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different of the Middle Volga and multiple groups in the Caucasus, including Chechens, Caucasian Avars, Avars, Ingush people, Ingush and others. With 20th-century migrations, Muslims in Western Europe have become a noticeable minority. According to the Pew Forum, the total number of Muslims in Europe in 2010 was about 44 million (6%), while the total number of Muslims in the European Union in 2007 was about 16 million (3.2%). Judaism has a long History of the Jews in Europe, history in Europe, but is a small minority religion, with History of the Jews in France, France (1%) the only European country with a Jewish population in excess of 0.5%. The Jewish population of Europe is composed primarily of two Jewish ethnic divisions, groups, the Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi and the Sephardi Jews, Sephardi. Ancestors of Ashkenazi Jews likely migrated to Central Europe Ashkenazi Jews#Origins, at least as early as the 8th century, while Sephardi Jews established themselves Spanish and Portuguese Jews, in Spain and Portugal at least one thousand years before that. Jews originated in the Levant where they resided for thousands of years until the 2nd century AD, when they spread around the Mediterranean and into Europe, although small communities were known to exist in Greece as well as the Balkans since at least the 1st century BC. Jewish history was notably affected by the Holocaust and emigration (including Aliyah, as well as emigration to American Jews, America) in the 20th century. The Jewish population of Europe in 2010 was estimated to be approximately 1.4 million (0.2% of European population) or 10% of the world's Jewish population. In the 21st century,
Online article
* *
Full text on google books
*
Online version
* part I: Europe, pp. 1–100. * * *Panikos Panayi, ''Outsiders: A History of European Minorities'' (London: Hambledon Press, 1999) * * * * * * * * *
Ethnic Power Relations (EPR) Atlas
' *Ron Balsdon,
The Cultural Mosaic of the European Union: Why National Boundaries and the Cultures Inside Still Matter
'
Migration Policy Institute – Country and Comparative Data
* * {{Western world Ethnic groups in Europe,
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different of the Middle Volga and multiple groups in the Caucasus, including Chechens, Caucasian Avars, Avars, Ingush people, Ingush and others. With 20th-century migrations, Muslims in Western Europe have become a noticeable minority. According to the Pew Forum, the total number of Muslims in Europe in 2010 was about 44 million (6%), while the total number of Muslims in the European Union in 2007 was about 16 million (3.2%). Judaism has a long History of the Jews in Europe, history in Europe, but is a small minority religion, with History of the Jews in France, France (1%) the only European country with a Jewish population in excess of 0.5%. The Jewish population of Europe is composed primarily of two Jewish ethnic divisions, groups, the Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi and the Sephardi Jews, Sephardi. Ancestors of Ashkenazi Jews likely migrated to Central Europe Ashkenazi Jews#Origins, at least as early as the 8th century, while Sephardi Jews established themselves Spanish and Portuguese Jews, in Spain and Portugal at least one thousand years before that. Jews originated in the Levant where they resided for thousands of years until the 2nd century AD, when they spread around the Mediterranean and into Europe, although small communities were known to exist in Greece as well as the Balkans since at least the 1st century BC. Jewish history was notably affected by the Holocaust and emigration (including Aliyah, as well as emigration to American Jews, America) in the 20th century. The Jewish population of Europe in 2010 was estimated to be approximately 1.4 million (0.2% of European population) or 10% of the world's Jewish population. In the 21st century,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
has the largest Jewish population by country, Jewish population in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
, followed by the United Kingdom, Germany, Russia and Ukraine.
In modern times, significant secularization since the 20th century, notably in Secularism in France, secularist France, Estonia and the Czech Republic. Currently, distribution of theism in Europe is very heterogeneous, with more than 95% in Poland, and less than 20% in the Czech Republic and Estonia. The 2005 Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer is a series of public opinion surveys conducted regularly on behalf of the European Commission and other EU Institutions since 1973. These surveys address a wide variety of topical issues relating to the European Union throughout ...
poll found that 52% of EU citizens believe in God. According to a Pew Research Center Survey in 2012 the Irreligion, Religiously Unaffiliated (Atheists and Agnostics) make up about 18.2% of the Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
an population in 2010. According to the same Survey the Religiously Unaffiliated make up the majority of the population in only two European countries: Czech Republic (76%) and Estonia (60%).
Pan-European identity
"Pan-European identity" or "Europatriotism" is an emerging sense of personal identification with Europe, or theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
as a result of the gradual process of European integration taking place over the last quarter of the 20th century, and especially in the period after the end of the Cold War, since the 1990s. The foundation of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, OSCE following the 1990s Paris Charter has facilitated this process on a political level during the 1990s and 2000s.
From the later 20th century, 'Europe' has come to be widely used as a synonym for the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
even though there are millions of people living on the European continent in non-EU member states. The prefix ''pan'' implies that the identity applies throughout Europe, and especially in an EU context, and 'pan-European' is often contrasted with nation-state, national identity.This is particularly the case among proponents of the so-called confederation, confederalist or neofunctionalism, neo-functionalist position on European integration. Eder and Spohn (2005:3) note: "The evolutionary thesis of the making of a European identity often goes with the assumption of a simultaneous decline of national identities. This substitution thesis reiterates the well-known confederalist/neo-functionalist position in the debate on European integration, arguing for an increasing replacement of the nation-state by European institutions, against the intergovernmentalist/realist position, insisting on the continuing primacy of the nation-state."
European ethnic groups by sovereign state
See also
* European diaspora *Central Asians *Demography of Europe *Emigration from Europe **European American **White Latin American *Ethnic groups in the Middle East *Eurolinguistics *Federal Union of European Nationalities * Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities *Genetic history of Europe **Y-DNA haplogroups in populations of Europe *Immigration to Europe **Afro-Europeans **Turks in Europe *Languages of Europe *List of ethnic groups *Nomadic peoples of Europe *Peoples of the Caucasus *White peopleNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * *Online article
* *
Full text on google books
*
Online version
* part I: Europe, pp. 1–100. * * *Panikos Panayi, ''Outsiders: A History of European Minorities'' (London: Hambledon Press, 1999) * * * * * * * * *
Further reading
* GROWup - Geographical Research On War, Unified Platform, ETH Zurich,Ethnic Power Relations (EPR) Atlas
' *Ron Balsdon,
The Cultural Mosaic of the European Union: Why National Boundaries and the Cultures Inside Still Matter
'
Migration Policy Institute – Country and Comparative Data
* * {{Western world Ethnic groups in Europe,