Early modern Europe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Early modern Europe, also referred to as the post-medieval period, is the period of
Early modern Europe, also referred to as the post-medieval period, is the period of
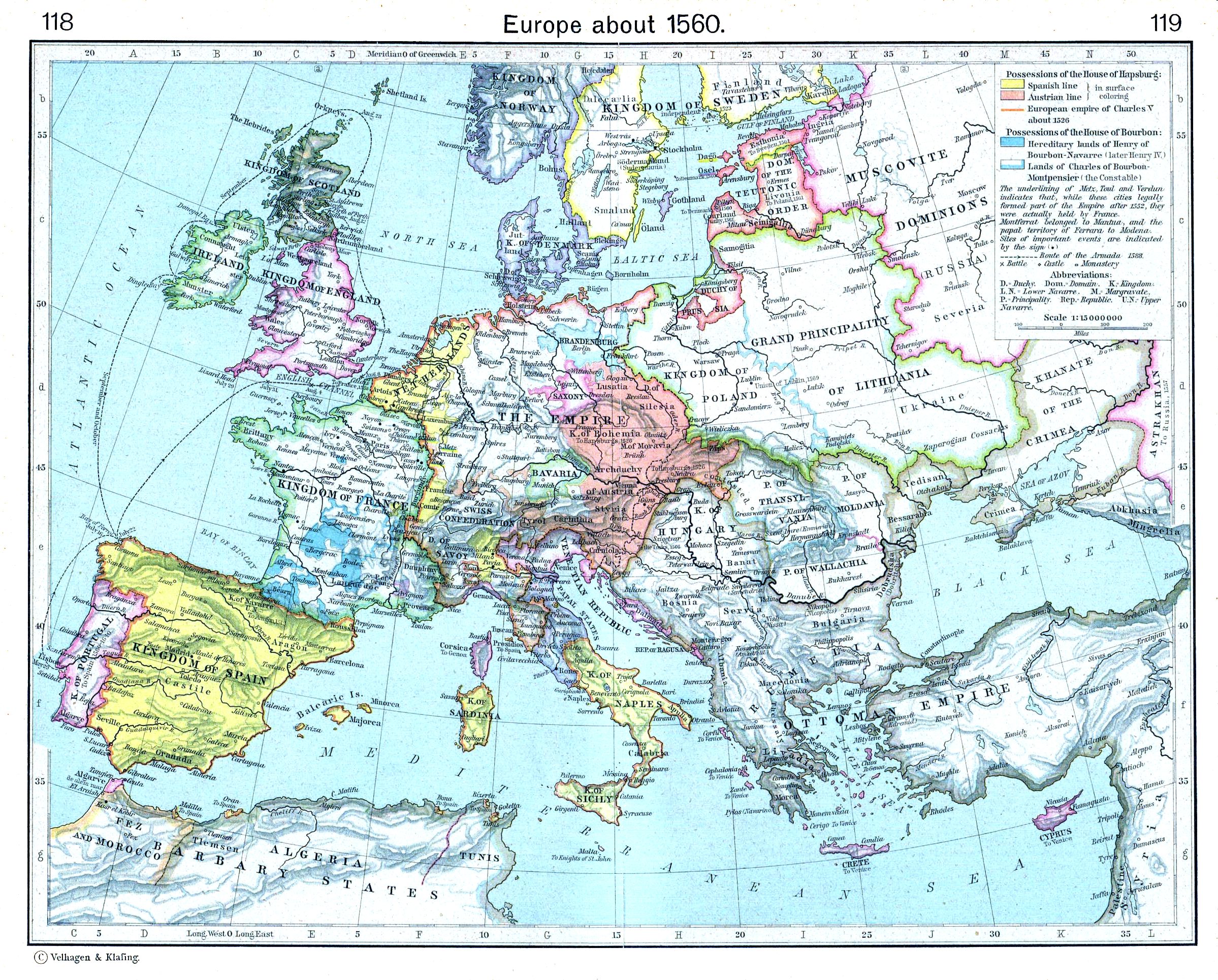 Regardless of the precise dates used to define its beginning and end points, the early modern period is generally agreed to have comprised the
Regardless of the precise dates used to define its beginning and end points, the early modern period is generally agreed to have comprised the
 The Reformation reshaped the
The Reformation reshaped the
 The 17th century saw very little peace in Europe – major wars were fought in 95 years (every year except 1610, 1669 to 1671, and 1680 to 1682.) The wars were unusually ugly. Europe in the late 17th century, 1648 to 1700, was an age of great intellectual, scientific, artistic and cultural achievement. Historian Frederick Nussbaum says it was:
"prolific in genius, in common sense, and in organizing ability. It could properly have been expected that intelligence, comprehension and high purpose would be applied to the control of human relations in general and to the relations between states and peoples in particular. The fact was almost completely opposite. It was a period of marked unintelligence, immorality and frivolity in the conduct of international relations, marked by wars undertaken for dimly conceived purposes, waged with the utmost brutality and conducted by reckless betrayals of allies."
The worst came during the
The 17th century saw very little peace in Europe – major wars were fought in 95 years (every year except 1610, 1669 to 1671, and 1680 to 1682.) The wars were unusually ugly. Europe in the late 17th century, 1648 to 1700, was an age of great intellectual, scientific, artistic and cultural achievement. Historian Frederick Nussbaum says it was:
"prolific in genius, in common sense, and in organizing ability. It could properly have been expected that intelligence, comprehension and high purpose would be applied to the control of human relations in general and to the relations between states and peoples in particular. The fact was almost completely opposite. It was a period of marked unintelligence, immorality and frivolity in the conduct of international relations, marked by wars undertaken for dimly conceived purposes, waged with the utmost brutality and conducted by reckless betrayals of allies."
The worst came during the
 This period refers to England 1558–1603. The
This period refers to England 1558–1603. The
online
* Dorn, Walter L. ''Competition For Empire 1740–1763'' (1940
online
* DuPlessis, Robert S. ''Transitions to capitalism in early modern Europe'' (2019). * Flinn, Michael W. ''The European Demographic System, 1500–1820'' (1981) * Gatti, Hilary. ''Ideas of Liberty in Early Modern Europe'' (2015). * Gershoy, Leo. ''From Despotism To Revolution: 1763–1789'' (1944
online
* Grafton, Anthony. ''Inky Fingers: The Making of Books in Early Modern Europe'' (2020). * Gribben, Crawford, and Graeme Murdock, eds. ''Cultures of Calvinism in Early Modern Europe'' (Oxford UP, 2019). * Gutmann, Myron P. ''Toward the Modern Economy: Early Industry in Europe, 1500–1800'' (1988) * Hesmyr, Atle: ''Scandinavia in the Early Modern Era''(2017). * Hill, David Jayne. ''A history of diplomacy in the international development of Europe'' (3 vol. 1914
online
* Jacob, Margaret C. ''Strangers nowhere in the world: the rise of cosmopolitanism in early modern Europe'' (2017). * Kennedy, Paul. ''The rise and fall of the great powers'' (2010). * Klein, Alexander, and Jelle Van Lottum. "The Determinants of International Migration in Early Modern Europe: Evidence from the Maritime Sector, c. 1700–1800." ''Social Science History'' 44.1 (2020): 143–16
online
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973), very detailed outline * Levine, David. "The Population of Europe: Early Modern Demographic Patterns." in ''Encyclopedia of European Social History,'' edited by Peter N. Stearns, (vol. 2, 2001), pp. 145–157
online
* Lindsay, J. O. ed. ''New Cambridge Modern History: The Old Regime, 1713–1763'' (1957
online
* Merriman, John. ''A History of Modern Europe: From the Renaissance to the Present'' (3rd ed. 2009, 2 vol), 1412 pp. * Mowat, R. B. ''History of European Diplomacy, 1451–1789'' (1928) 324 pp
online free
* Nussbaum, Frederick L. ''The triumph of science and reason, 1660–1685'' (1953), Despite the narrow title is a general survey of European history. * Parker, Geoffrey. ''The Military Revolution: Military Innovation and the Rise of the West, 1500–1800'' (1996) * Petrie, Charles. ''Earlier diplomatic history, 1492–1713'' (1949), covers all of Europe
online
** Petrie, Charles. ''Diplomatic History, 1713–1933'' (1946), broad summar
online
* Pollmann, Judith. ''Memory in early modern Europe, 1500–1800'' (Oxford UP, 2017). * Rice, Eugene F. ''The Foundations of Early Modern Europe, 1460–1559'' (2nd ed. 1994) 240 pp. * Schroeder, Paul. ''The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848'' (1994
online
advanced diplomatic history * Scott, Hamish, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of Early Modern European History, 1350–1750: Volume I: Peoples and Place'' (2015); Volume II: Cultures and Power (2015). * "The State Church in Early-Modern Europe." in ''Arts and Humanities Through the Eras'', edited by Edward I. Bleiberg, et al., (vol. 5: The Age of the Baroque and Enlightenment 1600–1800, Gale, 2005), pp. 336–341
online
* Stearns, Peter N., ed. ''Encyclopedia of European Social History'' (6 vol 2000), 3000 pp; overview vol. 1 pp. 165–77, plus hundreds of articles * Tallett, Frank. ''War and Society in Early Modern Europe: 1495–1715'' (2016). * Wiesner, Merry E. ''Early Modern Europe, 1450–1789'' (3rd ed. 2022) * Wiesner-Hanks, Merry E. ''Women and gender in early modern Europe'' (Cambridge UP, 2019). * Wolf, John B. ''The Emergence of the Great Powers, 1685–1715'' (1951
online
from the introduction to the pioneering '' Cambridge Modern History'' (1903)
Society for Renaissance Studies
{{DEFAULTSORT:Early Modern Europe * History of Europe by period Western culture
 Early modern Europe, also referred to as the post-medieval period, is the period of
Early modern Europe, also referred to as the post-medieval period, is the period of European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500–1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500).
The first early Eu ...
between the end of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and the beginning of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, roughly the mid 15th century to the late 18th century. Historians variously mark the beginning of the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
with the invention of moveable type
Movable type (US English; moveable type in British English) is the system and technology of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document (usually individual alphanumeric characters or punctuation ...
printing in the 1450s, the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
and end of the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
in 1453, the end of the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses, known at the time and in following centuries as the Civil Wars, were a series of armed confrontations, machinations, battles and campaigns fought over control of the English throne from 1455 to 1487. The conflict was fo ...
in 1485, the beginning of the High Renaissance
In art history, the High Renaissance was a short period of the most exceptional artistic production in the Italian states, particularly Rome, capital of the Papal States, and in Florence, during the Italian Renaissance. Most art historians stat ...
in Italy in the 1490s, the end of the Reconquista
The ''Reconquista'' (Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese for ) or the fall of al-Andalus was a series of military and cultural campaigns that European Christian Reconquista#Northern Christian realms, kingdoms waged ag ...
and subsequent voyages of Christopher Columbus
Between 1492 and 1504, the Italian explorer and navigator Christopher Columbus led four transatlantic maritime expeditions in the name of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain to the Caribbean and to Central and South America. These voyages led to t ...
to the Americas in 1492, or the start of the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
in 1517. The precise dates of its end point also vary and are usually linked with either the start of the French Revolution in 1789 or with the more vaguely defined beginning of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
in late 18th century England.
Some of the more notable trends and events of the early modern period included the Reformation and the religious conflicts it provoked (including the French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants (called Huguenots) from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease di ...
and the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
), the rise of capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
and modern nation state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
s, widespread witch hunts and European colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale colonization of the Americas, involving a number of European countries, took place primarily between the late 15th century and the early 19th century. The Norse explored and colonized areas of Europe a ...
.
Characteristics
The modern period was characterized by profound changes in many realms of human endeavor. Among the most important include the development of science as a formalized practice, increasingly rapid technological progress, and the establishment of secularized civic politics,law court
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a Socia ...
s and the nation state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
. Capitalist economies began to develop in a nascent form, first in the northern Italian republics such as Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
and Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
as well as in the cities of the Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
, and later in France, Germany and England. The early modern period also saw the rise and dominance of the economic theory of mercantilism
Mercantilism is a economic nationalism, nationalist economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports of an economy. It seeks to maximize the accumulation of resources within the country and use those resources ...
. As such, the early modern period is often associated with the decline and eventual disappearance (at least in Western Europe) of feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of struc ...
and serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed du ...
dom. The Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
greatly altered the religious balance of Christendom
The terms Christendom or Christian world commonly refer to the global Christian community, Christian states, Christian-majority countries or countries in which Christianity is dominant or prevails.SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christen ...
, creating a formidable new opposition to the dominance of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, especially in Northern Europe. The early modern period also witnessed the circumnavigation
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical object, astronomical body (e.g. a planet or natural satellite, moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth.
The first circumnaviga ...
of the Earth and the establishment of regular European contact with the Americas and South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
and East Asia. The ensuing rise of global systems of international economic, cultural and intellectual exchange played an important role in the development of capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their use for the purpose of obtaining profit. This socioeconomic system has developed historically through several stages and is defined by ...
and represents an identifiable early phase of globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
.
Periodization
 Regardless of the precise dates used to define its beginning and end points, the early modern period is generally agreed to have comprised the
Regardless of the precise dates used to define its beginning and end points, the early modern period is generally agreed to have comprised the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
, the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
, and the Enlightenment. As such, historians have attributed a number of fundamental changes to the period, notably the increasingly rapid progress of science and technology, the secularization of politics, and the diminution of the absolute authority of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
as well as the lessening of the influence of all faiths upon national governments. Many historians have identified the early modern period as the epoch in which individuals began to think of themselves as belonging to a national polity—a notable break from medieval modes of self-identification, which had been largely based upon religion (belonging to a universal Christendom
The terms Christendom or Christian world commonly refer to the global Christian community, Christian states, Christian-majority countries or countries in which Christianity is dominant or prevails.SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christen ...
), language, or feudal allegiance (belonging to the manor or extended household of a particular magnate
The term magnate, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
or lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power (social and political), power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the Peerage o ...
).
The beginning of the early modern period is not clear-cut, but is generally accepted to be in the late 15th century or early 16th century. Significant dates in this transitional phase from medieval to early modern Europe can be noted:
* 1450: The invention of the first European movable type
Movable type (US English; moveable type in British English) is the system and technology of printing and typography that uses movable Sort (typesetting), components to reproduce the elements of a document (usually individual alphanumeric charac ...
printing process by Johannes Gutenberg
Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg ( – 3 February 1468) was a German inventor and Artisan, craftsman who invented the movable type, movable-type printing press. Though movable type was already in use in East Asia, Gutenberg's inven ...
, a device that fundamentally changed the circulation of information. Movable type, which allowed individual characters to be arranged to form words and which is an invention separate from the printing press, had been invented earlier in China.
* 1453: The conquest of Constantinople by the Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
signalled the end of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
; the Battle of Castillon
The Battle of Castillon was a battle between the forces of England and France which took place on 17 July 1453 in Gascony near the town of Castillon-sur-Dordogne (later Castillon-la-Bataille).
On the day of the battle, the English commande ...
concluded the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
.
* 1485: The last Plantagenet
The House of Plantagenet ( /plænˈtædʒənət/ ''plan-TAJ-ə-nət'') was a royal house which originated from the French county of Anjou. The name Plantagenet is used by modern historians to identify four distinct royal houses: the Angev ...
king of England, Richard III
Richard III (2 October 1452 – 22 August 1485) was King of England from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the Plantagenet dynasty and its cadet branch the House of York. His defeat and death at the Battle of Boswor ...
, was killed at Bosworth and the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses, known at the time and in following centuries as the Civil Wars, were a series of armed confrontations, machinations, battles and campaigns fought over control of the English throne from 1455 to 1487. The conflict was fo ...
gave way to early modern Tudor monarchy, in the person of Henry VII.
* 1492: The first documented European voyage to the Americas by the Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
; the end of the Reconquista
The ''Reconquista'' (Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese for ) or the fall of al-Andalus was a series of military and cultural campaigns that European Christian Reconquista#Northern Christian realms, kingdoms waged ag ...
, with the final expulsion of the Moors
The term Moor is an Endonym and exonym, exonym used in European languages to designate the Muslims, Muslim populations of North Africa (the Maghreb) and the Iberian Peninsula (particularly al-Andalus) during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a s ...
from the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
; the Spanish government expels the Jews.
* 1494: French king Charles VIII invaded Italy, drastically altering the status quo and beginning a series of wars which would punctuate the Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( ) was a period in History of Italy, Italian history between the 14th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Western Europe and marked t ...
.
* 1513: First formulation of modern politics with the publication of Machiavelli's ''The Prince
''The Prince'' ( ; ) is a 16th-century political treatise written by the Italian diplomat, philosopher, and Political philosophy, political theorist Niccolò Machiavelli in the form of a realistic instruction guide for new Prince#Prince as gener ...
''.
* 1517: The Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
begins with Martin Luther
Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Pr ...
nailing his ninety-five theses to the door of the church in Wittenberg
Wittenberg, officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg, is the fourth-largest town in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, in the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. It is situated on the River Elbe, north of Leipzig and south-west of the reunified German ...
, Germany.
* 1526: Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand I (10 March 1503 – 25 July 1564) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1556, King of Bohemia, King of Hungary, Hungary, and List of rulers of Croatia, Croatia from 1526, and Archduke of Austria from 1521 until his death in 1564.Milan Kruhek ...
gains the crowns of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
and Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
.
* 1545: The Council of Trent
The Council of Trent (), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation at the time, it has been described as the "most ...
begins Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
and marks the end of the medieval Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
."Trent, Council of" in Cross, F. L. (ed.) ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church'', Oxford University Press, 2005 ().
The end date of the early modern period is variously associated with the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, which began in Britain in about 1750, or the beginning of the French Revolution in 1789, which drastically transformed the state of European politics and ushered in the Napoleonic era
The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France and history of Europe, Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly (French Revoluti ...
and modern Europe.
The role of nobles in the Feudal System
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring socie ...
had yielded to the notion of the Divine Right of Kings during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
(in fact, this consolidation of power from the land-owning nobles to the titular monarchs was one of the most prominent themes of the Middle Ages). Among the most notable political changes included the abolition of serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed du ...
and the crystallization of kingdoms into nation-states. Perhaps even more significantly, with the advent of the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
, the notion of Christendom
The terms Christendom or Christian world commonly refer to the global Christian community, Christian states, Christian-majority countries or countries in which Christianity is dominant or prevails.SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christen ...
as a unified political entity was destroyed. Many kings and rulers used this radical shift in the understanding of the world to further consolidate their sovereignty over their territories. For instance, many of the Germanic states (as well as English Reformation
The English Reformation began in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away first from the authority of the pope and bishops Oath_of_Supremacy, over the King and then from some doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church ...
) converted to Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
in an attempt to slip out of the grasp of the Pope.
The intellectual developments of the period included the creation of the economic theory of mercantilism
Mercantilism is a economic nationalism, nationalist economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports of an economy. It seeks to maximize the accumulation of resources within the country and use those resources ...
and the publication of enduringly influential works of political and social philosophy, such as Machiavelli's ''The Prince
''The Prince'' ( ; ) is a 16th-century political treatise written by the Italian diplomat, philosopher, and Political philosophy, political theorist Niccolò Machiavelli in the form of a realistic instruction guide for new Prince#Prince as gener ...
'' (1513) and Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, theologian, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VII ...
's ''Utopia
A utopia ( ) typically describes an imagined community or society that possesses highly desirable or near-perfect qualities for its members. It was coined by Sir Thomas More for his 1516 book ''Utopia (book), Utopia'', which describes a fictiona ...
'' (1515).
Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a reform-orientedschism
A schism ( , , or, less commonly, ) is a division between people, usually belonging to an organization, movement, or religious denomination. The word is most frequently applied to a split in what had previously been a single religious body, suc ...
from the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
initiated by Martin Luther
Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Pr ...
and continued by John Calvin
John Calvin (; ; ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French Christian theology, theologian, pastor and Protestant Reformers, reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of C ...
, Huldrych Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a Swiss Christian theologian, musician, and leader of the Reformation in Switzerland. Born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swis ...
, and other early Protestant Reformers. It is typically dated from 1517, lasting until the end of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
(1618–1648) with the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
in 1648. It was launched on 31 October 1517 by Martin Luther
Martin Luther ( ; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, Theology, theologian, author, hymnwriter, professor, and former Order of Saint Augustine, Augustinian friar. Luther was the seminal figure of the Reformation, Pr ...
, who posted his 95 Theses criticizing the practice of indulgences to the door of the Castle Church in Wittenberg
Wittenberg, officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg, is the fourth-largest town in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, in the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. It is situated on the River Elbe, north of Leipzig and south-west of the reunified German ...
, Germany, commonly used to post notices to the University community. It was very widely publicized across Europe and caught fire. Luther began by criticizing the sale of indulgences, insisting that the Pope had no authority over purgatory
In Christianity, Purgatory (, borrowed into English language, English via Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman and Old French) is a passing Intermediate state (Christianity), intermediate state after physical death for purifying or purging a soul ...
and that the Catholic doctrine of the merits of the saints had no foundation in the gospel. The Protestant position, however, would come to incorporate doctrinal changes such as '' sola scriptura'' and ''sola fide
(or simply ), meaning justification by faith alone, is a soteriological doctrine in Christian theology commonly held to distinguish the Lutheranism, Lutheran and Reformed tradition, Reformed traditions of Protestantism, among others, from th ...
''.
The Reformation ended in division and the establishment of new church movements. The four most important traditions to emerge directly from the Reformation were Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
ism, the Reformed (also called Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continenta ...
or Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
) tradition, Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
, and the Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism'; , earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
s. Subsequent Protestant churches generally trace their roots back to these initial four schools of the Reformation. It also led to the Catholic or Counter Reformation within the Roman Catholic Church through a variety of new spiritual movements, reforms of religious communities, the founding of seminaries, the clarification of Catholic theology as well as structural changes in the institution of the Church.
The largest Protestant groups were the Lutherans
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation in 15 ...
and Calvinists. Lutheran churches were founded mostly in Germany, the Baltics and Scandinavia, while the Reformed ones were founded in Switzerland, Hungary, France, the Netherlands and Scotland.
The initial movement within Germany diversified, and other reform impulses arose independently of Luther. The availability of the printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
provided the means for the rapid dissemination of religious materials in the vernacular. The core motivation behind the Reformation was theological
Theology is the study of religious belief from a religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of an ...
, though many other factors played a part, including the rise of nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
, the Western Schism
The Western Schism, also known as the Papal Schism, the Great Occidental Schism, the Schism of 1378, or the Great Schism (), was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 20 September 1378 to 11 November 1417, in which bishops residing ...
that eroded faith in the Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, the perceived corruption of the Roman Curia
The Roman Curia () comprises the administrative institutions of the Holy See and the central body through which the affairs of the Catholic Church are conducted. The Roman Curia is the institution of which the Roman Pontiff ordinarily makes use ...
, the impact of humanism
Humanism is a philosophy, philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential, and Agency (philosophy), agency of human beings, whom it considers the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The me ...
, and the new learning of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
that questioned much traditional thought.
There were also reformation movements throughout continental Europe known as the Radical Reformation
The Radical Reformation represented a response to perceived corruption both in the Catholic Church and in the expanding Magisterial Protestant movement led by Martin Luther and many others. Starting in Germany and Switzerland in the 16th cen ...
, which gave rise to the Anabaptist
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek language, Greek : 're-' and 'baptism'; , earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
, Moravian and other Pietistic movements.
The Roman Catholic Church responded with a Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
initiated by the Council of Trent
The Council of Trent (), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation at the time, it has been described as the "most ...
. Much work in battling Protestantism was done by the well-organised new order of the Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
. In general, Northern Europe, with the exception of most of Ireland, came under the influence of Protestantism. Southern Europe remained Roman Catholic, while Central Europe was a site of a fierce conflict, culminating in the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, which left it devastated.
Church of England
 The Reformation reshaped the
The Reformation reshaped the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
decisively after 1547. The separation of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
(or Anglican Church) from Rome under Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
, beginning in 1529 and completed in 1537, brought England alongside this broad Reformation movement; however, religious changes in the English national church proceeded more conservatively than elsewhere in Europe. Reformers in the Church of England alternated, for decades, between sympathies for ancient Catholic tradition and more Reformed principles, gradually developing, within the context of robustly Protestant doctrine, a tradition considered a middle way ('' via media'') between the Roman Catholic and Protestant traditions.
Consequences of the Protestant Reformation
The following outcomes of the Protestant Reformation regardinghuman capital
Human capital or human assets is a concept used by economists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a subs ...
formation, the Protestant ethic, economic development
In economics, economic development (or economic and social development) is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and object ...
, governance
Governance is the overall complex system or framework of Process, processes, functions, structures, Social norm, rules, Law, laws and Norms (sociology), norms born out of the Interpersonal relationship, relationships, Social interaction, intera ...
, and "dark" outcomes have been identified by scholars.
Historiography
Margaret C. Jacob argues that there has been a dramatic shift in the historiography of the Reformation. Until the 1960s, historians focused their attention largely on the great leaders and also the theologians of the 16th century, especially Luther, Calvin, and Zwingli. Their ideas were studied in depth. However, the rise of the new social history in the 1960s look at history from the bottom up, not from the top down. Historians began to concentrate on the values, beliefs and behavior of the people at large. She finds, "in contemporary scholarship, the Reformation was then seen as a vast cultural upheaval, a social and popular movement and textured and rich because of its diversity."Age of Enlightenment
"The Age of Enlightenment" refers to the 18th century in European philosophy, and is often thought of as part of a period which includes the Age of Reason. The term also more specifically refers to a historical intellectual movement, ''The Enlightenment''. This movement advocatedrationality
Rationality is the quality of being guided by or based on reason. In this regard, a person acts rationally if they have a good reason for what they do, or a belief is rational if it is based on strong evidence. This quality can apply to an ab ...
as a means to establish an authoritative system of aesthetics
Aesthetics (also spelled esthetics) is the branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of beauty and taste (sociology), taste, which in a broad sense incorporates the philosophy of art.Slater, B. H.Aesthetics ''Internet Encyclopedia of Ph ...
, ethics, and logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
. The intellectual leaders of this movement regarded themselves as a courageous elite, and regarded their purpose as one of leading the world toward progress and out of a long period of doubtful tradition, full of irrationality, superstition, and tyranny, which they believed began during a historical period they called the '' Dark Ages''. This movement also provided a framework for the American and French Revolutions, the Latin American independence movement, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
Constitution of May 3, and also led to the rise of liberalism and the birth of socialism
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
and communism
Communism () is a political sociology, sociopolitical, political philosophy, philosophical, and economic ideology, economic ideology within the history of socialism, socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a ...
. It is matched by the high baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
and classical eras in music, and the neo-classical period in the arts, and receives contemporary application in the unity of science movement which includes logical positivism
Logical positivism, also known as logical empiricism or neo-positivism, was a philosophical movement, in the empiricist tradition, that sought to formulate a scientific philosophy in which philosophical discourse would be, in the perception of ...
.
Difference between 'early modern' and the Renaissance
The expression "early modern" is sometimes used as a substitute for the termRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, and vice versa. However, "Renaissance" is properly used in relation to a diverse series of cultural developments; which occurred over several hundred years in many different parts of Europe—especially central and northern Italy—and span the transition from late Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
civilization and the opening of the early modern period.
The term "early modern" is most often applied to Europe, and its overseas empire. However, it has also been employed in the history of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. In the historiography of Japan, the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
from 1590 to 1868 is also sometimes referred to as the "early modern" period.
Diplomacy and warfare
 The 17th century saw very little peace in Europe – major wars were fought in 95 years (every year except 1610, 1669 to 1671, and 1680 to 1682.) The wars were unusually ugly. Europe in the late 17th century, 1648 to 1700, was an age of great intellectual, scientific, artistic and cultural achievement. Historian Frederick Nussbaum says it was:
"prolific in genius, in common sense, and in organizing ability. It could properly have been expected that intelligence, comprehension and high purpose would be applied to the control of human relations in general and to the relations between states and peoples in particular. The fact was almost completely opposite. It was a period of marked unintelligence, immorality and frivolity in the conduct of international relations, marked by wars undertaken for dimly conceived purposes, waged with the utmost brutality and conducted by reckless betrayals of allies."
The worst came during the
The 17th century saw very little peace in Europe – major wars were fought in 95 years (every year except 1610, 1669 to 1671, and 1680 to 1682.) The wars were unusually ugly. Europe in the late 17th century, 1648 to 1700, was an age of great intellectual, scientific, artistic and cultural achievement. Historian Frederick Nussbaum says it was:
"prolific in genius, in common sense, and in organizing ability. It could properly have been expected that intelligence, comprehension and high purpose would be applied to the control of human relations in general and to the relations between states and peoples in particular. The fact was almost completely opposite. It was a period of marked unintelligence, immorality and frivolity in the conduct of international relations, marked by wars undertaken for dimly conceived purposes, waged with the utmost brutality and conducted by reckless betrayals of allies."
The worst came during the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, 1618–1648, which had an extremely negative impact on the civilian population of Germany and surrounding areas, with massive loss of life and disruption of the economy and society.
Thirty Years' War: 1618–1648
The Reformation led to a series of religious wars that culminated in theThirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
(1618–1648), which devastated much of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, killing between 25% and 40% of its entire population. Roman Catholic House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful Dynasty, dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout ...
and its allies fought against the Protestant princes of Germany, supported at various times by Denmark, Sweden and France. The Habsburgs, who ruled Spain, Austria, the Crown of Bohemia, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Slovene Lands, the Spanish Netherlands
The Spanish Netherlands (; ; ; ) (historically in Spanish: , the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of t ...
and much of Germany and Italy, were staunch defenders of the Roman Catholic Church. Some historians believe that the era of the Reformation came to a close when Roman Catholic France allied itself with Protestant states against the Habsburg dynasty. For the first time since the days of Martin Luther, political and national convictions again outweighed religious convictions in Europe.
Two main tenets of the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
, which ended the Thirty Years' War, were:
* All parties would now recognise the Peace of Augsburg of 1555, by which each prince would have the right to determine the religion of his own state, the options being Roman Catholicism, Lutheranism, and now Calvinism (the principle of '' cuius regio, eius religio'').
* Christians living in principalities where their denomination was ''not'' the established church were guaranteed the right to practice their faith in public during allotted hours and in private at their will.
The treaty also effectively ended the Papacy's pan-European political power. Pope Innocent X
Pope Innocent X (6 May 1574 – 7 January 1655), born Giovanni Battista Pamphilj (or Pamphili), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 15 September 1644 to his death, in January 1655.
Born in Rome of a family fro ...
declared the treaty "null, void, invalid, iniquitous, unjust, damnable, reprobate, inane, empty of meaning and effect for all times" in his bull ''Zelo Domus Dei''. European sovereigns, Roman Catholic and Protestant alike, ignored his verdict.Cross, (ed.) "Westphalia, Peace of" ''Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church''
Scholars taking a "realist" perspective on wars and diplomacy have emphasized the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
(1648) as a dividing line. It ended the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
(1618–1648), where religion and ideology had been powerful motivating forces for warfare. Westphalia, in the realist view, ushered in a new international system of sovereign states of roughly equal strength, dedicated not to ideology or religion but to enhance status, and territorial gains. The Catholic Church, for example, no longer devoted its energies to the very difficult task of reclaiming dioceses lost to Protestantism, but to build large-scale missions in overseas colonial possessions that could convert the natives by the thousands Using devoted members of society such as the Jesuits. According to Hamish Scott, the realist model assumes that "foreign policies were guided entirely by "Realpolitik," by the resulting struggle for resources and, eventually, by the search for what became known as a 'balance of power.'
Diplomacy before 1700 was not well developed, and chances to avoid wars were too often squandered. In England, for example, King Charles II paid little attention to diplomacy, which proved disastrous. During the Dutch war of 1665–67, England had no diplomats stationed in Denmark or Sweden. When King Charles realized he needed them as allies, he sent special missions that were uninformed about local political, military, and diplomatic situations, and were ignorant of personalities and political factionalism. Ignorance produced a series of blunders that ruined their efforts to find allies. King Louis XIV of France, by contrast, developed the most sophisticated diplomatic service, with permanent ambassadors and lesser ministers in major and minor capitals, all preparing steady streams of information and advice to Paris. Diplomacy became a career that proved highly attractive to rich senior aristocrats who enjoyed very high society at royal courts, especially because they carried the status of the most powerful nation in Europe. Increasingly, other nations copied the French model; French became the language of diplomacy, replacing Latin. By 1700, the British and the Dutch, with small land armies, large navies, and large treasuries, used astute diplomacy to build alliances, subsidizing as needed land powers to fight on their side, or as in the case of the Hessians, hiring regiments of soldiers from mercenary princes in small countries. The balance of power was very delicately calculated, so that winning a battle here was worth the slice of territory there, with no regard to the wishes of the inhabitants. Important peacemaking conferences at Utrecht (1713), Vienna (1738), Aix-la-Chapelle (1748) and Paris (1763) had a cheerful, cynical, game-like atmosphere in which professional diplomats cashed in victories like casino chips in exchange for territory.
Major states
Holy Roman Empire
Since 1512, theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
was also known as the ''Holy Roman Empire of the German nation''. The Habsburg House of Austria held the position of Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
s since the mid-1400s and for the entire Early modern period. Despite the lack of a centralized political structure in a period in which national monarchies were emerging, the Habsburg Emperors of the Early modern period came close to form a universal monarchy in Western Europe.
The Habsburgs expanded their control within and outside the Holy Roman Empire as a result of the dynastic policy pursued by Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I (22 March 1459 – 12 January 1519) was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1508 until his death in 1519. He was never crowned by the Pope, as the journey to Rome was blocked by the Venetians. He proclaimed hi ...
. Maximilian I married Mary of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy (; ; 13 February 1457 – 27 March 1482), nicknamed the Rich, was a member of the House of Valois-Burgundy who ruled the Burgundian lands, comprising the Duchy of Burgundy, Duchy and Free County of Burgundy, County of Burgundy a ...
, thus bringing the Burgundian Netherlands
The Burgundian Netherlands were those parts of the Low Countries ruled by the Dukes of Burgundy during the Burgundian Age between 1384 and 1482. Within their Burgundian State, which itself belonged partly to the Holy Roman Empire and partly t ...
into the Habsburg inheritance. Their son, Philip the Handsome, married Joanna the Mad of Spain (daughter of Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II, also known as Ferdinand I, Ferdinand III, and Ferdinand V (10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), called Ferdinand the Catholic, was King of Aragon from 1479 until his death in 1516. As the husband and co-ruler of Queen Isabella I of ...
and Isabella of Castile). Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain (as Charles I) from 1516 to 1556, and Lord of the Netherlands as titular Duke of Burgundy (as Charles II) ...
(son of Philip and Joanna) inherited the Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands were the parts of the Low Countries that were ruled by sovereigns of the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. This rule began in 1482 and ended for the Northern Netherlands in 1581 and for the Southern Netherlands in 1797. ...
in 1506, Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain refers to Spain and the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy, also known as the Rex Catholicissimus, Catholic Monarchy, in the period from 1516 to 1700 when it was ruled by kings from the House of Habsburg. In t ...
and its territories in 1516, and Habsburg Austria in 1519.
The main opponents of the Habsburg Empire were the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
and the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
. The Habsburgs clashed with France in a series of Italian wars. The Battle of Pavia
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521–1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V, Holy Roman Empero ...
(1525) initiated the Habsburg primacy in Italy and the replacement of France as the main European power. Nevertheless, religious wars forced Charles V to abdicate in 1556 and divide the Habsburg possessions between Spain and Austria. The next Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand I completed the Council of Trent
The Council of Trent (), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation at the time, it has been described as the "most ...
and maintained Germany at peace until the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
(1618–1648). The Habsburgs controlled the elective monarchies of Hungary and Bohemia as well, and eventually turned these states into hereditary domains.
Spain
In 1492 theCatholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Isabella I of Castile, Queen Isabella I of Crown of Castile, Castile () and Ferdinand II of Aragon, King Ferdinand II of Crown of Aragón, Aragon (), whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of ...
of Castile and Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and ; ) is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces of Spain, ...
funded Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
's plan to sail west to reach the Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies) is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The ''Indies'' broadly referred to various lands in the East or the Eastern Hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found i ...
by crossing the Atlantic. He landed on a continent uncharted by Europeans and seen as a new world
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
, the Americas. To prevent conflict between Portugal and Castile (the crown under which Columbus made the voyage), the Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, signed in Tordesillas, Spain, on 7 June 1494, and ratified in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Crown of Castile, along a meridian (geography) ...
was signed dividing the world into two regions of exploration, where each had exclusive rights to claim newly discovered lands.
The structure of the Spanish Empire was established under the Spanish Habsburgs (1516–1700) and under the Spanish Bourbon monarchs, the empire was brought under greater crown control and increased its revenues from the Indies. The crown's authority in The Indies was enlarged by the papal grant of powers of patronage, giving it power in the religious sphere.
Under Philip II of Spain
Philip II (21 May 152713 September 1598), sometimes known in Spain as Philip the Prudent (), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and List of Sicilian monarchs, Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He ...
, Spain, rather than the Habsburg empire, was identified as a more powerful nation than France and England globally. Furthermore, despite attacks from other European states, Spain retained its position of dominance with apparent ease. Spain controlled the Netherlands until the Dutch revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt (; 1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, exc ...
, and important states in southern Italy. The Spanish claims to Naples and Sicily dated back to the 15th century, but had been marred by rival claims until the mid-16th century and the rule of Philip II. There would be no Italian revolts against Spanish rule until 1647. The death of the Ottoman emperor Suleiman the Magnificent
Suleiman I (; , ; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the Western world and as Suleiman the Lawgiver () in his own realm, was the List of sultans of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sultan between 1520 a ...
in 1566 and the naval victory over the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
at the Battle of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval warfare, naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League (1571), Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states arranged by Pope Pius V, inflicted a major defeat on the fleet of t ...
in 1571 cemented the status of Spain as a superpower in Europe and the world. The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies of the Spanish Monarch in the Americas, Asia ( Spanish Philippines), Europe and some territories in Africa and Oceania.
France
TheAncien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for " ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
(French for "old regime") was the political and social system of the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
from about 1450 until the French Revolution that started in 1789. The Ancien Régime was ruled by the late Valois and Bourbon dynasties. Much of the medieval political centralization of France had been lost in the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
, and the Valois Dynasty's attempts at re-establishing control over the scattered political centres of the country were hindered by the Wars of Religion). Much of the reigns of Henry IV, Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown.
...
and the early years of Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
were focused on administrative centralisation. Despite, however, the notion of " absolute monarchy" (typified by the king's right to issue '' lettres de cachet'') and the efforts by the kings to create a centralized state, Ancien Régime France remained a country of systemic irregularities: administrative (including taxation), legal, judicial, and ecclesiastic divisions and prerogatives frequently overlapped, while the French nobility struggled to maintain their own rights in the matters of local government and justice, and powerful internal conflicts (like the Fronde) protested against this centralization.
The need for centralization in this period was directly linked to the question of royal finances and the ability to wage war. The internal conflicts and dynastic crises of the 16th and 17th centuries (the wars between Catholics and Protestants and the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
's internal family conflict) and the territorial expansion of France in the 17th century demanded great sums which needed to be raised through taxes, such as the land tax (') and the tax on salt (') and by contributions of men and service from the nobility. The key to this centralization was the replacing of personal patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, art patronage refers to the support that princes, popes, and other wealthy and influential people ...
systems organized around the king and other nobles by institutional systems around the state. The creation of intendant
An intendant (; ; ) was, and sometimes still is, a public official, especially in France, Spain, Portugal, and Latin America. The intendancy system was a centralizing administrative system developed in France. In the War of the Spanish Success ...
s—representatives of royal power in the provinces—did much to undermine local control by regional nobles. The same was true of the greater reliance shown by the royal court on the "noblesse de robe" as judges and royal counselors. The creation of regional parlement
Under the French Ancien Régime, a ''parlement'' () was a provincial appellate court of the Kingdom of France. In 1789, France had 13 ''parlements'', the original and most important of which was the ''Parlement'' of Paris. Though both th ...
s had initially the same goal of facilitating the introduction of royal power into newly assimilated territories, but as the parlements gained in self-assurance, they began to be sources of disunity.
England
 This period refers to England 1558–1603. The
This period refers to England 1558–1603. The Elizabethan Era
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The Roman symbol of Britannia (a female ...
is the period associated with the reign of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudor. Her eventful reign, and its effect on history ...
(1558–1603) and was a golden age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the ''Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages of Man, Ages, Gold being the first and the one during wh ...
in English cultural history. It was the height of the English Renaissance
The English Renaissance was a Cultural movement, cultural and Art movement, artistic movement in England during the late 15th, 16th and early 17th centuries. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginni ...
, and saw the flowering of English literature
English literature is literature written in the English language from the English-speaking world. The English language has developed over more than 1,400 years. The earliest forms of English, a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian d ...
and poetry
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in ...
. This was also the time during which Elizabethan theatre
The English Renaissance theatre or Elizabethan theatre was the theatre of England from 1558 to 1642. Its most prominent playwrights were William Shakespeare, Christopher Marlowe and Ben Jonson.
Background
The term ''English Renaissance theatr ...
grew. William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
, among others, composed highly innovative and powerful plays. It was an age of expansion and exploration abroad. At home the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
was established and successfully defended against the Catholic powers of Spain and France.
The ''Jacobean era
The Jacobean era was the period in English and Scotland, Scottish history that coincides
with the reign of James VI and I, James VI of Scotland who also inherited the crown of England in 1603 as James I. The Jacobean era succeeds the Elizabeth ...
'' was the reign James I of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 unti ...
(1603–1625). Overseas exploration and establishment of trading factories sped up, with the first permanent settlements in North America at Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent British colonization of the Americas, English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James River, about southwest of present-day Willia ...
in 1607, in Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
in 1610, and at Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on t ...
in Massachusetts in 1620. One king now ruled England and Scotland; the latter was fully absorbed by the Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union refer to two acts of Parliament, one by the Parliament of Scotland in March 1707, followed shortly thereafter by an equivalent act of the Parliament of England. They put into effect the international Treaty of Union agree ...
.
The tumultuous Caroline era
The Caroline era is the period in English and Scottish history named for the 24-year reign of Charles I of England, Charles I (1625–1649). The term is derived from ''Carolus'', Latin for Charles. The Caroline era followed the Jacobean era, the ...
was the reign of King Charles I (1625–1645), followed by his beheading by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
's regime in 1649 . The Caroline era was dominated by the growing religious, political, and social conflict between the King and his supporters, termed the Royalist party, and the Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
opposition that evolved in response to particular aspects of Charles' rule. The colonization of North America continued apace, with new colonies in Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
(1634), Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
(1635), and Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
(1636).Godfrey Davies, ''The Early Stuarts, 1603–1660'' (Oxford UP, 1959).
Poland
In early modern Europe, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth was the largest country with a large population and was very powerful. It was the largest semi-democratically governed polity of its time. It had low taxes but managed to field thousands of Winged Hussars who composed of nobility who followed Sarmatism. The Polish military routinely beat other respectable opponents such as the Ottomans, the Swedes and the Russians.Papacy
The papacy continued to exercise significant diplomatic influence during the Early modern period. The Popes were frequently assembling Holy Leagues to assert Catholic supremacy in Europe. During the Renaissance, Julius II and Paul III were largely involved in theItalian Wars
The Italian Wars were a series of conflicts fought between 1494 and 1559, mostly in the Italian Peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the House of Valois, Valois kings o ...
and worked to preserve their primacy among the Italian princes. During the Counter-Reformation, the Papacy supported Catholic powers and factions all over Europe. Pope Pius V
Pope Pius V, OP (; 17 January 1504 – 1 May 1572), born Antonio Ghislieri (and from 1518 called Michele Ghislieri), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 January 1566 to his death, in May 1572. He was an ...
assembled the Catholic coalition that won the Battle of Lepanto
The Battle of Lepanto was a naval warfare, naval engagement that took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League (1571), Holy League, a coalition of Catholic states arranged by Pope Pius V, inflicted a major defeat on the fleet of t ...
against the Turks. Pope Sixtus V
Pope Sixtus V (; 13 December 1521 – 27 August 1590), born Felice Piergentile, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 April 1585 to his death, in August 1590. As a youth, he joined the Franciscan order, where h ...
sided with the Catholics during the French wars of religion
The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants (called Huguenots) from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease di ...
. Worldwide religious missions, such as the Jesuit China mission, were established by Pope Gregory XIII
Pope Gregory XIII (, , born Ugo Boncompagni; 7 January 1502 – 10 April 1585) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 May 1572 to his death in April 1585. He is best known for commissioning and being the namesake ...
. Gregory XIII is also responsible for the establishment of the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It went into effect in October 1582 following the papal bull issued by Pope Gregory XIII, which introduced it as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian cale ...
. Following the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought peace to the Holy Roman Empire ...
and the birth of nation-states, Papal claims to universal authority came effectively to an end.
Other political powers
*Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
* Early Modern Italy
** Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
** Republic of Florence, Duchy of Florence, Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (; ) was an Italian monarchy located in Central Italy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population ...
** Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
** Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
** Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
** Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
* Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal was a Portuguese monarchy, monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also known as the Kingdom of Portugal a ...
* Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
* Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
** Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
(Czech)
** Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
(Austria)
* Early Modern Germany
** Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
, Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
** Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria () was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarians, Bavarian tribes and ruled by List of rulers of Bavaria, dukes (''duces'') ...
, Electorate of Bavaria
** Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate was a Imperial State, constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire until it was annexed by the Electorate of Baden in 1803. From the end of the 13th century, its ruler was one of the Prince-electors who elected the Holy ...
* Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia, also known as the Tsardom of Moscow, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of tsar by Ivan the Terrible, Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter the Great in 1721.
...
, Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
* Early Modern Sweden
* Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway (Danish language, Danish and Norwegian language, Norwegian: ) is a term for the 16th-to-19th-century multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (includ ...
* Early Modern Romania
* Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
See also
*Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
* International relations 1648–1814
* Early Modern warfare
Early modern warfare is the era of warfare during early modern period following medieval warfare. It is associated with the start of the widespread use of gunpowder and the development of suitable weapons to use the explosive, including art ...
* Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of History of science, modern science during the early modern period, when developments in History of mathematics#Mathematics during the Scientific Revolution, mathemati ...
* Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
* Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and ...
* Catholic Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
* Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
* Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
References
Bibliography
* * * John Coffey (2000), ''Persecution and Toleration in Protestant England 1558–1689'', Studies in Modern History, Pearson Education * Benjamin J. Kaplan (2007), ''Divided by Faith. Religious Conflict and the Practice of Toleration in Early Modern Europe.'' Cambridge University Press * Joseph S. Freedman (1999), ''Philosophy and the Arts in Central Europe, 1500–1700: Teaching and Texts at Schools and Universities'' Aldershot: AshgateFurther reading
* Black, Jeremy. '' European International Relations, 1648–1815'' (2002) * Blanning, T. C. W. ''The Culture of Power and the Power of Culture: Old Regime Europe 1660–1789'' (2003) * Cameron, Euan. ''Early Modern Europe: An Oxford History'' (2001) * de Gouges, Linnea. ''Witch Hunts and State Building in Early Modern Europe'' Nisus Publications, 2017. * de Vries, Jan. ''The Economy of Europe in an Age of Crisis, 1600–1750'' (1976) * de Vries, Jan. ''European Urbanization, 1500–1800'' (1984) * Dewald, Jonathan. "The Early Modern Period." in ''Encyclopedia of European Social History'', edited by Peter N. Stearns, (vol. 1: 2001), pp. 165–177online
* Dorn, Walter L. ''Competition For Empire 1740–1763'' (1940
online
* DuPlessis, Robert S. ''Transitions to capitalism in early modern Europe'' (2019). * Flinn, Michael W. ''The European Demographic System, 1500–1820'' (1981) * Gatti, Hilary. ''Ideas of Liberty in Early Modern Europe'' (2015). * Gershoy, Leo. ''From Despotism To Revolution: 1763–1789'' (1944
online
* Grafton, Anthony. ''Inky Fingers: The Making of Books in Early Modern Europe'' (2020). * Gribben, Crawford, and Graeme Murdock, eds. ''Cultures of Calvinism in Early Modern Europe'' (Oxford UP, 2019). * Gutmann, Myron P. ''Toward the Modern Economy: Early Industry in Europe, 1500–1800'' (1988) * Hesmyr, Atle: ''Scandinavia in the Early Modern Era''(2017). * Hill, David Jayne. ''A history of diplomacy in the international development of Europe'' (3 vol. 1914
online
* Jacob, Margaret C. ''Strangers nowhere in the world: the rise of cosmopolitanism in early modern Europe'' (2017). * Kennedy, Paul. ''The rise and fall of the great powers'' (2010). * Klein, Alexander, and Jelle Van Lottum. "The Determinants of International Migration in Early Modern Europe: Evidence from the Maritime Sector, c. 1700–1800." ''Social Science History'' 44.1 (2020): 143–16
online
* Langer, William. ''An Encyclopedia of World History'' (5th ed. 1973), very detailed outline * Levine, David. "The Population of Europe: Early Modern Demographic Patterns." in ''Encyclopedia of European Social History,'' edited by Peter N. Stearns, (vol. 2, 2001), pp. 145–157
online
* Lindsay, J. O. ed. ''New Cambridge Modern History: The Old Regime, 1713–1763'' (1957
online
* Merriman, John. ''A History of Modern Europe: From the Renaissance to the Present'' (3rd ed. 2009, 2 vol), 1412 pp. * Mowat, R. B. ''History of European Diplomacy, 1451–1789'' (1928) 324 pp
online free
* Nussbaum, Frederick L. ''The triumph of science and reason, 1660–1685'' (1953), Despite the narrow title is a general survey of European history. * Parker, Geoffrey. ''The Military Revolution: Military Innovation and the Rise of the West, 1500–1800'' (1996) * Petrie, Charles. ''Earlier diplomatic history, 1492–1713'' (1949), covers all of Europe
online
** Petrie, Charles. ''Diplomatic History, 1713–1933'' (1946), broad summar
online
* Pollmann, Judith. ''Memory in early modern Europe, 1500–1800'' (Oxford UP, 2017). * Rice, Eugene F. ''The Foundations of Early Modern Europe, 1460–1559'' (2nd ed. 1994) 240 pp. * Schroeder, Paul. ''The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848'' (1994
online
advanced diplomatic history * Scott, Hamish, ed. ''The Oxford Handbook of Early Modern European History, 1350–1750: Volume I: Peoples and Place'' (2015); Volume II: Cultures and Power (2015). * "The State Church in Early-Modern Europe." in ''Arts and Humanities Through the Eras'', edited by Edward I. Bleiberg, et al., (vol. 5: The Age of the Baroque and Enlightenment 1600–1800, Gale, 2005), pp. 336–341
online
* Stearns, Peter N., ed. ''Encyclopedia of European Social History'' (6 vol 2000), 3000 pp; overview vol. 1 pp. 165–77, plus hundreds of articles * Tallett, Frank. ''War and Society in Early Modern Europe: 1495–1715'' (2016). * Wiesner, Merry E. ''Early Modern Europe, 1450–1789'' (3rd ed. 2022) * Wiesner-Hanks, Merry E. ''Women and gender in early modern Europe'' (Cambridge UP, 2019). * Wolf, John B. ''The Emergence of the Great Powers, 1685–1715'' (1951
online
External links
from the introduction to the pioneering '' Cambridge Modern History'' (1903)
Society for Renaissance Studies
{{DEFAULTSORT:Early Modern Europe * History of Europe by period Western culture