Electronic Circuits on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An electronic circuit is composed of individual
An electronic circuit is composed of individual
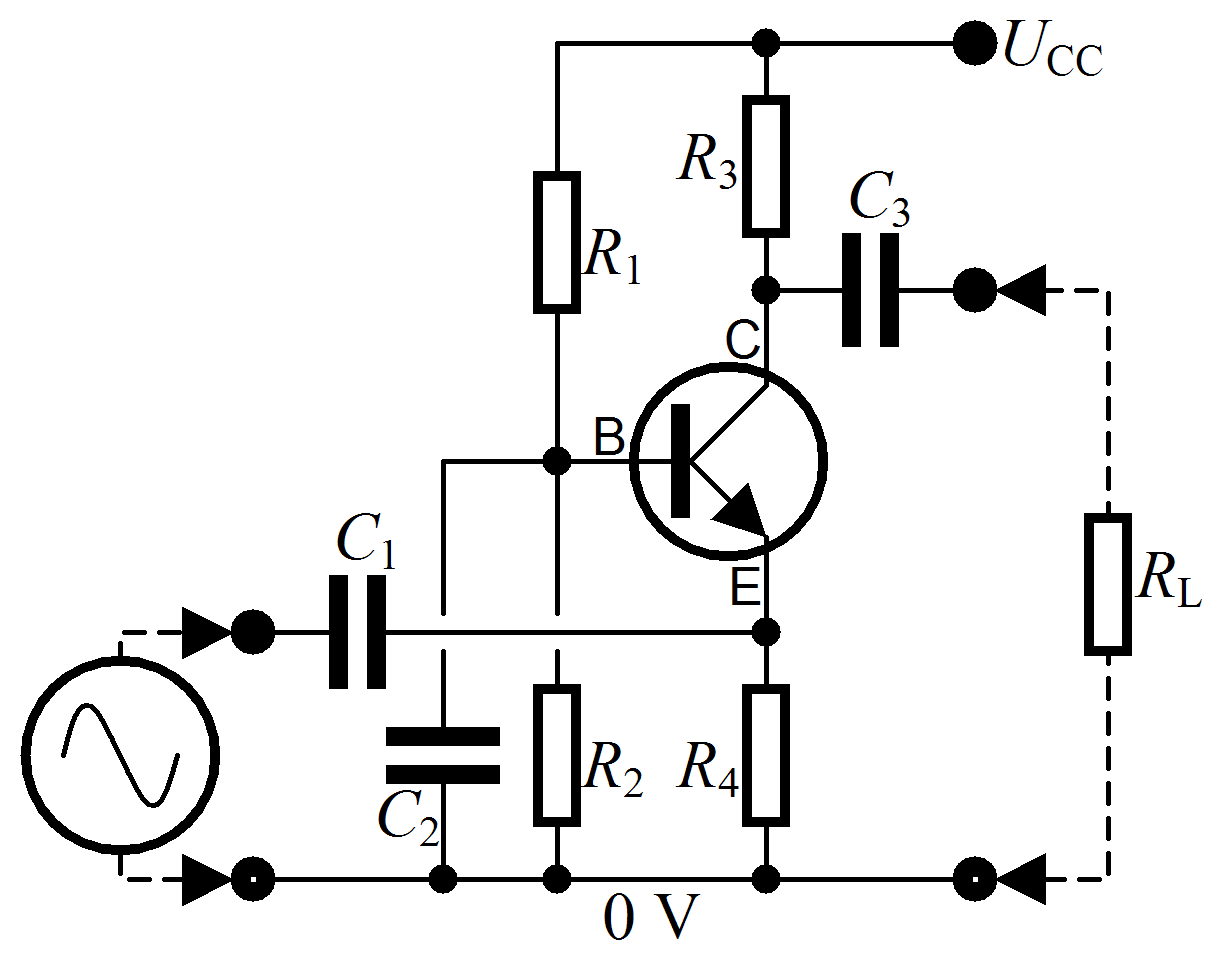 Analog electronic circuits are those in which current or
Analog electronic circuits are those in which current or  The basic components of analog circuits are wires, resistors, capacitors, inductors,
The basic components of analog circuits are wires, resistors, capacitors, inductors,
Electronics Circuits Textbook
Electronics Fundamentals
{{DEFAULTSORT:Electronic Circuit
 An electronic circuit is composed of individual
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic component
An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singula ...
s, such as resistors, transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s, capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s, inductors and diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance ...
s, connected by conductive wire
file:Sample cross-section of high tension power (pylon) line.jpg, Overhead power cabling. The conductor consists of seven strands of steel (centre, high tensile strength), surrounded by four outer layers of aluminium (high conductivity). Sample d ...
s or traces through which electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
can flow. It is a type of electrical circuit. For a circuit to be referred to as ''electronic'', rather than ''electrical'', generally at least one active component must be present. The combination of components and wires allows various simple and complex operations to be performed: signals can be amplified, computations can be performed, and data can be moved from one place to another.
Circuits can be constructed of discrete components connected by individual pieces of wire, but today it is much more common to create interconnections by photolithographic techniques on a laminated substrate (a printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
or PCB) and solder the components to these interconnections to create a finished circuit. In an integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
or IC, the components and interconnections are formed on the same substrate, typically a semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
such as doped silicon or (less commonly) gallium arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a Zincblende (crystal structure), zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monoli ...
.
An electronic circuit can usually be categorized as an analog circuit, a digital circuit
In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematica ...
, or a mixed-signal circuit (a combination of analog circuits and digital circuits). The most widely used semiconductor device
A semiconductor device is an electronic component that relies on the electronic properties of a semiconductor material (primarily silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors) for its function. Its conductivit ...
in electronic circuits is the MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
(metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three termi ...
).
Analog circuits
 Analog electronic circuits are those in which current or
Analog electronic circuits are those in which current or voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
may vary continuously with time to correspond to the information being represented.
 The basic components of analog circuits are wires, resistors, capacitors, inductors,
The basic components of analog circuits are wires, resistors, capacitors, inductors, diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance ...
s, and transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s. Analog circuits are very commonly represented in schematic diagrams, in which wires are shown as lines, and each component has a unique symbol. Analog circuit analysis employs Kirchhoff's circuit laws: all the currents at a node (a place where wires meet), and the voltage around a closed loop of wires is 0. Wires are usually treated as ideal zero-voltage interconnections; any resistance or reactance is captured by explicitly adding a parasitic element, such as a discrete resistor or inductor. Active components such as transistors are often treated as controlled current or voltage sources: for example, a field-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three termi ...
can be modeled as a current source from the source to the drain, with the current controlled by the gate-source voltage.
When the circuit size is comparable to a wavelength of the relevant signal frequency, a more sophisticated approach must be used, the distributed-element model. Wires are treated as transmission lines, with nominally constant characteristic impedance, and the impedances at the start and end determine transmitted and reflected waves on the line. Circuits designed according to this approach are distributed-element circuits. Such considerations typically become important for circuit boards at frequencies above a GHz; integrated circuits are smaller and can be treated as lumped elements for frequencies less than 10GHz or so.
Digital circuits
In digital electronic circuits, electric signals take on discrete values, to represent logical and numeric values. These values represent the information that is being processed. In the vast majority of cases, binary encoding is used: one voltage (typically the more positive value) represents a binary '1' and another voltage (usually a value near the ground potential, 0 V) represents a binary '0'. Digital circuits make extensive use oftransistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s, interconnected to create logic gate
A logic gate is a device that performs a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has, for ...
s that provide the functions of Boolean logic
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variable (mathematics), variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denot ...
: AND, NAND, OR, NOR, XOR and combinations thereof. Transistors interconnected so as to provide positive feedback are used as latches and flip flops, circuits that have two or more metastable states, and remain in one of these states until changed by an external input. Digital circuits therefore can provide logic and memory, enabling them to perform arbitrary computational functions. (Memory based on flip-flops is known as static random-access memory (SRAM). Memory based on the storage of charge in a capacitor, dynamic random-access memory
Dynamics (from Greek language, Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' "power (disambiguation), power") or dynamic may refer to:
Physics and engineering
* Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and t ...
(DRAM), is also widely used.)
The design process for digital circuits is fundamentally different from the process for analog circuits. Each logic gate regenerates the binary signal, so the designer need not account for distortion, gain control, offset voltages, and other concerns faced in an analog design. As a consequence, extremely complex digital circuits, with billions of logic elements integrated on a single silicon chip, can be fabricated at low cost. Such digital integrated circuits are ubiquitous in modern electronic devices, such as calculators, mobile phone handsets, and computers. As digital circuits become more complex, issues of time delay, logic races, power dissipation, non-ideal switching, on-chip and inter-chip loading, and leakage currents, become limitations to circuit density, speed and performance.
Digital circuitry is used to create general purpose computing chips, such as microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
s, and custom-designed logic circuits, known as application-specific integrated circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficienc ...
(ASICs). Field-programmable gate arrays
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of ...
(FPGAs), chips with logic circuitry whose configuration can be modified after fabrication, are also widely used in prototyping and development.
Mixed-signal circuits
Mixed-signal or hybrid circuits contain elements of both analog and digital circuits. Examples include comparators, timers, phase-locked loops,analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a Digital signal (signal processing), digi ...
s, and digital-to-analog converters. Most modern radio and communications circuitry uses mixed signal circuits. For example, in a receiver, analog circuitry is used to amplify and frequency-convert signals so that they reach a suitable state to be converted into digital values, after which further signal processing can be performed in the digital domain.
Design
Prototyping
References
External links
Electronics Circuits Textbook
Electronics Fundamentals
{{DEFAULTSORT:Electronic Circuit