East Timor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an
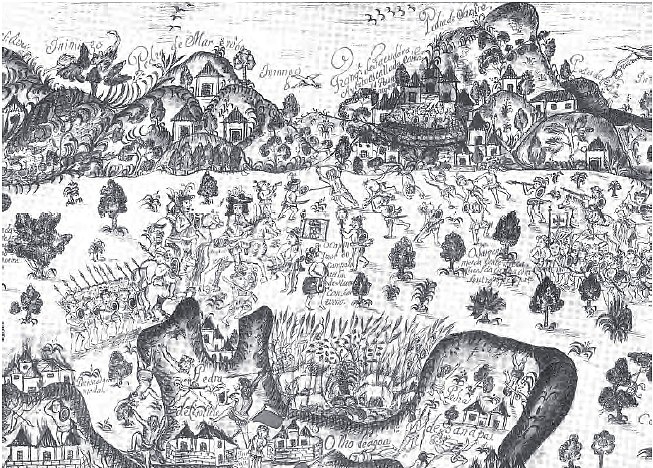 Early Portuguese presence on Timor was very limited; trade was directed through Portuguese settlements on other islands. Only in the 17th century did they establish a more direct presence on the island, a consequence of being driven out of other islands by the Dutch. After Solor was lost in 1613 the Portuguese moved to Flores. In 1646 the capital moved to
Early Portuguese presence on Timor was very limited; trade was directed through Portuguese settlements on other islands. Only in the 17th century did they establish a more direct presence on the island, a consequence of being driven out of other islands by the Dutch. After Solor was lost in 1613 the Portuguese moved to Flores. In 1646 the capital moved to
 Indonesian occupation of Timor was marked by violence and brutality. A detailed statistical report prepared for the Commission for Reception, Truth and Reconciliation in East Timor cited a minimum of 102,800 conflict-related deaths in the period between 1974 and 1999, including approximately 18,600 killings and 84,200 excess deaths from hunger and illness. Portuguese, Indonesian and Catholic Church data estimated 200,000 deaths. Repression and restrictions counteracted improvements in infrastructure and services, meaning there was little overall improvement in living standards; economic growth mostly benefited immigrants from elsewhere in Indonesia. A huge expansion of education was intended to increase Indonesian language use and internal security as much as it was for development.
Indonesian occupation of Timor was marked by violence and brutality. A detailed statistical report prepared for the Commission for Reception, Truth and Reconciliation in East Timor cited a minimum of 102,800 conflict-related deaths in the period between 1974 and 1999, including approximately 18,600 killings and 84,200 excess deaths from hunger and illness. Portuguese, Indonesian and Catholic Church data estimated 200,000 deaths. Repression and restrictions counteracted improvements in infrastructure and services, meaning there was little overall improvement in living standards; economic growth mostly benefited immigrants from elsewhere in Indonesia. A huge expansion of education was intended to increase Indonesian language use and internal security as much as it was for development.
 On 30 August 2001, the East Timorese voted in their first election organised by the UN to elect members of the Constituent Assembly. On 22 March 2002, the Constituent Assembly approved the Constitution. By May 2002, more than 205,000 refugees had returned. On 20 May 2002, the Constitution of the Democratic Republic of East Timor came into force and East Timor was recognised as independent by the UN. The Constituent Assembly was renamed the National Parliament, and
On 30 August 2001, the East Timorese voted in their first election organised by the UN to elect members of the Constituent Assembly. On 22 March 2002, the Constituent Assembly approved the Constitution. By May 2002, more than 205,000 refugees had returned. On 20 May 2002, the Constitution of the Democratic Republic of East Timor came into force and East Timor was recognised as independent by the UN. The Constituent Assembly was renamed the National Parliament, and
 The political system of East Timor is
The political system of East Timor is  Representatives in the unicameral
Representatives in the unicameral
island country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainlan ...
. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse
Oecusse (also variously ''Oecussi'', ''Ocussi'', ''Oekussi'', ''Oekusi'', ''Okusi'', ''Oé-Cusse''), also known as Oecusse-Ambeno (; ) and formerly just Ambeno, officially the Special Administrative Region Oecusse-Ambeno (), is an exclave, mun ...
on the island's north-western half, and the minor islands of Atauro
Atauro ( pt, Ilha de Ataúro, Tetum and Indonesian: ''Pulau Atauro'' or ''Ata'uro''), also known as Kambing Island ( id, Pulau Kambing), is an island and municipality ( pt, Município Ataúro, links=no, tet, Munisípiu Atauro, links=no or ...
and Jaco. Australia is the country's southern neighbour, separated by the Timor Sea
The Timor Sea ( id, Laut Timor, pt, Mar de Timor, tet, Tasi Mane or ) is a relatively shallow sea bounded to the north by the island of Timor, to the east by the Arafura Sea, and to the south by Australia.
The sea contains a number of reefs ...
. The country's size is . Dili is its capital and largest city.
East Timor came under Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
influence in the sixteenth century, remaining a Portuguese colony until 1975. Internal conflict preceded a unilateral declaration of independence and an Indonesian invasion and annexation. Resistance continued throughout Indonesian rule, and in 1999 a United Nations–sponsored act of self-determination led to Indonesia relinquishing control of the territory. On 20 May 2002, as ''Timor-Leste'', it became the first new sovereign state of the 21st century.
The national government runs on a semi-presidential system, with the popularly elected president sharing power with a prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
appointed by the National Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
. Power is centralised under the national government, although many local leaders have informal influence. The country maintains a policy of international cooperation, and is a member of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries
The Community of Portuguese Language Countries ( Portuguese: ''Comunidade dos Países de Língua Portuguesa''; abbreviated as the CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth (''Comunidade Lusófona''), is an international organization and pol ...
, an observer of the Pacific Islands Forum, and an applicant for ASEAN membership. The country remains relatively poor, with an economy that relies heavily on natural resources, especially oil, and foreign aid.
The total population is over 1.1 million, and is heavily skewed towards young people due to a high fertility rate. Education has led to the increasing literacy over the past half-century, especially in the two national languages of Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and Tetum
, nativename=Tetun
, states= Indonesia East Timor
, speakers=, mostly in Indonesia
, date=2010–2011
, ref=e18
, speakers2=50,000 L2-speakers in Indonesia and East Timor
, familycolor=Austronesian
, fam2=Malayo-Polynesian
, fam3= Central–East ...
. High ethnic and linguistic diversity is reflected by the 30 local dialects spoken in the country. The majority of the population is Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, which exists alongside strong local traditions, especially in rural areas.
Etymology
"Timor" is derived from ''timur'', meaning 'east' in Malay, thus resulting in a tautological place name meaning 'East East'. In Indonesian, this results in the name ''Timor Timur''. In Portuguese, the country is called ''Timor-Leste'' (''Leste'' meaning 'east'; ). In Tetum it is ''Timór Lorosa'e'' (''Lorosa'e'' can be literally translated as 'where the sun rises'). The official names under the Constitution are Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste in English, in Portuguese, and in Tetum. The official short form of the name is ''Timor-Leste'', and it uses the ISO codes TLS & TL.History
Prehistory and Classical era
Cultural remains atJerimalai
Jerimalai is a limestone cave southeast of Tutuala, on the eastern tip of East Timor. Fish remains and fish hooks excavated in Jerimalai provide evidence for advanced fishing technique by inhabitants of Timor 42,000 years ago.
Jerimalai has the ...
on the eastern tip of East Timor have been dated to 42,000 years ago. Descendants of at least three waves of migration are believed still to live in East Timor. The first is described by anthropologists as people of the Veddo-Australoid
Australo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, groups from Southeast Asia an ...
type. Around 3000 BC, a second migration brought Melanesians. Finally, proto-Malays arrived from south China and north Indochina. Timorese origin myths recount settlers sailing around the eastern end of the island before landing in the south. These people are sometimes noted as being from the Malay Peninsula or the Minangkabau Minangkabau may refer to:
* Minangkabau culture, culture of the Minangkabau people
* Minangkabau Culture Documentation and Information Center
* Minangkabau Express, an airport rail link service serving Minangkabau International Airport (''see belo ...
highlands of Sumatra. Austronesian migration to Timor may be associated with the development of agriculture on the island.
While information is limited about the political system of Timor during this period, the island had developed an interconnected series of polities governed by customary law. Small communities, centred around a particular sacred house, were part of wider ''sucos'' (or principalities), which were themselves part of larger kingdoms led by a ''liurai''. Rule of these kingdoms was dyadic, with the temporal power of the ''liurai'' balanced by the spiritual power of a ''rai nain'', who was generally associated with the primary sacred house of the kingdom. These polities were numerous and saw shifting alliances and relations, but many were stable enough that they survived from initial European documentation in the 16th century until the end of Portuguese rule.
From perhaps the thirteenth century, the island exported sandalwood. Timor was included in Southeast Asian, Chinese, and Indian trading networks by the fourteenth century, exporting sandalwood, honey, and wax. The island was recorded by the Majapahit Empire as a source of tribute. It was sandalwood that attracted European explorers to the island in the early sixteenth century. Early European presence was limited to trade, with the first Portuguese settlement being on the nearby island of Solor.
Portuguese era (1769–1975)
 Early Portuguese presence on Timor was very limited; trade was directed through Portuguese settlements on other islands. Only in the 17th century did they establish a more direct presence on the island, a consequence of being driven out of other islands by the Dutch. After Solor was lost in 1613 the Portuguese moved to Flores. In 1646 the capital moved to
Early Portuguese presence on Timor was very limited; trade was directed through Portuguese settlements on other islands. Only in the 17th century did they establish a more direct presence on the island, a consequence of being driven out of other islands by the Dutch. After Solor was lost in 1613 the Portuguese moved to Flores. In 1646 the capital moved to Kupang
Kupang ( id, Kota Kupang, ), formerly known as Koepang, is the capital of the Indonesian province of East Nusa Tenggara. At the 2020 C ensus, it had a population of 442,758; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 455,850. It is the largest ci ...
on Timor's west, before that was lost to the Dutch in 1652. The Portuguese then moved to Lifau
Lifau is a village and suco in the East Timor exclave of Oecusse District. The village is located west of the mouth of the Tono River. 1,938 people live in the suco.
History
Lifau was the first European settlement on the island of Timor. Do ...
, in what is now East Timor's Oecusse
Oecusse (also variously ''Oecussi'', ''Ocussi'', ''Oekussi'', ''Oekusi'', ''Okusi'', ''Oé-Cusse''), also known as Oecusse-Ambeno (; ) and formerly just Ambeno, officially the Special Administrative Region Oecusse-Ambeno (), is an exclave, mun ...
exclave. Effective European occupation in the east of the island only began in 1769, when the city of Dili was founded. A definitive border between the Dutch and Portuguese parts of the island was established by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in 1914 and remains the international boundary between the successor states Indonesia and East Timor, respectively.
For the Portuguese, East Timor remained little more than a neglected trading post, with minimal investment in infrastructure and education, until the late nineteenth century. Even when Portugal established actual control over the interior of its colony, investment remained minimal. Sandalwood continued to be the main export crop and coffee exports became significant in the mid-nineteenth century.
At the beginning of the twentieth century, a faltering domestic economy prompted the Portuguese to extract greater wealth from its colonies, which was met with East Timorese resistance. The colony was seen as an economic burden during the Great Depression and received little support or management from Portugal.
During World War II, Dili was occupied by the Allies, and later by the Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
. The mountainous interior of the colony became the scene of a guerrilla campaign, known as the Battle of Timor. Waged by East Timorese volunteers and Allied forces against the Japanese, the struggle killed between 40,000 and 70,000 East Timorese civilians. The Japanese eventually drove the last of the Australian and Allied forces out. Portuguese control resumed, however, after Japanese surrender at the end of World War II.
Portugal began investment in the colony in the 1950s, funding education and promoting coffee exports, but the economy did not improve substantially and infrastructure improvements were limited. Growth rates remained low, near 2%. Following the 1974 Portuguese revolution, Portugal effectively abandoned its colony in Timor, and civil war between East Timorese political parties broke out in 1975.
The Revolutionary Front for an Independent East Timor (Fretilin) resisted a Timorese Democratic Union
The Timorese Democratic Union ( pt, União Democrática Timorense, UDT) is a conservative political party in East Timor. It was the first party to be established in the country on May 11, 1974, following the Carnation Revolution in Portugal.
...
(UDT) coup attempt in August 1975, and unilaterally declared independence on 28 November 1975. Fearing a communist state within the Indonesian archipelago, the Indonesian military launched an invasion of East Timor in December 1975. Indonesia declared East Timor its 27th province on 17 July 1976. The United Nations Security Council opposed the invasion, and the territory's nominal status in the UN remained as "non-self-governing territory under Portuguese administration".
Indonesian occupation (1975–1999)
 Indonesian occupation of Timor was marked by violence and brutality. A detailed statistical report prepared for the Commission for Reception, Truth and Reconciliation in East Timor cited a minimum of 102,800 conflict-related deaths in the period between 1974 and 1999, including approximately 18,600 killings and 84,200 excess deaths from hunger and illness. Portuguese, Indonesian and Catholic Church data estimated 200,000 deaths. Repression and restrictions counteracted improvements in infrastructure and services, meaning there was little overall improvement in living standards; economic growth mostly benefited immigrants from elsewhere in Indonesia. A huge expansion of education was intended to increase Indonesian language use and internal security as much as it was for development.
Indonesian occupation of Timor was marked by violence and brutality. A detailed statistical report prepared for the Commission for Reception, Truth and Reconciliation in East Timor cited a minimum of 102,800 conflict-related deaths in the period between 1974 and 1999, including approximately 18,600 killings and 84,200 excess deaths from hunger and illness. Portuguese, Indonesian and Catholic Church data estimated 200,000 deaths. Repression and restrictions counteracted improvements in infrastructure and services, meaning there was little overall improvement in living standards; economic growth mostly benefited immigrants from elsewhere in Indonesia. A huge expansion of education was intended to increase Indonesian language use and internal security as much as it was for development. Fretilin
The Revolutionary Front for an Independent East Timor ( pt, Frente Revolucionária de Timor-Leste Independente, abbreviated as Fretilin) is a centre-left political party in East Timor. They presently hold 23 of 65 seats in the National Parliam ...
resisted the invasion, initially as an army, holding territory until November 1978, and then as a guerrilla resistance.
The 1991 Dili Massacre was a turning point for the independence cause and brought increased international pressure on Indonesia. Following the resignation of Indonesian President Suharto, the new President BJ Habibie, prompted by a letter from Australian Prime Minister John Howard, decided to hold a referendum on independence. A UN-sponsored agreement between Indonesia and Portugal allowed for a UN-supervised popular referendum in August 1999. A clear vote for independence was met with a punitive campaign of violence by East Timorese pro-integration militias supported by elements of the Indonesian military. In response, the Indonesian government allowed a multinational peacekeeping force, INTERFET
The International Force East Timor (INTERFET) was a multinational non-United Nations peacemaking task force, organised and led by Australia in accordance with United Nations resolutions to address the humanitarian and security crisis that took ...
, to restore order and aid East Timorese refugees and internally displaced persons. On 25 October 1999, the administration of East Timor was taken over by the UN through the United Nations Transitional Administration in East Timor (UNTAET). INTERFET deployment ended in February 2000 with the transfer of military command to the UN.
Contemporary era
Xanana Gusmão
José Alexandre "Xanana" Gusmão (; born 20 June 1946) is an East Timorese politician. A former rebel, he was the third President of the independent East Timor, serving from 2002 to 2007. He then became its fourth prime minister, serving from ...
was elected as the country's first president. On 27 September 2002 the country became a UN member state.
In 2006, a crisis of unrest and factional fighting forced 155,000 people to flee their homes; the United Nations sent in security forces to restore order. The following year, Gusmão declined to run for another term. While there were minor incidents in the build-up to the mid-year presidential elections, the process was peaceful overall and José Ramos-Horta was elected president. In June 2007, Gusmão ran in the parliamentary elections and became prime minister. In February 2008, Ramos-Horta was critically injured in an attempted assassination; Prime Minister Gusmão also faced gunfire separately but escaped unharmed. Australian reinforcements were immediately sent to help keep order. In March 2011, the UN handed over operational control of the police force to the East Timor authorities. The United Nations ended its peacekeeping mission on 31 December 2012.
Francisco Guterres
Francisco Guterres, popularly known as Lú-Olo (born 7 September 1954), is an East Timorese politician who served as president of East Timor from 20 May 2017 to 20 May 2022. He is also the president of the political party Fretilin, and he was ...
of the centre-left Fretilin party became president in May 2017. The main party of the AMP coalition, the National Congress for Timorese Reconstruction, led by Gusmão, was in power from 2007 to 2017, but the leader of Fretilin, Mari Alkatiri, formed a coalition government after the July 2017 parliamentary election. The new minority government soon fell, leading to a second general election in May 2018. In June 2018, former president and independence fighter, Jose Maria de Vasconcelos, known as Taur Matan Ruak, of the three-party coalition, Alliance of Change for Progress (AMP), became the new prime minister. José Ramos-Horta of the centre-left CNRT has served as the president of East Timor since 20 May 2022 after winning the April 2022 presidential election runoff against the incumbent president, Francisco Guterres.
Politics and government
 The political system of East Timor is
The political system of East Timor is semi-presidential
A semi-presidential republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has a ...
, based upon the Portuguese system. The constitution establishes both this separation of executive powers between the president and the prime minister; and the separation of powers between the executive, legislature, and judiciary. Individuals are not allowed to participate in both the legislature and the executive branch. While the legislature is intended to provide a check on the executive, in practice the executive has maintained control of the legislature, under all political parties. The executive, through the council of ministers, also holds some formal legislative powers. The judiciary operates independently, although there are instances of executive interference. Geographical access to courts remains a challenge and has prompted the development of mobile courts. Despite political rhetoric, the constitution and democratic institutions are almost universally respected. Elections are run by an independent body, and turnout is high. The political system has wide public acceptance.
Formally, the directly elected president holds relatively limited powers compared to those in similar systems, with no power over the appointment and dismissal of the prime minister and the council of ministers. Being directly elected, however, past presidents have wielded great informal power and influence. The prime minister is chosen by the parliament. If the president vetoes a legislative action, the parliament can overturn the veto with a two-thirds majority.
The head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
of East Timor is the president of the republic, who is elected by popular vote for a five-year term. Although the president's executive powers are somewhat limited, they do have the power to veto government legislation, initiate referendums, and to dissolve parliament in the event that it is unable to form a government or pass a budget. Following elections, the president usually appoints the leader of the majority party or coalition as prime minister of East Timor and the cabinet on the proposal of the latter. As head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
, the prime minister presides over the cabinet. The president is limited to two terms.
 Representatives in the unicameral
Representatives in the unicameral National Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
are elected by popular vote to a five-year term. The number of seats can vary from a minimum of fifty-two to a maximum of sixty-five. Parties must achieve 3% of the vote to enter parliament, with seats for qualifying parties allocated using the D'Hondt method. Elections occur within the framework of a competitive multi-party system. Upon independence, power was held by the Fretilin
The Revolutionary Front for an Independent East Timor ( pt, Frente Revolucionária de Timor-Leste Independente, abbreviated as Fretilin) is a centre-left political party in East Timor. They presently hold 23 of 65 seats in the National Parliam ...
political party, which was formed shortly before the Indonesian invasion and led its resistance. Given its history, Fretilin viewed itself as the natural party of government and supported a multi-party system, expecting the development of a dominant-party system. Support from the United Nations and the international community, both before and after independence, allowed the nascent political system to survive shocks such as the 2006 crisis.
Candidates in parliamentary elections run in a single national district in a party-list system. One in three of all candidates presented by political parties must be women. This system promotes a diversity of political parties, but gives voters little influence over the individual candidates selected by each party. Political parties or political coalitions must receive at least 4% of the total votes to enter parliament. Women hold more than a third of parliamentary seats, with parties required by law to run female candidates, but they are less prominent at other levels and within party leadership.
Political divisions exist along class lines and along geographical lines. There is broadly a divide between eastern and western areas of the country, stemming from differences that arose under Indonesian rule. Fretilin in particular is strongly linked to the Eastern areas. Political parties are more closely associated with prominent personalities more than with ideology. The National Congress for Timorese Reconstruction became the main opposition to Fretilin, following its establishment to allow Xanana Gusmão
José Alexandre "Xanana" Gusmão (; born 20 June 1946) is an East Timorese politician. A former rebel, he was the third President of the independent East Timor, serving from 2002 to 2007. He then became its fourth prime minister, serving from ...
to run for Prime Minister in the 2007 parliamentary elections. While both major parties have been relatively stable, they remain led by an "old guard" of individuals who came to prominence during the resistance against Indonesia.
Politics and administration is centred in the capital Dili, with the national government responsible for most civil services. Oecusse
Oecusse (also variously ''Oecussi'', ''Ocussi'', ''Oekussi'', ''Oekusi'', ''Okusi'', ''Oé-Cusse''), also known as Oecusse-Ambeno (; ) and formerly just Ambeno, officially the Special Administrative Region Oecusse-Ambeno (), is an exclave, mun ...
, separated from the rest of the country by Indonesian territory, is a special administrative region with some autonomy. The National Police of East Timor and Timor Leste Defence Force have held a monopoly on violence
In political philosophy, a monopoly on violence or monopoly on the legal use of force is the property of a polity that is the only entity in its jurisdiction to legitimately use force, and thus the supreme authority of that area.
While the mon ...
since 2008 and very few guns are present outside of these organisations. While there are allegations of abuse of power, there is some judicial oversight of police and public trust in the institution has grown. An active civil society
Civil society can be understood as the "third sector" of society, distinct from government and business, and including the family and the private sphere. Civil society organisations are concentrated in the capital, including student groups. Due to the structure of the economy, there are no powerful trade unions. The Catholic Church has strong influence in the country.
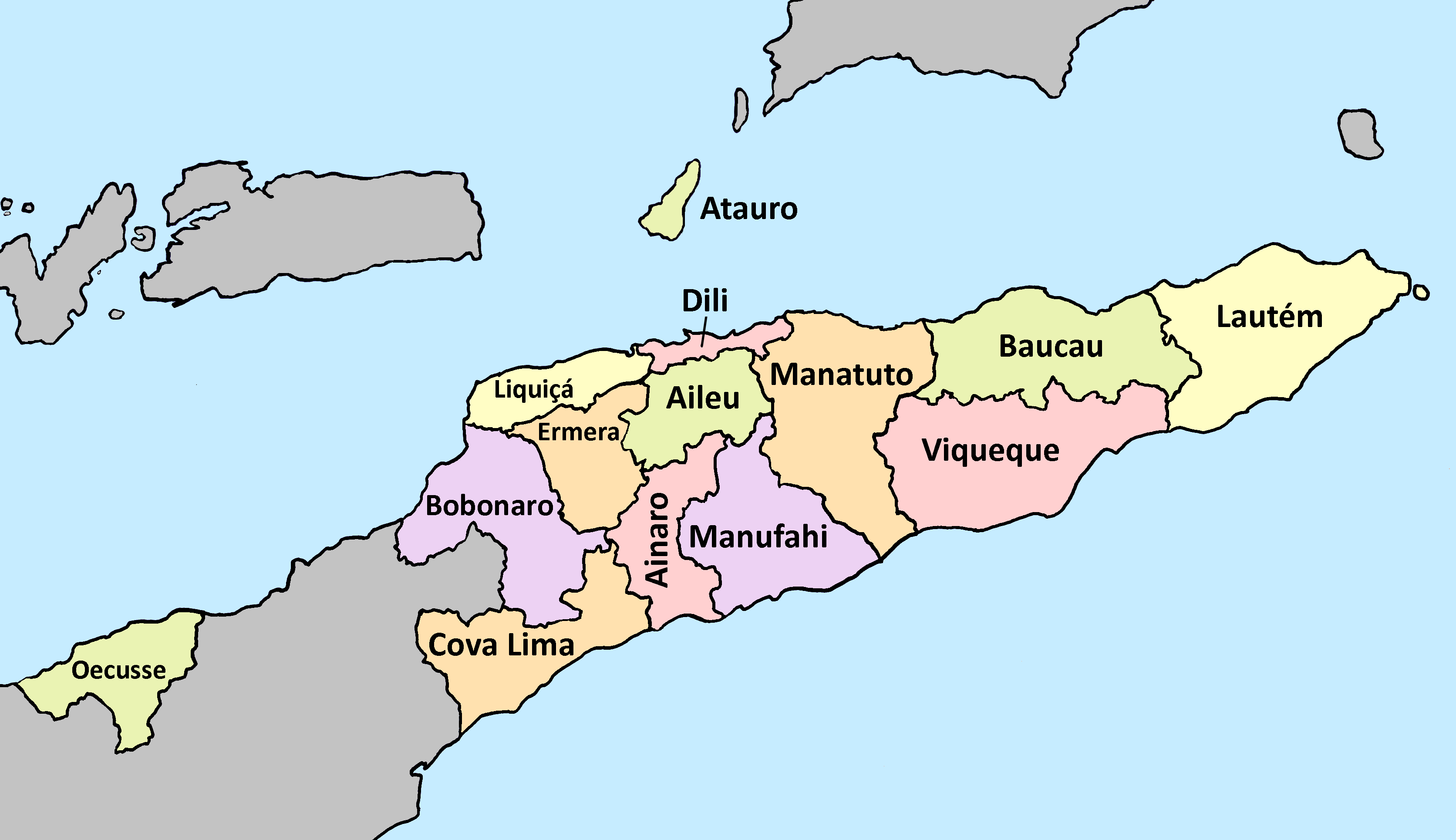 East Timor is divided into fourteen municipalities, which in turn are subdivided into 64 administrative posts, 442 ''sucos'' (villages), and 2,225 ''aldeias'' (hamlets). The municipalities are: Aileu, Ainaro,
East Timor is divided into fourteen municipalities, which in turn are subdivided into 64 administrative posts, 442 ''sucos'' (villages), and 2,225 ''aldeias'' (hamlets). The municipalities are: Aileu, Ainaro,
 International cooperation has always been important to East Timor, with donor funds making up 80% of the budget before oil revenues began to replace them. International forces also provided security, with five UN missions being sent to the country from 1999. The final one, the United Nations Integrated Mission in East Timor, began after the 2006 East Timorese crisis and concluded in 2012.
East Timor is a long-standing applicant to join ASEAN, having formally applied in 2011, and being granted observer status and accepted "in-principle" in November 2022. Despite a closer cultural affinity to Pacific nations, the country has targeted ASEAN membership since before its independence for both economic and security purposes, something which was seen as mutually exclusive with membership in Pacific bodies. ASEAN membership was sought to improve the relationship with Indonesia, although it has stalled due to a lack of support from some ASEAN states. East Timor is thus an observer to the Pacific Islands Forum and the Melanesian Spearhead Group. More broadly, the country is a leader within the Group of Seven Plus (g7+), an organisation of
International cooperation has always been important to East Timor, with donor funds making up 80% of the budget before oil revenues began to replace them. International forces also provided security, with five UN missions being sent to the country from 1999. The final one, the United Nations Integrated Mission in East Timor, began after the 2006 East Timorese crisis and concluded in 2012.
East Timor is a long-standing applicant to join ASEAN, having formally applied in 2011, and being granted observer status and accepted "in-principle" in November 2022. Despite a closer cultural affinity to Pacific nations, the country has targeted ASEAN membership since before its independence for both economic and security purposes, something which was seen as mutually exclusive with membership in Pacific bodies. ASEAN membership was sought to improve the relationship with Indonesia, although it has stalled due to a lack of support from some ASEAN states. East Timor is thus an observer to the Pacific Islands Forum and the Melanesian Spearhead Group. More broadly, the country is a leader within the Group of Seven Plus (g7+), an organisation of
 Located in between Southeast Asia and the South Pacific, the island of Timor is the largest of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which lie within the Malay archipelago. The island is surrounded by the Ombai and
Located in between Southeast Asia and the South Pacific, the island of Timor is the largest of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which lie within the Malay archipelago. The island is surrounded by the Ombai and  The climate is tropical with relatively stable temperatures throughout the year. A wet season lasts from December to May throughout the country, and lasts slightly longer in the south and the interior due to the effect of a monsoon from Australia. During this period, rainfall can reach per month. In the dry season, it drops to . The country is vulnerable to flooding and landslides that occur as a result of heavy rain, especially when rainfall levels are increased by the La Niña effect. The mountainous interior is cooler than the coasts. Coastal areas are heavily dependent on groundwater, which faces pressure from mismanagement, deforestation, and climate change. While the temperature is thought to have experienced a small increase due to climate change, there has been little change in rainfall patterns.
Coastal ecosystems around the country are diverse and varied, with vary spatially between the north and south coastlines, as well as between the eastern tip and areas more to the west. These ecosystems include coral reefs, as the country's waters are part of the
The climate is tropical with relatively stable temperatures throughout the year. A wet season lasts from December to May throughout the country, and lasts slightly longer in the south and the interior due to the effect of a monsoon from Australia. During this period, rainfall can reach per month. In the dry season, it drops to . The country is vulnerable to flooding and landslides that occur as a result of heavy rain, especially when rainfall levels are increased by the La Niña effect. The mountainous interior is cooler than the coasts. Coastal areas are heavily dependent on groundwater, which faces pressure from mismanagement, deforestation, and climate change. While the temperature is thought to have experienced a small increase due to climate change, there has been little change in rainfall patterns.
Coastal ecosystems around the country are diverse and varied, with vary spatially between the north and south coastlines, as well as between the eastern tip and areas more to the west. These ecosystems include coral reefs, as the country's waters are part of the
 The economy of East Timor is a market economy, which used to depend upon exports of a few commodities such as
The economy of East Timor is a market economy, which used to depend upon exports of a few commodities such as  This poverty belies significant wealth in terms of natural resources, which at the time of independence had per capita value equivalent to the wealth of an upper-middle income country. Over half of this was in oil, and over a quarter natural gas. The Timor-Leste Petroleum Fund was established in 2005 to turn these non-renewable resources into a more sustainable form of wealth. From 2005 to 2021, $23 billion earned from oil sales has entered the fund. $8 billion has been generated from investments, while $12 billion has been spent. A decrease in oil and gas reserves led to decreasing HDI beginning in 2010. 80% of government spending comes from this fund, which as of 2021 had $19 billion, 10 times greater than the size of the national budget. As oil income has decreased, the fund is at risk of being exhausted. Withdrawals have exceeded sustainable levels almost every year since 2009. Resources within the Bayu-Undan field are expected to soon run out, while extracting those within the so far undeveloped Greater Sunrise field has proven technically and politically challenging. Remaining potential reserves are also losing value as oil and gas become less favoured sources of energy.
The country's economy is dependent on government spending and, to a lesser extent, assistance from foreign donors. Government spending decreased beginning in 2012, which had knock-on effects in the private sector over the following years. The government and its state-owned oil company often invest in large private projects. Decreasing government spending was matched with a decrease in GDP growth. After the petroleum fund, the second largest source of government income is taxes. Tax revenue is less than 8% of GDP, lower than many other countries in the region and with similarly sized economies. Other government income comes from 23 "autonomous agencies", which include port authorities, infrastructure companies, and the National University of East Timor. Overall, government spending remains among the highest in the world, although investment into education, health, and water infrastructure is negligible.
This poverty belies significant wealth in terms of natural resources, which at the time of independence had per capita value equivalent to the wealth of an upper-middle income country. Over half of this was in oil, and over a quarter natural gas. The Timor-Leste Petroleum Fund was established in 2005 to turn these non-renewable resources into a more sustainable form of wealth. From 2005 to 2021, $23 billion earned from oil sales has entered the fund. $8 billion has been generated from investments, while $12 billion has been spent. A decrease in oil and gas reserves led to decreasing HDI beginning in 2010. 80% of government spending comes from this fund, which as of 2021 had $19 billion, 10 times greater than the size of the national budget. As oil income has decreased, the fund is at risk of being exhausted. Withdrawals have exceeded sustainable levels almost every year since 2009. Resources within the Bayu-Undan field are expected to soon run out, while extracting those within the so far undeveloped Greater Sunrise field has proven technically and politically challenging. Remaining potential reserves are also losing value as oil and gas become less favoured sources of energy.
The country's economy is dependent on government spending and, to a lesser extent, assistance from foreign donors. Government spending decreased beginning in 2012, which had knock-on effects in the private sector over the following years. The government and its state-owned oil company often invest in large private projects. Decreasing government spending was matched with a decrease in GDP growth. After the petroleum fund, the second largest source of government income is taxes. Tax revenue is less than 8% of GDP, lower than many other countries in the region and with similarly sized economies. Other government income comes from 23 "autonomous agencies", which include port authorities, infrastructure companies, and the National University of East Timor. Overall, government spending remains among the highest in the world, although investment into education, health, and water infrastructure is negligible.
 Private sector development has lagged due to human capital shortages, infrastructure weakness, an incomplete legal system, and an inefficient regulatory environment. Property rights remain ill-defined, with conflicting titles from Portuguese and Indonesian rule, as well as needing to accommodate traditional customary rights. As of 2010, 87.7% of urban (321,043 people) and 18.9% of rural (821,459 people) households have electricity, for an overall average of 38.2%. The private sector shrank between 2014 and 2018, despite a growing working age population. Agriculture and manufacturing are less productive per capita than at independence. Non-oil economic sectors have failed to develop, and growth in construction and administration is dependent on oil revenue. The dependence on oil shows some aspects of a
Private sector development has lagged due to human capital shortages, infrastructure weakness, an incomplete legal system, and an inefficient regulatory environment. Property rights remain ill-defined, with conflicting titles from Portuguese and Indonesian rule, as well as needing to accommodate traditional customary rights. As of 2010, 87.7% of urban (321,043 people) and 18.9% of rural (821,459 people) households have electricity, for an overall average of 38.2%. The private sector shrank between 2014 and 2018, despite a growing working age population. Agriculture and manufacturing are less productive per capita than at independence. Non-oil economic sectors have failed to develop, and growth in construction and administration is dependent on oil revenue. The dependence on oil shows some aspects of a
 East Timor recorded a population of 1,183,643 in its 2015 census. The population lives mainly along the coastline, where all urban areas are located. Those in urban areas generally have more formal education, employment prospects, and healthcare. While a strong gender disparity exists throughout the country, it is less severe in the urban capital. The wealthy minority often go abroad for health and education purposes. The population is young, with the median age being under 20. In particular, a large proportion of the population (almost 45% in 2015) are males between the ages of 15 and 24, the third largest male 'youth bulge' in the world.
The CIA's World Factbook lists the English-language demonym for East Timor as Timorese, as does the Government of Timor-Leste's website. Other reference sources list it as East Timorese. The word formerly used by the Portuguese to refer to native East Timorese and often employed as synonymous with the illiterate and uneducated, was adopted by Fretilin as a term of pride.
Healthcare received 6% of the national budget in 2021. From 1990 to 2019 life expectancy rose from 48.5 to 69.5. Expected years of schooling rose from 9.8 to 12.4 between 2000 and 2010, while mean years of schooling rose from 2.8 to 4.4. Progress since 2010 for these has been limited.
East Timor recorded a population of 1,183,643 in its 2015 census. The population lives mainly along the coastline, where all urban areas are located. Those in urban areas generally have more formal education, employment prospects, and healthcare. While a strong gender disparity exists throughout the country, it is less severe in the urban capital. The wealthy minority often go abroad for health and education purposes. The population is young, with the median age being under 20. In particular, a large proportion of the population (almost 45% in 2015) are males between the ages of 15 and 24, the third largest male 'youth bulge' in the world.
The CIA's World Factbook lists the English-language demonym for East Timor as Timorese, as does the Government of Timor-Leste's website. Other reference sources list it as East Timorese. The word formerly used by the Portuguese to refer to native East Timorese and often employed as synonymous with the illiterate and uneducated, was adopted by Fretilin as a term of pride.
Healthcare received 6% of the national budget in 2021. From 1990 to 2019 life expectancy rose from 48.5 to 69.5. Expected years of schooling rose from 9.8 to 12.4 between 2000 and 2010, while mean years of schooling rose from 2.8 to 4.4. Progress since 2010 for these has been limited.
 Ethnic background and linguistic group do not clearly define Timorese communities, with many communities within these broad groupings and many areas with overlaps and hybridisation between ethnic and linguistic groups. Familial relations and descent, which are interlinked with sacred house affiliation, are a more important indicator of identity. Each family group generally identifies with a single language or dialect. With this immense local variation in mind, there is a broad cultural and identity distinction between the east (Bacau, Lautém, and Viqueque Municipalities) and the west of the country, a product of history more than it is of linguistic and ethnic differences, although it is very loosely associated with the two language groups. There is a small
Ethnic background and linguistic group do not clearly define Timorese communities, with many communities within these broad groupings and many areas with overlaps and hybridisation between ethnic and linguistic groups. Familial relations and descent, which are interlinked with sacred house affiliation, are a more important indicator of identity. Each family group generally identifies with a single language or dialect. With this immense local variation in mind, there is a broad cultural and identity distinction between the east (Bacau, Lautém, and Viqueque Municipalities) and the west of the country, a product of history more than it is of linguistic and ethnic differences, although it is very loosely associated with the two language groups. There is a small
 East Timor's adult literacy rate in 2010 was 58.3%, up from 37.6% in 2001. At the end of Portuguese rule, literacy was at 5%. By 2021 it was 68% among adults, and 84% among those aged 15–24, being slightly higher among women than men. More girls than boys attend school, although some drop out upon reaching puberty. As of 2016 22% of working age women (15-49) and 19% of working age men had no education, 15% of women and 18% of men had some primary education, 52% of women and 51% of men had some secondary education, and 11% of women and 12% of men had higher education. Overall, 75% of women and 82% of men were literate. Primary schools exist throughout the country, although the quality of materials and teaching is often poor. Secondary schools are generally limited to municipal capitals. Education takes up 10% of the national budget. The country's main university is the National University of East Timor. There are also four colleges.
Since independence, both Indonesian and Tetum have lost ground as media of instruction, while
East Timor's adult literacy rate in 2010 was 58.3%, up from 37.6% in 2001. At the end of Portuguese rule, literacy was at 5%. By 2021 it was 68% among adults, and 84% among those aged 15–24, being slightly higher among women than men. More girls than boys attend school, although some drop out upon reaching puberty. As of 2016 22% of working age women (15-49) and 19% of working age men had no education, 15% of women and 18% of men had some primary education, 52% of women and 51% of men had some secondary education, and 11% of women and 12% of men had higher education. Overall, 75% of women and 82% of men were literate. Primary schools exist throughout the country, although the quality of materials and teaching is often poor. Secondary schools are generally limited to municipal capitals. Education takes up 10% of the national budget. The country's main university is the National University of East Timor. There are also four colleges.
Since independence, both Indonesian and Tetum have lost ground as media of instruction, while
 While the Constitution of East Timor enshrines the principles of freedom of religion and separation of church and state, Section 45 Comma 1 also acknowledges "the participation of the Catholic Church in the process of national liberation" in its preamble. Upon independence, the country joined the
While the Constitution of East Timor enshrines the principles of freedom of religion and separation of church and state, Section 45 Comma 1 also acknowledges "the participation of the Catholic Church in the process of national liberation" in its preamble. Upon independence, the country joined the
United States
 The many cultures within East Timor stem from the several waves of Austronesian and Melanesian migration that led to the current population, with unique identities and traditions developing within each petty kingdom. Portuguese authorities built upon traditional structures, blending Portuguese influence into the existing political and social systems. The presence of the Catholic Church created a point of commonality across the various ethnic groups, despite full conversion remaining limited. The Portuguese language also provided common linkages, even if direct Portuguese impact was limited. Under Indonesian rule, resistance strengthened cultural links to Catholicism and Portuguese. At the same time, Indonesian cultural influence was spread through schools and administration.
The preservation of traditional beliefs in the face of Indonesian attempts to suppress them became linked to the creation of the country's national identity. This national identity only began to emerge at the very end of Portuguese rule and during Indonesian rule. A civic identity begun to develop, most clearly expressed through enthusiasm for national-level democracy, and reflected in politics through a shift from resistance narratives to development ones. The capital has developed a more cosmopolitan culture, while rural areas maintain stronger traditional practices. Internal migration into urban areas, especially Dili, creates cultural links between these areas and rural hinterlands. Those in urban areas often continue to identify with a specific rural area, even those with multiple generations born in Dili.
The presence of so many ethnic and linguistic groups means cultural practices vary across the country. These practices reflect historical social structures and practices, where political leaders were regarded as having spiritual powers. Ancestry was an important component of leadership, with ancestors being an important part of cultural practices. Leaders often had influence over land-use, and these leaders continue to play an informal role in land disputes and other aspects of community practice today. An important traditional concept is ''lulik'', or sacredness. Some ''lulik'' ceremonies continue to reflect animist beliefs, for example through divination ceremonies which vary throughout the country. Sacred status can also be associated with objects, such as Portuguese flags which have been passed down within families.
The many cultures within East Timor stem from the several waves of Austronesian and Melanesian migration that led to the current population, with unique identities and traditions developing within each petty kingdom. Portuguese authorities built upon traditional structures, blending Portuguese influence into the existing political and social systems. The presence of the Catholic Church created a point of commonality across the various ethnic groups, despite full conversion remaining limited. The Portuguese language also provided common linkages, even if direct Portuguese impact was limited. Under Indonesian rule, resistance strengthened cultural links to Catholicism and Portuguese. At the same time, Indonesian cultural influence was spread through schools and administration.
The preservation of traditional beliefs in the face of Indonesian attempts to suppress them became linked to the creation of the country's national identity. This national identity only began to emerge at the very end of Portuguese rule and during Indonesian rule. A civic identity begun to develop, most clearly expressed through enthusiasm for national-level democracy, and reflected in politics through a shift from resistance narratives to development ones. The capital has developed a more cosmopolitan culture, while rural areas maintain stronger traditional practices. Internal migration into urban areas, especially Dili, creates cultural links between these areas and rural hinterlands. Those in urban areas often continue to identify with a specific rural area, even those with multiple generations born in Dili.
The presence of so many ethnic and linguistic groups means cultural practices vary across the country. These practices reflect historical social structures and practices, where political leaders were regarded as having spiritual powers. Ancestry was an important component of leadership, with ancestors being an important part of cultural practices. Leaders often had influence over land-use, and these leaders continue to play an informal role in land disputes and other aspects of community practice today. An important traditional concept is ''lulik'', or sacredness. Some ''lulik'' ceremonies continue to reflect animist beliefs, for example through divination ceremonies which vary throughout the country. Sacred status can also be associated with objects, such as Portuguese flags which have been passed down within families.
 Community life is centred around sacred houses (''Uma Lulik''), physical structures which serve as a representative symbol and identifier for each community. The architectural style of these houses varies between different parts of the country, although following widespread destruction by Indonesian forces many were rebuilt with cheap modern materials. The house as a concept extends beyond the physical object to the surrounding community. Kinship systems exist within and between houses. Traditional leaders, who stem from historically important families, retain key roles in administering justice and resolving disputes through methods that vary between communities. Such leaders are often elected to official leadership positions, joining cultural and historical status with modern political status. The concept of being part of a communal house has been extended to the nation, with Parliament serving as the national sacred house.
Art styles vary throughout the various ethnolinguistic groups of the island. Nonetheless, similar artistic motifs are present throughout, such as large animals and particular geometric patterns. Some art is traditionally associated with particular genders. For example, the
Community life is centred around sacred houses (''Uma Lulik''), physical structures which serve as a representative symbol and identifier for each community. The architectural style of these houses varies between different parts of the country, although following widespread destruction by Indonesian forces many were rebuilt with cheap modern materials. The house as a concept extends beyond the physical object to the surrounding community. Kinship systems exist within and between houses. Traditional leaders, who stem from historically important families, retain key roles in administering justice and resolving disputes through methods that vary between communities. Such leaders are often elected to official leadership positions, joining cultural and historical status with modern political status. The concept of being part of a communal house has been extended to the nation, with Parliament serving as the national sacred house.
Art styles vary throughout the various ethnolinguistic groups of the island. Nonetheless, similar artistic motifs are present throughout, such as large animals and particular geometric patterns. Some art is traditionally associated with particular genders. For example, the
''East Timor, politics and elections'' (in Chinese)/ 东帝汶政治与选举 (2001–2006): 国家建设及前景展望
Jean A. Berlie, Institute of Southeast Asian Studies of Jinan University editor, Jinan, China, published in 2007. *
Timor-Leste official government website
Timor-Leste official tourism website
General information
Timor-Leste
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
East Timor
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
East Timor
at ''
East Timor profile
Key Development Forecasts for Timor-Leste
from International Futures
Timor Leste Studies Association
{{Authority control * 1975 establishments in Asia 2002 establishments in Asia Countries in Asia Island countries of the Indian Ocean Island countries Former Portuguese colonies Least developed countries Maritime Southeast Asia Member states of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries Member states of the United Nations Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Portuguese-speaking countries and territories Republics Small Island Developing States Southeast Asian countries States and territories established in 1975 States and territories established in 2002 Malay-speaking countries and territories
Administrative divisions
 East Timor is divided into fourteen municipalities, which in turn are subdivided into 64 administrative posts, 442 ''sucos'' (villages), and 2,225 ''aldeias'' (hamlets). The municipalities are: Aileu, Ainaro,
East Timor is divided into fourteen municipalities, which in turn are subdivided into 64 administrative posts, 442 ''sucos'' (villages), and 2,225 ''aldeias'' (hamlets). The municipalities are: Aileu, Ainaro, Atauro
Atauro ( pt, Ilha de Ataúro, Tetum and Indonesian: ''Pulau Atauro'' or ''Ata'uro''), also known as Kambing Island ( id, Pulau Kambing), is an island and municipality ( pt, Município Ataúro, links=no, tet, Munisípiu Atauro, links=no or ...
, Baucau
Baucau ( pt, Baucau, tet, Baukau) is the second-largest city in East Timor, after Dili, the capital, which lies to its west.
Baucau has about 16,000 inhabitants, and is the capital of Baucau municipality, located in the eastern part of th ...
, Bobonaro
Bobonaro is a town in Bobonaro Subdistrict, Bobonaro District, East Timor., United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency The district capital is not in Bobonaro, but is in Maliana
Maliana is a city in East Timor, 149 kilome ...
, Cova Lima, Dili, Ermera, Lautém, Liquiçá, Manatuto
Manatuto is a city in Manatuto Municipality, East Timor.
Manatuto Vila has 3,692 inhabitants (Census 2015) and is capital of the subdistrict and district Manatuto. It is on the north coast of Timor, (about as the crow flies) east of Dili, ...
, Manufahi
Manufahi (, ) is one of the municipalities of East Timor. It has a population of 53,691 (2015 census) and an area of 1,323 km2. The capital of the municipality is Same.
Etymology
The present name of the municipality, ''Manufahi'', is ...
, Oecusse
Oecusse (also variously ''Oecussi'', ''Ocussi'', ''Oekussi'', ''Oekusi'', ''Okusi'', ''Oé-Cusse''), also known as Oecusse-Ambeno (; ) and formerly just Ambeno, officially the Special Administrative Region Oecusse-Ambeno (), is an exclave, mun ...
, and Viqueque.
The existing system of municipalities and administrative posts was established during Portuguese rule. While decentralisation is mentioned in the constitution, administrative powers generally remain with the national government operating out of Dili. Upon independence there was debate about how to implement decentralisation, with multiple models proposed which would create different levels of administration between the ''sucos'' and the central government. In most proposals, there were no specific provisions for ''suco'' level governance, and they were expected to continue to operate as mostly customary units. In the end, the existing districts were kept and renamed municipalities in 2009, and received very few powers. Each municipality is led by a civil servant appointed by the central government, a structure that was only put in place in 2016. The isolated Oecusse
Oecusse (also variously ''Oecussi'', ''Ocussi'', ''Oekussi'', ''Oekusi'', ''Okusi'', ''Oé-Cusse''), also known as Oecusse-Ambeno (; ) and formerly just Ambeno, officially the Special Administrative Region Oecusse-Ambeno (), is an exclave, mun ...
municipality, which has a strong identity and is fully surrounded by Indonesian territory, is specified by Articles 5 and 71 of the 2002 constitution to be governed by a special administrative policy and economic regime. Law 3/2014 of 18 June 2014 was created to implement this constitutional provision, which went into effect in January 2015 turning Oecusse into a Special Administrative Region. The region began operating its own civil service in June 2015. In January 2022 the island of Atauro
Atauro ( pt, Ilha de Ataúro, Tetum and Indonesian: ''Pulau Atauro'' or ''Ata'uro''), also known as Kambing Island ( id, Pulau Kambing), is an island and municipality ( pt, Município Ataúro, links=no, tet, Munisípiu Atauro, links=no or ...
, formerly an Administrative Post of Dili, became its own municipality.
Administration in the lowest levels of the administrative system of East Timor, the ''aldeias'' and ''sucos'', generally reflects traditional customs, reflecting community identity and relationships between local households. ''Sucos'' generally contain 2,000 to 3,000 inhabitants. Their long persistence and links to local governance means the ''sucos'' are the level of government that is linked to community identities, rather than any high level of administration. Such relationships are associated specifically with the kinship groups within that land however, rather than the land itself. Relationships between ''sucos'' also reflect customary practices, for example through the reciprocal exchanging of support for local initiatives. Laws passed in 2004 provided for the election of some ''suco'' officials, but assigned these positions no formal powers. An updated law in 2009 established the expected mandate of these positions, although it continue to leave them outside of the formal state system, reliant on municipal governments to provide formal administration and services. Further clarification was given in 2016, which entrenched the treatment of ''sucos'' and ''aldeias'' more as communities than formal levels of administration. Despite this lack of formal association with the state, ''suco'' leaders hold great influence and are often seen by their community as representatives of the state, and they have responsibilities usually associated with civic administration.
Foreign relations and military
fragile state
A fragile state or weak state is a country characterized by weak state capacity or weak state legitimacy leaving citizens vulnerable to a range of shocks. The World Bank, for example, deems a country to be ‘fragile’ if it (a) is eligible for ...
s. It is also a member of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries
The Community of Portuguese Language Countries ( Portuguese: ''Comunidade dos Países de Língua Portuguesa''; abbreviated as the CPLP), also known as the Lusophone Commonwealth (''Comunidade Lusófona''), is an international organization and pol ...
.
Continuing bilateral donors include Australia, Portugal, Germany, and Japan, and the country has a reputation for effectively and transparently using donor funds. Good relations with Australia and with Indonesia are a policy goal for the government, despite historical and more recent tensions. These countries are important economic partners, and provide most transport links to the country. China has also increased its presence as a donor, contributing to infrastructure in Dili.
The relationship with Australia was dominated from before independence by disputes over natural resources in the Timor Gap
The Timor Gap is an area of the Timor Sea between Australia and Timor Island. The island is divided between independent East Timor and West Timor province of Indonesia.
The Timor Gap is part of the Australia-East Timor border, Australia-Indones ...
which lies between them, which hampered the establishment of a mutually agreed border. The dominance of Australian hard power led East Timor to utilise public diplomacy and forums for international law to push their case. The dispute was resolved in 2018 following negotiations at the Permanent Court of Arbitration, when a maritime boundary between the two was established along with an agreement on natural resource revenues.
The Timor Leste Defence Force (F-FDTL) was established in 2001, replacing Falintil
The Armed Forces for the National Liberation of East Timor (, FALINTIL) originally began as the military wing of the political party FRETILIN of East Timor. It was established on 20 August 1975 in response to FRETILIN's political conflict wit ...
, and was restructured following the events of 2006. It is responsible not only for safeguarding against external threats, but also for tackling violent crime, a role in which it overlaps with the National Police of East Timor. The size of these forces remains small, with 2,200 soldiers in the regular army and 80 in a naval component. A single aircraft and seven patrol boats are operated, with plans to expand the naval component. There is some military cooperation with Australia, Portugal, and the United States.
Geography
 Located in between Southeast Asia and the South Pacific, the island of Timor is the largest of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which lie within the Malay archipelago. The island is surrounded by the Ombai and
Located in between Southeast Asia and the South Pacific, the island of Timor is the largest of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which lie within the Malay archipelago. The island is surrounded by the Ombai and Wetar Strait
Wetar Strait ( id, Selat Wetar, pt, Estreito de Wetar, tet, Estreitu Wetar) is an international strait in Southeast Asia. It separates the island of Wetar from the eastern part of the island of Timor. The strait is also the eastern portion ...
s of the rougher Banda Sea
The Banda Sea ( id, Laut Banda, pt, Mar de Banda, tet, Tasi Banda) is one of four seas that surround the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, connected to the Pacific Ocean, but surrounded by hundreds of islands, including Timor, as well as the Halma ...
in the north, and the calmer Timor Sea
The Timor Sea ( id, Laut Timor, pt, Mar de Timor, tet, Tasi Mane or ) is a relatively shallow sea bounded to the north by the island of Timor, to the east by the Arafura Sea, and to the south by Australia.
The sea contains a number of reefs ...
in the south. East Timor shares the island with Indonesia, which separates the main part of the country from the Oecusse
Oecusse (also variously ''Oecussi'', ''Ocussi'', ''Oekussi'', ''Oekusi'', ''Okusi'', ''Oé-Cusse''), also known as Oecusse-Ambeno (; ) and formerly just Ambeno, officially the Special Administrative Region Oecusse-Ambeno (), is an exclave, mun ...
exclave. The island of Atauro
Atauro ( pt, Ilha de Ataúro, Tetum and Indonesian: ''Pulau Atauro'' or ''Ata'uro''), also known as Kambing Island ( id, Pulau Kambing), is an island and municipality ( pt, Município Ataúro, links=no, tet, Munisípiu Atauro, links=no or ...
lies north of the mainland, with the fourth area being the small island of Jaco. The Savu Sea
The Savu Sea (or the Sawu Sea) ( id, Laut Sawu, pt, Mar de Savu, tet, Tasi Savu) is a small sea within Indonesia named for the island of Savu (Sawu) on its southern boundary. It is bounded by Savu and Rai Jua to the south, the islands of ...
lies north of Oecusse. The country is about long and wide, with a total land area of . This territory is situated between 8′15S – 10′30S latitude and 125′50E – 127′30E longitude. The country's coastline covers around , while the main land border with Indonesia is long, and the Oecusse land border is around long. Maritime borders exist with Australia to the south and Indonesia elsewhere. East Timor has an exclusive economic zone of .
The interior of the country is mountainous, with ridges of inactive volcanic mountains extending along the island. Almost half of the country has a slope of at least 40%. The south is slightly less mountainous, and has some plains near the coastline. The highest point is Tatamailau (also known as Mount Ramelau) at . Most rivers dry up at least partially during the dry season. Outside of some coastal areas and river valleys, the soil is shallow and prone to erosion, and its quality is poor. The capital, largest city, and main port is Dili, and the second-largest city is the eastern town of Baucau
Baucau ( pt, Baucau, tet, Baukau) is the second-largest city in East Timor, after Dili, the capital, which lies to its west.
Baucau has about 16,000 inhabitants, and is the capital of Baucau municipality, located in the eastern part of th ...
.
 The climate is tropical with relatively stable temperatures throughout the year. A wet season lasts from December to May throughout the country, and lasts slightly longer in the south and the interior due to the effect of a monsoon from Australia. During this period, rainfall can reach per month. In the dry season, it drops to . The country is vulnerable to flooding and landslides that occur as a result of heavy rain, especially when rainfall levels are increased by the La Niña effect. The mountainous interior is cooler than the coasts. Coastal areas are heavily dependent on groundwater, which faces pressure from mismanagement, deforestation, and climate change. While the temperature is thought to have experienced a small increase due to climate change, there has been little change in rainfall patterns.
Coastal ecosystems around the country are diverse and varied, with vary spatially between the north and south coastlines, as well as between the eastern tip and areas more to the west. These ecosystems include coral reefs, as the country's waters are part of the
The climate is tropical with relatively stable temperatures throughout the year. A wet season lasts from December to May throughout the country, and lasts slightly longer in the south and the interior due to the effect of a monsoon from Australia. During this period, rainfall can reach per month. In the dry season, it drops to . The country is vulnerable to flooding and landslides that occur as a result of heavy rain, especially when rainfall levels are increased by the La Niña effect. The mountainous interior is cooler than the coasts. Coastal areas are heavily dependent on groundwater, which faces pressure from mismanagement, deforestation, and climate change. While the temperature is thought to have experienced a small increase due to climate change, there has been little change in rainfall patterns.
Coastal ecosystems around the country are diverse and varied, with vary spatially between the north and south coastlines, as well as between the eastern tip and areas more to the west. These ecosystems include coral reefs, as the country's waters are part of the Coral Triangle
The Coral Triangle (CT) is a roughly triangular area in the tropical waters around the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and Timor-Leste. This area contains at least 500 species of reef-building corals in e ...
biodiversity hotspot. The easternmost area of East Timor consists of the Paitchau
Paitchau (also Gunung Paitchau, or Paitchao, or Paitxau; locally, Pai Tekau Ile) is a mountain in the Tutuala subdistrict, Lautém District of East Timor. Situated within Nino Konis Santana National Park, it is south of Lake Ira Lalaro. Though p ...
Range and the Lake Ira Lalaro
Lake Ira Lalaro (also Iralalaro, Ira-Lalaro, Surubec, Suro Bec) is a freshwater lake in Mehara, Subdistrict Tutuala, Lautém District, East Timor. It is the largest of the island of Timor, and thus too of the country. The lake is part of the Mou ...
area, which contains the country's first conservation area, the Nino Konis Santana National Park
The Nino Konis Santana National Park is East Timor's first national park. The park, established on 15 August 2007, covers . It links important bird areas such as Lore, Mount Paitchau, Lake Ira Lalaro, and Jaco Island. The park also includes o ...
. It contains the last remaining tropical dry forested area within the country. It hosts a number of unique plant and animal species and is sparsely populated. The northern coast is characterised by a number of coral reef systems that have been determined to be at risk.
There are around 41,000 terrestrial plant species in the country, with around 35% of the land being forested in the mid 2010s. The forests of the northern coast, central uplands, and southern coast are distinct. East Timor is home to the Timor and Wetar deciduous forests ecoregion. There is some environmental protection in law, but it has not been a government priority. In addition to climate change, local ecosystems are threatened by deforestation, land degradation, overfishing, and pollution.
Economy
 The economy of East Timor is a market economy, which used to depend upon exports of a few commodities such as
The economy of East Timor is a market economy, which used to depend upon exports of a few commodities such as coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
, marble, petroleum, and sandalwood. Internally, market operations are limited by widespread poverty. The country uses the United States dollar. The economy is generally open to foreign investment, although a prohibition on foreigners owning land means many require a local partner in the country. Competition is limited by the small size of the economy, rather than any government barriers. There are far more imports than exports, and prices for goods are often higher than in nearby countries. Inflation is strongly affected by government spending. Growth has been slow, averaging just 2.5% per year from 2011 to 2021.
Most of the country is very poor, with just more than 40% living under the national poverty line. This poverty is especially prevalent in rural areas, where many are subsistence farmers or fishermen. Even in urban areas, the majority are poor. Overall, women are poorer than men, often being employed in lower-paying careers. Malnutrition is common, with over half of children showing stunted growth
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition (or more precisely undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth ...
. While 91% of married working age (15-49) men were employed as of 2016, only 43% of married working age women were. There are small disparities in favour of men in terms of home and land ownership and owning a bank account. The eastern three municipalities, which contain around a quarter of the population, has less poverty than the western areas, which contain 50% of the popuation.
94% of domestic fish catch comes from the ocean, especially coastal fisheries. 66% of families are in part supported by subsistence activities, however the country as a whole does not produce enough food to be self-sustaining, and thus relies on imports. Agricultural work carries the implication of poverty, and the sector receives little investment from the government. Those in the capital of Dili are on average better off, although they remain poor by international standards. The small size of the private sector means the government is often the customer of public businesses. A quarter of the national population works in the informal economy, with the official public and private sectors employing 9% each. Of those of working age, around 23% are in the cash economy, 21% are students, and 27% are subsistence farmers and fishers. The economy is mostly cash-based, with little commercial credit available from banks. Remittances from overseas workers add up to around $100 million annually.
resource curse
The resource curse, also known as the paradox of plenty or the poverty paradox, is the phenomenon of countries with an abundance of natural resources (such as fossil fuels and certain minerals) having less economic growth, less democracy, or worse ...
. Coffee made up 90% of all non-fossil fuel exports from 2013-2019, with all such exports totaling to around US$20 million annually. In 2017, the country was visited by 75,000 tourists.
Demographics
Gross national income
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign ...
per capita similarly peaked in 2010, and has decreased since. As of 2016, 45.8% of East Timorese were impoverished, 16.3% severely so. The fertility rate, which at the time of independence was the highest in the world at 7.8, dropped to 4.2 by 2016. It is relatively higher in rural areas, and among poorer and less literate households. As of 2016, the average household size was 5.3, with 41% of people aged under 15, and 18% of households headed by women. Infant mortality stood at 30 per 1,000, down from 60 per 1,000 in 2003. 46% of children under 5 showed stunted growth
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition (or more precisely undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth ...
, down from 58% in 2010. Working age adult obesity increased from 5% to 10% during the same time period. As of 2016 40% of children, 23% of women, and 13% of men had anemia.
Ethnicity and language
 Ethnic background and linguistic group do not clearly define Timorese communities, with many communities within these broad groupings and many areas with overlaps and hybridisation between ethnic and linguistic groups. Familial relations and descent, which are interlinked with sacred house affiliation, are a more important indicator of identity. Each family group generally identifies with a single language or dialect. With this immense local variation in mind, there is a broad cultural and identity distinction between the east (Bacau, Lautém, and Viqueque Municipalities) and the west of the country, a product of history more than it is of linguistic and ethnic differences, although it is very loosely associated with the two language groups. There is a small
Ethnic background and linguistic group do not clearly define Timorese communities, with many communities within these broad groupings and many areas with overlaps and hybridisation between ethnic and linguistic groups. Familial relations and descent, which are interlinked with sacred house affiliation, are a more important indicator of identity. Each family group generally identifies with a single language or dialect. With this immense local variation in mind, there is a broad cultural and identity distinction between the east (Bacau, Lautém, and Viqueque Municipalities) and the west of the country, a product of history more than it is of linguistic and ethnic differences, although it is very loosely associated with the two language groups. There is a small mestiço
Mestiço is a Portuguese term that referred to persons born from a couple in which one was an aboriginal person and the other a European.
Mestiço community in Brazil
in Colonial Brazil, it was initially used to refer to , persons born from ...
population of mixed Portuguese and local descent. There is a small Chinese minority, most of whom are Hakka. Many Chinese left in the mid-1970s, but a significant number have also returned to East Timor following the end of Indonesian occupation. East Timor has a small community of Timorese Indian, specifically Goan descent, as well as historical immigration from Africa and Yemen.
Likely reflecting the mixed origins of the different ethnolinguistic groups of the island, the indigenous languages fall into two language families: Austronesian and Papuan. Depending on how they are classified, there are up to 19 indigenous languages with up to 30 dialects. Aside from Tetum, Ethnologue lists the following indigenous languages: Adabe
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby islands Liran and Atauro, the latter island separate from the mainland of East Timor, north of Dili.
Background
The four identified prin ...
, Baikeno, Bunak, Fataluku, Galoli, Habun, Idaté, Kairui-Midiki, Kemak, Lakalei, Makasae, Makuv'a
Makuva, also known as Maku'a or Lóvaia, is an apparently extinct Austronesian language spoken at the northeast tip of East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an isl ...
, Mambae, Nauete, Tukudede, and Waima'a. According to the Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger, there are six endangered languages in East Timor: Adabe
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby islands Liran and Atauro, the latter island separate from the mainland of East Timor, north of Dili.
Background
The four identified prin ...
, Habu, Kairui-Midiki, Maku'a, Naueti, and Waima'a. The largest Malayo-Polynesian group is the Tetum
, nativename=Tetun
, states= Indonesia East Timor
, speakers=, mostly in Indonesia
, date=2010–2011
, ref=e18
, speakers2=50,000 L2-speakers in Indonesia and East Timor
, familycolor=Austronesian
, fam2=Malayo-Polynesian
, fam3= Central–East ...
, mostly around Dili or the western border. Other Malayo-Polynesian languages with native speakers of more than 40,000 are Mambai in the central mountains south of Dili, Baikeno
Uab Meto or Dawan is an Austronesian language spoken by Atoni people of West Timor. The language has a variant spoken in the East Timorese exclave of Oecussi-Ambeno, called Baikenu. Baikenu uses words derived from Portuguese, for example, ''obr ...
in Oecusse, Kemak in the north-west interior, and Tokodede
Tokodede (also known as Tukude, Tocodede, Tokodé, and Tocod) is one of the languages of East Timor, spoken by about 39,000 people in the municipality of Liquiçá, especially the administrative posts of Maubara and Liquiçá along the northe ...
on the northwest coast. The main Papuan languages
The Papuan languages are the non- Austronesian and non- Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geogr ...
spoken are Bunak
The Bunak (also known as Bunaq, Buna', Bunake) people are an ethnic group that live in the mountainous region of central Timor, split between the political boundary between West Timor, Indonesia, particularly in Lamaknen District and East Timor. ...
in the centre of Timor, especially within Bobonaro Municipality; Makasae
Makasae (also known as Makassai, Macassai, Ma'asae, Makasai) is a Papuan language spoken by about 100,000 people in the eastern part of East Timor, in the districts of Baucau and Viqueque, just to the west of Fataluku. It is the most widely spok ...
in the eastern Baucau
Baucau ( pt, Baucau, tet, Baukau) is the second-largest city in East Timor, after Dili, the capital, which lies to its west.
Baucau has about 16,000 inhabitants, and is the capital of Baucau municipality, located in the eastern part of th ...
and Viqueque municipalities; and Fataluku in the eastern Lautém Municipality
Lautém ( pt, Município Lautém, ) is one of the municipalities (formerly districts) of East Timor, at the eastern end of the country. It has a population of 64,135 (census 2010) and an area of 1,813 km². Its capital is Lospalos, which ...
. The 2015 census found that the most commonly spoken mother tongues were Tetum Prasa (mother tongue for 30.6% of the population), Mambai (16.6%), Makasai
Makasae (also known as Makassai, Macassai, Ma'asae, Makasai) is a Papuan language spoken by about 100,000 people in the eastern part of East Timor, in the districts of Baucau (district), Baucau and Viqueque (district), Viqueque, just to the west ...
(10.5%), Tetum Terik (6.05%), Baikenu (5.87%), Kemak (5.85%), Bunak
The Bunak (also known as Bunaq, Buna', Bunake) people are an ethnic group that live in the mountainous region of central Timor, split between the political boundary between West Timor, Indonesia, particularly in Lamaknen District and East Timor. ...
(5.48%), Tokodede
Tokodede (also known as Tukude, Tocodede, Tokodé, and Tocod) is one of the languages of East Timor, spoken by about 39,000 people in the municipality of Liquiçá, especially the administrative posts of Maubara and Liquiçá along the northe ...
(3.97%), and Fataluku (3.52%). Other indigenous languages accounted for 10.47%, while 1.09% of the population spoke foreign languages natively.
East Timor's two official languages are Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and Tetum
, nativename=Tetun
, states= Indonesia East Timor
, speakers=, mostly in Indonesia
, date=2010–2011
, ref=e18
, speakers2=50,000 L2-speakers in Indonesia and East Timor
, familycolor=Austronesian
, fam2=Malayo-Polynesian
, fam3= Central–East ...
. In addition, English and Indonesian are designated by the constitution as "working languages". This is within the Final and Transitional Provisions, which do not set a final date. In 2012, 35% could speak, read, and write Portuguese, which is up significantly from less than 5% in the 2006 UN Development Report. Portuguese is recovering as it has now been made the main official language of Timor, and is being taught in most schools. The use of Portuguese for government information and in the court system provides some barriers to access for those who do not speak it. Tetum is also not understood by everyone in the country. According to the Observatory of the Portuguese Language, the East Timorese literacy rate was 77.8% in Tetum, 55.6% in Indonesian, and 39.3% in Portuguese, and that the primary literacy rate increased from 73% in 2009 to 83% in 2012. According to the 2015 census, 50% of the population between the ages of 14 and 24 can speak and understand Portuguese. The 2015 census found around 15% of those over the age of five were literate in English.
Education
 East Timor's adult literacy rate in 2010 was 58.3%, up from 37.6% in 2001. At the end of Portuguese rule, literacy was at 5%. By 2021 it was 68% among adults, and 84% among those aged 15–24, being slightly higher among women than men. More girls than boys attend school, although some drop out upon reaching puberty. As of 2016 22% of working age women (15-49) and 19% of working age men had no education, 15% of women and 18% of men had some primary education, 52% of women and 51% of men had some secondary education, and 11% of women and 12% of men had higher education. Overall, 75% of women and 82% of men were literate. Primary schools exist throughout the country, although the quality of materials and teaching is often poor. Secondary schools are generally limited to municipal capitals. Education takes up 10% of the national budget. The country's main university is the National University of East Timor. There are also four colleges.
Since independence, both Indonesian and Tetum have lost ground as media of instruction, while
East Timor's adult literacy rate in 2010 was 58.3%, up from 37.6% in 2001. At the end of Portuguese rule, literacy was at 5%. By 2021 it was 68% among adults, and 84% among those aged 15–24, being slightly higher among women than men. More girls than boys attend school, although some drop out upon reaching puberty. As of 2016 22% of working age women (15-49) and 19% of working age men had no education, 15% of women and 18% of men had some primary education, 52% of women and 51% of men had some secondary education, and 11% of women and 12% of men had higher education. Overall, 75% of women and 82% of men were literate. Primary schools exist throughout the country, although the quality of materials and teaching is often poor. Secondary schools are generally limited to municipal capitals. Education takes up 10% of the national budget. The country's main university is the National University of East Timor. There are also four colleges.
Since independence, both Indonesian and Tetum have lost ground as media of instruction, while Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
has increased: in 2001 only 8.4% of primary school and 6.8% of secondary school students attended a Portuguese-medium school; by 2005 this had increased to 81.6% for primary and 46.3% for secondary schools. Indonesian formerly played a considerable role in education, being used by 73.7% of all secondary school students as a medium of instruction, but by 2005 Portuguese was used by most schools in Baucau
Baucau ( pt, Baucau, tet, Baukau) is the second-largest city in East Timor, after Dili, the capital, which lies to its west.
Baucau has about 16,000 inhabitants, and is the capital of Baucau municipality, located in the eastern part of th ...
, Manatuto
Manatuto is a city in Manatuto Municipality, East Timor.
Manatuto Vila has 3,692 inhabitants (Census 2015) and is capital of the subdistrict and district Manatuto. It is on the north coast of Timor, (about as the crow flies) east of Dili, ...
, as well as the capital district. Portugal provides support to about 3% of the public schools in East Timor, focused on those in urban areas, further encouraging the use of the Portuguese language.
Religion
 While the Constitution of East Timor enshrines the principles of freedom of religion and separation of church and state, Section 45 Comma 1 also acknowledges "the participation of the Catholic Church in the process of national liberation" in its preamble. Upon independence, the country joined the
While the Constitution of East Timor enshrines the principles of freedom of religion and separation of church and state, Section 45 Comma 1 also acknowledges "the participation of the Catholic Church in the process of national liberation" in its preamble. Upon independence, the country joined the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
to become the only two predominantly Roman Catholic states in Asia, although nearby parts of eastern Indonesia such as Flores and parts of Western New Guinea also have Roman Catholic majorities.
According to the 2015 census, 97.57% of the population is Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
; 1.96% Protestant; 0.24% Muslim; 0.08% Traditional; 0.05% Buddhist; 0.02% Hindu, and 0.08% other religions. A 2016 survey conducted by the Demographic and Health Survey programme showed that Catholics made up 98.3% of the population, Protestants 1.2%, and Muslims 0.3%.
The number of churches grew from 100 in 1974 to more than 800 in 1994, with Church membership having grown considerably under Indonesian rule as '' Pancasila'', Indonesia's state ideology, requires all citizens to believe in one God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
and does not recognise traditional beliefs. East Timorese animist belief systems did not fit with Indonesia's constitutional monotheism, resulting in mass conversions to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
. Portuguese clergy were replaced with Indonesian priests and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
and Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
was replaced by Indonesian mass. While just 20% of East Timorese called themselves Catholics at the time of the 1975 invasion, the figure surged to reach 95% by the end of the first decade after the invasion. The Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
divides East Timor into three dioceses: the Archdiocese of Díli, the Diocese of Baucau, and the Diocese of Maliana. In rural areas, Roman Catholicism is syncretised with local animist beliefs. The number of Protestants and Muslims declined significantly after September 1999, as these groups were disproportionately represented among supporters of integration with Indonesia. Fewer than half of previous Protestant congregations existed after September 1999, and many Protestants were among those who remained in West Timor.International Religious Freedom Report 2007: Timor-LesteUnited States
Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor
The Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor Affairs (DRL) is a bureau within the United States Department of State. The bureau is under the purview of the Under Secretary of State for Civilian Security, Democracy, and Human Rights.
DRL's resp ...
(14 September 2007). ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.''
Culture
 The many cultures within East Timor stem from the several waves of Austronesian and Melanesian migration that led to the current population, with unique identities and traditions developing within each petty kingdom. Portuguese authorities built upon traditional structures, blending Portuguese influence into the existing political and social systems. The presence of the Catholic Church created a point of commonality across the various ethnic groups, despite full conversion remaining limited. The Portuguese language also provided common linkages, even if direct Portuguese impact was limited. Under Indonesian rule, resistance strengthened cultural links to Catholicism and Portuguese. At the same time, Indonesian cultural influence was spread through schools and administration.
The preservation of traditional beliefs in the face of Indonesian attempts to suppress them became linked to the creation of the country's national identity. This national identity only began to emerge at the very end of Portuguese rule and during Indonesian rule. A civic identity begun to develop, most clearly expressed through enthusiasm for national-level democracy, and reflected in politics through a shift from resistance narratives to development ones. The capital has developed a more cosmopolitan culture, while rural areas maintain stronger traditional practices. Internal migration into urban areas, especially Dili, creates cultural links between these areas and rural hinterlands. Those in urban areas often continue to identify with a specific rural area, even those with multiple generations born in Dili.
The presence of so many ethnic and linguistic groups means cultural practices vary across the country. These practices reflect historical social structures and practices, where political leaders were regarded as having spiritual powers. Ancestry was an important component of leadership, with ancestors being an important part of cultural practices. Leaders often had influence over land-use, and these leaders continue to play an informal role in land disputes and other aspects of community practice today. An important traditional concept is ''lulik'', or sacredness. Some ''lulik'' ceremonies continue to reflect animist beliefs, for example through divination ceremonies which vary throughout the country. Sacred status can also be associated with objects, such as Portuguese flags which have been passed down within families.
The many cultures within East Timor stem from the several waves of Austronesian and Melanesian migration that led to the current population, with unique identities and traditions developing within each petty kingdom. Portuguese authorities built upon traditional structures, blending Portuguese influence into the existing political and social systems. The presence of the Catholic Church created a point of commonality across the various ethnic groups, despite full conversion remaining limited. The Portuguese language also provided common linkages, even if direct Portuguese impact was limited. Under Indonesian rule, resistance strengthened cultural links to Catholicism and Portuguese. At the same time, Indonesian cultural influence was spread through schools and administration.
The preservation of traditional beliefs in the face of Indonesian attempts to suppress them became linked to the creation of the country's national identity. This national identity only began to emerge at the very end of Portuguese rule and during Indonesian rule. A civic identity begun to develop, most clearly expressed through enthusiasm for national-level democracy, and reflected in politics through a shift from resistance narratives to development ones. The capital has developed a more cosmopolitan culture, while rural areas maintain stronger traditional practices. Internal migration into urban areas, especially Dili, creates cultural links between these areas and rural hinterlands. Those in urban areas often continue to identify with a specific rural area, even those with multiple generations born in Dili.
The presence of so many ethnic and linguistic groups means cultural practices vary across the country. These practices reflect historical social structures and practices, where political leaders were regarded as having spiritual powers. Ancestry was an important component of leadership, with ancestors being an important part of cultural practices. Leaders often had influence over land-use, and these leaders continue to play an informal role in land disputes and other aspects of community practice today. An important traditional concept is ''lulik'', or sacredness. Some ''lulik'' ceremonies continue to reflect animist beliefs, for example through divination ceremonies which vary throughout the country. Sacred status can also be associated with objects, such as Portuguese flags which have been passed down within families.
 Community life is centred around sacred houses (''Uma Lulik''), physical structures which serve as a representative symbol and identifier for each community. The architectural style of these houses varies between different parts of the country, although following widespread destruction by Indonesian forces many were rebuilt with cheap modern materials. The house as a concept extends beyond the physical object to the surrounding community. Kinship systems exist within and between houses. Traditional leaders, who stem from historically important families, retain key roles in administering justice and resolving disputes through methods that vary between communities. Such leaders are often elected to official leadership positions, joining cultural and historical status with modern political status. The concept of being part of a communal house has been extended to the nation, with Parliament serving as the national sacred house.
Art styles vary throughout the various ethnolinguistic groups of the island. Nonetheless, similar artistic motifs are present throughout, such as large animals and particular geometric patterns. Some art is traditionally associated with particular genders. For example, the
Community life is centred around sacred houses (''Uma Lulik''), physical structures which serve as a representative symbol and identifier for each community. The architectural style of these houses varies between different parts of the country, although following widespread destruction by Indonesian forces many were rebuilt with cheap modern materials. The house as a concept extends beyond the physical object to the surrounding community. Kinship systems exist within and between houses. Traditional leaders, who stem from historically important families, retain key roles in administering justice and resolving disputes through methods that vary between communities. Such leaders are often elected to official leadership positions, joining cultural and historical status with modern political status. The concept of being part of a communal house has been extended to the nation, with Parliament serving as the national sacred house.
Art styles vary throughout the various ethnolinguistic groups of the island. Nonetheless, similar artistic motifs are present throughout, such as large animals and particular geometric patterns. Some art is traditionally associated with particular genders. For example, the Tais
''Tais'' is a form of ''Tenun'' weaving tradition native to the eastern Indonesian regions of the Maluku Islands, the Tanimbar Islands, and the East Nusa Tenggara Islands (in Timor Island, the political government divided into West Timor of ...
textiles that play a widespread role in traditional life throughout the island are traditionally handwoven by women. Different tais
''Tais'' is a form of ''Tenun'' weaving tradition native to the eastern Indonesian regions of the Maluku Islands, the Tanimbar Islands, and the East Nusa Tenggara Islands (in Timor Island, the political government divided into West Timor of ...
patterns are associated with different communities and more broadly linguistic groups. Many buildings within central Dili maintain historical Portuguese architecture.
Traditional rituals retain important, often mixed in with more modern aspects. A strong oral history is highlighted in individuals able to recite long stories or poetry. This history, or ''Lia nain'', passed down traditional knowledge. There remains a strong tradition of poetry. Prime Minister Xanana Gusmão, for example, is a distinguished poet, earning the moniker "poet warrior".
See also
* Outline of East Timor *Index of East Timor-related articles
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (; ), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-west ...
* List of topics on the Portuguese Empire in the East
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * , a bibliographic reference, launched by PMXanana Gusmão
José Alexandre "Xanana" Gusmão (; born 20 June 1946) is an East Timorese politician. A former rebel, he was the third President of the independent East Timor, serving from 2002 to 2007. He then became its fourth prime minister, serving from ...
''East Timor, politics and elections'' (in Chinese)/ 东帝汶政治与选举 (2001–2006): 国家建设及前景展望
Jean A. Berlie, Institute of Southeast Asian Studies of Jinan University editor, Jinan, China, published in 2007. *
External links
GovernmentTimor-Leste official government website
Timor-Leste official tourism website
General information
Timor-Leste
'' The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
East Timor
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
East Timor
at ''
Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
''
East Timor profile
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
*
Key Development Forecasts for Timor-Leste
from International Futures
Timor Leste Studies Association
{{Authority control * 1975 establishments in Asia 2002 establishments in Asia Countries in Asia Island countries of the Indian Ocean Island countries Former Portuguese colonies Least developed countries Maritime Southeast Asia Member states of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries Member states of the United Nations Members of the Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Portuguese-speaking countries and territories Republics Small Island Developing States Southeast Asian countries States and territories established in 1975 States and territories established in 2002 Malay-speaking countries and territories