Elam on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Elam (;  ''hatamti''; Cuneiform Elamite: ; Sumerian: ;
''hatamti''; Cuneiform Elamite: ; Sumerian: ;
 in
in
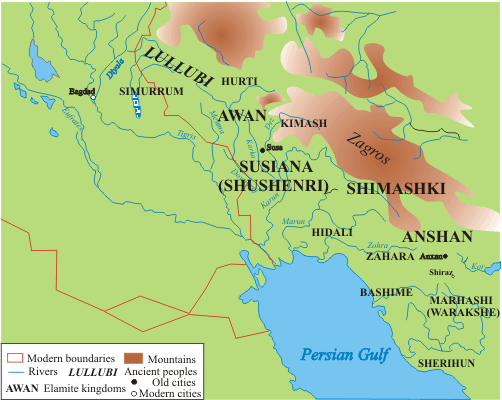
 In geographical terms, Susiana basically represents the Iranian province of
In geographical terms, Susiana basically represents the Iranian province of
''The Archaeology of Elam: Formation and Transformation of an Ancient Iranian State.''
Cambridge World Archaeology. Cambridge University Press, 2015 p11 Disagreements over the location also exist in the Jewish historical sources says Daniel T. Potts. Some ancient sources draw a distinction between Elam as the highland area of Khuzestan, and Susiana as the lowland area. Yet in other ancient sources 'Elam' and 'Susiana' seem equivalent. The uncertainty in this area extends also to modern scholarship. Since the discovery of ancient Anshan, and the realization of its great importance in Elamite history, the definitions were changed again. Some modern scholars argued that the center of Elam lay at Anshan and in the highlands around it, and not at Susa in lowland Khuzistan. Potts disagrees suggesting that the term 'Elam' was primarily constructed by the Mesopotamians to describe the area in general terms, without referring specifically either to the lowlanders or the highlanders,
 Proto-Elamite civilization grew up east of the
Proto-Elamite civilization grew up east of the  The Proto-Elamite city of Susa was founded around 4000 BC in the watershed of the river Karun. It is considered to be the site of Proto-Elamite cultural formation. During its early history, it fluctuated between submission to
The Proto-Elamite city of Susa was founded around 4000 BC in the watershed of the river Karun. It is considered to be the site of Proto-Elamite cultural formation. During its early history, it fluctuated between submission to
 The Old Elamite period began around 2700 BC. Historical records mention the conquest of Elam by Enmebaragesi, the
The Old Elamite period began around 2700 BC. Historical records mention the conquest of Elam by Enmebaragesi, the
 The Awan dynasty (2350–2150 BC) was partly contemporary with that of the Mesopotamian emperor
The Awan dynasty (2350–2150 BC) was partly contemporary with that of the Mesopotamian emperor
 The succeeding dynasty, often called the
The succeeding dynasty, often called the
File:Indus round seal with impression Elongated buffalo with Harappan scrpit imported to Susa in 2600-1700 BCE LOUVRE Sb5614.jpg, Indus round seal with impression. Elongated buffalo with Harappan symbol imported to Susa in 2600–1700 BC. Found in the tell of the Susa acropolis. Louvre Museum, reference Sb 5614
File:Indus carnelian beads with white design imported to Susa in 2600-1700 BCE LOUVRE Sb 13099.jpg, Indus carnelian beads with white design, etched in white with an acid, imported to Susa in 2600–1700 BC. Found in the tell of the Susa acropolis. Louvre Museum, reference Sb 17751. These beads are identical with beads found in the Indus Civilization site of
here
File:Indus Valley Civilization weight excavated in Susa. Louvre Museum Sb 17774.jpg, Indus Valley Civilization weight in veined
 The Middle Elamite period began with the rise of the Anshanite dynasties around 1500 BC. Their rule was characterized by an "Elamisation" of Susa, and the kings took the title "king of Anshan and Susa". While the first of these dynasties, the Kidinuids continued to use the Akkadian language frequently in their inscriptions, the succeeding Igihalkids and Shutrukids used Elamite with increasing regularity. Likewise, Elamite language and culture grew in importance in Susiana. The Kidinuids (c. 1500 – 1400 BC) are a group of five rulers of uncertain affiliation. They are identified by their use of the older title, "king of Susa and of Anshan", and by calling themselves "servant of Kirwashir", an Elamite deity, thereby introducing the pantheon of the highlands to Susiana. The city of Susa itself is one of the oldest in the world dating back to around 4200 BC. Since its founding Susa was known as a central power location for the Elamites and for later Persian dynasties. Susa's power would peak during the Middle Elamite period, when it would be the region's capital.
The Middle Elamite period began with the rise of the Anshanite dynasties around 1500 BC. Their rule was characterized by an "Elamisation" of Susa, and the kings took the title "king of Anshan and Susa". While the first of these dynasties, the Kidinuids continued to use the Akkadian language frequently in their inscriptions, the succeeding Igihalkids and Shutrukids used Elamite with increasing regularity. Likewise, Elamite language and culture grew in importance in Susiana. The Kidinuids (c. 1500 – 1400 BC) are a group of five rulers of uncertain affiliation. They are identified by their use of the older title, "king of Susa and of Anshan", and by calling themselves "servant of Kirwashir", an Elamite deity, thereby introducing the pantheon of the highlands to Susiana. The city of Susa itself is one of the oldest in the world dating back to around 4200 BC. Since its founding Susa was known as a central power location for the Elamites and for later Persian dynasties. Susa's power would peak during the Middle Elamite period, when it would be the region's capital.
 Of the Igehalkids (c. 1400 – 1210 BC), ten rulers are known, though their number was possibly larger. Some of them married
Of the Igehalkids (c. 1400 – 1210 BC), ten rulers are known, though their number was possibly larger. Some of them married
 Under the Shutrukids (c. 1210 – 1100 BC), the Elamite empire reached the height of its power. Shutruk-Nakhkhunte and his three sons, Kutir-Nakhkhunte II, Shilhak-In-Shushinak, and Khutelutush-In-Shushinak were capable of frequent military campaigns into Kassite Babylonia (which was also being ravaged by the empire of
Under the Shutrukids (c. 1210 – 1100 BC), the Elamite empire reached the height of its power. Shutruk-Nakhkhunte and his three sons, Kutir-Nakhkhunte II, Shilhak-In-Shushinak, and Khutelutush-In-Shushinak were capable of frequent military campaigns into Kassite Babylonia (which was also being ravaged by the empire of
 The later Neo-Elamite period is characterized by a significant migration of
The later Neo-Elamite period is characterized by a significant migration of  His successor Tempti-Khumma-In-Shushinak (664–653 BC) attacked Assyria, but was defeated and killed by
His successor Tempti-Khumma-In-Shushinak (664–653 BC) attacked Assyria, but was defeated and killed by
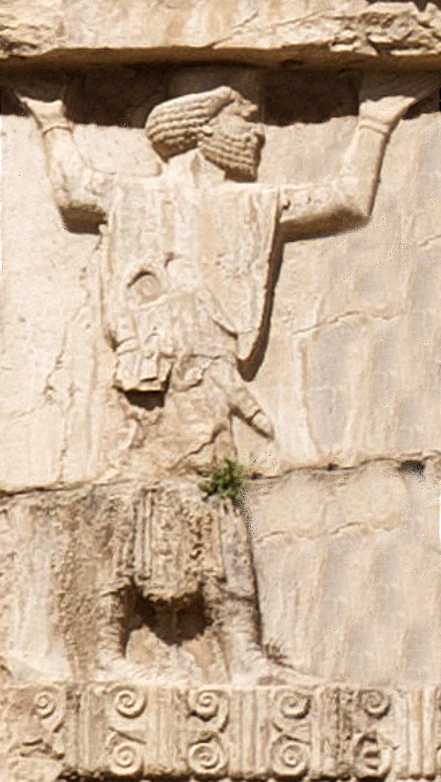 The devastation was a little less complete than Ashurbanipal boasted, and a weak and fragmented Elamite rule was resurrected soon after with Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, son of Humban-umena III (not to be confused with Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, son of Indada, a petty king in the first half of the 6th century). Elamite royalty in the final century preceding the Achaemenids was fragmented among different small kingdoms, the united Elamite nation having been destroyed and colonised by the Assyrians. The three kings at the close of the 7th century (Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, Khallutush-In-Shushinak and Atta-Khumma-In-Shushinak) still called themselves "king of Anzan and of Susa" or "enlarger of the kingdom of Anzan and of Susa", at a time when the Achaemenid Persians were already ruling Anshan under Assyrian dominance.
The various Assyrian Empires, which had been the dominant force in the
The devastation was a little less complete than Ashurbanipal boasted, and a weak and fragmented Elamite rule was resurrected soon after with Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, son of Humban-umena III (not to be confused with Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, son of Indada, a petty king in the first half of the 6th century). Elamite royalty in the final century preceding the Achaemenids was fragmented among different small kingdoms, the united Elamite nation having been destroyed and colonised by the Assyrians. The three kings at the close of the 7th century (Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, Khallutush-In-Shushinak and Atta-Khumma-In-Shushinak) still called themselves "king of Anzan and of Susa" or "enlarger of the kingdom of Anzan and of Susa", at a time when the Achaemenid Persians were already ruling Anshan under Assyrian dominance.
The various Assyrian Empires, which had been the dominant force in the  The prophet Ezekiel describes the status of their power in the 12th year of the Hebrew
The prophet Ezekiel describes the status of their power in the 12th year of the Hebrew

 This life-size votive offering of Queen
This life-size votive offering of Queen
 The Elamites practised
The Elamites practised
File:Kaftar elam.jpg, A 4.5 inch long
In modern Iran, Ilam Province and Khuzestan Province are named after Elam civilization. Khuzestan means land of the Khuzis and Khuzi itself is a
Lengua e historia elamita
by Enrique Quintana
History of the Elamite EmpireElamite ArtStele of King Untash NapirishaStatue of Queen Napir AsuElamite SealsAll Empires – The Elamite EmpirePersepolis Fortification Archive ProjectIran Before IraniansEncyclopædia Iranica: ElamModelling population dispersal and language origins during the last 120,000 years
*Hamid-Reza Hosseini, ''Shush at the foot of
''Shush dar dāman-e Louvre'', in Persian, Jadid Online, 10 March 2009
br
(6 min 31 sec) *https://web.archive.org/web/20160222154459/http://www.elamit.net/ {{Coord, 29, 54, N, 52, 24, E, display=title, source:fiwiki States and territories established in the 3rd millennium BC States and territories disestablished in the 6th century BC Ancient Asia Ancient history of Iran Chalcolithic states in Asia Bronze Age countries in Asia Iron Age countries in Asia 27th-century BC establishments Historical regions
Linear Elamite
Linear Elamite was a writing system used in Elam during the Bronze Age between , and known mainly from a few extant monumental inscriptions. It was used contemporaneously with Elamite cuneiform and records the Elamite language. The French archa ...
:  ''hatamti''; Cuneiform Elamite: ; Sumerian: ;
''hatamti''; Cuneiform Elamite: ; Sumerian: ; Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
: ; he, עֵילָם ''ʿēlām''; peo, 𐎢𐎺𐎩 ''hūja'') was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of modern-day Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan
Khuzestan Province (also spelled Xuzestan; fa, استان خوزستان ''Ostān-e Xūzestān'') is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. It is in the southwest of the country, bordering Iraq and the Persian Gulf. Its capital is Ahvaz and it cover ...
and Ilam Province as well as a small part of southern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
. The modern name ''Elam'' stems from the Sumerian transliteration ''elam(a)'', along with the later Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
''elamtu'', and the Elamite ''haltamti.'' Elamite states were among the leading political forces of the Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, ...
. In classical literature
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classic ...
, Elam was also known as Susiana ( ; grc, Σουσιανή ''Sousiānḗ''), a name derived from its capital Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
.
Elam was part of the early urbanization of the Near East during the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "Rock (geology), stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin ''wikt:aeneus, aeneus'' "of copper"), is an list of archaeologi ...
period (Copper Age). The emergence of written records from around 3000 BC also parallels Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
ian history, where slightly earlier records have been found. In the Old Elamite period (Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pr ...
), Elam consisted of kingdoms on the Iranian plateau, centered in Anshan, and from the mid-2nd millennium BC, it was centered in Susa in the Khuzestan lowlands. Its culture played a crucial role during the Persian Achaemenid dynasty
The Achaemenid dynasty (Old Persian: ; Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) was an ancient Persian royal dynasty that ruled the Achaemenid Empire, an Iranian empire that stretched from Egypt and Southeastern Europe in the west to the Ind ...
that succeeded Elam, when the Elamite language remained among those in official use. Elamite is generally considered a language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
unrelated to any other languages. In accordance with geographical and archaeological matches, some historians argue that the Elamites comprise a large portion of the ancestors of the modern day Lurs
Lurs () are an Iranian people living in the mountains of western Iran. The four Luri branches are the Bakhtiari, Mamasani, Kohgiluyeh and Lur proper, who are principally linked by the Luri language.
Lorestan Province is named after the Lur ...
whose language, Luri, split from Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle P ...
.
Etymology
The Elamite languageendonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
of Elam as a country appears to have been ''Hatamti'' ( in
in Linear Elamite
Linear Elamite was a writing system used in Elam during the Bronze Age between , and known mainly from a few extant monumental inscriptions. It was used contemporaneously with Elamite cuneiform and records the Elamite language. The French archa ...
), or ''Haltami'' ( Cuneiform Elamite: ).
Exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group ...
s included the Sumerian names ''NIM.MAki''𒉏𒈠𒆠 and ''ELAM'', the Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
''Elamû'' (masculine/neuter) and ''Elamītu'' (feminine) meant "resident of Susiana, Elamite".
In prehistory, Elam was centered primarily in modern Khuzestān and Ilam. The name Khuzestān is derived ultimately from peo, 𐎢𐎺𐎩 (''hūja'') meaning Susa/Elam. This became pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭰 (''hūz'') "Susiana", and in modern fa, خوز (''xuz''), compounded with the toponymic suffix '' -stån'' "place".
Geography
 In geographical terms, Susiana basically represents the Iranian province of
In geographical terms, Susiana basically represents the Iranian province of Khuzestan
Khuzestan Province (also spelled Xuzestan; fa, استان خوزستان ''Ostān-e Xūzestān'') is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. It is in the southwest of the country, bordering Iraq and the Persian Gulf. Its capital is Ahvaz and it cover ...
around the river Karun. In ancient times, several names were used to describe this area. The ancient geographer Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
was the earliest to call the area ''Susiana'', referring to the country around Susa.
Another ancient geographer, Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, viewed Elam and Susiana as two different geographic regions. He referred to Elam ("land of the Elymaei") as primarily the highland area of Khuzestan.D. T. Potts''The Archaeology of Elam: Formation and Transformation of an Ancient Iranian State.''
Cambridge World Archaeology. Cambridge University Press, 2015 p11 Disagreements over the location also exist in the Jewish historical sources says Daniel T. Potts. Some ancient sources draw a distinction between Elam as the highland area of Khuzestan, and Susiana as the lowland area. Yet in other ancient sources 'Elam' and 'Susiana' seem equivalent. The uncertainty in this area extends also to modern scholarship. Since the discovery of ancient Anshan, and the realization of its great importance in Elamite history, the definitions were changed again. Some modern scholars argued that the center of Elam lay at Anshan and in the highlands around it, and not at Susa in lowland Khuzistan. Potts disagrees suggesting that the term 'Elam' was primarily constructed by the Mesopotamians to describe the area in general terms, without referring specifically either to the lowlanders or the highlanders,
"Elam is not an Iranian term and has no relationship to the conception which the peoples of highland Iran had of themselves. They were Anshanites, Marhashians, Shimashkians, Zabshalians, Sherihumians, Awanites, etc. That Anshan played a leading role in the political affairs of the various highland groups inhabiting southwestern Iran is clear. But to argue that Anshan is coterminous with Elam is to misunderstand the artificiality and indeed the alienness of Elam as a construct imposed from without on the peoples of the southwestern highlands of the Zagros mountain range, the coast of Fars and the alluvial plain drained by the Karun-Karkheh river system.
History
Prehistorically the area was well settled during the Ubaid period and shared many aspects of Ubaid cultures. Knowledge of Elamite history remains largely fragmentary, reconstruction being based on mainlyMesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
n (Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
ian, Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
, Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n and Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
n) sources. The history of Elam is conventionally divided into three periods, spanning more than two millennia. The period before the first Elamite period is known as the proto-Elamite period:
*Proto-Elamite
The Proto-Elamite period, also known as Susa III, is a chronological era in the ancient history of the area of Elam, dating from . In archaeological terms this corresponds to the late Banesh period. Proto-Elamite sites are recognized as the old ...
: c. 3200 – c. 2700 BC (Proto-Elamite script in Susa)
*Old Elamite period: c. 2700 – c. 1500 BC (earliest documents until the Sukkalmah Dynasty
The Sukkalmah Dynasty (c. 1900-1500 BCE), also Epartid Dynasty after the founder Eparti/Ebarat, was an early dynasty of West Asia in the ancient region of Elam, to the southeast of Babylonia. It corresponds to the latest part of the Old Elamit ...
)
*Middle Elamite period: c. 1500 – c. 1100 BC (Anzanite dynasty until the Babylonian invasion of Susa)
*Neo-Elamite period: c. 1100 – 540 BC (characterized Assyrian and Median influence. 539 BC marks the beginning of the Achaemenid period.)
Proto-Elamite (c. 3500 – c. 2700 BC)
 Proto-Elamite civilization grew up east of the
Proto-Elamite civilization grew up east of the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
and Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
alluvial plains; it was a combination of the lowlands and the immediate highland areas to the north and east. At least three proto-Elamite states merged to form Elam: Anshan, Awan
Awan may refer to:
Places
* Awan (ancient city), a city-state in Elam in the 3rd millennium BCE
* Awan (region), a town in Guna district, Madhya Pradesh, India
* Awan, Bhulath, a village in Kapurthala district, Punjab, India, Punjab, Pakistan ...
, and Shimashki. References to Awan are generally older than those to Anshan, and some scholars suggest that both states encompassed the same territory, in different eras (see Hanson, Encyclopædia Iranica). To this core Shushiana was periodically annexed and broken off. In addition, some Proto-Elamite sites are found well outside this area, spread out on the Iranian plateau; such as Warakshe, Sialk (now a suburb of the modern city of Kashan) and Jiroft
Jiroft ( fa, جیرفت, also Romanized as Jīroft; formerly, Sabzāwārān, Sabzevārān, Sabzevārān-e Jiroft, and Sabzvārān) is a city and capital of Jiroft County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 95,031, in ...
in Kerman Province. The state of Elam was formed from these lesser states as a response to invasion from Sumer during the Old Elamite period. Elamite strength was based on an ability to hold these various areas together under a coordinated government that permitted the maximum interchange of the natural resources unique to each region. Traditionally, this was done through a federated governmental structure.
 The Proto-Elamite city of Susa was founded around 4000 BC in the watershed of the river Karun. It is considered to be the site of Proto-Elamite cultural formation. During its early history, it fluctuated between submission to
The Proto-Elamite city of Susa was founded around 4000 BC in the watershed of the river Karun. It is considered to be the site of Proto-Elamite cultural formation. During its early history, it fluctuated between submission to Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
n and Elamite power. The earliest levels (22—17 in the excavations conducted by Le Brun, 1978) exhibit pottery that has no equivalent in Mesopotamia, but for the succeeding period, the excavated material allows identification with the culture of Sumer of the Uruk period
The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BC; also known as Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named af ...
. Proto-Elamite
The Proto-Elamite period, also known as Susa III, is a chronological era in the ancient history of the area of Elam, dating from . In archaeological terms this corresponds to the late Banesh period. Proto-Elamite sites are recognized as the old ...
influence from Mesopotamia in Susa becomes visible from about 3200 BC, and texts in the still undeciphered Proto-Elamite writing system continue to be present until about 2700 BC. The Proto-Elamite period ends with the establishment of the Awan dynasty. The earliest known historical figure connected with Elam is the king Enmebaragesi of Kish (c. 2650 BC?), who subdued it, according to the Sumerian king list
The ''Sumerian King List'' (abbreviated ''SKL'') or ''Chronicle of the One Monarchy'' is an ancient literary composition written in Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims to power of various city-states and king ...
. Elamite history can only be traced from records dating to beginning of the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad () and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one r ...
(2335–2154 BC) onwards.
The Proto-Elamite states in Jiroft
Jiroft ( fa, جیرفت, also Romanized as Jīroft; formerly, Sabzāwārān, Sabzevārān, Sabzevārān-e Jiroft, and Sabzvārān) is a city and capital of Jiroft County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 95,031, in ...
and Zabol (not universally accepted), present a special case because of their great antiquity.
In ancient Luristan, bronze-making tradition goes back to the mid-3rd millennium BC, and has many Elamite connections. Bronze objects from several cemeteries in the region date to the Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia) I, and to Ur-III period c. 2900–2000 BC. These excavations include Kalleh Nisar, Bani Surmah, Chigha Sabz, Kamtarlan, Sardant, and Gulal-i Galbi.
Old Elamite period (c. 2700 – c. 1500 BC)

 The Old Elamite period began around 2700 BC. Historical records mention the conquest of Elam by Enmebaragesi, the
The Old Elamite period began around 2700 BC. Historical records mention the conquest of Elam by Enmebaragesi, the Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
ian king of Kish in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
. Three dynasties ruled during this period. Twelve kings of each of the first two dynasties, those of Awan
Awan may refer to:
Places
* Awan (ancient city), a city-state in Elam in the 3rd millennium BCE
* Awan (region), a town in Guna district, Madhya Pradesh, India
* Awan, Bhulath, a village in Kapurthala district, Punjab, India, Punjab, Pakistan ...
(or ''Avan''; c. 2400 – c. 2100 BC) and Simashki (c. 2100 – c. 1970 BC), are known from a list from Susa dating to the Old Babylonian period
The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to BC – BC, and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynast ...
. Two Elamite dynasties said to have exercised brief control over parts of Sumer in very early times include Awan and Hamazi
Hamazi or Khamazi ( Sumerian: , ''ha-ma-zi''ki, or ''Ḫa-ma-zi2''ki) was an ancient kingdom or city-state of some importance that reached its peak c. 2500–2400 BC. Its exact location is unknown, but is thought to have been located in the ...
; and likewise, several of the stronger Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
ian rulers, such as Eannatum
Eannatum ( sux, ) was a Sumerian '' Ensi'' (ruler or king) of Lagash circa 2500–2400 BCE. He established one of the first verifiable empires in history: he subdued Elam and destroyed the city of Susa as well as several other Iranian cities, ...
of Lagash and Lugal-anne-mundu
Lugal-Anne-Mundu ( sux, , , ca. 24th century BC) was the most important king of the city-state of Adab in Sumer. The ''Sumerian king list'' claims he reigned for 90 years, following the defeat of Mesh-ki-ang-Nanna II, son of Nanni, of Ur. Th ...
of Adab, are recorded as temporarily dominating Elam.
Awan dynasty
 The Awan dynasty (2350–2150 BC) was partly contemporary with that of the Mesopotamian emperor
The Awan dynasty (2350–2150 BC) was partly contemporary with that of the Mesopotamian emperor Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; akk, ''Šarrugi''), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highl ...
, who not only defeated the Awan king Luh-ishan and subjected Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
, but attempted to make the East Semitic Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
the official language there. From this time, Mesopotamian sources concerning Elam become more frequent, since the Mesopotamians had developed an interest in resources (such as wood, stone, and metal) from the Iranian plateau, and military expeditions to the area became more common. With the collapse of Akkad under Sargon's great great-grandson, Shar-kali-sharri
Shar-Kali-Sharri (, '' DShar-ka-li-Sharri''; reigned c. 2217–2193 BC middle chronology, c. 2153–2129 BC short chronology) was a king of the Akkadian Empire.
Rule
Succeeding his father Naram-Sin in c. 2217 BC, he came to the throne in an age ...
, Elam declared independence under the last Awan king, Kutik-Inshushinak (c. 2240 – c. 2220 BC), and threw off the Akkadian language, promoting in its place the brief Linear Elamite
Linear Elamite was a writing system used in Elam during the Bronze Age between , and known mainly from a few extant monumental inscriptions. It was used contemporaneously with Elamite cuneiform and records the Elamite language. The French archa ...
script. Kutik-Inshushinnak conquered Susa and Anshan, and seems to have achieved some sort of political unity. Following his reign, the Awan dynasty collapsed as Elam was temporarily overrun by the Guti, another pre-Iranic people from what is now north west Iran who also spoke a language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
.
Shimashki dynasty
About a century later, the Sumerian king Shulgi of the Neo-Sumerian Empire retook the city ofSusa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
and the surrounding region. During the first part of the rule of the Simashki dynasty, Elam was under intermittent attack from the Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
ians of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
and also Gutians from northwestern Iran, alternating with periods of peace and diplomatic approaches. The Elamite state of Simashki at this time also extended into northern Iran, and possibly even as far as the Caspian Sea. Shu-Sin of Ur gave one of his daughters in marriage to a prince of Anshan. But the power of the Sumerians was waning; Ibbi-Sin in the 21st century did not manage to penetrate far into Elam, and in 2004 BC, the Elamites, allied with the people of Susa and led by king Kindattu
Kindattu (, ''ki-in-da-tu'', also Kindadu, reigned ca. 2000 BC, middle Chronology) was the 6th king of the Shimashki Dynasty,D. T. Potts (2016). ''The Archaeology of Elam.'' Cambridge University Press. p. 135. in Elam (in present-day southwest Ira ...
, the sixth king of Simashki, managed to sack Ur and lead Ibbi-Sin into captivity, ending the third dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC ( middle chronology) Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider t ...
. The Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
kings of Isin
Isin (, modern Arabic: Ishan al-Bahriyat) is an archaeological site in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq. Excavations have shown that it was an important city-state in the past.
History of archaeological research
Ishan al-Bahriyat was visited ...
, successor state to Ur, managed to drive the Elamites out of Ur, rebuild the city, and to return the statue of Nanna that the Elamites had plundered.
Sukkalmah dynasty
 The succeeding dynasty, often called the
The succeeding dynasty, often called the Sukkalmah dynasty
The Sukkalmah Dynasty (c. 1900-1500 BCE), also Epartid Dynasty after the founder Eparti/Ebarat, was an early dynasty of West Asia in the ancient region of Elam, to the southeast of Babylonia. It corresponds to the latest part of the Old Elamit ...
(c. 1970 – c. 1770 BC) after "Great regents", the title borne by its members, also called the Epartid dynasty after the name of its founder Ebarat/ Eparti, was roughly contemporary with the Old Assyrian Empire, and Old Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
n period in Mesopotamia, being younger by approximately sixty years than the Akkadian speaking Old Assyrian Empire in Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia is the name used for the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the region has been ...
, and almost seventy-five years older than the Old Babylonian Empire. This period is said by many to be confusing and difficult to reconstruct. It was apparently founded by Eparti I. During this time, Susa was under Elamite control, but Akkadian speaking Mesopotamian states such as Larsa and Isin
Isin (, modern Arabic: Ishan al-Bahriyat) is an archaeological site in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq. Excavations have shown that it was an important city-state in the past.
History of archaeological research
Ishan al-Bahriyat was visited ...
continually tried to retake the city. Around 1850 BC Kudur-Mabuk, apparently king of another Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
state to the north of Larsa, managed to install his son, Warad-Sin
Warad-Sin (, ARAD- Dsuen) ruled the ancient Near East city-state of Larsa from 1770 BC to 1758 BC (short chronology). There are indications that his father Kudur-Mabuk was co-regent or at very least the power behind the throne. His sister En-an ...
, on the throne of Larsa, and Warad-Sin's brother, Rim-Sin, succeeded him and conquered much of southern Mesopotamia for Larsa.
Notable Eparti dynasty rulers in Elam during this time include Sirukdukh (c. 1850 BC), who entered various military coalitions to contain the power of the south Mesopotamian states; Siwe-Palar-Khuppak Siwe-Palar-Khuppak was the '' Sukkalmah'' (ruler) of Elam from around 1778 to 1745 B.C.E.
Around 1767 B.C.E, Siwe-Palar-Khuppak formed a coalition with Zimri-Lim of Mari and Hammurabi of Babylon. He led this coalition against Eshnunna, conquering ...
, who for some time was the most powerful person in the area, respectfully addressed as "Father" by Mesopotamian kings such as Zimrilim of Mari, Shamshi-Adad I
Shamshi-Adad ( akk, Šamši-Adad; Amorite: ''Shamshi-Addu''), ruled 1808–1776 BC, was an Amorite warlord and conqueror who had conquered lands across much of Syria, Anatolia, and Upper Mesopotamia.Some of the Mari letters addressed to Shamsi ...
of Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
, and even Hammurabi of Babylon; and Kudur-Nahhunte, who plundered the temples of southern Mesopotamia, the north being under the control of the Old Assyrian Empire. But Elamite influence in southern Mesopotamia did not last. Around 1760 BC, Hammurabi drove out the Elamites, overthrew Rim-Sin of Larsa, and established a short lived Babylonian Empire in Mesopotamia. Little is known about the latter part of this dynasty, since sources again become sparse with the Kassite
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babyl ...
rule of Babylon (from c. 1595 BC).
Trade with the Indus Valley civilization
Many archaeological finds suggest that maritime trade along the shores of Africa and Asia started several millennia ago. Trade between theIndus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
and the cities of Mesopotamia and Elam, can be inferred from numerous find of Indus artifacts, particularly in the excavation at Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
. Various objects made with shell species that are characteristic of the Indus coast, particularly ''Trubinella Pyrum'' and ''Fasciolaria Trapezium'', have been found in the archaeological sites of Mesopotamia and Susa dating from around 2500–2000 BC. Carnelian beads from the Indus were found in Susa in the excavation of the tell of the citadel. In particular, carnelian beads with an etched design in white were probably imported from the Indus Valley, and made according to a technique of acid-etching developed by the Harappa
Harappa (; Urdu/ pnb, ) is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal. The Bronze Age Harappan civilisation, now more often called the Indus Valley Civilisation, is named after the site, which takes its name from a ...
ns.
Exchanges seem to have waned after 1900 BC, together with the disappearance of the Indus valley civilization.
Dholavira
Dholavira ( gu, ધોળાવીરા) is an archaeological site at Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District, in the state of Gujarat in western India, which has taken its name from a modern-day village south of it. This village is ...
.
File:Indus bracelet made of Fasciolaria Trapezium or Xandus Pyrum imported to Susa in 2600-1700 BCE LOUVRE Sb14473.jpg, Indus bracelet made of ''Fasciolaria Trapezium'' or ''Turbinella pyrum'' imported to Susa in 2600–1700 BC. Found in the tell of the Susa acropolis. Louvre Museum, reference Sb 14473. This type of bracelet was manufactured in Mohenjo-daro, Lothal and Balakot. It is engraved with a chevron design which is characteristic of all shell bangles of the Indus Valley, visiblhere
File:Indus Valley Civilization weight excavated in Susa. Louvre Museum Sb 17774.jpg, Indus Valley Civilization weight in veined
jasper
Jasper, an aggregate of microgranular quartz and/or cryptocrystalline chalcedony and other mineral phases,Kostov, R. I. 2010. Review on the mineralogical systematics of jasper and related rocks. – Archaeometry Workshop, 7, 3, 209-213PDF/ref ...
, excavated in Susa in a 12th-century BC princely tomb. Louvre Museum Sb 17774.
Middle Elamite period (c. 1500 – c. 1100 BC)
Anshan and Susa
 The Middle Elamite period began with the rise of the Anshanite dynasties around 1500 BC. Their rule was characterized by an "Elamisation" of Susa, and the kings took the title "king of Anshan and Susa". While the first of these dynasties, the Kidinuids continued to use the Akkadian language frequently in their inscriptions, the succeeding Igihalkids and Shutrukids used Elamite with increasing regularity. Likewise, Elamite language and culture grew in importance in Susiana. The Kidinuids (c. 1500 – 1400 BC) are a group of five rulers of uncertain affiliation. They are identified by their use of the older title, "king of Susa and of Anshan", and by calling themselves "servant of Kirwashir", an Elamite deity, thereby introducing the pantheon of the highlands to Susiana. The city of Susa itself is one of the oldest in the world dating back to around 4200 BC. Since its founding Susa was known as a central power location for the Elamites and for later Persian dynasties. Susa's power would peak during the Middle Elamite period, when it would be the region's capital.
The Middle Elamite period began with the rise of the Anshanite dynasties around 1500 BC. Their rule was characterized by an "Elamisation" of Susa, and the kings took the title "king of Anshan and Susa". While the first of these dynasties, the Kidinuids continued to use the Akkadian language frequently in their inscriptions, the succeeding Igihalkids and Shutrukids used Elamite with increasing regularity. Likewise, Elamite language and culture grew in importance in Susiana. The Kidinuids (c. 1500 – 1400 BC) are a group of five rulers of uncertain affiliation. They are identified by their use of the older title, "king of Susa and of Anshan", and by calling themselves "servant of Kirwashir", an Elamite deity, thereby introducing the pantheon of the highlands to Susiana. The city of Susa itself is one of the oldest in the world dating back to around 4200 BC. Since its founding Susa was known as a central power location for the Elamites and for later Persian dynasties. Susa's power would peak during the Middle Elamite period, when it would be the region's capital.
Kassite invasions
 Of the Igehalkids (c. 1400 – 1210 BC), ten rulers are known, though their number was possibly larger. Some of them married
Of the Igehalkids (c. 1400 – 1210 BC), ten rulers are known, though their number was possibly larger. Some of them married Kassite
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babyl ...
princesses. The Kassites were also a language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
speaking people from the Zagros Mountains who had taken Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
shortly after its sacking by the Hittite Empire in 1595 BC. The Kassite king of Babylon Kurigalzu II
Kurigalzu II (c. 1332–1308 BC short chronology) was the 22nd king of the Kassite or 3rd dynasty that ruled over Babylon. In more than twelve inscriptions, Kurigalzu names Burna-Buriaš II as his father. Kurigalzu II was possibly placed on th ...
who had been installed on the throne by Ashur-uballit I
Ashur-uballit I ''(Aššur-uballiṭ I)'', who reigned between 1363 and 1328 BC, was the first king of the Middle Assyrian Empire. After his father Eriba-Adad I had broken Mitanni influence over Assyria, Ashur-uballit I's defeat of the Mitanni ...
of the Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
(1366–1020 BC), temporarily occupied Elam around 1320 BC, and later (c. 1230 BC) another Kassite king, Kashtiliash IV
Kaštiliašu IV was the twenty-eighth Kassite king of Babylon and the kingdom contemporarily known as Kar-Duniaš, c. 1232–1225 BC (short chronology). He succeeded Šagarakti-Šuriaš, who could have been his father, ruled for eight years,Kin ...
, fought Elam unsuccessfully. Kassite-Babylonian power waned, as they became dominated by the northern Mesopotamian Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
. Kiddin-Khutran of Elam repulsed the Kassites by defeating Enlil-nadin-shumi
Enlil-nādin-šumi, inscribed mdEN.LĺL-MU-MUKinglist A, BM 33332, ii 8. or mdEN.LĺL''-na-din-''MU,Chronicle P, BM 92807, iv 14, 16. meaning “Enlil is the giver of a name,” was a king of Babylon, c. 1224 BC, following the overthrow of K ...
in 1224 BC and Adad-shuma-iddina around 1222–1217 BC. Under the Igehalkids, Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
inscriptions were rare, and Elamite highland gods became firmly established in Susa.
Elamite Empire
 Under the Shutrukids (c. 1210 – 1100 BC), the Elamite empire reached the height of its power. Shutruk-Nakhkhunte and his three sons, Kutir-Nakhkhunte II, Shilhak-In-Shushinak, and Khutelutush-In-Shushinak were capable of frequent military campaigns into Kassite Babylonia (which was also being ravaged by the empire of
Under the Shutrukids (c. 1210 – 1100 BC), the Elamite empire reached the height of its power. Shutruk-Nakhkhunte and his three sons, Kutir-Nakhkhunte II, Shilhak-In-Shushinak, and Khutelutush-In-Shushinak were capable of frequent military campaigns into Kassite Babylonia (which was also being ravaged by the empire of Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
during this period), and at the same time were exhibiting vigorous construction activity—building and restoring luxurious temples in Susa and across their Empire. Shutruk-Nakhkhunte raided Babylonia, carrying home to Susa trophies like the statues of Marduk
Marduk (Cuneiform: dAMAR.UTU; Sumerian: ''amar utu.k'' "calf of the sun; solar calf"; ) was a god from ancient Mesopotamia and patron deity of the city of Babylon. When Babylon became the political center of the Euphrates valley in the time of ...
and Manishtushu, the Manishtushu Obelisk, the Stele of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organised, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian language, Akkadian, p ...
and the stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek language, Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ...
of Naram-Sin. In 1158 BC, after much of Babylonia had been annexed by Ashur-Dan I of Assyria and Shutruk-Nakhkhunte, the Elamites defeated the Kassites permanently, killing the Kassite king of Babylon, Zababa-shuma-iddin
Zababa-šuma-iddinaWritten as md''Za-ba''4''-ba''4-MU-AŠ. was the 35th and next to last king of the Kassite or 3rd dynasty of Babylon, who reigned for just one year,''Kinglist A'', column 2, line 14. ca. 1158 BC (short chronology). He was withou ...
, and replacing him with his eldest son, Kutir-Nakhkhunte, who held it no more than three years before being ejected by the native Akkadian speaking Babylonians. The Elamites then briefly came into conflict with Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
, managing to take the Assyrian city of Arrapha
Arrapha or Arrapkha (Akkadian: ''Arrapḫa''; ar, أررابخا ,عرفة) was an ancient city in what today is northeastern Iraq, thought to be on the site of the modern city of Kirkuk.
In 1948, ''Arrapha'' became the name of the residential ...
(modern Kirkuk
Kirkuk ( ar, كركوك, ku, کەرکووک, translit=Kerkûk, , tr, Kerkük) is a city in Iraq, serving as the capital of the Kirkuk Governorate, located north of Baghdad. The city is home to a diverse population of Turkmens, Arabs, Kurds ...
) before being ultimately defeated and having a treaty forced upon them by Ashur-Dan I.
Kutir-Nakhkhunte's son Khutelutush-In-Shushinak was probably of an incestuous relation of Kutir-Nakhkhunte's with his own daughter, Nakhkhunte-utu. He was defeated by Nebuchadnezzar I
Nebuchadnezzar I or Nebuchadrezzar I (), reigned 1121–1100 BC, was the fourth king of the Second Dynasty of Isin and Fourth Dynasty of Babylon. He ruled for 22 years according to the ''Babylonian King List C'', and was the most prominent monar ...
of Babylon, who sacked Susa and returned the statue of Marduk, but who was then himself defeated by the Assyrian king Ashur-resh-ishi I
Aššur-rēša-iši I, inscribed m''aš-šur-''SAG''-i-ši'' and meaning “Aššur has lifted my head,” ruled 1132–1115 BC, son of Mutakkil-Nusku, was a king of Assyria, the 86th to appear on the Assyrian King ListAssyrian King List’s: Nass ...
. He fled to Anshan, but later returned to Susa, and his brother Shilhana-Hamru-Lagamar may have succeeded him as last king of the Shutrukid dynasty. Following Khutelutush-In-Shushinak, the power of the Elamite empire began to wane seriously, for after the death of this ruler, Elam disappears into obscurity for more than three centuries.
Neo-Elamite period (c. 1100 – 540 BC)
Neo-Elamite I (c. 1100 – c. 770 BC)
Very little is known of this period. Anshan was still at least partially Elamite. There appear to have been unsuccessful alliances of Elamites, Babylonians,Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
ns and other peoples against the powerful Neo Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
(911–605 BC); the Babylonian king Mar-biti-apla-ushur (984–979 BC) was of Elamite origin, and Elamites are recorded to have fought unsuccessfully with the Babylonian king Marduk-balassu-iqbi against the Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n forces under Shamshi-Adad V (823–811 BC).
Neo-Elamite II (c. 770 – 646 BC)

 The later Neo-Elamite period is characterized by a significant migration of
The later Neo-Elamite period is characterized by a significant migration of Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
speaking Iranians to the Iranian plateau. Assyrian sources beginning around 800 BC distinguish the "powerful Medes", i.e. the actual Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
, Parthians Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
, Sagartians, Margians, Bactrians
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southw ...
, Sogdians etc.. Among these pressuring tribes were the '' Parsu'', first recorded in 844 BC as living on the southeastern shore of Lake Urmiah
Lake Urmia;
az, اۇرمۇ گؤلۆ, script=Arab, italic=no, Urmu gölü;
ku, گۆلائوو رمیەیێ, Gola Ûrmiyeyê;
hy, Ուրմիա լիճ, Urmia lich;
arc, ܝܡܬܐ ܕܐܘܪܡܝܐ is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is l ...
, but who by the end of this period would cause the Elamites' original home, the Iranian Plateau, to be renamed Persia proper. These newly arrived Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
were also conquered by Assyria, and largely regarded as vassals of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew ...
until the late 7th century.
More details are known from the late 8th century BC, when the Elamites were allied with the Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
n chieftain Merodach-baladan to defend the cause of Babylonian independence from Assyria. Khumbanigash (743–717 BC) supported Merodach-baladan against Sargon II
Sargon II ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is gener ...
, apparently without success; while his successor, Shutruk-Nakhkhunte II (716–699 BC), was routed by Sargon's troops during an expedition in 710, and another Elamite defeat by Sargon's troops is recorded for 708. The Assyrian dominion over Babylon was underlined by Sargon's son Sennacherib, who defeated the Elamites, Chaldeans and Babylonians and dethroned Merodach-baladan for a second time, installing his own son Ashur-nadin-shumi
Ashur-nadin-shumi ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur gives a name")' was a son of the Neo-Assyrian king Sennacherib and was appointed by him as the king of Babylon, ruling southern Mesopotamia from 700 BC to his capture and execution b ...
on the Babylonian throne in 700.
Shutruk-Nakhkhunte II, the last Elamite to claim the old title "king of Anshan and Susa", was murdered by his brother Khallushu, who managed to briefly capture the Assyrian governor of Babylonia Ashur-nadin-shumi and the city of Babylon in 694 BC. Sennacherib soon responded by invading and ravaging Elam. Khallushu was in turn assassinated by Kutir-Nakhkhunte, who succeeded him but soon abdicated in favor of Khumma-Menanu III (692–689 BC). Khumma-Menanu recruited a new army to help the Babylonians and Chaldeans against the Assyrians at the battle of Halule in 691. Both sides claimed the victory in their annals, but Babylon was destroyed by Sennacherib only two years later, and its Elamite allies defeated in the process.
The reigns of Khumma-Khaldash I (688–681 BC) and Khumma-Khaldash II (680–675 BC) saw a deterioration of Elamite-Babylonian relations, and both of them raided Sippar. At the beginning of Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
's reign in Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
(681–669 BC), Nabu-zer-kitti-lišir, an ethnically Elamite governor in the south of Babylonia, revolted and besieged Ur, but was routed by the Assyrians and fled to Elam where the king of Elam, fearing Assyrian repercussions, took him prisoner and put him to the sword.
Urtaku (674–664 BC) for some time wisely maintained good relations with the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Inheriting the throne a ...
(668–627 BC), who sent wheat to Susiana during a famine. But these friendly relations were only temporary, and Urtaku was killed in battle during a failed Elamite attack on Assyria.
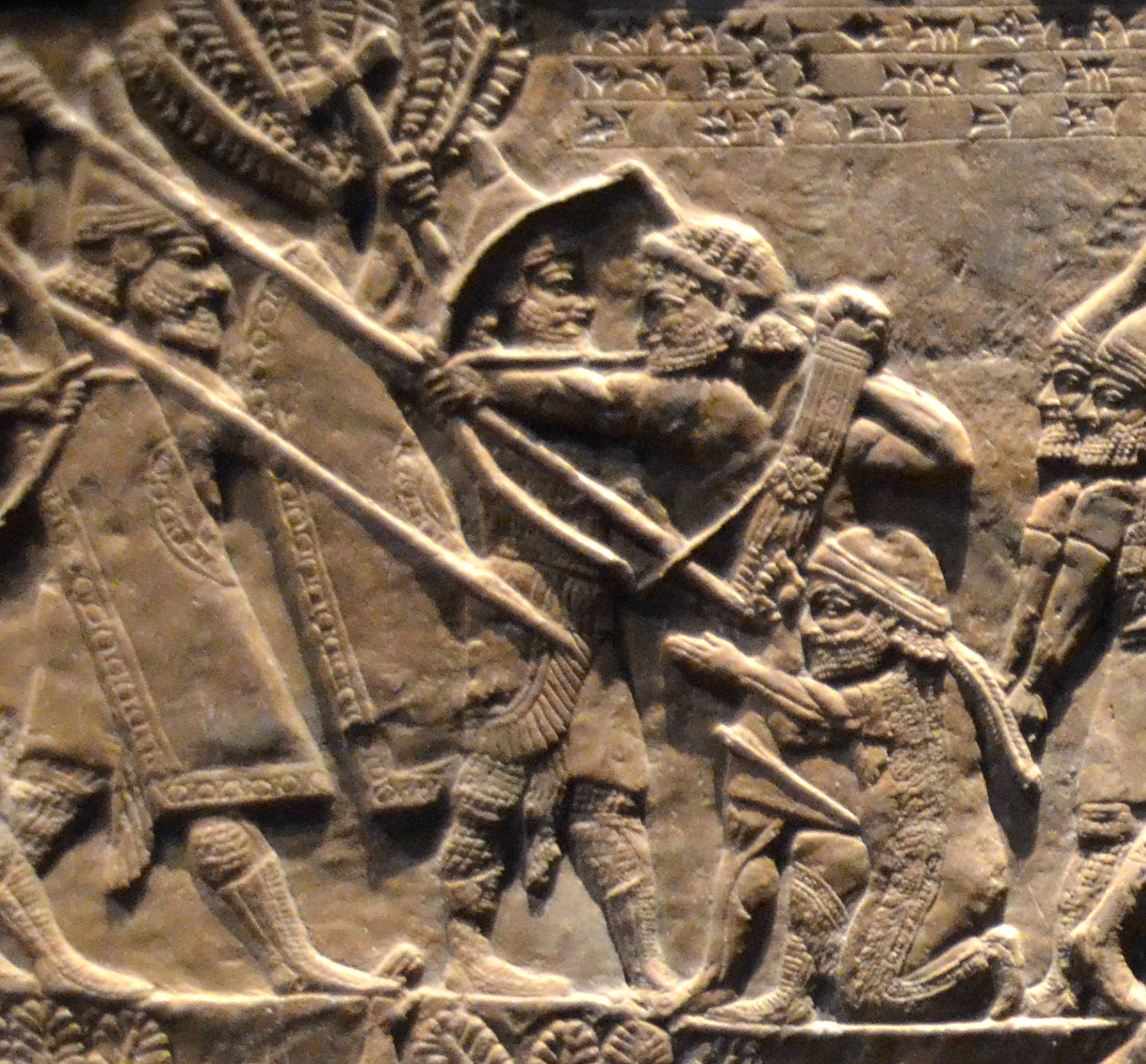
 His successor Tempti-Khumma-In-Shushinak (664–653 BC) attacked Assyria, but was defeated and killed by
His successor Tempti-Khumma-In-Shushinak (664–653 BC) attacked Assyria, but was defeated and killed by Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Inheriting the throne a ...
following the battle of the Ulaï in 653 BC; and Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
itself was sacked and occupied by the Assyrians. In this same year the Assyrian vassal Median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic f ...
state to the north fell to the invading Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
and Cimmerians under Madyes, and displacing another Assyrian vassal people, the ''Parsu'' (Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
) to Anshan which their king Teispes captured that same year, turning it for the first time into an Indo-Iranian kingdom under Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n dominance that would a century later become the nucleus of the Achaemenid dynasty
The Achaemenid dynasty (Old Persian: ; Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) was an ancient Persian royal dynasty that ruled the Achaemenid Empire, an Iranian empire that stretched from Egypt and Southeastern Europe in the west to the Ind ...
. The Assyrians successfully subjugated and drove the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
and Cimmerians from their Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ian colonies, and the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
, Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
and Parthians Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
remained vassals of Assyria.
A brief respite to the Elamites was provided by the civil war between Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Inheriting the throne a ...
and his own brother Shamash-shum-ukin, whom their father Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
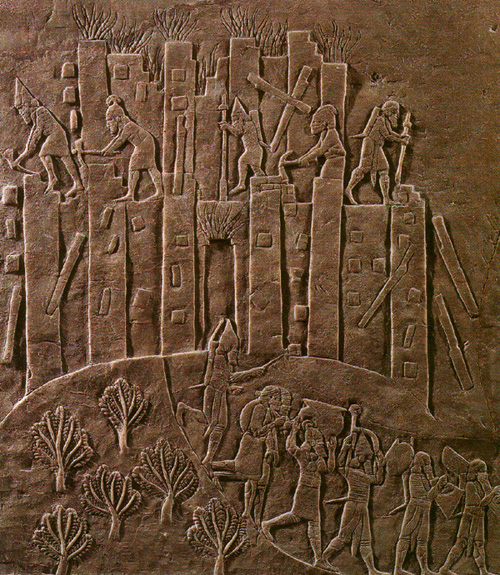
had installed as the vassal king of Babylon. The Elamites gave support to Shamash-shum-ukin, but also engaged in fighting among themselves. Babylon was besieged in midsummer of 650 BC, and fell by 648 BC; Shamash-shum-ukin died in a fire. The Elamite kingdom was greatly weakened by rebellions and civil wars; kings from 651 to 640 had short reigns before being usurped, overthrown, or captured by the Assyrians. Having dealt with his brother, Ashurbanipal sensed an opportunity to devastate Elam. In 646 BC Ashurbanipal devastated Susiana with ease, and sacked Susa. He installed several vassal kings such as Tammaritu Tammaritu may refer to:
* Tammaritu (son of Teumman) (died 653 BCE), King of Elam from 664 to 653 BCE
* Tammaritu I, ruler of Elam from 653 to 652 BCE
* Tammaritu II, ruler of Elam from 652 until 650 or 649 BCE
{{disambiguation, hn ...
, although these quickly broke off relations with Assyria over their pillages. The last Elamite king, Khumma-Khaldash III, was captured in 640 BC by Ashurbanipal, who annexed and destroyed the country.
In a tablet unearthed in 1854 by Henry Austin Layard, Ashurbanipal boasts of the destruction he had wrought:
Neo-Elamite III (646–539 BC)
 The devastation was a little less complete than Ashurbanipal boasted, and a weak and fragmented Elamite rule was resurrected soon after with Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, son of Humban-umena III (not to be confused with Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, son of Indada, a petty king in the first half of the 6th century). Elamite royalty in the final century preceding the Achaemenids was fragmented among different small kingdoms, the united Elamite nation having been destroyed and colonised by the Assyrians. The three kings at the close of the 7th century (Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, Khallutush-In-Shushinak and Atta-Khumma-In-Shushinak) still called themselves "king of Anzan and of Susa" or "enlarger of the kingdom of Anzan and of Susa", at a time when the Achaemenid Persians were already ruling Anshan under Assyrian dominance.
The various Assyrian Empires, which had been the dominant force in the
The devastation was a little less complete than Ashurbanipal boasted, and a weak and fragmented Elamite rule was resurrected soon after with Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, son of Humban-umena III (not to be confused with Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, son of Indada, a petty king in the first half of the 6th century). Elamite royalty in the final century preceding the Achaemenids was fragmented among different small kingdoms, the united Elamite nation having been destroyed and colonised by the Assyrians. The three kings at the close of the 7th century (Shuttir-Nakhkhunte, Khallutush-In-Shushinak and Atta-Khumma-In-Shushinak) still called themselves "king of Anzan and of Susa" or "enlarger of the kingdom of Anzan and of Susa", at a time when the Achaemenid Persians were already ruling Anshan under Assyrian dominance.
The various Assyrian Empires, which had been the dominant force in the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
, Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, Arabian peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
and East Mediterranean for much of the period from the first half of the 14th century BC, began to unravel after the death of Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Inheriting the throne a ...
in 627 BC, descending into a series of bitter internal civil wars which also spread to Babylonia. The Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
, Parthians Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
and Sagartians, who had been largely subject to Assyria since their arrival in the region around 1000 BC, quietly took full advantage of the anarchy in Assyria, and in 616 BC freed themselves from Assyrian rule.
The Medians took control of Elam during this period. Cyaxares
Cyaxares (Median language, Median: ; Old Persian: ; Akkadian language, Akkadian: ; Phrygian language, Old Phrygian: ; grc, wikt:Κυαξάρης, Κυαξαρης, Kuaxarēs; Latin: ; reigned 625–585 BCE) was the third king of the Medes.
C ...
the king of the Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
, Parthians Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
and Sagartians entered into an alliance with a coalition of fellow former vassals of Assyria, including Nabopolassar
Nabopolassar (Babylonian cuneiform: , meaning "Nabu, protect the son") was the founder and first king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from his coronation as king of Babylon in 626 BC to his death in 605 BC. Though initially only aimed at res ...
of Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
and Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
, and also the Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
and Cimmerians, against Sin-shar-ishkun of Assyria, who was faced with unremitting civil war in Assyria itself. This alliance then attacked a disunited and war weakened Assyria, and between 616 BC and 599 BC at the very latest, had conquered its vast empire which stretched from the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
and the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
, and from Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
and Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
.
The major cities in Assyria itself were gradually taken; Arrapha
Arrapha or Arrapkha (Akkadian: ''Arrapḫa''; ar, أررابخا ,عرفة) was an ancient city in what today is northeastern Iraq, thought to be on the site of the modern city of Kirkuk.
In 1948, ''Arrapha'' became the name of the residential ...
(modern Kirkuk
Kirkuk ( ar, كركوك, ku, کەرکووک, translit=Kerkûk, , tr, Kerkük) is a city in Iraq, serving as the capital of the Kirkuk Governorate, located north of Baghdad. The city is home to a diverse population of Turkmens, Arabs, Kurds ...
) and Kalhu (modern Nimrud
Nimrud (; syr, ܢܢܡܪܕ ar, النمرود) is an ancient Assyrian city located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah ( ar, السلامية), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a m ...
) in 616 BC, Ashur, Dur-Sharrukin and Arbela (modern Erbil
Erbil, also called Hawler (, ar, أربيل, Arbīl; syr, ܐܲܪܒܹܝܠ, Arbel), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It lies in the Erbil Governorate. It has an estimated population of around 1,600,000.
H ...
) in 613, Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ba ...
falling in 612, Harran
Harran (), historically known as Carrhae ( el, Kάρραι, Kárrhai), is a rural town and district of the Şanlıurfa Province in southeastern Turkey, approximately 40 kilometres (25 miles) southeast of Urfa and 20 kilometers from the border ...
in 608 BC, Carchemish
Carchemish ( Turkish: ''Karkamış''; or ), also spelled Karkemish ( hit, ; Hieroglyphic Luwian: , /; Akkadian: ; Egyptian: ; Hebrew: ) was an important ancient capital in the northern part of the region of Syria. At times during i ...
in 605 BC, and finally Dur-Katlimmu by 599 BC. Elam, already largely destroyed and subjugated by Assyria, thus became easy prey for the Median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic f ...
dominated Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
, and was incorporated into the Median Empire
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
(612–546 BC) and then the succeeding Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
(546–332 BC), with Assyria suffering the same fate. (see Achaemenid Assyria, Athura).
 The prophet Ezekiel describes the status of their power in the 12th year of the Hebrew
The prophet Ezekiel describes the status of their power in the 12th year of the Hebrew Babylonian Captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital city of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, following their defeat ...
in 587 BC:
Their successors Khumma-Menanu and Shilhak-In-Shushinak II bore the simple title "king", and the final king Tempti-Khumma-In-Shushinak used no honorific at all. In 540 BC, Achaemenid rule began in Susa.
Elymais (187 BC – 224 AD)
Elymaïs was the location of the death of Antiochus III the Great who was killed while pillaging a temple ofBel BEL can be an abbreviation for:
* The ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 country code for Belgium
* ''BEL'' or bell character in the C0 control code set
* Belarusian language, in the ISO 639-2 and SIL country code lists
* Bharat Electronics Limited, an Indian sta ...
in 187 BC. Following the rise and fall of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
and the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, a new dynasty of Elamite rulers established Elymais from 147 BC to 224 AD, usually under the suzerainty of the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqu ...
, until the advent of the unified Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
in 224 AD.
Art

Statuettes
Dated to approximately the 12th century BC, gold and silver figurines of Elamite worshippers are shown carrying a sacrificial goat. These divine and royal statues were meant to assure the king of the enduring protection of the deity, well-being and a long life. Works which showed a ruler and his performance of a ritual action were intended to eternalize the effectiveness of such deeds. Found near the Temple ofInshushinak
Inshushinak ( Linear Elamite: ''Inšušnak'', Cuneiform: , ''dinšušinakki''; possibly from Sumerian '' en-šušin-a ', "lord of Susa") was one of the major gods of the Elamites and the protector deity of Susa. He was called ''rišar napa ...
in Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
, these statuettes would have been considered charged with beneficial power.
While archaeologists cannot be certain that the location where these figures were found indicates a date before or in the time of the Elamite king Shilhak-Inshushinak, stylistic features can help ground the figures in a specific time period. The hairstyle and costume of the figures which are strewn with dots and hemmed with short fringe at the bottom, and the precious metals point to a date in the latter part of the second millennium BC rather than to the first millennium.
In general, any gold or silver statuettes which represent the king making a sacrifice not only served a religious function, but was also a display of wealth.
Seals
Elamite seals reached their peak of complexity in the 4th millennium BC when their shape became cylindrical rather than stamp-like. Seals were primarily used as a form of identification and were often made out of precious stones. Because seals for different time periods had different designs and themes, seals and seal impressions can be used to track the various phases of the Elamite Empire and can teach a lot about the empire in ways which other forms of documentation cannot.“Cylinder Seal and Modern Impression: Worshiper before a Seated Ruler or Deity; Seated Female under a Grape Arbor , Work of Art , Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History , The Metropolitan Museum of Art.” The Met's Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, www.metmuseum.org/toah/works-of-art/1987.343/. The seal pictured shows two seated figures holding cups with a man in front of them wearing a long robe next to a table. A man is sitting on a throne, presumably the king, and is in a wrapped robe. The second figure, perhaps his queen, is draped in a wide, flounced garment and is elevated on a platform beneath an overhanging vine. A crescent is shown in the field.Statue of Queen Napir-Asu
Napir-Asu
Napir-Asu (fl. 14th century BCE) was an Elamite queen, who was the wife of King Untash-Napirisha. A statue of her by the bronzeworkers of Susa is one of the finest examples of bronze metal-working to be discovered.
Biography
Whilst Napir-Asu's ...
was commissioned around 1300 BC in Susa, Iran. It is made of copper using the lost-wax
Lost-wax casting (also called "investment casting", "precision casting", or ''cire perdue'' which has been adopted into English from the French, ) is the process by which a duplicate metal sculpture (often silver, gold, brass, or bronze) is ...
casting method and rests on a solid bronze frame that weighs 1750 kg (3760 lb). This statue is different from many other Elamite statues of women because it resembles male statues due to the wide belt on the dress and the patterns which closely resemble those on male statues.
The inscription on the side of the statue curses anyone, specifically men, who attempts to destroy the statue: "I, Napir-Asu, wife of Untash-Napirisha
Untash-Napirisha was king of Elam (in present-day southwest Iran) during the Middle Elamite period, circa 1300 BCE. He was the son of the previous Elamite king, Humban-Numena. He was named after Napirisha, an Elamite deity.
He founded and built ...
. He who would seize my statue, who would smash it, who would destroy its inscription, who would erase my name, may he be smitten by the curse of Napirisha, of Kiririsha, and of Inshushinka, that his name shall become extinct, that his offspring be barren, that the forces of Beltiya, the great goddess, shall sweep down on him. This is Napir-Asu's offering."
Stele of Untash Napirisha
The stele of the Elamite king,Untash-Napirisha
Untash-Napirisha was king of Elam (in present-day southwest Iran) during the Middle Elamite period, circa 1300 BCE. He was the son of the previous Elamite king, Humban-Numena. He was named after Napirisha, an Elamite deity.
He founded and built ...
was believed to have been commissioned in the 12th century BC.
It was moved from the original religious capital of Chogha Zanbil to the city of Susa by the successor king, Shutruk-Nahnante. Four registers of the stele are left. The remains depict the god Inshushinak validating the legitimacy of who is thought to be Shutruk-Nahnante. In the periphery are two priestesses, deity hybrids of fish and women holding streams of water, and two half-man half-mouflon guardians of the sacred tree. The names of the two priestesses are carved on their arms.Borne interactive du département des Antiquités orientales. Malbran-Labat Florence, Les Inscriptions de Suse : briques de l'époque paléo-élamite à l'empire néo-élamite, Paris, Éditions de la Réunion des musées nationaux, 1995, p.168–169. Miroschedji Pierre de, "Le Dieu élamite au serpent", in : Iranica antiqua, Vol.16, 1981, Gand, Ministère de l'Éducation et de la Culture, 1989, p.13–14, pl.8.
King Untash Napirisha dedicated the stele to the god Ishushinak. Like other forms of art in the ancient Near East, this one portrays a king ceremonially recognizing a deity. This stele is unique in that the acknowledgement between king and god is reciprocal.
Religion
 The Elamites practised
The Elamites practised polytheism
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, t ...
. Due to scarcity of sources, past scholars assumed that Elamite religion must have been characterized by the "ill-defined character of the individual gods and goddesses. ...Most of them were not only ineffable beings whose real name was either not uttered or was unknown, but also sublime ideas, not to be exactly defined by the human race." Worship also varied between localities. However, more recent scholarship shows that Elamite deities most likely were not any less defined than these of their Sumerian, Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
and Hurrian
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Norther ...
neighbors.
Inscriptions of many Elamite kings indicate that a concept of a supreme triad consisting of Inshushinak
Inshushinak ( Linear Elamite: ''Inšušnak'', Cuneiform: , ''dinšušinakki''; possibly from Sumerian '' en-šušin-a ', "lord of Susa") was one of the major gods of the Elamites and the protector deity of Susa. He was called ''rišar napa ...
(originally the civic protector god of Susa, eventually the leader of the triad and guarantor of the monarchy), Kiririsha
Kiririsha ( Elamite: “great lady”) was a major goddess worshiped in Elam.
Early scholarship incorrectly identified her as one and the same as Pinikir, an unrelated goddess from a different part of Elam.
Character
Kiririsha is regarded as ...
(an earth/mother goddess in southern Elam), and Napirisha existed. In the Neo-Elamite period Humban, previously a deity of limited relevance in known sources, emerged as a divine source of royal power.
Another significant deity was Pinikir, an astral goddess of love, similar to Ishtar. Some researchers, especially in the 1960s and 1970s, saw her as a mother goddess, and possibly originally chief deity, in northern Elam, later supplanted by or identified with Kiririsha, but this view is no longer supported by scholars.
There were also imported deities, such as Beltiya, Nergal
Nergal ( Sumerian: d''KIŠ.UNU'' or ; ; Aramaic: ܢܸܪܓܲܠ; la, Nirgal) was a Mesopotamian god worshiped through all periods of Mesopotamian history, from Early Dynastic to Neo-Babylonian times, with a few attestations under indicating hi ...
or Nanaya; some native Elamite deities had Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
or Sumerian names as well (ex. Manzat, Inshushinak
Inshushinak ( Linear Elamite: ''Inšušnak'', Cuneiform: , ''dinšušinakki''; possibly from Sumerian '' en-šušin-a ', "lord of Susa") was one of the major gods of the Elamites and the protector deity of Susa. He was called ''rišar napa ...
and his attendants), indicating a long history of interchange. Some Elamite deities were also venerated outside Elam: Pinikir was known to the Hurrians and Hittites, Simut appeared in Babylonian personal names, and an Assyrian text mentions Khumban, Napirisha and Yabru (Jabru) as protectors of the king.
List of Elamite gods
Language
Elamite is traditionally thought to be alanguage isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
, and completely unrelated to the neighbouring Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant ...
, Sumerian and Kassite
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babyl ...
, Hurrian
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Norther ...
(also isolates), and the later arriving Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
Iranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
that came to dominate the region of Elam from the 6th century BC. It was written in a cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge- ...
adapted from the Semitic Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic ...
script of Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
and Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
, although the very earliest documents were written in the quite different "Linear Elamite" script. In 2006, two even older inscriptions in a similar script were discovered at Jiroft
Jiroft ( fa, جیرفت, also Romanized as Jīroft; formerly, Sabzāwārān, Sabzevārān, Sabzevārān-e Jiroft, and Sabzvārān) is a city and capital of Jiroft County, Kerman Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 95,031, in ...
to the east of Elam, leading archaeologists to speculate that Linear Elamite had originally spread from further east to Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
. It seems to have developed from an even earlier writing known as "proto-Elamite", but scholars are not unanimous on whether or not this script was used to write Elamite or another language, as it has not yet been deciphered. Several stages of the language are attested; the earliest date back to the third millennium BC, the latest to the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
.
The Elamite language may have survived as late as the early Islamic period
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main ...
(roughly contemporary with the early medieval period
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
in Europe). Among other Islamic medieval historians, Ibn al-Nadim, for instance, wrote that "The Iranian languages are Fahlavi ( Pahlavi), Dari
Dari (, , ), also known as Dari Persian (, ), is the variety of the Persian language spoken in Afghanistan. Dari is the term officially recognised and promoted since 1964 by the Afghan government for the Persian language,Lazard, G.Darī ...
(not to be confused with Dari Persian in modern Afghanistan), Khuzi, Persian and Suryani (Assyrian
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyri ...
)", and Ibn Moqaffa noted that ''Khuzi'' was the unofficial language of the royalty of Persia, "Khuz" being the corrupted name for Elam.
Suggested relations to other language families
While Elamite is viewed as alanguage isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
by the vast majority of linguists, a minority of scholars have proposed that the Elamite language could be related to the Dravidian languages
The Dravidian languages (or sometimes Dravidic) are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in southern India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant im ...
. David McAlpine believes Elamite may be related to the living Dravidian languages. This hypothesis is considered under the rubric of Elamo-Dravidian languages.
Legacy
The Assyrians had utterly destroyed the Elamite nation, but new polities emerged in the area after Assyrian power faded. Among the nations that benefited from the decline of the Assyrians were the Iranian tribes, whose presence around Lake Urmia to the north of Elam is attested from the 9th century BC in Assyrian texts. Some time after that region fell to Madius the Scythian (653 BC), Teispes, son of Achaemenes, conquered Elamite Anshan in the mid 7th century BC, forming a nucleus that would expand into the Persian Empire. They were largely regarded as vassals of the Assyrians, and the Medes, Mannaeans, and Persians paid tribute to Assyria from the 10th century BC until the death ofAshurbanipal
Ashurbanipal ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Inheriting the throne a ...
in 627 BC. After his death, the Medes played a major role in the destruction of the weakened Assyrian Empire in 612 BC.
The rise of the Achaemenids in the 6th century BC brought an end to the existence of Elam as an independent political power "but not as a cultural entity" (''Encyclopædia Iranica'', Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
). Indigenous Elamite traditions, such as the use of the title "king of Anshan" by Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
; the "Elamite robe" worn by Cambyses I of Anshan and seen on the famous winged genii at Pasargadae
Pasargadae (from Old Persian ''Pāθra-gadā'', "protective club" or "strong club"; Modern Persian: ''Pāsārgād'') was the capital of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great (559–530 BC), who ordered its construction and the locatio ...
; some glyptic styles; the use of Elamite as the first of three official languages of the empire used in thousands of administrative texts found at Darius’ city of Persepolis; the continued worship of Elamite deities; and the persistence of Elamite religious personnel and cults supported by the crown, formed an essential part of the newly emerging Achaemenid culture in Persian Iran. The Elamites thus became the conduit by which achievements of the Mesopotamian civilizations were introduced to the tribes of the Iranian plateau.
Conversely, remnants of Elamite had "absorbed Iranian influences in both structure and vocabulary" by 500 BC, suggesting a form of cultural continuity or fusion connecting the Elamite and the Persian periods.
The name of "Elam" survived into the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
and beyond. In its Greek form, '' Elymais'', it emerges as designating a semi-independent state under Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
n suzerainty during the 2nd century BC to the early 3rd century AD. In Acts 2:8–9 in the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
, the language of the ''Elamitēs'' is one of the languages heard at the Pentecost
Pentecost (also called Whit Sunday, Whitsunday or Whitsun) is a Christian holiday which takes place on the 50th day (the seventh Sunday) after Easter Sunday. It commemorates the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the Apostles and other followers ...
. From 410 onwards Elam (Beth Huzaye) was the senior metropolitan province of the Church of the East
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
, surviving into the 14th century. Indian Carmelite historian John Marshal has proposed that the root of Carmelite
, image =
, caption = Coat of arms of the Carmelites
, abbreviation = OCarm
, formation = Late 12th century
, founder = Early hermits of Mount Carmel
, founding_location = Mount Ca ...
history in present day India could be traced to the promise of restoration of Elam (Jeremiah 49:39).
lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
dove is studded with gold pegs. Dated 1200 BC from Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
, a city later on shared with the Achaemenids.
File:Eshkaft-e Salman II.jpg, Elamite reliefs
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
at Eshkaft-e Salman
Eshkaft-e Salman or ''Shekaft-e Salman''
Location
On the southwest side of the valley, 2.5 km from the town center of Izeh, southwest Iran, is the majestic “''romantic grotto''” of Shekaft-e Salman (“Salomon’s Cave”) where a ...
. The picture of a woman with dignity shows the importance of women in the Elamite era.
Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle P ...
name for Elamites.See ''Encyclopædia Iranica
''Encyclopædia Iranica'' is a project whose goal is to create a comprehensive and authoritative English language encyclopedia about the history, culture, and civilization of Iranian peoples from prehistory to modern times.
Scope
The ''Encyc ...
'', Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
, Vol 1, p687-689.
See also
* List of rulers of Elam * Jiroft culture *Jam Arjan
Arjan bowl (Persian: ''Jaam-e Arjan'') is a bronze bowl dated between 800 B.C and 500 B.C. It was discovered in 1982 after a bulldozer working on the Marun Dam project cut into a rock tomb near Behbahan, Iran.
Arjan is the ancient name of Behb ...
References
Sources
*Quintana Cifuentes, E., "Historia de Elam el vecino mesopotámico", Murcia, 1997. ''Estudios Orientales''. IPOA-Murcia. *Quintana Cifuentes, E., "Textos y Fuentes para el estudio del Elam", Murcia, 2000.'' Estudios Orientales''. IPOA-Murcia. * Quintana Cifuentes, E.,'' La Lengua Elamita (Irán pre-persa)'', Madrid, 2010. Gram Ediciones. *Khačikjan, Margaret: ''The Elamite Language'', Documenta Asiana IV, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche Istituto per gli Studi Micenei ed Egeo-Anatolici, 1998 * * *''Persians: Masters of Empire'', Time-Life Books, Alexandria, Virginia (1995) * *D. T. Potts, "Elamites and Kassites in the Persian Gulf",''Journal of Near Eastern Studies'', vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 111–119, (April 2006) * *McAlpin, David W., ''Proto Elamo Dravidian: The Evidence and Its Implications'', American Philosophy Society (1981) *Vallat, François. 2010. "The History of Elam". The Circle of Ancient Iranian Studies (CAIS) * *Giuseppe Valenza, Elamiti Elimioti Elimi Il Teatro Genealogico degli Elimi nel crocevia del Mediterraneo. Marostica, 2022, ISBN 978-88-908854-2-6.Further reading
* Zohouriyan, Maryam, Seyyed Mehdi Mousavi Kouhpar, Javad Neyestani, and Alireza Hozhabri Nobari. “Semiology of the Gryphon Motif in Ancient Elamite Architecture”. In: ''Central Asiatic Journal'' 62, no. 2 (2019): 227–32. https://doi.org/10.13173/centasiaj.62.2.0227.External links
Lengua e historia elamita
by Enrique Quintana
History of the Elamite Empire
*Hamid-Reza Hosseini, ''Shush at the foot of
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the '' Venus de Milo''. A central ...
'''Shush dar dāman-e Louvre'', in Persian, Jadid Online, 10 March 2009
br
(6 min 31 sec) *https://web.archive.org/web/20160222154459/http://www.elamit.net/ {{Coord, 29, 54, N, 52, 24, E, display=title, source:fiwiki States and territories established in the 3rd millennium BC States and territories disestablished in the 6th century BC Ancient Asia Ancient history of Iran Chalcolithic states in Asia Bronze Age countries in Asia Iron Age countries in Asia 27th-century BC establishments Historical regions