An emergency position-indicating radiobeacon (EPIRB) is a type of
emergency locator beacon
An emergency locator beacon is a radio beacon, a portable battery powered radio transmitter, used to geolocalization, locate airplanes, vessels, and persons in distress and in need of immediate rescue. Various types of emergency locator beacons ar ...
for commercial and recreational boats; it is a portable, battery-powered
radio transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmissio ...
used in emergencies to
locate boaters in distress and in need of immediate rescue. In the event of an emergency, such as a ship sinking or medical emergency onboard, the transmitter is activated and begins transmitting a continuous 406 MHz distress radio signal, which is used by
search-and-rescue teams to quickly locate the emergency and render aid.
The distress signal is detected by
satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
s operated by an international consortium of rescue services,
COSPAS-SARSAT
The International Cospas-Sarsat Programme is a satellite-aided search and rescue (SAR) initiative. It is organized as a treaty-based, nonprofit, intergovernmental, humanitarian cooperative of 45 nations and agencies (see infobox). It is dedica ...
, which can detect emergency beacons anywhere on Earth transmitting on the distress frequency of 406 MHz. The satellites calculate the position or utilize the GPS coordinates of the beacon and quickly pass the information to the appropriate local
first responder
A first responder is a person with specialized training who is among the first to arrive and provide assistance or incident resolution at the scene of an emergency. First responders typically include Law enforcement, law enforcement officers (co ...
organization, which performs the search and rescue. As the search and rescue team approach the search areas, they use
Direction Finding
Direction finding (DF), radio direction finding (RDF), or radiogoniometry is the use of radio waves to determine the direction to a radio source. The source may be a cooperating radio transmitter or may be an inadvertent source, a naturall ...
(DF) equipment to locate the beacon using the 121.5 MHz homing signal, or in newer EPIRBs, the
AIS location signal. The basic purpose of this system is to help rescuers find survivors within the so-called "golden day" (the first 24 hours following a traumatic event) during which the majority of survivors can usually be saved.
The feature distinguishing a modern EPIRB, often called GPIRB, from other types of emergency beacon is that it contains a
GPS receiver
A satellite navigation (satnav) device or GPS device is a device that uses satellites of the Global Positioning System (GPS) or similar global navigation satellite systems (GNSS).
A satnav device can determine the user's geographic coordinat ...
and broadcasts its position, usually accurate within , to facilitate location. Previous emergency beacons without a GPS can only be localized to within by the COSPAS satellites and relied heavily upon the 121.5 MHz homing signal to pin-point the beacons location as they arrived on scene.
The standard frequency of a modern EPIRB is 406 MHz. It is an internationally regulated
mobile radiocommunication service that aids
search-and-rescue operations to detect and locate
distressed watercraft,
aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
, and people.
The first form of these beacons was the 121.5 MHz ELT, which was designed as an automatic locator beacon for crashed military aircraft. These beacons were first used in the 1950s by the U.S. military and were mandated for use on many types of commercial and
general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations except for commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services for other ...
aircraft beginning in the early 1970s.
The frequency and signal format used by the ELT beacons was not designed for satellite detection, which resulted in a system with poor location detection abilities and long delays in detection of activated beacons. The satellite detection network was built after the ELT beacons were already in general use, with the first satellite not being launched until 1982, and even then, the satellites only provided detection, with location accuracy being roughly .
The technology was later expanded to cover use on vessels at sea (EPIRB), individual persons (PLB), and starting in 2016, maritime survivor locating devices (MSLD).
All have migrated from using 121.500 MHz as their primary frequency to using 406 MHz, which was designed for satellite detection and location, however most models still broadcast a secondary signal on 121.5 MHz as well, as this helps rescue teams pinpoint the location of survivors once in their vicinity with more accuracy (within 2km) than the 406 MHz frequency allows on its own.
Since the inception of COSPAS-SARSAT in 1982, distress radio beacons have assisted in the rescue of over 50,000 people in more than 7,000 distress situations. In 2010 alone, the system provided information used to rescue 2,388 persons in 641 distress situations.
Types of emergency locator beacons
The several types of emergency locator beacons are distinguished by the environment for which they were designed to be used:
* ELT (emergency locator transmitters) are carried on aircraft and are activated in the event of a crash.
** Activated by G-switch (crash sensor) or manually by cockpit remote switch or ON switch on ELT.
* EPIRB (emergency position-indicating radio beacons) are carried on ships and boats, and signal maritime distress.
** Activated by water when the beacon is out of the bracket or manually by the ON switch on the EPIRB.
* SEPIRB (submarine emergency position-indicating radio beacons) are EPIRBs designed only for use on submarines.
* SSAS (
ship security alert systems) are used to indicate possible piracy or terrorism attacks discreetly on sea-going vessels.
** Activated by discreet switch/button in the ship's bridge or cabin, or manually on the SSAS.
* PLB (personal locator beacons) are carried by individuals and intended to indicate a person in distress who is away from normal
emergency services
Emergency services and rescue services are organizations that ensure public safety, security, and health by addressing and resolving different emergencies. Some of these agencies exist solely for addressing certain types of emergencies, while ot ...
; e.g.,
9-1-1
911, sometimes written , is an emergency telephone number for Argentina, Canada, the Dominican Republic, Fiji, Jordan, Mexico, Pakistan, Maldives, Palau, Panama, Iraq, the Philippines, Sint Maarten, the United States, and Uruguay, as well as ...
. They are also used for crew-saving applications in shipping and lifeboats at terrestrial systems. In
New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
, some police stations and the
NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service
The National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) is a directorate of the New South Wales Department of Planning and Environment and responsible for managing more than 890 national parks and reserves, covering over 7.5 million hectares of land ac ...
provide personal locator beacons to
hiker
A hike is a long, vigorous walking, walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century. Long hikes as part of a religious pilgrimage have existed for a much longer tim ...
s for no charge.
** Activated manually by deploying antenna and pressing the ON button/switch.
Distress alerts transmitted from ELTs, EPIRBs, SSAS, and PLBs are received and processed by the
International Cospas-Sarsat Programme
The International Cospas-Sarsat Programme is a satellite-aided search and rescue (SAR) initiative. It is organized as a treaty-based, nonprofit, intergovernmental, humanitarian cooperative of 45 nations and agencies (see infobox). It is dedica ...
, the international
satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
system for search and rescue (SAR). These beacons transmit a 406 MHz distress signal every 50 seconds, varying over a span of 2.5 seconds to avoid multiple beacons always transmitting at the same time.
When manually activated, or automatically activated upon immersion or impact, such beacons send out a
distress signal
A distress signal, also known as a distress call, is an internationally recognized means for obtaining help. Distress signals are communicated by transmitting radio signals, displaying a visually observable item or illumination, or making a sou ...
. The signals are monitored worldwide and the location of the distress is detected by non-
geostationary satellites using the
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described ...
for
trilateration
Trilateration is the use of distances (or "ranges") for determining the unknown position coordinates of a point of interest, often around Earth ( geopositioning).
When more than three distances are involved, it may be called multilateration, f ...
, and in more recent EPIRBs, also by
GPS.
Loosely related devices, including
search and rescue transponder
A search and rescue transponder (SART) is a self-contained, waterproof transponder intended for emergency use at sea. These devices may be either a radar-SART, or a GPS-based AIS-SART (automatic identification system SART).
The radar-SART is u ...
s (SART),
AIS-SART
An AIS-SART is a self-contained radio device used to locate a survival craft or distressed vessel by sending updated position reports using a standard Automatic Identification System (AIS) class-A position report. The position and time synchroniz ...
,
avalanche transceiver
An avalanche transceiver or avalanche beacon is a type of emergency locator beacon, a radio transceiver (a transmitter and receiver in one unit) operating at 457 kHz for the purpose of finding people buried under snow. They are widely carrie ...
s, and
RECCO
Recco (Latin: ''Ricina'' / ''Recina'') is a ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Genoa, region of Liguria, Italy.
Recco is home to the September 8 fireworks festival honoring the Virgin Mary. The town is also known for being home to the most ...
do not operate on 406 MHz, thus are covered in separate articles.
International COSPAS-SARSAT Programme
Cospas-Sarsat
The International Cospas-Sarsat Programme is a satellite-aided search and rescue (SAR) initiative. It is organized as a treaty-based, nonprofit, intergovernmental, humanitarian cooperative of 45 nations and agencies (see infobox). It is dedica ...
is an international organization that has been a model of international cooperation, even during the
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
. SARSAT means search-and-rescue satellite-aided tracking. COSPAS (''КОСПАС'') is an
acronym
An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial Letter (alphabet), letter of each wor ...
for the Russian words "''COsmicheskaya'' ''Sistema Poiska Avariynyh Sudov''" (Космическая Система Поиска Аварийных Судов), which translates to "space system for the search of vessels in distress". A consortium of USSR, the U.S., Canada, and France formed the organization in 1982. Since then, 29 other countries have joined.
The satellites used in the system include:
* LEOSAR or Low Earth Orbiting Search and Rescue Satellites
** The LEOSAR system calculates the location of distress events using Doppler processing techniques. Doppler processing is based upon the principle that the frequency of the distress beacon, as "heard" by the satellite instrument, is affected by the relative velocity of the satellite with respect to the beacon. By monitoring the change of the beacon frequency of the received beacon signal and knowing the exact position of the satellite, the LUT is able to calculate the location of the beacon.
* GEOSAR or Geosynchronous Earth Orbiting Search and Rescue Satellites
** As a GEOSAR satellite remains fixed relative to the Earth rotating with the earth around the equator, GEOSAR satellites utilize the GPS provided by the EPIRB, PLB, or ELT to provide rescuers with beacon position information.
* MEOSAR or Mid-Earth Orbiting Search and Rescue Satellites
** The newest of the Cospas Sarsat satellites, detect EPIRB, PLB, and ELT distress signals in almost real-time (i.e within 5 minutes) including the beacons location with or without GPS.
** The new MEOSAR system also provides the framework along with the
Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) for EPIRBs, PLBs, and EPIRBs to utilize the new Return Link Service or RLS that provides a confirmation message from Search and Rescue back to the beacon to let the survivors know their distress message was confirmed.
Cospas-Sarsat defines standards for beacons, auxiliary equipment to be mounted on conforming weather and communication satellites, ground stations, and communications methods. The satellites communicate the beacon data to their ground stations, which forward it to main control centers of each nation that can initiate a rescue effort.
Cospas Sarsat Monitoring include:
* Local User Terminals (LUTs)
* Mission Control Centers (MCC)
* Rescue Coordination Center (RCC)
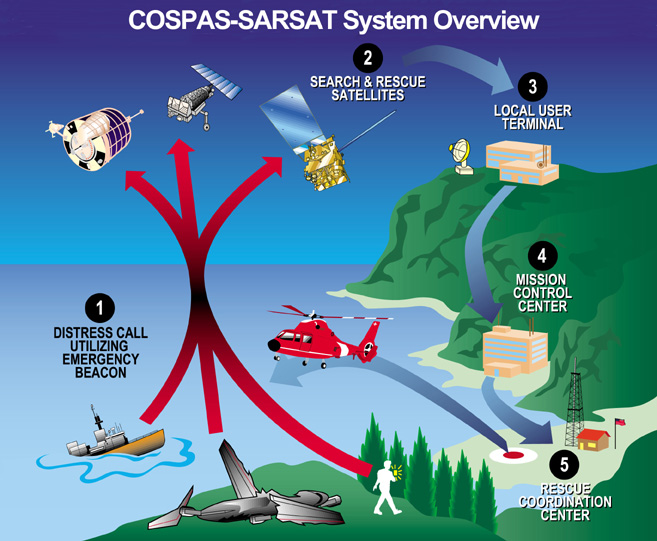
Detection and location
A transmission is typically detected and processed in this manner:
# The transmitter is activated, either automatically in a crash or after sinking, or manually by survivors of an emergency situation.
# At least one satellite picks up the beacon's transmission.
# The satellites transfer the beacon's signal to their respective ground control stations.
# The ground stations process the signals and forward the data, including approximate location, to a national authority.
# The national authority forwards the data to a rescue authority
# The rescue authority uses its own receiving equipment afterwards to locate the beacon and commence its own rescue or recovery operations.
Once the satellite data is received, less than a minute is needed to forward them to any signatory nation. The primary means of detection and location is by the COSPAS-SARSAT satellites. However, additional means of location are frequently used. For example, the FAA requires that all pilots monitor 121.500 MHz whenever possible, and the
USCG
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the armed forces of the United States. It is one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, mi ...
has a network of direction finder sites along the coastlines.
The
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
maintains a near-real-time map that shows SARSAT U.S. Rescues.
Several systems are in use, with beacons of varying expense, different types of satellites, and varying performance. Carrying even the oldest systems provides an immense improvement in safety over carrying none.
The types of satellites in the network are:
* LEOSAR
** Support Doppler detection and reception of encoded position
** Receivers are payloads on various Low Earth Orbit satellites
* MEOSAR
** Medium Earth Orbiting Search and Rescue
** Receivers are payloads on the U.S. GPS satellites, on the Russian GLONASS satellites, and on the European GALILEO satellites.
* GEOSAR
** Supports only reception of encoded position
** Receivers are payloads on various geosynchronous satellites, including some of the U.S. GOES weather satellites (including
GOES-16
GOES-16, formerly known as GOES-R before reaching geostationary orbit, is the first of the GOES-R series of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) operated by NASA and th ...
).
When one of the COSPAS-SARSAT satellites detects a beacon, the detection is passed to one of the program's roughly 30
Mission Control Centers, such as USMCC (in Suitland, Maryland), where the detected location and beacon details are used to determine to which
rescue coordination centre (for example, the U.S. Coast Guard's PACAREA RCC, in Alameda, California) to pass the alert.
Beacon operation
GPS-based, registered
The 406-MHz beacons with GPS track with a precision of 100 m in the 70% of the world closest to the equator, and send a serial number so the responsible authority can look up phone numbers to notify the registrant (e.g., next-of-kin) in four minutes.
The GPS system permits stationary, wide-view geosynchronous communications satellites to enhance the Doppler position received by
low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial object ...
satellites. EPIRB beacons with built-in GPS are usually called GPIRBs, for GPS position-indicating radio beacon or global position-indicating radio beacon.
However, rescue cannot begin until a Doppler track is available. The COSPAS-SARSAT specifications say that a beacon location is not considered "resolved" unless at least two Doppler tracks match or a Doppler track confirms an encoded (GPS) track. One or more GPS tracks are not sufficient.
High-precision registered
An intermediate technology 406-MHz beacon (now mostly obsolete in favor of GPS-enabled units) has worldwide coverage, locates within 2 km (12.5 km
2 search area), notifies kin and rescuers in 2 hours maximum (46 min average), and has a serial number to look up phone numbers, etc. This can take up to two hours because it has to use moving weather satellites to locate the beacon. To help locate the beacon, the beacon's frequency is controlled to 2 parts per billion, and its power is five watts.
Both of the above types of beacons usually include an auxiliary 25-milliwatt beacon at
121.5 MHz to guide rescue aircraft.
Traditional ELT, unregistered
The oldest, cheapest beacons are aircraft ELTs that send an anonymous warble on the aviation band
distress frequency at 121.5 MHz. The frequency is often routinely monitored by commercial aircraft, but has not been monitored by satellite since Feb. 1, 2009.
These distress signals could be detected by satellite over only 60% of the earth, required up to 6 hours for notification, located within (search area of 1200 km
2), were anonymous, and could not be located well because their frequency is only accurate to 50 parts per million and the signals were broadcast using only 75–100 milliwatts of power. Coverage was partial because the satellite had to be in view of both the beacon and a ground station at the same time; the satellites did not store and forward the beacon's position. Coverage in polar and Southern Hemisphere areas was poor.
False alarms were common, as the beacon transmitted on the aviation emergency frequency, with interference from other electronic and electrical systems. To reduce false alarms, a beacon was confirmed by a second
satellite pass, which could easily slow confirmation of a 'case' of distress to as much as 4 hours (although in rare circumstances, the satellites could be positioned such that immediate detection becomes possible.)
Location by Doppler (without GPS)
The Cospas-Sarsat system was made possible by
Doppler
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described ...
processing. Local-user terminals (LUTs) detecting nongeostationary satellites interpret the Doppler frequency shift heard by LEOSAR and MEOSAR satellites as they pass over a beacon transmitting at a fixed frequency. The interpretation determines both bearing and range. The range and bearing are measured from the rate of change of the heard frequency, which varies both according to the path of the satellite in space and the rotation of the earth. This
triangulates the position of the beacon. A faster change in the Doppler indicates that the beacon is closer to the satellite's
orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
. If the beacon is moving toward or away from the satellite track due to the Earth's rotation, it is on one side or other of the satellite's path. Doppler shift is zero at the
closest point of approach between the beacon and the orbit.
If the beacon's frequency is more precise, it can be located more precisely, saving search time, so modern 406-MHz beacons are accurate to 2 parts per billion, giving a search area of only 2 km
2, compared to the older beacons accurate to 50 parts per million that had 200 km
2 of search area.
To increase the useful power, and handle multiple simultaneous beacons, modern 406-MHz beacons transmit in bursts, and remain silent for about 50 seconds.
Russia developed the original system, and its success drove the desire to develop the improved 406-MHz system. The original system was a brilliant adaptation to the low-quality beacons, originally designed to aid air searches. It used just a simple, lightweight transponder on the satellite, with no digital recorders or other complexities. Ground stations listened to each satellite as long as it was above the horizon. Doppler shift was used to locate the beacon(s). Multiple beacons were separated when a computer program analysed the signals with a
fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). A Fourier transform converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in ...
. Also, two satellite passes per beacon were used. This eliminated false alarms by using two measurements to verify the beacon's location from two different bearings. This prevented false alarms from VHF channels that affected a single satellite. Regrettably, the second satellite pass almost doubled the average time before notification of the rescuing authority. However, the notification time was much less than a day.
Satellites
Receivers are auxiliary systems mounted on several types of satellites. This substantially reduces the program's cost. The weather satellites that carry the SARSAT receivers are in "ball of yarn" orbits, inclined at 99 degrees. The longest period that all satellites can be out of line-of-sight of a beacon is about two hours. The first satellite constellation was launched in the early 1970s by the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, Canada, France and the United States.
Some geosynchronous satellites have beacon receivers. Since the end of 2003, there are four such geostationary satellites (GEOSAR) that cover more than 80% of the surface of the earth. As with all geosynchronous satellites, they are located above the equator. The GEOSAR satellites do not cover the polar caps. Since they see the Earth as a whole, they see the beacon immediately, but have no motion, and thus no Doppler frequency shift to locate it. However, if the beacon transmits GPS data, the geosynchronous satellites give nearly instantaneous response.
Search-and-rescue response
Emergency beacons operating on 406 MHz transmit a unique 15-, 22-, or 30-character serial number called a hex code. When the beacon is purchased, the hex code should be registered with the relevant national (or international) authority. After one of the mission control centers has detected the signal, this registration information is passed to the rescue coordination center, which then provides the appropriate search-and-rescue agency with crucial information, such as:
* phone numbers to call
* a description of the vessel, aircraft, vehicle, or person (in the case of a PLB)
* the home port of a vessel or aircraft
* any additional information that may be useful to SAR agencies
Registration information allows SAR agencies to start a rescue more quickly. For example, if a shipboard telephone number listed in the registration is unreachable, it could be assumed that a real distress event is occurring. Conversely, the information provides a quick and easy way for the SAR agencies to check and eliminate false alarms (potentially sparing the beacon's owner from significant false alert fines).
An unregistered 406-MHz beacon still carries some information, such as the manufacturer and serial number of the beacon, and in some cases, an
MMSI
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international ''maritime telephone number'', a temporarily assigned UID issued by that object's current flag state (unlike an IMO number, which is a permanent global UID ...
or aircraft
tail number/
ICAO 24-bit address. Despite the clear benefits of registration, an unregistered 406-MHz beacon is very substantially better than a 121.5-MHz beacon, because the hex code received from a 406-MHz beacon confirms the authenticity of the signal as a real distress signal.
Beacons operating on 121.5 MHz and 243.0 MHz only simply transmit an anonymous siren tone, thus carry no position or identity information to SAR agencies. Such beacons now rely solely on the terrestrial or aeronautical monitoring of the frequency.
Responsible agencies
RCCs are responsible for a geographic area, known as a "search-and-rescue region of responsibility" (SRR). SRRs are designated by the
International Maritime Organization
The International Maritime Organization (IMO; ; ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating maritime transport. The IMO was established following agreement at a ...
and the
International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international sch ...
. RCCs are operated unilaterally by personnel of a single military service (e.g. an air force, or a navy) or a single civilian service (e.g. a national police force, or a coast guard).
Americas
These international search-and-rescue points of contact receive SAR alerts from the USMCC.
= United States
=
The U.S. NOAA operates the U.S. Mission Control Center (USMCC) in Suitland, Maryland.
It distributes beacon signal reports to one or more of these RCCs:
The US Coast Guard web page for EPIRBs states: "You may be fined for false activation of an unregistered EPIRB. The US Coast Guard routinely refers cases involving the nondistress activation of an EPIRB (e.g., as a hoax, through gross negligence, carelessness, or improper storage and handling) to the Federal Communications Commission. The FCC will prosecute cases based upon evidence provided by the Coast Guard, and will issue warning letters or notices of apparent liability for fines up to $10,000."
= Canada
=
The Canadian Mission Control Centre receives and distributes distress alerts.
In Canada, the
Canadian Coast Guard
The Canadian Coast Guard (CCG; ) is the coast guard of Canada. Formed in 1962, the coast guard is tasked with marine search and rescue (SAR), communication, navigation, and transportation issues in Canadian waters, such as navigation aids and i ...
and
Canadian Forces Search and Rescue (
Royal Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; ) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environmental commands within the unified Can ...
and
Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; , ''MRC'') is the Navy, naval force of Canada. The navy is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of February 2024, the RCN operates 12 s, 12 s, 4 s, 4 s, 8 s, and several auxiliary ...
) are partners in Joint Rescue Co-ordination Centres; CCG operates Maritime Rescue Subcentres to offload work from JRCC.
Europe
= United Kingdom
=
The United Kingdom, the
Department for Transport
The Department for Transport (DfT) is a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, ministerial department of the Government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for the English transport network and a limited number of transport ...
,
Maritime and Coastguard Agency
The Maritime and Coastguard Agency (MCA) is an executive agency of the United Kingdom that is responsible for implementing British and international maritime law and safety policy. It works to prevent the loss of lives at sea and to prevent mar ...
operates the Mission Control Centre (UKMCC), which receives and distributes distress alerts.
In the UK, the Distress and Diversion Cell of the Royal Air Force provides continuous monitoring of 121.5 MHz and 243.0 MHz, with autotriangulation from a network of terrestrial receivers on both frequencies.
Russia
In Russia, operations are supported by the Federal State Unitary Enterprise Morsvyazsputnik.
Asia
In Hong Kong, operations are supported by the Hong Kong Marine Department's
(MRCC)
In India, operations are supported by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
and by the
Indian Coast Guard
The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) is a maritime law enforcement and search and rescue agency of India with jurisdiction over its territorial waters including its contiguous zone and Exclusive economic zone of India, exclusive economic zone. It was st ...
's
Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre Mumbai (MRCC)
In China, operations are supported by the Maritime Safety Administration, Bureau of Harbour Superintendency.
In Japan, operations are supported by the Japan Coast Guard
In Vietnam, operations are supported by the Ministry of Transport, Vietnam Maritime Administration (VINAMARINE).
In Singapore, operations are supported by the Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore.
In the Republic of Korea, operations are supported by the Korea Coast Guard.
In Indonesia, operations are supported by the National SAR Agency of Indonesia (BASARNAS).
In Taiwan, operations are supported by the International Telecommunication Development Company (ITDC)
Phase-out of 121.5 MHz satellite alerting service
Because of the extremely high numbers of false alerts on the 121.500 MHz frequency (over 98% of all COSPAS-SARSAT alerts), the IMO eventually requested a termination of COSPAS-SARSAT processing of 121.5 MHz signals. The ICAO Council also agreed to this phase-out request, and the COSPAS-SARSAT Council decided that future satellites would no longer carry the 121.5 MHz search and rescue repeater (SARR). Since 1 February 2009, only 406 MHz beacons are detected by the international
Cospas-Sarsat
The International Cospas-Sarsat Programme is a satellite-aided search and rescue (SAR) initiative. It is organized as a treaty-based, nonprofit, intergovernmental, humanitarian cooperative of 45 nations and agencies (see infobox). It is dedica ...
SAR satellite system. This affects all maritime beacons (EPIRBs), all aviation beacons (ELTs) and all personal beacons (PLBs). In other words, Cospas-Sarsat has ceased satellite detection and processing of 121.5/243 MHz beacons. These older beacons are now only detectable by ground-based receivers and aircraft.
EPIRBs that do not transmit on 406 MHz are banned on boats in the United States and in many other jurisdictions. More information about the switch to 406 MHz is available o
Cospas-Sarsat's 121.5/243 Phase-Outpage.
Despite the switch to 406 MHz, pilots and ground stations are encouraged to continue to monitor for transmissions on the emergency frequencies, as most 406 MHz beacons are required to be equipped with 121.5 "homers." Furthermore, the 121.5 MHz frequency remains the official global VHF aircraft voice distress frequency.
FAA transition status
In a Safety Recommendation released September 2007, the U.S.
National Transportation Safety Board
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) is an independent U.S. government investigative agency responsible for civil transportation accident investigation. In this role, the NTSB investigates and reports on aviation accidents and inci ...
once again recommended that the U.S. FAA require all aircraft have 406 MHz ELTs.
[Safety recommendation (A-07-51)](_blank)
National Transportation Safety Board. 4 September 2007. They first recommended this back in 2000 and after vigorous opposition by
AOPA
The Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA) is a Frederick, Maryland-based American non-profit political organization that advocates for general aviation. AOPA's membership consists mainly of general aviation pilots in the United States ...
, the FAA declined to do so. Citing two recent accidents, one with a 121.5 MHz ELT and one with a 406 MHz ELT, the NTSB concludes that switching all ELTs to 406 MHz is a necessary goal to work towards.
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
has conducted crash tests with small airplanes to investigate how ELTs perform.
Emergency Locator Transmitters
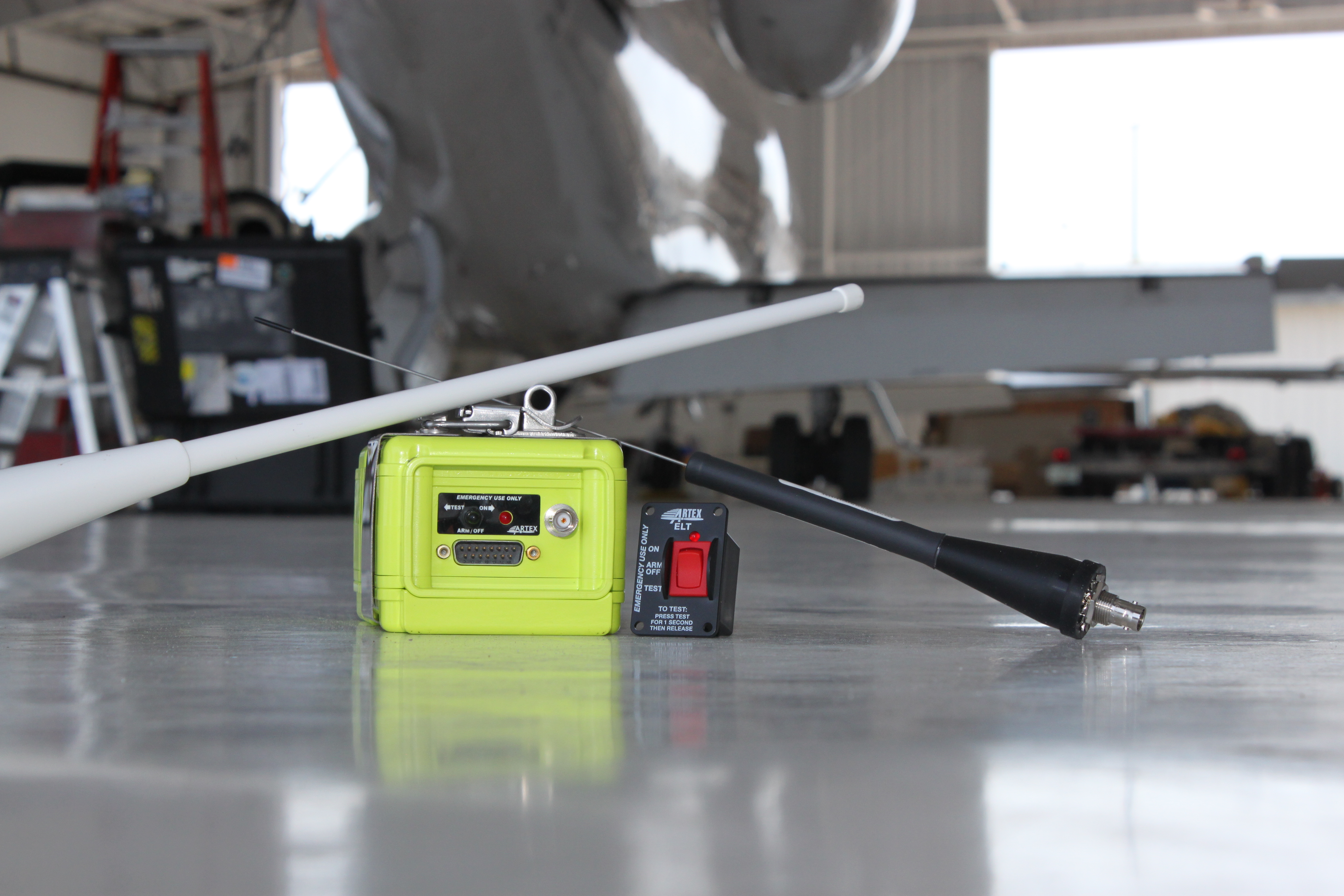

Emergency Locator Transmitters (ELTs) are expensive devices (average cost for aviation use is $1500–3000
). In commercial aircraft, a
cockpit voice recorder
A flight recorder is an electronic recording device placed in an aircraft for the purpose of facilitating the investigation of aviation accidents and incidents. The device may often be referred to colloquially as a "black box", an outdated nam ...
or
flight data recorder
A flight recorder is an electronic recording device placed in an aircraft for the purpose of facilitating the investigation of aviation accidents and incidents. The device may often be referred to colloquially as a "black box", an outdated nam ...
must contain an
underwater locator beacon. In the US, ELTs are required to be permanently installed in most general aviation aircraft, depending upon the type or location of operation.
The specifications for the design of ELTs are published by the
RTCA, and in the specification the alarm signal is defined as an AM signal (A3X and/or N0N emissions), containing a swept tone ranging from 1600 Hz to 300 Hz (downwards), with 2-4 sweeps per second.
When activated, 406 MHz units transmit a 0.5 second, 5-watt digital burst every 50 seconds, varying within a span of ±2.5 seconds somewhat randomly, so as to avoid multiple ELTs always having their beacons synchronized.
As pe
14 CFR 91.207.a.1 ELTs built according t
TSO-C91 (of the type described below as "
Traditional ELT, unregistered") have not been permitted for new installations since June 21, 1995; the replacing standard was TSO-C91a. Furthermore, TSO-C91/91a ELTs are being replaced / supplemented by the TSO C126 406 MHz ELT, a far superior unit.
ELTs are unique among distress radiobeacons in that they have
impact monitors and are activated by
g-force
The g-force or gravitational force equivalent is a Specific force, mass-specific force (force per unit mass), expressed in Unit of measurement, units of standard gravity (symbol ''g'' or ''g''0, not to be confused with "g", the symbol for ...
.
Although monitoring of 121.5 and 243 MHz (Class B) distress signals by satellite ceased in February 2009, the FAA has not mandated an upgrade of older ELT units to 406 MHz in United States aircraft. Transport Canada has put forward a proposed regulatory requirement that requires upgrade to Canadian registered aircraft to either a 406 MHz ELT or an alternate means system; however, elected officials have overruled the recommendation of Transport Canada for the regulation and have asked for a looser regulation to be drafted by Transport Canada. Recent information indicates Transport Canada may permit private, general aviation flight with only an existing 121.5 MHz ELT if there is a placard visible to all passengers stating to the effect that the aircraft does not comply with international recommendations for the carriage of the 406 MHz emergency alerting device and is not detectable by satellites in the event of a crash.
In the case of 121.5 MHz beacons, the frequency is known in aviation as the "VHF Guard" emergency frequency, and all U.S. civilian pilots (private and commercial) are required, by FAA policy, to monitor this frequency when it is possible to do so. The frequency can be used by
Automatic Direction Finder
An automatic direction finder (ADF) is a marine or aircraft Radio navigation, radio-navigation instrument that automatically and continuously displays the relative bearing from the ship or aircraft to a suitable radio station. ADF receivers are n ...
(ADF) radionavigation equipment, which is being phased out in favor of
VOR and
GPS but is still found on many aircraft. ELTs are relatively large, and would fit in a cube about on a side, and weigh .
ELTs were first mandated in 1973 by FAA technical standard order (TSO-C91). The original TSO-C91, and updated TSO-C91A were officially deprecated as of February 2, 2009, when reception of the 121.5 MHz signal was deactivated on all of the SAR satellite, in favor of the C126 ELT models, with their 406 MHz
Cospas-Sarsat
The International Cospas-Sarsat Programme is a satellite-aided search and rescue (SAR) initiative. It is organized as a treaty-based, nonprofit, intergovernmental, humanitarian cooperative of 45 nations and agencies (see infobox). It is dedica ...
beacons. However, the 121.5 MHz signal is still used for close-in direction finding of a downed aircraft.
ELT activation
Automatic ELTs have
impact monitors activated by
g-force
The g-force or gravitational force equivalent is a Specific force, mass-specific force (force per unit mass), expressed in Unit of measurement, units of standard gravity (symbol ''g'' or ''g''0, not to be confused with "g", the symbol for ...
. Numerous activities, such as
aerobatics
Aerobatics is the practice of flying maneuvers involving aircraft attitudes that are not used in conventional passenger-carrying flights. The term is a portmanteau of "aeroplane" and "acrobatics". Aerobatics are performed in aeroplanes and gl ...
, hard landings, movement by ground crews and aircraft maintenances, can generate false alarms, which can interfere with and cannot be distinguished from genuine emergency transmissions.
ELT sub-classification
Emergency locator transmitters (ELTs) for aircraft may be classed as follows:
* A: automatically ejected
* AD: automatic deployable
* F: Fixed
* AF: automatic fixed
* AP: automatic portable
* W: water activated
* S: survival
Within these classes, an ELT may be either a digital 406 MHz beacon, or an analog beacon (
see below).
Obsolete ELTs
* Any ELT that is not a 406 MHz ELT with a Hex Code became obsolete February 1, 2009.
According to the U.S.
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is a Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation that regulates civil aviation in t ...
, ground testing of A-, B-, and S-type ELTs is to be done within the first 5 minutes of each hour. Testing is restricted to three audio sweeps. Type I and II devices (those transmitting at 406 MHz) have a self test function and must not be activated except in an actual emergency.
Timeline of ELT development
* Automatic SOS radios were developed as early as the 1930s.
* The
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
institutes development of a "Crash-Locator Beacon" and a "Crash-Locator Bearing Recorder" in the early 1950s.
* In the UK, by 1959 the first automatic beacon for liferafts had been produced by
Ultra Electronics
Ultra Electronics Holdings is a British defence and security company. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index until it was acquired by Cobham, which is itself owned by Advent International.
The ...
, and at the same time Burndept produced the TALBE (Talk and Listen Beacon Equipmen
- VHF, and SARBE - Search-And-Rescue-Beacon Equipment (UHF) range of beacons which were used by the
Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (FAA) is the naval aviation component of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy (RN). The FAA is one of five :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, RN fighting arms. it is a primarily helicopter force, though also operating the Lockhee ...
and later,
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
. Later, SARBE beacons included a radio for voice communication by the survivor with the rescuing personnel.
* Jan 9 1964: FAA Advisory Circular 170-4 investigated ELTs
* Mar 17 1969: FAA Advisory Circular 91-19 advised pilots to install ELTs
* A
Saturday Evening Post
''The Saturday Evening Post'' is an American magazine published six times a year. It was published weekly from 1897 until 1963, and then every other week until 1969. From the 1920s to the 1960s, it was one of the most widely circulated and influ ...
article covered the death of 16-year-old Carla Corbus, who survived, though badly injured, along with her mother, for 54 days after the plane her step-dad was flying crashed in the Trinity Alps of California in March 1967. He was lost and died in the woods looking for rescue.
* The winter 1969 search for the
Hawthorne Nevada Airlines Flight 708
Hawthorne Nevada Airlines Flight 708 was a domestic non-scheduled passenger flight between Hawthorne Industrial Airport, Nevada (HTH) and Bob Hope Airport, Hollywood-Burbank Airport, California (BUR/KBUR) that crashed into terrain near the talles ...
"Gamblers' Special"
DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner manufactured by the Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II.
It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper ...
that crashed on February 18, 1969 in the Sierra Nevada Mountains. Five aircraft crashed and five searchers were killed while trying to find Flight 708.
* Carriage requirements for emergency locator beacons on most US non-jet powered fixed-wing civil aircraft became law on December 29, 1970, with the signing of Senate bill S.2193, "The Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970," Public Law 91-596. as a last-minute rider to the Occupational Safety and Health Act.
Senator Peter Dominick (R-Colorado) added the unrelated beacon language as a rider to the bill, which became section 31 of the law. (Earlier in the session he tried to add the requirements as an amendment to House bill H.R. 14465, the "Airport and Airways Development Act of 1969," but was unsuccessful.) It required most general aviation aircraft to install ELTs by Dec. 30, 1973, and it preempted all the state ELT laws. The federal ELT law left the matter of alerting vague, although the initial idea was alerting by over flying aircraft which could receive an ELT's 75-milliwatt signal from 50 nautical miles away. The law set the compliance dates as one year after passage for newly manufactured or imported aircraft (December 30, 1971), and three years for existing aircraft (December 30, 1973). In response to the law, the
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is a Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation that regulates civil aviation in t ...
(FAA) published on March 13, 1971, Notice of Proposed Rule Making (NPRM) 71–7 with the proposed amendments to the
Federal Aviation Regulations
The Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs) are rules prescribed by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) governing all aviation activities in the United States. The FARs comprise Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations (14 CFR). A wide var ...
(FAR). After public comment, the final rules were published in the Federal Register on September 21, 1971.
* The disappearance of U.S. Congressmen
Hale Boggs and
Nick Begich in a general aviation aircraft on October 16, 1972 sparked the then largest ever search and rescue effort, which proved fruitless. This high-profile event further hastened the mandating of ELTs aboard aircraft.
* The RTCA published DO-145, DO-146, and DO-147, which the FAA then adopted the three DO documents as Technical Standard Order TSO C91.
* After problems with the C-91 ELTs, The FAA responded to the defective early ELTs by outlawing the installation of C-91 ELTs and certifying C91a ELTs with an improved gravity switch, improved crash and fire-worthy casing, and batteries that work in colder temperatures.
* March 16, 1973: AC 20–85, Emergency Locator Transmitters and Receivers
* Dec 23, 1992: TSO-C126, 406 MHz Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) defines the 406 MHz ELT
Emergency Position-Indicating Radio Beacon
Emergency Position-Indicating Radio Beacons (EPIRBs) are a development of the ELT designed specifically for use on boats and ships, and basic models tend to be less expensive than ELTs (average cost is $800
). As such, instead of using an impact sensor to activate the beacon, they typically use a water-sensing device or a submerged-sensing device that activates and releases a floating beacon after it has been submerged in between 1 and 4 meters of water. In addition to the 406 MHz signal mandated by C/S T.001, the IMO and ICAO require an auxiliary 121.5 MHz at another frequency in order to support the large installed base of 121.5 MHz direction finding equipment.
The
RTCM (Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services) maintains specifications specific to EPIRB devices. The alarm signal is defined as an AM signal (A3X and/or N0N emissions), containing a swept tone ranging from 1600 Hz to 300 Hz (either upwards or downwards), with 2-4 sweeps per second.
EPIRBs with an
AIS transmitter are allocated
MMSI
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international ''maritime telephone number'', a temporarily assigned UID issued by that object's current flag state (unlike an IMO number, which is a permanent global UID ...
numbers in the range 974yyzzzz.

EPIRB sub-classification
Emergency position-indicating radio beacons (EPIRBs) are sub-classified as follows:
Recognized categories:
* Category I – 406/121.5 MHz. Float-free, automatically activated EPIRB. Detectable by satellite anywhere in the world. Recognized by GMDSS.
* Category II – 406/121.5 MHz. Similar to Category I, except is manually activated. Some models are also water activated.
Obsolete classes:
* Class A – 121.5/243 MHz. Float-free, automatically activating. Due to limited signal coverage and possible lengthy delays in signal recognition, the U.S. Coast Guard no longer recommends use of this type. These devices have been phased out by the U.S.
Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, internet, wi-fi, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains j ...
(FCC) and ''are no longer recognized''.
* Class B – 121.5/243 MHz. Manually activated version of Class A. These devices have been phased out by the FCC and ''are no longer recognized''.
* Class S – 121.5/243 MHz. Similar to Class B, except it floats, or is an integral part of a
survival craft (lifeboat) or
survival suit. These devices have been phased out by the FCC and ''are no longer recognized''. Their use is no longer recommended by the U.S. Coast Guard.
* Class C –
Marine VHF
Marine VHF radio is a worldwide system of two way radio, two way radio transceivers on ships and watercraft used for bidirectional voice communication from ship-to-ship, ship-to-shore (for example with harbormasters), and in certain circumstan ...
ch15/16. Manually activated, these beacons operate on maritime channels only, and therefore are not detectable by satellite or normal aircraft. Designed for small crafts operating close to shore, this type was only recognized in the United States. Use of these units was phased out in 1999. These devices have been phased out by the FCC and ''are no longer recognized''.
*
Inmarsat-E – This entered service in 1997 and service ended 1 December 2006; all former users have switched to Category I or II 406 MHz EPIRBs. These beacons were float-free, automatically activated EPIRBs operated on 1646 MHz and were detectable by the Inmarsat geostationary satellite system, and were recognized by
GMDSS, but not by the United States. In September 2004, Inmarsat announced that it was terminating its ''Inmarsat E'' EPIRB service as of December 2006 due to a lack of interest in the maritime community.
* Furthermore, the U.S. Coast Guard recommend that no EPIRB of any type manufactured before 1989 be used.
EPIRBs are a component of the
Global Maritime Distress and Safety System
The Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is a worldwide system for automated emergency signal communication for ships at sea developed by the United Nations' International Maritime Organization (IMO) as part of the SOLAS Convention ...
(GMDSS). Most commercial off-shore working vessels with passengers are required to carry a self-deploying EPIRB, while most in-shore and fresh-water craft are not.
As part of the United States efforts to prepare beacon users for the end of 121.5 MHz frequency processing by satellites, the FCC has prohibited the use of 121.5 MHz EPIRBs as of January 1, 2007 (47 CFR 80.1051). See
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charting the seas, conducting deep-sea exploratio ...
's statemen
on the 121.5/243 phaseout.
EPIRB activation
Automatic EPIRBs are water activated. Some EPIRBs also "deploy"; this means that they physically depart from their mounting bracket on the exterior of the vessel (usually by going into the water.)
For a marine EPIRB to begin transmitting a signal (or "activate") it first needs to come out of its bracket (or "deploy"). Deployment can happen either manually where someone must physically remove it from its bracket or automatically where water pressure will cause a
hydrostatic
Hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and "the pressure in a fluid or exerted by a fluid on an immersed body". The word "hydrostatics" is sometimes used to refer specifically to water and o ...
release unit to separate the EPIRB from its bracket. If it does not come out of the bracket it will not activate. There is a magnet in the bracket which operates a
reed safety switch in the EPIRB. This prevents accidental activation if the unit gets wet from rain or turbulent seas.
Once deployed, EPIRBs can be activated, depending on the circumstances, either manually (crewman flicks a switch) or automatically (when water contacts the unit's "sea-switch".) All modern EPIRBs provide both methods of activation and deployment, and thus are labelled "Manual and Automatic Deployment and Activation."
Automatic hydrostatic release unit
A hydrostatic release unit is designed to deploy automatically when submerged to a prescribed depth; the pressure of the water activates a mechanism which releases the EPIRB.

Submarine Emergency Positioning Indicating Radio Beacon
A Submarine Emergency Positioning Indicating Radio Beacon (SEPIRB) is an EPIRB that is approved for use on
submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
s. Two are carried on board and can be fired from the
submerged signal ejectors.
Ship Security Alert System
A Ship Security Alert System (SSAS) is a special variety of an EPIRB designed to alert the ship's owner(s) of a possible piracy or terrorist attack. They thus have several distinguishing operational differences:
* They are manually activated by hidden buttons or switches, much like the alarms bank tellers use.
* They are prohibited from emitting a homing signal on 121.5 MHz so as to make transmissions more covert.
* The COSPAS-SARSAT system sends the distress message to the vessel's country of origin, regardless of the location of the vessel.
As with EPIRBs, the RTCM maintains specifications for SSAS devices.
Personal Locator Beacon

Personal Locator Beacons (PLBs) are designed for use by individuals who are hiking, kayaking, or conducting other activities on land or water where they are not in or associated with an aircraft or vessel that is equipped with its own ELT or EPIRB. As with EPIRBs, the RTCM maintains specifications for PLB devices.
PLBs vary in size from cigarette-packet to paperback book and weigh 200 g to 1 kg ( to 2 lb). They can be purchased from marine suppliers, aircraft refitters, and (in Australia and the United States) hiking supply stores. The units have a useful life of 10 years, operate across a range of conditions , and transmit for 24 to 48 hours. The alarm signal is defined as an AM signal (A3X and/or N0N emissions), containing a swept tone ranging from 300 Hz to 1600 Hz (upwards), with 2–4 sweeps per second. PLBs shall sweep upward.
PLB alerts are passed to State and Local agencies.
They must be registered to a specific person (with NOAA in the U.S.).
PLB equipment is required to include 406 MHz plus a homing frequency on 121.5 MHz.
As of 2017, PLBs must have an internal GPS.
PLB sub-classification
There are two kinds of personal locator beacon (PLB):
* PLB with GPS data (internally or externally provided)
* PLB with no GPS data
All PLBs transmit in digital mode on 406 MHz. There are AIS PLBs that transmit on VHF 70.
Personal locator beacons operating on 406 MHz must be
registered. PLBs should not be used in cases where normal emergency response (such as
9-1-1
911, sometimes written , is an emergency telephone number for Argentina, Canada, the Dominican Republic, Fiji, Jordan, Mexico, Pakistan, Maldives, Palau, Panama, Iraq, the Philippines, Sint Maarten, the United States, and Uruguay, as well as ...
) exists.
Obsolete PLBs
* U.S. Military forces at one time used 121.5/243.0 MHz beacons such as the "PRC-106," which had a built-in VHF radio. The military is replacing them with modern 406 MHz PLBs.
Beacon content
The most important aspect of a beacon in classification is the mode of transmission. There are two valid transmission modes: digital and analog. Where digital usually has a longer range, analog is more reliable. Analog beacons are useful to search parties and SAR aircraft, though they are no longer monitored by satellite.
Analog 121.500 MHz homing signal
All ELTs, all PLBs, and most EPIRBs are required to have a low-power homing signal, that is identical to the original 121.500 MHz VHF beacon signal. However, due to the extremely large number of false alarms that the old beacons generated, the transmit power was greatly reduced, and because the VHF transmitter typically uses the same antenna as the UHF beacon, the radiated signal is further reduced by the inherent inefficiencies of transmitting with an antenna not tuned to the transmitted signal.
Digital 406 MHz beacons
406 MHz UHF beacons transmit bursts of digital information to orbiting satellites, and may also contain a low-power integrated analog (121.500 MHz)
homing beacon
An emergency locator beacon is a radio beacon, a portable battery powered radio transmitter, used to locate airplanes, vessels, and persons in distress and in need of immediate rescue. Various types of emergency locator beacons are carried by air ...
. They can be uniquely identified (via
GEOSAR). Advanced beacons encode a
GPS or
GLONASS
GLONASS (, ; ) is a Russian satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the second navigational system in operation with global cove ...
position into the signal. All beacons are located by Doppler triangulation to confirm the location. The digital data identifies the registered user. A phone call by authorities to the registered phone number often eliminates false alarms (false alarms are the typical case). If there is a problem, the beacon location data guides search and rescue efforts. No beacon is ignored. Anonymous beacons are confirmed by two Doppler tracks before beginning beacon location efforts.
The distress message transmitted by a 406 beacon contains the information such as:
* Which country the beacon originates from.
* A unique 15-digit hexadecimal beacon identification code (a "15-hex ID").
* The encoded identification of the vessel or aircraft in distress, either as an
MMSI
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international ''maritime telephone number'', a temporarily assigned UID issued by that object's current flag state (unlike an IMO number, which is a permanent global UID ...
value, or as, in the case of an ELT, either the aircraft's
registration or its
ICAO 24-bit address (from its Mode-S transponder)''.''
* When equipped, a GPS position.
* Whether or not the beacon contains a 121.5 MHz homing transmitter.
The digital distress message generated by the beacon varies according to the above factors and is encoded in 30
hexadecimal
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a Numeral system#Positional systems in detail, positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbo ...
characters. The unique 15-character digital identity (the 15-hex ID) is hard-coded in the firmware of the beacon. The 406.025 MHz carrier signal is modulated plus or minus 1.1 radians with the data encoded using
Manchester encoding
In telecommunications and data storage, Manchester code (also known as phase encoding, or PE) is a line code in which the encoding of each data bit is either low then high, or high then low, for equal time. It is a self-clocking signal with no ...
, which ensures a net zero phase shift aiding Doppler location
406 MHz beacon facts and transmission schedule
* 406 MHz beacons transmit for a quarter of a second immediately when turned on, and then transmit a digital burst once every 50 seconds thereafter. Both
GEOSAR and
LEOSAR satellites monitor these signals.
* The repetition period shall not be so stable that any two transmitters appear to be synchronized closer than a few seconds over a 5-minute period. The intent is that no two beacons will have all of their bursts coincident. The period shall be randomised around a mean value of 50 seconds, so that time intervals between transmission are randomly distributed on the interval 47.5 to 52.5 seconds. (specification for first-generation beacons)
* Preliminary specification for second-generation beacons. From beacon activation a total of
initial transmissions shall be made separated by fixed
s ± 0.1sintervals. The first transmission shall commence within
seconds of beacon activation. Transmissions shall then occur at nominally
0second intervals until
0 ± 1minutes after beacon activation. The repetition period between the start of two successive transmissions shall be randomised around the stated nominal value, so that intervals between successive transmissions are randomly distributed over ±
seconds. Subsequent transmissions
BD
* 406 MHz beacons will be the only beacons compatible with the
MEOSAR (DASS) system.
* 406 MHz beacons must be registered (
see below).
Hex codes
Example hex codes look like the following: 90127B92922BC022FF103504422535
* A bit telling whether the message is short (15 hex digits) or long (30 hex digits) format.
* A country code, which lets the worldwide COSPAS/SARSAT central authority identify the national authority responsible for the beacon.
* Embedded 15-Hex ID or 15-hex transmitted distress message, for example, 2024F72524FFBFF The hex ID is printed or stamped on the outside of the beacon and is hard-coded into its
firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
. The 15-hex ID can only be reprogrammed by certified distress radiobeacon technicians. The national authority uses this number to look up phone numbers and other contact information for the beacon. This is crucial to handle the large number of false alarms generated by beacons.
* A location protocol number, and type of location protocol: EPIRB or MMSI, as well as all the data fields of that location protocol. If the beacon is equipped with
GPS or
GLONASS
GLONASS (, ; ) is a Russian satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the second navigational system in operation with global cove ...
, a rough (rounded)
latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
and
longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
giving the beacon's current position. In some aircraft beacons, this data is taken from the aircraft's navigation system.
* When a beacon is sold to another country, the purchaser is responsible for having the beacon reprogrammed with a new country code and to
register
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), ...
it with their nation's beacon registry, and the seller is responsible to
de-register the deprecated beacon ID with their national beacon registry.
* One can use the beacon decoder web page at Cospas-Sarsat to extract the 15-hex ID from the 30-hex distress message.
Frequencies
Distress beacons transmit
distress signal
A distress signal, also known as a distress call, is an internationally recognized means for obtaining help. Distress signals are communicated by transmitting radio signals, displaying a visually observable item or illumination, or making a sou ...
s on the following key frequencies; the frequency used distinguishes the capabilities of the beacon. A ''recognized'' beacon can operate on one of the three (currently)
Cospas-Sarsat
The International Cospas-Sarsat Programme is a satellite-aided search and rescue (SAR) initiative. It is organized as a treaty-based, nonprofit, intergovernmental, humanitarian cooperative of 45 nations and agencies (see infobox). It is dedica ...
satellite-compatible frequencies. In the past, other frequencies were also used as a part of the
search and rescue
Search and rescue (SAR) is the search for and provision of aid to people who are in distress or imminent danger. The general field of search and rescue includes many specialty sub-fields, typically determined by the type of terrain the search ...
system.
Cospas-Sarsat (satellite) compatible beacon frequencies
* see above for transmission schedule
* 406 MHz
UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter ...
-
carrier signal
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or frequ ...
at 406.025-406.076 MHz ± 0.005 MHz
[https://web.archive.org/web/20060520033357/http://www.cospas-sarsat.com/DocumentsRSeries/r9oct28.pdf]
Channel frequency (status)
* Ch-1 A: 406.022 MHz (reference)
* Ch-2 B: 406.025 MHz (in use today)
* Ch-3 C: 406.028 MHz (in use today)
* Ch-4 D: 406.031 MHz
* Ch-5 E: 406.034 MHz
* Ch-6 F: 406.037 MHz (in use today)
* Ch-7 G: 406.040 MHz (in use today)
* Ch-8 H: 406.043 MHz
* Ch-9 I: 406.046 MHz
* Ch-10 J: 406.049 MHz (operational at a future date)
* Ch-11 K: 406.052 MHz (operational at a future date)
* Ch-12 L: 406.055 MHz
* Ch-13 M: 406.058 MHz
* Ch-14 N: 406.061 MHz (operational at a future date)
* Ch-15 O: 406.064 MHz (operational at a future date)
* Ch-16 P: 406.067 MHz
* Ch-17 Q: 406.070 MHz
* Ch-18 R: 406.073 MHz (operational at a future date)
* Ch-19 S: 406.076 MHz (operational at a future date)
Cospas-Sarsat unsupported beacon frequencies
*
Marine VHF radio channels 15/16 – these channels are used only on the obsolete Class C EPIRBs
* The obsolete
Inmarsat-E beacons transmitted to
Inmarsat
Inmarsat is a British communications satellite, satellite telecommunications company, offering global mobile services. It provides telephone and data services to users worldwide, via portable or mobile terminals which communicate with groun ...
satellites on 1646 MHz UHF.
* 121.5 MHz
VHF ± 6
kHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base uni ...
(frequency band protected to ±50 kHz)
(Satellite detection ceased on 1 February 2009, but this frequency is still used for short-range location during a search and rescue operation)
* 243.0 MHz UHF ± 12 kHz (frequency band protected to ± 100 kHz)
(prior to 1 February 2009 – COSPAS-SARSAT Compatible)
License and registration requirements
License
In
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
and
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different context ...
(and most jurisdictions in Europe) no special license is required to operate an EPIRB. In some countries (for example the Netherlands) a marine radio operators license is required. The following paragraphs define other requirements relating to EPIRBs, ELTs, and PLBs.
Registration
All distress alerting beacons operating on 406 MHz should be registered; all vessels and aircraft operating under
International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea
The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is an international maritime treaty which sets out minimum safety standards in the construction, equipment and operation of merchant ships. The International Maritime Organiza ...
(SOLAS) and
International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international sch ...
(ICAO) regulations must register their beacons. Some national administrations (including the United States, Canada, Australia, and the UK) also require registration of 406 MHz beacons.
* There is no charge to register 406 MHz beacons.
* The U.S. Coast Guard warns that a user's "life may be saved as a result of registered emergency information" because it can respond more quickly to signals from registered beacons.
* Unless the national registry authority advises otherwise, personal information contained in a beacon is used exclusively for SAR distress alert resolution purposes.
Th
Cospas-Sarsat Handbook of Beacon Regulationsprovides the status of 406 MHz beacon regulations in specific countries and extracts of some international regulations pertaining to 406 MHz beacons.
The following list shows the agencies accepting 406 beacon registrations by country:
* United States –
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
* Canada �
Canadian Beacon Registry CFB Trenton
Canadian Forces Base Trenton (also CFB Trenton), formerly RCAF Station Trenton, is a Canadian Forces base located within the city of Quinte West, Ontario. It is operated as an air force base by the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and is the hub ...
for civil beacons, CMCC for military beacons
* Australia –
Australian Maritime Safety Authority
Australian Maritime Safety Authority (AMSA) is an Australian statutory authority responsible for the regulation and safety oversight of Australia's shipping fleet and management of Australia's International Maritime Organization, international ...
(AMSA)
* United Kingdom –
United Kingdom Maritime and Coastguard Agency (MCA)
* Greece �
Ministry of Merchant Marine and
Hellenic Civil Aviation Authority
* France –
CNES
CNES () is the French national space agency. Headquartered in central Paris, the agency is overseen by the ministries of the Armed Forces, Economy and Finance and Higher Education, Research and Innovation.
It operates from the Toulouse Spac ...
* Italy �
Stazione Satellitare Italiana - Cospas Sarsat* Netherlands �
Agentschap Telecom (NL)* Denmark -
Danish Maritime Authority
* New Zealand - New Zealand Rescue Coordination Centr
* Switzerland - Federal Office for Civil Aviatio
* International �
Cospas-Sarsat International 406 MHz Beacon Registration Database (IBRD)
Specifications
Several regulations and technical specifications govern emergency locator beacons:
* FAA
** AC 20–85, Emergency Locator Transmitters and Receivers, March 16, 1973
** AC 170-4 Jan 9 1964 investigated ELTs
** AC 91-19 mar 17 1969 advised pilots to install ELTs
** ''
Code of Federal Regulations
In the law of the United States, the ''Code of Federal Regulations'' (''CFR'') is the codification of the general and permanent regulatory law, regulations promulgated by the executive departments and agencies of the federal government of the ...
'' §91.207 Emergency locator transmitters.
** TSO-C91
** TSO-C91a
** TSO-C126: 406 MHz Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT)
** TSO-C126a: 406 MHz Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT)
** TSO-C126b: 406 MHz Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT)
*
Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics
** DO-127?
** DO-145
** DO-146
** DO-147
*
Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services
** Special Committee (SC) 110 on Emergency Beacons (EPIRBs and PLBs)
** Special Committee (SC) 119 on Maritime Survivor Locator Devices
** Special Committee (SC) 121 on Automatic Identification Systems (AIS) and digital Messaging
** Special Committee (SC) 128 on
Satellite Emergency Notification Device
A Satellite Emergency Notification Device or SEND is a portable emergency notification and locating device which uses commercial satellite systems rather than the COSPAS-SARSAT satellite system. An example of this device is SPOT.
The devices use ...
(SEND)
* Cospas-Sarsat
** C/S A.001: Cospas-Sarsat Data Distribution Plan
** C/S A.002: Cospas-Sarsat Mission Control Centres Standard Interface Description
** C/S T.001 Specification for COSPAS-SARSAT 406 MHz Distress Beacons
** C/S T.007: COSPAS‑SARSAT 406 MHz Distress Beacons Type Approval Standard
** C/S T.015: Specification and Type Approval Standard for 406 MHz Ship Security Alert Beacons
** C/S G.003, Introduction to the Cospas-Sarsat System
** C/S G.004, Cospas-Sarsat Glossary
** C/S G.005, Guidelines on 406 MHz Beacon Coding, Registration, and Type Approval
** C/S S.007, Handbook of Beacon Regulations
* IMO
* ITU
** Recommendation ITU-R M.633 (IMO's technical requirements for the 406 MHz EPIRB signal)
** Report ITU-R M.2285-0 Maritime survivor locating systems and devices (man overboard systems) -- An overview of systems and their mode of operation
* ICAO
* IEC
** IEC 61097-2: Global maritime distress and safety system (GMDSS) - Part 2: COSPASSARSAT EPIRB - Satellite emergency position indicating radio beacon operating on 406 MHz - Operational and performance requirements, methods of testing and required test results
EPIRB hydrostatic release device requirements
*
Safety of Life a Sea Convention
** SOLAS 74.95
* ISO
** ISO 15734
* U.S. Federal Regulations
*
CFR title 46 Vol 6 Section 160.062* U.S. Coast Guard Regulations
USCG 160.162ref>
*** Corrosion resistance test
*** Temperature tests
*** Submergence and manual release test
*** Strength tests
*** Technical tests on the membrane
*** Performance test
Alternative technologies
There are also other personal devices in the marketplace which do not meet the standard for 406 MHz devices.
Maritime Survivor Locator Device
A Maritime Survivor Locator Device (MSLD) is a
man-overboard locator beacon. In the U.S., rules were established in 2016 in 47 C.F.R. Part 95
MOB devices with
DSC DSC or Dsc may refer to:
Education
* Doctor of Science (D.Sc.)
* District Selection Committee, an entrance exam in India
* Doctor of Surgical Chiropody, superseded in the 1960s by Doctor of Podiatric Medicine
Educational institutions
* Dyal Sin ...
or
AIS are allocated
MMSI
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international ''maritime telephone number'', a temporarily assigned UID issued by that object's current flag state (unlike an IMO number, which is a permanent global UID ...
numbers in the range 972yyzzzz.
A MSLD may transmit on 121.500 MHz, or one of these: 156.525 MHz, 156.750 MHz, 156.800 MHz, 156.850 MHz, 161.975 MHz, 162.025 MHz (bold are Canadian-required frequencies). Although sometimes defined in the same standards as the COSPAS-SARSAT beacons, MSLDs can not be detected by that satellite network, and are instead intended only for short-range
Direction finding
Direction finding (DF), radio direction finding (RDF), or radiogoniometry is the use of radio waves to determine the direction to a radio source. The source may be a cooperating radio transmitter or may be an inadvertent source, a naturall ...
equipment mounted on the vessel on which the survivor was traveling.
AIS SART
These devices are distinct from traditional SAR radar transponders (
SART
Sart is a name for the settled inhabitants of Central Asia which has had shifting meanings over the centuries. According to Great Soviet Encyclopedia, before the October Revolution of 1917, the name “Sart” was used in ...
), as they transmit AIS messages containing accurate GPS position information and include a
GPS receiver and a transmitter on
VHF AIS channels, so they show up on ship AIS receivers. They are lightweight and can be used to equip inflatable
liferafts.
AIS-SART devices are allocated
MMSI
A Maritime Mobile Service Identity (MMSI) is effectively a maritime object's international ''maritime telephone number'', a temporarily assigned UID issued by that object's current flag state (unlike an IMO number, which is a permanent global UID ...
numbers in the range 970YYxxxx.
SEND—Satellite Emergency Notification Device
These devices are commonly referred to as SEND (Satellite Emergency Notification Device), and examples include SPOT and inReach.
APRS
APRS is used by
amateur radio operator
An amateur radio operator is someone who uses equipment at an amateur radio station to engage in two-way personal communications with other amateur operators on radio frequencies assigned to the amateur radio service. Amateur radio operators ...
s to track positions and send short messages. Most APRS packets contain a
GPS latitude and longitude, so they can be used for both normal and emergency tracking. They also are routed to the Internet, where they are archived for some period of time, and viewable by others. There are several emergency packet types that can indicate distress. Since it is part of the amateur radio service, it costs nothing to transmit on and uses the extensive network, however, one must be a licensed amateur radio operator. There is also no guarantee that an APRS distress packet report would be seen or handled by
emergency responders. It would have to be seen by an amateur radio operator and forwarded on.
See also
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Notes
References
* COSPAS-SARSAT, Document C/S T.001 October 1999
* FCC, Part 80 and
GMDSS
* MED, 0735/2001
* RTCM, Standard for 406 MHz Satellite EPIRBs
External links
Cospas-Sarsat – the International Satellite System For Search and RescueITU – Maritime mobile Access and Retrieval System (MARS)NOAA SARSAT websiteNOAA notice of planned phasing out of 121.5/243 MHz beacons in 2009
ICAO/IMO Working Paper 10 to 14 September 2007 – Joint Working Group on Harmonization of Aeronautical and Maritime Search and RescueOperation of a Hydrostatic Release Unit*
Rescue Coordination Centres (RCCs) and SAR Points of Contact (SPOCs)RCC MessagesThe History and Experience of the International COSPAS-SARSAT Programme for Satellite-Aided Search and Rescue
{{Authority control
Aircraft emergency systems
Beacons
Emergency communication
International telecommunications
Radio stations and systems ITU
Rescue equipment
Radio geopositioning
 An emergency position-indicating radiobeacon (EPIRB) is a type of
An emergency position-indicating radiobeacon (EPIRB) is a type of  Emergency Locator Transmitters (ELTs) are expensive devices (average cost for aviation use is $1500–3000). In commercial aircraft, a
Emergency Locator Transmitters (ELTs) are expensive devices (average cost for aviation use is $1500–3000). In commercial aircraft, a 
