Edward Hobart Seymour on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Edward Hobart Seymour, (30 April 1840 – 2 March 1929) was a

 Seymour turned his trains around and headed back toward Tianjin. But, he found the bridge across the Hai River he had crossed a few days before now destroyed by the Boxers or the Chinese army. The sailors, perhaps more comfortable near water, chose to follow the river – although the railroad route was shorter and ran through open country. Along the heavily populated river banks were Boxer-infested villages every one-half mile. Seymour's retreat down the Hai River was slow and difficult, covering only three miles the first day. Additional casualties included
Seymour turned his trains around and headed back toward Tianjin. But, he found the bridge across the Hai River he had crossed a few days before now destroyed by the Boxers or the Chinese army. The sailors, perhaps more comfortable near water, chose to follow the river – although the railroad route was shorter and ran through open country. Along the heavily populated river banks were Boxer-infested villages every one-half mile. Seymour's retreat down the Hai River was slow and difficult, covering only three miles the first day. Additional casualties included
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
officer. As a junior officer he served in the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
during the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
. He then took part in the sinking of the war-junks, the Battle of Canton and the Battle of Taku Forts during the Second Opium War and then saw action again at the Battle of Cixi during the Taiping Rebellion
The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive rebellion and civil war that was waged in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Han, Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It laste ...
.
Seymour went on to be Second-in-Command of the Channel Squadron and then Admiral Superintendent of Naval Reserves. After that he became Commander-in-Chief, China Station. During the Boxer Rebellion, he led an expedition of 2,000 sailors and marines from Western and Japanese warships to relieve the besieged diplomatic legations in Peking. The expedition was defeated by Chinese and Boxer forces and had to return to Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
. Although the mission had failed, when Seymour arrived back at Portsmouth he and his men were welcomed by thousands of people lining the beach and pier.
Early career
Born the son of the Reverend Richard Seymour and Frances Seymour (née Smith), Seymour was educated atRadley College
Radley College, formally St Peter's College, Radley, is a public school (independent boarding school for boys) near Radley, Oxfordshire, England, which was founded in 1847. The school covers including playing fields, a golf course, a lake, an ...
and Eastman's Royal Naval Academy
Eastman's Royal Naval Academy, originally in Southsea and later at Winchester, both in England, was a preparatory school. Between 1855 and 1923 it was known primarily as a school that prepared boys for entry to the Royal Navy. Thereafter, it was ...
, Southsea
Southsea is a seaside resort and a geographic area of Portsmouth, Portsea Island in England. Southsea is located 1.8 miles (2.8 km) to the south of Portsmouth's inner city-centre. Southsea is not a separate town as all of Portsea Island's s ...
and joined the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
at Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
in 1852. He was appointed to the corvette and, having been promoted to midshipman, then transferred to the paddle frigate in 1853.Heathcote, p. 227 He served in HMS ''Terrible'' in the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
throughout the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
. He was appointed to the second-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer gun ...
, flagship of his uncle Sir Michael Seymour, Commander-in-Chief, China Station
The Commander-in-Chief, China was the admiral in command of what was usually known as the China Station, at once both a British Royal Navy naval formation and its admiral in command. It was created in 1865 and deactivated in 1941.
From 1831 to 18 ...
in 1857 and took part in the sinking of the war-junks in June 1857, the Battle of Canton in December 1857 and the Battle of Taku Forts in May 1858 during the Second Opium War.
Seymour returned to Portsmouth and joined the steam frigate after which he attended the training ship and then the gunnery school . Promoted to sub-lieutenant on 4 May 1859, he returned to China and, during the voyage, was awarded the Royal Humane Society
The Royal Humane Society is a British charity which promotes lifesaving intervention. It was founded in England in 1774 as the ''Society for the Recovery of Persons Apparently Drowned'', for the purpose of rendering first aid in cases of near dro ...
medal for an unsuccessful attempt to save a marine who had fallen overboard. Promoted to lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often ...
on 11 February 1860, he joined the frigate , flagship of the Commander-in-Chief, China Station, and saw action again at the Battle of Taku Forts in August 1860. He became commanding officer of the paddle steamer at Canton and then transferred to the paddle sloop before joining the frigate , the new flagship of the Commander-in-Chief, China Station, and took part in the Battle of Cixi in September 1862 during the Taiping Rebellion
The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive rebellion and civil war that was waged in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Han, Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It laste ...
.
Seymour became flag lieutenant to the Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth
The Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth, was a senior commander of the Royal Navy for hundreds of years. The commanders-in-chief were based at premises in High Street, Portsmouth from the 1790s until the end of Sir Thomas Williams's tenure, his succes ...
in 1863 and then joined the Royal Yacht in 1865. Promoted to commander on 5 March 1866, after a tour in a whaling ship to obtain experience of arctic waters, he joined the Coast Guard
A coast guard or coastguard is a maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with customs and security duties to ...
in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
in 1868 and then became commanding officer of the gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies.
History Pre-ste ...
on the West Coast of Africa Station in June 1869.Heathcote, p. 228 After taking part in operations against African pirates in 1870, he became commanding officer of the despatch vessel in the Channel Squadron
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
in January 1872 and then of the despatch vessel later that year, also in the Channel Squadron.
Promoted to captain on 13 March 1873, Seymour spent a year at the Royal Naval College, Greenwich
The Royal Naval College, Greenwich, was a Royal Navy training establishment between 1873 and 1998, providing courses for naval officers. It was the home of the Royal Navy's staff college, which provided advanced training for officers. The equi ...
and then became commanding officer of the troopship . He went on to be commanding officer of the cruiser in the Mediterranean Fleet in April 1880 and commanding officer of the battleship in the Mediterranean Fleet in November 1882. He briefly commanded the converted liner when Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
n forces seized Afghan
Afghan may refer to:
*Something of or related to Afghanistan, a country in Southern-Central Asia
*Afghans, people or citizens of Afghanistan, typically of any ethnicity
** Afghan (ethnonym), the historic term applied strictly to people of the Pas ...
territory in March 1885 during the Panjdeh Incident
The Panjdeh Incident (known in Russian historiography as the Battle of Kushka) was an armed engagement between the Emirate of Afghanistan and the Russian Empire in 1885 that led to a diplomatic crisis between the British Empire and the Russian ...
. He went on to be flag captain to the Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth in May 1886 and, having been appointed a Companion of the Order of the Bath on 21 June 1887, he became assistant to the Admiral Superintendent of Naval Reserves in December 1887.
Promoted to rear-admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarde ...
on 14 July 1889, Seymour became Second-in-Command of the Channel Squadron, with his flag in the battleship , in April 1894. Promoted to vice-admiral on 9 November 1895, he became Admiral Superintendent of Naval Reserves later that year. He was advanced to Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by George I on 18 May 1725. The name derives from the elaborate medieval ceremony for appointing a knight, which involved bathing (as a symbol of purification) as o ...
on 22 June 1897.
Commander-in-Chief, China Station

Boxer Rebellion
Seymour became Commander-in-Chief,China Station
The Commander-in-Chief, China was the admiral in command of what was usually known as the China Station, at once both a British Royal Navy naval formation and its admiral in command. It was created in 1865 and deactivated in 1941.
From 1831 to 18 ...
, with his flag in the battleship , on 18 February 1898.''Navy List March 1901, corrected to 18 February 1901'', page 217 In early 1900 the Boxers, a rural mass movement, decided to rid China of Western influence and in June 1900 they advanced on Peking
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
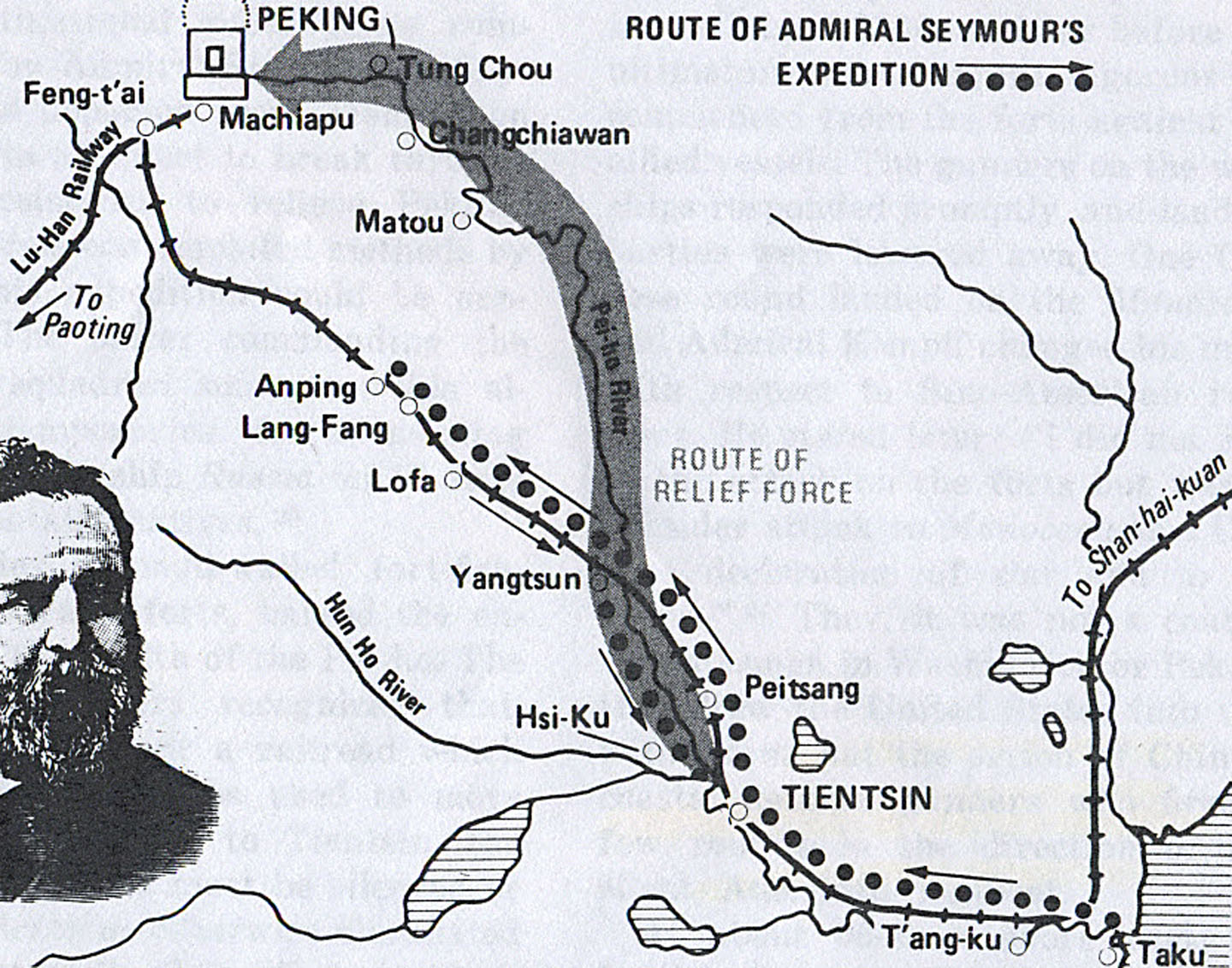
, initiating the Boxer Rebellion. The diplomatic legations in Peking requested military support. On 9 June 1900 Sir Claude MacDonald the British Minister cabled Seymour, reporting that the situation in Beijing "was hourly becoming more serious" and that "troops should be landed and all arrangements made for an advance to Peking at once." In response Seymour assembled a lightly armed force of 2,000 sailors and marines from Western and Japanese warships in Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
. The expedition headed for Beijing by train. Seymour's force consisted of 916 British, 455 Germans, 326 Russians, 158 French, 112 Americans, 54 Japanese, 41 Italians, and 26 Austrians.
On the first day the allied force travelled twenty five miles without incident, crossing a bridge at Yancun over the Hai River
The Hai River (海河, lit. "Sea River"), also known as the Peiho, ("White River"), or Hai Ho, is a Chinese river connecting Beijing to Tianjin and the Bohai Sea.
The Hai River at Tianjin is formed by the confluence of five watercourses: the ...
unopposed although Chinese General Nie Shicheng and thousands of his soldiers were camped there. The next few days went slowly as Seymour had to repair railroad track and fight off Boxer attacks as his trains advanced. On 14 June 1900, several hundred Boxers armed with swords, spears, and clumsy gingals attacked Seymour twice and killed five Italian sailors who had been acting as pickets. The Americans counted 102 Boxer bodies left on the battlefield at the end of one battle.
On 16 June 1900 there was an allied European and Japanese attack on the Dagu Forts. As a result of the attack in Dagu, the Chinese government decided to resist Seymour's expedition and kill or expel all foreigners in northern China. So, on 18 June 1900, Seymour's force was suddenly attacked by several thousand well-armed Chinese Imperial soldiers – who had not opposed Seymour's passage a few days early. The expedition fought off the attack, reportedly killing hundreds of Chinese at a loss of seven dead and 57 wounded. However, the need to care for the wounded, a shortage of supplies and ammunition, and the likelihood of additional Chinese attacks forced Seymour and his officers to decide on a retreat to Tianjin.
Retreat

 Seymour turned his trains around and headed back toward Tianjin. But, he found the bridge across the Hai River he had crossed a few days before now destroyed by the Boxers or the Chinese army. The sailors, perhaps more comfortable near water, chose to follow the river – although the railroad route was shorter and ran through open country. Along the heavily populated river banks were Boxer-infested villages every one-half mile. Seymour's retreat down the Hai River was slow and difficult, covering only three miles the first day. Additional casualties included
Seymour turned his trains around and headed back toward Tianjin. But, he found the bridge across the Hai River he had crossed a few days before now destroyed by the Boxers or the Chinese army. The sailors, perhaps more comfortable near water, chose to follow the river – although the railroad route was shorter and ran through open country. Along the heavily populated river banks were Boxer-infested villages every one-half mile. Seymour's retreat down the Hai River was slow and difficult, covering only three miles the first day. Additional casualties included John Jellicoe
Admiral of the Fleet John Rushworth Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, (5 December 1859 – 20 November 1935) was a Royal Navy officer. He fought in the Anglo-Egyptian War and the Boxer Rebellion and commanded the Grand Fleet at the Battle of Jutlan ...
who suffered a near fatal wound. By 22 June 1900, the allies were out of food and down to less than 10 rounds of ammunition per man – except for the Americans who had brought ample ammunition. But, "there was no thought of surrender," said Lieutenant Wurtzbaugh. "The intention was to fight to the last with the bayonet." On 23 June 1900, six miles from Tianjin, Seymour came across the Xigu fort and arsenal which inexplicably was nearly undefended by Chinese soldiers. The foreign sailors and marines took refuge in the arsenal which contained a wealth of arms and ammunition and some food. Realizing its mistake in leaving the arsenal undefended, the Chinese army attempted to dislodge Seymour, now well-armed, but were unsuccessful.
A Chinese servant of the British slipped through to Tianjin and requested rescue for Seymour. Two thousand allied soldiers marched out of the city to the arsenal on 25 June 1900 and the next day escorted Seymour's men back to Tianjin. The Chinese did not oppose their passage. A missionary reported their arrival in Tianjin. "I shall never forget to my dying day, the long string of dusty travel-worn soldiers, who for a fortnight had been living on quarter rations, and fighting every day…the men were met by kind ladies with pails of tea which the poor fellows drunk as they had never drunk before – some bursting into tears." Seymour's casualties were 62 dead and 232 wounded.
Later career
Promoted to full admiral on 24 May 1901, Seymour arrived back at Portsmouth where he was welcomed by thousands of people lining the beach and pier and honoured by a visit by theLords of the Admiralty
This is a list of Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty (incomplete before the Restoration, 1660).
The Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty were the members of The Board of Admiralty, which exercised the office of Lord High Admiral when it was ...
to his flagship. He had been advanced to Knight Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by George I of Great Britain, George I on 18 May 1725. The name derives from the elaborate medieval ceremony for appointing a knight, which involved Bathing#Medieval ...
(GCB) on 9 November 1900; in late September 1901 he was received in a personal audience by King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria and ...
, who presented him with the insignia of the order. He was also awarded the Prussian Order of the Red Eagle
The Order of the Red Eagle (german: Roter Adlerorden) was an order of chivalry of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was awarded to both military personnel and civilians, to recognize valor in combat, excellence in military leadership, long and faithful se ...
, First class, with the crossed swords in April 1902.
In May 1902, he was part of a delegation led by the Duke of Connaught
Duke of Connaught and Strathearn was a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom that was granted on 24 May 1874 by Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland to her third son, Prince Arthur. At the same time, he was also ...
to take part in the enthronement ceremonies in Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a Madrid metropolitan area, metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the Largest cities of the Europ ...
for the young King Alfonso XIII of Spain
Alfonso XIII (17 May 1886 – 28 February 1941), also known as El Africano or the African, was King of Spain from 17 May 1886 to 14 April 1931, when the Second Spanish Republic was proclaimed. He was a monarch from birth as his father, Alfo ...
, and he was awarded the Spanish Crosses of Naval Merit
The Cross of Naval Merit ( es, Cruces del Mérito Naval) is a Spanish military award for gallantry or merit in war or peace. Awarded to members of the Spanish Naval Forces, Guardia Civil or civilians.
History and Attribution
Established on ...
.
Seymour was among the original recipients of the Order of Merit (OM) in the 1902 Coronation Honours
The 1902 Coronation Honours were announced on 26 June 1902, the date originally set for the coronation of King Edward VII. The coronation was postponed because the King had been taken ill two days before, but he ordered that the honours list shou ...
list published on 26 June 1902, and received the order from King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria and ...
at Buckingham Palace on 8 August 1902. He was also appointed First and Principal Naval Aide-de-Camp
Below is a list of First and Principal Naval Aides-de-Camp, an office established by William IV of the United Kingdom in 1830:
First and Principal Naval Aides-de-Camp
*1830-1846: Lord Amelius Beauclerk
*1846-1866: Sir William Parker, Bt.
*18 ...
to the King on 3 October 1902.
Promoted to Admiral of the Fleet on 20 February 1905 and appointed a Knight Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order
The Royal Victorian Order (french: Ordre royal de Victoria) is a dynastic order of knighthood established in 1896 by Queen Victoria. It recognises distinguished personal service to the British monarch, Canadian monarch, Australian monarch, or ...
on 15 May 1906, Seymour became commander of a squadron, with his flag in the battlecruiser , sent to attend celebrations in Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
in 1909.Heathcote, p. 229 In November 1909 he was sworn in the Privy Council. He retired from the Navy in April 1910 and died at his home in Maidenhead on 2 March 1929.
Family
Seymour neither married nor had any children.References
Sources
* * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
* * , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Seymour, Edward Hobart Royal Navy admirals of the fleet Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Bath Knights Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order Members of the Order of Merit Royal Navy personnel of the Crimean War Royal Navy personnel of the Second Opium WarEdward Hobart Seymour
Admiral of the Fleet Sir Edward Hobart Seymour, (30 April 1840 – 2 March 1929) was a Royal Navy officer. As a junior officer he served in the Black Sea during the Crimean War. He then took part in the sinking of the war-junks, the Battle of ...
1840 births
1929 deaths
People educated at Radley College
Royal Navy personnel of the Boxer Rebellion
People educated at Eastman's Royal Naval Academy
Members of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom
British Weihaiwei people
British military personnel of the Taiping Rebellion
People from Stratford-on-Avon District