EarSketch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
EarSketch is a free educational programming environment. Its core purpose is to teach coding in two widely used languages, Python and
Each chapter has several sections, a summary, a quiz, screencasts, and associated slides. The curriculum is positioned in the right side of the window. It is a textbook for EarSketch that includes chapters about major computing principles, Python and JavaScript, as well as an introduction to computer science. The curriculum is divided in the following sections: * 3 units, namely: ** Unit 1 is an introduction to EarSketch, computing and to basic musical concepts (tempo and pitch, effects...), ** Unit 2 focuses on loops, string operations, musical form and beat, ** Unit 3 introduces conditionals, data structures, and randomness, * Optional more in-depth chapters, * The API documentation, which describes all the functions that are specific to EarSketch, * A university-level introduction to computer science section, * Teacher materials, which include lesson plans, examples, slides, and evaluation tools. * An Hour of code tutorial: Hour of code is a worldwide initiative to engage students in computer science, by providing 60 minute-long ludic introduction tutorials (for instance with
The units are divided into chapters. Each chapter has several sections, a summary, a quiz, and associated slides. The curriculum contains Python and JavaScript example code that can be pasted into the code editor.
JavaScript
JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ...
, through music composing and remixing. This learning environment was developed first at Georgia Institute of Technology
The Georgia Institute of Technology, commonly referred to as Georgia Tech or, in the state of Georgia, as Tech or The Institute, is a public research university and institute of technology in Atlanta, Georgia. Established in 1885, it is part of ...
, (from 2011) under Prof. Jason Freeman ( School of Music) and Prof. Brian Magerko (School of Literature, Media, and Communication
The School of Literature, Media, and Communication (LMC) is one of six units of the Ivan Allen College of Liberal Arts at the Georgia Institute of Technology. The School focuses primarily on interdisciplinary approaches to the humanities, social s ...
).
EarSketch is web-based, which means users can access it with their web-browsers, and with no installation. No account is required to create projects or view existing projects.
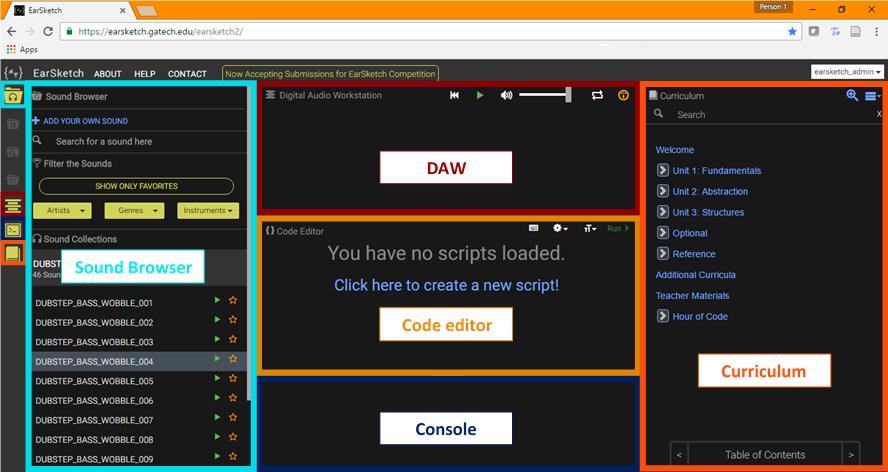
EarSketch comprises different elements: a curriculum, a digital audio workstation
A digital audio workstation (DAW) is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integra ...
(or DAW), a code editor, console, and a sound browser. EarSketch's sound library was created by Young Guru
Gimel Androus Keaton (born February 27, 1974), better known by his stage name Young Guru, is an American audio engineer, record producer, disc jockey, and record executive from Wilmington, Delaware. In 2019, Young Guru won a Grammy Award for Be ...
, Jay Z's sound engineer, and famous sound designer Richard Devine.
Purpose
EarSketch has two main goals: to make computer science more engaging for students, and to diversify the population of students interested in computer science.Engagement in computer science at school
The US has a shortage of computer science students, not only because not all schools are offering CS classes, but also because students do not enroll in such classes. A study published in 2009 states: "The percentage of U.S. high school students taking STEM courses has increased over the last 20 years across all STEM disciplines except computer science where it dropped from 25% to 19%". Considering this, and the fact that all fields of the economy incorporate computing in their operations, EarSketch proposes to motivate students to enroll in CS classes and to pursue CS studies in higher education. EarSketch attempts to reach this goal by adding a musical side to coding. This strategy is a STEAMs approach to education that integrates arts into STEM teaching. A study conducted at Georgia Tech showed statistically significant results in this domain: students who study with EarSketch have been shown to make progress both in content knowledge and attitude towards CS (self-confidence, motivation, intent to persist, etc.).Participation in computing
Today female and minority students in CS classes are, like in other engineering fields, underrepresented (with 22% of female students, 13% of African American students in US classes in 2015). EarSketch has demonstrated success in tackling this issue, partly because of the focus on popular genres of music such as dubstep, and because EarSketch provides a creative, expressive, and authentic environment (since students compose their own music).History
Origin of the name EarSketch
The name EarSketch originated in a different project from co-creators Freeman and Magerko focused on collaborative composition and music analysis via drawing. That project never came to fruition, but the idea of collaborative music-making (and the name) remained in a new project focused more on coding and computer science education. Though sketching is no longer a focus of EarSketch, the environment does offer drawing and animation features through P5.First version: Reaper-based desktop application
The initial version of EarSketch, released in 2012, was built inside ofREAPER
A reaper is a farm implement or person that reaps (cuts and often also gathers) crops at harvest when they are ripe. Usually the crop involved is a cereal grass. The first documented reaping machines were Gallic reapers that were used in Rom ...
, a commercial digital audio workstation
A digital audio workstation (DAW) is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integra ...
with extensive support for coding via the ReaScript API for Python and the JavaScript plugin authoring architecture. As the project grew, the Reaper-based version of EarSketch was eventually retired due to its dependence on commercial software, the inability of the team to create an integrated user interface to author code, view musical results in the DAW, find sounds, and challenges installing the software in school computer labs.
Current version: web application
The project then evolved to become a website in 2014. This allowed students to start coding without having to download software. The website uses theweb audio API
HTML5 Audio is a subject of the HTML5 specification, incorporating audio input, playback, and synthesis, as well as speech to text, in the browser.
<audio> element
The element represents a sound, or an audio stream. It is commonly used ...
and runs on a private server. New versions are release approximately once per month.
EarSketch is not just a software: the EarSketch team works hand in hand with teachers to build the curriculum, and trains teachers every year in summer professional development workshops.
Funding
EarSketch received funding from theNational Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
(NSF) (CNS #1138469, DRL #1417835, DUE #1504293, and DRL #1612644), the Scott Hudgens Family Foundation, the Arthur M. Blank
Arthur M. Blank (born September 27, 1942) is an American businessman and a co-founder of the home improvement retailer The Home Depot.
He also currently owns two professional sports teams based in Atlanta, Georgia - the Atlanta Falcons of the N ...
Family Foundation, and the Google Inc. Fund of Tides Foundation.
Sections
EarSketch is aweb application
A web application (or web app) is application software that is accessed using a web browser. Web applications are delivered on the World Wide Web to users with an active network connection.
History
In earlier computing models like client-serve ...
, and when opening a session, users see different sections: the curriculum, the code editor, the console, the Digital Audio Workstation, and the browser.

The curriculum
The curriculum is aligned with AP Computer Science Principles but can be used in any introductory programming course.Each chapter has several sections, a summary, a quiz, screencasts, and associated slides. The curriculum is positioned in the right side of the window. It is a textbook for EarSketch that includes chapters about major computing principles, Python and JavaScript, as well as an introduction to computer science. The curriculum is divided in the following sections: * 3 units, namely: ** Unit 1 is an introduction to EarSketch, computing and to basic musical concepts (tempo and pitch, effects...), ** Unit 2 focuses on loops, string operations, musical form and beat, ** Unit 3 introduces conditionals, data structures, and randomness, * Optional more in-depth chapters, * The API documentation, which describes all the functions that are specific to EarSketch, * A university-level introduction to computer science section, * Teacher materials, which include lesson plans, examples, slides, and evaluation tools. * An Hour of code tutorial: Hour of code is a worldwide initiative to engage students in computer science, by providing 60 minute-long ludic introduction tutorials (for instance with
Minecraft
''Minecraft'' is a sandbox game developed by Mojang Studios. The game was created by Markus "Notch" Persson in the Java programming language. Following several early private testing versions, it was first made public in May 2009 before bein ...
or frozen
Frozen may refer to:
* the result of freezing
* a paralysis response in extreme cases of fear
Films
* ''Frozen'' (1997 film), a film by Wang Xiaoshuai
* ''Frozen'' (2005 film), a film by Juliet McKoen
* ''Frozen'' (2007 film), a film by Sh ...
components).https://code.org/learn, consulted in November 2016 This particular tutorial is an introduction to computer science where students compose their first song with EarSketch.
The units are divided into chapters. Each chapter has several sections, a summary, a quiz, and associated slides. The curriculum contains Python and JavaScript example code that can be pasted into the code editor.
The code editor and console
EarSketch's code editor is located in the window at the center of the page. When the code is executed, it will create the music in the Digital Audio Workstation. If there is an error in the code, a message explaining the error will appear in the console, located under the code editor.The digital audio workstation
Adigital audio workstation
A digital audio workstation (DAW) is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integra ...
(DAW) is a tool used by a majority of music producers which helps manipulate audio samples (or audio files), add effects, and accomplish other tasks in the composition process. EarSketch's DAW is located in the top center section, above the code editor. It contains tracks: each line is a track, and corresponds to an instrument. With code commands, the user will add sound samples in these tracks, as well as effects, such as volume changes, reverberation, delay, etc.
When the code is executed, the DAW will be filled with the sound samples, and the user can play the music they just coded.
The browser: scripts and sounds
In order to compose music, EarSketch coders can use samples. Audio samples are located in the sound browser, in the left window, which allows for sound file search, and personal sound file upload. In the left section, users can also show the script browser. A script is a code file, and different scripts will create different musics in the DAW.Main feature examples
Although the code written in the code editor will be either in Python or JavaScript, there are EarSketch-specific functions that allow for the user to accomplish music related tasks. Here are some examples: * One of the basic functions of EarSketch is fitMedia(), which places a sample sound in the Digital Audio Workstation. * Another important function is MakeBeat(), that takes as input astring
String or strings may refer to:
*String (structure), a long flexible structure made from threads twisted together, which is used to tie, bind, or hang other objects
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Strings'' (1991 film), a Canadian anim ...
and a file name. The string corresponds to times when the file should be played, sustained, or when there should be silence. This is a common way of creating percussive lines in music programming languages. For instance, in EarSketch, '0' indicates that the file should play, then '-' means a silence, and '+' means keep playing the sample. So if we use the string "0-000+++", it means play the audio file on the first sixteenth note, then there is a silence, then the file is played three times in a row, and finally, the file keeps playing through the three last sixteenth notes.
* Another example would be setEffect(), which adds effects to a track. Effects are common in Digital Audio Workstations as they are an indispensable element of music production. Here are some examples of effects:
** Volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). Th ...
: this modifies the loudness of a track. It can be used to emphasize a particular track compared to the rest of the instruments. It can also be used to fade in and fade out the music to have a smoother beginning and end.
** Reverb
Reverberation (also known as reverb), in acoustics, is a persistence of sound, after a sound is produced. Reverberation is created when a sound or signal is reflected causing numerous reflections to build up and then decay as the sound is abs ...
: this makes the samples sound like they were being played in a room that echoes the sounds.
** Delay: this produces an artificial echo.
** Frequency filters: these will modify the sound by either attenuating or highlighting certain frequencies.
References
{{Reflist Coding schools Educational programming languages