Eggshell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An eggshell is the outer covering of a hard-shelled egg and of some forms of eggs with soft outer coats.
An eggshell is the outer covering of a hard-shelled egg and of some forms of eggs with soft outer coats.


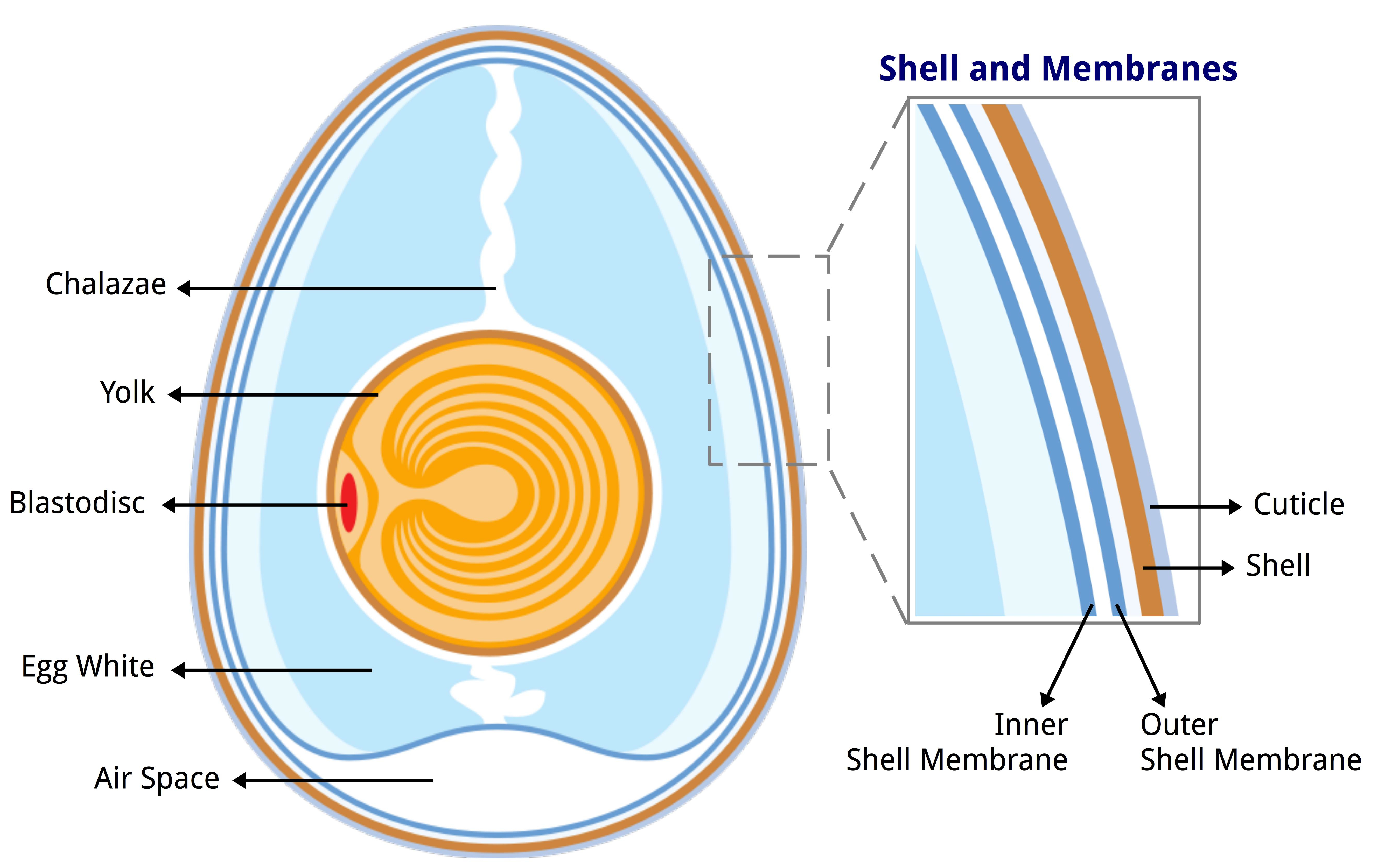 The
The 
 The fibrous chicken shell membranes are added in the proximal (white) isthmus of the oviduct. In the distal (red) isthmus mammillae or mammillary knobs are deposited on the surface of the outer membrane in a regular array pattern. The mammillae are proteoglycan-rich and are thought to control calcification. In the shell gland (similar to a mammalian uterus), mineralization starts at the mammillae. The shell gland fluid contains very high levels of
The fibrous chicken shell membranes are added in the proximal (white) isthmus of the oviduct. In the distal (red) isthmus mammillae or mammillary knobs are deposited on the surface of the outer membrane in a regular array pattern. The mammillae are proteoglycan-rich and are thought to control calcification. In the shell gland (similar to a mammalian uterus), mineralization starts at the mammillae. The shell gland fluid contains very high levels of
Fossil eggshellsFeeding for Stronger Egg Shells
{{Eggs Zoology Animal reproductive system Eggs
 An eggshell is the outer covering of a hard-shelled egg and of some forms of eggs with soft outer coats.
An eggshell is the outer covering of a hard-shelled egg and of some forms of eggs with soft outer coats.
Diversity
Worm eggs
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a bro ...
eggs present a two layered structure: an external vitellin layer made of chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
that confers mechanical resistance and an internal lipid-rich layer that makes the egg chamber impermeable.
Insect eggs

Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pa ...
s and other arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s lay a large variety of styles and shapes of eggs. Some of them have gelatinous or skin-like coverings, others have hard eggshells. Softer shells are mostly protein. It may be fibrous or quite liquid. Some arthropod eggs do not actually have shells, rather, their outer covering is actually the outermost embryonic membrane, the choroid, which serves to protect inner layers. The choroid itself can be a complex structure, and it may have different layers within it. It may have an outermost layer called an ''exochorion''. Eggs which must survive in dry conditions usually have hard eggshells, made mostly of dehydrated or mineralized proteins with pore systems to allow respiration. Arthropod eggs can have extensive ornamentation on their outer surfaces.
Fish, amphibian and reptile eggs
Fish
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as we ...
and amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
s generally lay eggs which are surrounded by the extraembryonic membranes but do not develop a shell, hard or soft, around these membranes. Some fish and amphibian eggs have thick, leathery coats, especially if they must withstand physical force or desiccation. These types of eggs can also be very small and fragile.
While many reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalia ...
s lay eggs with flexible, calcified eggshells, there are some that lay hard eggs. Eggs laid by snakes generally have leathery shells which often adhere to one another. Depending on the species, turtles and tortoises lay hard or soft eggs. Several species lay eggs which are nearly indistinguishable from bird eggs.
Bird eggs

 The
The bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
egg is a fertilized gamete
A gamete (; , ultimately ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. In species that produce ...
(or, in the case of some birds, such as chickens, possibly unfertilized) located on the yolk surface and surrounded by albumen
Egg white is the clear liquid (also called the albumen or the glair/glaire) contained within an egg. In chickens it is formed from the layers of secretions of the anterior section of the hen's oviduct during the passage of the egg. It forms a ...
, or egg white. The albumen in turn is surrounded by two shell membranes (inner and outer membranes) and then the eggshell. The chicken eggshell is 95-97% calcium carbonate crystals, which are stabilized by a protein matrix. Without the protein, the crystal structure would be too brittle to keep its form and the organic matrix is thought to have a role in deposition of calcium during the mineralization process. The structure and composition of the avian eggshell serves to protect the egg against damage and microbial contamination, prevention of desiccation, regulation of gas and water exchange for the growing embryo, and provides calcium for embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
. Eggshell formation requires gram amounts of calcium being deposited within hours, which must be supplied via the hen's diet.

calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
and bicarbonate ion
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemica ...
s. The thick calcified layer of the eggshell forms in columns from the mammillae structures, and is known as the palisade layer. Between these palisade columns are narrow pores that traverse the eggshell and allow gaseous exchange. The cuticle forms the final, outer layer of the eggshell.
While the bulk of eggshell is made of calcium carbonate, it is now thought that the protein matrix has an important role to play in eggshell strength. These proteins affect crystallization, which in turn affects the eggshell structure. Moreover, the concentration of eggshell proteins decreases over the life of the laying hen, as does eggshell strength.
In an average laying hen, the process of shell formation takes around 20 hours. Pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compou ...
ation is added to the shell by papillae lining the oviduct, coloring it any of a variety of colors and patterns depending on species. Since eggs are usually laid blunt end first, that end is subjected to most pressure during its passage and consequently shows the most color.
As they contain mainly calcium carbonate, bird eggshells dissolve in various acids, including the vinegar used in cooking. While dissolving, the calcium carbonate in an eggshell reacts with the acid to form carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
.
Environmental issues
The US food industry generates 150,000 tons of shell waste per year. The disposal methods for waste eggshells are 26.6% as fertilizer, 21.1% as animal feed ingredients, 26.3% discarded in municipal dumps, and 15.8% used in other ways.Daengprok W, Garnjanagoonchorn W, Mine Y: Fermented pork sausage fortified with commercial or hen eggshell calcium lactate. Meat Science 2002, 62:199-204. Many landfills are unwilling to take the waste because the shells and the attached membrane attract vermin. Together with the calcium carbonate eggshell and protein-rich membrane are useless. Recent inventions have allowed for the egg cracking industry to separate the eggshell from the eggshell membrane. The eggshell is mostly made up of calcium carbonate and the membrane is valuable protein. When separated both products have an array of uses.Mammal eggs
Monotremes, egg-laying mammals, lay soft-shelled eggs similar to those of reptiles. The shell is deposited on the egg in layers within the uterus. The egg can take up fluids and grow in size during this process, and the final, most rigid layer is not added until the egg is full-size.Egg teeth
Hatching birds, amphibian and egg-laying reptiles have an egg-tooth used to start an exit hole in the hard eggshell.Use
Eggshell waste is fundamentally composed of calcium carbonate, and has the potential to be used as raw material in the production of lime.Pharmaceuticals
The rich calcium carbonate shell has been used in the application for calcium deficiency therapies in humans and animals.Daengprok W, Issigonis K, Mine Y, Pornsinpatip P, Garnjanagoonchorn W, Naivikul O: Chicken eggshell matrix proteins enhance calcium transport in the human intestinal epithelial cells, Caco-Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2003, 51:6056-6061. A single eggshell has a mass of six grams which yields around 2200 mg of calcium (6000 mg × 0.95 × 0.4= 2280 mg). Eggshell particles are used in toothpaste as an anti-tartar agent. Powdered eggshells have been used for bonemineralization
Mineralization may refer to:
* Mineralization (biology), when an inorganic substance precipitates in an organic matrix
** Biomineralization, a form of mineralization
** Mineralization of bone, an example of mineralization
** Mineralized tissues ar ...
and growth.Wei Z, Li B, Xu C: Application of waste eggshell as low-cost solid catalyst for biodiesel production lectronic resource Bioresource Technology 2009, 100:2883-2885.
Food industry
Recent applications of eggshells include producing calcium lactate as a firming agent, a flavor enhancer, a leavening agent, a nutrient supplement, a stabilizer, and thickener. Eggshells are also used as a calcium supplement in orange juice.Hecht J: Eggshells break into collagen market. New Scientist 1999, 161:6-6.Other uses
Eggshells have been incorporated intofertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s as a soil conditioner.Yoo S, Kokoszka J, Zou P, Hsieh JS: Utilization of calcium carbonate particles from eggshell waste as coating pigments for ink-jet printing paper lectronic resource Bioresource Technology 2009, 100:6416-6421. They have also been used as a supplement to animal feed. More recently the egg calcium carbonate particles have been used as coating pigments for ink-jet printing. Powdered eggshells are also used in making paper pulp. Recently eggshell waste has been used as a low cost catalyst for biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oi ...
production. Chicken eggshells have been additionally incorporated as a calcium precursor into the synthesis of calcium-based metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
Recently, researchers have utilized chicken eggshells as a biofiller with a conducting polymer to enhance its sensing properties. Typically, eggshells were used as biofiller in polyaniline matrix to detect ammonia gas. The optimum ratio between eggshells and polyaniline could enhance this sensor measurement.N A Mazlan, J M Sapari, K P Sambasevam, Synthesis and fabrication of polyaniline/eggshell composite in ammonia detection, Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol 30, No. 2, 50-57 (2020).https://ojs.materialsconnex.com/index.php/jmmm/article/view/649
See also
* Eggshell skull rule, intort
A tort is a civil wrong that causes a claimant to suffer loss or harm, resulting in legal liability for the person who commits the tortious act. Tort law can be contrasted with criminal law, which deals with criminal wrongs that are punishable ...
law
* Walk on eggshells, an idiom in the English language
* Eggshell membrane
Eggshell membrane or shell membrane is the clear film lining eggshells, visible when one peels a boiled bird egg. Chicken eggshell membranes are used as a dietary supplement.
Eggshell membrane is derived commercially from the eggshells of indust ...
, a dietary supplement
References
Further reading
*External links
Fossil eggshells
{{Eggs Zoology Animal reproductive system Eggs