East African Rift on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
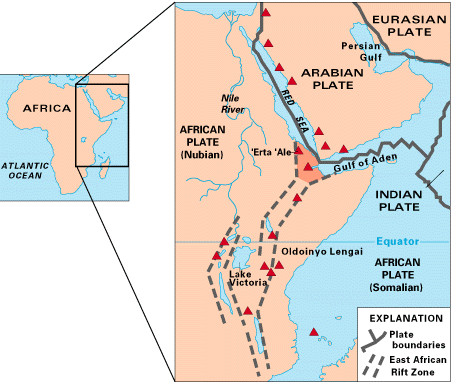 The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in
 A series of distinct rift basins, the East African Rift System extends over thousands of kilometers. The EAR consists of two main branches. The Eastern Rift Valley (also known as Gregory Rift) includes the
A series of distinct rift basins, the East African Rift System extends over thousands of kilometers. The EAR consists of two main branches. The Eastern Rift Valley (also known as Gregory Rift) includes the
 The African continental crust is generally cool and strong. Many
The African continental crust is generally cool and strong. Many
 The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a larger Great Rift Valley that extended north to Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
.
A narrow zone, the rift is a developing divergent tectonic plate boundary where the African Plate is in the process of splitting into two tectonic plates, called the Somali Plate and the Nubian Plate, at a rate of 6-7 mm per year. The rift system consists of three microplates, the Victoria Microplate to the north, and the Rovuma and Lwandle microplates to the south. The Victoria Microplate is rotating anti-clockwise with respect to the African plate. Its rotation is caused by the configuration of mechanically weaker and stronger lithospheric regions in the EARS.
Extent
Main Ethiopian Rift
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
, running eastward from the Afar Triple Junction
The Afar Triple Junction (also called the Afro-Arabian Rift System) is located along a divergent plate boundary dividing the Nubian, Somali, and Arabian plates. This area is considered a present-day example of continental rifting leading to s ...
, which continues south as the Kenyan Rift Valley. The Western Rift Valley includes the Albertine Rift, and farther south, the valley of Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, is an African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
It is the fifth largest f ...
. To the north of the Afar Triple Junction, the rift follows one of two paths: west to the Red Sea Rift or east to the Aden Ridge
The Aden Ridge is a part of an active oblique rift system located in the Gulf of Aden, between Somalia and the Arabian Peninsula to the north. The rift system marks the divergent boundary between the Somali and Arabian tectonic plates, extending ...
in the Gulf of Aden.
The EAR runs from the Afar Triple Junction in the Afar Triangle of Ethiopia through eastern Africa, terminating in Mozambique. The EAR transects through Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, Congo DR, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The ...
, Rwanda
Rwanda (; rw, u Rwanda ), officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of Central Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator ...
, Burundi
Burundi (, ), officially the Republic of Burundi ( rn, Repuburika y’Uburundi ; Swahili: ''Jamuhuri ya Burundi''; French: ''République du Burundi'' ), is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley at the junction between the African Gr ...
, Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
, Malawi
Malawi (; or aláwi Tumbuka: ''Malaŵi''), officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northe ...
and Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
. It also runs offshore of the coast of Mozambique along the Kerimba and Lacerda grabens, which are joined by the Davie Ridge, a relic fracture zone that cuts across the West Somali basin, straddling the boundary between Tanzania and Mozambique. The Davie Ridge ranges between wide, with a west-facing scarp (east-plunging arch) along the southern half of its length that rises to above the sea floor. Its movement is concurrent with the EAR.
Competing theories on geologic evolution
Over time, many theories have tried to clarify the evolution of the East African Rift. In 1972 it was proposed that the EAR was not caused by tectonic activity, but rather by differences in crustal density. Since the 1990s, evidence has been found in favor of mantle plumes beneath the EAR. Others proposed an African superplume causing mantle deformation. Although the effects of deep-rootedmantle plumes
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hots ...
are an important hypothesis, their location and dynamics are poorly understood, and a matter of active research. The question is still debated.
The most recent and accepted view is the theory put forth in 2009: that magmatism and plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of larg ...
have a feedback with one another, controlled by oblique rifting conditions. According to this theory, lithospheric thinning generates volcanic activity, further increasing magmatic processes such as intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s and numerous small plumes. These processes further thin the lithosphere in saturated areas, making the thinning lithosphere behave like a mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a div ...
. According to marine geologist Kathleen Crane
Kathleen (Kathy) Crane (born 1951) is an American marine geologist, best known for her contributions to the discovery of hydrothermal vents on the Galápagos Rift along the East Pacific Rise in the mid-1970s.
Education
Crane received a Bachelo ...
, the rift could eventually cause eastern Africa to separate from the mainland, although this potential event could take tens of millions of years.
Studies that contribute to the broader understanding on the evolution of rifts can be grouped into the techniques of isotope geochemistry, seismic tomography and geodynamical modeling.
Isotope geochemistry
The varying geochemical signatures of a suite of Ethiopian lavas suggest multiple plume sources: at least one of deep mantle origin, and one from within the subcontinental lithosphere. In accordance, a 2014 study 2014 compares the geochemical signature of rare earthisotopes
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers ( mass numbers ...
from xenolith
A xenolith ("foreign rock") is a rock fragment ( country rock) that becomes enveloped in a larger rock during the latter's development and solidification. In geology, the term ''xenolith'' is almost exclusively used to describe inclusions in ig ...
s and lava samples collected in the EAR. The results corroborate the coexistence of a superplume "common to the entire rift" with another mantle material source being either of subcontinental type or of mid-ocean ridge type.
Seismic tomography
The geophysical method ofseismic tomography
Seismic tomography or seismotomography is a technique for imaging the subsurface of the Earth with seismic waves produced by earthquakes or explosions. P-, S-, and surface waves can be used for tomographic models of different resolutions based on ...
is a suitable tool to investigate Earth's subsurface structures deeper than the crust. It is an inverse problem technique that models which are the velocities of the inner Earth that reproduce the seismographic data recorded all around the world. Recent improvements of tomographic Earth models of P-wave
A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an earthquake to arrive at any ...
and S-wave velocities suggest that a superplume upwelling from the lower mantle at the northeastern EAR feeds plumes of smaller scale into the upper mantle.
Geodynamical modeling
Parallel to geological and geophysical measures (e.g. isotope ratios and seismic velocities) it is constructive to test hypotheses on computer based geodynamical models. A 3D numerical geodynamic model of the plume-crust coupling was capable of reproducing the lateral asymmetry of the EAR around the Tanzania craton. Numerical modeling of plume-induced continental break-up shows two distinct stages, crustal rifting followed by lithospheric breakup, and the upwelling between stages of an upper mantle plume.Geologic evolution
Prior to rifting, enormous continental flood basalts erupted on the surface and uplift of theEthiopian
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
, Somali, and East African plateaus occurred. The first stage of rifting of the EAR is characterized by rift localization and magmatism along the entire rift zone. Periods of extension alternated with times of relative inactivity. There was also the reactivation of a pre-Cambrian weakness in the crust, a suture zone of multiple cratons, displacement along large boundary faults, and the development of deep asymmetric basins. The second stage of rifting is characterized by the deactivation of large boundary faults, the development of internal fault segments, and the concentration of magmatic activity towards the rifts.
Today, the narrow rift segments of the East African Rift system form zones of localized strain. These rifts are the result of the actions of numerous normal faults which are typical of all tectonic rift zones. As aforementioned, voluminous magmatism and continental flood basalts characterize some of the rift segments, while other segments, such as the Western branch, have only very small volumes of volcanic rock.
Petrology
 The African continental crust is generally cool and strong. Many
The African continental crust is generally cool and strong. Many craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
s are found throughout the EAR, such as the Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
and Kaapvaal cratons. The cratons are thick, and have survived for billions of years with little tectonic activity. They are characterized by greenstone belts, tonalites, and other high-grade metamorphic lithologies. The cratons are of significant importance in terms of mineral resources
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
, with major deposits of gold, antimony, iron, chromium and nickel.
A large volume of continental flood basalts erupted during the Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but t ...
, with the majority of the volcanism coinciding with the opening of the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden approximately 30 Ma. The composition of the volcanics are a continuum of ultra-alkaline to tholeiitic and felsic rocks. It has been suggested that the diversity of the compositions could be partially explained by different mantle source regions. The EAR also cuts through old sedimentary rocks deposited in ancient basins.
Volcanism and seismicity
The East African Rift Zone includes a number of active and dormant volcanoes, among them:Mount Kilimanjaro
Mount Kilimanjaro () is a dormant volcano in Tanzania. It has three volcanic cones: Kibo, Mawenzi, and Shira. It is the highest mountain in Africa and the highest free-standing mountain above sea level in the world: above sea level and a ...
, Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya (Kikuyu language, Kikuyu: ''Kĩrĩnyaga'', Kamba language, Kamba, ''Ki Nyaa'') is the highest mountain in Kenya and the Highest mountain peaks of Africa, second-highest in Africa, after Mount Kilimanjaro, Kilimanjaro. The highest pea ...
, Mount Longonot, Menengai
Menengai Crater is a massive shield volcano with one of the biggest calderas in the world, in the Great Rift Valley, Kenya. It is the largest volcano caldera in Kenya and the second largest volcano caldera in Africa. Volcanic formed rich loam soil ...
Crater, Mount Karisimbi, Mount Nyiragongo, Mount Meru and Mount Elgon
Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya, north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda.
, as well as the Crater Highlands
The Crater Highlands (Ngorongoro Highlands) are a geological region along the East African Rift in the Arusha Region and parts of northern Manyara Region in north Tanzania.
Geology
The highlands are located in a spreading zone at the inters ...
in Tanzania. Although most of these mountains lie outside of the rift valley, the EAR created them.
Notable active examples of EAR volcanism include Erta Ale, Dalaffilla
Dalaffilla, also called Gabuli, or Alu-Dalafilla is a high stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, str ...
(also called Gabuli, Alu-Dalafilla), and Ol Doinyo Lengai. Erta Ale is a basaltic shield volcano in the Afar Region of northeastern Ethiopia, continuously active since at least 1967, with a summit lava lake documented since at least 1906. The 2008 eruption of Dalafilla, its only documented activity since the start of the Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
, is the largest recorded eruption in Ethiopian history. Ol Doinyo Lengai is currently the only active natrocarbonatite volcano on Earth. Its magma contains almost no silica; typical lava flows have viscosities
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its drag (physics), resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quant ...
of less than 100 Pa s, comparable to olive oil at 26 °C. EAR-related volcanic structures with dated activity since the onset of the Holocene include approximately 50 in Ethiopia, 17 in Kenya, and 9 in Tanzania.
The EAR is the largest seismically active rift system on Earth today. The majority of earthquakes
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fro ...
occur near the Afar Depression, with the largest typically occurring along or near major border faults. Seismic events in the past century are estimated to have reached a maximum moment magnitude of 7.0. The seismicity trends parallel to the rift system, with a shallow focal depth of beneath the rift axis. Further away from the rift axis, focal depths can be below . Focal mechanism
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the deformation in the source region that generates the seismic waves. In the case of a fault-related event it refers to the orientation of the fault plane that slipped and the slip vector and ...
solutions strike NE and frequently demonstrate normal dip-slip faulting, although left-lateral motion is also observed.
Discoveries in human evolution
The Rift Valley in East Africa has been a rich source ofhominid
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the ...
fossils that allow the study of human evolution. The rapidly eroding highlands quickly filled the valley with sediments, creating a favorable environment for the preservation of remains. The bones of several hominid ancestors of modern humans have been found here, including those of " Lucy", a partial australopithecine
Australopithecina or Hominina is a subtribe in the tribe Hominini. The members of the subtribe are generally ''Australopithecus'' ( cladistically including the genera ''Homo'', '' Paranthropus'', and ''Kenyanthropus''), and it typically inclu ...
skeleton discovered by anthropologist Donald Johanson
Donald Carl Johanson (born June 28, 1943) is an American paleoanthropologist. He is known for discovering, with Yves Coppens and Maurice Taieb, the fossil of a female hominin australopithecine known as "Lucy" in the Afar Triangle region of Hada ...
dating back over 3 million years. Richard
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'stro ...
and Mary Leakey have also done significant work in this region.
In 2008, two other hominid ancestors have been discovered here: a 10-million-year-old ape called '' Chororapithecus abyssinicus'', found in the Afar rift in eastern Ethiopia, and ''Nakalipithecus nakayamai
''Nakalipithecus nakayamai'' is an extinct species of great ape from Nakali, Kenya, from about 9.9–9.8 million years ago during the Late Miocene. It is known from a right jawbone with 3 molars and from 11 isolated teeth, and the specimen is p ...
'', which is also 10 million years old.
See also
*Baikal Rift Zone The Baikal Rift Zone is a series of continental rifts centered beneath Lake Baikal in southeastern Russia. Current strain in the rifts tends to be extending with some shear movement. A series of basins form along the zone for more than , creatin ...
*Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface area after ...
* Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province
* West Antarctic Rift System
*West and Central African Rift System
The West and Central African Rift System (WCARS) is a rift system composed of two coeval Cretaceous rift sub-systems, the West African Rift sub-system (WAS) and the Central African Rift sub-system (CAS). These are genetically related, but are ph ...
References
{{coord, 3.0000, S, 35.5000, E, source:wikidata, display=title Cenozoic rifts and grabens Great Rift Valley