English Channel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (
 The word ''channel'' was first recorded in
The word ''channel'' was first recorded in
 The French name has been used since at least the 17th century. The name is usually said to refer to the sleeve (french: link=no, la manche) shape of the Channel. Folk etymology has derived it from a Celtic word meaning 'channel' that is also the source of the name for
The French name has been used since at least the 17th century. The name is usually said to refer to the sleeve (french: link=no, la manche) shape of the Channel. Folk etymology has derived it from a Celtic word meaning 'channel' that is also the source of the name for
 The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the English Channel as follows:
The IHO defines the southwestern limit of the North Sea as "a line joining the Walde Lighthouse (France, 1°55'E) and Leathercoat Point (England, 51°10'N)". The Walde Lighthouse is east of Calais (), and Leathercoat Point is at the north end of St Margaret's Bay, Kent, some North-East of Dover ().
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the English Channel as follows:
The IHO defines the southwestern limit of the North Sea as "a line joining the Walde Lighthouse (France, 1°55'E) and Leathercoat Point (England, 51°10'N)". The Walde Lighthouse is east of Calais (), and Leathercoat Point is at the north end of St Margaret's Bay, Kent, some North-East of Dover ().
 The Strait of Dover (french: Pas de Calais, link=no), at the Channel's eastern end, is its narrowest point, while its widest point lies between
The Strait of Dover (french: Pas de Calais, link=no), at the Channel's eastern end, is its narrowest point, while its widest point lies between  There are several major islands in the Channel, the most notable being the Isle of Wight off the English coast, and the Channel Islands, British Crown Dependencies off the coast of France. The coastline, particularly on the French shore, is deeply indented; several small islands close to the coastline, including
There are several major islands in the Channel, the most notable being the Isle of Wight off the English coast, and the Channel Islands, British Crown Dependencies off the coast of France. The coastline, particularly on the French shore, is deeply indented; several small islands close to the coastline, including
 The Channel is of geologically recent origin, having been dry land for most of the
The Channel is of geologically recent origin, having been dry land for most of the
 Remnants of a mesolithic boatyard have been found on the Isle of Wight. Wheat was traded across the Channel about 8,000 years ago. "... Sophisticated social networks linked the Neolithic front in southern Europe to the Mesolithic peoples of northern Europe." The
Remnants of a mesolithic boatyard have been found on the Isle of Wight. Wheat was traded across the Channel about 8,000 years ago. "... Sophisticated social networks linked the Neolithic front in southern Europe to the Mesolithic peoples of northern Europe." The
 The attack on Lindisfarne in 793 is generally considered the beginning of the Viking Age. For the next 250 years the Scandinavian raiders of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark dominated the North Sea, raiding monasteries, homes, and towns along the coast and along the rivers that ran inland. According to the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' they began to settle in Britain in 851. They continued to settle in the British Isles and the continent until around 1050, with some raids recorded along the channel coast of England, including at Wareham, Portland, near Weymouth and along the river Teign in Devon.
The fiefdom of Normandy was created for the Viking leader
The attack on Lindisfarne in 793 is generally considered the beginning of the Viking Age. For the next 250 years the Scandinavian raiders of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark dominated the North Sea, raiding monasteries, homes, and towns along the coast and along the rivers that ran inland. According to the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' they began to settle in Britain in 851. They continued to settle in the British Isles and the continent until around 1050, with some raids recorded along the channel coast of England, including at Wareham, Portland, near Weymouth and along the river Teign in Devon.
The fiefdom of Normandy was created for the Viking leader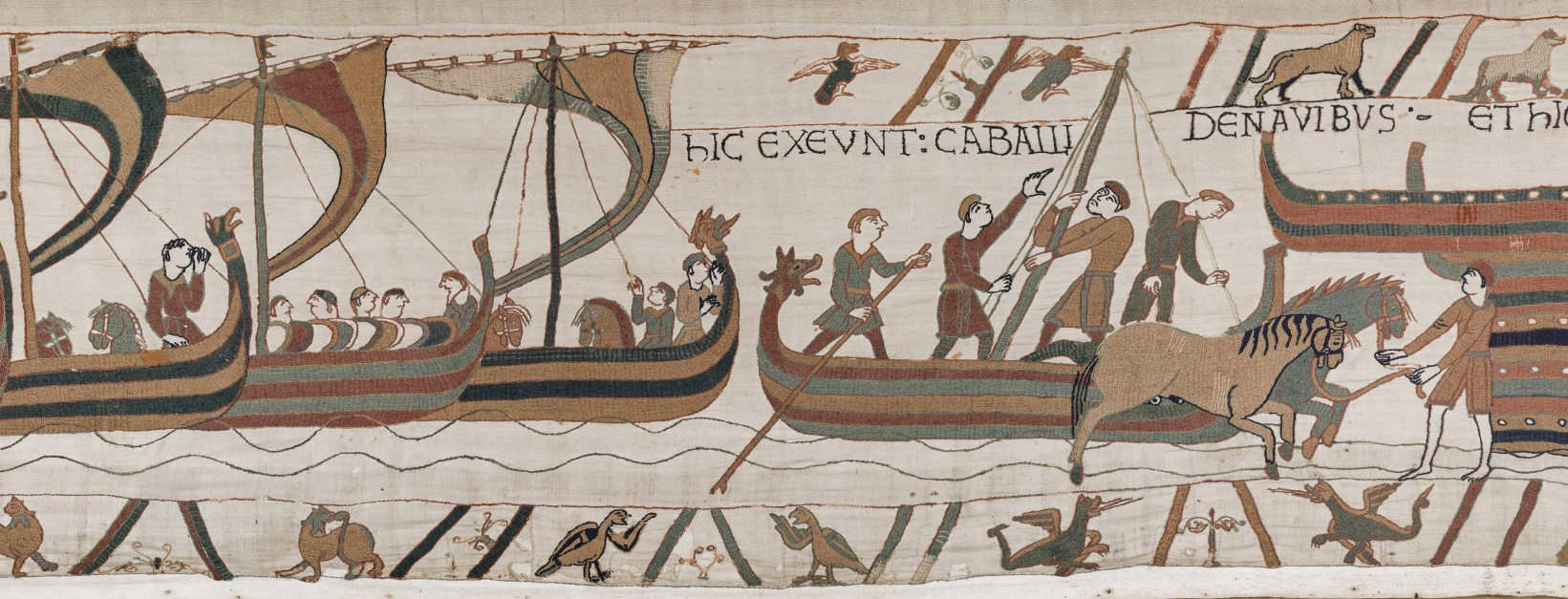  Rollo's descendant William, Duke of Normandy became king of England in 1066 in the Norman Conquest beginning with the Battle of Hastings, while retaining the fiefdom of Normandy for himself and his descendants. In 1204, during the reign of King John, mainland Normandy was taken from England by France under
Rollo's descendant William, Duke of Normandy became king of England in 1066 in the Norman Conquest beginning with the Battle of Hastings, while retaining the fiefdom of Normandy for himself and his descendants. In 1204, during the reign of King John, mainland Normandy was taken from England by France under
 From the reign of Elizabeth I, English foreign policy concentrated on preventing invasion across the Channel by ensuring no major European power controlled the potential Dutch and Flemish invasion ports. Her climb to the pre-eminent sea power of the world began in 1588 as the attempted invasion of the Spanish Armada was defeated by the combination of outstanding naval tactics by the English and the Dutch under command of Charles Howard, 1st Earl of Nottingham with Sir Francis Drake second in command, and the following stormy weather. Over the centuries the
From the reign of Elizabeth I, English foreign policy concentrated on preventing invasion across the Channel by ensuring no major European power controlled the potential Dutch and Flemish invasion ports. Her climb to the pre-eminent sea power of the world began in 1588 as the attempted invasion of the Spanish Armada was defeated by the combination of outstanding naval tactics by the English and the Dutch under command of Charles Howard, 1st Earl of Nottingham with Sir Francis Drake second in command, and the following stormy weather. Over the centuries the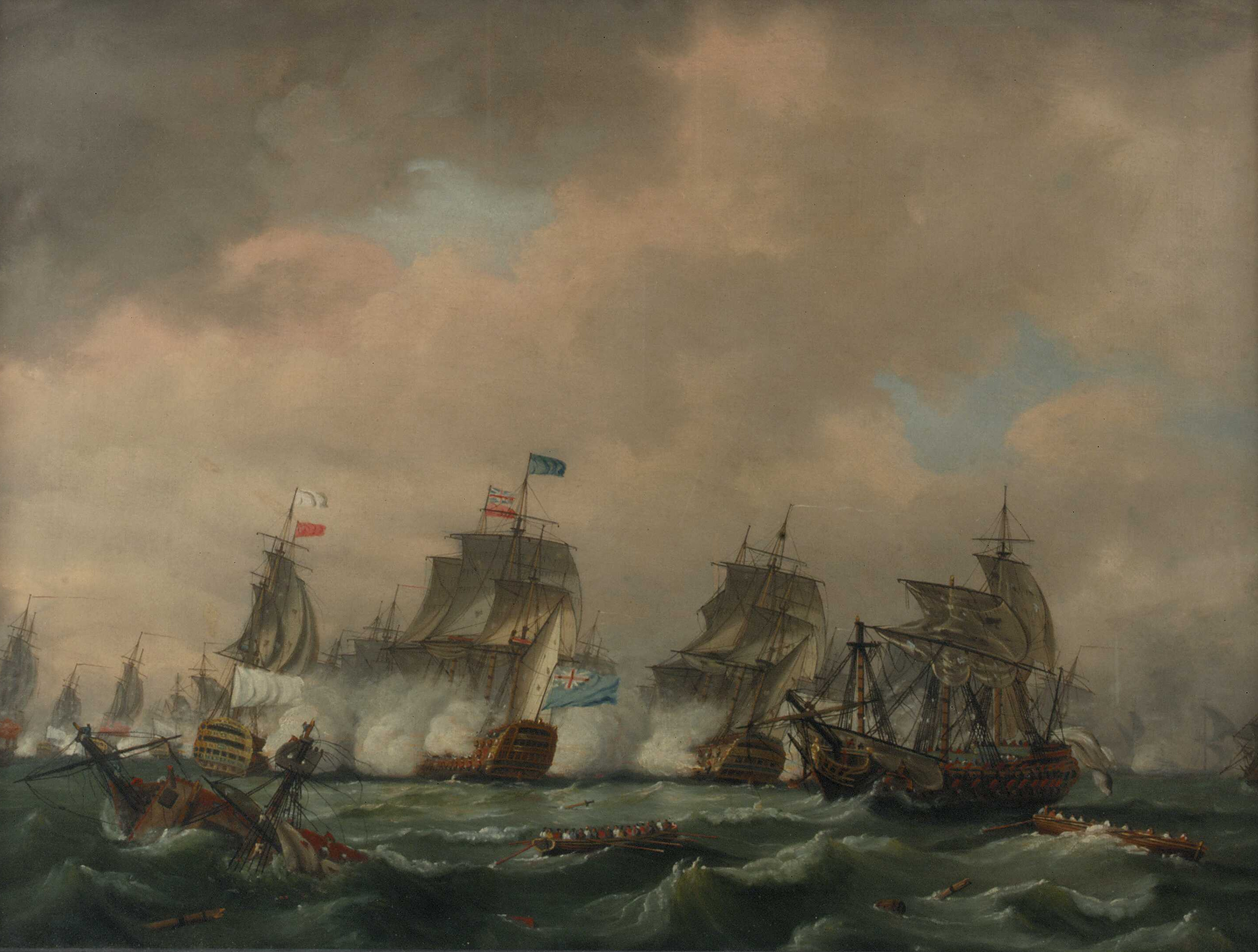  The building of the British Empire was possible only because the
The building of the British Empire was possible only because the
 During the Second World War, naval activity in the
During the Second World War, naval activity in the 

 * Brighton– Worthing–
* Brighton– Worthing–
 * Le Havre: 248,547 inhabitants
* Calais: 104,852
* Saint-Malo: 50,675
*
* Le Havre: 248,547 inhabitants
* Calais: 104,852
* Saint-Malo: 50,675
*
 The two dominant cultures are English on the north shore of the Channel, French on the south. However, there are also a number of minority languages that are or were found on the shores and islands of the English Channel, which are listed here, with the Channel's name in the specific language following them.
;Celtic Languages
: br, Mor Breizh, Sea of Brittany
: kw, Mor Bretannek
: ga, Muir nIocht, Merciful Sea
;Germanic languages
: English
: nl, het Kanaal, the Channel. (Dutch previously had a larger range, and extended into parts of modern-day France as
The two dominant cultures are English on the north shore of the Channel, French on the south. However, there are also a number of minority languages that are or were found on the shores and islands of the English Channel, which are listed here, with the Channel's name in the specific language following them.
;Celtic Languages
: br, Mor Breizh, Sea of Brittany
: kw, Mor Bretannek
: ga, Muir nIocht, Merciful Sea
;Germanic languages
: English
: nl, het Kanaal, the Channel. (Dutch previously had a larger range, and extended into parts of modern-day France as
 The shore-based long-range traffic control system was updated in 2003 and there is a series of traffic separation systems in operation. Though the system is inherently incapable of reaching the levels of safety obtained from aviation systems such as the traffic collision avoidance system, it has reduced accidents to one or two per year.
Marine
The shore-based long-range traffic control system was updated in 2003 and there is a series of traffic separation systems in operation. Though the system is inherently incapable of reaching the levels of safety obtained from aviation systems such as the traffic collision avoidance system, it has reduced accidents to one or two per year.
Marine
 The ferry routes crossing the English Channel, include (have included):-
* Dover– Calais
* Dover– Dunkirk
* Newhaven–
The ferry routes crossing the English Channel, include (have included):-
* Dover– Calais
* Dover– Dunkirk
* Newhaven–
 The coastal resorts of the Channel, such as Brighton and
The coastal resorts of the Channel, such as Brighton and
." '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' Online. Retrieved 17 October 2009. Louis Blériot (France) piloted the first airplane to cross in 1909. On 26 September 2008, Swiss
Cotentinais
Cotentinais is the dialect of the Norman language spoken in the Cotentin Peninsula of France. It is one of the strongest dialects of the language on the mainland.
Dialects
Due to the relative lack of standardisation of Norman, there are five ...
) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais
Guernésiais, also known as ''Dgèrnésiais'', Guernsey French, and Guernsey Norman French, is the variety of the Norman language spoken in Guernsey. It is sometimes known on the island simply as "patois". As one of the langues d'oïl, it has it ...
), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kanaal, "The Channel"; german: Ärmelkanal, "Sleeve Channel" ( French: ''la Manche;'' also called the British Channel or simply the Channel) is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busiest shipping area in the world.
It is about long and varies in width from at its widest to at its narrowest in the Strait of Dover."English Channel". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 2004. It is the smallest of the shallow seas around the continental shelf of Europe, covering an area of some .
The Channel was a key factor in Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
becoming a naval superpower and has been utilised by Britain as a natural defence mechanism by which many would-be invasions, such as the Napoleonic Wars and those of Adolf Hitler in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, were halted.
The population around the English Channel is predominantly located on the English coast and the major languages spoken in this region are English and French.
Names
The name first appears in Roman sources as (or , meaning the British Ocean or British Sea). Variations of this term were used by influential writers such as Ptolemy, and remained popular with British and continental authors well into the modern era. Other Latin names for the sea include (the Gaulish Ocean) which was used by Isidore of Seville in the sixth century. The term ''British Sea'' is still used in Cornwall andBrittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
, with the sea known as in Cornish and in Breton. While it is likely that these names derive from the Latin term, it is possible that they predate the arrival of the Romans in the area. The modern Welsh
The history of the Welsh language (Welsh: ''Hanes yr iaith Gymraeg'') spans over 1400 years, encompassing the stages of the language known as Primitive Welsh, Old Welsh, Middle Welsh, and Modern Welsh.
Origins
Welsh evolved from British, the C ...
is often given as (the Lord's/Prince's Sea), however this name originally described both the Channel and the North Sea combined.
Anglo-Saxon texts make reference to the sea as ('South Sea'), but this term fell out of favour, as later English authors followed the same conventions as their Latin and Norman contemporaries. One English name that did persist was the ''Narrow Seas'', a collective term for the channel and North Sea. As England (followed by Great Britain and the United Kingdom) claimed sovereignty over the sea, a Royal Navy Admiral was appointed with maintaining duties in the two seas. The office was maintained until 1822, when several European nations (including the United Kingdom) adopted a three-mile limit to territorial waters.
English Channel
 The word ''channel'' was first recorded in
The word ''channel'' was first recorded in Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
in the 13th century and was borrowed from Old French (a variant form of 'canal'). By the middle of the fifteenth century an Italian map based on Ptolemy's description named the sea as ''Britanicus Oceanus nunc Canalites Anglie'' (British Ocean but now English Channel). The map is possibly the first recorded use of the term ''English Channel'' and the description suggests the name had recently been adopted.
In the sixteenth century, Dutch maps referred to the sea as the (English Channel) and by the 1590s, William Shakespeare used the word ''Channel'' in his history plays of Henry VI, suggesting that by that time, the name was popularly understood by English people.
By the eighteenth century, the name ''English Channel'' was in common usage in England. Following the Acts of Union 1707, this was replaced in official maps and documents with ''British Channel'' or ''British Sea'' for much of the next century. However, the term English Channel remained popular and was finally in official usage by the nineteenth century.
 The French name has been used since at least the 17th century. The name is usually said to refer to the sleeve (french: link=no, la manche) shape of the Channel. Folk etymology has derived it from a Celtic word meaning 'channel' that is also the source of the name for
The French name has been used since at least the 17th century. The name is usually said to refer to the sleeve (french: link=no, la manche) shape of the Channel. Folk etymology has derived it from a Celtic word meaning 'channel' that is also the source of the name for the Minch
The Minch ( gd, An Cuan Sgitheanach, ', ', '), also called North Minch, is a strait in north-west Scotland, separating the north-west Highlands and the northern Inner Hebrides from Lewis and Harris in the Outer Hebrides. It was known as ("Sco ...
in Scotland, but this name is not attested before the 17th century, and French and British sources of that time are clear about its etymology. The name in French has been directly adapted in other Romance languages ( es, Canal de la Mancha, pt, Canal da Mancha, it, Canale della Manica, ro, Canalul Mânecii) as well as German (''Ärmelkanal'').
Nature
Geography
 The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the English Channel as follows:
The IHO defines the southwestern limit of the North Sea as "a line joining the Walde Lighthouse (France, 1°55'E) and Leathercoat Point (England, 51°10'N)". The Walde Lighthouse is east of Calais (), and Leathercoat Point is at the north end of St Margaret's Bay, Kent, some North-East of Dover ().
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the English Channel as follows:
The IHO defines the southwestern limit of the North Sea as "a line joining the Walde Lighthouse (France, 1°55'E) and Leathercoat Point (England, 51°10'N)". The Walde Lighthouse is east of Calais (), and Leathercoat Point is at the north end of St Margaret's Bay, Kent, some North-East of Dover ().
 The Strait of Dover (french: Pas de Calais, link=no), at the Channel's eastern end, is its narrowest point, while its widest point lies between
The Strait of Dover (french: Pas de Calais, link=no), at the Channel's eastern end, is its narrowest point, while its widest point lies between Lyme Bay
Lyme Bay is an area of the English Channel off the south coast of England. The south western counties of Devon and Dorset front onto the bay.
The exact definitions of the bay vary. The eastern boundary is usually taken to be Portland Bill on the ...
and the Gulf of Saint Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany, on the English Channel coast.
The walled city had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth from local extortion and overseas adventures. In 1944, the Alli ...
, near its midpoint. It is relatively shallow, with an average depth of about at its widest part, reducing to a depth of about between Dover and Calais. Eastwards from there the adjoining North Sea reduces to about in the Broad Fourteens where it lies over the watershed of the former land bridge between East Anglia and the Low Countries. It reaches a maximum depth of in the submerged valley of Hurd's Deep
Hurd's Deep (or Hurd Deep) is an underwater valley in the English Channel, northwest of the Channel Islands. Its maximum depth is about 180 m (590 ft; 98 fathoms), making it the deepest point in the English Channel.
Etymology
It is m ...
, west-northwest of Guernsey.
The eastern region along the French coast between Cherbourg and the mouth of the Seine river
)
, mouth_location = Le Havre/Honfleur
, mouth_coordinates =
, mouth_elevation =
, progression =
, river_system = Seine basin
, basin_size =
, tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle
, tributaries ...
at Le Havre is frequently referred to as the ''Bay of the Seine'' (french: link=no, Baie de Seine).
Chausey
Chausey () is a group of small islands, islets and rocks off the coast of Normandy, in the English Channel. It lies from Granville and forms a ''quartier'' of the Granville commune in the Manche ''département''. Chausey forms part of the Chan ...
and Mont Saint-Michel, are within French jurisdiction. The Cotentin Peninsula
The Cotentin Peninsula (, ; nrf, Cotentîn ), also known as the Cherbourg Peninsula, is a peninsula in Normandy that forms part of the northwest coast of France. It extends north-westward into the English Channel, towards Great Britain. To its w ...
in France juts out into the Channel, whilst on the English side there is a small parallel strait known as the Solent
The Solent ( ) is a strait between the Isle of Wight and Great Britain. It is about long and varies in width between , although the Hurst Spit which projects into the Solent narrows the sea crossing between Hurst Castle and Colwell Bay t ...
between the Isle of Wight and the mainland. The Celtic Sea
The Celtic Sea ; cy, Y Môr Celtaidd ; kw, An Mor Keltek ; br, Ar Mor Keltiek ; french: La mer Celtique is the area of the Atlantic Ocean off the southern coast of Ireland bounded to the east by Saint George's Channel; other limits includ ...
is to the west of the Channel.
The Channel acts as a funnel that amplifies the tidal range from less than a metre as observed at sea to more than 6 metres as observed in the Channel Islands, the west coast of the Cotentin Peninsula
The Cotentin Peninsula (, ; nrf, Cotentîn ), also known as the Cherbourg Peninsula, is a peninsula in Normandy that forms part of the northwest coast of France. It extends north-westward into the English Channel, towards Great Britain. To its w ...
and the north coast of Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
. The time difference of about six hours between high water at the eastern and western limits of the Channel is indicative of the tidal range being amplified further by resonance.
In the UK Shipping Forecast
The Shipping Forecast is a BBC Radio broadcast of weather reports and forecasts for the seas around the coasts of the British Isles. It is produced by the Met Office and broadcast by BBC Radio 4 on behalf of the Maritime and Coastguard Agency. ...
the Channel is divided into the following areas, from the east:
* Dover
* Wight
* Portland
* Plymouth
Geological origins
 The Channel is of geologically recent origin, having been dry land for most of the
The Channel is of geologically recent origin, having been dry land for most of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
period. Before the Devensian glaciation (the most recent glacial period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betwe ...
, which ended around 10,000 years ago), Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
and Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
were part of continental Europe, linked by an unbroken Weald–Artois anticline
The Weald–Artois Anticline, or Wealden Anticline, is a large anticline, a geological structure running between the regions of the Weald in southern England and Artois in northern France. The fold formed during the Alpine orogeny, from the late ...
, a ridge that acted as a natural dam holding back a large freshwater pro-glacial lake in the Doggerland
Doggerland was an area of land, now submerged beneath the North Sea, that connected Britain to continental Europe. It was flooded by rising sea levels around 6500–6200 BCE. The flooded land is known as the Dogger Littoral. Geological sur ...
region, now submerged under the North Sea. During this period the North Sea and almost all of the British Isles were covered by ice. The lake was fed by meltwater from the Baltic and from the Caledonian and Scandinavian ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at La ...
s that joined to the north, blocking its exit. The sea level was about lower than it is today. Then, between 450,000 and 180,000 years ago, at least two catastrophic glacial lake outburst flood
A glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) is a type of outburst flood caused by the failure of a dam containing a glacial lake. An event similar to a GLOF, where a body of water contained by a glacier melts or overflows the glacier, is called a j� ...
s breached the Weald–Artois anticline.
The first flood of 450 thousand years ago would have lasted for several months, releasing as much as one million cubic metres of water per second.
* The flood started with large but localized waterfalls over the ridge, which excavated depressions now known as the ''Fosses Dangeard''. The flow eroded the retaining ridge, causing the rock dam to fail and releasing lake water into the Atlantic. After multiple episodes of changing sea level, during which the ''Fosses Dangeard'' were largely infilled by various layers of sediment, another catastrophic flood some 180,000 years ago carved a large bedrock-floored valley, the Lobourg Channel, some 500 m wide and 25 m deep, from the southern North Sea basin through the centre of the Straits of Dover and into the English Channel. It left streamlined islands, longitudinal erosional grooves, and other features characteristic of catastrophic megaflood events, still present on the sea floor and now revealed by high-resolution sonar. Through the scoured channel passed a river, the Channel River, which drained the combined Rhine and Thames westwards to the Atlantic.
The flooding destroyed the ridge that connected Britain to continental Europe, although a land connection across the southern North Sea would have existed intermittently at later times when periods of glaciation resulted in lowering of sea levels. At the end of the last glacial period, rising sea levels finally severed the last land connection.
Ecology
As a busy shipping lane, the Channel experiences environmental problems following accidents involving ships with toxic cargo and oil spills. Indeed, over 40% of the UK incidents threatening pollution occur in or very near the Channel. One occurrence was the MSC ''Napoli'', which on 18 January 2007 was beached with nearly 1700 tonnes of dangerous cargo in Lyme Bay, a protected World Heritage Site coastline. The ship had been damaged and was en route to Portland Harbour. The English Channel, despite being a busy shipping lane, remains in part a haven for wildlife. Atlantic oceanic species are more common in the westernmost parts of the channel, particularly to the west of Start Point, Devon, but can sometimes be found further east towards Dorset and the Isle of Wight. Seal sightings are becoming more common along the English Channel, with both Grey Seal andHarbour Seal
The harbor (or harbour) seal (''Phoca vitulina''), also known as the common seal, is a true seal found along temperate and Arctic marine coastlines of the Northern Hemisphere. The most widely distributed species of pinniped (walruses, eared se ...
recorded frequently.
Human history
The Channel, which delayed human reoccupation of Great Britain for more than 100,000 years, has in historic times been both an easy entry for seafaring people and a key natural defence, halting invading armies while in conjunction with control of the North Sea allowing Britain to blockade the continent. The most significant failed invasion threats came when the Dutch and Belgian ports were held by a major continental power, e.g. from the Spanish Armada in 1588, Napoleon during the Napoleonic Wars, andNazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Successful invasions include the Roman conquest of Britain, the Norman Conquest in 1066 and the Glorious Revolution of 1688, while the concentration of excellent harbours in the Western Channel on Britain's south coast made possible the largest amphibious invasion in history, the Normandy Landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and ...
in 1944. Channel naval battles include the Battle of the Downs
The Battle of the Downs took place on 21 October 1639 (New Style), during the Eighty Years' War. A Spanish fleet, commanded by Admiral Antonio de Oquendo, was decisively defeated by a Dutch force under Lieutenant-Admiral Maarten Tromp. Vict ...
(1639), Battle of Dover (1652), the Battle of Portland (1653), the Battle of La Hougue
The Battles of Barfleur and La Hougue took place during the Nine Years' War, between 19 May O.S. (29 May N.S.) and 4 June O.S. (14 June N.S.) 1692. The first was fought near Barfleur on 19 May O.S. (29 May N.S.), with later actions occurring ...
(1692) and the engagement between USS ''Kearsarge'' and CSS ''Alabama'' (1864).
In more peaceful times the Channel served as a link joining shared cultures and political structures, particularly the huge Angevin Empire
The Angevin Empire (; french: Empire Plantagenêt) describes the possessions of the House of Plantagenet during the 12th and 13th centuries, when they ruled over an area covering roughly half of France, all of England, and parts of Ireland and W ...
from 1135 to 1217. For nearly a thousand years, the Channel also provided a link between the Modern Celtic regions and languages of Cornwall and Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
. Brittany was founded by Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
who fled Cornwall and Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
after Anglo-Saxon encroachment. In Brittany, there is a region known as "Cornouaille
Cornouaille (; br, Kernev, Kerne) is a historical region on the west coast of Brittany in West France. The name is cognate with Cornwall in neighbouring Great Britain. This can be explained by the settlement of Cornouaille by migrant princ ...
" (Cornwall) in French and "Kernev" in Breton. In ancient times there was also a " Domnonia" (Devon) in Brittany as well.
In February 1684, ice formed on the sea in a belt wide off the coast of Kent and wide on the French side.
Route to Britain
 Remnants of a mesolithic boatyard have been found on the Isle of Wight. Wheat was traded across the Channel about 8,000 years ago. "... Sophisticated social networks linked the Neolithic front in southern Europe to the Mesolithic peoples of northern Europe." The
Remnants of a mesolithic boatyard have been found on the Isle of Wight. Wheat was traded across the Channel about 8,000 years ago. "... Sophisticated social networks linked the Neolithic front in southern Europe to the Mesolithic peoples of northern Europe." The Ferriby Boats
The Ferriby Boats are three Bronze-Age British sewn plank-built boats, parts of which were discovered at North Ferriby in the East Riding of the English county of Yorkshire. Only a small number of boats of a similar period have been found ...
, Hanson Log Boats and the later Dover Bronze Age Boat
The Dover Bronze Age boat is one of fewer than 20 Bronze Age boats so far found in Britain. It dates to 1575–1520 BC, which may make it one of the oldest substantially intact ''boat'' in the world (older boat finds are small fragments, some l ...
could carry a substantial cross-Channel cargo.
Diodorus Siculus and Pliny both suggest trade between the rebel Celtic tribes of Armorica
Armorica or Aremorica (Gaulish: ; br, Arvorig, ) is the name given in ancient times to the part of Gaul between the Seine and the Loire that includes the Brittany Peninsula, extending inland to an indeterminate point and down the Atlantic Coast ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
Britain flourished. In 55 BC Julius Caesar invaded, claiming that the Britons had aided the Veneti against him the previous year. He was more successful in 54 BC, but Britain was not fully established as part of the Roman Empire until completion of the invasion by Aulus Plautius
Aulus Plautius was a Roman politician and general of the mid-1st century. He began the Roman conquest of Britain in 43, and became the first governor of the new province, serving from 43 to 46 CE.
Career
Little is known of Aulus Plautius's e ...
in 43 AD. A brisk and regular trade began between ports in Roman Gaul and those in Britain. This traffic continued until the end of Roman rule in Britain in 410 AD, after which the early Anglo-Saxons left less clear historical records.
In the power vacuum left by the retreating Romans, the Germanic Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, Saxons, and Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
began the next great migration across the North Sea. Having already been used as mercenaries in Britain by the Romans, many people from these tribes crossed during the Migration Period, conquering and perhaps displacing the native Celtic populations.
Norsemen and Normans
 The attack on Lindisfarne in 793 is generally considered the beginning of the Viking Age. For the next 250 years the Scandinavian raiders of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark dominated the North Sea, raiding monasteries, homes, and towns along the coast and along the rivers that ran inland. According to the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' they began to settle in Britain in 851. They continued to settle in the British Isles and the continent until around 1050, with some raids recorded along the channel coast of England, including at Wareham, Portland, near Weymouth and along the river Teign in Devon.
The fiefdom of Normandy was created for the Viking leader
The attack on Lindisfarne in 793 is generally considered the beginning of the Viking Age. For the next 250 years the Scandinavian raiders of Norway, Sweden, and Denmark dominated the North Sea, raiding monasteries, homes, and towns along the coast and along the rivers that ran inland. According to the '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' they began to settle in Britain in 851. They continued to settle in the British Isles and the continent until around 1050, with some raids recorded along the channel coast of England, including at Wareham, Portland, near Weymouth and along the river Teign in Devon.
The fiefdom of Normandy was created for the Viking leader Rollo
Rollo ( nrf, Rou, ''Rolloun''; non, Hrólfr; french: Rollon; died between 928 and 933) was a Viking who became the first ruler of Normandy, today a region in northern France. He emerged as the outstanding warrior among the Norsemen who had se ...
(also known as Robert of Normandy). Rollo had besieged Paris but in 911 entered vassalage to the king of the West Franks Charles the Simple
Charles III (17 September 879 – 7 October 929), called the Simple or the Straightforward (from the Latin ''Carolus Simplex''), was the king of West Francia from 898 until 922 and the king of Lotharingia from 911 until 919–923. He was a mem ...
through the Treaty of St.-Claire-sur-Epte. In exchange for his homage and fealty, Rollo legally gained the territory he and his Viking allies had previously conquered. The name "Normandy" reflects Rollo's Viking (i.e. "Northman") origins.
The descendants of Rollo and his followers adopted the local Gallo-Romance language and intermarried with the area's inhabitants and became the Normans – a Norman French-speaking mixture of Scandinavians, Hiberno-Norse, Orcadians, Anglo-Danish, and indigenous Franks and Gauls.
 Rollo's descendant William, Duke of Normandy became king of England in 1066 in the Norman Conquest beginning with the Battle of Hastings, while retaining the fiefdom of Normandy for himself and his descendants. In 1204, during the reign of King John, mainland Normandy was taken from England by France under
Rollo's descendant William, Duke of Normandy became king of England in 1066 in the Norman Conquest beginning with the Battle of Hastings, while retaining the fiefdom of Normandy for himself and his descendants. In 1204, during the reign of King John, mainland Normandy was taken from England by France under Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
, while insular Normandy (the Channel Islands) remained under English control. In 1259, Henry III of England recognised the legality of French possession of mainland Normandy under the Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
. His successors, however, often fought to regain control of mainland Normandy.
With the rise of William the Conqueror the North Sea and Channel began to lose some of their importance. The new order oriented most of England and Scandinavia's trade south, toward the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
and the Orient.
Although the British surrendered claims to mainland Normandy and other French possessions in 1801, the monarch of the United Kingdom retains the title Duke of Normandy in respect to the Channel Islands. The Channel Islands (except for Chausey
Chausey () is a group of small islands, islets and rocks off the coast of Normandy, in the English Channel. It lies from Granville and forms a ''quartier'' of the Granville commune in the Manche ''département''. Chausey forms part of the Chan ...
) are Crown Dependencies of the British Crown. Thus the Loyal toast
A loyal toast is a salute given to the sovereign monarch or head of state of the country in which a formal gathering is being given, or by expatriates of that country, whether or not the particular head of state is present. It is usually a mat ...
in the Channel Islands is ''Le roi, notre Duc'' ("The King, our Duke"). The British monarch is understood to ''not'' be the Duke of Normandy in regards of the French region of Normandy described herein, by virtue of the Treaty of Paris of 1259, the surrender of French possessions in 1801, and the belief that the rights of succession to that title are subject to Salic Law which excludes inheritance through female heirs.
French Normandy was occupied by English forces during the Hundred Years' War in 1346–1360 and again in 1415–1450.
England and Britain: Naval superpower
 From the reign of Elizabeth I, English foreign policy concentrated on preventing invasion across the Channel by ensuring no major European power controlled the potential Dutch and Flemish invasion ports. Her climb to the pre-eminent sea power of the world began in 1588 as the attempted invasion of the Spanish Armada was defeated by the combination of outstanding naval tactics by the English and the Dutch under command of Charles Howard, 1st Earl of Nottingham with Sir Francis Drake second in command, and the following stormy weather. Over the centuries the
From the reign of Elizabeth I, English foreign policy concentrated on preventing invasion across the Channel by ensuring no major European power controlled the potential Dutch and Flemish invasion ports. Her climb to the pre-eminent sea power of the world began in 1588 as the attempted invasion of the Spanish Armada was defeated by the combination of outstanding naval tactics by the English and the Dutch under command of Charles Howard, 1st Earl of Nottingham with Sir Francis Drake second in command, and the following stormy weather. Over the centuries the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
slowly grew to be the most powerful in the world.
 The building of the British Empire was possible only because the
The building of the British Empire was possible only because the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
eventually managed to exercise unquestioned control over the seas around Europe, especially the Channel and the North Sea. During the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
, France attempted to launch an invasion of Britain. To achieve this France needed to gain control of the Channel for several weeks, but was thwarted following the British naval victory at the Battle of Quiberon Bay
The Battle of Quiberon Bay (known as ''Bataille des Cardinaux'' in French) was a decisive naval engagement during the Seven Years' War. It was fought on 20 November 1759 between the Royal Navy and the French Navy in Quiberon Bay, off the coast ...
in 1759 and was unsuccessful (The last French landing on English soil being in 1690 with a raid on Teignmouth, although the last French raid on British soil was a raid on Fishguard, Wales in 1797).
Another significant challenge to British domination of the seas came during the Napoleonic Wars. The Battle of Trafalgar took place off the coast of Spain against a combined French and Spanish fleet and was won by Admiral Horatio Nelson, ending Napoleon's plans for a cross-Channel invasion and securing British dominance of the seas for over a century.
First World War
The exceptional strategic importance of the Channel as a tool for blockading was recognised by the First Sea Lord Admiral Fisher in the years beforeWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. "Five keys lock up the world! Singapore, the Cape, Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, Gibraltar, Dover." However, on 25 July 1909 Louis Blériot made the first Channel crossing from Calais to Dover in an aeroplane. Blériot's crossing signalled a change in the function of the Channel as a barrier-moat for England against foreign enemies.
Because the ''Kaiserliche Marine
{{italic title
The adjective ''kaiserlich'' means "imperial" and was used in the German-speaking countries to refer to those institutions and establishments over which the ''Kaiser'' ("emperor") had immediate personal power of control.
The term wa ...
'' surface fleet could not match the British Grand Fleet, the Germans developed submarine warfare, which was to become a far greater threat to Britain. The Dover Patrol
The Dover Patrol and later known as the Dover Patrol Force was a Royal Navy command of the First World War, notable for its involvement in the Zeebrugge Raid on 22 April 1918. The Dover Patrol formed a discrete unit of the Royal Navy based at Dove ...
, set up just before the war started, escorted cross-Channel troopships and prevented submarines from sailing in the Channel, obliging them to travel to the Atlantic via the much longer route around Scotland.
On land, the German army attempted to capture French Channel ports in the Race to the Sea
The Race to the Sea (; , ) took place from about 1914 during the First World War, after the Battle of the Frontiers () and the German advance into France. The invasion had been stopped at the First Battle of the Marne and was followed by the ...
but although the trenches are often said to have stretched "from the frontier of Switzerland to the English Channel", they reached the coast at the North Sea. Much of the British war effort in Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
was a bloody but successful strategy to prevent the Germans reaching the Channel coast.
At the outset of the war, an attempt was made to block the path of U-boats through the Dover Strait with naval minefields. By February 1915, this had been augmented by a stretch of light steel netting called the Dover Barrage
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidston ...
, which it was hoped would ensnare submerged submarines. After initial success, the Germans learned how to pass through the barrage, aided by the unreliability of British mines. On 31 January 1917, the Germans restarted unrestricted submarine warfare leading to dire Admiralty predictions that submarines would defeat Britain by November, the most dangerous situation Britain faced in either world war.
The Battle of Passchendaele in 1917 was fought to reduce the threat by capturing the submarine bases on the Belgian coast, though it was the introduction of convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used ...
s and not capture of the bases that averted defeat. In April 1918 the Dover Patrol carried out the Zeebrugge Raid against the U-boat bases. During 1917, the Dover Barrage was re-sited with improved mines and more effective nets, aided by regular patrols by small warships equipped with powerful searchlights. A German attack on these vessels resulted in the Battle of Dover Strait in 1917. A much more ambitious attempt to improve the barrage, by installing eight massive concrete towers across the strait was called the Admiralty M-N Scheme
'The Admiralty M-N Scheme' (sometimes given as "Project M-N") was a World War I British plan to close the Strait of Dover in the English Channel to German U-boats, by means of a chain of either eight or twelve massive towers linked by anti-submar ...
but only two towers were nearing completion at the end of the war and the project was abandoned.
The naval blockade in the Channel and North Sea was one of the decisive factors in the German defeat in 1918.
Second World War
European theatre
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat during World War II. It saw heavy fighting across Europe for almost six years, starting with Germany's invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 and ending with the ...
was primarily limited to the Atlantic. During the Battle of France in May 1940, the German forces succeeded in capturing both Boulogne and Calais, thereby threatening the line of retreat for the British Expeditionary Force. By a combination of hard fighting and German indecision, the port of Dunkirk was kept open allowing 338,000 Allied troops to be evacuated in Operation Dynamo. More than 11,000 were evacuated from Le Havre during Operation Cycle and a further 192,000 were evacuated from ports further down the coast in Operation Aerial
Operation Aerial was the evacuation of Allied forces and civilians from ports in western France from 15 to 25 June 1940 during the Second World War. The evacuation followed the Allied military collapse in the Battle of France against Nazi Germ ...
in June 1940. The early stages of the Battle of Britain featured German air attacks on Channel shipping and ports; despite these early successes against shipping the Germans did not win the air supremacy
Aerial supremacy (also air superiority) is the degree to which a side in a conflict holds control of air power over opposing forces. There are levels of control of the air in aerial warfare. Control of the air is the aerial equivalent of comm ...
necessary for Operation Sealion
Operation Sea Lion, also written as Operation Sealion (german: Unternehmen Seelöwe), was Nazi Germany's code name for the plan for an invasion of the United Kingdom during the Battle of Britain in the Second World War. Following the Battle o ...
, the projected cross-Channel invasion.
The Channel subsequently became the stage for an intensive coastal war, featuring submarines, minesweepers
A minesweeper is a small warship designed to remove or detonate naval mines. Using various mechanisms intended to counter the threat posed by naval mines, minesweepers keep waterways clear for safe shipping.
History
The earliest known usage of ...
, and Fast Attack Craft.
The narrow waters of the Channel were considered too dangerous for major warships until the Normandy Landings
The Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and ...
with the exception, for the German Kriegsmarine, of the Channel Dash
The Channel Dash (german: Unternehmen Zerberus, Operation Cerberus) was a German naval operation during the Second World War. ( Cerberus), a three-headed dog of Greek mythology who guards the gate to Hades. A (German Navy) squadron comprisin ...
(Operation Cerberus) in February 1942, and this required the support of the Luftwaffe in Operation Thunderbolt.


Dieppe
Dieppe (; Norman: ''Dgieppe'') is a coastal commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France.
Dieppe is a seaport on the English Channel at the mouth of the river Arques. A regular ferry service runs to N ...
was the site of an ill-fated Dieppe Raid by Canadian and British armed forces. More successful was the later Operation Overlord ( D-Day), a massive invasion of German-occupied France by Allied troops. Caen, Cherbourg, Carentan, Falaise and other Norman towns endured many casualties in the fight for the province, which continued until the closing of the so-called Falaise gap between Chambois and Montormel, then liberation of Le Havre.
The Channel Islands were the only part of the British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
occupied by Germany (excepting the part of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
occupied by the Afrika Korps
The Afrika Korps or German Africa Corps (, }; DAK) was the German expeditionary force in Africa during the North African Campaign of World War II. First sent as a holding force to shore up the Italian defense of its African colonies, the ...
at the time of the Second Battle of El Alamein
The Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October – 11 November 1942) was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa had prevented th ...
, which was a protectorate and not part of the Commonwealth). The German occupation of 1940–1945 was harsh, with some island residents being taken for slave labour on the Continent; native Jews sent to concentration camps
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply ...
; partisan resistance and retribution; accusations of collaboration; and slave labour (primarily Russians and eastern Europeans) being brought to the islands to build fortifications. The Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
blockaded the islands from time to time, particularly following the liberation of mainland Normandy in 1944. Intense negotiations resulted in some Red Cross humanitarian aid, but there was considerable hunger and privation during the occupation, particularly in the final months, when the population was close to starvation. The German troops on the islands surrendered on 9 May 1945, a day after the final surrender in mainland Europe.
Population
The English Channel coast is far more densely populated on the English shore. The most significant towns and cities along both the English and French sides of the Channel (each with more than 20,000 inhabitants, ranked in descending order; populations are the urban area populations from the 1999 French census, 2001 UK census, and 2001 Jersey census) are as follows:England
 * Brighton– Worthing–
* Brighton– Worthing–Littlehampton
Littlehampton is a town, seaside resort, and pleasure harbour, and the most populous civil parish in the Arun District of West Sussex, England. It lies on the English Channel on the eastern bank of the mouth of the River Arun. It is south sout ...
: 461,181 inhabitants, made up of:
** Brighton: 155,919
** Worthing: 96,964
** Hove: 72,335
** Littlehampton
Littlehampton is a town, seaside resort, and pleasure harbour, and the most populous civil parish in the Arun District of West Sussex, England. It lies on the English Channel on the eastern bank of the mouth of the River Arun. It is south sout ...
: 55,716
** Lancing–Sompting
Sompting is a village and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the coastal Adur (district), Adur District of West Sussex, England between Lancing, West Sussex, Lancing and Worthing. It is half grassland slopes and half developed plain at ...
: 30,360
* Portsmouth: 442,252, including
** Gosport: 79,200
* Bournemouth & Poole: 383,713
* Southampton: 304,400
* Plymouth: 258,700
* Torbay
Torbay is a borough and unitary authority in Devon, south west England. It is governed by Torbay Council and consists of of land, including the resort towns of Torquay, Paignton and Brixham, located on east-facing Tor Bay, part of Lyme ...
( Torquay): 129,702
* Hastings– Bexhill: 126,386
* Exeter: 119,600
* Eastbourne: 106,562
* Bognor Regis
Bognor Regis (), sometimes simply known as Bognor (), is a town and seaside resort in West Sussex on the south coast of England, south-west of London, west of Brighton, south-east of Chichester and east of Portsmouth. Other nearby towns i ...
: 62,141
* Folkestone– Hythe: 60,039
* Weymouth: 56,043
* Dover: 39,078
* Walmer
Walmer is a town in the district of Dover, Kent, in England. Located on the coast, the parish of Walmer is south-east of Sandwich, Kent. Largely residential, its coastline and castle attract many visitors. It has a population of 6,693 (2001), i ...
– Deal: 35,941
* Exmouth: 32,972
* Falmouth– Penryn: 28,801
* Ryde: 22,806
* St Austell: 22,658
* Seaford: 21,851
* Falmouth: 21,635
* Penzance: 20,255
France
 * Le Havre: 248,547 inhabitants
* Calais: 104,852
* Saint-Malo: 50,675
*
* Le Havre: 248,547 inhabitants
* Calais: 104,852
* Saint-Malo: 50,675
* Lannion
Lannion ( ; ) is a commune in the Côtes-d'Armor department in Brittany in northwestern France. It is a subprefecture of Côtes-d'Armor, the capital of Trégor and the center of an urban area of almost 60,000 inhabitants.
Climate
Lannion ha ...
– Perros-Guirec: 48,990
* Saint-Brieuc: 45,879
* Boulogne-sur-Mer: 42,537
* Cherbourg: 42,318
* Dieppe
Dieppe (; Norman: ''Dgieppe'') is a coastal commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France.
Dieppe is a seaport on the English Channel at the mouth of the river Arques. A regular ferry service runs to N ...
: 42,202
* Morlaix
Morlaix (; br, Montroulez) is a commune in the Finistère department of Brittany in northwestern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department.
Leisure and tourism
The old quarter of the town has winding streets of cobbled stones and overha ...
: 35,996
* Dinard
Dinard (; br, Dinarzh, ; Gallo: ''Dinard'') is a commune in the Ille-et-Vilaine department, Brittany, northwestern France.
Dinard is on the Côte d'Émeraude of Brittany. Its beaches and mild climate make it a holiday destination, and this ...
: 25,006
* Étaples– Le Touquet-Paris-Plage: 23,994
* Fécamp
Fécamp () is a commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region in north-western France.
Geography
Fécamp is situated in the valley of the river Valmont, at the heart of the Pays de Caux, on the Alabaster Coast. It is aroun ...
: 22,717
* Eu– Le Tréport: 22,019
* Trouville-sur-Mer–Deauville
Deauville () is a commune in the Calvados department, Normandy, northwestern France. Major attractions include its harbour, race course, marinas, conference centre, villas, Grand Casino, and sumptuous hotels. The first Deauville Asian Film F ...
: 20,406
Channel Islands
*Saint Helier
St Helier (; Jèrriais: ; french: Saint-Hélier) is one of the twelve parishes of Jersey, the largest of the Channel Islands in the English Channel. St Helier has a population of 35,822 – over one-third of the total population of Jersey – ...
, Jersey: 28,310 inhabitants
* Saint Peter Port
St. Peter Port (french: Saint-Pierre Port) is a town and one of the ten parishes on the island of Guernsey in the Channel Islands. It is the capital of the Bailiwick of Guernsey as well as the main port. The population in 2019 was 18,958.
St. ...
, Guernsey: 16,488 inhabitants
* Saint Anne, Alderney: 2,200 inhabitants
* Sark
Sark (french: link=no, Sercq, ; Sercquiais: or ) is a part of the Channel Islands in the southwestern English Channel, off the coast of Normandy, France. It is a royal fief, which forms part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, with its own set of ...
: 600 inhabitants
* Herm: 60 inhabitants
Culture and languages
 The two dominant cultures are English on the north shore of the Channel, French on the south. However, there are also a number of minority languages that are or were found on the shores and islands of the English Channel, which are listed here, with the Channel's name in the specific language following them.
;Celtic Languages
: br, Mor Breizh, Sea of Brittany
: kw, Mor Bretannek
: ga, Muir nIocht, Merciful Sea
;Germanic languages
: English
: nl, het Kanaal, the Channel. (Dutch previously had a larger range, and extended into parts of modern-day France as
The two dominant cultures are English on the north shore of the Channel, French on the south. However, there are also a number of minority languages that are or were found on the shores and islands of the English Channel, which are listed here, with the Channel's name in the specific language following them.
;Celtic Languages
: br, Mor Breizh, Sea of Brittany
: kw, Mor Bretannek
: ga, Muir nIocht, Merciful Sea
;Germanic languages
: English
: nl, het Kanaal, the Channel. (Dutch previously had a larger range, and extended into parts of modern-day France as French Flemish
French Flemish (French Flemish: , Standard Dutch: , french: flamand français) is a West Flemish dialect spoken in the north of contemporary France. Place names attest to Flemish having been spoken since the 8th century in the part of Fland ...
.)
;Romance languages
: french: La Manche
: Gallo: ''Manche'', ''Grand-Mè'', ''Mè Bertone''
: Norman, including the Channel Island vernaculars:
:* Anglo-Norman (extinct, but fossilised in certain English law phrases)
:* Auregnais
Auregnais, Aoeur'gnaeux, or Aurignais was the Norman dialect of the Channel Island of Alderney (french: Aurigny, Auregnais: ''aoeur'gny'' or ''auregny''). It was closely related to the Guernésiais (Guernsey), Jèrriais ( Jersey), and Sercqui ...
(extinct)
:* Cotentinais
Cotentinais is the dialect of the Norman language spoken in the Cotentin Peninsula of France. It is one of the strongest dialects of the language on the mainland.
Dialects
Due to the relative lack of standardisation of Norman, there are five ...
: ''Maunche''
:* Guernésiais
Guernésiais, also known as ''Dgèrnésiais'', Guernsey French, and Guernsey Norman French, is the variety of the Norman language spoken in Guernsey. It is sometimes known on the island simply as "patois". As one of the langues d'oïl, it has it ...
:
:* Jèrriais:
:* Sercquais
: Picard
Most other languages tend towards variants of the French and English forms, but notably Welsh has .
Economy
Shipping
The Channel has traffic on both the UK–Europe and North Sea–Atlantic routes, and is the world's busiest seaway, with over 500 ships per day. Following an accident in January 1971 and a series of disastrous collisions with wreckage in February, the Dover TSS, the world's first radar-controlled traffic separation scheme, was set up by the International Maritime Organization. The scheme mandates that vessels travelling north must use the French side, travelling south the English side. There is a separation zone between the two lanes. In December 2002 the MV ''Tricolor'', carrying £30m of luxury cars, sank northwest of Dunkirk after collision in fog with the container ship ''Kariba''. The cargo ship ''Nicola'' ran into the wreckage the next day. There was no loss of life. The shore-based long-range traffic control system was updated in 2003 and there is a series of traffic separation systems in operation. Though the system is inherently incapable of reaching the levels of safety obtained from aviation systems such as the traffic collision avoidance system, it has reduced accidents to one or two per year.
Marine
The shore-based long-range traffic control system was updated in 2003 and there is a series of traffic separation systems in operation. Though the system is inherently incapable of reaching the levels of safety obtained from aviation systems such as the traffic collision avoidance system, it has reduced accidents to one or two per year.
Marine GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
systems allow ships to be preprogrammed to follow navigational channels accurately and automatically, further avoiding risk of running aground, but following the fatal collision between Dutch Aquamarine and Ash in October 2001, Britain's Marine Accident Investigation Branch
The Marine Accident Investigation Branch (MAIB) is a UK government organisation, authorised to investigate all maritime accidents in UK waters and accidents involving UK registered ships worldwide. Investigations are limited to establishing cau ...
(MAIB) issued a safety bulletin saying it believed that in these most unusual circumstances GPS use had actually contributed to the collision. The ships were maintaining a very precise automated course, one directly behind the other, rather than making use of the full width of the traffic lanes as a human navigator would.
A combination of radar difficulties in monitoring areas near cliffs, a failure of a CCTV system, incorrect operation of the anchor, the inability of the crew to follow standard procedures of using a GPS to provide early warning of the ship dragging the anchor and reluctance to admit the mistake and start the engine led to the MV ''Willy'' running aground in Cawsand Bay
Cawsand Bay is a bay on the southeast coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom.
The bay takes its name from the village of Cawsand at , to the northeast of the Rame Peninsula. Cawsand Bay is oriented north–south, opening eastward into Pl ...
, Cornwall, in January 2002. The MAIB report makes it clear that the harbour controllers were informed of impending disaster by shore observers before the crew were themselves aware. The village of Kingsand
Kingsand ( kw, Porthruw) and Cawsand are twin villages in southeast Cornwall, United Kingdom.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 201 ''Plymouth & Launceston'' The villages are situated on the Rame Peninsula and are in the parish of Maker-w ...
was evacuated for three days because of the risk of explosion, and the ship was stranded for 11 days.
Ferry
 The ferry routes crossing the English Channel, include (have included):-
* Dover– Calais
* Dover– Dunkirk
* Newhaven–
The ferry routes crossing the English Channel, include (have included):-
* Dover– Calais
* Dover– Dunkirk
* Newhaven–Dieppe
Dieppe (; Norman: ''Dgieppe'') is a coastal commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France.
Dieppe is a seaport on the English Channel at the mouth of the river Arques. A regular ferry service runs to N ...
* Plymouth–Roscoff
Roscoff (; br, Rosko) is a commune in the Finistère département of Brittany in northwestern France.
Roscoff is renowned for its picturesque architecture, labelled (small town of character) since 2009. Roscoff is also a traditional departure ...
* Poole– Cherbourg
* Poole– Jersey and Guernsey
* Poole–Saint Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany, on the English Channel coast.
The walled city had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth from local extortion and overseas adventures. In 1944, the Alli ...
* Portsmouth–Cherbourg
* Portsmouth–Jersey and Guernsey
* Portsmouth– Le Havre
* Portsmouth– Ouistreham
* Portsmouth–Saint Malo
* Rosslare–Cherbourg
* Rosslare–Roscoff
* Weymouth–Saint Malo
*Brighton Marina to Dieppe (using the SeaJet for a 100 minute crossing)
Channel Tunnel
Many travellers cross beneath the Channel using the Channel Tunnel, first proposed in the early 19th century and finally opened in 1994, connecting the UK and France by rail. It is now routine to travel between Paris or Brussels and London on theEurostar
Eurostar is an international high-speed rail service connecting the United Kingdom with France, Belgium and the Netherlands. Most Eurostar trains travel through the Channel Tunnel between the United Kingdom and France, owned and operate ...
train. Freight trains also use the tunnel. Cars, coaches and lorries are carried on Eurotunnel Shuttle
Eurotunnel Le Shuttle (sometimes shortened to Le Shuttle or The Shuttle) is a railway shuttle service between Coquelles (near Calais) in Pas-de-Calais, France and Cheriton (near Folkestone) in Kent, United Kingdom. It conveys road vehicl ...
trains between Folkestone and Calais.
Tourism
 The coastal resorts of the Channel, such as Brighton and
The coastal resorts of the Channel, such as Brighton and Deauville
Deauville () is a commune in the Calvados department, Normandy, northwestern France. Major attractions include its harbour, race course, marinas, conference centre, villas, Grand Casino, and sumptuous hotels. The first Deauville Asian Film F ...
, inaugurated an era of aristocratic tourism in the early 19th century. Short trips across the Channel for leisure purposes are often referred to as Channel Hopping.
Renewable energy
The Rampion Wind Farm is an offshore wind farm located in the Channel, off the coast of West Sussex. Other offshore wind farms planned on the French side of the Channel.History of Channel crossings
As one of the narrowest and most well-known international waterways lacking dangerous currents, the Channel has been the first objective of numerous innovative sea, air, and human powered crossing technologies. Pre-historic people sailed from the mainland to England for millennia. At the end of the last Ice Age, lower sea levels even permitted walking across.By boat
Pierre Andriel crossed the English Channel aboard the ''Élise
Élise, Elise, Elyse or Elize is the shortened feminine French form of Elizabeth, coming originally from the Hebrew name אלישבע (אלי = My God שבע = oath) and meaning "My God is an oath" or "My God is abundance".
People Élise
* Él ...
'', ex the Scottish p.s. "Margery" in March 1816, one of the earliest seagoing voyages by steam ship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
.
The paddle steamer ''Defiance'', Captain William Wager, was the first steamer to cross the Channel to Holland, arriving there on 9 May 1816.
On 10 June 1821, English-built paddle steamer ''Rob Roy'' was the first passenger ferry to cross channel. The steamer was purchased subsequently by the French postal administration and renamed ''Henri IV'' and put into regular passenger service a year later. It was able to make the journey across the Straits of Dover in around three hours.
In June 1843, because of difficulties with Dover harbour, the South Eastern Railway company developed the Boulogne-sur-Mer- Folkestone route as an alternative to Calais-Dover. The first ferry crossed under the command of Captain Hayward.
In 1974 a Welsh coracle piloted by Bernard Thomas of Llechryd crossed the English Channel to France in 13 hours. The journey was undertaken to demonstrate how the Bull Boats of the Mandan Indians of North Dakota could have been copied from coracles introduced by Prince Madog in the 12th century.
The Mountbatten class hovercraft (MCH) entered commercial service in August 1968, initially between Dover and Boulogne but later also Ramsgate ( Pegwell Bay) to Calais. The journey time Dover to Boulogne was roughly 35 minutes, with six trips per day at peak times. The fastest crossing of the English Channel by a commercial car-carrying hovercraft was 22 minutes, recorded by the ''Princess Anne'' MCH SR-N4 Mk3 on 14 September 1995,
By air
The first aircraft to cross the Channel was a balloon in 1785, piloted by Jean Pierre François Blanchard (France) and John Jeffries (US).Blanchard, Jean-Pierre-François." '' Encyclopædia Britannica'' Online. Retrieved 17 October 2009. Louis Blériot (France) piloted the first airplane to cross in 1909. On 26 September 2008, Swiss
Yves Rossy
Yves Rossy (born 27 August 1959) is a Swiss military-trained pilot and an aviation enthusiast. He is known as the inventor of a series of experimental individual jet packs, the latest using carbon-fiber wings for flight. Often referred to as " ...
aka ''Jetman'' became the first person to cross the English Channel with a Jet Powered Wing,
He jumped from a Pilatus Porter over Calais, France, Rossy crossed the English Channel where he deployed his parachute and landed in Dover
The first flying car to have crossed the English Channel is a Pégase designed by the French company Vaylon on 14 June 2017. It was piloted by a Franco-Italian pilot Bruno Vezzoli. This crossing was carried out as part of the first road and air trip from Paris to London in a flying car. Pegase is a 2 seats road approved dune buggy and a powered paraglider
Powered paragliding, also known as paramotoring or PPG, is a form of ultralight aviation where the pilot wears a back-pack motor (a paramotor) which provides enough thrust to take off using a paraglider. It can be launched in still air, and ...
. The takeoff was at 8:03 a.m. from Ambleteuse
Ambleteuse (; vls, Ambeltuwe) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in northern France.
History
Ambleteuse began as a hamlet of a few huts in the middle of the dunes, from which the derisory name of “carcahuttes" (huts made from old-b ...
in the North of France and landing was at East Studdal, near Dover. The flight was completed in 1 hour and 15 minutes for a total distance covered of including over the English Channel at an altitude of .
On 12 June 1979, the first human-powered aircraft to cross the English Channel was the '' Gossamer Albatross'', built by American aeronautical engineer
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is sim ...
Dr. Paul B. MacCready's company AeroVironment, and piloted by Bryan Allen. The crossing was completed in 2 hours and 49 minutes.
On 4 August 2019, Frenchman Franky Zapata
Franky Zapata (; born 27 September 1978) is a French personal watercraft pilot who is the inventor of the Flyboard and Flyboard Air, and founder of Zapata Racing. Since 2012, Zapata's efforts have been focused on the development and manufacture ...
became the first person to cross the English Channel on a jet-powered Flyboard Air
Flyboard Air is a type of jetpack/ hoverboard powered by gas turbines. It was invented by French water-craft rider Franky Zapata, founder of Zapata racing.
It achieved a Guinness World Record for farthest flight by hoverboard in April 2016 of ...
. The board was powered by a kerosene-filled backpack. Zapata made the journey in 22 minutes, having landed on a boat half-way across to refuel.
By swimming
The sport of Channel swimming traces its origins to the latter part of the 19th century when Captain Matthew Webb made the first observed and unassisted swim across the Strait of Dover, swimming from England to France on 24–25 August 1875 in 21 hours 45 minutes. Up to 1927, fewer than ten swimmers (including the first woman,Gertrude Ederle
Gertrude Caroline Ederle (October 23, 1906 – November 30, 2003) was an American competition swimmer, Olympic champion, and world record-holder in five events. On August 6, 1926, she became the first woman to swim across the English Channel. ...
in 1926) had managed to successfully swim the English Channel, and many dubious claims had been made. The Channel Swimming Association (CSA) was founded to authenticate and ratify swimmers' claims to have swum the Channel and to verify crossing times. The CSA was dissolved in 1999 and was succeeded by two separate organisations: CSA Ltd (CSA) and the Channel Swimming and Piloting Federation (CSPF), both observe and authenticate cross-Channel swims in the Strait of Dover. The Channel Crossing Association was also set up to cater for unorthodox crossings.
The team with the most Channel swims to its credit is the Serpentine Swimming Club in London, followed by the international Sri Chinmoy
Chinmoy Kumar Ghose (27 August 1931 – 11 October 2007), better known as Sri Chinmoy, was an Indian spiritual leader who taught meditation in the West after moving to New York City in 1964.nexceptional cases the French Maritime Authorities may grant authority for unorthodox craft to cross French territorial waters within the Traffic Separation Scheme when these craft set off from the British coast, on condition that the request for authorisation is sent to them with the opinion of the British Maritime Authorities."
The fastest verified swim of the Channel was by the Australian Trent Grimsey on 8 September 2012, in 6 hours 55 minutes, beating the previous record set in 2007 by Bulgarian swimmer Petar Stoychev.
There may have been some unreported swims of the Channel, by people intent on entering Britain in circumvention of immigration controls. A failed attempt to cross the Channel by two Syrian refugees in October 2014 came to light when their bodies were discovered on the shores of the North Sea in Norway and the Netherlands.
Full Channel swim lists and swimmer information
Oceanus Britannicus or British Sea
Channel swimmers website
Archives of long distance swimming
Channel Swimming and Piloting Federation
Channel Swimming Association
Air Battle over the English Channel (1940) {{Authority control English coast European seas France–United Kingdom border Geography of Northwestern Europe Landforms of Brittany Landforms of Normandy Landforms of Hauts-de-France Marginal seas of the Atlantic Ocean Bodies of water of the North Sea Bays of England Bays of Metropolitan France Southern England
By car
On 16 September 1965, twoAmphicar
The Amphicar Model 770 is an amphibious automobile which was launched at the 1961 New York Auto Show, manufactured in West Germany and marketed from 1961 to 1968. Production stopped in 1965.
Designed by Hans Trippel, the amphibious vehicle ...
s crossed from Dover to Calais.Autocar article entitled Cars Ahoy published 10 December 1965
Other types
PLUTO was war-time fuel delivery project of "pipelines under the ocean" from England to France. Though plagued with technical difficulties during the Battle of Normandy, the pipelines delivered about 8% of the fuel requirements of the allied forces between D-Day and VE-Day.See also
* English Channel migrant crossings (2018–present) * France–UK border * Anguilla Channel * Booze cruise *Guadeloupe Passage
The Guadeloupe Passage is a strait in the Caribbean. It separates Guadeloupe from Montserrat and from Antigua and Barbuda.
* Invasions of the British Isles
* List of firsts in aviation
* Phoenix breakwaters
The Phoenix breakwaters were a set of reinforced concrete caissons built as part of the artificial Mulberry harbours that were assembled as part of the preparations for the Normandy landings during World War II. They were constructed by civil eng ...
Explanatory notes
References
External links
Full Channel swim lists and swimmer information
Oceanus Britannicus or British Sea
Channel swimmers website
Archives of long distance swimming
Channel Swimming and Piloting Federation
Channel Swimming Association
Air Battle over the English Channel (1940) {{Authority control English coast European seas France–United Kingdom border Geography of Northwestern Europe Landforms of Brittany Landforms of Normandy Landforms of Hauts-de-France Marginal seas of the Atlantic Ocean Bodies of water of the North Sea Bays of England Bays of Metropolitan France Southern England