England–Wales Border on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The England–Wales border ( cy, Y ffin rhwng Cymru a Lloegr; shortened: Ffin Cymru a Lloegr), sometimes referred to as the Wales–England border or the Anglo-Welsh border, runs for from the


 The modern boundary between Wales and England runs from the
The modern boundary between Wales and England runs from the
 Before and during the
Before and during the
 During the Roman occupation, the tribes of Wales (
During the Roman occupation, the tribes of Wales (

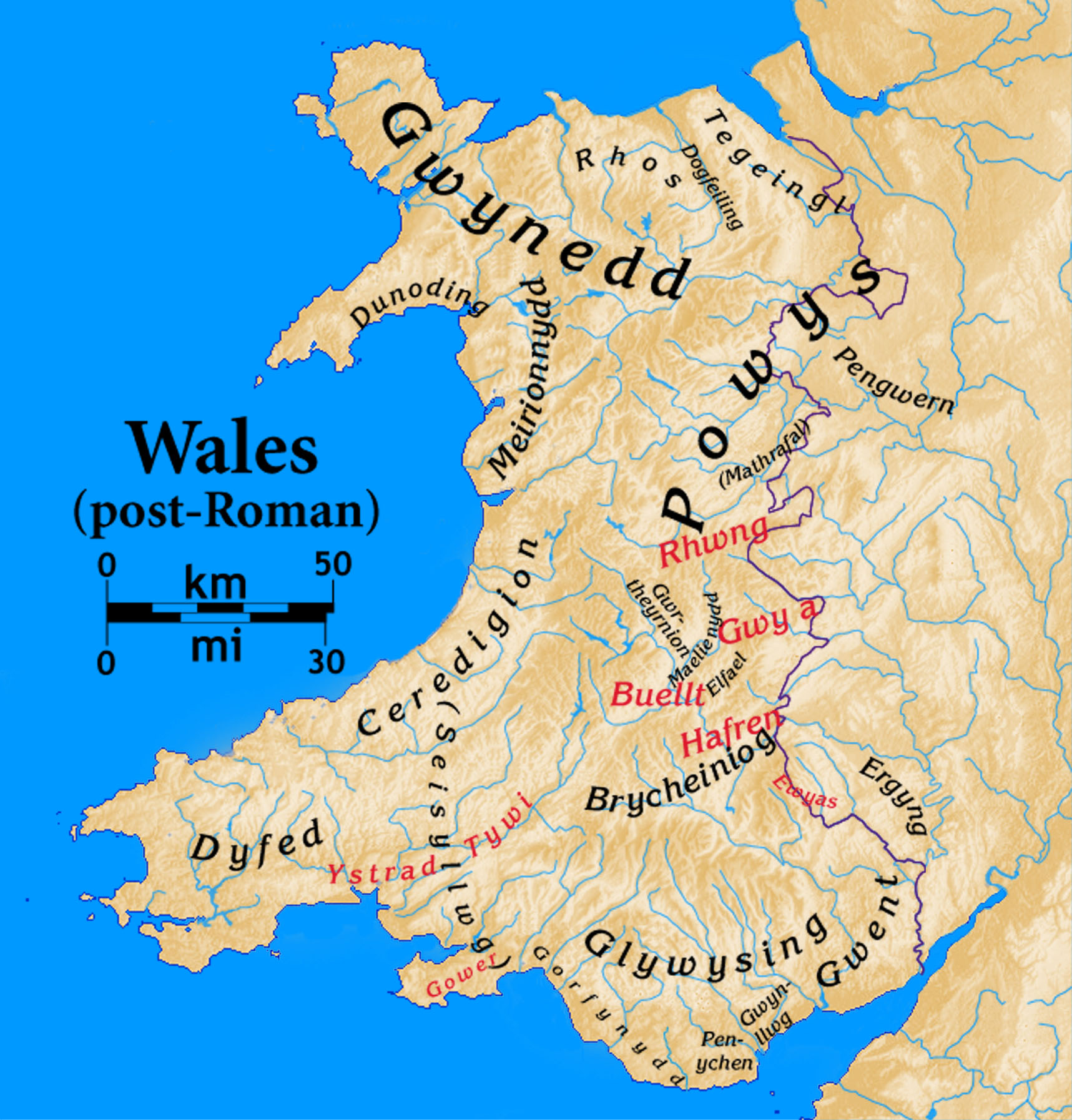 The
The
 After
After
 Immediately after the
Immediately after the 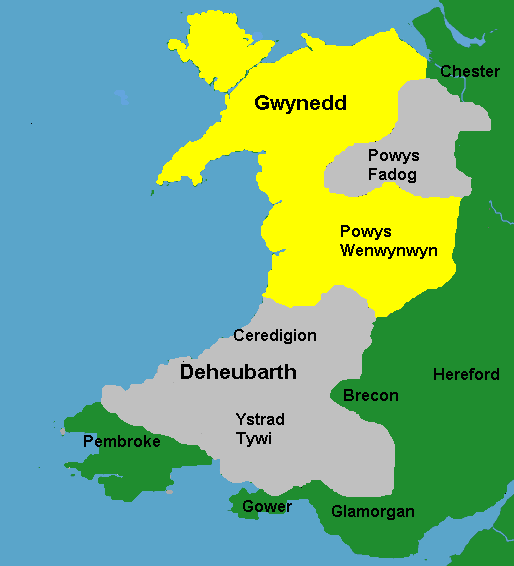 The Marches, or ''Marchia Wallia'', were to a greater or lesser extent independent of both the English monarchy and the
The Marches, or ''Marchia Wallia'', were to a greater or lesser extent independent of both the English monarchy and the
 The first legislation applying solely to Wales since the 16th century was passed in 1881. Subsequently, the border between England and Wales has taken on increasing legal and political significance.
Until the Welsh Disestablishment in 1920, the
The first legislation applying solely to Wales since the 16th century was passed in 1881. Subsequently, the border between England and Wales has taken on increasing legal and political significance.
Until the Welsh Disestablishment in 1920, the
 The Lost Lands of Wales was a minor political idea of the mid-1960s which called into question the status of areas along the east side of the England–Wales border, which its proponents regarded as Welsh. The idea related to parts of the counties of
The Lost Lands of Wales was a minor political idea of the mid-1960s which called into question the status of areas along the east side of the England–Wales border, which its proponents regarded as Welsh. The idea related to parts of the counties of
 In general, placenames of Welsh origin are found to the west of the border, and those of English origin to the east. However, many historically Welsh names are also found east of the border, particularly around
In general, placenames of Welsh origin are found to the west of the border, and those of English origin to the east. However, many historically Welsh names are also found east of the border, particularly around
Dee estuary
The Dee Estuary ( cy, Aber Dyfrdwy) is a large estuary by means of which the River Dee flows into Liverpool Bay. The estuary starts near Shotton after a five-mile (8 km) 'canalised' section and the river soon swells to be several mile ...
, in the north, to the Severn estuary
The Severn Estuary ( cy, Aber Hafren) is the estuary of the River Severn, flowing into the Bristol Channel between South West England and South Wales. Its high tidal range, approximately , means that it has been at the centre of discussions in t ...
in the south, separating England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
.
It has followed broadly the same line since the 8th century, and in part that of Offa's Dyke
Offa's Dyke ( cy, Clawdd Offa) is a large linear earthwork that roughly follows the border between England and Wales. The structure is named after Offa, the Anglo-Saxon king of Mercia from AD 757 until 796, who is traditionally believed to ha ...
; the modern boundary was fixed in 1536, when the former marcher lord
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in ...
ships which occupied the border area were abolished and new county
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
boundaries were created. The administrative boundary of Wales was confirmed in the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
. Whether Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire ( cy, Sir Fynwy) is a county in the south-east of Wales. The name derives from the historic county of the same name; the modern county covers the eastern three-fifths of the historic county. The largest town is Abergavenny, wit ...
was part of Wales, or an English county treated for most purposes as though it were Welsh, was also settled by the 1972 Act, which included it in Wales.
Geography

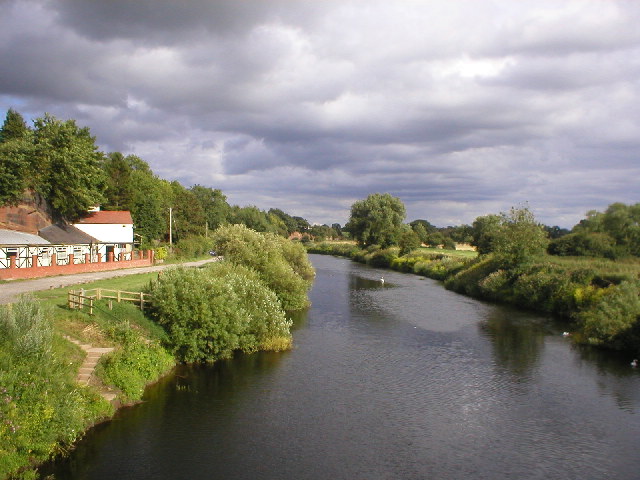
 The modern boundary between Wales and England runs from the
The modern boundary between Wales and England runs from the salt marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is domin ...
es of the Dee estuary adjoining the Wirral Peninsula
Wirral (; ), known locally as The Wirral, is a peninsula in North West England. The roughly rectangular peninsula is about long and wide and is bounded by the River Dee to the west (forming the boundary with Wales), the River Mersey to ...
, across reclaimed land to the River Dee at Saltney just west of Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
. It then loops south to include within England an area southwest of Chester, before rejoining the Dee, and then loops east of the river to include within Wales a large area known as Maelor, formerly an exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
of Flintshire
, settlement_type = County
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_shield = Arms of Flint ...
, between Bangor-on-Dee (in Wales) and Whitchurch, Shropshire
Whitchurch is a market town in the north of Shropshire, England. It lies east of the Welsh border, 2 miles south of the Cheshire border, north of the county town of Shrewsbury, south of Chester, and east of Wrexham. At the 2011 Census, the ...
(in England). Returning to the River Dee as far as Chirk
Chirk ( cy, Y Waun) is a town and community in Wrexham County Borough, Wales, south of Wrexham, between it and Oswestry. At the 2011 census, it had a population of 4,468. Historically in the traditional county of Denbighshire, and later Clw ...
, the boundary then loops to the west, following Offa's Dyke itself for about , and including within England the town of Oswestry
Oswestry ( ; ) is a market town, civil parish and historic railway town in Shropshire, England, close to the Welsh border. It is at the junction of the A5, A483 and A495 roads.
The town was the administrative headquarters of the Borough ...
, before reaching the River Vyrnwy
The River Vyrnwy ( cy, Afon Efyrnwy, ) is a river which flows through northern Powys, Wales, and Shropshire, England. The name derives from Severn, the river of which it is a tributary.
Course
The river used to be sourced from the many rivers ...
at Llanymynech
Llanymynech is a village straddling the border between Montgomeryshire/ Powys, Wales, and Shropshire, England, about 9 miles (14 km) north of the Welsh town of Welshpool. The name is Welsh for "Church of the Monks". The village is on the ...
. It follows the Vyrnwy to its confluence with the River Severn
, name_etymology =
, image = SevernFromCastleCB.JPG
, image_size = 288
, image_caption = The river seen from Shrewsbury Castle
, map = RiverSevernMap.jpg
, map_size = 288
, map_c ...
, and then continues southwards, rising over Long Mountain east of Welshpool
Welshpool ( cy, Y Trallwng) is a market town and community in Powys, Wales, historically in the county of Montgomeryshire. The town is from the Wales–England border and low-lying on the River Severn; its Welsh language name ''Y Trallwng'' m ...
. East of Montgomery, the boundary again follows the line of Offa's Dyke for about , before looping eastwards to include within Wales a large area near Churchstoke
Churchstoke or Church Stoke ( cy, Yr Ystog) is a village, community and electoral ward in Montgomeryshire, Powys, Wales. Located in the southeast of the Vale of Montgomery, it is overlooked by Todleth Hill, Roundton Hill and Corndon Hill. The ...
including Corndon Hill. It then runs westwards to the River Teme
The River Teme (pronounced ; cy, Afon Tefeidiad) rises in Mid Wales, south of Newtown, and flows southeast roughly forming the border between England and Wales for several miles through Knighton before entering England in the vicinity of B ...
, and follows the river southeastwards through Knighton before turning south towards the River Lugg
The River Lugg ( cy, Afon Llugwy) rises near Llangynllo in Radnorshire, Wales. It flows through the border town of Presteigne and then through Herefordshire, England, where it meets its main tributary, the River Arrow, to the south of Leomi ...
at Presteigne
Presteigne (; cy, Llanandras: the church of St. Andrew) is a town and community in Radnorshire, Powys, Wales on the south bank of the River Lugg. Formerly the county town of the historic county of Radnorshire, the town has, in common with ...
, which is within Wales.
The boundary continues southwards across hills to the River Wye
The River Wye (; cy, Afon Gwy ) is the fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn estuary. For much of its length the river forms part of the border between England and Wales ...
, and follows the river upstream for a short distance to Hay-on-Wye
Hay-on-Wye ( cy, Y Gelli Gandryll), simply known locally as "Hay" ( cy, Y Gelli), is a market town and community in Powys, Wales; it was historically in the county of Brecknockshire. With over twenty bookshops, it is often described as "the to ...
, on the Welsh side of the border. It continues southwards and rises through and across the Black Mountains, following the Hatterall Ridge past Llanthony
Llanthony (, cy, Llanddewi Nant Honddu ) is a village in the community of Crucorney on the northern edge of Monmouthshire, South East Wales, United Kingdom.
Location
Llanthony is located in the Vale of Ewyas, a deep and long valley with ...
on the Welsh side and Longtown, Herefordshire
Longtown is a linear village and parish in Herefordshire, England. The parish includes the village of Clodock and had a population in mid-2010 of 543, increasing to 620 at the 2011 Census.
Location
Longtown is located north east of Abergaven ...
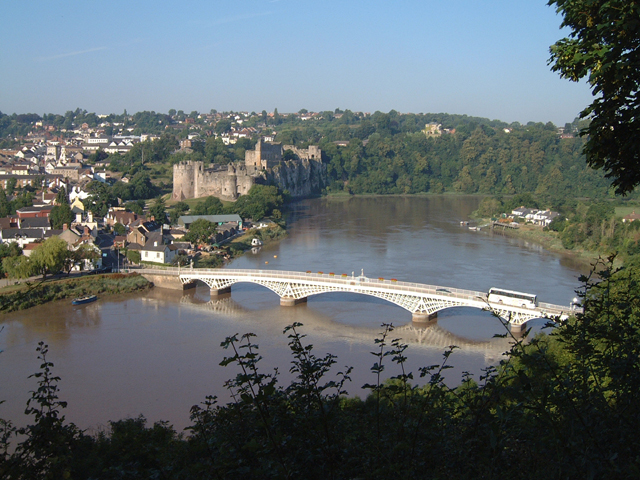
on the English side, to reach the River Monnow near Pandy. It then generally follows the river, past Pontrilas (in England) and Skenfrith (in Wales), towards Monmouth
Monmouth ( , ; cy, Trefynwy meaning "town on the Monnow") is a town and community in Wales. It is situated where the River Monnow joins the River Wye, from the Wales–England border. Monmouth is northeast of Cardiff, and west of London. ...
, looping eastwards to include the town itself and a surrounding area within Wales. At Redbrook
Redbrook is a village in Gloucestershire, England, adjoining the border with Monmouthshire, Wales. It is located on the River Wye and is within the Wye Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
History
Both Upper and Lower Redbrook were ment ...
, the boundary again reaches the Wye, and follows the river southwards, past Tintern and Chepstow
Chepstow ( cy, Cas-gwent) is a town and community in Monmouthshire, Wales, adjoining the border with Gloucestershire, England. It is located on the tidal River Wye, about above its confluence with the River Severn, and adjoining the wester ...
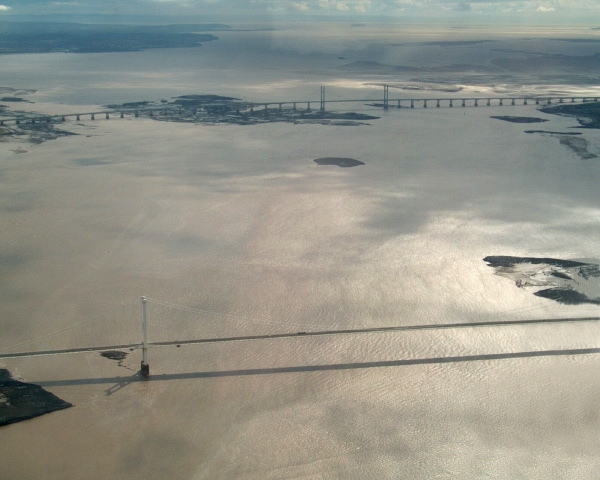
on the Welsh side, to its confluence with the Severn at the Severn Bridge. The boundary then continues down the Severn estuary
The Severn Estuary ( cy, Aber Hafren) is the estuary of the River Severn, flowing into the Bristol Channel between South West England and South Wales. Its high tidal range, approximately , means that it has been at the centre of discussions in t ...
towards the Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River Se ...
, with the small island of Flat Holm being administered as part of Wales and the neighbouring island of Steep Holm as part of England.
Administrative boundary
The boundary passes betweenFlintshire
, settlement_type = County
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_shield = Arms of Flint ...
, Wrexham County Borough
Wrexham County Borough ( cy, Bwrdeistref Sirol Wrecsam) is a county borough, with city status, in the north-east of Wales. It borders England to the east and south-east, Powys to the south-west, Denbighshire to the west and Flintshire to the ...
, Powys
Powys (; ) is a county and preserved county in Wales. It is named after the Kingdom of Powys which was a Welsh successor state, petty kingdom and principality that emerged during the Middle Ages following the end of Roman rule in Britain.
Geog ...
, and Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire ( cy, Sir Fynwy) is a county in the south-east of Wales. The name derives from the historic county of the same name; the modern county covers the eastern three-fifths of the historic county. The largest town is Abergavenny, wit ...
in Wales and Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county tow ...
, Shropshire
Shropshire (; alternatively Salop; abbreviated in print only as Shrops; demonym Salopian ) is a landlocked historic county in the West Midlands region of England. It is bordered by Wales to the west and the English counties of Cheshire to ...
, Herefordshire
Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouths ...
and Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of ...
in England.
There are several places where the border runs along the centre of a lane or street, resulting in properties on one side of the street being in Wales and those on the other side being in England. Notable examples include Boundary Lane in Saltney and the main street of Llanymynech.
History
Ancient Britain
 Before and during the
Before and during the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
occupation of Britain, all the native inhabitants of the island (other than the Pictish/Caledonian tribes of what is now northern Scotland—and also excepting the Lloegyr of greater south-east Britain) spoke Brythonic languages
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; cy, ieithoedd Brythonaidd/Prydeinig; kw, yethow brythonek/predennek; br, yezhoù predenek) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family; the other is Goidelic. ...
, a sub-family of the Insular Celtic languages
Insular Celtic languages are the group of Celtic languages of Brittany, Great Britain, Ireland, and the Isle of Man. All surviving Celtic languages are in the Insular group, including Breton, which is spoken on continental Europe in Brittany ...
, and were regarded as Britons. The topographical contrast between the mountainous western areas and the generally lower-lying areas to the east is reflected in the nature of ancient settlements, with the majority of hillforts in Britain found in this western area.
Roman era
 During the Roman occupation, the tribes of Wales (
During the Roman occupation, the tribes of Wales (Ordovices
The Ordovīcēs (Common Brittonic: *''Ordowīcī'') were one of the Celtic tribes living in Great Britain before the Roman invasion. Their tribal lands were located in present-day North Wales and England, between the Silures to the south and the ...
, Deceangli, Demetae, and especially the Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobun ...
) were noted by Roman authors as fiercely resisting any occupation. As such the border area became a centre of military activity, with legions based at ''Deva
Deva may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Deva'' (1989 film), a 1989 Kannada film
* ''Deva'' (1995 film), a 1995 Tamil film
* ''Deva'' (2002 film), a 2002 Bengali film
* Deva (2007 Telugu film)
* ''Deva'' (2017 film), a 2017 Marathi film
* Deva ...
'' (Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
), ''Viroconium
Viroconium or Uriconium, formally Viroconium Cornoviorum, was a Roman city, one corner of which is now occupied by Wroxeter, a small village in Shropshire, England, about east-south-east of Shrewsbury. At its peak, Viroconium is estimated to ...
'' ( Wroxeter), and '' Isca Augusta'' (Caerleon
Caerleon (; cy, Caerllion) is a town and community in Newport, Wales. Situated on the River Usk, it lies northeast of Newport city centre, and southeast of Cwmbran. Caerleon is of archaeological importance, being the site of a notable Roman ...
).
In most of Wales, the militaristic nature of the occupation was in stark contrast to that of southeast Britain. As such, by the end of Roman rule, there would have been a cultural border, between the highly Romanised Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, ...
in the east, and the more independent and tribal kingdoms to the west. This western area was, however, largely Christian, and a number of successor states
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th- ...
attempted to continue Roman practices. The most successful of these were the Kingdom of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain.
Based in northwest Wales, ...
in the northwest, the Kingdom of Gwent
Gwent ( owl, Guent) was a medieval Welsh kingdom, lying between the Rivers Wye and Usk. It existed from the end of Roman rule in Britain in about the 5th century until the Norman invasion of Wales in the 11th century. Along with its neighb ...
and Glywysing
Glywysing was, from the sub-Roman period to the Early Middle Ages, a petty kingdom in south-east Wales. Its people were descended from the Iron Age tribe of the Silures, and frequently in union with Gwent, merging to form Morgannwg.
Name and ...
in the southeast, the Kingdom of Dyfed
The Kingdom of Dyfed (), one of several Welsh petty kingdoms that emerged in 5th-century sub-Roman Britain in southwest Wales, was based on the former territory of the Demetae (modern Welsh ''Dyfed''). The medieval Irish narrative, '' The Expul ...
in the southwest and the Kingdom of Powys in the east. Powys roughly coincided with the territory of the Celtic Cornovii
The Cornovii is the name by which two, or three, tribes were known in Roman Britain. One tribe was in the area centred on present-day Shropshire, one was in Caithness in northernmost Scotland, and there was probably one in Cornwall. The name h ...
tribe whose ''civitas'' or administrative centre during the Roman period was at ''Viroconium''. Gwynedd, at the height of its power, extended as far east as the Dee estuary. Gradually, from the 5th century onwards, pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. I ...
tribes from the east, including the Angles and Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, conquered eastern and southern Britain, which later became England.
In the south, the Welsh kingdom of Gwent
Gwent ( owl, Guent) was a medieval Welsh kingdom, lying between the Rivers Wye and Usk. It existed from the end of Roman rule in Britain in about the 5th century until the Norman invasion of Wales in the 11th century. Along with its neighb ...
broadly covered the same area as the pre-Roman Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobun ...
, traditionally the area between the rivers Usk, Wye and the Severn estuary. It was centred at different times on '' Venta'' ( Caerwent), from which it derived its name, and ''Isca Augusta'' (Caerleon). Gwent generally allied with, and at various times was joined with, the smaller Welsh kingdom of Ergyng, centred in present-day southern Herefordshire west of the Wye (and deriving its name from the Roman town of '' Ariconium''); and the larger kingdom of Glywysing
Glywysing was, from the sub-Roman period to the Early Middle Ages, a petty kingdom in south-east Wales. Its people were descended from the Iron Age tribe of the Silures, and frequently in union with Gwent, merging to form Morgannwg.
Name and ...
in modern Glamorgan
, HQ = Cardiff
, Government = Glamorgan County Council (1889–1974)
, Origin=
, Code = GLA
, CodeName = Chapman code
, Replace =
* West Glamorgan
* Mid Glamorgan
* South Glamorgan
, Mot ...
. The name Glywysing may indicate that it was founded by a British native of '' Glevum'' (Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east o ...
).
Medieval era
 The
The Battle of Mons Badonicus
The Battle of Badon /ˈbeɪdən/ also known as the Battle of Mons Badonicus ( la, obsessio isBadonici montis, "Blockade/Siege of the Badonic Hill"; ''Bellum in monte Badonis'', "Battle on Badon Hill"; ''Bellum Badonis'', "Battle of Badon"; Old ...
, circa 500, could have been fought near Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
between the British, the victors, and Anglo-Saxons attempting to reach the Severn estuary, but its date and location are very uncertain and it may equally well have taken place in Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lor ...
or Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of , ...
. However, it is more certain that the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
emerged in the 6th and 7th centuries in the upper Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
valley, Cotswolds
The Cotswolds (, ) is a region in central-southwest England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and Evesham Vale.
The area is defined by the bedrock of J ...
and Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
areas. In 577, the Battle of Deorham in the southern Cotswolds was won by the Anglo-Saxons, and led to Wessex extending its control to the Severn estuary and the cities of Gloucester, Cirencester
Cirencester (, ; see below for more variations) is a market town in Gloucestershire, England, west of London. Cirencester lies on the River Churn, a tributary of the River Thames, and is the largest town in the Cotswolds. It is the home of ...
, and Bath. This severed the land link between the Britons of Wales and those of the south west peninsula. By about 600, however, the area of modern Gloucestershire east of the Severn, as well as most of Worcestershire
Worcestershire ( , ; written abbreviation: Worcs) is a county in the West Midlands of England. The area that is now Worcestershire was absorbed into the unified Kingdom of England in 927, at which time it was constituted as a county (see H ...
, was controlled by another group, the Hwicce
Hwicce () was a tribal kingdom in Anglo-Saxon England. According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', the kingdom was established in 577, after the Battle of Deorham. After 628, the kingdom became a client or sub-kingdom of Mercia as a result of th ...
, who may have arisen from intermarriage between Anglo-Saxon and British leading families, possibly the successors to the pre-Roman Dobunni. The Hwicce came increasingly under Mercian hegemony.
At the Battle of Chester in 616, the forces of Powys and other allied Brythonic kingdoms were defeated by the Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
ns under Æthelfrith. This divided the Britons of Wales from those in Northern England
Northern England, also known as the North of England, the North Country, or simply the North, is the northern area of England. It broadly corresponds to the former borders of Angles, Angle Northumbria, the Anglo-Scandinavian Scandinavian York, K ...
, including Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancas ...
, Cumbria, and south west Scotland
South West Scotland is an ambiguous term that can include Ayrshire, Galloway, Dumfriesshire, the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright, as well as Lanarkshire, Renfrewshire. However the inclusion or exclusion of these areas is to an extent arbitrary: the only ...
, an area which became known as ''"Yr Hen Ogledd
Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the historical region which is now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages. Its population sp ...
"'' or "the Old North". Within a few decades, the Welsh became engaged in further defensive warfare against the increasingly powerful kingdom of Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879)Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527–918
, era=Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, y ...
, based at Tamworth in what became the West Midlands of England. The capital of Powys, Pengwern
Pengwern was a Brythonic settlement of sub-Roman Britain situated in what is now the English county of Shropshire, adjoining the modern Welsh border. It is generally regarded as being the early seat of the kings of Powys before its establish ...
, at or near modern Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , also ) is a market town, civil parish, and the county town of Shropshire, England, on the River Severn, north-west of London; at the 2021 census, it had a population of 76,782. The town's name can be pronounced as either 'Sh ...
, was conquered by Oswiu of Northumbria
Oswiu, also known as Oswy or Oswig ( ang, Ōswīg; c. 612 – 15 February 670), was King of Bernicia from 642 and of Northumbria from 654 until his death. He is notable for his role at the Synod of Whitby in 664, which ultimately brought the ch ...
in 656 when he had become overlord of the Mercians. Powys then withdrew from the lowland areas now in southern Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county tow ...
, Shropshire
Shropshire (; alternatively Salop; abbreviated in print only as Shrops; demonym Salopian ) is a landlocked historic county in the West Midlands region of England. It is bordered by Wales to the west and the English counties of Cheshire to ...
and Herefordshire
Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouths ...
, which became known to Welsh poets as "The Paradise of Powys". The areas were occupied by Anglo-Saxon groups who became sub-kingdoms of Mercia, the ''Wreocensǣte'' or Wrekinset in the northern part of what became Shropshire, and the ''Magonsæte
Magonsæte was a minor sub-kingdom of the greater Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Mercia, thought to be coterminous with the Diocese of Hereford.
The British territory of Pengwern was conquered by Oswiu of Northumbria in 656, while he was overlord of th ...
'' in the southern part. Further south, the area north west of the Severn later known as the Forest of Dean
The Forest of Dean is a geographical, historical and cultural region in the western part of the county of Gloucestershire, England. It forms a roughly triangular plateau bounded by the River Wye to the west and northwest, Herefordshire to ...
seems to have remained in British (that is, Welsh) hands until about 760.
Offa's Dyke
 After
After Ine of Wessex
Ine, also rendered Ini or Ina, ( la, Inus; c. AD 670 – after 726) was King of Wessex from 689 to 726. At Ine's accession, his kingdom dominated much of southern England. However, he was unable to retain the territorial gains of his predecess ...
abdicated in 726, Æthelbald of Mercia established Mercia's hegemony over the Anglo-Saxons south of the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between ...
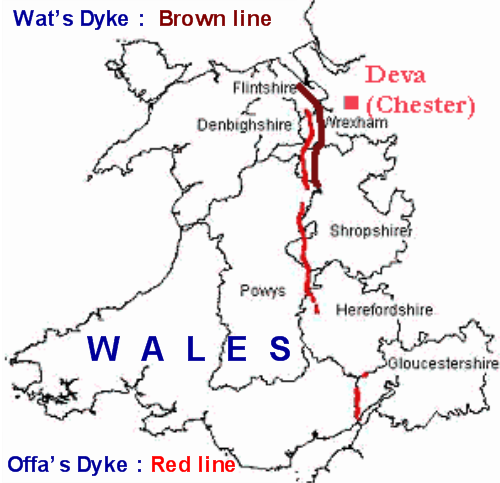
. However, campaigns by Powys against Mercia led to the building of Wat's Dyke, an earthwork boundary extending from the Severn valley near Oswestry to the Dee at Basingwerk
Basingwerk Abbey ( cy, Abaty Dinas Basing) is a Grade I listed ruined abbey near Holywell, Flintshire, Wales. The abbey, which was founded in the 12th century, belonged to the Order of Cistercians. It maintained significant lands in the Engl ...
in what became Flintshire
, settlement_type = County
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_shield = Arms of Flint ...
, perhaps to protect recently acquired lands. After Æthelbald was killed in 757, a brief civil war in Mercia then ended in victory for his distant cousin, Offa
Offa (died 29 July 796 AD) was King of Mercia, a kingdom of Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æth ...
. As king, he rebuilt Mercia's hegemony over the southern English through military campaigns, and also caused the construction of Offa's Dyke, around the years 770 and 780.
Offa's Dyke
Offa's Dyke ( cy, Clawdd Offa) is a large linear earthwork that roughly follows the border between England and Wales. The structure is named after Offa, the Anglo-Saxon king of Mercia from AD 757 until 796, who is traditionally believed to ha ...
is a massive linear earthwork, up to wide (including its surrounding ditch) and high. It is much larger and longer than Wat's Dyke, and runs roughly parallel to it. The earthwork was generally dug with the displaced soil piled into a bank on the Mercian (eastern) side, providing an open view into Wales and suggesting that it was built by Mercia to guard against attacks or raids from Powys. The late 9th-century writer Asser
Asser (; ; died 909) was a Welsh monk from St David's, Dyfed, who became Bishop of Sherborne in the 890s. About 885 he was asked by Alfred the Great to leave St David's and join the circle of learned men whom Alfred was recruiting for his ...
wrote that Offa ''"terrified all the neighbouring kings and provinces around him, and ... had a great dyke built between Wales and Mercia from sea to sea"''. In the mid-20th century, Sir Cyril Fox
Sir Cyril Fred Fox (16 December 1882 – 15 January 1967) was an English archaeologist and museum director.
Fox became keeper of archaeology at the National Museum of Wales, and subsequently served as director from 1926 to 1948. His most ...
completed a major survey of the Dyke and stated that it ran from the Dee to the Severn, as Asser suggested, but with gaps, especially in the Herefordshire area, where natural barriers of strong rivers or dense forests provided sufficient defence. More recent research by David Hill and Margaret Worthington concluded that there is little evidence for the Dyke stretching "from sea to sea", but that the earthwork built by Offa stretched some between Rushock Hill
Rushock is a small village in Herefordshire, England. It lies about 1 mile north-east of Kington. The population of the civil parish was 131 at the 2011 census.
Rushock was mentioned in the Domesday Book under the name of ''Ruiscop'', when th ...
near Kington in Herefordshire, and Treuddyn
Treuddyn is a village, community and electoral ward in Flintshire, Wales, located just off the A5104 road, around 4 miles south-east of Mold and 3 miles north-west of Caergwrle. The community includes the nearby village of Coed Talon, to the e ...
in Flintshire. Earthworks in the far north and south, including sections overlooking the Wye valley
The Wye Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB; cy, Dyffryn Gwy) is an internationally important protected landscape straddling the border between England and Wales.
The River Wye ( cy, Afon Gwy) is the fourth-longest river in th ...
and east of the Wye at Beachley
Beachley is a village in Gloucestershire, England, near the border with Monmouthshire, Wales. It is located on a peninsula at the confluence of the rivers Wye and Severn, where the Severn Bridge ends and the smaller secondary bridge over the Ri ...
, may in their view have been built for different purposes at different times, although their conclusions are themselves disputed.
Offa's Dyke largely remained the frontier between the Welsh and English in later centuries. By the 9th century, the expanding power of Mercia led to it gaining control over Ergyng and nearby Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester, England, Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. ...
. The system of shire
Shire is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries such as Australia and New Zealand. It is generally synonymous with county. It was first used in Wessex from the begin ...
s which was later to form the basis of local administration throughout England and eventually Wales originated in Wessex, where it became established during the 8th century. Wessex and Mercia gradually established an occasionally unstable alliance, with Wessex gaining the upper hand. According to Asser, the southern Welsh kings, including Hywel ap Rhys of Glywysing, commended themselves to Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bo ...
of Wessex in about 885. Alfred's son Edward the Elder
Edward the Elder (17 July 924) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 899 until his death in 924. He was the elder son of Alfred the Great and his wife Ealhswith. When Edward succeeded to the throne, he had to defeat a challenge from his cousin ...
also secured homage from the Welsh, although sporadic border unrest continued. In the early 10th century, a document known as ''The Ordinance Concerning the Dunsaete'' records procedures for dealing with disputes between the English and the Welsh, and implies that areas west of the Wye in Archenfield were still culturally Welsh. It stated that the English should only cross into the Welsh side, and vice versa, in the presence of an appointed man who had the responsibility of making sure that the foreigner was safely escorted back to the crossing point. In 926, Edward's successor Athelstan, "King of the English", summoned the Welsh kings including Hywel Dda of Deheubarth
Deheubarth (; lit. "Right-hand Part", thus "the South") was a regional name for the realms of south Wales, particularly as opposed to Gwynedd (Latin: ''Venedotia''). It is now used as a shorthand for the various realms united under the House o ...
to a meeting at Hereford, and according to William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury ( la, Willelmus Malmesbiriensis; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as " ...
laid down the boundary between England and Wales, particularly the disputed southern stretch where he specified that the eastern bank of the Wye should form the boundary.
By the mid-eleventh century, most of Wales had become united under the king of Gwynedd
Gwynedd (; ) is a county and preserved county (latter with differing boundaries; includes the Isle of Anglesey) in the north-west of Wales. It shares borders with Powys, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, an ...
, Gruffudd ap Llywelyn
Gruffydd ap Llywelyn ( 5 August 1063) was King of Wales from 1055 to 1063. He had previously been King of Gwynedd and Powys in 1039. He was the son of King Llywelyn ap Seisyll and Angharad daughter of Maredudd ab Owain, and the great-great ...
. In 1055, he marched on Hereford and sacked the city. He also seized Morgannwg
Morgannwg was a medieval Welsh kingdom formed via the merger of the kingdoms of the Kingdom of Glywysing and the Kingdom of Gwent.
Formation of Morgannwg
First under King Morgan the Generous (fl. ) until the end of the reign of his descendant ...
and the Kingdom of Gwent, together with substantial territories east of Offa's Dyke, and raided as far as Chester and Leominster
Leominster ( ) is a market town in Herefordshire, England, at the confluence of the River Lugg and its tributary the River Kenwater. The town is north of Hereford and south of Ludlow in Shropshire. With a population of 11,700, Leominster i ...
. He claimed sovereignty over the whole of Wales, a claim recognised by the English, and historian John Davies states that Gruffudd was ''"the only Welsh king ever to rule over the entire territory of Wales."''. However, after his most powerful ally – Earl Elfgar of Mercia and East Anglia – died, Harold and Tostig Godwinson took advantage of the situation – Gruffudd being besieged in Snowdonia – and invaded Wales. In 1063, Gruffudd was killed by his own men. Harold returned many of the Welsh princes their lands, so that after Harold's death at the Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings nrf, Batâle dé Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conque ...
, Wales was again divided without a leader to resist the Normans.
March of Wales
 Immediately after the
Immediately after the Norman conquest of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqu ...
, King William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
installed one of his most trusted confidants, William FitzOsbern, as Earl of Hereford. By 1071 he had started the building of Chepstow Castle
Chepstow Castle ( cy, Castell Cas-gwent) at Chepstow, Monmouthshire, Wales is the oldest surviving post-Roman stone fortification in Britain. Located above cliffs on the River Wye, construction began in 1067 under the instruction of the Norman ...
, the first castle in Britain built of stone, near the mouth of the Wye. It served as a base from which the Normans continued to expand westward into south Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
, establishing a castle at Caerleon and extinguishing the Welsh kingdom of Gwent. William also installed Roger de Montgomerie at Shrewsbury, and Hugh d'Avranches at Chester, creating a new expansionist earldom
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant " chieftain", particula ...
in each case. In the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
of 1086, Norman lands are recorded west of the Wye at Chepstow and Caldicot in the Gwent Levels ( cy, Gwent Is-coed); over the whole of north east Wales as far west as the River Clwyd
The River Clwyd ( Welsh: ''Afon Clwyd'') is a river in Wales that rises in the Clocaenog Forest () northwest of Corwen. Its total length is .
It flows due south until, at Melin-y-wig, it veers north-eastwards, tracking the A494 and passing ...
, an area known to the Welsh as the '' Perfeddwlad''; and west of Offa's Dyke, especially in Powys where a new castle was named, after its lord, Montgomery.
Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
no doubt records the extent of English penetration into Wales. This suggests that Offa's Dyke still approximately represented the boundary between England and Wales. However, during the anarchy of Stephen various Welsh princes were able to occupy lands beyond it, including Whittington, Shropshire
Whittington is a village and civil parish in north west Shropshire, England, lying east and north-east of Oswestry. The parish had a population of 2,592 at the 2011 census. The village of Whittington is in the centre of the parish, and three sm ...
(see Whittington Castle) and Maelor Saesneg, hitherto in England. These lands were brought under English lordship by Henry II of England
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin kin ...
, but became Marcher lord
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in ...
ships, and so part of Wales. This involved a loss of direct rule by the English crown.
Over the next four centuries, Norman lords established mostly small lordships, at times numbering over 150, between the Dee and Severn and further west. The precise dates and means of formation of the lordships varied, as did their size. Hundreds of small castles, mostly of the motte and bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy t ...
type, were built in the border area in the 12th and 13th centuries, predominantly by Norman lords as assertions of power as well as defences against Welsh raiders and rebels. Many new towns were established across the area, some such as Chepstow, Monmouth
Monmouth ( , ; cy, Trefynwy meaning "town on the Monnow") is a town and community in Wales. It is situated where the River Monnow joins the River Wye, from the Wales–England border. Monmouth is northeast of Cardiff, and west of London. ...
, Ludlow
Ludlow () is a market town in Shropshire, England. The town is significant in the history of the Welsh Marches and in relation to Wales. It is located south of Shrewsbury and north of Hereford, on the A49 road which bypasses the town. The ...
and Newtown becoming successful trading centres, and these tended to be a focus of English settlement. However, the Welsh continued to attack English soil and supported rebellions against the Normans.
Principality of Wales
The Principality of Wales ( cy, Tywysogaeth Cymru) was originally the territory of the native Welsh princes of the House of Aberffraw from 1216 to 1283, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales during its height of 1267–1277. Following the co ...
, which remained based in Gwynedd in the north west of the country. By the early 12th century, they covered the areas which would later become Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire ( cy, Sir Fynwy) is a county in the south-east of Wales. The name derives from the historic county of the same name; the modern county covers the eastern three-fifths of the historic county. The largest town is Abergavenny, wit ...
and much of Flintshire
, settlement_type = County
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_shield = Arms of Flint ...
, Montgomeryshire, Radnorshire
, HQ = Presteigne
, Government = Radnorshire County Council (1889–1974) Radnorshire District Council (1974–1996)
, Origin =
, Status = historic county, administrative county
, Start ...
, Brecknockshire, Glamorgan
, HQ = Cardiff
, Government = Glamorgan County Council (1889–1974)
, Origin=
, Code = GLA
, CodeName = Chapman code
, Replace =
* West Glamorgan
* Mid Glamorgan
* South Glamorgan
, Mot ...
, Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire
Pembrokeshire ( ; cy, Sir Benfro ) is a county in the south-west of Wales. It is bordered by Carmarthenshire to the east, Ceredigion to the northeast, and the rest by sea. The county is home to Pembrokeshire Coast National Park. The Park oc ...
. Some of the lordships, such as Oswestry, Whittington, Clun
Clun ( cy, Colunwy) is a town in south west Shropshire, England, and the Shropshire Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The 2011 census recorded 680 people living in the town.Combined populations for the two output areas covering the t ...
, and Wigmore had been part of England at the time of Domesday, while others such as the Lordship of Powys were Welsh principalities that passed by marriage into the hands of Norman barons. In ecclesiastical terms, the ancient diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associ ...
s of Bangor and St. Asaph
St Asaph (; cy, Llanelwy "church on the Elwy") is a city and community on the River Elwy in Denbighshire, Wales. In the 2011 Census it had a population of 3,355, making it the second-smallest city in Britain in terms of population and urban ...
in the north, and St. David's
St Davids or St David's ( cy, Tyddewi, , " David's house”) is a city and a community (named St Davids and the Cathedral Close) with a cathedral in Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Alun. It is the resting place of Saint Da ...
and Llandaff
Llandaff (; cy, Llandaf ; from 'church' and ''River Taff, Taf'') is a district, Community (Wales), community and coterminous electoral ward in the north of Cardiff, capital of Wales. It was incorporated into the city in 1922. It is the seat of ...
in the south, collectively defined an area which included both the Principality and the March, and coincided closely with later definitions of Wales.
The Principality of Wales
The Principality of Wales ( cy, Tywysogaeth Cymru) was originally the territory of the native Welsh princes of the House of Aberffraw from 1216 to 1283, encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales during its height of 1267–1277. Following the co ...
( cy, Tywysogaeth Cymru) covered the lands ruled by the Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rule ...
directly, and was formally founded in 1216, and later recognised by the 1218 Treaty of Worcester between Llywelyn ab Iorwerth, Prince of Gwynedd, and King John of England
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin ...
. Encompassing two-thirds of modern Wales, the principality operated as an effectively independent entity from the reign of Llywelyn until 1283 (though it underwent a period of contraction during the early part of the reign of Dafydd ap Llywelyn in the 1240s, and again for several years from the beginning of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd's rule in 1246). Its independence was characterised by a separate legal jurisprudence based on the well established laws of '' Cyfraith Hywel'', and by the increasingly sophisticated court
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in acco ...
of the Aberffraw dynasty.
The Statute of Rhuddlan
The Statute of Rhuddlan (12 Edw 1 cc.1–14; cy, Statud Rhuddlan ), also known as the Statutes of Wales ( la, Statuta Valliae) or as the Statute of Wales ( la, Statutum Valliae, links=no), provided the constitutional basis for the government of ...
in 1284 followed the conquest of the Principality by Edward I of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a va ...
. It assumed the lands held by the Princes of Gwynedd under the title "Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rule ...
" as legally part of the lands of England, and established shire counties on the English model over those areas. The Council of Wales
The Council for Wales and Monmouthshire ( cy, Cyngor Cymru a Mynwy) was an appointed advisory body announced in 1948 and established in 1949 by the UK government under Labour prime minister Clement Attlee, to advise the government on matters ...
, based at Ludlow Castle, was also established in the 15th century to govern the area.
Formation of "England and Wales" and county boundaries
However, the Marches remained outside the shire system, and at least nominally outside the control of the English monarchy, until the first Laws in Wales Act was introduced in 1535 underHenry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
. This, and a further Act in 1542, had the effect of annexing Wales to England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
and creating a single state and legal jurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' + 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, areas of jurisdiction apply to local, state, and federal levels.
J ...
, commonly referred to as England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is En ...
. The powers of the marcher lordships were abolished, and their areas formed into new counties, or amalgamated into existing ones.
At this point, the boundary between England and Wales, which has existed ever since, was effectively fixed. In the border areas, five new counties were created – Denbighshire, Montgomeryshire, Radnorshire, Brecknockshire and Monmouthshire – and Flintshire gained some additional territory. However, several of the marcher lordships were incorporated in whole or in part into English counties. The lordships of Ludlow, Clun, Caus and part of Montgomery were incorporated into Shropshire; and Wigmore, Huntington, Clifford and most of Ewyas were included in Herefordshire. According to John Davies:
Thus was created the border between Wales and England, a border which has survived until today. It did not follow the old line of Offa's Dyke nor the eastern boundary of the Welsh dioceses; it excluded districts such as Oswestry and Ewias, where the Welsh language would continue to be spoken for centuries, districts which it would not be wholly fanciful to consider as ''Cambria irredenta''. Yet, as the purpose of the statute was to incorporate Wales into England, the location of the Welsh border was irrelevant to the purposes of its framers.An 1844 Act of Parliament later abolished several
enclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
s. One of these, Welsh Bicknor, was an exclave of Monmouthshire between Gloucestershire and Herefordshire.
Monmouthshire
Although Monmouthshire was included in the 16th century legislation, it was treated anomalously, with the result that its legal status as a Welsh county fell into some ambiguity and doubt until the 20th century. It was omitted from the second Act of Union, which established the Court of Great Sessions, and like English shires it was given two Knights of the Shire, rather than one as elsewhere in Wales. However, in ecclesiastical terms, almost all of the county remained within the Diocese of Llandaff, and most of its residents at the time spokeWelsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
. In the late 17th century under Charles II it was added to the Oxford circuit of the English Assizes, following which, according to the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica
A notable ongoing event was the race for the South Pole.
Events January
* January 1 – A decade after federation, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory are added to the Commonwealth of Australia.
* ...
, it gradually "came to be regarded as an English county". Under that interpretation, the boundary between England and Wales passed down the Rhymney valley, along Monmouthshire's western borders with Brecknockshire and Glamorgan, so including Newport, and other industrialised parts of what would now generally be considered to be South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
, within England.
The 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica unambiguously described the county as part of England, but noted that "whenever an act ..is intended to apply to ales Ales may refer to:
Places
* Alès, a town and commune in southern France
* Ales, Sardinia, a small town in the province of Oristano on Sardinia in Italy
People with the surname
* Alexander Ales (1500–1565), Scottish theologian
* Mikoláš Ale ...
alone, then Wales is always coupled with Monmouthshire". Some legislation and UK government decisions, such as the establishment of a "Royal Commission on Ancient and Historical Monuments in Wales and Monmouthshire" in 1908, referred to "Wales and Monmouthshire", so that it was treated as one with Wales rather than as a legal part of Wales. The county's status continued to be a matter of debate in Parliament, especially as Welsh nationalism and devolution climbed the political agenda in the 20th century. In 1921 the area was included within the Church in Wales
The Church in Wales ( cy, Yr Eglwys yng Nghymru) is an Anglican church in Wales, composed of six dioceses.
The Archbishop of Wales does not have a fixed archiepiscopal see, but serves concurrently as one of the six diocesan bishops. The pos ...
. The Welsh Office
The Welsh Office ( cy, Swyddfa Gymreig) was a department in the Government of the United Kingdom with responsibilities for Wales. It was established in April 1965 to execute government policy in Wales, and was headed by the Secretary of State f ...
, established in 1965, included Monmouthshire within its remit, and in 1969 George Thomas, Secretary of State for Wales
The secretary of state for Wales ( cy, ysgrifennydd gwladol Cymru), also referred to as the Welsh secretary, is a secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with responsibility for the Wales Office. The incumbent is a member ...
, proposed to fully incorporate Monmouthshire into Wales. The issue was finally clarified in law by the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
, which provided that "in every act passed on or after 1 April 1974, and in every instrument made on or after that date under any enactment (whether before, on or after that date) "Wales", subject to any alterations of boundaries..." included "the administrative county of Monmouthshire and the county borough of Newport". The legal boundary between England and Wales therefore passes along Monmouthshire's eastern boundaries with Herefordshire
Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouths ...
and Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of ...
, essentially along the River Monnow and River Wye
The River Wye (; cy, Afon Gwy ) is the fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn estuary. For much of its length the river forms part of the border between England and Wales ...
.
The border today
English and Welsh boundaries
 The first legislation applying solely to Wales since the 16th century was passed in 1881. Subsequently, the border between England and Wales has taken on increasing legal and political significance.
Until the Welsh Disestablishment in 1920, the
The first legislation applying solely to Wales since the 16th century was passed in 1881. Subsequently, the border between England and Wales has taken on increasing legal and political significance.
Until the Welsh Disestablishment in 1920, the Diocese of St Asaph
The Diocese of Saint Asaph is a diocese of the Church in Wales in north-east Wales, named after Saint Asaph, its second bishop.
Geography
The Anglican Diocese of St Asaph in the north-east corner of Wales stretches from the borders of Chester i ...
covered parts of north-west Shropshire. The parishes transferred to the Diocese of Lichfield were: Criftins, Hengoed, Kinnerley, Knockin, Llanyblodwell, Llanymynech, Melverley, Morton, Oswestry, St Martins, Selattyn, Trefonen, Weston Rhyn and Whittington.
In 1965, a separate department of state
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs of other na ...
was established for Wales – the Welsh Office
The Welsh Office ( cy, Swyddfa Gymreig) was a department in the Government of the United Kingdom with responsibilities for Wales. It was established in April 1965 to execute government policy in Wales, and was headed by the Secretary of State f ...
– which assumed an increasing range of administrative responsibilities from Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea. It is the main thoroughfare running south from Trafalgar Square towards Parliament Sq ...
. By 1992, the Welsh Office oversaw housing
Housing, or more generally, living spaces, refers to the construction and assigned usage of houses or buildings individually or collectively, for the purpose of shelter. Housing ensures that members of society have a place to live, whether ...
, local government
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loc ...
, roads, historic buildings, health
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organ ...
, education, economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and ...
, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
, fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, ...
and urban regeneration
Urban renewal (also called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address urban decay in cities. Urban renewal involves the clearing out of bligh ...
, although the extent to which it was able to be autonomous from England in public policy
Public policy is an institutionalized proposal or a decided set of elements like laws, regulations, guidelines, and actions to solve or address relevant and real-world problems, guided by a conception and often implemented by programs. Public ...
is a matter of debate.
The establishment of devolved government
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
in Wales through the Welsh Assembly
The Senedd (; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees certain taxes and scrutinises the Welsh ...
, set up in 1999, has led to a divergence between England and Wales on some government policies. One such is the fact that prescription charges were abolished in Wales in 2007. In 2008, residents of the village of Audlem, Cheshire, from the border, "voted" to become part of Wales in what was originally a joke ballot. Some residents sought to make a case for securing Welsh benefits such as free hospital parking and prescriptions. The modern border lies between the town of Knighton and its railway station, and divides the village of Llanymynech
Llanymynech is a village straddling the border between Montgomeryshire/ Powys, Wales, and Shropshire, England, about 9 miles (14 km) north of the Welsh town of Welshpool. The name is Welsh for "Church of the Monks". The village is on the ...
where a pub straddles the line. Knighton is the only town that can claim to be on the border as well as on Offa's Dyke
Offa's Dyke ( cy, Clawdd Offa) is a large linear earthwork that roughly follows the border between England and Wales. The structure is named after Offa, the Anglo-Saxon king of Mercia from AD 757 until 796, who is traditionally believed to ha ...
. The postal and ecclesiastical borders are in places slightly different – for example the Shropshire village of Chirbury
Chirbury () is a village in west Shropshire, England. It is situated in the Vale of Montgomery, close to the Wales–England border ( at its nearest), which is to its north, west and south. The A490 and B4386 routes cross at Chirbury.
It is t ...
has Montgomery, as its post town
A post town is a required part of all postal addresses in the United Kingdom and Ireland, and a basic unit of the postal delivery system.Royal Mail, ''Address Management Guide'', (2004) Including the correct post town in the address increases ...
, and the Welsh town of Presteigne
Presteigne (; cy, Llanandras: the church of St. Andrew) is a town and community in Radnorshire, Powys, Wales on the south bank of the River Lugg. Formerly the county town of the historic county of Radnorshire, the town has, in common with ...
is in the English Diocese of Hereford
The Diocese of Hereford is a Church of England diocese based in Hereford, covering Herefordshire, southern Shropshire and a few parishes within Worcestershire in England, and a few parishes within Powys and Monmouthshire in Wales. The cathedral i ...
.
National League North
The National League North, formerly Conference North, is a division of the National League in England, immediately below the National League division. Along with the National League South, it is at the second level of the National League Syst ...
football club Chester F.C.'s ground at Deva Stadium straddles the border, with the car park and some of the offices in England but the pitch in Wales. In the 2021–22 season, the club were threatened with legal action for failing to apply the COVID-19 regulations applying in Wales and allowing crowds to attend matches at the ground.
A competition was launched in 2005 to design one or more new iconic images, along the same lines as the "Angel of the North
The ''Angel of the North'' is a contemporary sculpture by Antony Gormley, located in Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, England. Completed in 1998, it is believed to be the largest sculpture of an angel in the world and is viewed by an estimated 33 ...
", to be placed at the borders of Wales. This became known as the "Landmark Wales" project, and a shortlist of 15 proposals was unveiled in 2007. However, the proposal was shelved after it failed to receive Lottery
A lottery is a form of gambling that involves the drawing of numbers at random for a prize. Some governments outlaw lotteries, while others endorse it to the extent of organizing a national or state lottery. It is common to find some degree of ...
funding.
The main road links over the border in the south are the M4 Second Severn Crossing and the M48 Severn Bridge.
In July 2017, the Welsh Secretary, Alun Cairns, announced that tolls would be abolished at the end of 2018, claiming that this would boost the South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
economy by around £100m a year. In September 2017, Cairns confirmed that tolls would be reduced in January 2018 when VAT was removed. All tolls ceased on 17 December 2018.
Lost Lands of Wales
 The Lost Lands of Wales was a minor political idea of the mid-1960s which called into question the status of areas along the east side of the England–Wales border, which its proponents regarded as Welsh. The idea related to parts of the counties of
The Lost Lands of Wales was a minor political idea of the mid-1960s which called into question the status of areas along the east side of the England–Wales border, which its proponents regarded as Welsh. The idea related to parts of the counties of Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county tow ...
, Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of ...
, Herefordshire
Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouths ...
and Shropshire
Shropshire (; alternatively Salop; abbreviated in print only as Shrops; demonym Salopian ) is a landlocked historic county in the West Midlands region of England. It is bordered by Wales to the west and the English counties of Cheshire to ...
.
The '' Lost Lands Liberation League'' was reportedly a minor group in the 1960s claiming to recover the "Lost Lands" for Wales. Some Welsh nationalist organisations have campaigned on the issue, although Plaid Cymru
Plaid Cymru ( ; ; officially Plaid Cymru – the Party of Wales, often referred to simply as Plaid) is a centre-left to left-wing, Welsh nationalist political party in Wales, committed to Welsh independence from the United Kingdom.
Plaid wa ...
does not. The group is associated with Gethin ap Gruffydd
Gethin ap Gruffydd () (aka, Gethin ap Iestyn Gruffydd) is a Welsh political and cultural activist, born in Merthyr Tydfil.
Anti-Sais Front/Patriotic Front 1964–1969
After leaving school Gruffydd found work at a textile wholesaler in Bath, Some ...
.
Place names
 In general, placenames of Welsh origin are found to the west of the border, and those of English origin to the east. However, many historically Welsh names are also found east of the border, particularly around
In general, placenames of Welsh origin are found to the west of the border, and those of English origin to the east. However, many historically Welsh names are also found east of the border, particularly around Oswestry
Oswestry ( ; ) is a market town, civil parish and historic railway town in Shropshire, England, close to the Welsh border. It is at the junction of the A5, A483 and A495 roads.
The town was the administrative headquarters of the Borough ...
in northern Shropshire, such as Gobowen and Trefonen
Trefonen is a small village located approximately south-west of Oswestry, and three miles east of the England-Wales border, in Shropshire, England. The name translates into "village of the ash trees" in English. In 2001, the total population ...
; in southern Shropshire, such as Clun
Clun ( cy, Colunwy) is a town in south west Shropshire, England, and the Shropshire Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The 2011 census recorded 680 people living in the town.Combined populations for the two output areas covering the t ...
; and in southern Herefordshire, such as Kilpeck and Pontrilas. Most of these areas were not incorporated fully into England until the 16th century, and native Welsh speakers still lived there until at least the 19th century. Equally, placenames of English origin can be found on the Welsh side of the border where there was Mercian and Norman settlement, particularly in the north east, such as Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start ...
, Wrexham
Wrexham ( ; cy, Wrecsam; ) is a city and the administrative centre of Wrexham County Borough in Wales. It is located between the Welsh mountains and the lower Dee Valley, near the border with Cheshire in England. Historically in the count ...
and Prestatyn
Prestatyn is a seaside town and community in Denbighshire, Wales. Historically a part of Flintshire, it is located on the Irish Sea coast, to the east of Rhyl. Prestatyn has a population of 19,085,
History Prehistory
There is evidence that ...
; in English Maelor, such as Overton; in central Powys, such as Newtown and Knighton; and in southeastern Monmouthshire, including Chepstow
Chepstow ( cy, Cas-gwent) is a town and community in Monmouthshire, Wales, adjoining the border with Gloucestershire, England. It is located on the tidal River Wye, about above its confluence with the River Severn, and adjoining the wester ...
and Shirenewton
Shirenewton ( cy, Drenewydd Gelli-farch) is a village and community in Monmouthshire, south east Wales. It is located 3 miles due west of Chepstow, 5 miles (8 km) by road. The village stands around 500 feet (154 m) above sea level, and has ...
.
See also
*Anglo-Scottish border
The Anglo-Scottish border () is a border separating Scotland and England which runs for between Marshall Meadows Bay on the east coast and the Solway Firth in the west. The surrounding area is sometimes referred to as "the Borderlands".
The ...
* Berwick upon Tweed
* Church of England border polls 1915–1916
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* Chri ...
* Cross-border derby
The cross-border derby is a football match played between Wrexham and Chester. The clubs are 12 miles apart but are Welsh and English respectively (though Chester's Deva Stadium straddles the England–Wales border, and its pitch lies entirely ...
* Cultural relationship between the Welsh and the English
* Debatable lands
* History of Wales
* List of Anglo-Welsh Wars
This is an incomplete list of the wars and battles between the Anglo-Saxons who later formed into the Kingdom of England and the Britons (the pre-existing Britons (historical), Brythonic population of Britain south of the Antonine Wall who came to ...
* Little England beyond Wales
Little England beyond Wales is a name that has been applied to an area of southern Pembrokeshire and southwestern Carmarthenshire in Wales, which has been English in language and culture for many centuries despite its remoteness from England. ...
* Lloegyr
* Monmouthshire (historic)
, Status= Historic county Ceremonial county (until 1974) Administrative county (1889–1974)
, Start= 1535
, Origin= Laws in Wales Act 1535
, Motto= Faithful to both (Utrique Fideli ...
* Offa's Dyke Path
Offa's Dyke Path ( cy, Llwybr Clawdd Offa) is a long-distance footpath loosely following the Wales–England border. Officially opened on 10 July 1971, by Lord Hunt, it is one of Britain's National Trails and draws walkers from throughout th ...
* Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border
The Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, sometimes referred to as the Irish border or British–Irish border, runs for Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland, 1999
* Severnside derby
* Welsh Marches
The Welsh Marches ( cy, Y Mers) is an imprecisely defined area along the border between England and Wales in the United Kingdom. The precise meaning of the term has varied at different periods.
The English term Welsh March (in Medieval Latin ...
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:England-Wales border 1536 establishments in England 1536 establishments in Wales English law Geographic history of the United Kingdom Irredentism Welsh nationalism History of Shropshire History of Cheshire History of Gloucestershire History of Herefordshire Territorial evolution