Eurasian Steppes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe
File:DNV Devinska Kobyla.jpg, Devínska Kobyla, Bratislava,
File:Філія ЛПЗ НАНУ "Стрільцівський степ" Stipa tirsa (ЧКУ).jpg, The
File:Уральские горы - panoramio (1).jpg, Wooded Ural Mountains of
File:Astana-steppe-7748.jpg, The steppe in
File:Тувинские просторы.jpg, Uvs Lake Basin,
File:Участок Адон-Челон.JPG, The Daurian forest steppe
File:Khövsgöl Aimag17.JPG, The Mongolian-Manchurian grassland in the Khövsgöl Province,
File:Przewalski mongolie.jpg,
The primary domesticated animals raised were sheep and goats with fewer cattle than one might expect. Camels were used in the drier areas for transport as far west as


 The nomads would occasionally tolerate colonies of peasants on the steppe in the few areas where farming was possible. These were often captives who grew grain for their nomadic masters. Along the fringes there were areas that could be used for either plowland or grassland. These alternated between one and the other depending on the relative strength of the nomadic and agrarian heartlands. Over the last few hundred years, the Russian steppe and much of Inner Mongolia has been cultivated. The fact that most of the Russian steppe is not irrigated implies that it was maintained as grasslands as a result of the military strength of the nomads.
The nomads would occasionally tolerate colonies of peasants on the steppe in the few areas where farming was possible. These were often captives who grew grain for their nomadic masters. Along the fringes there were areas that could be used for either plowland or grassland. These alternated between one and the other depending on the relative strength of the nomadic and agrarian heartlands. Over the last few hundred years, the Russian steppe and much of Inner Mongolia has been cultivated. The fact that most of the Russian steppe is not irrigated implies that it was maintained as grasslands as a result of the military strength of the nomads.

 Along the northern fringe of the Eurasian steppe, nomads would collect tribute from and blend with the forest tribes (see
Along the northern fringe of the Eurasian steppe, nomads would collect tribute from and blend with the forest tribes (see
The importance of the Eurasian steppe to the study of international relations
in ''Journal of International Relations and Development'' {{coord missing, Russia Grasslands of Asia Grasslands of Europe Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands Ecoregions of Asia Ecoregions of Europe Geography of Central Asia Geography of East Asia Geography of Siberia Geography of Eastern Europe Grasslands of Russia History of Pakistan Social history of India Central Asia East Asia Eastern Europe Southern Europe Western Europe Eurasia
 The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of ...
of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands
Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The predominant vegetation in this biome consists of grass and/or shrubs. The climate is temperate and ranges from semi-arid to semi ...
biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
. It stretches through Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
and Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester riv ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, Western Russia
European Russia (russian: Европейская Россия, russian: европейская часть России, label=none) is the western and most populated part of Russia. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the cou ...
, Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
and Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
, with one major exclave, the Pannonian steppe or Puszta, located mostly in Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
.
Since the Paleolithic age, the Steppe Route has connected Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
, Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both Geography, geographical and culture, ethno-cultural terms. The modern State (polity), states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
economically, politically and culturally through overland trade routes. The Steppe route is a predecessor not only of the Silk Road which developed during antiquity and the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, but also of the Eurasian Land Bridge
The Eurasian Land Bridge (), sometimes called the New Silk Road (, ), is the rail transport route for moving freight and passengers overland between Pacific seaports in the Russian Far East and China and seaports in Europe. The route, a transc ...
in the modern era. It has been home to nomadic empires and many large tribal
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflic ...
confederations
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
and ancient states throughout history, such as the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
, Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
Hi ...
, Cimmeria, Sarmatia
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th c ...
, Hunnic Empire, Chorasmia
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
, Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, Sogdia, Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into th ...
, Mongol Empire and Göktürk Khaganate.
Geography
Divisions
The Eurasian Steppe extends for 8,000 kilometres (5,000 miles) from near the mouth of theDanube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
almost to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. It is bounded on the north by the forests of European Russia, Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
and Asian Russia. There is no clear southern boundary although the land becomes increasingly dry as one moves south. The steppe narrows at two points, dividing it into three major parts.
Pannonian steppe (exclave)
The Pannonian steppe is an exclave of the Eurasian Steppe belt. It is found in modern-dayAustria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
and Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
.
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
Image:Puszta Seewinkel.JPG, The Pannonian steppe in Seewinkel, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
File:Thebner Kogel sl14.jpg, The Pannonian steppe in Devínska Kobyla, Bratislava, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
File:Pferde halten das Gras kurz für die Störche.jpg, Danube-Auen National Park
Donau-Auen National Park (german: Nationalpark Donau-Auen) covers 93 square kilometres in Vienna and Lower Austria and is one of the largest remaining floodplains of the Danube in Middle Europe.
The German word ''Aue'' (variant ''Au'') means ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
Pontic–Caspian steppe (Western Steppe)
ThePontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extend ...
begins near the mouth of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
and extends northeast almost to Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering an ...
and then southeast to the southern tip of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
. Its northern edge was a broad band of forest steppe
A forest steppe is a temperate-climate ecotone and habitat type composed of grassland interspersed with areas of woodland or forest.
Locations
Forest steppe primarily occurs in a belt of forest steppes across northern Eurasia from the eastern ...
which has now been obliterated by the conversion of the whole area to agricultural land. In the southeast the Black Sea–Caspian Steppe extends between the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
and Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
to the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
. In the west, the Great Hungarian Plain
The Great Hungarian Plain (also known as Alföld or Great Alföld, hu, Alföld or ) is a plain occupying the majority of the modern territory of Hungary. It is the largest part of the wider Pannonian Plain. (However, the Great Hungarian plain ...
is an island of steppe separated from the main steppe by the mountains of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
. On the north shore of the Black Sea, the Crimean Peninsula
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
has some interior steppe and ports on the south coast which link the steppe to the civilizations of the Mediterranean basin.
Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extend ...
near Krynychne, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
.
File:Обитатели Азово-Сивашского заповедника на Бирючем острове.jpg, The Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extend ...
in Henichesk
Henichesk ( uk, Гені́чеськ, Heniches’k, ; rus, links=on, Гени́ческ, r=Genichesk, p=ɡʲɪˈnʲit͡ɕɪsk) is a port city along the Sea of Azov in the Kherson Oblast of southern Ukraine. It serves as the administrative centre ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
.
File:MD.GE.Bugeac - sector de stepă în nordul Bugeacului (I) - apr 2018.jpg, Steppes in Gagauzia, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
.
File:MD.GE.Dezghingea - sector de stepă în nordul Bugeacului (II) - apr 2018.jpg, Steppes in Gagauzia, Dezghingea, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
.
Ural–Caspian Narrowing
TheUral Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
extend south to a point about 650 km (400 mi) northeast of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
.
Beloretsky District
Beloretsky District (russian: Белоре́цкий район; ba, Белорет районы) is an administrativeConstitution of the Republic of Bashkortostan, Article 64 and municipalLaw #126-z district (raion), one of the fifty-four ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
File:The Valley of the Belaya River.jpg, The Bashkiriya National Park is situated in the southern end of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
File:Bashkiria's mountains.jpg, The Bashkiriya National Park, Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
File:Гуси на Нугушском водохранилище.jpg, The Bashkiriya National Park, Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
Kazakh Steppe (Central Steppe)
The Kazakh Steppe extends from theUrals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
to Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang". Bounded by the ...
. To the south, it grades off into semi-desert and desert which is interrupted by two great rivers, the Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
(Oxus) and Syr Darya (Jaxartes), which flow northwest into the Aral Sea and provide irrigation for agriculture. In the southeast is the densely populated Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley (; ; ) in Central Asia lies mainly in eastern Uzbekistan, but also extends into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Divided into three republics of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse and in the ...
and west of it the great oasis cities of Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2 ...
, Samarkand and Bukhara along the Zeravshan River
The Zeravshan; uz, Zeravshon, Зеравшон, زېرەۋشان; from Persian fa, , Zarâfšân – meaning "the spreader of gold" is a river in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan, Central Asia. Its name, "spreader of gold" in Persian, refers to th ...
. The southern area has a complex history (see Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
and Greater Iran), while in the north, the Kazakh Steppe proper was relatively isolated from the main currents of written history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world his ...
.
Akmola Region
Akmola Region ( kz, Ақмола облысы, translit=Aqmola oblysy; russian: Акмолинская область, Akmolinskaya oblast) is a centrally located region of Kazakhstan. Its capital is Kokshetau. The national capital, Astana, is en ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
.
File:Step.JPG, The steppes in Akmola Province
Akmola Region ( kz, Ақмола облысы, translit=Aqmola oblysy; russian: Акмолинская область, Akmolinskaya oblast) is a centrally located region of Kazakhstan. Its capital is Kokshetau. The national capital, Astana, is ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
.
File:Вторичная ковылковая степь на залежи на террасе Аягоза вблизи Аягоза в Восточно-Казахстанской области.JPG, The Kazakh Steppe in the Ayagoz District, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
.
File:Steppe of western Kazakhstan in the early spring.jpg, The Kazakh Steppe in the early spring.
Dzungarian Narrowing
On the east side of the former Sino-Soviet border, mountains extend north almost to the forest zone with only limited grassland inDzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang". Bounded by the ...
.
The east-west Tian Shan Mountains
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘ ...
divide the steppe into Dzungaria in the north and the Tarim Basin to the south. ''Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang". Bounded by the ...
'' is bounded by the Tarbagatai Mountains
The Tarbagatai Mountains ( mn, , , translit. ''Tarvagatai nuruu'', literally: "range with marmots"; ; kk, Тарбағатай жотасы, ''Tarbağatai jotasy'') are a range of mountains located in the north-western parts of Xinjiang, China, ...
on the west and the Mongolian Altai Mountains on the east, neither of which is a significant barrier. Dzungaria has good grassland around the edges and a central desert. It often behaved as a westward extension of Mongolia and connected Mongolia to the Kazakh Steppe. To the north of Dzungaria are mountains and the Siberian forest. To the south and west of Dzungaria, and separated from it by the Tian Shan
The Tian Shan,, , otk, 𐰴𐰣 𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, , tr, Tanrı Dağı, mn, Тэнгэр уул, , ug, تەڭرىتاغ, , , kk, Тәңіртауы / Алатау, , , ky, Теңир-Тоо / Ала-Тоо, , , uz, Tyan-Shan / Tangritog‘ ...
mountains, is an area about twice the size of Dzungaria, the oval Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
. The Tarim Basin is too dry to support even a nomadic population, but around its edges rivers flow down from the mountains giving rise to a ring of cities which lived by irrigation agriculture and east-west trade. The Tarim Basin formed an island of near civilization in the center of the steppe. The Northern Silk Road
The Northern Silk Road is an ancient trackway in northern China originating in the early capital of Xi'an and extending north of the Taklamakan Desert to reach the ancient kingdoms of Parthia, Bactria and eventually Persia and Rome. It is the nor ...
went along the north and south sides of the Tarim Basin and then crossed the mountains west to the Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley (; ; ) in Central Asia lies mainly in eastern Uzbekistan, but also extends into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Divided into three republics of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse and in the ...
. At the west end of the basin the Pamir Mountains connect the Tian Shan Mountains to the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
. To the south, the Kunlun Mountains separate the Tarim Basin from the thinly peopled Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the ...
.
Tuva Republic
Tuva (; russian: Тува́) or Tyva ( tyv, Тыва), officially the Republic of Tuva (russian: Респу́блика Тыва́, r=Respublika Tyva, p=rʲɪˈspublʲɪkə tɨˈva; tyv, Тыва Республика, translit=Tyva Respublika ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
File:Летний день на озере Дус-Холь.jpg, Dus-Khol lake, Tuva Republic
Tuva (; russian: Тува́) or Tyva ( tyv, Тыва), officially the Republic of Tuva (russian: Респу́блика Тыва́, r=Respublika Tyva, p=rʲɪˈspublʲɪkə tɨˈva; tyv, Тыва Республика, translit=Tyva Respublika ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
File:Dus-Khol lake outskirts.jpg, The grassland in Tuva Republic
Tuva (; russian: Тува́) or Tyva ( tyv, Тыва), officially the Republic of Tuva (russian: Респу́блика Тыва́, r=Respublika Tyva, p=rʲɪˈspublʲɪkə tɨˈva; tyv, Тыва Республика, translit=Tyva Respublika ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
File:Dus-Khol lake 3.jpg, Dus-Khol Lake, Tandinsky District, Tuva Republic
Tuva (; russian: Тува́) or Tyva ( tyv, Тыва), officially the Republic of Tuva (russian: Респу́блика Тыва́, r=Respublika Tyva, p=rʲɪˈspublʲɪkə tɨˈva; tyv, Тыва Республика, translit=Tyva Respublika ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
Mongolian-Manchurian steppe (Eastern Steppe)
The Mongol Steppe includes bothMongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
and the Chinese province of Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
. The two are separated by a relatively dry area marked by the Gobi Desert. South of the Mongol Steppe is the high and thinly peopled Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the ...
. The northern edge of the plateau is the Gansu or Hexi Corridor
The Hexi Corridor (, Xiao'erjing: حْسِ ظِوْلاْ, IPA: ), also known as the Gansu Corridor, is an important historical region located in the modern western Gansu province of China. It refers to a narrow stretch of traversable and rela ...
, a belt of moderately dense population that connects China proper
China proper, Inner China, or the Eighteen Provinces is a term used by some Western writers in reference to the "core" regions of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China. This term is used to express a distinction between the "core" regions pop ...
with the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
. The Hexi Corridor
The Hexi Corridor (, Xiao'erjing: حْسِ ظِوْلاْ, IPA: ), also known as the Gansu Corridor, is an important historical region located in the modern western Gansu province of China. It refers to a narrow stretch of traversable and rela ...
was the main route of the Silk Road. In the southeast the Silk Road led over some hills to the east-flowing Wei River
The Wei River () is a major river in west-central China's Gansu and Shaanxi provinces. It is the largest tributary of the Yellow River and very important in the early development of Chinese civilization.
The source of the Wei River is close to ...
valley which led to the North China Plain.
South of the Khingan Mountains and north of the Taihang Mountains
The Taihang Mountains () are a Chinese mountain range running down the eastern edge of the Loess Plateau in Shanxi, Henan and Hebei provinces. The range extends over from north to south and has an average elevation of . The principal peak is ...
, the Mongolian-Manchurian steppe extends east into Manchuria as the Liao Xi steppe. In Manchuria, the steppe grades off into forest and mountains without reaching the Pacific. The central area of forest-steppe was inhabited by pastoral and agricultural peoples, while to the north and east was a thin population of hunting tribes of the Siberian type.
Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
.
File:Khövsgöl Aimag12.JPG, Grass steppe in the Khövsgöl Province, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
.
File:Сопки на севере озера Зун-Торей.jpg, Daursky Nature Reserve
The Daurian Nature Reserve (Даурский заповедник ''Daurskiy zapavyednik'') is a Russian 'zapovednik' (strict nature reserve) situated in the southern part of the Zabaykalsky Krai in Siberia, Russia, close to the border with Mongol ...
in the southern part of the Zabaykalsky Krai in Siberia, Russia, close to the border with Mongolia.
File:Grasslands-menggu.JPG, The Mongolian-Manchurian grassland in Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a ...
, China.
Fauna
Big mammals of the Eurasian steppe were thePrzewalski's horse
Przewalski's horse (, , (Пржевальский ), ) (''Equus ferus przewalskii'' or ''Equus przewalskii''), also called the takhi, Mongolian wild horse or Dzungarian horse, is a rare and endangered horse originally native to the steppes of ...
, the saiga antelope
The saiga antelope (, ''Saiga tatarica''), or saiga, is a critically endangered antelope which during antiquity inhabited a vast area of the Eurasian steppe spanning the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains in the northwest and Caucasus in t ...
, the Mongolian gazelle
The Mongolian gazelle (''Procapra gutturosa''), or dzeren (russian: Дзерэн), is a medium-sized antelope native to the semiarid Central Asian steppes of Mongolia, as well as some parts of Siberia and China. The name ''dzeren'' is Russian ...
, the goitered gazelle, the wild Bactrian camel
The wild Bactrian camel (''Camelus ferus'') is a critically endangered species of camel living in parts of northwestern China and southwestern Mongolia. It is closely related to the Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''). Both are large, doub ...
and the onager
The onager (; ''Equus hemionus'' ), A new species called the kiang (''E. kiang''), a Tibetan relative, was previously considered to be a subspecies of the onager as ''E. hemionus kiang'', but recent molecular studies indicate it to be a distinct ...
. The gray wolf and the corsac fox
The corsac fox (''Vulpes corsac''), also known simply as a corsac, is a medium-sized fox found in steppes, semi-deserts and deserts in Central Asia, ranging into Mongolia and northern China. Since 2004, it has been classified as ''least concern ...
and occasionally the brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear species found across Eurasia and North America. In North America, the populations of brown bears are called grizzly bears, while the subspecies that inhabits the Kodiak Islands of Alaska is ...
are predators roaming the steppe. Smaller mammal species are the Mongolian gerbil, the little souslik and the bobak marmot
The bobak marmot (''Marmota bobak''), also known as the steppe marmot, is a species of marmot that inhabits the steppes of Eastern Europe and Central Asia. It is a social animal and inhabits steppe grassland, including cultivated field borders. ...
.
Furthermore, the Eurasian steppe is home to a great variety of bird species. Threatened bird species living there are for example the imperial eagle, the lesser kestrel
The lesser kestrel (''Falco naumanni'') is a small falcon. This species breeds from the Mediterranean across Afghanistan and Central Asia, to China and Mongolia. It is a summer migrant, wintering in Africa and Pakistan and sometimes even to Indi ...
, the great bustard
The great bustard (''Otis tarda'') is a bird in the bustard family, the only member of the genus ''Otis''. It breeds in open grasslands and farmland from northern Morocco, South and Central Europe, to temperate Central and East Asia. European po ...
, the pale-back pigeon and the white-throated bushchat.
Przewalski horse
Przewalski's horse (, , (Пржевальский ), ) (''Equus ferus przewalskii'' or ''Equus przewalskii''), also called the takhi, Mongolian wild horse or Dzungarian horse, is a rare and endangered horse originally native to the steppes of Ce ...
File:Yawning corsac fox.jpg, Corsac fox
The corsac fox (''Vulpes corsac''), also known simply as a corsac, is a medium-sized fox found in steppes, semi-deserts and deserts in Central Asia, ranging into Mongolia and northern China. Since 2004, it has been classified as ''least concern ...
File:Saiga tartarica.jpg, Saiga antelope
The saiga antelope (, ''Saiga tatarica''), or saiga, is a critically endangered antelope which during antiquity inhabited a vast area of the Eurasian steppe spanning the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains in the northwest and Caucasus in t ...
File:Asiatic Wild ass.jpg, Onager
The onager (; ''Equus hemionus'' ), A new species called the kiang (''E. kiang''), a Tibetan relative, was previously considered to be a subspecies of the onager as ''E. hemionus kiang'', but recent molecular studies indicate it to be a distinct ...
Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the ...
. There were some yaks along the edge of Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
. The horse was used for transportation and warfare. The horse was first domesticated on the Pontic–Caspian or Kazakh steppe sometime before 3000 BC, but it took a long time for mounted archery
A horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, f ...
to develop and the process is not fully understood. The stirrup does not seem to have been completely developed until 300 AD (see Stirrup, Saddle
The saddle is a supportive structure for a rider of an animal, fastened to an animal's back by a girth. The most common type is equestrian. However, specialized saddles have been created for oxen, camels and other animals. It is not k ...
, Composite bow
A composite bow is a traditional bow made from horn, wood, and sinew laminated together, a form of laminated bow. The horn is on the belly, facing the archer, and sinew on the outer side of a wooden core. When the bow is drawn, the sinew (stre ...
, Domestication of the horse
A number of hypotheses exist on many of the key issues regarding the domestication of the horse. Although horses appeared in Paleolithic cave art as early as 30,000 BCE, these were wild horses and were probably hunted for meat.
How and when ho ...
and related articles).
Ecoregions
TheWorld Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wor ...
divides the Eurasian steppe's temperate grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur na ...
s, savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
s and shrublands into a number of ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of ...
s, distinguished by elevation, climate, rainfall, and other characteristics and home to distinct animal and plant communities
A plant community is a collection or association of plant species within a designated geographical unit, which forms a relatively uniform patch, distinguishable from neighboring patches of different vegetation types. The components of each plant ...
and species and distinct habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s.
* Alai–Western Tian Shan steppe
The Alai-Western Tian Shan steppe ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0801) covers the foothills on the western edge of the Tien Shan and Alay Mountains of Central Asia. This territory is mostly in southeastern Uzbekistan, with a portion running north into Kazak ...
(Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan)
* Altai steppe and semi-desert (Kazakhstan)
* Baraba steppe (Russia)
* Daurian forest steppe (China, Mongolia, Russia)
* Emin Valley steppe (China, Kazakhstan)
* Kazakh forest steppe (Kazakhstan, Russia)
* Kazakh Steppe (Kazakhstan, Russia)
* Kazakh Uplands
The Kazakh Uplands ( kk, Сарыарқа, ''Saryarqa'' - "Yellow Ridge", russian: Казахский мелкосопочник, Kazakhskiy Melkosopochnik), also known as the Kazakh Hummocks, is a large peneplain formation extending throughout th ...
(Kazakhstan)
* Mongolian-Manchurian grassland (China, Mongolia, Russia)
* Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extend ...
(Moldova, Romania, Russia, Ukraine)
* Sayan Intermontane steppe
The Sayan intermontane steppe ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0815) is sometimes referred to as a "steppe island", being an expanse of grassland and shrubs surrounded by mountain forests in the Tyva Republic of south central Siberia, Russia. The Altai Mounta ...
(Russia)
* Selenge–Orkhon forest steppe (Mongolia, Russia)
* South Siberian forest steppe
The South Siberian forest steppe ecoregion (WWF ID: PA0817) is a patchwork of grasslands and forests in the low-lying areas of south central Siberia. The region is one of high biodiversity as a transition zone between the West Siberian taiga to t ...
(Russia)
* Tian Shan foothill arid steppe (China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan)
* Pannonian Steppe (Hungary, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovakia, Austria, Slovenia)
Human activities
Trade habits
The major centers of population and high culture in Eurasia are Europe, the Middle East, India and China. For some purposes it is useful to treat Greater Iran as a separate region. All these regions are connected by the Eurasian Steppe route which was an active predecessor of the Silk Road. The latter started in the Guanzhong region of China and ran west along the Hexi Corridor to the Tarim Basin. From there it went southwest to Greater Iran and turned southeast to India or west to the Middle East and Europe. A minor branch went northwest along the great rivers and north of the Caspian Sea to the Black Sea. When faced with a rich caravan the steppe nomads could either rob it, or tax it, or hire themselves out as guards. Economically these three forms of taxation or parasitism amounted to the same thing. Trade was usually most vigorous when a strong empire controlled the steppe and reduced the number of petty chieftains preying on trade. The silk road first became significant and Chinese silk began reaching the Roman Empire about the time that the Emperor of Han pushed Chinese power west to the Tarim Basin.Agriculture
 The nomads would occasionally tolerate colonies of peasants on the steppe in the few areas where farming was possible. These were often captives who grew grain for their nomadic masters. Along the fringes there were areas that could be used for either plowland or grassland. These alternated between one and the other depending on the relative strength of the nomadic and agrarian heartlands. Over the last few hundred years, the Russian steppe and much of Inner Mongolia has been cultivated. The fact that most of the Russian steppe is not irrigated implies that it was maintained as grasslands as a result of the military strength of the nomads.
The nomads would occasionally tolerate colonies of peasants on the steppe in the few areas where farming was possible. These were often captives who grew grain for their nomadic masters. Along the fringes there were areas that could be used for either plowland or grassland. These alternated between one and the other depending on the relative strength of the nomadic and agrarian heartlands. Over the last few hundred years, the Russian steppe and much of Inner Mongolia has been cultivated. The fact that most of the Russian steppe is not irrigated implies that it was maintained as grasslands as a result of the military strength of the nomads.
Language
According to the most widely held hypothesis of the origin of theIndo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
, the Kurgan hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and par ...
, their common ancestor is thought to have originated on the Pontic-Caspian steppe. The Tocharians
The Tocharians, or Tokharians ( US: or ; UK: ), were speakers of Tocharian languages, Indo-European languages known from around 7600 documents from around 400 to 1200 AD, found on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin (modern Xinjiang, China). ...
were an early Indo-European branch in the Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Northwest China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydr ...
. At the beginning of written history the entire steppe population west of Dzungaria spoke Iranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
. From about 500 AD the Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia ( Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic l ...
replaced the Iranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
first on the steppe, and later in the oases north of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. Additionally, Hungarian speakers, a branch of the Uralic language family, who previously lived in the steppe in what is now Southern Russia, settled in the Carpathian basin
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large Sedimentary basin, basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The Geomorphology, geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewh ...
in year 895. Mongolic languages are in Mongolia. In Manchuria one finds Tungusic languages
The Tungusic languages (also known as Manchu-Tungus and Tungus) form a language family spoken in Eastern Siberia and Manchuria by Tungusic peoples. Many Tungusic languages are endangered. There are approximately 75,000 native speakers of the doz ...
and some others.
Religion
Tengrism
Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is an ethnic and old state Turko- Mongolic religion originating in the Eurasian steppes, based on folk shamanism, animism and generally centered around the titular sky god Tengri. ...
was introduced by Turko-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventually a ...
nomads. Nestorianism and Manichaeism
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian Empire, Parthian ...
spread to the Tarim Basin and into China, but they never became established majority religions. Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
spread from the north of India to the Tarim Basin and found a new home in China. By about 1400 AD, the entire steppe west of Dzungaria
Dzungaria (; from the Mongolian words , meaning 'left hand') is a geographical subregion in Northwest China that corresponds to the northern half of Xinjiang. It is thus also known as Beijiang, which means "Northern Xinjiang". Bounded by the ...
had adopted Islam. By about 1600 AD, Islam was established in the Tarim Basin while Dzungaria and Mongolia had adopted Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
.
History
Warfare
Raids between tribes were prevalent throughout the region's history. This relates to the ease with which a defeated enemy's flocks and herds can be driven away, making raiding profitable. In terms of warfare and raiding, in relation to sedentary societies, the horse gave the nomads an advantage of mobility. Horsemen could raid a village and retreat with their loot before aninfantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
-based army could be mustered and deployed. When confronted with superior infantry, horsemen could simply ride away, retreat and regroup. Outside of Europe and parts of the Middle East, agrarian societies had difficulty raising a sufficient supply of war horse
The first evidence of horses in warfare dates from Eurasia between 4000 and 3000 BC. A Sumerian illustration of warfare from 2500 BC depicts some type of equine pulling wagons. By 1600 BC, improved harness and chariot designs ...
s and often had to enlist cavalry from their nomadic enemies (as mercenaries). Nomads could not easily be pursued onto the steppe since the steppe could not easily support a land army. If the Chinese sent an army into Mongolia, the nomads
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
would flee and come back when the Chinese ran out of supplies. But the steppe nomads were relatively few and their rulers had difficulty holding together enough clans and tribes to field a large army. If steppe nomads conquered an agricultural area they often lacked the skills to administer it. If they tried to hold agrarian land they gradually absorbed the civilization of their subjects, lost their nomadic skills and were either assimilated or driven out.
Relations with neighbors

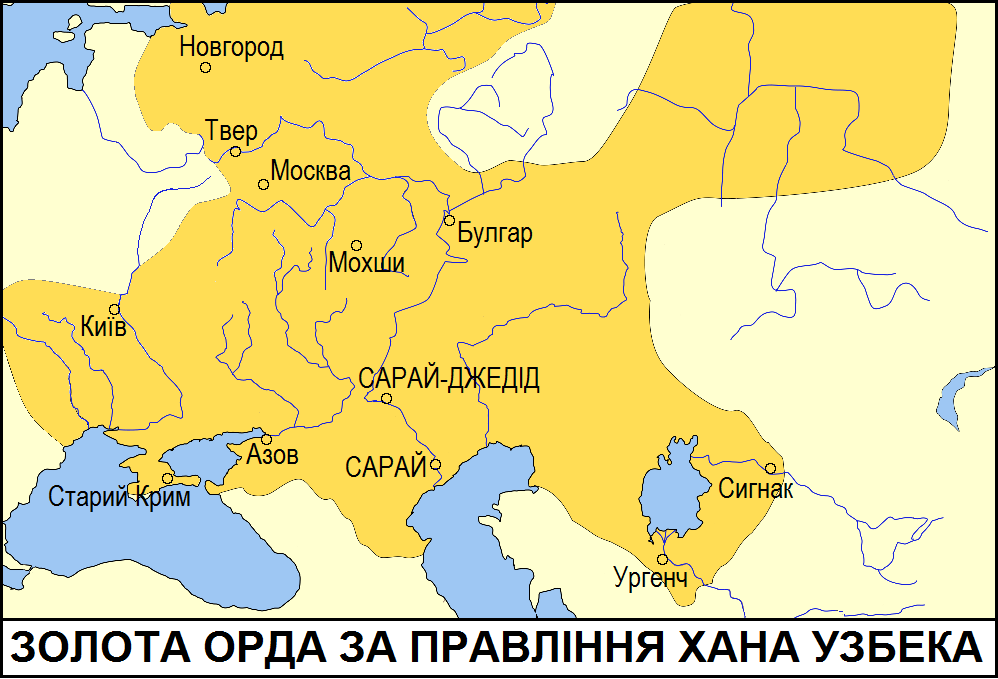
 Along the northern fringe of the Eurasian steppe, nomads would collect tribute from and blend with the forest tribes (see
Along the northern fringe of the Eurasian steppe, nomads would collect tribute from and blend with the forest tribes (see Khanate of Sibir
The Khanate of Sibir (also Khanate of Turan,
sty, Себер ханлыгы) was a Tatar Khanate located in southwestern Siberia with a Turco-Mongol ruling class. Throughout its history, members of the Shaybanid and Taibugid dynasties often con ...
, Buryats). Russia paid tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
(compare ''yasak
''Yasak'' or ''yasaq'', sometimes ''iasak'', (russian: ясак; akin to Yassa) is a Turkic word for "tribute" that was used in Imperial Russia to designate fur tribute exacted from the indigenous peoples of Siberia.
Origin
The origins of yasa ...
'') to the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
from about 1240 to 1480.
South of the Kazakh steppe the nomads blended with the sedentary population, partly because the Middle East has significant areas of steppe (taken by force in past invasions) and pastoralism. There was a sharp cultural divide between Mongolia and China and almost constant warfare from the dawn of history until the Qing conquest of Dzungaria in 1757. The nomads collected large amounts of tribute from the Chinese and several Chinese dynasties were of steppe origin. Perhaps because of the mixture of agriculture and pastoralism in Manchuria its inhabitants, the Manchu, knew how to deal with both nomads and the settled populations and therefore were able to conquer much of northern China when both Chinese and Mongols were weak.
Legacy of the Eurasian steppe's nomads
Russian culture and people were much influenced by the Asian nomads in the Russian steppe and the adjoining steppes and deserts. The steppe culture of Russia was shaped in Russia through cross-cultural contact mostly by Slavic, Tatar-Turkic, Mongolian and Iranian people. Rus' rulers would ally themselves by marriage with fellow-steppe peoples. In addition to ethnicity, also instruments such as thedomra
The ''domra'' (Cyrillic: до́мра, ) is a long-necked Belarusian, Russian, and Ukrainian folk string instrument of the lute family with a round body and three or four metal strings.
History
The first known mention of domra is in ''Admonit ...
, traditional costumes such as the kaftan
A kaftan or caftan (; fa, خفتان, ) is a variant of the robe or tunic. Originating in Asia, it has been worn by a number of cultures around the world for thousands of years. In Russian usage, ''kaftan'' instead refers to a style of men's ...
and the sarafan
A sarafan ( rus, сарафа́н, p=sərɐˈfan, from fa, سراپا ''sarāpā'', literally " romhead to feet") is a long, trapezoidal Russian jumper dress (pinafore dress) worn by girls and women and forming part of Russian traditional fo ...
, Ukrainian Cossack and tea culture
Tea culture is defined by the way tea is made and consumed, by the way the people interact with tea, and by the aesthetics surrounding tea drinking.
Tea plays an important role in some countries. It is commonly consumed at social events, and ...
were strongly influenced by the culture of Asian nomadic peoples. The Eurasian steppes play a major role in Eastern Europe history and the steppes are a subject of many Slavic as well as Russian folk-songs
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has b ...
.
Historical peoples and nations
*Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
15th-3rd centuries BC
* Chorasmia
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
13th–3rd centuries BC
* Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
12th–7th centuries BC
* Magyars 11th century BC – 8th century AD
* Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
8th–4th centuries BC
* Sogdiana
Sogdia ( Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empi ...
8th–4th centuries BC
* Issedones The Issedones (Ἰσσηδόνες) were an ancient people of Central Asia at the end of the trade route leading north-east from Scythia, described in the lost ''Arimaspeia'' of Aristeas, by Herodotus in his ''History'' (IV.16-25) and by Ptolemy in ...
7th–1st century BC
* Massagetae
The Massagetae or Massageteans (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Sakā tigraxaudā (Old Persian: , "wearer of pointed caps") or Orthocorybantians (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ),: As for the term “Orthocorybantii”, this is a translati ...
7th–1st century BC
* Thyssagetae
The Thyssagetae ( grc, Θυσσαγέται) were an ancient tribe described by Herodotus as occupying a district to the north-east of Scythia, separated from the Budini by a "desert" that took seven days to cross.Herodotus. ''Histories'', 4.22.1: ...
7th–3rd century BC
* Donghu 7th – 2nd century BC
* Dahae
The Dahae, also known as the Daae, Dahas or Dahaeans (Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: , , , ; Latin: ; Chinese: ; Persian: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian nomadic tribal confederation, who inhabited the steppes of Central Asia.
Ident ...
7th BC-5th century AD
* Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
6th–1st centuries BC
* Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
5th century BC – 5th century AD
* Bulgars 7th century BC–7th century AD
* Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
4th century BC – 14th century AD
* Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
3rd century BC – 2nd century AD
* Iazyges
The Iazyges (), singular Ἰάζυξ. were an ancient Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In BC, they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Dacian steppe between th ...
3rd century BC – 5th century AD
* Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
2nd century BC – 1st century AD
* Tauri
The Tauri (; in Ancient Greek), or Taurians, also Scythotauri, Tauri Scythae, Tauroscythae (Pliny, ''H. N.'' 4.85) were an ancient people settled on the southern coast of the Crimea peninsula, inhabiting the Crimean Mountains in the 1st millenn ...
* Wusun
The Wusun (; Eastern Han Chinese *''ʔɑ-suən'' < (140 BCE < 436 BCE): *''Ɂâ-sûn'') were an ancient semi-
1st century BC – 6th century AD
* Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into th ...
1st–3rd centuries
* Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
3rd–6th centuries
* Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
2nd–5th centuries
* Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
3rd–5th centuries
* Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
3rd–8th centuries
* Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
4th–8th centuries
* Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
4th–8th centuries
* Early Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central and Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the S ...
5th-10th centuries
* Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
5th–11th centuries
* Avars 5th–9th centuries
* Hepthalites 5th–7th centuries
* Eurasian Avars 6th–8th centuries
* Göktürks 6th–8th centuries
* Sabirs
The Sabirs (Savirs, Suars, Sawar, Sawirk among others; el, Σάβιροι) were nomadic people who lived in the north of the Caucasus beginning in the late-5th -7th century, on the eastern shores of the Black Sea, in the Kuban area, and possibly ...
6th–8th centuries
* Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
7th–11th centuries
* Onogurs
The Onoğurs or Oğurs (Ὀνόγουροι, Οὔρωγοι, Οὔγωροι; Onογurs, Ογurs; "ten tribes", "tribes"), were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between 5th and 7th cen ...
8th century
* Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
8th–11th centuries
* Bashkirs
, native_name_lang = bak
, flag = File:Bashkirs of Baymak rayon.jpg
, flag_caption = Bashkirs of Baymak in traditional dress
, image =
, caption =
, population = approx. 2 million
, popplace ...
10th century-present day
* Kipchaks and Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
11th–13th centuries
* Crimean Goths
The Crimean Goths were Greuthungi-Gothic tribes who remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the longest-lasting of the Gothic communities. Their existence is well attested through the ages, though the exact p ...
* Mongol Empire 13th–14th centuries
* Chagatai Khanate
The Chagatai Khanate, or Chagatai Ulus ( xng, , translit=Čaɣatay-yin Ulus; mn, Цагаадайн улс, translit=Tsagaadain Uls; chg, , translit=Čağatāy Ulusi; fa, , translit=Xânât-e Joghatây) was a Mongol and later Turkicized kh ...
13th–15th centuries
* Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
13th–15th centuries
* Kazakh Khanate 15th–19th centuries
* Cossacks, Kalmyks, Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
, Volga Tatars
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars ( tt-Cyrl, татарлар, tatarlar) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are Russia's second-largest ethnicity after ...
, Nogais
The Nogais ( Nogai: Ногай, , Ногайлар, ) are a Turkic ethnic group who live in the North Caucasus region. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia and Astrakhan Oblast; some als ...
and other Turkic states and tribes 15th–18th centuries
* Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
18th–20th centuries
* Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
20th century
* Gagauzia, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
20th–21st centuries
See also
*Eurasian nomads
The Eurasian nomads were a large group of nomadic peoples from the Eurasian Steppe, who often appear in history as invaders of Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, Eastern Asia, and South Asia.
A nomad is a member of people having no permanent ab ...
* Great Hungarian Plain
The Great Hungarian Plain (also known as Alföld or Great Alföld, hu, Alföld or ) is a plain occupying the majority of the modern territory of Hungary. It is the largest part of the wider Pannonian Plain. (However, the Great Hungarian plain ...
* Izyum Trail
* Little Hungarian Plain
The Little Hungarian Plain or Little Alföld ( Hungarian: ''Kisalföld'', Slovak: ''Malá dunajská kotlina'', German: ''Kleine Ungarische Tiefebene'') is a plain (tectonic basin) of approximately 8,000 km² in northwestern Hungary, south- ...
* Steppe Route
References
Bibliography
* John of Plano Carpini, "History of the Mongols," in Christopher Dawson, (ed.), Mission to Asia, Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2005, pp. 3–76. * Barthold, W., Turkestan Down to the Mongol Invasion, T. Minorsky, (tr.), New Delhi: Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers, 1992. * Christian, David, A History of Russia, Central Asia and Mongolia, Volume 1: Inner Eurasia from Prehistory to the Mongol Empire’, Malden MA, Oxford, UK, Carlton, Australia: Blackwell Publishing 1998. * Fletcher, Joseph F., Studies on Chinese and Islamic Inner Asia, Beatrice Forbes Manz, (ed.), Aldershot, Hampshire: Variorum, 1995, IX. * Grousset, René, The Empire of the Steppes: a History of Central Asia, Naomi Walford, (tr.), New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1970. * Krader, Lawrence, "Ecology of Central Asian Pastoralism," Southwestern Journal of Anthropology, Vol. 11, No. 4, (1955), pp. 301–326. * Lattimore, Owen, "The Geographical Factor in Mongol History," in Owen Lattimore, (ed.), Studies in Frontier History: Collected Papers 1928–1958, London: Oxford University Press, 1962, pp. 241–258. * Sinor, Denis, "The Inner Asian Warrior," in Denis Sinor, (Collected Studies Series), Studies in Medieval Inner Asia, Aldershot, Hampshire: Ashgate, Variorum, 1997, XIII. * Sinor, Denis, "Horse and Pasture in Inner Asian History," in Denis Sinor, (Collected Studies Series), Inner Asia and its Contacts with Medieval Europe, London: Variorum, 1977, II.External links
The importance of the Eurasian steppe to the study of international relations
in ''Journal of International Relations and Development'' {{coord missing, Russia Grasslands of Asia Grasslands of Europe Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands Ecoregions of Asia Ecoregions of Europe Geography of Central Asia Geography of East Asia Geography of Siberia Geography of Eastern Europe Grasslands of Russia History of Pakistan Social history of India Central Asia East Asia Eastern Europe Southern Europe Western Europe Eurasia