Einsatzgruppen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of

 In response to
In response to

 All four main took part in mass shootings from the early days of the war. Initially the targets were adult Jewish men, but by August the net had been widened to include women, children, and the elderly—the entire Jewish population. Initially there was a semblance of legality given to the shootings, with trumped-up charges being read out (arson, sabotage, black marketeering, or refusal to work, for example) and victims being murdered by a firing squad. As this method proved too slow, the began to take their victims out in larger groups and shot them next to, or even inside, mass graves that had been prepared. Some started to use automatic weapons, with survivors being murdered with a pistol shot.
As word of the massacres got out, many Jews fled; in Ukraine, 70 to 90 per cent of the Jews ran away. This was seen by the leader of VI as beneficial, as it would save the regime the costs of deporting the victims further east over the Urals. In other areas the invasion was so successful that the had insufficient forces to immediately murder all the Jews in the conquered territories. A situation report from C in September 1941 noted that not all Jews were members of the Bolshevist apparatus, and suggested that the total elimination of Jewry would have a negative impact on the economy and the food supply. The Nazis began to round their victims up into concentration camps and ghettos and rural districts were for the most part rendered (free of Jews). Jewish councils were set up in major cities and forced labour gangs were established to make use of the Jews as slave labour until they were totally eliminated, a goal that was postponed until 1942.
The used public hangings as a terror tactic against the local population. An B report, dated 9 October 1941, described one such hanging. Due to suspected partisan activity near Demidov, all male residents aged 15 to 55 were put in a camp to be screened. The screening produced seventeen people who were identified as "partisans" and "Communists". Five members of the group were hanged while 400 local residents were assembled to watch; the rest were shot.
All four main took part in mass shootings from the early days of the war. Initially the targets were adult Jewish men, but by August the net had been widened to include women, children, and the elderly—the entire Jewish population. Initially there was a semblance of legality given to the shootings, with trumped-up charges being read out (arson, sabotage, black marketeering, or refusal to work, for example) and victims being murdered by a firing squad. As this method proved too slow, the began to take their victims out in larger groups and shot them next to, or even inside, mass graves that had been prepared. Some started to use automatic weapons, with survivors being murdered with a pistol shot.
As word of the massacres got out, many Jews fled; in Ukraine, 70 to 90 per cent of the Jews ran away. This was seen by the leader of VI as beneficial, as it would save the regime the costs of deporting the victims further east over the Urals. In other areas the invasion was so successful that the had insufficient forces to immediately murder all the Jews in the conquered territories. A situation report from C in September 1941 noted that not all Jews were members of the Bolshevist apparatus, and suggested that the total elimination of Jewry would have a negative impact on the economy and the food supply. The Nazis began to round their victims up into concentration camps and ghettos and rural districts were for the most part rendered (free of Jews). Jewish councils were set up in major cities and forced labour gangs were established to make use of the Jews as slave labour until they were totally eliminated, a goal that was postponed until 1942.
The used public hangings as a terror tactic against the local population. An B report, dated 9 October 1941, described one such hanging. Due to suspected partisan activity near Demidov, all male residents aged 15 to 55 were put in a camp to be screened. The screening produced seventeen people who were identified as "partisans" and "Communists". Five members of the group were hanged while 400 local residents were assembled to watch; the rest were shot.
 A operated in
A operated in  In late 1941, the settled into headquarters in Kaunas, Riga, and Tallinn. A grew less mobile and faced problems because of its small size. The Germans relied increasingly on the Latvian and similar groups to perform massacres of Jews.
Such extensive and enthusiastic collaboration with the has been attributed to several factors. Since the Russian Revolution of 1905, the and other borderlands had experienced a political culture of violence. The 1940–1941 Soviet occupation had been profoundly traumatic for residents of the Baltic states and areas that had been part of Poland until 1939; the population was brutalised and terrorised, and the existing familiar structures of society were destroyed.
Historian Erich Haberer has suggested that many survived and made sense of the "totalitarian atomization" of society by seeking conformity with communism. As a result, by the time of the German invasion in 1941, many had come to see conformity with a totalitarian regime as socially acceptable behaviour; thus, people simply transferred their allegiance to the German regime when it arrived. Some who had collaborated with the Soviet regime sought to divert attention from themselves by naming Jews as collaborators and murdering them.
In late 1941, the settled into headquarters in Kaunas, Riga, and Tallinn. A grew less mobile and faced problems because of its small size. The Germans relied increasingly on the Latvian and similar groups to perform massacres of Jews.
Such extensive and enthusiastic collaboration with the has been attributed to several factors. Since the Russian Revolution of 1905, the and other borderlands had experienced a political culture of violence. The 1940–1941 Soviet occupation had been profoundly traumatic for residents of the Baltic states and areas that had been part of Poland until 1939; the population was brutalised and terrorised, and the existing familiar structures of society were destroyed.
Historian Erich Haberer has suggested that many survived and made sense of the "totalitarian atomization" of society by seeking conformity with communism. As a result, by the time of the German invasion in 1941, many had come to see conformity with a totalitarian regime as socially acceptable behaviour; thus, people simply transferred their allegiance to the German regime when it arrived. Some who had collaborated with the Soviet regime sought to divert attention from themselves by naming Jews as collaborators and murdering them.
 B, C, and D did not immediately follow A's example in systematically murdering all Jews in their areas. The commanders, with the exception of A's Stahlecker, were of the opinion by the fall of 1941 that it was impossible to murder the entire Jewish population of the Soviet Union in one sweep, and thought the murders should stop. An report dated 17 September advised that the Germans would be better off using any skilled Jews as labourers rather than shooting them. Also, in some areas poor weather and a lack of transportation led to a slowdown in deportations of Jews from points further west. Thus, an interval passed between the first round of massacres in summer and fall, and what American historian Raul Hilberg called the second sweep, which started in December 1941 and lasted into the summer of 1942. During the interval, the surviving Jews were forced into ghettos.
A had already murdered almost all Jews in its area, so it shifted its operations into Belarus to assist B. In Dnepropetrovsk in February 1942, D reduced the city's Jewish population from 30,000 to 702 over the course of four days. The German Order Police and local collaborators provided the extra manpower needed to perform all the shootings. Haberer wrote that, as in the Baltic states, the Germans could not have murdered so many Jews so quickly without local help. He points out that the ratio of Order Police to auxiliaries was 1 to 10 in both Ukraine and Belarus. In rural areas the proportion was 1 to 20. This meant that most Ukrainian and Belarusian Jews were murdered by fellow Ukrainians and Belarusians commanded by German officers rather than by Germans.
The second wave of exterminations in the Soviet Union met with armed resistance in some areas, though the chance of success was poor. Weapons were typically primitive or home-made. Communications were impossible between ghettos in various cities, so there was no way to create a unified strategy. Few in the ghetto leadership supported resistance for fear of reprisals on the ghetto residents. Mass break-outs were sometimes attempted, though survival in the forest was nearly impossible due to the lack of food and the fact that escapees were often tracked down and murdered.
B, C, and D did not immediately follow A's example in systematically murdering all Jews in their areas. The commanders, with the exception of A's Stahlecker, were of the opinion by the fall of 1941 that it was impossible to murder the entire Jewish population of the Soviet Union in one sweep, and thought the murders should stop. An report dated 17 September advised that the Germans would be better off using any skilled Jews as labourers rather than shooting them. Also, in some areas poor weather and a lack of transportation led to a slowdown in deportations of Jews from points further west. Thus, an interval passed between the first round of massacres in summer and fall, and what American historian Raul Hilberg called the second sweep, which started in December 1941 and lasted into the summer of 1942. During the interval, the surviving Jews were forced into ghettos.
A had already murdered almost all Jews in its area, so it shifted its operations into Belarus to assist B. In Dnepropetrovsk in February 1942, D reduced the city's Jewish population from 30,000 to 702 over the course of four days. The German Order Police and local collaborators provided the extra manpower needed to perform all the shootings. Haberer wrote that, as in the Baltic states, the Germans could not have murdered so many Jews so quickly without local help. He points out that the ratio of Order Police to auxiliaries was 1 to 10 in both Ukraine and Belarus. In rural areas the proportion was 1 to 20. This meant that most Ukrainian and Belarusian Jews were murdered by fellow Ukrainians and Belarusians commanded by German officers rather than by Germans.
The second wave of exterminations in the Soviet Union met with armed resistance in some areas, though the chance of success was poor. Weapons were typically primitive or home-made. Communications were impossible between ghettos in various cities, so there was no way to create a unified strategy. Few in the ghetto leadership supported resistance for fear of reprisals on the ghetto residents. Mass break-outs were sometimes attempted, though survival in the forest was nearly impossible due to the lack of food and the fact that escapees were often tracked down and murdered.
 After a time, Himmler found that the killing methods used by the were inefficient: they were costly, demoralising for the troops, and sometimes did not kill the victims quickly enough. Many of the troops found the massacres to be difficult if not impossible to perform. Some of the perpetrators suffered physical and mental health problems, and many turned to drink. As much as possible, the leaders militarized the genocide. The historian Christian Ingrao notes an attempt was made to make the shootings a collective act without individual responsibility. Framing the shootings in this way was not psychologically sufficient for every perpetrator to feel absolved of guilt. Browning notes three categories of potential perpetrators: those who were eager to participate right from the start, those who participated in spite of moral qualms because they were ordered to do so, and a significant minority who refused to take part. A few men spontaneously became excessively brutal in their killing methods and their zeal for the task. Commander of D, SS-
After a time, Himmler found that the killing methods used by the were inefficient: they were costly, demoralising for the troops, and sometimes did not kill the victims quickly enough. Many of the troops found the massacres to be difficult if not impossible to perform. Some of the perpetrators suffered physical and mental health problems, and many turned to drink. As much as possible, the leaders militarized the genocide. The historian Christian Ingrao notes an attempt was made to make the shootings a collective act without individual responsibility. Framing the shootings in this way was not psychologically sufficient for every perpetrator to feel absolved of guilt. Browning notes three categories of potential perpetrators: those who were eager to participate right from the start, those who participated in spite of moral qualms because they were ordered to do so, and a significant minority who refused to take part. A few men spontaneously became excessively brutal in their killing methods and their zeal for the task. Commander of D, SS-
 The kept official records of many of their massacres and provided detailed reports to their superiors. The
The kept official records of many of their massacres and provided detailed reports to their superiors. The
 Several leaders, including Ohlendorf, claimed at the trial to have received an order before Operation Barbarossa requiring them to murder all Soviet Jews. To date no evidence has been found that such an order was ever issued. German prosecutor Alfred Streim noted that if such an order had been given, post-war courts would only have been able to convict the leaders as ''accomplices'' to mass murder. However, if it could be established that the had committed mass murder without orders, then they could have been convicted as ''perpetrators'' of mass murder, and hence could have received stiffer sentences, including capital punishment.
Streim postulated that the existence of an early comprehensive order was a fabrication created for use in Ohlendorf's defence. This theory is now widely accepted by historians. Longerich notes that most orders received by the leaders—especially when they were being ordered to carry out criminal activities—were vague, and couched in terminology that had a specific meaning for members of the regime. Leaders were given briefings about the need to be "severe" and "firm"; all Jews were to be viewed as potential enemies that had to be dealt with ruthlessly. British historian Sir Ian Kershaw argues that Hitler's apocalyptic remarks before Barbarossa about the necessity for a war without mercy to "annihilate" the forces of "Judeo-Bolshevism" were interpreted by commanders as permission and encouragement to engage in extreme antisemitic violence, with each commander to use his own discretion about how far he was prepared to go.
Most of the perpetrators of Nazi war crimes were never charged, and returned unremarked to civilian life. The West German Central Prosecution Office of Nazi War Criminals only charged about a hundred former members with war crimes. And as time went on, it became more difficult to obtain prosecutions; witnesses grew older and were less likely to be able to offer valuable testimony. Funding for trials was inadequate, and the governments of Austria and Germany became less interested in obtaining convictions for wartime events, preferring to forget the Nazi past.
Several leaders, including Ohlendorf, claimed at the trial to have received an order before Operation Barbarossa requiring them to murder all Soviet Jews. To date no evidence has been found that such an order was ever issued. German prosecutor Alfred Streim noted that if such an order had been given, post-war courts would only have been able to convict the leaders as ''accomplices'' to mass murder. However, if it could be established that the had committed mass murder without orders, then they could have been convicted as ''perpetrators'' of mass murder, and hence could have received stiffer sentences, including capital punishment.
Streim postulated that the existence of an early comprehensive order was a fabrication created for use in Ohlendorf's defence. This theory is now widely accepted by historians. Longerich notes that most orders received by the leaders—especially when they were being ordered to carry out criminal activities—were vague, and couched in terminology that had a specific meaning for members of the regime. Leaders were given briefings about the need to be "severe" and "firm"; all Jews were to be viewed as potential enemies that had to be dealt with ruthlessly. British historian Sir Ian Kershaw argues that Hitler's apocalyptic remarks before Barbarossa about the necessity for a war without mercy to "annihilate" the forces of "Judeo-Bolshevism" were interpreted by commanders as permission and encouragement to engage in extreme antisemitic violence, with each commander to use his own discretion about how far he was prepared to go.
Most of the perpetrators of Nazi war crimes were never charged, and returned unremarked to civilian life. The West German Central Prosecution Office of Nazi War Criminals only charged about a hundred former members with war crimes. And as time went on, it became more difficult to obtain prosecutions; witnesses grew older and were less likely to be able to offer valuable testimony. Funding for trials was inadequate, and the governments of Austria and Germany became less interested in obtaining convictions for wartime events, preferring to forget the Nazi past.
United States Holocaust Memorial Museum article on
The Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team {{Authority control Military units and formations of Germany in World War II The Holocaust in Ukraine The Holocaust in Latvia The Holocaust in Lithuania The Holocaust in Estonia The Holocaust in Russia The Holocaust in Belarus The Holocaust in Poland Holocaust terminology Gestapo Reinhard Heydrich Reich Security Main Office Police of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
(1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the implementation of the so-called " Final Solution to the Jewish question" () in territories conquered by Nazi Germany, and were involved in the murder of much of the intelligentsia and cultural elite of Poland, including members of the Catholic priesthood. Almost all of the people they murdered were civilians, beginning with the intelligentsia and swiftly progressing to Soviet political commissars, Jews, and Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic Itinerant groups in Europe, itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have Ro ...
, as well as actual or alleged partisans throughout Eastern Europe.
Under the direction of Heinrich Himmler and the supervision of SS- Reinhard Heydrich, the operated in territories occupied by the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
(German armed forces) following the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
in September 1939 and the invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941. The worked hand-in-hand with the Order Police battalions on the Eastern Front to carry out operations ranging from the murder of a few people to operations which lasted over two or more days, such as the massacre at Babi Yar with 33,771 Jews murdered in two days, and the Rumbula massacre (with about 25,000 Jews murdered in two days of shooting). As ordered by Nazi leader Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
, the ''Wehrmacht'' cooperated with the , providing logistical support for their operations, and participated in the mass murders. Historian Raul Hilberg estimates that between 1941 and 1945 the , related agencies, and foreign auxiliary personnel murdered more than two million people, including 1.3 million of the 5.5 to 6 million Jews murdered during the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
.
After the close of World War II, 24 senior leaders of the were prosecuted in the Einsatzgruppen trial in 1947–48, charged with crimes against humanity
Crimes against humanity are widespread or systemic acts committed by or on behalf of a ''de facto'' authority, usually a state, that grossly violate human rights. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity do not have to take place within the ...
and war crimes. Fourteen death sentences and two life sentences were handed out. However, only four of these death sentences were carried out. Four additional leaders were later tried and executed by other nations.
Formation and Aktion T4
The were formed under the direction of SS- Reinhard Heydrich and operated by the (SS) before and duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. The had their origins in the ad hoc formed by Heydrich to secure government buildings and documents following the in Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
in March 1938. Originally part of the (Security Police; SiPo), two units of were stationed in the Sudetenland in October 1938. When military action turned out not to be necessary due to the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
, the were assigned to confiscate government papers and police documents. They also secured government buildings, questioned senior civil servants, and arrested as many as 10,000 Czech communists and German citizens. From September 1939, the (Reich Security Main Office; RSHA) had overall command of the .
As part of the drive by the Nazi regime to remove so-called "undesirable" elements from the German population, from September to December 1939 the and others took part in Action T4, a program of systematic murder of persons with physical and mental disabilities and patients of psychiatric hospitals. Aktion T4 mainly took place from 1939 to 1941, but the murders continued until the end of the war. Initially the victims were shot by the and others, but gas chambers were put into use by spring 1940.
Invasion of Poland

 In response to
In response to Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
's plan to invade Poland on 1 September 1939, Heydrich re-formed the to travel in the wake of the German armies. Membership at this point was drawn from the SS, the (Security Service; SD), the police, and the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
. Heydrich placed SS- Werner Best in command, who assigned to choose personnel for the task forces and their subgroups, called , from among educated people with military experience and a strong ideological commitment to Nazism. Some had previously been members of paramilitary groups such as the . Heydrich instructed Wagner in meetings in late July that the should undertake their operations in cooperation with the (Order Police; Orpo) and military commanders in the area. Army intelligence was in constant contact with to coordinate their activities with other units.
Initially numbering 2,700 men (and ultimately 4,250 in Poland), the 's mission was to murder members of the Polish leadership most clearly identified with Polish national identity: the intelligentsia, members of the clergy, teachers, and members of the nobility. As stated by Hitler: "... there must be no Polish leaders; where Polish leaders exist they must be killed, however harsh that sounds". SS- Lothar Beutel, commander of IV, later testified that Heydrich gave the order for these murders at a series of meetings in mid-August. The lists of people to be murderedhad been drawn up by the SS as early as May 1939, using dossiers collected by the SD from 1936 forward. The performed these murders with the support of the , a paramilitary group consisting of ethnic Germans living in Poland. Members of the SS, the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
, and the also shot civilians during the Polish campaign. Approximately 65,000 civilians were murdered by the end of 1939. In addition to leaders of Polish society, they murdered Jews, prostitutes, Romani people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic Itinerant groups in Europe, itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have Ro ...
, and the mentally ill. Psychiatric patients in Poland were initially murdered by shooting, but by spring 1941 gas vans were widely used.
Seven of battalion strength (around 500 men) operated in Poland. Each was subdivided into five of company strength (around 100 men).
* I, commanded by SS- Bruno Streckenbach
Bruno Streckenbach (7 February 1902 – 28 October 1977) was a German SS functionary during the Nazi era. He was the head of Administration and Personnel Department of the Reich Security Main Office (RSHA). Streckenbach was responsible for many ...
, acted with 14th Army
* II, SS- Emanuel Schäfer
Emanuel Schäfer (20 April 1900 – 4 December 1974) was a high-ranking SS functionary (SS-''Oberführer'') and a protégé of Reinhard Heydrich in Nazi Germany.
Born in 1900, Schäfer served in World War I. Post-war, he participated in fa ...
, acted with 10th Army
* III, SS- Herbert Fischer, acted with 8th Army
* IV, SS- Lothar Beutel, acted with 4th Army
* V, SS- Ernst Damzog
Ernst Damzog (30 October 1882 – 24 July 1945) was a German policeman, who was a member of the SS of Nazi Germany and served in the Gestapo. He was responsible for the mass murder of Poles and Jews committed in the territory of occupied Poland ...
, acted with 3rd Army
* VI, SS- Erich Naumann
Erich Naumann (29 April 1905 – 7 June 1951) was an SS-Brigadeführer, member of the SD, and a convicted war criminal. Naumann had a key role in the Holocaust in Eastern Europe as the commander of Einsatzgruppe VI and the commander of Einsat ...
, acted in Wielkopolska
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city ...
* VII, SS- Udo von Woyrsch
Udo Gustav Wilhelm Egon von Woyrsch (24 July 1895 – 14 January 1983) was a high-ranking SS official in Nazi Germany who participated in implementation of the regime's racial policies during World War II.
First World War
From early 1914 ...
and SS- Otto Rasch
Emil Otto Rasch (7 December 1891 – 1 November 1948) was a high-ranking German Nazi official and Holocaust perpetrator, who commanded Einsatzgruppe C in northern and central Ukraine until October 1941. After World War II, Rasch was indicted for ...
, acted in Upper Silesia and Cieszyn Silesia
Though they were formally under the command of the army, the received their orders from Heydrich and for the most part acted independently of the army. Many senior army officers were only too glad to leave these genocidal actions to the task forces, as the murders violated the rules of warfare as set down in the Geneva Conventions
upright=1.15, Original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are four treaties, and three additional protocols, that establish international legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war. The singular term ''Geneva Conv ...
. However, Hitler had decreed that the army would have to tolerate and even offer logistical support to the when it was tactically possible to do so. Some army commanders complained about unauthorised shootings, looting, and rapes committed by members of the and the , to little effect. For example, when Johannes Blaskowitz
Johannes Albrecht Blaskowitz (10 July 1883 – 5 February 1948) was a German '' Generaloberst'' during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords. After joining the Imperial German Army i ...
sent a memorandum of complaint to Hitler about the atrocities, Hitler dismissed his concerns as "childish", and Blaskowitz was relieved of his post in May 1940. He continued to serve in the army but never received promotion to field marshal.
The final task of the in Poland was to round up the remaining Jews and concentrate them in ghettos within major cities with good railway connections. The intention was to eventually remove all the Jews from Poland, but at this point their final destination had not yet been determined. Together, the ''Wehrmacht'' and the also drove tens of thousands of Jews eastward into Soviet-controlled territory.
Preparations for Operation Barbarossa
On 13 March 1941, in the lead-up toOperation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
, the planned invasion of the Soviet Union, Hitler dictated his "Guidelines in Special Spheres re: Directive No. 21 (Operation Barbarossa)". Sub-paragraph B specified that Heinrich Himmler would be given "special tasks" on direct orders from the Führer, which he would carry out independently. This directive was intended to prevent friction between the ''Wehrmacht'' and the SS in the upcoming offensive. Hitler also specified that criminal acts against civilians perpetrated by members of the ''Wehrmacht'' during the upcoming campaign would not be prosecuted in the military courts, and thus would go unpunished.
In a speech to his leading generals on 30 March 1941, Hitler described his envisioned war against the Soviet Union. General Franz Halder, the Army's Chief of Staff, described the speech:
Though General Halder did not record any mention of Jews, German historian Andreas Hillgruber argued that because of Hitler's frequent contemporary statements about the coming war of annihilation against " Judeo-Bolshevism", his generals would have understood Hitler's call for the destruction of the Soviet Union as also comprising a call for the destruction of its Jewish population. The genocide was often described using euphemisms such as "special tasks" and "executive measures"; victims were often described as having been shot while trying to escape. In May 1941, Heydrich verbally passed on the order to murder the Soviet Jews to the SiPo NCO School in Pretzsch, where the commanders of the reorganised were being trained for Operation Barbarossa. In spring 1941, Heydrich and the First Quartermaster of the , General Eduard Wagner, successfully completed negotiations for co-operation between the and the German Army to allow the implementation of the "special tasks". Following the Heydrich-Wagner agreement on 28 April 1941, Field Marshal Walther von Brauchitsch ordered that when Operation Barbarossa began, all German Army commanders were to immediately identify and register all Jews in occupied areas in the Soviet Union, and fully co-operate with the .
In further meetings held in June 1941 Himmler outlined to top SS leaders the regime's intention to reduce the population of the Soviet Union by 30 million people, not only through direct murder of those considered racially inferior, but by depriving the remainder of food and other necessities of life.
Organisation starting in 1941
For Operation Barbarossa, initially four were created, each numbering 500–990 men to comprise a total force of 3,000. A, B, and C were to be attached to Army Groups North,Centre
Center or centre may refer to:
Mathematics
*Center (geometry), the middle of an object
* Center (algebra), used in various contexts
** Center (group theory)
** Center (ring theory)
* Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity ...
, and South; D was assigned to the 11th Army. The for Special Purposes operated in eastern Poland starting in July 1941. The were under the control of the RSHA, headed by Heydrich and later by his successor, SS- Ernst Kaltenbrunner. Heydrich gave them a mandate to secure the offices and papers of the Soviet state and Communist Party; to liquidate all the higher cadres of the Soviet state; and to instigate and encourage pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian ...
s against Jewish populations. The men of the were recruited from the SD, Gestapo, (Kripo), Orpo, and Waffen-SS. Each was under the operational control of the Higher SS Police Chiefs in its area of operations. In May 1941, General Wagner and SS- Walter Schellenberg agreed that the in front-line areas were to operate under army command, while the army provided the with all necessary logistical support. Given their main task was defeating the enemy, the army left the pacification of the civilian population to the , who offered support as well as prevented subversion. This did not preclude their participation in acts of violence against civilians, as many members of the ''Wehrmacht'' assisted the in rounding up and murdering Jews of their own accord.
Heydrich acted under orders from Himmler, who supplied security forces on an "as needed" basis to the local SS and Police Leaders. Led by SD, Gestapo, and Kripo officers, included recruits from the Orpo, Security Service and Waffen-SS, augmented by uniformed volunteers from the local auxiliary police force. Each was supplemented with Waffen-SS and Order Police battalions as well as support personnel such as drivers and radio operators. On average, the Order Police formations were larger and better armed, with heavy machine-gun detachments, which enabled them to carry out operations beyond the capability of the SS. Each death squad followed an assigned army group as they advanced into the Soviet Union. During the course of their operations, the commanders received assistance from the ''Wehrmacht''. Activities ranged from the murder of targeted groups of individuals named on carefully prepared lists, to joint citywide operations with which lasted for two or more days, such as the massacres at Babi Yar, perpetrated by the Police Battalion 45
The Police Battalion 45 (''Polizeibattalion 45'') was a formation of the German Order Police (uniformed police) during the Nazi era. During Operation Barbarossa, it was subordinated to the SS and deployed in German-occupied areas, specifically ...
, and at Rumbula, by Battalion 22, reinforced by local (auxiliary police). The SS brigades, wrote historian Christopher Browning
Christopher Robert Browning (born May 22, 1944) is an American historian who is the professor emeritus of history at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (UNC). A specialist on the Holocaust, Browning is known for his work documenting ...
, were "only the thin cutting edge of German units that became involved in political and racial mass murder."
Many leaders were highly educated; for example, nine of seventeen leaders of A held doctorate degrees. Three were commanded by holders of doctorates, one of whom SS- Otto Rasch
Emil Otto Rasch (7 December 1891 – 1 November 1948) was a high-ranking German Nazi official and Holocaust perpetrator, who commanded Einsatzgruppe C in northern and central Ukraine until October 1941. After World War II, Rasch was indicted for ...
) held a double doctorate.
Additional were created as additional territories were occupied. E operated in Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Fascist It ...
under three commanders, SS- , SS- Günther Herrmann, and lastly SS- Wilhelm Fuchs
Oberführer and Oberst of Police Wilhelm Fuchs (1 September 1898, in Mannheim – 24 January 1947, in Belgrade) was a Nazi Einsatzkommando leader. From April 1941 to January 1942 he commanded Einsatzgruppe Serbia. From 15 September 1943 th ...
. The unit was subdivided into five located in Vinkovci, Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ; cyrl, Сарајево, ; ''see names in other languages'') is the capital and largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area including Sarajevo ...
, Banja Luka
Banja Luka ( sr-Cyrl, Бања Лука, ) or Banjaluka ( sr-Cyrl, Бањалука, ) is the second largest city in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the largest city of Republika Srpska. Banja Luka is also the ''de facto'' capital of this entity. ...
, Knin, and Zagreb
Zagreb ( , , , ) is the capital (political), capital and List of cities and towns in Croatia#List of cities and towns, largest city of Croatia. It is in the Northern Croatia, northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slop ...
. F worked with Army Group South. G operated in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
, commanded by SS- . H was assigned to Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
. K and L, under SS- Emanuel Schäfer
Emanuel Schäfer (20 April 1900 – 4 December 1974) was a high-ranking SS functionary (SS-''Oberführer'') and a protégé of Reinhard Heydrich in Nazi Germany.
Born in 1900, Schäfer served in World War I. Post-war, he participated in fa ...
and SS- Ludwig Hahn, worked alongside 5th and 6th Panzer Armies during the Ardennes offensive
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive, was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II. The battle lasted from 16 December 1944 to 28 January 1945, towards the end of the war i ...
. Hahn had previously been in command of in Greece.
Other and included (operated in Carinthia, on the border between Slovenia and Austria) under SS- Paul Blobel, (Yugoslavia) (Luxembourg), (Norway) commanded by SS- Franz Walter Stahlecker, (Yugoslavia) under SS- Wilhelm Fuchs
Oberführer and Oberst of Police Wilhelm Fuchs (1 September 1898, in Mannheim – 24 January 1947, in Belgrade) was a Nazi Einsatzkommando leader. From April 1941 to January 1942 he commanded Einsatzgruppe Serbia. From 15 September 1943 th ...
and SS- August Meysner, ' (Lithuania, Poland), and (Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
), commanded by SS- Walter Rauff.
Killings in the Soviet Union
After the invasion of the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941, the 's main assignment was to kill civilians, as in Poland, but this time its targets specifically included Soviet Communist Party commissars and Jews. In a letter dated 2 July 1941 Heydrich communicated to his SS and Police Leaders that the were to execute all senior and middle ranking Comintern officials; all senior and middle ranking members of the central, provincial, and district committees of the Communist Party; extremist and radical Communist Party members; people's commissars; and Jews in party and government posts. Open-ended instructions were given to execute "other radical elements (saboteurs, propagandists, snipers, assassins, agitators, etc.)." He instructed that any pogroms spontaneously initiated by the population of the occupied territories were to be quietly encouraged. On 8 July, Heydrich announced that all Jews were to be regarded as partisans, and gave the order for all male Jews between the ages of 15 and 45 to be shot. On 17 July Heydrich ordered that the were to murder all JewishRed Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
prisoners of war, plus all Red Army prisoners of war from Georgia and Central Asia, as they too might be Jews. Unlike in Germany, where the Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of ...
of 1935 defined as Jewish anyone with at least three Jewish grandparents, the defined as Jewish anyone with at least one Jewish grandparent; in either case, whether or not the person practised the religion was irrelevant. The unit was also assigned to exterminate Romani people and the mentally ill. It was common practice for the to shoot hostages.
As the invasion began, the Germans pursued the fleeing Red Army, leaving a security vacuum. Reports surfaced of Soviet guerrilla activity in the area, with local Jews immediately suspected of collaboration. Heydrich ordered his officers to incite anti-Jewish pogroms in the newly occupied territories. Pogroms, some of which were orchestrated by the , broke out in Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
. Within the first few weeks of Operation Barbarossa, 10,000 Jews had been murdered in 40 pogroms, and by the end of 1941 some 60 pogroms had taken place, claiming as many as 24,000 victims. However, Franz Walter Stahlecker
Franz Walter Stahlecker (10 October 1900 – 23 March 1942) was commander of the SS security forces (''Sicherheitspolizei'' (SiPo) and the ''Sicherheitsdienst'' (SD) for the ''Reichskommissariat Ostland'' in 1941–42. Stahlecker commanded ''Ein ...
, commander of A, reported to his superiors in mid-October that the residents of Kaunas were not spontaneously starting pogroms, and secret assistance by the Germans was required. A similar reticence was noted by B in Russia and Belarus and C in Ukraine; the further east the travelled, the less likely the residents were to be prompted into murdering their Jewish neighbours.

 All four main took part in mass shootings from the early days of the war. Initially the targets were adult Jewish men, but by August the net had been widened to include women, children, and the elderly—the entire Jewish population. Initially there was a semblance of legality given to the shootings, with trumped-up charges being read out (arson, sabotage, black marketeering, or refusal to work, for example) and victims being murdered by a firing squad. As this method proved too slow, the began to take their victims out in larger groups and shot them next to, or even inside, mass graves that had been prepared. Some started to use automatic weapons, with survivors being murdered with a pistol shot.
As word of the massacres got out, many Jews fled; in Ukraine, 70 to 90 per cent of the Jews ran away. This was seen by the leader of VI as beneficial, as it would save the regime the costs of deporting the victims further east over the Urals. In other areas the invasion was so successful that the had insufficient forces to immediately murder all the Jews in the conquered territories. A situation report from C in September 1941 noted that not all Jews were members of the Bolshevist apparatus, and suggested that the total elimination of Jewry would have a negative impact on the economy and the food supply. The Nazis began to round their victims up into concentration camps and ghettos and rural districts were for the most part rendered (free of Jews). Jewish councils were set up in major cities and forced labour gangs were established to make use of the Jews as slave labour until they were totally eliminated, a goal that was postponed until 1942.
The used public hangings as a terror tactic against the local population. An B report, dated 9 October 1941, described one such hanging. Due to suspected partisan activity near Demidov, all male residents aged 15 to 55 were put in a camp to be screened. The screening produced seventeen people who were identified as "partisans" and "Communists". Five members of the group were hanged while 400 local residents were assembled to watch; the rest were shot.
All four main took part in mass shootings from the early days of the war. Initially the targets were adult Jewish men, but by August the net had been widened to include women, children, and the elderly—the entire Jewish population. Initially there was a semblance of legality given to the shootings, with trumped-up charges being read out (arson, sabotage, black marketeering, or refusal to work, for example) and victims being murdered by a firing squad. As this method proved too slow, the began to take their victims out in larger groups and shot them next to, or even inside, mass graves that had been prepared. Some started to use automatic weapons, with survivors being murdered with a pistol shot.
As word of the massacres got out, many Jews fled; in Ukraine, 70 to 90 per cent of the Jews ran away. This was seen by the leader of VI as beneficial, as it would save the regime the costs of deporting the victims further east over the Urals. In other areas the invasion was so successful that the had insufficient forces to immediately murder all the Jews in the conquered territories. A situation report from C in September 1941 noted that not all Jews were members of the Bolshevist apparatus, and suggested that the total elimination of Jewry would have a negative impact on the economy and the food supply. The Nazis began to round their victims up into concentration camps and ghettos and rural districts were for the most part rendered (free of Jews). Jewish councils were set up in major cities and forced labour gangs were established to make use of the Jews as slave labour until they were totally eliminated, a goal that was postponed until 1942.
The used public hangings as a terror tactic against the local population. An B report, dated 9 October 1941, described one such hanging. Due to suspected partisan activity near Demidov, all male residents aged 15 to 55 were put in a camp to be screened. The screening produced seventeen people who were identified as "partisans" and "Communists". Five members of the group were hanged while 400 local residents were assembled to watch; the rest were shot.
Babi Yar
The largest mass shooting perpetrated by the took place on 29 and 30 September 1941 at Babi Yar, a ravine northwest ofKyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
city center in Ukraine that had fallen to the Germans on 19 September. The perpetrators included a company of Waffen-SS attached to C under Rasch, members of 4a under SS- Friedrich Jeckeln, and some Ukrainian auxiliary police. The Jews of Kyiv were told to report to a certain street corner on 29 September; anyone who disobeyed would be shot. Since word of massacres in other areas had not yet reached Kyiv and the assembly point was near the train station, they assumed they were being deported. People showed up at the rendezvous point in large numbers, laden with possessions and food for the journey.
After being marched northwest of the city centre, the victims encountered a barbed wire barrier and numerous Ukrainian police and German troops. Thirty or forty people at a time were told to leave their possessions and were escorted through a narrow passageway lined with soldiers brandishing clubs. Anyone who tried to escape was beaten. Soon the victims reached an open area, where they were forced to strip, and then were herded down into the ravine. People were forced to lie down in rows on top of the bodies of other victims, and they were shot in the back of the head or the neck by members of the execution squads.
The murders continued for two days, claiming a total of 33,771 victims. Sand was shovelled and bulldozed over the bodies and the sides of the ravine were dynamited to bring down more material. Anton Heidborn, a member of 4a, later testified that three days later that there were still people alive among the corpses. Heidborn spent the next few days helping smooth out the "millions" of banknotes taken from the victims' possessions. The clothing was taken away, destined to be re-used by German citizens. Jeckeln's troops shot more than 100,000 Jews by the end of October.
Killings in Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia
 A operated in
A operated in Baltic states
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone ...
of Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia (the three Baltic countries which had been occupied by the Soviet Union in 1940–1941). According to its own reports to Himmler, A murdered almost 140,000 people in the five months following the 1941 German invasion: 136,421 Jews, 1,064 Communists, 653 people with mental illnesses, 56 partisans, 44 Poles, five Romani, and one Armenian were reported murdered between 22 June and 25 November 1941.
Upon entering Kaunas, Lithuania, on 25 June 1941, the released the criminals from the local jail and encouraged them to join the pogrom which was underway. Between 23 and 27 June 1941, 4,000 Jews were murdered on the streets of Kaunas and in nearby open pits and ditches. Particularly active in the Kaunas pogrom was the so-called "Death Dealer of Kaunas", a young man who murdered Jews with a crowbar at the Lietukis Garage before a large crowd that cheered each murder with much applause; he occasionally paused to play the Lithuanian national anthem " Tautiška giesmė" on his accordion before resuming the murders.
As A advanced into Lithuania, it actively recruited local nationalists and antisemitic groups. In July 1941, local Lithuanian collaborators, pejoratively called "White Armbands" (), joined the massacres. A pogrom in the Latvian capital Riga in early July 1941 killed 400 Jews. Latvian nationalist Viktors Arājs and his supporters undertook a campaign of arson against synagogues. On 2 July, A commander Stahlecker appointed Arājs to head the , a of about 300 men, mostly university students. Together, A and the murdered 2,300 Jews in Riga on 6–7 July. Within six months, Arājs and collaborators would murder about half of Latvia's Jewish population.
Local officials, the , and the (Auxiliary Police) played a key role in rounding up and massacring local Jews in German-occupied Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. These groups also helped the and other killing units to identify Jews. For example, in Latvia, the , consisting of auxiliary police organised by the Germans and recruited from former Latvian army and police officers, ex-, members of the Pērkonkrusts, and university students, assisted in the murder of Latvia's Jewish citizens. Similar units were created elsewhere, and provided much of the manpower for the Holocaust in Eastern Europe.
With the creation of units such as the in Latvia and the in Lithuania, the attacks changed from the spontaneous mob violence of the pogroms to more systematic massacres. With extensive local help, A was the first to attempt to systematically exterminate all the Jews in its area. Latvian historian Modris Eksteins Modris Eksteins ( lv, Modris Ekšteins; born December 13, 1943) is a Latvian Canadian historian with a special interest in German history and modern culture.
Born in Riga, Latvia, his works include ''Rites of Spring: The Great War and the Birth of ...
wrote:
 In late 1941, the settled into headquarters in Kaunas, Riga, and Tallinn. A grew less mobile and faced problems because of its small size. The Germans relied increasingly on the Latvian and similar groups to perform massacres of Jews.
Such extensive and enthusiastic collaboration with the has been attributed to several factors. Since the Russian Revolution of 1905, the and other borderlands had experienced a political culture of violence. The 1940–1941 Soviet occupation had been profoundly traumatic for residents of the Baltic states and areas that had been part of Poland until 1939; the population was brutalised and terrorised, and the existing familiar structures of society were destroyed.
Historian Erich Haberer has suggested that many survived and made sense of the "totalitarian atomization" of society by seeking conformity with communism. As a result, by the time of the German invasion in 1941, many had come to see conformity with a totalitarian regime as socially acceptable behaviour; thus, people simply transferred their allegiance to the German regime when it arrived. Some who had collaborated with the Soviet regime sought to divert attention from themselves by naming Jews as collaborators and murdering them.
In late 1941, the settled into headquarters in Kaunas, Riga, and Tallinn. A grew less mobile and faced problems because of its small size. The Germans relied increasingly on the Latvian and similar groups to perform massacres of Jews.
Such extensive and enthusiastic collaboration with the has been attributed to several factors. Since the Russian Revolution of 1905, the and other borderlands had experienced a political culture of violence. The 1940–1941 Soviet occupation had been profoundly traumatic for residents of the Baltic states and areas that had been part of Poland until 1939; the population was brutalised and terrorised, and the existing familiar structures of society were destroyed.
Historian Erich Haberer has suggested that many survived and made sense of the "totalitarian atomization" of society by seeking conformity with communism. As a result, by the time of the German invasion in 1941, many had come to see conformity with a totalitarian regime as socially acceptable behaviour; thus, people simply transferred their allegiance to the German regime when it arrived. Some who had collaborated with the Soviet regime sought to divert attention from themselves by naming Jews as collaborators and murdering them.
Rumbula
In November 1941 Himmler was dissatisfied with the pace of the exterminations in Latvia, as he intended to move Jews from Germany into the area. He assigned SS- Jeckeln, one of the perpetrators of the Babi Yar massacre, to liquidate the Riga ghetto. Jeckeln selected a site about southeast of Riga near the Rumbula railway station, and had 300 Russian prisoners of war prepare the site by digging pits in which to bury the victims. Jeckeln organised around 1,700 men, including 300 members of the , 50 German SD men, and 50 Latvian guards, most of whom had already participated in mass-murdering of civilians. These troops were supplemented by Latvians, including members of the Riga city police, battalion police, and ghetto guards. Around 1,500 able-bodied Jews would be spared execution so their slave labour could be exploited; a thousand men were relocated to a fenced-off area within the ghetto and 500 women were temporarily housed in a prison and later moved to a separate nearby ghetto, where they were put to work mending uniforms. Although Rumbula was on the rail line, Jeckeln decided that the victims should travel on foot from Riga to the execution ground. Trucks and buses were arranged to carry children and the elderly. The victims were told that they were being relocated, and were advised to bring up to of possessions. The first day of executions, 30 November 1941, began with the perpetrators rousing and assembling the victims at 4:00 am. The victims were moved in columns of a thousand people toward the execution ground. As they walked, some SS men went up and down the line, shooting people who could not keep up the pace or who tried to run away or rest. When the columns neared the prepared execution site, the victims were driven some from the road into the forest, where any possessions that had not yet been abandoned were seized. Here the victims were split into groups of fifty and taken deeper into the forest, near the pits, where they were ordered to strip. The victims were driven into the prepared trenches, made to lie down, and shot in the head or the back of the neck by members of Jeckeln's bodyguard. Around 13,000 Jews from Riga were murdered at the pits that day, along with a thousand Jews from Berlin who had just arrived by train. On the second day of the operation, 8 December 1941, the remaining 10,000 Jews of Riga were murdered in the same way. About a thousand were murdered on the streets of the city or on the way to the site, bringing the total number of deaths for the two-day extermination to 25,000 people. For his part in organising the massacre, Jeckeln was promoted to Leader of the SS Upper Section,Ostland
The Reichskommissariat Ostland (RKO) was established by Nazi Germany in 1941 during World War II. It became the civilian occupation regime in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and the western part of Byelorussian SSR. German planning documents i ...
.
Second sweep
 B, C, and D did not immediately follow A's example in systematically murdering all Jews in their areas. The commanders, with the exception of A's Stahlecker, were of the opinion by the fall of 1941 that it was impossible to murder the entire Jewish population of the Soviet Union in one sweep, and thought the murders should stop. An report dated 17 September advised that the Germans would be better off using any skilled Jews as labourers rather than shooting them. Also, in some areas poor weather and a lack of transportation led to a slowdown in deportations of Jews from points further west. Thus, an interval passed between the first round of massacres in summer and fall, and what American historian Raul Hilberg called the second sweep, which started in December 1941 and lasted into the summer of 1942. During the interval, the surviving Jews were forced into ghettos.
A had already murdered almost all Jews in its area, so it shifted its operations into Belarus to assist B. In Dnepropetrovsk in February 1942, D reduced the city's Jewish population from 30,000 to 702 over the course of four days. The German Order Police and local collaborators provided the extra manpower needed to perform all the shootings. Haberer wrote that, as in the Baltic states, the Germans could not have murdered so many Jews so quickly without local help. He points out that the ratio of Order Police to auxiliaries was 1 to 10 in both Ukraine and Belarus. In rural areas the proportion was 1 to 20. This meant that most Ukrainian and Belarusian Jews were murdered by fellow Ukrainians and Belarusians commanded by German officers rather than by Germans.
The second wave of exterminations in the Soviet Union met with armed resistance in some areas, though the chance of success was poor. Weapons were typically primitive or home-made. Communications were impossible between ghettos in various cities, so there was no way to create a unified strategy. Few in the ghetto leadership supported resistance for fear of reprisals on the ghetto residents. Mass break-outs were sometimes attempted, though survival in the forest was nearly impossible due to the lack of food and the fact that escapees were often tracked down and murdered.
B, C, and D did not immediately follow A's example in systematically murdering all Jews in their areas. The commanders, with the exception of A's Stahlecker, were of the opinion by the fall of 1941 that it was impossible to murder the entire Jewish population of the Soviet Union in one sweep, and thought the murders should stop. An report dated 17 September advised that the Germans would be better off using any skilled Jews as labourers rather than shooting them. Also, in some areas poor weather and a lack of transportation led to a slowdown in deportations of Jews from points further west. Thus, an interval passed between the first round of massacres in summer and fall, and what American historian Raul Hilberg called the second sweep, which started in December 1941 and lasted into the summer of 1942. During the interval, the surviving Jews were forced into ghettos.
A had already murdered almost all Jews in its area, so it shifted its operations into Belarus to assist B. In Dnepropetrovsk in February 1942, D reduced the city's Jewish population from 30,000 to 702 over the course of four days. The German Order Police and local collaborators provided the extra manpower needed to perform all the shootings. Haberer wrote that, as in the Baltic states, the Germans could not have murdered so many Jews so quickly without local help. He points out that the ratio of Order Police to auxiliaries was 1 to 10 in both Ukraine and Belarus. In rural areas the proportion was 1 to 20. This meant that most Ukrainian and Belarusian Jews were murdered by fellow Ukrainians and Belarusians commanded by German officers rather than by Germans.
The second wave of exterminations in the Soviet Union met with armed resistance in some areas, though the chance of success was poor. Weapons were typically primitive or home-made. Communications were impossible between ghettos in various cities, so there was no way to create a unified strategy. Few in the ghetto leadership supported resistance for fear of reprisals on the ghetto residents. Mass break-outs were sometimes attempted, though survival in the forest was nearly impossible due to the lack of food and the fact that escapees were often tracked down and murdered.
Transition to gassing
 After a time, Himmler found that the killing methods used by the were inefficient: they were costly, demoralising for the troops, and sometimes did not kill the victims quickly enough. Many of the troops found the massacres to be difficult if not impossible to perform. Some of the perpetrators suffered physical and mental health problems, and many turned to drink. As much as possible, the leaders militarized the genocide. The historian Christian Ingrao notes an attempt was made to make the shootings a collective act without individual responsibility. Framing the shootings in this way was not psychologically sufficient for every perpetrator to feel absolved of guilt. Browning notes three categories of potential perpetrators: those who were eager to participate right from the start, those who participated in spite of moral qualms because they were ordered to do so, and a significant minority who refused to take part. A few men spontaneously became excessively brutal in their killing methods and their zeal for the task. Commander of D, SS-
After a time, Himmler found that the killing methods used by the were inefficient: they were costly, demoralising for the troops, and sometimes did not kill the victims quickly enough. Many of the troops found the massacres to be difficult if not impossible to perform. Some of the perpetrators suffered physical and mental health problems, and many turned to drink. As much as possible, the leaders militarized the genocide. The historian Christian Ingrao notes an attempt was made to make the shootings a collective act without individual responsibility. Framing the shootings in this way was not psychologically sufficient for every perpetrator to feel absolved of guilt. Browning notes three categories of potential perpetrators: those who were eager to participate right from the start, those who participated in spite of moral qualms because they were ordered to do so, and a significant minority who refused to take part. A few men spontaneously became excessively brutal in their killing methods and their zeal for the task. Commander of D, SS- Otto Ohlendorf
Otto Ohlendorf (; 4 February 1907 – 7 June 1951) was a German SS functionary and Holocaust perpetrator during the Nazi era. An economist by education, he was head of the (SD) Inland, responsible for intelligence and security within Germ ...
, particularly noted this propensity towards excess, and ordered that any man who was too eager to participate or too brutal should not perform any further executions.
During a visit to Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative stat ...
in August 1941, Himmler witnessed an mass execution first-hand and concluded that shooting Jews was too stressful for his men. By November he made arrangements for any SS men suffering ill health from having participated in executions to be provided with rest and mental health care. He also decided a transition should be made to gassing the victims, especially the women and children, and ordered the recruitment of expendable native auxiliaries who could assist with the murders. Gas vans, which had been used previously to murder mental patients, began to see service by all four main from 1942. However, the gas vans were not popular with the , because removing the dead bodies from the van and burying them was a horrible ordeal. Prisoners or auxiliaries were often assigned to do this task so as to spare the SS men the trauma. Some of the early mass murders at extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
s used carbon monoxide fumes produced by diesel engines, similar to the method used in gas vans, but by as early as September 1941 experiments were begun at Auschwitz using Zyklon B, a cyanide-based pesticide gas.
Plans for the total eradication of the Jewish population of Europe—eleven million people—were formalised at the Wannsee Conference, held on 20 January 1942. Some would be worked to death, and the rest would be murdered in the implementation of the Final Solution of the Jewish question (german: link=no, Die Endlösung der Judenfrage). Permanent killing centres at Auschwitz, Belzec, Chelmno, Majdanek, Sobibor, Treblinka, and other Nazi extermination camps replaced mobile death squads as the primary method of mass-murder. The remained active, however, and were put to work fighting partisans, particularly in Belarus.
After the fall of Stalingrad in February 1943, Himmler realised that Germany would likely lose the war, and ordered the formation of a special task force, '' Sonderaktion 1005'', under SS- Paul Blobel. The unit's assignment was to visit mass graves all along the Eastern Front to exhume bodies and burn them in an attempt to cover up the genocide. The task remained unfinished at the end of the war, and many mass graves remain unmarked and unexcavated.
By 1944 the Red Army had begun to push the German forces out of Eastern Europe, and the retreated alongside the ''Wehrmacht''. By late 1944, most personnel had been folded into Waffen-SS combat units or transferred to permanent death camps. Hilberg estimates that between 1941 and 1945 the and related agencies killed more than two million people, including 1.3 million Jews. The total number of Jews murdered during the war is estimated at 5.5 to six million people.
Plans for the Middle East and Britain
According to research by German historiansKlaus-Michael Mallmann
Klaus-Michael Mallmann (born 3 November 1948, in Kaiserslautern) is a German historian at the University of Stuttgart.
Scientific career
Mallmann studied history, Sociology, Politics and German studies at the Saarland University. In 1979 he was aw ...
and , Einsatzgruppe Egypt
Einsatzgruppe Egypt (German: ) was an SS unit led by SS-Obersturmbannführer Walther Rauff, which was formed in occupied Greece during World War II. Einsatzgruppen ("deployment groups") were paramilitary death squads that operated within Germa ...
, led by Walter Rauff, was raised in 1942 in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
. The unit was to enter Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
and Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
once German forces arrived there. According to Mallmann and Cüppers, the unit's purpose was to carry out mass-murder of the Jewish populations in those areas. Given its small staff of only 24 men, Mallmann and Cüppers theorize the unit would have needed help from local residents and from the to complete their assignment. Former Iraqi prime minister Rashid Ali al-Gaylani and the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem Haj Amin al-Husseini played roles, engaging in antisemitic radio propaganda, preparing to recruit volunteers, and in raising an Arab-German Battalion that would also follow Egypt to the Middle East. On 20 July 1942 Rauff was sent to Tobruk to report to Field Marshal Erwin Rommel, Commander of the . Since Rommel was 500 km away at the First Battle of El Alamein, it is unlikely that the two met. According to historian Haim Saadon, Director of the Center of Research on North African Jewry in World War II, Rauff's documents show that his foremost concern was assisting the ''Wehrmacht'', and his plan for this was to place the Jews in forced labour camps. In relative terms, the North African Jews largely escaped the Final Solution. The plans for Egypt were set aside after the Allied victory at the Second Battle of El Alamein.
Had Operation Sea Lion, the German plan for an invasion of the United Kingdom been launched, six were scheduled to follow the invasion force into Britain. They were provided with a list called the ('Special Search List, G.B'), known as The Black Book after the war, of 2,300 people to be immediately imprisoned by the Gestapo. The list included Churchill, members of the cabinet, prominent journalists and authors, and members of the Czechoslovak government-in-exile.
Jäger Report
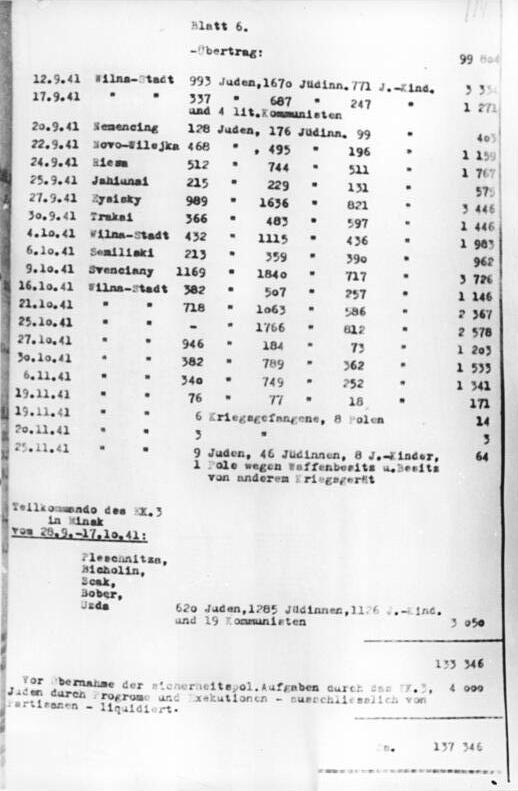
 The kept official records of many of their massacres and provided detailed reports to their superiors. The
The kept official records of many of their massacres and provided detailed reports to their superiors. The Jäger Report
The so-called Jäger Report, also Jaeger Report (full title: ''Complete tabulation of executions carried out in the Einsatzkommando 3 zone up to December 1, 1941'') was written on 1 December 1941 by Karl Jäger, commander of ''Einsatzkommando'' ...
, filed by Commander SS- Karl Jäger
Karl Jäger (; 20 September 1888 – 22 June 1959) was a German mid-ranking official in the '' SS'' of Nazi Germany and ''Einsatzkommando'' leader who perpetrated acts of genocide during the Holocaust.
Early life and career
Jäger was born in Sch ...
on 1 December 1941 to his superior, Stahlecker (head of A), covers the activities of III in Lithuania over the five-month period from 2 July 1941 to 25 November 1941.
Jäger's report provides an almost daily running total of the liquidations of 137,346 people, the vast majority of them Jews. The report documents the exact date and place of massacres, the number of victims, and their breakdown into categories (Jews, Communists, criminals, and so on). Women were shot from the very beginning, but initially in fewer numbers than men. Children were first included in the tally starting in mid-August, when 3,207 people were murdered in Rokiškis
Rokiškis () is a city in northeastern Lithuania with a population of about 14,400.
History
The legend of the founding of Rokiškis tells about a hunter called Rokas who had been hunting for hares ( Lit. "kiškis"). However, cities ending in " ...
on 15–16 August 1941. For the most part the report does not give any military justification for the murderes; people were murdered solely because they were Jews. In total, the report lists over 100 executions in 71 different locations. Jäger wrote: "I can state today that the goal of solving the Jewish problem in Lithuania has been reached by 3. There are no more Jews in Lithuania, apart from working Jews and their families." In a February 1942 addendum to the report, Jäger increased the total number of victims to 138,272, giving a breakdown of 48,252 men, 55,556 women, and 34,464 children. Only 1,851 of the victims were non-Jewish.
Jäger escaped capture by the Allies when the war ended. He lived in Heidelberg under his own name until his report was discovered in March 1959. Arrested and charged, Jäger committed suicide on 22 June 1959 in a Hohenasperg prison while awaiting trial for his crimes.
Involvement of the ''Wehrmacht''
The murders took place with the knowledge and support of the German Army in the east. As ordered by Hitler, the ''Wehrmacht'' cooperated with the , providing logistical support for their operations, and participated in the mass killings. On 10 October 1941 Field Marshal Walther von Reichenau drafted an order to be read to the German Sixth Army on the Eastern Front. Now known as the Severity Order, it read in part: Field Marshal Gerd von Rundstedt of Army Group South expressed his "complete agreement" with the order. He sent out a circular to the generals under his command urging them to release their own versions and to impress upon their troops the need to exterminate the Jews. General Erich von Manstein, in an order to his troops on 20 November, stated that "the Jewish-Bolshevist system must be exterminated once and for all." Manstein sent a letter to D commanding officer Ohlendorf complaining that it was unfair that the SS was keeping all of the murdered Jews' wristwatches for themselves instead of sharing with the Army. Beyond this trivial complaint, the Army and the worked closely and effectively. On 6 July 1941 4b of C reported that "Armed forces surprisingly welcome hostility against the Jews". Few complaints about the murders were ever raised by ''Wehrmacht'' officers. On 8 September, D reported that relations with the German Army were "excellent". In the same month, Stahlecker of A wrote that Army Group North had been exemplary in co-operating with the exterminations and that relations with the 4th Panzer Army, commanded by GeneralErich Hoepner
Erich Kurt Richard Hoepner (14 September 1886 – 8 August 1944) was a German general during World War II. An early proponent of mechanisation and armoured warfare, he was a Wehrmacht army corps commander at the beginning of the war, leading ...
, were "very close, almost cordial". In the south, the Romanian Army worked closely with D to massacre Ukrainian Jews, murdering around 26,000 Jews in the Odessa massacre. The German historian Peter Longerich thinks it probable that the ''Wehrmacht'', along with the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN), incited the Lviv pogroms, during which 8,500 to 9,000 Jews were murdered by the native population and C in July 1941. Moreover, most people on the home front in Germany had some idea of the massacres being committed by the . British historian Hugh Trevor-Roper noted that although Himmler had forbidden photographs of the murders, it was common for both the men of the and for bystanders to take pictures to send to their loved ones, which he felt suggested widespread approval of the massacres.
Officers in the field were well aware of the killing operations being conducted by the . The ''Wehrmacht'' tried to justify their considerable involvement in the massacres as being anti-partisan operations rather than racist attacks, but Hillgruber wrote that this was just an excuse. He states that those German generals who claimed that the were a necessary anti-partisan response were lying, and maintained that the slaughter of about 2.2 million defenceless civilians for reasons of racist ideology cannot be justified.
Einsatzgruppen trial
After the close of World War II, 24 senior leaders of the were prosecuted in the Einsatzgruppen Trial in 1947–48, part of the Subsequent Nuremberg Trials held under United States military authority. The men were charged withcrimes against humanity
Crimes against humanity are widespread or systemic acts committed by or on behalf of a ''de facto'' authority, usually a state, that grossly violate human rights. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity do not have to take place within the ...
, war crimes, and membership in the SS (which had been declared a criminal organization). Fourteen death sentences and two life sentences were among the judgments; only four executions were carried out, on 7 June 1951; the rest were reduced to lesser sentences. Four additional leaders were later tried and executed by other nations.
 Several leaders, including Ohlendorf, claimed at the trial to have received an order before Operation Barbarossa requiring them to murder all Soviet Jews. To date no evidence has been found that such an order was ever issued. German prosecutor Alfred Streim noted that if such an order had been given, post-war courts would only have been able to convict the leaders as ''accomplices'' to mass murder. However, if it could be established that the had committed mass murder without orders, then they could have been convicted as ''perpetrators'' of mass murder, and hence could have received stiffer sentences, including capital punishment.
Streim postulated that the existence of an early comprehensive order was a fabrication created for use in Ohlendorf's defence. This theory is now widely accepted by historians. Longerich notes that most orders received by the leaders—especially when they were being ordered to carry out criminal activities—were vague, and couched in terminology that had a specific meaning for members of the regime. Leaders were given briefings about the need to be "severe" and "firm"; all Jews were to be viewed as potential enemies that had to be dealt with ruthlessly. British historian Sir Ian Kershaw argues that Hitler's apocalyptic remarks before Barbarossa about the necessity for a war without mercy to "annihilate" the forces of "Judeo-Bolshevism" were interpreted by commanders as permission and encouragement to engage in extreme antisemitic violence, with each commander to use his own discretion about how far he was prepared to go.
Most of the perpetrators of Nazi war crimes were never charged, and returned unremarked to civilian life. The West German Central Prosecution Office of Nazi War Criminals only charged about a hundred former members with war crimes. And as time went on, it became more difficult to obtain prosecutions; witnesses grew older and were less likely to be able to offer valuable testimony. Funding for trials was inadequate, and the governments of Austria and Germany became less interested in obtaining convictions for wartime events, preferring to forget the Nazi past.
Several leaders, including Ohlendorf, claimed at the trial to have received an order before Operation Barbarossa requiring them to murder all Soviet Jews. To date no evidence has been found that such an order was ever issued. German prosecutor Alfred Streim noted that if such an order had been given, post-war courts would only have been able to convict the leaders as ''accomplices'' to mass murder. However, if it could be established that the had committed mass murder without orders, then they could have been convicted as ''perpetrators'' of mass murder, and hence could have received stiffer sentences, including capital punishment.
Streim postulated that the existence of an early comprehensive order was a fabrication created for use in Ohlendorf's defence. This theory is now widely accepted by historians. Longerich notes that most orders received by the leaders—especially when they were being ordered to carry out criminal activities—were vague, and couched in terminology that had a specific meaning for members of the regime. Leaders were given briefings about the need to be "severe" and "firm"; all Jews were to be viewed as potential enemies that had to be dealt with ruthlessly. British historian Sir Ian Kershaw argues that Hitler's apocalyptic remarks before Barbarossa about the necessity for a war without mercy to "annihilate" the forces of "Judeo-Bolshevism" were interpreted by commanders as permission and encouragement to engage in extreme antisemitic violence, with each commander to use his own discretion about how far he was prepared to go.
Most of the perpetrators of Nazi war crimes were never charged, and returned unremarked to civilian life. The West German Central Prosecution Office of Nazi War Criminals only charged about a hundred former members with war crimes. And as time went on, it became more difficult to obtain prosecutions; witnesses grew older and were less likely to be able to offer valuable testimony. Funding for trials was inadequate, and the governments of Austria and Germany became less interested in obtaining convictions for wartime events, preferring to forget the Nazi past.
See also
*Functionalism versus intentionalism
Functionalism may refer to:
* Functionalism (architecture), the principle that architects should design a building based on the purpose of that building
* Functionalism in international relations, a theory that arose during the inter-War period
...
* Glossary of Nazi Germany
* List of Nazi Party leaders and officials
* Myth of the clean ''Wehrmacht''
* Porajmos
References
Explanatory notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * *External links
United States Holocaust Memorial Museum article on
The Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team {{Authority control Military units and formations of Germany in World War II The Holocaust in Ukraine The Holocaust in Latvia The Holocaust in Lithuania The Holocaust in Estonia The Holocaust in Russia The Holocaust in Belarus The Holocaust in Poland Holocaust terminology Gestapo Reinhard Heydrich Reich Security Main Office Police of Nazi Germany