Epidemiology of obesity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


Obesity and overweight.
Fact sheet, updated June 2016. Geneva. Retrieved 22 Sept 2017. Increases in obesity have been seen most in urban settings. Since body fat can be measured in several ways, statistics on the epidemiology of obesity vary between sources. While BMI is the most basic and commonly used indicator of obesity, other measures include waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, skinfold thicknesses, and bioelectrical impedance. The rate of obesity increases with age at least up to 50 or 60 years old. Sex- and gender-based differences also influence the prevalence of obesity. Globally there are more obese women than men, but the numbers differ depending on how obesity is measured.
 Between the 1970s and the 2000s, rates of obesity in most European countries have increased. During the 1990s and 2000s, the 27 countries making up the EU reported rates of obesity from 10–27% in men and from 10–38% in women.
The most recent combined
Between the 1970s and the 2000s, rates of obesity in most European countries have increased. During the 1990s and 2000s, the 27 countries making up the EU reported rates of obesity from 10–27% in men and from 10–38% in women.
The most recent combined
/ref>
 Epidemiological data show that, among high-income countries, obesity prevalence is highest in the United States and Mexico.
Epidemiological data show that, among high-income countries, obesity prevalence is highest in the United States and Mexico.
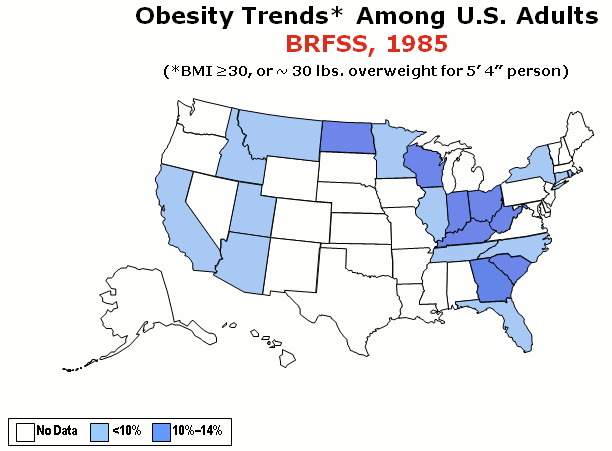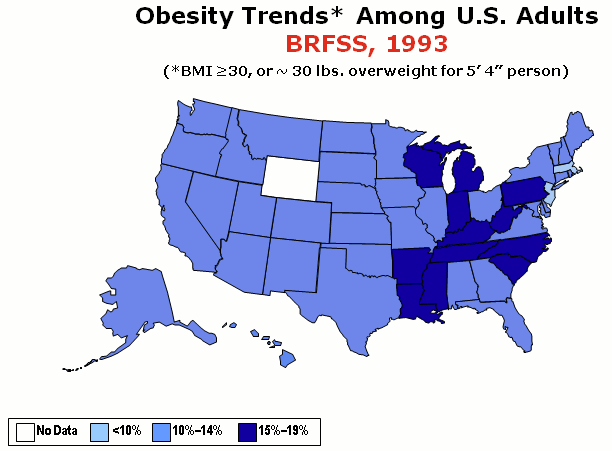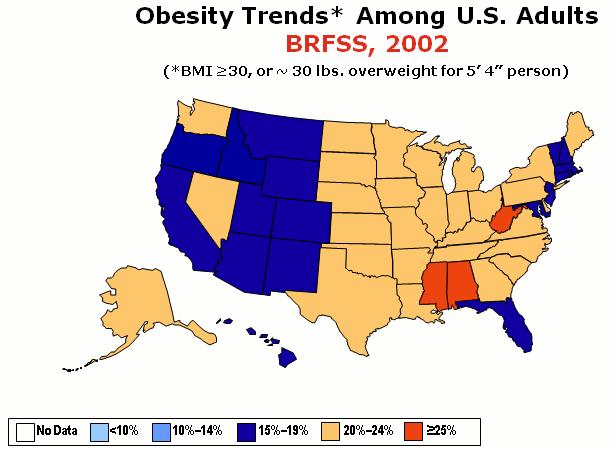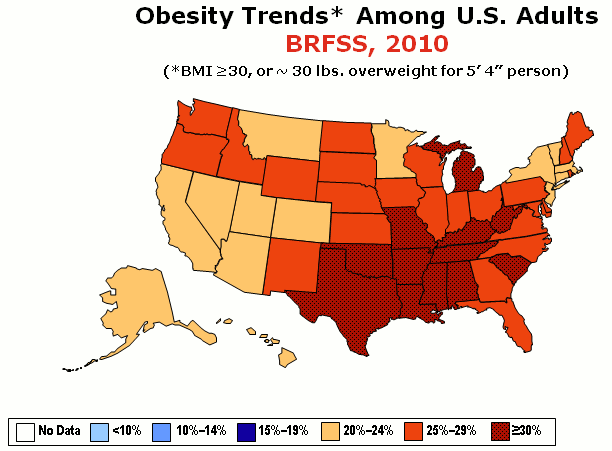 Obesity rates in the United States have nearly tripled since the 1960s. In 1962, about 13% of adult Americans were obese,https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/2010/071.pdf and by 2002, obesity rates reached 33% of the adult population. According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Study collected between the 1970s and 2004, the prevalence of overweight and obesity increased steadily among all groups of Americans.
The numbers continue to rise; as of 2007, 33% of men and 36% of women were obese, and by 2015–2016, 39.6% of the total adult population (37.9% of men and 41.1% of women) had obesity. As of 2017-2018, 42.4% of U.S. adults aged 20 and over were obese (43% for men and 41.9% for women).
Obesity rates vary between diverse social groups, with some racial groups and low-income individuals more likely to be obese while other minorities show lower rates. As of 2014 the rates were as low as 12% for non-Hispanic Asian women and as high as 57% among African American women.
The incidence of obesity also varies with geography. The American South has been referred to as the " Stroke belt", "Obesity belt", or "Diabetes belt", to reflect the fact that residents of the region have high rates of these three conditions, compared to people of the same race/ethnicity elsewhere in the country.
Based on a study in 2008, estimates of obesity that rely on self-reported data arrive at a rate of 22% among non-Hispanic white females, whereas studies that involve direct measurement show that the rate was closer to 34% at that time.
The prevalence of class III (morbid) obesity (BMI ≥ 40) has increased the most dramatically, from 1.3% in the late 1970s, to 2.9% in 1988-94, to 4.7% in 2000, to 5.7% in 2008, and to 7.7% in 2014. Among African American women, its prevalence is estimated to be as high as 17%.
The rate of increase in the incidence of obesity began to slow in the 2000s, but as of 2014, obesity, severe obesity, and obesity in children continued to rise.
Obesity rates in the United States have nearly tripled since the 1960s. In 1962, about 13% of adult Americans were obese,https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/2010/071.pdf and by 2002, obesity rates reached 33% of the adult population. According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Study collected between the 1970s and 2004, the prevalence of overweight and obesity increased steadily among all groups of Americans.
The numbers continue to rise; as of 2007, 33% of men and 36% of women were obese, and by 2015–2016, 39.6% of the total adult population (37.9% of men and 41.1% of women) had obesity. As of 2017-2018, 42.4% of U.S. adults aged 20 and over were obese (43% for men and 41.9% for women).
Obesity rates vary between diverse social groups, with some racial groups and low-income individuals more likely to be obese while other minorities show lower rates. As of 2014 the rates were as low as 12% for non-Hispanic Asian women and as high as 57% among African American women.
The incidence of obesity also varies with geography. The American South has been referred to as the " Stroke belt", "Obesity belt", or "Diabetes belt", to reflect the fact that residents of the region have high rates of these three conditions, compared to people of the same race/ethnicity elsewhere in the country.
Based on a study in 2008, estimates of obesity that rely on self-reported data arrive at a rate of 22% among non-Hispanic white females, whereas studies that involve direct measurement show that the rate was closer to 34% at that time.
The prevalence of class III (morbid) obesity (BMI ≥ 40) has increased the most dramatically, from 1.3% in the late 1970s, to 2.9% in 1988-94, to 4.7% in 2000, to 5.7% in 2008, and to 7.7% in 2014. Among African American women, its prevalence is estimated to be as high as 17%.
The rate of increase in the incidence of obesity began to slow in the 2000s, but as of 2014, obesity, severe obesity, and obesity in children continued to rise.


World Health Organisation Global Database on Body Mass Index
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Epidemiology Of Obesity Obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
has been observed throughout human history. Many early depictions of the human form in art and sculpture appear obese. However, it was not until the 20th century that obesity became common — so much so that, in 1997, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO) formally recognized obesity as a global epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
and estimated that the worldwide prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled since 1975. Obesity is defined as having a body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass ( weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and ...
(BMI) greater than or equal to 30 kg/m2, and in June 2013 the American Medical Association classified it as a disease.
In countries of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), one child out of five is overweight or obese. Once considered a problem only of high-income countries
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a nation with a gross national income per capita of US$12,696 or more in 2020, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with "First World" a ...
, obesity rates are rising worldwide. Globally, there are now more people who are obese than who are underweight, a trend observed in every region over the world except parts of sub-Saharan Africa and Asia. In 2013, an estimated 2.1 billion adults were overweight, as compared with 857 million in 1980. Of adults who are overweight, 31% are obese.World Health OrganizationObesity and overweight.
Fact sheet, updated June 2016. Geneva. Retrieved 22 Sept 2017. Increases in obesity have been seen most in urban settings. Since body fat can be measured in several ways, statistics on the epidemiology of obesity vary between sources. While BMI is the most basic and commonly used indicator of obesity, other measures include waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, skinfold thicknesses, and bioelectrical impedance. The rate of obesity increases with age at least up to 50 or 60 years old. Sex- and gender-based differences also influence the prevalence of obesity. Globally there are more obese women than men, but the numbers differ depending on how obesity is measured.
Africa
Obesity rates in Western Africa are estimated to be 10%. Rates of obesity among women are three times those found in men. In urban West Africa rates of obesity doubled between the 1990s and 2000s.Egypt
In Egypt, according to data from the 2016 Global Burden of Disease study, overweight and obesity (as measured by high BMI) was the country's leading risk factor driving the most death and disability combined.Asia
China
In the twenty first century, China faces challenges of obesity and chronic disease. This is believed to be primarily due to the rapid declines in physical activity and changing dietary habits which have occurred between the 1980s and the 2000s. The decline in physical activity is attributed to increasing technology in the workplace and changing leisure activities. In 1989 65% of Chinese had jobs that required heavy labor. This decreased to 51% in the year 2000. Combined with this has been a change to a diet higher in meat and oil, and an increase in overall available calories. Available calories per person increased from per day in 1980 to per day in 2002. Rates of overweight and obese adults increased 12.9% in 1991 to 27.3% in 2004. Overall rates of obesity are below 5% in China as a whole but are greater than 20% in some cities.India
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
has reached epidemic proportions in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
in the 21st century, with morbid obesity affecting 5% of the country's population. Obesity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and NGOs such as the Indian Heart Association
The Indian Heart Association (IHA), along with the Indian Stroke Association (ISA), is an organization dedicated to raising cardiovascular and stroke health awareness among the South Asian population.
The organisation was founded by Harvard Medi ...
have been raising awareness about this issue.Indian Heart Association Webpage 30 April 2015. Iran
In Iran the prevalence of obesity was 26.3% in 2008. Prevalence of obesity was more among women (39.5%) than men (14.5%).Japan
Using the WHO criteria Japan has the lowest rate of obesity among theOECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
member countries at 3.2%. However, as Asian populations are particularly susceptible to the health risks of excess adipose tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular ...
the Japanese have redefined obesity as any BMI greater than 25. Using this cut off value the prevalence of obesity in Japan would be 20%, a threefold increase from 1962 to 2002. A 2008 report stated that 28.6% of men and 20.6% of women in Japan were considered to be obese.
Pakistan
Changing lifestyles, owing to urbanisation, as well as diet issues are the main reasons for obesity in Pakistan. According to a recent study, approximately one out of four Pakistani adults (or 22.2% of individuals) are classified as obese.Taiwan
In 2002, 15% of children from 6 to 12 years of age were overweight; by gender, 15.5% of males and 14.4% of females were overweight. In the same age range, 12% of children were obese; by gender, 14.7% of males and 9.1% of females were categorized as obese. In 2005, 14.9% children from 6 to 12 years of age were overweight; by gender, 15.85% of males and 14.02% of females were overweight. 10.3% were categorized as obese; by gender, 10.92% of males and 9.73% of females were categorized as obese. Based on these numbers, the trends were inconclusive, although with more than 10% of the age group being obese, obesity does appear to be a problem.Europe
 Between the 1970s and the 2000s, rates of obesity in most European countries have increased. During the 1990s and 2000s, the 27 countries making up the EU reported rates of obesity from 10–27% in men and from 10–38% in women.
The most recent combined
Between the 1970s and the 2000s, rates of obesity in most European countries have increased. During the 1990s and 2000s, the 27 countries making up the EU reported rates of obesity from 10–27% in men and from 10–38% in women.
The most recent combined Eurostat
Eurostat ('European Statistical Office'; DG ESTAT) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg, Luxembourg, Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide stati ...
statistics, for 2009, show that, among the 19 EU Member States for which data are available, the proportion of obese people in the adult population varied in 2008/9 between 8.0% (Romania) and 23.9% (UK) for women and between 7.6% (Romania) and 24.7% (Malta) for men. Overall the UK had the highest proportions, and Romania the lowest. Men, the elderly and people with lower educations also have significantly higher obesity rates.Eurostat – Statistics Explained: Overweight and obesity – BMI_statistics, see 'Source data for tables, figures and maps'/ref>
United Kingdom
In the UK the rate of obesity has increased about fourfold over the last 30 years, reaching levels of 22–24% in 2008/9.North America
Canada
The number of Canadians who are obese has risen dramatically in recent years. In 2004, direct measurements of height and weight found 23.1% of Canadians older than 18 had a BMI greater than 30. When broken down into degrees of obesity, 15.2% were class I (BMI 30–34.9), 5.1% were class II (BMI 35–39.9), and 2.7%, class III (BMI ≥ 40). This is in contrast to self-reported data the previous year of 15.2% and in 1978/1979 of 13.8%. The greatest increases occurred among the more severe degrees of obesity; class III obesity increased from 0.9% to 2.7% from 1978/1979 to 2004. Obesity in Canada varies by ethnicity; people of Aboriginal origin have a significantly higher rate of obesity (37.6%) than the national average. In children obesity has substantially increased between 1989 and 2004 with rates in boys increasing from 2% to 10% and rates among girls increasing from 2% to 9%.Mexico
Mexico has one of the highest rates of obesity amongOECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate ...
countries, second only to the United States. To combat the epidemic, in 2014 Mexico implemented new taxes levied on food with excessive energy content and on sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
- sweetened beverages.
United States
 Obesity rates in the United States have nearly tripled since the 1960s. In 1962, about 13% of adult Americans were obese,https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/2010/071.pdf and by 2002, obesity rates reached 33% of the adult population. According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Study collected between the 1970s and 2004, the prevalence of overweight and obesity increased steadily among all groups of Americans.
The numbers continue to rise; as of 2007, 33% of men and 36% of women were obese, and by 2015–2016, 39.6% of the total adult population (37.9% of men and 41.1% of women) had obesity. As of 2017-2018, 42.4% of U.S. adults aged 20 and over were obese (43% for men and 41.9% for women).
Obesity rates vary between diverse social groups, with some racial groups and low-income individuals more likely to be obese while other minorities show lower rates. As of 2014 the rates were as low as 12% for non-Hispanic Asian women and as high as 57% among African American women.
The incidence of obesity also varies with geography. The American South has been referred to as the " Stroke belt", "Obesity belt", or "Diabetes belt", to reflect the fact that residents of the region have high rates of these three conditions, compared to people of the same race/ethnicity elsewhere in the country.
Based on a study in 2008, estimates of obesity that rely on self-reported data arrive at a rate of 22% among non-Hispanic white females, whereas studies that involve direct measurement show that the rate was closer to 34% at that time.
The prevalence of class III (morbid) obesity (BMI ≥ 40) has increased the most dramatically, from 1.3% in the late 1970s, to 2.9% in 1988-94, to 4.7% in 2000, to 5.7% in 2008, and to 7.7% in 2014. Among African American women, its prevalence is estimated to be as high as 17%.
The rate of increase in the incidence of obesity began to slow in the 2000s, but as of 2014, obesity, severe obesity, and obesity in children continued to rise.
Obesity rates in the United States have nearly tripled since the 1960s. In 1962, about 13% of adult Americans were obese,https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/2010/071.pdf and by 2002, obesity rates reached 33% of the adult population. According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Study collected between the 1970s and 2004, the prevalence of overweight and obesity increased steadily among all groups of Americans.
The numbers continue to rise; as of 2007, 33% of men and 36% of women were obese, and by 2015–2016, 39.6% of the total adult population (37.9% of men and 41.1% of women) had obesity. As of 2017-2018, 42.4% of U.S. adults aged 20 and over were obese (43% for men and 41.9% for women).
Obesity rates vary between diverse social groups, with some racial groups and low-income individuals more likely to be obese while other minorities show lower rates. As of 2014 the rates were as low as 12% for non-Hispanic Asian women and as high as 57% among African American women.
The incidence of obesity also varies with geography. The American South has been referred to as the " Stroke belt", "Obesity belt", or "Diabetes belt", to reflect the fact that residents of the region have high rates of these three conditions, compared to people of the same race/ethnicity elsewhere in the country.
Based on a study in 2008, estimates of obesity that rely on self-reported data arrive at a rate of 22% among non-Hispanic white females, whereas studies that involve direct measurement show that the rate was closer to 34% at that time.
The prevalence of class III (morbid) obesity (BMI ≥ 40) has increased the most dramatically, from 1.3% in the late 1970s, to 2.9% in 1988-94, to 4.7% in 2000, to 5.7% in 2008, and to 7.7% in 2014. Among African American women, its prevalence is estimated to be as high as 17%.
The rate of increase in the incidence of obesity began to slow in the 2000s, but as of 2014, obesity, severe obesity, and obesity in children continued to rise.
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
is one of the leading health issues in the United States, with some estimates suggesting that obesity results in about 300,000 excess deaths per year. However, in 2005 using different methodology, research at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
produced a nationwide estimate of 129,000 excess deaths per year relative to individuals with a BMI of 21 to 25. In contrast, a 2013 review found that obesity was not associated with higher mortality than normal weight, and that overweight was associated with lower mortality than was normal weight.
South America and the Caribbean
Surveys in different Caribbean countries found that 7-20% of males and 22-48% of females over the age of 15 are obese. Trinidad and Tobago has the highest obesity in the Caribbean, with over 30% of its adult population overweight, ranking the country sixth in the world. The Bahamas have a major obesity epidemic: 48.6% of people between 15 and 64 years old are obese. A female adolescent from the Bahamas is more likely to be overweight than her male counterpart. In Jamaica, 7.2% of men over the age of 20 are obese, while 31.5% of women are obese.Oceania and the Pacific

Australia
According to self-reported and measured results of the 2007–2008 National Health Survey, 61% of Australians were overweight (above a 25 BMI), with 24% falling into the "obese" category (above a 30 BMI). Men were more likely to be overweight (67.7%) and obese (25.5%) than women (30.9% and 23.4% respectively).New Zealand
Obesity in New Zealand has become an important national health concern in recent years, with high numbers of people afflicted in every age and ethnic group. In 2011/12, 28.4% of New Zealand adults were obese, a number only surpassed in theEnglish-speaking world
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the '' Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest languag ...
by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
.
South Pacific
Many of the island nations of the South Pacific have very high rates of obesity.Nauru
Nauru ( or ; na, Naoero), officially the Republic of Nauru ( na, Repubrikin Naoero) and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Oceania, in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in ...
has the highest rates of obesity in the world (94.5%) followed by Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
, the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states compr ...
, and the American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internatio ...
. Being big has traditionally been associated with health, beauty, and status and many of these beliefs remain prevalent today.
See also
*Consumer Goods Forum The Consumer Goods Forum is a global organization of 400 consumer goods companies with the likes of Amazon and Kellogg being involved. It represents combined sales of 2.5 trillion Euros across 70 countries and 10 million employees.
Overview
The C ...
*Food industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditional, ...
* Food politics
* Epidemiology of childhood obesity
* Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome
*Obesogen
Obesogens are foreign chemical compounds that are hypothesised to disrupt normal development and balance of lipid metabolism, which in some cases, can lead to obesity. Obesogens may be functionally defined as chemicals that inappropriately alt ...
* Overnutrition
*Sugar industry
The sugar industry subsumes the production, processing and marketing of sugars (mostly sucrose and fructose). Globally, most sugar is extracted from sugar cane (~80% predominantly in the tropics) and sugar beet (~ 20%, mostly in temperate cl ...
*Ultra-processed food
Ultra-processed foods, also referred to as ultra-processed food products (UPP), are food and drink products that have undergone specified types of food processing, usually by transnational and other very large ' Big food' corporations. These fo ...
*World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
References
External links
World Health Organisation Global Database on Body Mass Index
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Epidemiology Of Obesity Obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...