Electorate of Bavaria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Electorate of Bavaria () was a quasi-independent hereditary electorate of the

 Whatever lustre the international position won by Maximilian I might add to the electoral house, on Bavaria itself its effect during the next two centuries was more dubious. Maximilian's son, Ferdinand Maria (1651–1679), who was a minor when he succeeded, did much indeed to repair the wounds caused by the Thirty Years' War, encouraging agriculture and industries, and building or restoring numerous churches and monasteries. In 1669, moreover, he again called a meeting of the diet, which had been suspended since 1612.
His constructive work, however, was largely undone by his son Maximilian II Emanuel (1679–1726), whose far-reaching ambition set him warring against the
Whatever lustre the international position won by Maximilian I might add to the electoral house, on Bavaria itself its effect during the next two centuries was more dubious. Maximilian's son, Ferdinand Maria (1651–1679), who was a minor when he succeeded, did much indeed to repair the wounds caused by the Thirty Years' War, encouraging agriculture and industries, and building or restoring numerous churches and monasteries. In 1669, moreover, he again called a meeting of the diet, which had been suspended since 1612.
His constructive work, however, was largely undone by his son Maximilian II Emanuel (1679–1726), whose far-reaching ambition set him warring against the
 In 1792 the French Revolutionary Army overran the Palatinate; in 1795 the French, under Jean Victor Moreau, invaded Bavaria itself, advanced to Munich – where they were received with joy by the long-suppressed Liberals – and laid siege to
In 1792 the French Revolutionary Army overran the Palatinate; in 1795 the French, under Jean Victor Moreau, invaded Bavaria itself, advanced to Munich – where they were received with joy by the long-suppressed Liberals – and laid siege to  Between the French and the Austrians, Bavaria was now in a bad situation. Before the death of Charles Theodore (16 February 1799) the Austrians had again occupied the country, in preparation for renewing the war with France. Maximilian IV Joseph (of Palatine Zweibrücken), the new elector, succeeded to a difficult inheritance. Though his own sympathies, and those of his all-powerful minister, Maximilian von Montgelas, were, if anything, French rather than Austrian, the state of the Bavarian finances, and the fact that the Bavarian troops were scattered and disorganized, placed him helpless in the hands of Austria; on 2 December 1800 the
Between the French and the Austrians, Bavaria was now in a bad situation. Before the death of Charles Theodore (16 February 1799) the Austrians had again occupied the country, in preparation for renewing the war with France. Maximilian IV Joseph (of Palatine Zweibrücken), the new elector, succeeded to a difficult inheritance. Though his own sympathies, and those of his all-powerful minister, Maximilian von Montgelas, were, if anything, French rather than Austrian, the state of the Bavarian finances, and the fact that the Bavarian troops were scattered and disorganized, placed him helpless in the hands of Austria; on 2 December 1800 the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
from 1623 to 1806, when it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
The Wittelsbach dynasty which ruled the Duchy of Bavaria was the younger branch of the family which also ruled the Electoral Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire until it was annexed by the Electorate of Baden in 1803. From the end of the 13th century, its ruler was one of the Prince-electors who elected the Holy Roman Empero ...
. The head of the elder branch was one of the seven prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
according to the Golden Bull of 1356, but Bavaria was excluded from the electoral dignity. In 1621, Frederick V, Elector Palatine was put under the imperial ban for his role in the Bohemian Revolt against Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand II (9 July 1578 – 15 February 1637) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, King of Hungary, Hungary, and List of Croatian monarchs, Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II, Archduke of Austr ...
, and the electoral dignity and territory of the Upper Palatinate was conferred upon his loyal cousin, Duke Maximilian I of Bavaria. Although the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
would create a new electoral title for Frederick V's son, with the exception of a brief period during the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
, Maximilian's descendants would continue to hold the original electoral dignity until the extinction of his line in 1777. At that point the two lines were joined in personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
until the end of the Holy Roman Empire. In 1805, after the Peace of Pressburg, the then-elector, Maximilian Joseph, raised himself to the dignity of King of Bavaria, and the Holy Roman Empire was abolished the year after.
Geography
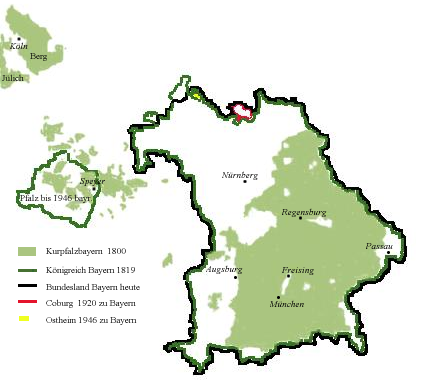
The Electorate of Bavaria consisted of most of the modern regions of Upper Bavaria, Lower Bavaria, and the Upper Palatinate. Before 1779, it also included the Innviertel, now part of modernAustria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
. This was ceded to the Habsburgs by the Treaty of Teschen, which ended the War of the Bavarian Succession. There were a considerable number of independent enclaves and jurisdictions within those broad areas, however, including the principalities of Palatinate-Neuburg and Palatinate-Sulzbach in the Upper Palatinate, which were held by cadet branches of the Palatinate line of the Wittelsbachs; the ecclesiastical states of Freising, Regensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
, and Passau
Passau (; ) is a city in Lower Bavaria, Germany. It is also known as the ("City of Three Rivers"), as the river Danube is joined by the Inn (river), Inn from the south and the Ilz from the north.
Passau's population is about 50,000, of whom ...
, and the imperial free city of Regensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
. For administration purposes Bavaria was already from 1507 divided into four stewardships ('): Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
, Burghausen, Landshut and Straubing. With the acquisition of the Upper Palatinate during the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
the stewardship Amberg was added. In 1802 they were abolished by the minister Maximilian von Montgelas. In 1805 shortly before the elevation Tyrol and Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( ; ; , , or ) is the westernmost States of Austria, state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the second-highest popu ...
were united with Bavaria, same as several of these enclaves.
Dignities
By virtue of his electoral title, the Elector of Bavaria was a member of the Council of Electors in the Imperial Diet as well as Archsteward of the Holy Roman Empire; he also held the dignity of Imperial Vicar during imperial vacancies along with the Elector of Saxony, a duty he undertook in 1657–1658, 1740–1742, 1745, 1790, and 1792. In theCouncil of Princes
The Imperial Diet (; ) was the deliberative body of the Holy Roman Empire. It was not a legislative body in the contemporary sense; its members envisioned it more like a central forum where it was more important to negotiate than to decide.
Its ...
of the Diet prior to the personal union of 1777 he held individual voices as Duke of Bavaria and (after 1770) Princely Landgrave of Leuchtenberg. In the Imperial Circles he was, along with the Archbishop of Salzburg, co-director of the Bavarian Circle, a circle territorially dominated by the elector's lands. He also held lands in the Swabian Circle. After 1777 these lands were joined by most of the Palatine lands, including the Electoral Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire until it was annexed by the Electorate of Baden in 1803. From the end of the 13th century, its ruler was one of the Prince-electors who elected the Holy Roman Empero ...
, the Duchies of Jülich and Berg, Palatinate-Neuburg, Palatinate-Sulzbach, Palatinate-Veldenz, and other territories. The final Palatine territory of Palatine Zweibrücken was united with Bavaria in 1799 when its duke inherited the Bavarian and Palatine thrones.
History
Thirty Years' War
When he had succeeded to the throne of the Duchy of Bavaria in 1597, Maximilian I had found it encumbered with debt and filled with disorder, but ten years of his vigorous rule effected a remarkable change. The finances and the judicial system were reorganised, a class of civil servants and a national militia founded, and several small districts were brought under the duke's authority. The result was a unity and order in the duchy which enabled Maximilian to play an important part in theThirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
; during the earlier years of which he was so successful as to acquire the Upper Palatinate and the electoral dignity which had been enjoyed since 1356 by the elder branch of the Wittelsbach family. In spite of subsequent reverses, Maximilian retained these gains at the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
in 1648. During the later years of this war Bavaria, especially the northern part, suffered severely. In 1632 the Swedes
Swedes (), or Swedish people, are an ethnic group native to Sweden, who share a common ancestry, Culture of Sweden, culture, History of Sweden, history, and Swedish language, language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countries, ...
invaded, and when Maximilian violated the Treaty of Ulm in 1647, the French and the Swedes ravaged the land. After repairing this damage to some extent, the elector died at Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (; Austro-Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an Independent city#Germany, independent city on the Danube, in Upper Bavaria, with 142,308 inhabitants (as of 31 December 2023). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan ...
in September 1651, leaving his state much stronger than he had found it. The addition of the Upper Palatinate made Bavaria compact; the acquisition of the electoral vote made it influential; and the electorate was able to play a part in European politics which internal strife had rendered impossible for the past four hundred years.
Absolutism

Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and, on the side of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, in the great struggle of the Spanish succession. He shared in the defeat at the Battle of Blenheim, near Höchstädt, on 13 August 1704. Placed under the imperial ban, his dominions were temporarily partitioned between Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
and the elector palatine by the Treaty of Ilbersheim, and only restored to him, harried and exhausted, at the Treaty of Baden in 1714; the first Bavarian peasant insurrection, known as '' Sendling's night of murder'', having been crushed by the Austrian occupiers in 1706.
Untaught by Maximilian II Emmanuel's experience, his son, Charles Albert (1726–1745), devoted all his energies to increasing the European prestige and power of his house. The death of the Emperor Charles VI proved his opportunity: he disputed the validity of the Pragmatic Sanction which secured the Habsburg succession to Maria Theresa, allied himself with France, conquered Upper Austria
Upper Austria ( ; ; ) is one of the nine States of Austria, states of Austria. Its capital is Linz. Upper Austria borders Germany and the Czech Republic, as well as the other Austrian states of Lower Austria, Styria, and Salzburg (state), Salzbur ...
, was crowned king of Bohemia at Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
and, in 1742, emperor at Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
. The price he had to pay, however, was the occupation of Bavaria itself by Austrian troops; and, though the invasion of Bohemia in 1744 by Frederick II of Prussia enabled him to return to Munich, at his death on 20 January 1745 it was left to his successor to make what terms he could for the recovery of his dominions.
Maximilian III Joseph (1745–1777), by the Treaty of Füssen signed on 22 April 1745, obtained the restitution of his dominions in return for a formal acknowledgment of the Pragmatic Sanction. He was a man of enlightenment, did much to encourage agriculture, industries and the exploitation of the mineral wealth of the country, founded the Academy of Sciences at Munich, and abolished the Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
censorship of the press. At his death, without issue, on 30 December 1777, the Bavarian line of the Wittelsbachs became extinct, and the succession passed to Charles Theodore, the elector palatine. After a separation of four and a half centuries, the Electoral Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire until it was annexed by the Electorate of Baden in 1803. From the end of the 13th century, its ruler was one of the Prince-electors who elected the Holy Roman Empero ...
, to which the duchies of Jülich and Berg had been added, was thus reunited with Bavaria.
Palatinate-Bavaria
So great an accession of strength to a neighbouring state, whose ambition she had so recently had just reason to fear, proved intolerable to Austria, which laid claim to a number of lordships —forming one-third of the whole Bavarian inheritance – as lapsed fiefs of the Bohemian, Austrian, and imperial crowns. These were at once occupied by Austrian troops, with the secret consent of Charles Theodore himself, who was without legitimate heirs, and wished to obtain from the emperor the elevation of his natural children to the status of princes of the Empire. The protests of the next heir, Charles II, Duke of Zweibrücken (Deux-Ponts), supported by the king ofPrussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, led to the War of Bavarian Succession. By the peace of Teschen (13 May 1779) the Innviertel was ceded to Austria, and the succession secured to Charles of Zweibrücken.
For Bavaria itself Charles Theodore did less than nothing. He felt himself a foreigner among foreigners, and his favourite scheme, the subject of endless intrigues with the Austrian cabinet and the immediate cause of Frederick II's League of Princes ( Fürstenbund) of 1785, was to exchange Bavaria for the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The period began with the acquisition by the Austrian Habsburg monarchy of the former Spanish Netherlands under the Treaty of Ras ...
and the title of king of Burgundy. For the rest, the enlightened internal policy of his predecessor was abandoned. The funds of the suppressed order of Jesus, which Maximilian Joseph had destined for the reform of the educational system of the country, were used to endow a province of the knights of St John of Jerusalem, for the purpose of combating the enemies of the faith. The government was inspired by the narrowest clericalism, which culminated in the attempt to withdraw the Bavarian bishops from the jurisdiction of the great German metropolitans and place them directly under that of the pope. On the eve of the French Revolution the intellectual and social condition of Bavaria remained that of the Middle Ages.
Revolutionary and Napoleonic periods
 In 1792 the French Revolutionary Army overran the Palatinate; in 1795 the French, under Jean Victor Moreau, invaded Bavaria itself, advanced to Munich – where they were received with joy by the long-suppressed Liberals – and laid siege to
In 1792 the French Revolutionary Army overran the Palatinate; in 1795 the French, under Jean Victor Moreau, invaded Bavaria itself, advanced to Munich – where they were received with joy by the long-suppressed Liberals – and laid siege to Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (; Austro-Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an Independent city#Germany, independent city on the Danube, in Upper Bavaria, with 142,308 inhabitants (as of 31 December 2023). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan ...
. Charles Theodore, who had done nothing to prevent wars or to resist the invasion, fled to Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
, leaving a regency, the members of which signed a convention with Moreau, by which he granted an armistice in return for a heavy contribution (7 September 1796). Between the French and the Austrians, Bavaria was now in a bad situation. Before the death of Charles Theodore (16 February 1799) the Austrians had again occupied the country, in preparation for renewing the war with France. Maximilian IV Joseph (of Palatine Zweibrücken), the new elector, succeeded to a difficult inheritance. Though his own sympathies, and those of his all-powerful minister, Maximilian von Montgelas, were, if anything, French rather than Austrian, the state of the Bavarian finances, and the fact that the Bavarian troops were scattered and disorganized, placed him helpless in the hands of Austria; on 2 December 1800 the
Between the French and the Austrians, Bavaria was now in a bad situation. Before the death of Charles Theodore (16 February 1799) the Austrians had again occupied the country, in preparation for renewing the war with France. Maximilian IV Joseph (of Palatine Zweibrücken), the new elector, succeeded to a difficult inheritance. Though his own sympathies, and those of his all-powerful minister, Maximilian von Montgelas, were, if anything, French rather than Austrian, the state of the Bavarian finances, and the fact that the Bavarian troops were scattered and disorganized, placed him helpless in the hands of Austria; on 2 December 1800 the Bavarian Army
The Bavarian Army () was the army of the Electorate of Bavaria, Electorate (1682–1806) and then Kingdom of Bavaria, Kingdom (1806–1918) of Bavaria. It existed from 1682 as the standing army of Bavaria until the merger of the military sovereig ...
was involved in the Austrian defeat at Hohenlinden, and Moreau once more occupied Munich. By the Treaty of Lunéville
The Treaty of Lunéville (or Peace of Lunéville) was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville on 9 February 1801. The signatory parties were the French Republic and Emperor Francis II, who signed on his own behalf as ruler of the hereditary do ...
(9 February 1801) Bavaria lost the Palatinate and the duchies of Zweibrücken and Jülich.
In view of the scarcely disguised ambitions and intrigues of the Austrian court, Montgelas now believed that the interests of Bavaria lay in a frank alliance with the French Republic
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
; he succeeded in overcoming the reluctance of Maximilian Joseph; and, on 24 August, a separate treaty of peace and alliance with France was signed at Paris. By the third article of this the First Consul undertook to see that the compensation promised under the 7th article of the Treaty of Lunéville for the territory ceded on the left bank of the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, should be carried out at the expense of the Empire in the manner most agreeable to Bavaria (see de Martens, ''Recueil'', vol. vii. p. 365).
In 1803, accordingly, in the territorial rearrangements consequent on Napoleon's suppression of the ecclesiastical states, and of many free cities of the Empire, Bavaria received the bishoprics of Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is, after Nuremberg and Fürth, the Franconia#Towns and cities, third-largest city in Franconia located in the north of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Lower Franconia. It sp ...
, Bamberg
Bamberg (, , ; East Franconian German, East Franconian: ''Bambärch'') is a town in Upper Franconia district in Bavaria, Germany, on the river Regnitz close to its confluence with the river Main (river), Main. Bamberg had 79,000 inhabitants in ...
, Augsburg
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavaria, Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a College town, university town and the regional seat of the Swabia (administrative region), Swabia with a well ...
and Freisingen, part of that of Passau
Passau (; ) is a city in Lower Bavaria, Germany. It is also known as the ("City of Three Rivers"), as the river Danube is joined by the Inn (river), Inn from the south and the Ilz from the north.
Passau's population is about 50,000, of whom ...
, the territories of twelve abbeys, and seventeen cities and villages, the whole forming a compact territory which more than compensated for the loss of her outlying provinces on the Rhine. Montgelas now aspired to raise Bavaria to the rank of a first-rate power, and he pursued this object during the Napoleonic epoch with consummate skill, allowing fully for the preponderance of France – so long as it lasted – but never permitting Bavaria to sink, like so many of the states of the Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austrian Empire, Austria ...
, into a mere French dependency.
End of the Electorate of Bavaria
On 25 August 1805, Bavaria signed the Treaty of Bogenhausen with France. The primary consequence of the treaty was Bavaria's military support for Napoleon. Bavarian troops under GeneralKarl Philipp von Wrede
Karl (or Carl) Philipp Josef, Fürst, Prince von Wrede (; 29 April 176712 December 1838) was a Bavarian field marshal. He was an ally of Napoleonic France until he negotiated the Treaty of Ried with Austria in 1813. Thereafter Bavaria joined the c ...
fought the Austrians
Austrians (, ) are the citizens and Nationality, nationals of Austria. The English term ''Austrians'' was applied to the population of Archduchy of Austria, Habsburg Austria from the 17th or 18th century. Subsequently, during the 19th century, ...
at Iglau in Bohemia, which contributed to the simultaneous French victory at Austerlitz on 2 December 1805.
In the war of 1805, in accordance with a treaty of alliance signed at Würzburg
Würzburg (; Main-Franconian: ) is, after Nuremberg and Fürth, the Franconia#Towns and cities, third-largest city in Franconia located in the north of Bavaria. Würzburg is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Lower Franconia. It sp ...
on 23 September, Bavarian troops, for the first time since the days of Charles VII, fought side by side with the French, and by the Treaty of Pressburg, signed on 26 December, the Prince-Bishopric of Eichstätt, the Margravate of Burgau
Burgau () is a Town#Germany, town in Günzburg (district), the district of Günzburg in Swabia (Bavaria), Swabia, Bavaria. Burgau lies on the river Mindel (river), Mindel and has a population of just under 10,000.
History
The territory around ...
, the Lordship of Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( ; ; , , or ) is the westernmost States of Austria, state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the second-highest popu ...
, the countships of Hohenems and Königsegg-Rothenfels, the lordships of Argen and Tettnang, and the city of Lindau with its territory were to be added to Bavaria. On the other hand, Würzburg, obtained in 1803, was to be ceded by Bavaria to the elector of Salzburg in exchange for Tyrol . By the 1st article of the treaty the emperor already acknowledged the assumption by the elector of the title of king, as Maximilian I. The price which Maximilian had reluctantly to pay for this accession of dignity was the marriage of his daughter Augusta with Eugène de Beauharnais.
The electorate existed until 1806, when Bavaria was proclaimed a kingdom. It had its origins in the Franco-Bavarian Treaty of Brno of 10–12 December 1805 and in the Peace of Pressburg on 26 December 1805 between the plenipotentiaries of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and the Holy Roman and Austrian Emperor Francis II & I concluded a peace treaty, because Austria now had to cede the counties of Tyrol and Vorarlberg to Bavaria. Duke and Elector Maximilian IV Joseph was proclaimed King Maximilian I Joseph on 1 January 1806 in Munich as the first king of Bavaria. From 1 January 1806, the Bavarian royal title initially read:
"By the grace of God, King of Bavaria, Archpalatine Count of the Holy Roman Empire, Archtruchsess and Elector."
The formal exit of Bavaria from the Holy Roman Empire, renouncing the electoral dignity, did not take place until July 1806 with the Rheinbund Act. The new king still served as an elector until Bavaria left the Holy Roman Empire (1 August 1806). On 15 March 1806 Max Joseph had ceded the Duchy of Berg to Napoleon. Shortly thereafter, the Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austrian Empire, Austria ...
was formed and Maximilian Joseph, with the other princes who joined that body, announced his secession from the Holy Roman Empire. On 6 August 1806, the Holy Roman Empire was dissolved after surviving for a thousand years.
See also
* * IlluminatiReferences
{{Electors of the Holy Roman Empire after 1356 States and territories disestablished in 1806 History of Bavaria Early modern history of GermanyBavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
1623 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
17th century in the Holy Roman Empire
18th century in the Holy Roman Empire
19th century in Germany
1806 disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire
Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...