

The
culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
of
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
is rooted in its
art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
,
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
,
film, different types of
music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
,
economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes ...
,
literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
, and
philosophy. European culture is largely rooted in what is often referred to as its "common
cultural heritage".
Definition

There were a great number of perspectives which can be taken on the subject, it is impossible to form a single, all-embracing conception of European culture. Nonetheless, there are core elements which are generally agreed upon as forming the cultural foundation of modern Europe. One list of these elements given by K. Bochmann includes:
[K. Bochmann (1990) ''L'idée d'Europe jusqu'au XXè siècle'', quoted in Berting (2006:52). Cf. Davies (1996:15): "No two lists of the main constituents of European civilization would ever coincide. But many items have always featured prominently: from the roots of the Christian world in Greece, Rome and Judaism to modern phenomena such as the Enlightenment, modernization, romanticism, nationalism, liberalism, imperialism, totalitarianism."]
* A common cultural and spiritual heritage derived from
Greco-Roman antiquity,
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
,
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
, the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
, and its
Humanism
Humanism is a philosophy, philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and Agency (philosophy), agency of Human, human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical in ...
, the political thinking of the
Enlightenment, and the
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
, and the developments of
Modernity
Modernity, a topic in the humanities and social sciences, is both a historical period (the modern era) and the ensemble of particular socio-cultural norms, attitudes and practices that arose in the wake of the Renaissancein the "Age of Reas ...
, including all types of
socialism
Socialism is a left-wing Economic ideology, economic philosophy and Political movement, movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to Private prop ...
;
* A rich and dynamic material culture that has been extended to the other continents as the result of
industrialization and
colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colony, colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose the ...
during the "
Great Divergence
The Great Divergence or European miracle is the socioeconomic shift in which the Western world (i.e. Western Europe and the parts of the New World where its people became the dominant populations) overcame pre-modern growth constraints and eme ...
";
* A specific conception of the individual expressed by the existence of, and respect for, a legality that guarantees
human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
and the
liberty of the individual;
* A plurality of states with different political orders, which are feeding each other with new ideas;
* Respect for peoples, states, and nations outside Europe.
Berting says that these points fit with "Europe's most positive realizations".
The concept of European culture is generally linked to the classical definition of the
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania. . In this definition, Western culture is the set of
literary,
scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
,
political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that stud ...
,
art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
istic, and
philosophical
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
principles which set it apart from other civilizations. Much of this set of traditions and knowledge is collected in the
Western canon
The Western canon is the body of high culture literature, music, philosophy, and works of art that are highly valued in the West; works that have achieved the status of classics. However, not all these works originate in the Western world, ...
. The term has come to apply to countries whose history has been strongly marked by European immigration or settlement during the 18th and 19th centuries, such as
the Americas, and
Australasia, and is not restricted to Europe.
The
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
laureate in Literature
Thomas Stearns Eliot, in his 1948 book ''Notes Towards the Definition of Culture'', credited the prominent
Christian influence upon the European culture: "It is in Christianity that our arts have developed; it is in Christianity that the laws of Europe have--until recently--been rooted."
Art

Prehistoric art
Surviving European
prehistoric art mainly comprises sculpture and rock art. It includes the oldest known representation of the human body, the
Venus of Hohle Fel, dating from 40,000 to 35,000 BC, found in
Schelklingen
Schelklingen is a town in the district of Alb-Donau in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. It is situated 10 km north of Ehingen, and 20 km west of Ulm. Schelklingen and 82% of its territory form part of the Swabian Jura Biosphere Reserve.
...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, and the
Löwenmensch figurine
The figurine, also called the Lion-man of , is a prehistoric ivory sculpture discovered in Hohlenstein-Stadel, a German cave in 1939. The German name, , meaning "lion-person" or "lion-human", is used most frequently because it was discovered ...
, from about 30,000 BC, the oldest undisputed piece of figurative art. The
Swimming Reindeer of about 11,000 BCE is among the finest
Magdalenian carvings in bone or antler of animals in the
art of the Upper Paleolithic
The art of the Upper Paleolithic represents the oldest form of prehistoric art. Figurative art is present in Europe and Southeast Asia, beginning between about 40,000 to 35,000 years ago.
Non-figurative cave paintings, consisting of hand ...
. At the beginning of the
Mesolithic in Europe, the figurative sculpture was greatly reduced, and remained a less common element in art than relief decoration of practical objects until the Roman period, despite some works such as the
Gundestrup cauldron from the
European Iron Age and the Bronze Age
Trundholm sun chariot
The Trundholm sun chariot ( da, Solvognen), is a Nordic Bronze Age artifact discovered in Denmark. It is a representation of the sun chariot, a bronze statue of a horse and a large bronze disk, which are placed on a device with spoked wheels.
...
. The oldest European cave art dates back to 40,800 and can be found in the
El Castillo Cave in Spain, but cave art exists across the continent. Rock painting was also performed on cliff faces, but fewer of those paintings have survived because of erosion. One well-known example is the rock paintings of
Astuvansalmi in the
Saimaa
Saimaa ( , ; sv, Saimen) is a lake located in the Finnish Lakeland area in southeastern Finland. At approximately , it is the largest lake in Finland, and the fourth largest natural freshwater lake in Europe.
The name Saimaa likely comes from a ...
area of Finland.
The
Rock Art of the Iberian Mediterranean Basin forms a distinct group with the human figure the main focus, often seen in large groups, with battles, dancing, and hunting all represented, as well as other activities and details such as clothing. The figures are generally rather sketchily depicted in thin paint, with the relationships between the groups of humans and animals more carefully depicted than individual figures. Prehistoric
Celtic art
Celtic art is associated with the peoples known as Celts; those who spoke the Celtic languages in Europe from pre-history through to the modern period, as well as the art of ancient peoples whose language is uncertain, but have cultural and styli ...
is another distinct grouping from much of
Iron Age Europe
In Europe, the Iron Age is the last stage of the prehistoric period and the first of the protohistoric periods,The Junior Encyclopædia Britannica: A reference library of general knowledge. (1897). Chicago: E.G. Melvin. (seriously? 1897 "Junior ...
and survives mainly in the form of high-status metalwork skillfully decorated with complex, elegant, and mostly abstract designs, often using curving and spiral forms. Full-length human figures of any size are so rare that their absence may represent a religious taboo. As the Romans conquered Celtic territories, the style vanished, except in the
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
, where it influenced the
Insular style
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, was produced in the post-Roman era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term derives from ''insula'', the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style dif ...
of the Early Middle Ages.
Classical art
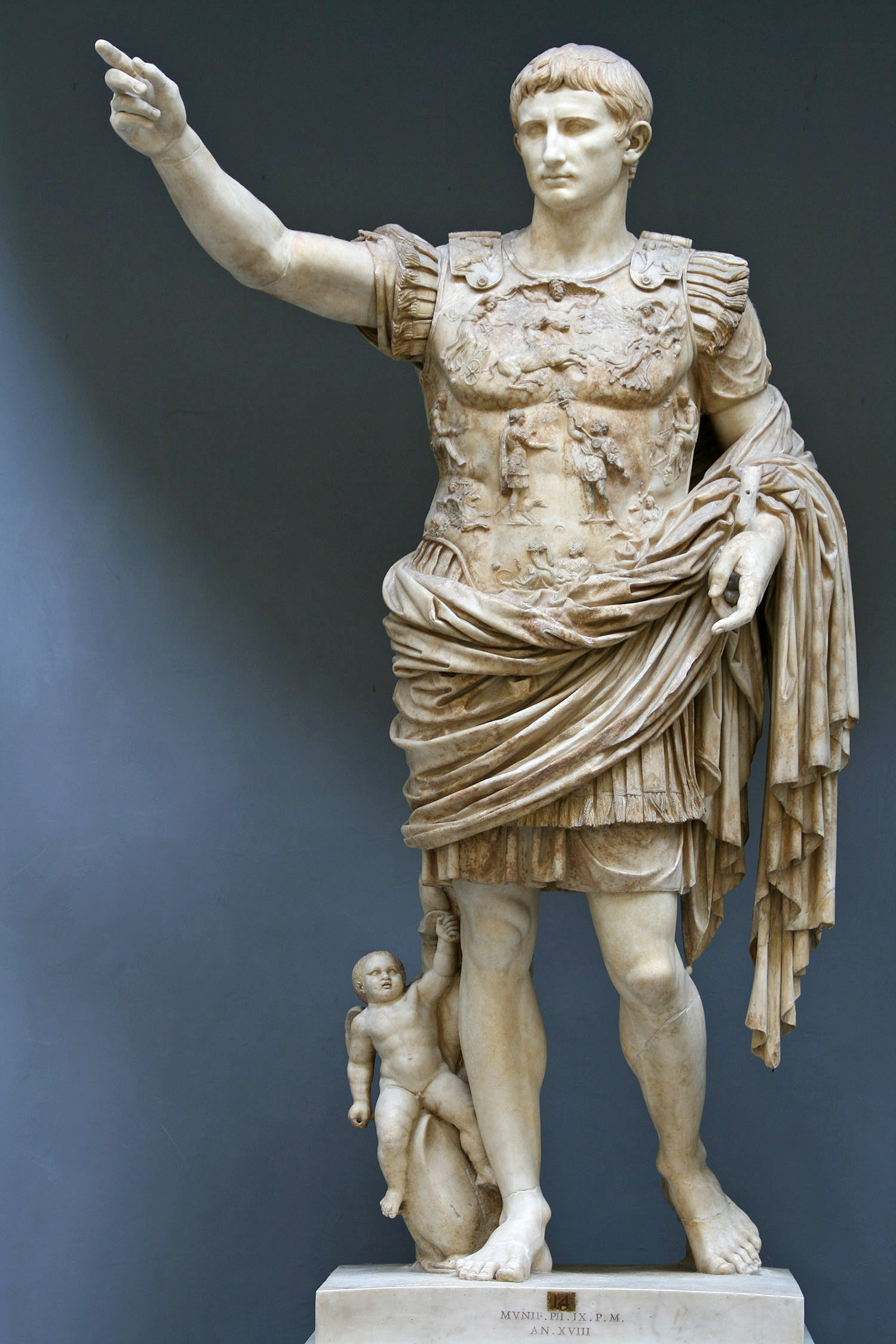 Ancient Greek art
Ancient Greek art stands out among that of other ancient cultures for its development of naturalistic but idealized depictions of the human body, in which largely nude male figures were generally the focus of innovation. The rate of stylistic development between about 750 and 300 BC was remarkable by ancient standards, and in surviving works is best seen in
Ancient Greek sculpture
The sculpture of ancient Greece is the main surviving type of fine ancient Greek art as, with the exception of painted ancient Greek pottery, almost no ancient Greek painting survives. Modern scholarship identifies three major stages in monument ...
. There were important innovations in painting, which have to be essentially reconstructed due to the lack of original survivals of quality, other than the distinct field of painted pottery.
Black-figure pottery
Black-figure pottery painting, also known as the black-figure style or black-figure ceramic ( grc, , }), is one of the styles of painting on antique Greek vases. It was especially common between the 7th and 5th centuries BCE, although there are ...
and the subsequent
red-figure pottery are famous and influential examples of the Ancient Greek decorative arts.
Roman art
The art of Ancient Rome, and the territories of its Republic and later Empire, includes architecture, painting, sculpture and mosaic work. Luxury objects in metal-work, gem engraving, ivory carvings, and glass are sometimes considered to be min ...
was influenced by Greece and can in part be taken as a descendant of ancient Greek painting and sculpture, but was also strongly influenced by the more local
Etruscan art of Italy. The sculpture was perhaps considered as the highest form of art by Romans, but figure painting was also very highly regarded. The
Roman sculpture is primarily portraiture derived from the upper classes of society as well as depictions of the gods. However, Roman painting does have important unique characteristics. Among surviving Roman paintings are wall paintings, many from villas in
Campania, in Southern Italy, especially at
Pompeii and
Herculaneum. Such painting can be grouped into four main "styles" or periods and may contain the first examples of
trompe-l'œil
''Trompe-l'œil'' ( , ; ) is an artistic term for the highly realistic optical illusion of three-dimensional space and objects on a two-dimensional surface. ''Trompe l'oeil'', which is most often associated with painting, tricks the viewer into ...
, pseudo-perspective, and pure landscape.
Early Christian art grew out of Roman popular, and later Imperial, art and adapted its
iconography from these sources.
Medieval art
Medieval art can be broadly categorized into the Byzantine art of the Eastern Roman Empire, and the Gothic art that emerged in Western Europe over the same period.
Byzantine art was strongly influenced by its classical heritage but distinguished itself by the development of a new, abstract, aesthetic, marked by anti-naturalism and a favor for symbolism. The subject matter of monumental Byzantine art was primarily religious and imperial: the two themes are often combined, as in the portraits of later Byzantine emperors that decorated the interior of the sixth-century church of
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
in Constantinople. However, the Byzantines inherited the
Early Christian distrust of
monumental sculpture in religious art, and produced only
relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
s, of which very few survivals are anything like life-size, in sharp contrast to the medieval art of the West, where monumental sculpture revived from
Carolingian art onwards. Small ivories were also mostly in relief. The so-called "minor arts" were very important in Byzantine art, and luxury items, including ivories carved in relief as formal presentation
Consular diptych
In Late Antiquity, a consular diptych was a type of diptych intended as a de-luxe commemorative object. The diptychs were generally in ivory, wood or metal and decorated with rich relief sculpture. A consular diptych was commissioned by a ''consu ...
s or caskets such as the
Veroli casket,
hardstone carvings,
enamels,
glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching ...
, jewelry, metalwork, and
figured silks were produced in large quantities throughout the Byzantine era.

Migration Period art
Migration Period art denotes the artwork of the Germanic peoples during the Migration period (c. 300 – 900). It includes the Migration art of the Germanic tribes on the continent, as well the start of the Insular art or Hiberno-Saxon art of the ...
includes the art of the Germanic tribes on the continent, as well the start of the distinct
Insular art or Hiberno-Saxon art of the
Anglo-Saxon and Celtic fusion in the
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
. It covers many different styles of art including the polychrome style and the Scythian and Germanic
animal style. After
Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
, Migration Period art developed into various schools of Early
Medieval art in Western Europe, which are normally classified by region, such as
Anglo-Saxon art and
Carolingian art, before the continent-wide styles of
Romanesque art and finally
Gothic art
Gothic art was a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Northern, Southern and ...
developed.
 Romanesque art
Romanesque art and
Gothic art
Gothic art was a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Northern, Southern and ...
dominated Western and Central Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the
Renaissance style in the 15th century or later, depending on the region. The Romanesque style was greatly influenced by Byzantine and Insular art. Religious art, such as church sculpture and decorated manuscripts, was particularly prominent. Art of the period was characterized by a very vigorous style in both sculpture and painting. Colors tended to be very striking and mostly primary. Compositions usually had little depth, and needed to be flexible to be squeezed into the shapes of
historiated initial
A historiated initial is an initial, an enlarged letter at the beginning of a paragraph or other section of text, that contains a picture. Strictly speaking, a historiated initial depicts an identifiable figure or a specific scene, while an in ...
s, column capitals, and church
tympanums. Figures often varied in size in relation to their importance, and landscape backgrounds, if attempted at all, were closer to abstract decorations than realism.
Gothic art developed from Romanesque art in Northern France in the 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of
Gothic architecture. It spread to all of
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, and much of
Southern and
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
. In the late 14th century, the sophisticated court style of
International Gothic developed, which continued to evolve until the late 15th century. In many areas, especially England and Germany, Late Gothic art continued well into the 16th century. Gothic art was often
typological in nature, showing the stories of the New Testament and the Old Testament side by side. Saints' lives were often depicted. Images of the
Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
changed from the Byzantine iconic form to a more human and affectionate mother, often showing the refined manners of a courtly lady.
Secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
art came into its own during the gothic period alongside the creation of a
bourgeois class who could afford to patronize the arts and commission works. Increased literacy and a growing body of
secular vernacular literature encouraged the representation of secular themes in art. With the growth of cities, trade
guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
s were formed, and artists were often required to be members of a
painters' guild
The Guild of Saint Luke was the most common name for a city guild for painters and other artists in early modern Europe, especially in the Low Countries. They were named in honor of the Evangelist Luke, the patron saint of artists, who was ident ...
—as a result, because of better record-keeping, more artists are known to us by name in this period than any previous.
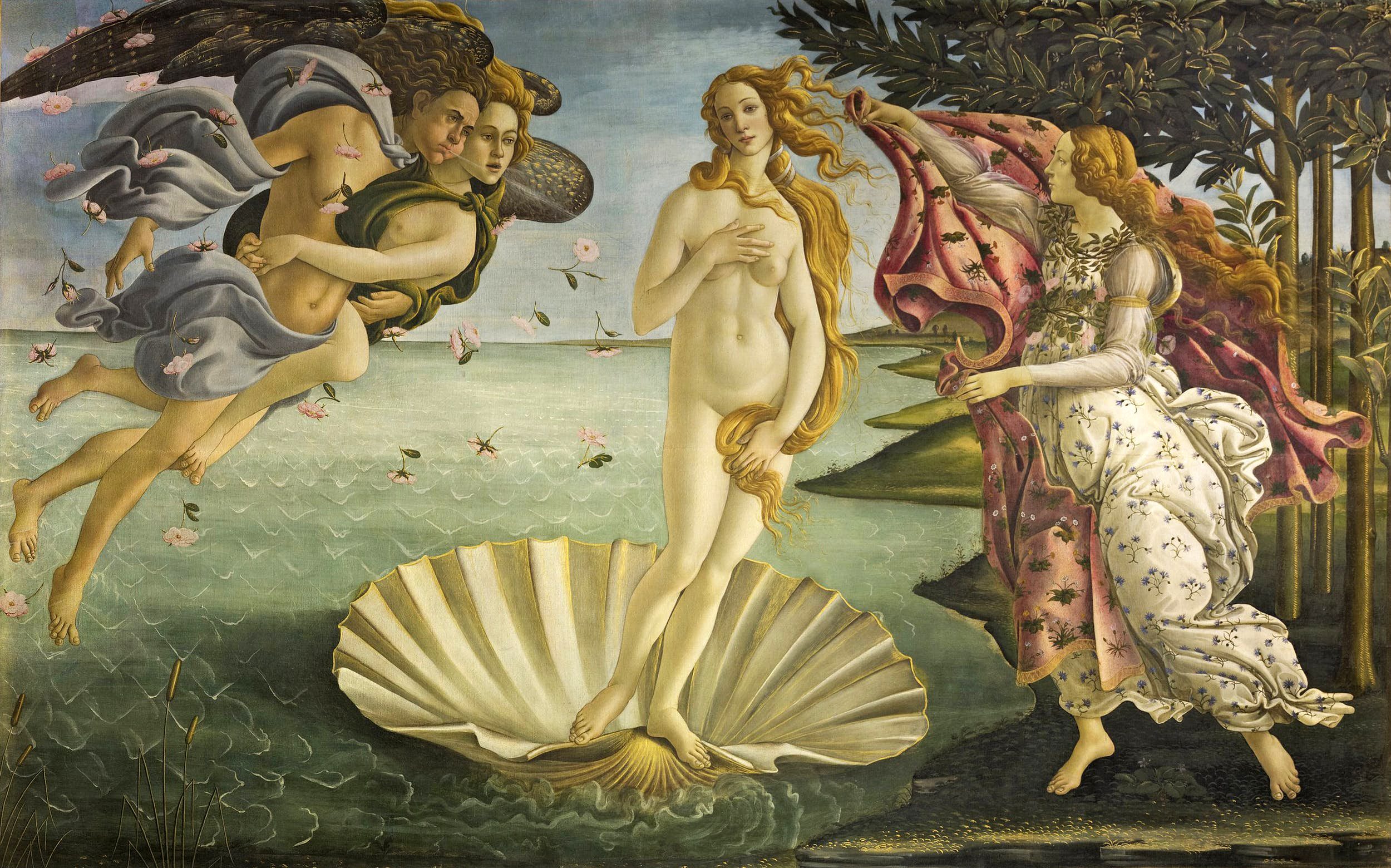
Renaissance art

Renaissance art
Renaissance art (1350 – 1620 AD) is the painting, sculpture, and decorative arts of the period of European history known as the Renaissance, which emerged as a distinct style in Italy in about AD 1400, in parallel with developments which occ ...
emerged as a distinct style in northern Italy from around 1420, in parallel with developments which occurred in
philosophy,
literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
,
music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
, and
science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
. It took as its foundation the art of
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, but was also influenced by the art of Northern Europe and contemporary scientific knowledge. Renaissance artists painted a wide variety of
themes. Religious
altarpieces,
fresco cycles, and small works for private devotion were very popular. Painters in both Italy and northern Europe frequently turned to
Jacobus de Voragine
Jacobus de Voragine (c. 123013/16 July 1298) was an Italian chronicler and archbishop of Genoa. He was the author, or more accurately the compiler, of the '' Golden Legend'', a collection of the legendary lives of the greater saints of the medi ...
's ''
Golden Legend
The ''Golden Legend'' (Latin: ''Legenda aurea'' or ''Legenda sanctorum'') is a collection of hagiographies by Jacobus de Voragine that was widely read in late medieval Europe. More than a thousand manuscripts of the text have survived.Hilary ...
'' (1260), a highly influential sourcebook for the lives of
saints that had already had a strong influence on Medieval artists. Interest in classical antiquity and
Renaissance humanism also resulted in many
Mythological and
history paintings. Decorative
ornament, often used in painted architectural elements, was especially influenced by classical Roman motifs.


Techniques characteristic of Renaissance art include the use of
proportion and
linear perspective
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, ...
;
foreshortening
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, ...
, to create an illusion of depth;
sfumato, a technique of softening of sharp outlines by subtle blending of tones to give the illusion of depth or three-dimensionality; and
chiaroscuro, the effect of using a strong contrast between light and dark to give the illusion of depth or three-dimensionality.
Mannerism, Baroque and Rococo
Renaissance Classicism spawned two different movements—
Mannerism and the
Baroque. Mannerism, a reaction against the idealist perfection of Classicism, employed distortion of light and spatial frameworks in order to emphasize the emotional content of a painting and the emotions of the painter. Where High Renaissance art emphasizes proportion, balance, and ideal beauty, Mannerism exaggerates such qualities, often resulting in compositions that are asymmetrical or unnaturally elegant. The style is notable for its intellectual sophistication as well as its artificial (as opposed to naturalistic) qualities. It favors compositional tension and instability rather than the balance and clarity of earlier Renaissance paintings.
In contrast, Baroque art took the representationalism of the Renaissance to new heights, emphasizing detail, movement, lighting, and drama. Perhaps the best-known Baroque painters are
Caravaggio,
Rembrandt,
Peter Paul Rubens
Sir Peter Paul Rubens (; ; 28 June 1577 – 30 May 1640) was a Flemish artist and diplomat from the Duchy of Brabant in the Southern Netherlands (modern-day Belgium). He is considered the most influential artist of the Flemish Baroque tradi ...
, and
Diego Velázquez. Baroque art is often seen as part of the
Counter-Reformation— the revival of spiritual life in the
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. Religious and political themes are widely explored within the Baroque artistic context, and both paintings and sculptures are characterized by a strong element of drama, emotion, and theatricality. Baroque art was particularly ornate and elaborate in nature, often using rich, warm colors with dark undertones.
Dutch Golden Age painting
Dutch Golden Age painting is the painting of the Dutch Golden Age, a period in Dutch history roughly spanning the 17th century, during and after the later part of the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) for Dutch independence.
The new Dutch Republ ...
is a distinct subset of Baroque, leading to the development of secular genres such as
still life,
genre paintings of everyday scenes, and
landscape painting
Landscape painting, also known as landscape art, is the depiction of natural scenery such as mountains, valleys, trees, rivers, and forests, especially where the main subject is a wide view—with its elements arranged into a coherent compo ...
.
By the 18th century, Baroque art had developed into
Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
in France. Rococo art was even more elaborate than the Baroque, but it was less serious and more playful. The artistic movement no longer placed emphasis on politics and religion, focusing instead on lighter themes such as romance, celebration, and appreciation of nature. Furthermore, it sought inspiration from the artistic forms and ornamentation of
Far Eastern Asia, resulting in the rise in favor of
porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
figurines and
chinoiserie
(, ; loanword from French '' chinoiserie'', from '' chinois'', "Chinese"; ) is the European interpretation and imitation of Chinese and other East Asian artistic traditions, especially in the decorative arts, garden design, architecture, lite ...
in general. Rococo soon fell out of favor, being seen by many as a gaudy and superficial movement emphasizing aesthetics over meaning.
Neoclassical, Romanticism, and Realism
Neoclassicism began in the 18th century as a counter-movement opposing Rococo. It desired for a return to the simplicity, order, and 'purism' of classical antiquity, especially ancient Greece and Rome. Neoclassicism was the artistic component of the intellectual movement known as
the Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
. Neoclassicism had become widespread in Europe throughout the 18th century, especially in the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. In many ways, Neoclassicism can be seen as a political movement as well as an artistic and cultural one. Neoclassical art places emphasis on order, symmetry, and classical simplicity; common themes in Neoclassical art include courage and war, as were commonly explored in ancient Greek and Roman art.
Ingres,
Canova, and
Jacques-Louis David are among the best-known neoclassicists.
Just as Mannerism rejected Classicism,
Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
rejected the aesthetic of the Neoclassicists, specifically the highly objective and ordered nature of Neoclassicism, favoring instead a more individual and emotional approach to the arts. Emphasis was placed on nature, especially when aiming to portray the power and beauty of the natural world, and emotions. Romantic art often used colors in order to express feelings and emotions. Romantic art was inspired by ancient Greek and Roman art and mythology, but also takes much of its aesthetic qualities from
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
ism and
Gothicism, as well as later mythology and
folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging ...
. Among the greatest Romantic artists were
Eugène Delacroix,
Francisco Goya,
J.M.W. Turner,
John Constable,
Caspar David Friedrich, and
William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. ...
.
In response to these changes caused by
Industrialisation, the movement of
Realism emerged, which sought to accurately portray the conditions and hardships of the poor in the hopes of changing society. In contrast with Romanticism, which was essentially optimistic about mankind, Realism offered a stark vision of poverty and despair. While Romanticism glorified nature, Realism portrayed life in the depths of an urban wasteland. Like Romanticism,
Realism was a literary as well as an artistic movement. Other contemporary movements were more
Historicist
Historicism is an approach to explaining the existence of phenomena, especially social and cultural practices (including ideas and beliefs), by studying their history, that is, by studying the process by which they came about. The term is widely u ...
in nature, such as the
Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, which attempted to return art to its state of "purity" prior to
Raphael, and the
Arts and Crafts Movement, which reacted against the impersonality of mass-produced goods and advocated a return to medieval craftsmanship.
Music

Classical music
Pre-1600
This broad era encompasses
early music, which generally comprises
Medieval music (500–1400) and
Renaissance music (1400–1600), but sometimes includes
Baroque music (1600–1760).
Post-1600
This era includes the
common practice period
In European art music, the common-practice period is the era of the tonal system. Most of its features persisted from the mid-Baroque period through the Classical and Romantic periods, roughly from 1650 to 1900. There was much stylistic evoluti ...
from approximately 1600 to 1900, as well as the
modernist and
postmodernist
Postmodernism is an intellectual stance or mode of discourseNuyen, A.T., 1992. The Role of Rhetorical Devices in Postmodernist Discourse. Philosophy & Rhetoric, pp.183–194. characterized by skepticism toward the " grand narratives" of modern ...
styles that emerged after 1900 and which continue to the present day.
Modern music
Folk music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has b ...
: Europe has a wide and diverse range of indigenous music, sharing common features in rural, traveling, or maritime communities. Folk music is embedded in an unwritten, oral tradition, but was increasingly transcribed from the nineteenth century onwards. Many classical composers used folk melodies, and folk has influenced some popular music in Europe. See the
list of European folk music.
Popular music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Fu ...
: Europe has also imported many different genres of popular music, including
Rock,
Blues,
R&B Soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun '' soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest atte ...
,
Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with its roots in blues and ragtime. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a m ...
,
Hip-Hop and
Pop. Various genres associated with and named after Europe are rooted in
Electronic dance music (EDM), and include
Europop
Europop (also spelled Euro pop) is a style of pop music that originated in Europe during the mid-to-late 1960s and developed to today's form throughout the late 1970s. Europop topped the charts throughout the 1980s and 1990s, with revivals and ...
,
Eurodisco
Eurodisco (also spelled as Euro disco) is the variety of European forms of electronic dance music that evolved from disco in the late 1970s, incorporating elements of pop and rock into a disco-like continuous dance atmosphere. Many Eurodisco ...
,
Eurodance and
Eurobeat
Eurobeat refers to two styles of dance music that originated in Europe: one is a British variant of Italian Eurodisco-influencedAng, Ien & Morley, David (2005). "Cultural Studies: Volume 3, Issue 2". ''Routledge''. pgs. 171, 173, 170. . "Eurore ...
.
Media
Television
Radio
Newspapers
Architecture

Prehistoric architecture
The Neolithic long house was a long, narrow timber dwelling built by the first farmers in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
beginning at least as early as the period 5000 to 6000
BC.
Knap of Howar and
Skara Brae, the
Orkney Islands, Scotland, are stone-built Neolithic settlements dating from 3,500 BC.
Megaliths
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
found in Europe and the Mediterranean were also erected in the Neolithic period. See
Neolithic architecture
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several par ...
.
Ancient classical architecture


Ancient Greek architecture
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greek-speaking people (''Hellenic'' people) whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC unti ...
was produced by the
Greek-speaking people whose
culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
flourished on the Greek mainland, the
Peloponnese, the
Aegean Islands, and in colonies in
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD. Ancient Greek architecture is distinguished by its highly formalized characteristics, both of structure and decoration. The formal vocabulary of ancient Greek architecture, in particular the division of architectural style into three defined orders: the
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of c ...
, the
Ionic Order, and the
Corinthian Order, was to have a profound effect on the History of architecture, Western architecture of later periods.
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Ancient Greek Architecture, Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but differed from Greek buildings, becoming a new Architecture, architectural style. The two styles are often considered one body of classical architecture. Roman architecture flourished in the Roman Republic and even more so under the Roman Empire, Empire, when the great majority of surviving buildings were constructed. It used new materials, particularly concrete, and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make buildings that were typically strong and well-engineered. Large numbers remain in some form across the empire, sometimes complete and still in use.

Medieval architecture
Romanesque architecture combines features of Ancient Roman architecture, ancient Roman and Byzantine architecture, Byzantine buildings and other local traditions. It is known for its massive quality, thick walls, round arches, sturdy Pier (architecture), pillars, groin vaults, large towers, and decorative Arcade (architecture), arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms, frequently of a very regular, symmetrical plan; the overall appearance is one of simplicity when compared with the Gothic buildings that were to follow. The style can be identified right across Europe, despite regional characteristics and different materials, and is most frequently seen in churches. Plenty of examples of this architecture are found alongside the Camino de Santiago.
Gothic architecture flourished in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
during the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. Originating in 12th century France and lasting into the 16th century, Gothic architecture was known during the period as ''Opus Francigenum'' ("French work"), with the term ''Gothic'' first appearing during the latter part of the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
. Its characteristics include the Ogive, pointed arch, the ribbed vault (which evolved from the joint vaulting of Romanesque architecture), and the flying buttress. Gothic architecture is most familiar as the architecture of many of the great cathedrals, abbeys, and churches of Europe.
Renaissance and baroque architecture

Renaissance architecture began in the early 14th and lasted until the early 17th century. It demonstrates a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman architectural thought and material culture, particularly the symmetry,
proportion, geometry, and the regularity of parts of ancient buildings. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to France, Germany, England, Russia, and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact
Palladian architecture was derived from and inspired by the designs of the Italian Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). Palladio's work was strongly based on the symmetry, perspective, and values of the formal classical temple architecture of the Ancient Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans. From the 17th century, Palladio's interpretation of this classical architecture was adapted as the style known as Palladianism. It continued to develop until the end of the 18th century, and continued to be popular in Europe throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries, where it was frequently employed in the design of public and municipal buildings.
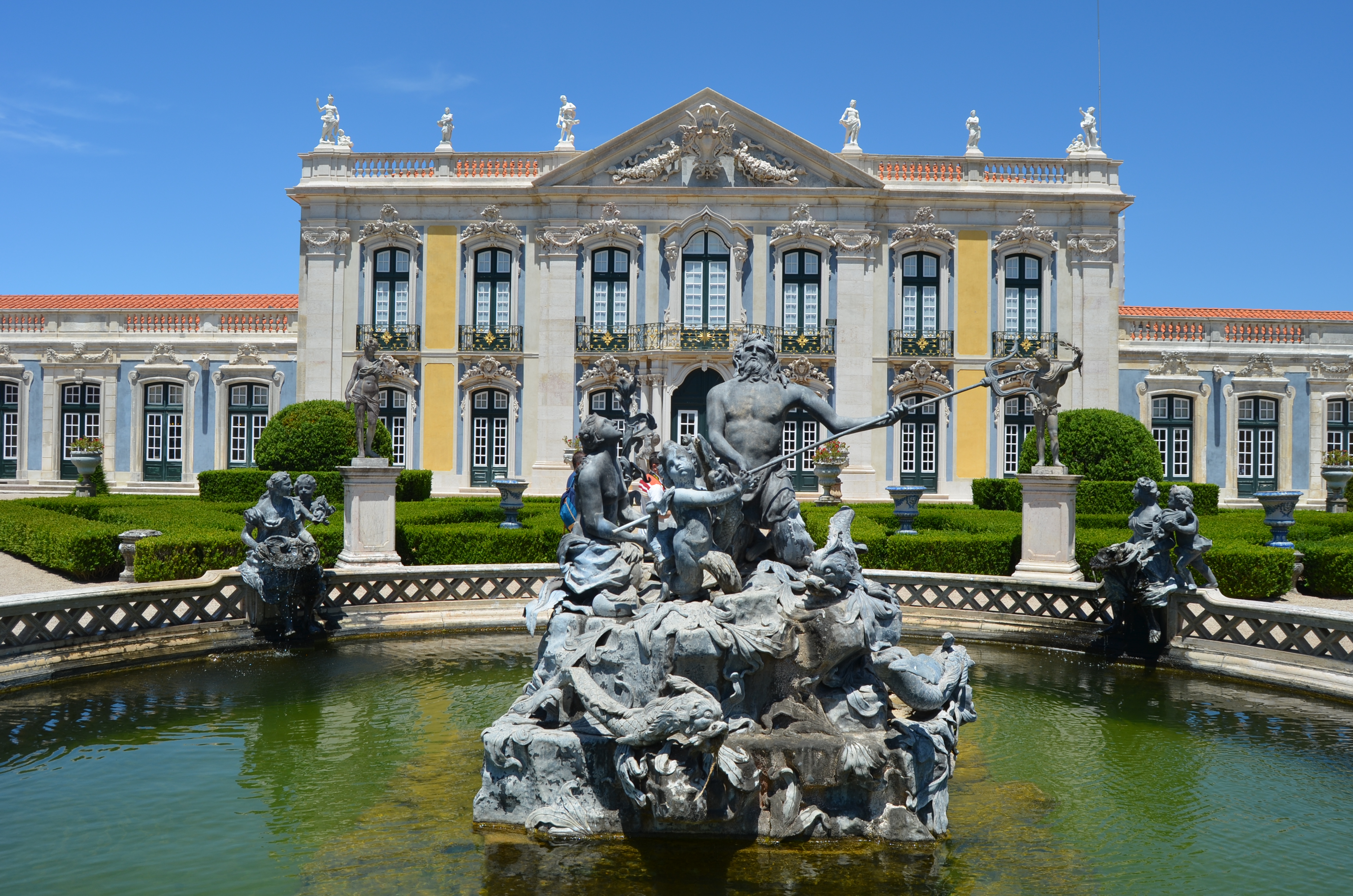

Baroque architecture began in 16th-century Italy. It took the Roman architecture, Roman vocabulary of Renaissance architecture and used it in a new rhetorical and theatrical fashion. It was, initially at least, directly linked to the
Counter-Reformation, a movement within the Catholic Church to reform itself in response to the Protestant Reformation. Baroque was characterized by new explorations of form, light, and shadow, and a freer treatment of classical elements. It reached its extreme form in the
Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
style.
19th-century architecture


Revivalism (architecture), Revivalism was a hallmark of nineteenth-century European architecture. Revivals of the Romanesque Revival architecture, Romanesque, Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic, Renaissance Revival architecture, Renaissance, and Baroque Revival architecture, Baroque styles all took place, alongside revivals of the Classical styles. Regional styles, such as English Tudor Revival architecture, Tudor, were also revived, as well as non-European styles, such as Chinese (Chinoiserie) and Egyptian Revival architecture, Egyptian. These revivals often used elements of the original style in a freer way than original examples, sometimes borrowing from multiple styles at once. At Alnwick Castle, for example, Gothic revival elements were added to the exterior of the original medieval castle, while the interiors were designed in a Renaissance style.
Art Nouveau, Art Nouveau architecture was a reaction against the eclectic styles which dominated European architecture in the second half of the 19th century. It was expressed through decoration. The buildings were covered with ornament in curving forms, based on flowers, plants, or animals: butterflies, peacocks, swans, irises, cyclamens, orchids, and water lilies. Façades were asymmetrical, and often decorated with polychrome ceramic tiles. The decoration usually suggested movement; there was no distinction between the structure and the ornament.
20th-century and modern architecture
Art Deco, Art Deco architecture began in Brussels in 1903–4. Early buildings had clean lines, rectangular forms, and no decoration on the facades; they marked a clean break with the art nouveau style. After the First World War, art deco buildings of steel and reinforced concrete began to appear in large cities across Europe and the United States. Buildings became more decorated, and interiors were extremely colorful and dynamic, combining sculpture, murals, and ornate geometric design in marble, glass, ceramics, and stainless steel.
Modern architecture, Modernist architecture is a term applied to a group of styles of
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
that emerged in the first half of the 20th century and became dominant after World War II. It was based upon new technologies of construction, particularly the use of glass, steel, and reinforced concrete; and upon a rejection of the traditional neoclassical architecture and Beaux-Arts architecture, Beaux-Arts styles that were popular in the 19th century. Modernist architecture continued to be the dominant architectural style for institutional and corporate buildings into the 1980s, when it was challenged by Postmodern architecture, postmodernism.

Expressionist architecture is a form of modern architecture that began during the first decades of the 20th century, in parallel with the Expressionism, expressionist visual and performing arts that especially developed and dominated in
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. In the 1950s, the second movement of expressionist architecture developed, initiated by the Notre Dame du Haut, Ronchamp Chapel Notre-Dame-du-Haut (1950–1955) by Le Corbusier. The style was individualistic, but tendencies include Distortion of form for an emotional effect, efforts at achieving the new, original, and visionary, and a conception of architecture as a work of art.
Postmodern architecture emerged in the 1960s as a reaction against the austerity, formality, and lack of variety of modern architecture, particularly in the International Style (architecture), international style advocated by Le Corbusier and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe. Embraced in the USA first, it spread to Europe. In contrast to Modernist buildings, Postmodern buildings have curved forms, decorative elements, asymmetry, bright colors, and features often borrowed from earlier periods. Colors and textures unrelated to the structure or function of the building. While rejecting the "puritanism" of modernism, it called for a return to ornament, and an accumulation of citations and collages borrowed from past styles. It borrowed freely from classical architecture, rococo, neoclassical architecture, the Viennese secession, the British arts and crafts movement, the German Jugendstil.
Deconstructivism, Deconstructivist architecture is a movement of postmodern architecture which appeared in the 1980s, which gives the impression of the fragmentation of the constructed building. It is characterized by an absence of harmony, continuity, or symmetry. Its name comes from the idea of "Deconstruction", a form of semiotic analysis developed by the French philosopher Jacques Derrida. Besides fragmentation, Deconstructivism often manipulates the structure's surface skin and creates by non-Rectilinear polygon, rectilinear shapes which appear to distort and dislocate Design principles and elements, elements of architecture. The finished visual appearance is characterized by unpredictability and controlled chaos.
Literature


Classical literature
Medieval literature
Renaissance literature
Early modern literature
Modern literature
Film
Auguste and Louis Lumière, Antoine Lumière realized, on 28 December 1895, the first projection, with the Cinematograph, in Paris.
In 1897, Georges Méliès established the first cinema studio on a rooftop property in Montreuil, near Paris.
Some notable European film movements include German Expressionism, Italian neorealism, French New Wave, Polish Film School, New German Cinema, Cinema of Portugal, Portuguese Cinema Novo, Movida Madrileña, Czechoslovak New Wave, Dogme 95, New French Extremity, and Romanian New Wave.
File:Marlene-Dietrich-1936.jpg, Marlene Dietrich
File:Emir kusturica 72 9643.jpg, Emir Kusturica
File:Brigitte Bardot - 1962.jpg, Brigitte Bardot
File:Ingmar Bergman Smultronstallet.jpg, Ingmar Bergman, first president of the European Film Academy
File:Hitchcock, Alfred 02.jpg, Alfred Hitchcock, Sir Alfred Hitchcock
File:Cinecittà - Entrance.jpg, Cinecittà film studios
The cinema of Europe has its own awards, the European Film Awards.
Main festivals : Cannes Film Festival (France), Berlin International Film Festival (Germany). The Venice Film Festival (Italy) or Mostra Internazionale d'Arte Cinematografica di Venezia, is the oldest film festival in the world. Philippe Binant realized, on 2 February 2000, the first digital cinema projection in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
.
Science


Classical science
See: History of science in classical antiquity
Medieval science
See: History of science, post-classical science
Renaissance science
See: History of science in the Renaissance
Early modern science
See: Scientific Revolution, Science in the Age of Enlightenment, and Romanticism in science, Romanticism in Science
Modern science
See: Science and technology in Europe, Science and Technology in Europe
Philosophy
European
philosophy is a predominant strand of philosophy globally, and is central to philosophical enquiry in the Americas and most other parts of the world which have fallen under its influence. The Greek schools of philosophy in Classical antiquity, antiquity provide the basis of philosophical discourse that extends to today. Christian thought had a huge influence on many fields of European philosophy (as European philosophy has been on Christian thought too), sometimes as a reaction. Many political ideologies were theorized in Europe, such as capitalism, communism, fascism,
socialism
Socialism is a left-wing Economic ideology, economic philosophy and Political movement, movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to Private prop ...
, or anarchism.
Classical
See: Ancient philosophy
Medieval
See: Medieval philosophy
Renaissance
See: Renaissance philosophy
Modern
See: Age of Enlightenment.
Contemporary
See: 20th-century philosophy and Contemporary philosophy
Religion

Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
has been the dominant religion shaping European culture for at least the last 1700 years.
[Cambridge University Historical Series, ''An Essay on Western Civilization in Its Economic Aspects'', p.40: Hebraism, like Hellenism, has been an all-important factor in the development of Western Civilization; Judaism, as the precursor of Christianity, has indirectly had had much to do with shaping the ideals and morality of western nations since the Christian era.][Caltron J.H Hayas, ''Christianity and Western Civilization'' (1953), Stanford University Press, p.2: That certain distinctive features of our Western civilization — the civilization of western Europe and of America— have been shaped chiefly by Judaeo - Graeco - Christianity, Catholic and Protestant.][Horst Hutter, University of New York, ''Shaping the Future: Nietzsche's New Regime of the Soul And Its Ascetic Practices'' (2004), p.111:three mighty founders of Western culture, namely Socrates, Jesus, and Plato.][Fred Reinhard Dallmayr, ''Dialogue Among Civilizations: Some Exemplary Voices'' (2004), p.22: Western civilization is also sometimes described as "Christian" or "Judaeo- Christian" civilization.] Modern philosophical thought has very much been influenced by Christian philosophers such as St Thomas Aquinas and Erasmus. And throughout most of its history, Europe has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture, The Christian culture was the predominant force in Western culture, western civilization, guiding the course of
philosophy,
art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
, and science.
The notion of "
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and the Western World" has been intimately connected with the concept of "Christendom, Christianity and Christendom" many even attribute Christianity for being the link that created a unified European identity.
Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
is the largest religion in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, with 76.2% of
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
ans considering themselves Christians, Christian in 2010, As 2010, Catholics were the largest Christians, Christian group in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, accounting for more than 48% of European Christians. The second-largest Christian group in Europe was the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox, who made up 32% of European Christians. About 19% of European Christians were part of the Protestant tradition. Russia is the largest Christian country in Europe by population, followed by
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Italy. In 2012 Europe constituted in absolute terms the Christianity by country, world's largest Christian population.
Historically, Europe has been the center and cradle of Christian civilization.
Catholicism
See: Catholic Church in Europe
Protestantism
See: Reformation, Protestant Reformation
Eastern Orthodoxy
See: Eastern Orthodoxy in Europe
Islam
Judaism
Other religions
See: Hinduism by country, Buddhism in Europe, Sikhism by country
Atheism
See: Religion in Europe, History of atheism, History of Atheism, Atheism during the Age of Enlightenment
Cuisine
The cuisines of European countries are diverse by themselves, although there are common characteristics that distinguish European cooking from cuisines of Asia, Asian countries and others.
[ "European Cuisine."Europeword.com](_blank)
Accessed July 2011. Compared with traditional cooking of Asian countries, for example, meat is more prominent and substantial in serving-size. Steak, in particular, is a common dish across Europe. European cuisines also put substantial emphasis on sauces as condiments, seasonings, or accompaniments (in part due to the difficulty of seasonings penetrating the often larger pieces of meat used in European cooking). Dairy products are often utilized in the cooking process. Wheat-flour bread has long been the most common source of starch in this cuisine, along with pasta, dumplings, and pastries, although the potato has become a major starch plant in the diet of Europeans and their diaspora since the European colonization of the Americas.
File:Wiener-Schnitzel02.jpg, Austrian Wiener Schnitzel
File:Margaux94 1.jpg, French wine
File:Pastasorten3.JPG, Italian pasta
File:Cuisine of Belgium - IMG 4556.JPG, Belgian chocolate
File:Paella de marisco 01.jpg, Spanish paella
File:04526 Christmas Eve Table, 2010 Sanok.JPG, Northern European Rollmops
File:Roquefort cheese.jpg, Roquefort cheese
File:Saucisson 02.JPG, Charcuterie
File:MussakasMeMelitsanesKePatates01.JPG, Greek moussaka
File:Bulgarian yogurt.JPG, Bulgarian yogurt
File:Mulgipuder.jpg, Estonian ''mulgipuder'' porridge
File:Homerton College - Shepherd's pie (cropped).jpg, English shepherd's Pie
Fashion

The earliest definite examples of needles originate from the Solutrean culture, which existed in France and Spain from 19,000 BC to 15,000 BC. The earliest dyed flax fibers have been found in a cave in the Republic of Georgia and date back to 36,000 BP. See Clothing in ancient Rome, 1100–1200 in fashion, 1200–1300 in fashion, 1300–1400 in fashion, 1400–1500 in fashion, 1500–1550 in fashion, 1550–1600 in fashion, 1600–1650 in fashion, 1650–1700 in fashion, Textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution
Sport
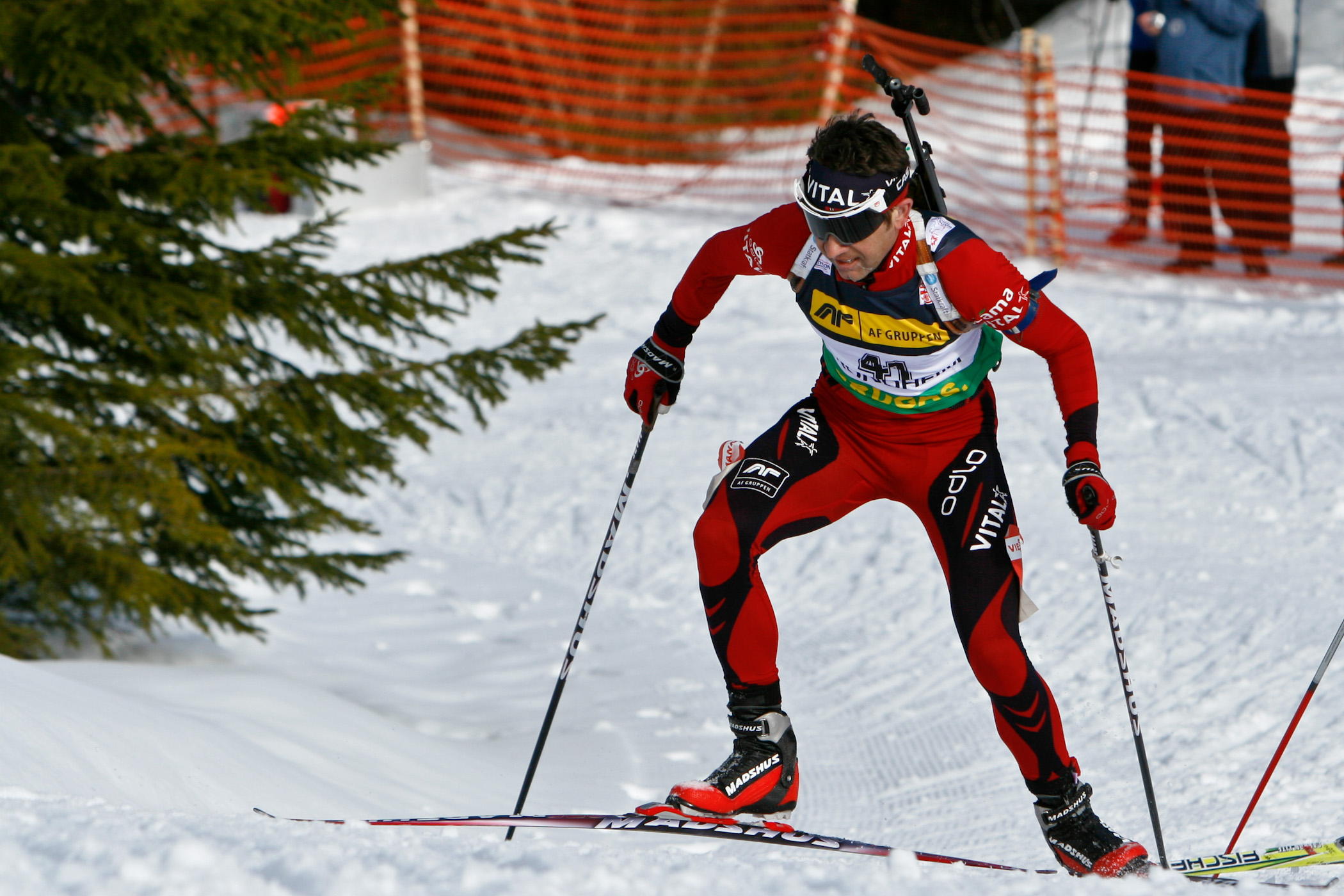


History
Olympics
See: Olympic Games, History of the Olympics
Contemporary sports
* Association football, which has its origins in the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. The oldest association is The Football Association of England (1863), and the first international match was between Scotland and England (1872). It is now the world's most popular sport and is played throughout Europe.
* Cricket has its origins in southeast England. It is popular throughout England and Wales, and parts of the Netherlands. It is also popular in other areas in Northwest Europe. It is however, very popular worldwide, especially in Africa, Australia, New Zealand, and the Indian subcontinent.
* Cycling, which is also immensely popular as a means of transport, has most of its sporting adherents in Europe. Tour de France is the world's most-watched live annual sporting event. The bicycle itself is probably from France (see History of the bicycle).
* The discus throw, javelin throw, and shot put have their origins in ancient Greece. The Olympic Games, Olympics, both ancient and modern, have their origins too in Europe, and have a massive influence globally.
* Field Hockey, as a modern game, began in 18th century England, with Ireland having the oldest federation. It is popular in
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, the Indian subcontinent, Australia and East Asia. Ice hockey, popular in Europe and North America, may derive from this sport.
* Golf, one of the most popular sports in Europe, Asia, and North America, has its origins in Scotland, with the oldest course being at Musselburgh.
* Team handball, Handball, which is popular in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and elsewhere, has its origins in ancient history, antiquity. The modern game is from Denmark and
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, with Germany having been involved in both the first women's and men's internationals.
* Rugby League and Rugby Union were both created in England. They both have similar origins to football. Rugby Union is the older of the two codes and has rules that date from 1845 (see articles: History of rugby league and History of rugby union). They History of rugby league#The schism in England, acrimoniously split in the late 19th century over the treatment of injured players. Rugby league gradually changed its laws over the next century with the end result that today both sports have little in common, apart from the basics. They have both been carried abroad by colonization, particularly to many former British colonies. American Football and Canadian Football are derivatives of rugby.
* Tennis which originates from England, and related games such as Table Tennis, derive from the game Real Tennis which is from France. It is popular throughout the world.

Regional sports

In addition, Europe has numerous national or regional sports which do not command a large international following outside of emigrant groups. These include:
* Alpine Wrestling in Switzerland.
* Bandy in Russia, Sweden, and Finland
* Basque Pelota in parts of Spain and France, and which has been brought to the Americas by emigrants.
* Bullfighting in Spain, Portugal, and parts of southern France near the Spain, Spanish Border.
* Gaelic Football in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, which influenced Australian rules football.
* Gaelic Handball (Republic of Ireland, Ireland) which was taken to the United States in the form of American Handball.
* Hurling in Republic of Ireland, Ireland.
* Korfbal in the Netherlands and Belgium.
* Pesäpallo ''(Boboll)'' in Finland
* Pétanque, Boules, Irish Road Bowling, Skittles (sport), Skittles, Bocce, and Bowls and others are variations of bowling games which are popular throughout Europe and have been spread around the world.
* Rounders from England now popular in northwest Europe from which Baseball derives.
* Shinty in Scotland,
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, which influenced ice hockey in Canada (''see also Shinny'').
* Trotting in southern Europe.
Some sports competitions feature a Team Europe, European team gathering athletes from different European countries. These teams use the European flag as an emblem. The most famous of these competitions is the Ryder Cup in golf. Some sporting organizations hold European Championships like European Cricket Council, the European Games, the European Rugby Cup (Club/Regional competition), the European SC Championships, the FIRA - Association of European Rugby, the IIHF, the Mitropa Cup, the Rugby League European Federation - Rugby League European Championship, European Championship, the Sport in the European Union and the UEFA.
European politics


Overview
See: History of Europe
European Union
See: Politics of the European Union
Capital of Culture
Each year since 1985 one or more cities across Europe are chosen as European Capital of Culture,
BURKSIENE, Valentina, Jaroslav DVORAK, and Gabriele Burbulyte-Tsiskarishvili (2018) Sustainability and sustainability marketing in competing for the title of European Capital of Culture. Organizacija 51.1 5
/ref> an EU initiative. Here are the past and future capitals:
* 1985: Athens
* 1986: Florence
* 1987: Amsterdam
* 1988: Berlin
* 1989: Paris
* 1990: Glasgow
* 1991: Dublin
* 1992: Madrid
* 1993: Antwerp
* 1994: Lisbon
* 1995: Luxembourg
* 1996: Copenhagen
* 1997: Thessaloniki
* 1998: Stockholm
* 1999: Weimar
* 2000: Avignon, Bergen, Bologna, Brussels, Helsinki, Kraków, Prague, Reykjavík, Santiago de Compostela
* 2001: Rotterdam, Porto
* 2002: Bruges, Salamanca
* 2003: Graz
* 2004: Genoa, Lille
* 2005: Cork
* 2006: Patras
* 2007: Sibiu, Luxembourg, Greater Region
* 2008: Liverpool, Stavanger
* 2009: Vilnius, Linz
* 2010: Essen (representing the Ruhr), Istanbul, Pécs
* 2011: Turku, Tallinn
* 2012: Guimarães, Maribor
* 2013: Marseille, Košice
* 2014: Umeå, Riga
* 2015: Mons, Plzeň
* 2016: San Sebastián, Wrocław
* 2017: Aarhus, Paphos
* 2018: Valletta, Malta and Leeuwarden
* 2019: Plovdiv and Matera
* 2020: Galway and Rijeka
Symbols
See also
* Compendium of cultural policies and trends in Europe
* Cultural policies of the European Union
* Europalia
* European dances
* European Heritage Day
* Europeanisation
* Romano-Germanic culture
* Western culture
* Westernization
References
Bibliography
*
External links
Eurolinguistix.com
Europe.org.uk
- online European culture magazine (EU London Office)
TheEuropeanLibrary.org
The European Library, gateway to Europe's national libraries
Europeana.eu
European Digital Library
Europa.eu
EU Culture Portal (archived)
{{Authority control
European culture,
 The
The  There were a great number of perspectives which can be taken on the subject, it is impossible to form a single, all-embracing conception of European culture. Nonetheless, there are core elements which are generally agreed upon as forming the cultural foundation of modern Europe. One list of these elements given by K. Bochmann includes:K. Bochmann (1990) ''L'idée d'Europe jusqu'au XXè siècle'', quoted in Berting (2006:52). Cf. Davies (1996:15): "No two lists of the main constituents of European civilization would ever coincide. But many items have always featured prominently: from the roots of the Christian world in Greece, Rome and Judaism to modern phenomena such as the Enlightenment, modernization, romanticism, nationalism, liberalism, imperialism, totalitarianism."
* A common cultural and spiritual heritage derived from Greco-Roman antiquity,
There were a great number of perspectives which can be taken on the subject, it is impossible to form a single, all-embracing conception of European culture. Nonetheless, there are core elements which are generally agreed upon as forming the cultural foundation of modern Europe. One list of these elements given by K. Bochmann includes:K. Bochmann (1990) ''L'idée d'Europe jusqu'au XXè siècle'', quoted in Berting (2006:52). Cf. Davies (1996:15): "No two lists of the main constituents of European civilization would ever coincide. But many items have always featured prominently: from the roots of the Christian world in Greece, Rome and Judaism to modern phenomena such as the Enlightenment, modernization, romanticism, nationalism, liberalism, imperialism, totalitarianism."
* A common cultural and spiritual heritage derived from Greco-Roman antiquity, 
 Ancient Greek art stands out among that of other ancient cultures for its development of naturalistic but idealized depictions of the human body, in which largely nude male figures were generally the focus of innovation. The rate of stylistic development between about 750 and 300 BC was remarkable by ancient standards, and in surviving works is best seen in
Ancient Greek art stands out among that of other ancient cultures for its development of naturalistic but idealized depictions of the human body, in which largely nude male figures were generally the focus of innovation. The rate of stylistic development between about 750 and 300 BC was remarkable by ancient standards, and in surviving works is best seen in 
 Romanesque art and
Romanesque art and 

 Techniques characteristic of Renaissance art include the use of proportion and
Techniques characteristic of Renaissance art include the use of proportion and 



 Renaissance architecture began in the early 14th and lasted until the early 17th century. It demonstrates a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman architectural thought and material culture, particularly the symmetry, proportion, geometry, and the regularity of parts of ancient buildings. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to France, Germany, England, Russia, and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact
Palladian architecture was derived from and inspired by the designs of the Italian Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). Palladio's work was strongly based on the symmetry, perspective, and values of the formal classical temple architecture of the Ancient Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans. From the 17th century, Palladio's interpretation of this classical architecture was adapted as the style known as Palladianism. It continued to develop until the end of the 18th century, and continued to be popular in Europe throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries, where it was frequently employed in the design of public and municipal buildings.
Renaissance architecture began in the early 14th and lasted until the early 17th century. It demonstrates a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman architectural thought and material culture, particularly the symmetry, proportion, geometry, and the regularity of parts of ancient buildings. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to France, Germany, England, Russia, and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact
Palladian architecture was derived from and inspired by the designs of the Italian Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). Palladio's work was strongly based on the symmetry, perspective, and values of the formal classical temple architecture of the Ancient Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans. From the 17th century, Palladio's interpretation of this classical architecture was adapted as the style known as Palladianism. It continued to develop until the end of the 18th century, and continued to be popular in Europe throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries, where it was frequently employed in the design of public and municipal buildings.
 Baroque architecture began in 16th-century Italy. It took the Roman architecture, Roman vocabulary of Renaissance architecture and used it in a new rhetorical and theatrical fashion. It was, initially at least, directly linked to the Counter-Reformation, a movement within the Catholic Church to reform itself in response to the Protestant Reformation. Baroque was characterized by new explorations of form, light, and shadow, and a freer treatment of classical elements. It reached its extreme form in the
Baroque architecture began in 16th-century Italy. It took the Roman architecture, Roman vocabulary of Renaissance architecture and used it in a new rhetorical and theatrical fashion. It was, initially at least, directly linked to the Counter-Reformation, a movement within the Catholic Church to reform itself in response to the Protestant Reformation. Baroque was characterized by new explorations of form, light, and shadow, and a freer treatment of classical elements. It reached its extreme form in the  Revivalism (architecture), Revivalism was a hallmark of nineteenth-century European architecture. Revivals of the Romanesque Revival architecture, Romanesque, Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic, Renaissance Revival architecture, Renaissance, and Baroque Revival architecture, Baroque styles all took place, alongside revivals of the Classical styles. Regional styles, such as English Tudor Revival architecture, Tudor, were also revived, as well as non-European styles, such as Chinese (Chinoiserie) and Egyptian Revival architecture, Egyptian. These revivals often used elements of the original style in a freer way than original examples, sometimes borrowing from multiple styles at once. At Alnwick Castle, for example, Gothic revival elements were added to the exterior of the original medieval castle, while the interiors were designed in a Renaissance style.
Art Nouveau, Art Nouveau architecture was a reaction against the eclectic styles which dominated European architecture in the second half of the 19th century. It was expressed through decoration. The buildings were covered with ornament in curving forms, based on flowers, plants, or animals: butterflies, peacocks, swans, irises, cyclamens, orchids, and water lilies. Façades were asymmetrical, and often decorated with polychrome ceramic tiles. The decoration usually suggested movement; there was no distinction between the structure and the ornament.
Revivalism (architecture), Revivalism was a hallmark of nineteenth-century European architecture. Revivals of the Romanesque Revival architecture, Romanesque, Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic, Renaissance Revival architecture, Renaissance, and Baroque Revival architecture, Baroque styles all took place, alongside revivals of the Classical styles. Regional styles, such as English Tudor Revival architecture, Tudor, were also revived, as well as non-European styles, such as Chinese (Chinoiserie) and Egyptian Revival architecture, Egyptian. These revivals often used elements of the original style in a freer way than original examples, sometimes borrowing from multiple styles at once. At Alnwick Castle, for example, Gothic revival elements were added to the exterior of the original medieval castle, while the interiors were designed in a Renaissance style.
Art Nouveau, Art Nouveau architecture was a reaction against the eclectic styles which dominated European architecture in the second half of the 19th century. It was expressed through decoration. The buildings were covered with ornament in curving forms, based on flowers, plants, or animals: butterflies, peacocks, swans, irises, cyclamens, orchids, and water lilies. Façades were asymmetrical, and often decorated with polychrome ceramic tiles. The decoration usually suggested movement; there was no distinction between the structure and the ornament.
 Expressionist architecture is a form of modern architecture that began during the first decades of the 20th century, in parallel with the Expressionism, expressionist visual and performing arts that especially developed and dominated in
Expressionist architecture is a form of modern architecture that began during the first decades of the 20th century, in parallel with the Expressionism, expressionist visual and performing arts that especially developed and dominated in 





 The earliest definite examples of needles originate from the Solutrean culture, which existed in France and Spain from 19,000 BC to 15,000 BC. The earliest dyed flax fibers have been found in a cave in the Republic of Georgia and date back to 36,000 BP. See Clothing in ancient Rome, 1100–1200 in fashion, 1200–1300 in fashion, 1300–1400 in fashion, 1400–1500 in fashion, 1500–1550 in fashion, 1550–1600 in fashion, 1600–1650 in fashion, 1650–1700 in fashion, Textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution
The earliest definite examples of needles originate from the Solutrean culture, which existed in France and Spain from 19,000 BC to 15,000 BC. The earliest dyed flax fibers have been found in a cave in the Republic of Georgia and date back to 36,000 BP. See Clothing in ancient Rome, 1100–1200 in fashion, 1200–1300 in fashion, 1300–1400 in fashion, 1400–1500 in fashion, 1500–1550 in fashion, 1550–1600 in fashion, 1600–1650 in fashion, 1650–1700 in fashion, Textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution




