Electromyoneurography on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Electromyoneurography (EMNG) is the combined use of
.
 Electromyoneurography has a variety of modern applications. The high level of sensitivity that electromyoneurography employs makes it ideal for detecting peripheral nerve damage as well as a variety of myopathies in their early stages. This electrophysiological data obtaining technique has been able to heighten diagnostic capabilities when looking at peripheral neuropathy disorders like
Electromyoneurography has a variety of modern applications. The high level of sensitivity that electromyoneurography employs makes it ideal for detecting peripheral nerve damage as well as a variety of myopathies in their early stages. This electrophysiological data obtaining technique has been able to heighten diagnostic capabilities when looking at peripheral neuropathy disorders like
 The needle is normally attached to a recording device known as an electromyography machine. The results show the appearance of
The needle is normally attached to a recording device known as an electromyography machine. The results show the appearance of
electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
and electroneurography This technique allows for the measurement of a peripheral nerve's conduction velocity upon stimulation (electroneurography) alongside electrical recording of muscular activity (electromyography). Their combined use proves to be clinically relevant by allowing for both the source and location of a particular neuromuscular disease to be known, and for more accurate diagnoses.
Characteristics
Electromyoneurography is a technique that uses surface electrical probes to obtain electrophysiological readings fromnerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
and muscle cells. The nerve activity is generally recorded using surface electrodes, stimulating the nerve at one site and recording from another with a minimum distance between the two. The time difference of the potential
Potential generally refers to a currently unrealized ability. The term is used in a wide variety of fields, from physics to the social sciences to indicate things that are in a state where they are able to change in ways ranging from the simple r ...
is a measure of the time taken for the potential
Potential generally refers to a currently unrealized ability. The term is used in a wide variety of fields, from physics to the social sciences to indicate things that are in a state where they are able to change in ways ranging from the simple r ...
to travel the distance across the two sites and is a measure of the conduction velocity along the nerve. The amplitude of the potential
Potential generally refers to a currently unrealized ability. The term is used in a wide variety of fields, from physics to the social sciences to indicate things that are in a state where they are able to change in ways ranging from the simple r ...
, measured baseline to peak, or peak to peak, is a measure of the number of fibers conducting the response. Abnormality in data obtained from nerve measurements, such as absent or low amplitude, indicates potential nerve damage.
This technique is used in many medical fields today. One example of its use is to detect neuropathy due to diseases like diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
. It can also be used to detect muscle weakness or paralysis due to sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
or multi-organ failure in coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
tose patients. This method remains a largely used medical technique due to its efficiency and relative simplicity. It is especially attractive due to the lack of special precautions or preparation involved with this procedure. There is minimal pain and no significant risks except those associated with needle use."Electroneuromyography." MedInstitute Y&C Institute of medical rehabilitation. MedInstitute, n.d. Web. 26 Apr 2013. History
The technique of electromyoneurography was first practiced in the late 1970s by the American Academy of General Practice. The use of this technique enhances diagnostic capability by defining and localizing the target site. In 1978, Milton B. Spiegel, research physician with The Rehabilitation Institute of South Florida, wrote one of the first major academic papers surrounding the uses and benefits of electromyoneurography. It was in this paper that Dr. Spiegel suggested that pre-examination of the patients'range of motion
Range of motion (or ROM) is the linear or angular distance that a moving object may normally travel while properly attached to another.
In biomechanics and strength training, ROM refers to the angular distance and direction a joint can move be ...
and reflexes would eliminate time and exploration of nerve entrapments during the electromyoneurographic procedure.
In the early 1980s, the practice of utilizing electromyoneurography became more widely accepted in the medical community, specifically aiding in the diagnoses of neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
, radiculopathy
Radiculopathy (; ), also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly (a neuropathy). Radiculopathy can result in pain (radicular pain), weakness, altered se ...
, and axonopathy
Polyneuropathy () is damage or disease affecting peripheral nerves (peripheral neuropathy) in roughly the same areas on both sides of the body, featuring weakness, numbness, and burning pain. It usually begins in the hands and feet and may progre ...
. As to more recent use, electromyoneurography has been employed throughout the 21st century, aiding in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome, abnormal glucose levels, and many other myopathies. This procedure now analyzes the nerve conduction and muscle potentials through the use of H-Reflex
The H-reflex (or Hoffmann's reflex) is a reflectory reaction of muscles after electrical stimulation of sensory fibers ( Ia afferents stemming from muscle spindles) in their innervating nerves (for example, those located behind the knee). The H ...
and F-Wave studies. Combined with a pre-examination, electromyoneurography is utilized to detect neuromuscular abnormalities.
Modern Application
 Electromyoneurography has a variety of modern applications. The high level of sensitivity that electromyoneurography employs makes it ideal for detecting peripheral nerve damage as well as a variety of myopathies in their early stages. This electrophysiological data obtaining technique has been able to heighten diagnostic capabilities when looking at peripheral neuropathy disorders like
Electromyoneurography has a variety of modern applications. The high level of sensitivity that electromyoneurography employs makes it ideal for detecting peripheral nerve damage as well as a variety of myopathies in their early stages. This electrophysiological data obtaining technique has been able to heighten diagnostic capabilities when looking at peripheral neuropathy disorders like radiculopathy
Radiculopathy (; ), also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly (a neuropathy). Radiculopathy can result in pain (radicular pain), weakness, altered se ...
, and axonopathy in addition to myopathies such as muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affe ...
, myotonia
Myotonia is a symptom of a small handful of certain neuromuscular disorders characterized by delayed relaxation (prolonged contraction) of the skeletal muscles after voluntary contraction or electrical stimulation, and the muscle shows an abnor ...
, and myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, ...
. Electromyoneurography was the main technique used in a study to detect diabetic polyneuropathy, a serious condition that is progressive in nature.
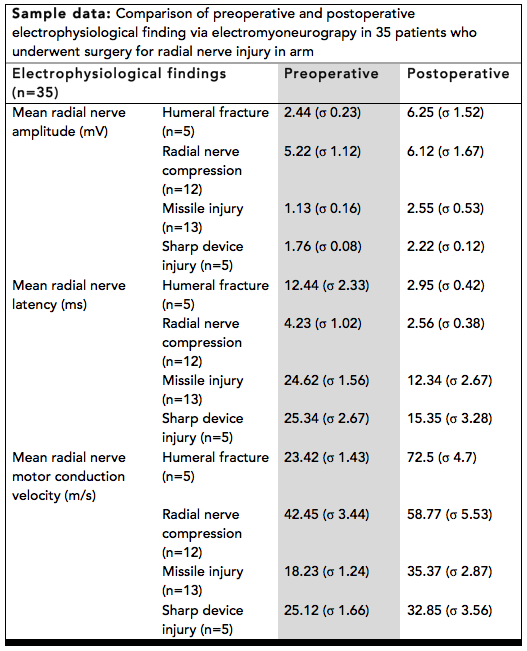
Electromyoneurography can also be used to measure patient recovery from surgical procedures, such as nerve repair. A study conducted on patients with proximal radial nerve injuries used the procedure to indicate the degree of both pre- and postoperative nerve damage. In this particular study, electromyoneurography was the preferred method of measuring recovery, chosen over magnetic resonance imaging (MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
) and computed tomography ( CT) scans. When looking at the sample data table, one can see that postoperative patients generally see an increase in mean radial nerve amplitude, a decrease in mean radial nerve latency and increases in nerve motor conduction velocity. These results are all general trends that would be expected when operating on damaged nerves in effort to increase their performance.
Electromyoneurography's unique combination of recording in muscle and nerve simultaneously typically results in a higher level of diagnostic ability in the field of medicine. This heightened utility often results in a lesser demand for more invase techniques for acquiring electrophysiological data, such as myelography, a procedure where complications are not uncommon and the amount of attention required for post-operative care is more involved.
Conditions Diagnosed with Electromyoneurography
Electromyoneurography has been found to be particularly useful in diagnosing the following neuromuscular conditions, though it is not an exhaustive list:Procedure Outline
In an electromyoneurography procedure, recording of the muscle is done by insertion of a needle. The recordings are taken when the muscle is at rest and when the muscle is contracting; the muscle will contract based on the directions of the one performing the test (instructing the patient to move certain body parts in certain directions forming muscle contractions). Various regions of muscle on the body are examined in an electromyoneurography test and the procedure lasts anywhere between 30 and 60 minutes (2–5 minutes per muscle). In addition to examining the muscles, theconduction velocity
In neuroscience, nerve conduction velocity (CV) is the speed at which an electrochemical impulse propagates down a neural pathway. Conduction velocities are affected by a wide array of factors, which include age, sex, and various medical conditio ...
of nerve signals are measured. The nerve's ability to transmit signals is tested by inserting recording electrodes to capture the data and signal electrodes to initiate signals down a nerve by applying a small shock. Self-generated potentials also occur naturally for recording, in addition to the artificial "shock". Evaluating a nerve's conduction velocity, together with testing potentials, allows for a beneficial diagnosis that can detect pain and sensory problems at the neuromuscular level.
Expected Test Results
 The needle is normally attached to a recording device known as an electromyography machine. The results show the appearance of
The needle is normally attached to a recording device known as an electromyography machine. The results show the appearance of action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
or graded potential
Graded potentials are changes in membrane potential that vary according to the size of the stimulus, as opposed to being all-or-none. They include diverse potentials such as receptor potentials, electrotonic potentials, subthreshold membrane pot ...
spikes. While interpretation of the results requires background knowledge, irregular data can be used to diagnose many diseases. If the activity of the nerves at rest is abnormal, this may indicate nerve lesion, radiculopathy
Radiculopathy (; ), also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly (a neuropathy). Radiculopathy can result in pain (radicular pain), weakness, altered se ...
, or lower motor nerve degeneration. The amplitude or duration of the potential spike may also be used to gather information. A decreased amplitude or duration may indicate nerve damage due to a muscle diseases, whereas an increase in these demonstrates reinervation, or repair by new nerve connections to the muscles, has occurred.
{{clear
References