Equidae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Equidae (commonly known as the horse family) is the taxonomic
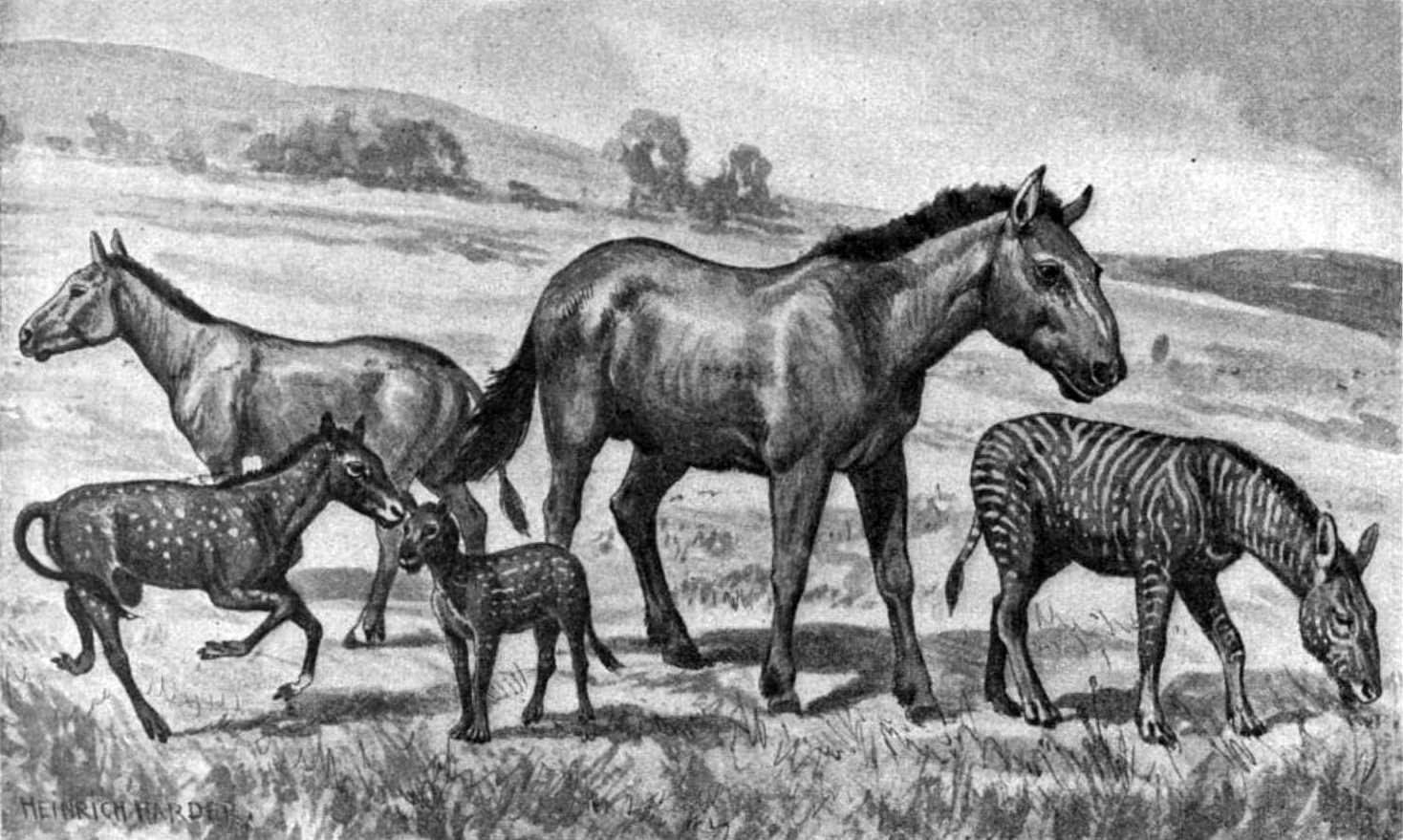 The oldest known
The oldest known


 * Order
* Order
family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
of horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s and related animals, including asses, zebras
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped Animal coat, coats. There are three Extant taxon, living species: Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), the plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and t ...
, and many extinct species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
known only from fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
s. The family evolved more than 50 million years ago, in the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
epoch, from a small, multi-toed ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined ...
into larger, single-toed animals. All extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
species are in the genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
'' Equus'', which originated in North America. Equidae belongs to the order Perissodactyla
Perissodactyla (, ), or odd-toed ungulates, is an order of ungulates. The order includes about 17 living species divided into three families: Equidae (horses, asses, and zebras), Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). They t ...
, which includes the extant tapir
Tapirs ( ) are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a Suidae, pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk (proboscis). Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South America, South and Centr ...
s and rhinoceros
A rhinoceros ( ; ; ; : rhinoceros or rhinoceroses), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates (perissodactyls) in the family (biology), famil ...
, and several extinct families. It is more specifically grouped within the superfamily Equoidea
Equoidea is a superfamily of hippomorph perissodactyls containing the Equidae, Palaeotheriidae, and other basal equoids of unclear affinities, of which members of the genus '' Equus'' are the only extant species. The earliest fossil record of ...
, the only other family being the extinct Palaeotheriidae
Palaeotheriidae is an extinct family of herbivorous perissodactyl mammals that inhabited Europe, with less abundant remains also known from Asia, from the mid-Eocene to the early Oligocene. They are classified in Equoidea, along with the livin ...
.
The term equid refers to any member of this family, including any equine
Equinae is a subfamily of the family Equidae, known from the Hemingfordian stage of the Early Miocene (16 million years ago) onwards. They originated in North America, before dispersing to every continent except Australia and Antarctica. They are ...
.
Evolution
 The oldest known
The oldest known fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
s assigned to Equidae were found in North America, and date from the early Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
epoch, 54 million years ago. They were once assigned to the genus ''Hyracotherium
''Hyracotherium'' ( ; "hyrax-like beast") is an extinction, extinct genus of small (about 60 cm in length) perissodactyl ungulates that was found in the London Clay formation. This small, fox-sized animal is (for some scientists) considered t ...
'', but the type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
of that genus is now regarded as a palaeothere. The other species have been split off into different genera. These early equids were fox-sized animals with three toes on the hind feet, and four on the front feet. They were herbivorous browsers on relatively soft plants, and already adapted for running. The complexity of their brains suggest that they already were alert and intelligent animals. Later species reduced the number of toes, and developed teeth more suited for grinding up grasses and other tough plant food.
The equids, like other perissodactyls, are hindgut fermenters. They have evolved specialized teeth that cut and shear tough plant matter to accommodate their fibrous diet. Their seemingly inefficient digestion strategy is a result of their size at the time of its evolution, as they would have already had to be relatively large mammals to be supported on such a strategy.
The family became relatively diverse during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
epoch, with many new species appearing. By this time, equids were more truly horse like, having developed the typical body shape of the modern animals. Many of these species bore the main weight of their bodies on their central third toe, with the others becoming reduced and barely touching the ground, if at all. The sole surviving genus, ''Equus'', had evolved by the early Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
epoch, and spread rapidly through the world.
Classification



 * Order
* Order Perissodactyla
Perissodactyla (, ), or odd-toed ungulates, is an order of ungulates. The order includes about 17 living species divided into three families: Equidae (horses, asses, and zebras), Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). They t ...
(In addition to Equidae, Perissodactyla includes four species of tapir
Tapirs ( ) are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a Suidae, pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk (proboscis). Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South America, South and Centr ...
in a single genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
, as well as five living species (belonging to four genera) of rhinoceros
A rhinoceros ( ; ; ; : rhinoceros or rhinoceroses), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates (perissodactyls) in the family (biology), famil ...
.) † indicates extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
taxa.
** Family Equidae
*** Subfamily †Hyracotheriinae
**** Genus †'' Epihippus''
**** Genus †'' Haplohippus''
**** Genus †''Eohippus
''Eohippus'' is an extinct genus of small equid ungulates. The only species is ''E. angustidens'', which was long considered a species of ''Hyracotherium'' (now strictly defined as a member of the Palaeotheriidae rather than the Equidae). Its rem ...
''
**** Genus †'' Minippus''
**** Genus †'' Orohippus''
**** Genus †'' Pliolophus''
**** Genus †'' Protorohippus''
**** Genus †'' Sifrhippus''
**** Genus †'' Xenicohippus''
*** Subfamily †Anchitheriinae
The Anchitheriinae are an extinct subfamily of the Perissodactyla family Equidae, the same family which includes modern horses, zebras and donkeys. This subfamily is more primitive than the living members of the family. The group first appeared ...
**** Genus †'' Anchitherium''
**** Genus †'' Archaeohippus''
**** Genus †'' Desmatippus''
**** Genus †'' Hypohippus''
**** Genus †'' Kalobatippus''
**** Genus †'' Megahippus''
**** Genus †''Mesohippus
''Mesohippus'' (Greek language, Greek: / meaning "middle" and / meaning "horse") is an extinct genus of early horse. It lived 37 to 32 million years ago in the Early Oligocene. Like many fossil horses, ''Mesohippus'' was common in North America. ...
''
**** Genus †'' Miohippus''
**** Genus †'' Parahippus''
**** Genus †'' Sinohippus''
*** Subfamily Equinae
Equinae is a subfamily of the family Equidae, known from the Hemingfordian stage of the Early Miocene (16 million years ago) onwards. They originated in North America, before dispersing to every continent except Australia and Antarctica. They ar ...
**** Genus †''Merychippus
''Merychippus'' is an extinct proto-horse of the family Equidae that was endemic to North America during the Miocene, 15.97–5.33 million years ago. It had three toes on each foot and is the first horse known to have Grazing (behaviour), grazed ...
''
**** Genus †''Scaphohippus
''Scaphohippus'' is an extinct Miocene genus of equine, with two known species, known from fossils found in California, New Mexico, Montana, and Nebraska.
History
Both species in the genus were originally described as members of the wastebaske ...
''
**** Genus †'' Acritohippus''
**** Tribe †Hipparionini
Hipparionini is a tribe of three-toed horses in the subfamily Equinae. They had body forms similar to modern equines, with high-crowned teeth. They first appeared in North America during the Early Miocene around 17 million years ago, before migrat ...
***** Genus †'' Eurygnathohippus''
***** Genus †''Hipparion
''Hipparion'' is an extinct genus of three-toed, medium-sized equine belonging to the extinct tribe Hipparionini, which lived about 10-5 million years ago. While the genus formerly included most hipparionines, the genus is now more narrowly defi ...
''
***** Genus †'' Hippotherium''
***** Genus †''Nannippus
''Nannippus'' is an extinct genus of three-toed horse endemic to North America during the Miocene through Pleistocene, about 13.3—1.8 million years ago (Mya), living around 11.5 million years. This ancient species of three-toed horse grew up to ...
''
***** Genus †''Neohipparion
''Neohipparion'' (Greek: "new" (neos), "pony" (hipparion)) is an extinction, extinct genus of equid, from the Neogene (Miocene to Pliocene) of North America and Central America. Fossils of this horse have been found in Texas, Florida, Kansas, ...
''
***** Genus †'' Proboscidipparion''
***** Genus †'' Pseudhipparion''
**** Tribe Equini
***** Genus †''Haringtonhippus
''Haringtonhippus'' is an extinct genus of equine from the Pleistocene of North America The genus is monospecific, consisting of the species ''H. francisci'', initially described in 1915 by Oliver Perry Hay as ''Equus francisci''. Members of the ...
''Hay, Oliver P. (1915). "Contributions to the Knowledge of the Mammals of the Pleistocene of North America". Proceedings of the United States National Museum. 48 (2086): 535–549.
***** Genus †'' Heteropliohippus''
***** Genus †'' Parapliohippus''
***** Genus †'' Calippus''
***** Genus †''Protohippus
''Protohippus'' is an extinct three-toed genus of horse. It was roughly the size of a modern donkey. Fossil evidence suggests that it lived during the Late Miocene (Clarendonian to Hemphillian
The Hemphillian North American Stage on the geologic ...
''
***** Genus †'' Astrohippus''
***** Genus †''Dinohippus
''Dinohippus'' ( Greek: "Terrible horse") is an extinct equid which was endemic to North America from the late Hemphillian stage of the Miocene through the Zanclean stage of the Pliocene (10.3—3.6 mya) and in existence for approximately . Foss ...
''
***** Genus '' Equus'' (22 species, 7 extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
)
***** Genus †'' Cremohipparion''
***** Genus †''Hippidion
''Hippidion'' (meaning ''little horse'') is an extinct genus of equine that lived in South America from the Late Pliocene to the end of the Late Pleistocene (Lujanian), between 2.5 million and 11,000 years ago. They were one of two lineages of eq ...
''
***** Genus †'' Pliohippus''
References
{{Authority control Extant Ypresian first appearances Mammal families Taxa named by John Edward Gray