Eclass on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
ECLASS (formerly styled as eCl@ss) is a data standard for the
 The association offers the following memberships:
* Ordinary members: Ordinary members can be companies, associations or public bodies or regional authorities.
* Supporting members: The purpose of supporting membership is to give natural persons or companies the opportunity to get to know the work of the association, to support it financially and professionally and to receive suitable information on classification, standardization, etc. on the basis of a reduced membership fee.
In addition to the usual association bodies such as the General Assembly and the Board, the association also has the following bodies:
* A Head Office for the coordination and implementation of ongoing tasks as assigned by the Board: The operational and administrative activities of the association are carried out by a Head Office on behalf of the Board. In addition to the Head Office in Germany (at the German Economic Institute), ECLASS maintains regional offices in China, Austria, Portugal, Spain, South Korea, the USA and Switzerland.
The association offers the following memberships:
* Ordinary members: Ordinary members can be companies, associations or public bodies or regional authorities.
* Supporting members: The purpose of supporting membership is to give natural persons or companies the opportunity to get to know the work of the association, to support it financially and professionally and to receive suitable information on classification, standardization, etc. on the basis of a reduced membership fee.
In addition to the usual association bodies such as the General Assembly and the Board, the association also has the following bodies:
* A Head Office for the coordination and implementation of ongoing tasks as assigned by the Board: The operational and administrative activities of the association are carried out by a Head Office on behalf of the Board. In addition to the Head Office in Germany (at the German Economic Institute), ECLASS maintains regional offices in China, Austria, Portugal, Spain, South Korea, the USA and Switzerland.
 The ECLASS standard is a hierarchical system, similar to the UNSPSC classification system, for grouping products and services. It consists of four levels of hierarchy (classes): Segment (Level 1), Main Group (Level 2), Group (Level 3) and Subgroup (Level 4). The hierarchy shows that a superordinate class comprises its subordinate classes, i.e. they are logically assigned to it.
The ECLASS standard is a hierarchical system, similar to the UNSPSC classification system, for grouping products and services. It consists of four levels of hierarchy (classes): Segment (Level 1), Main Group (Level 2), Group (Level 3) and Subgroup (Level 4). The hierarchy shows that a superordinate class comprises its subordinate classes, i.e. they are logically assigned to it.
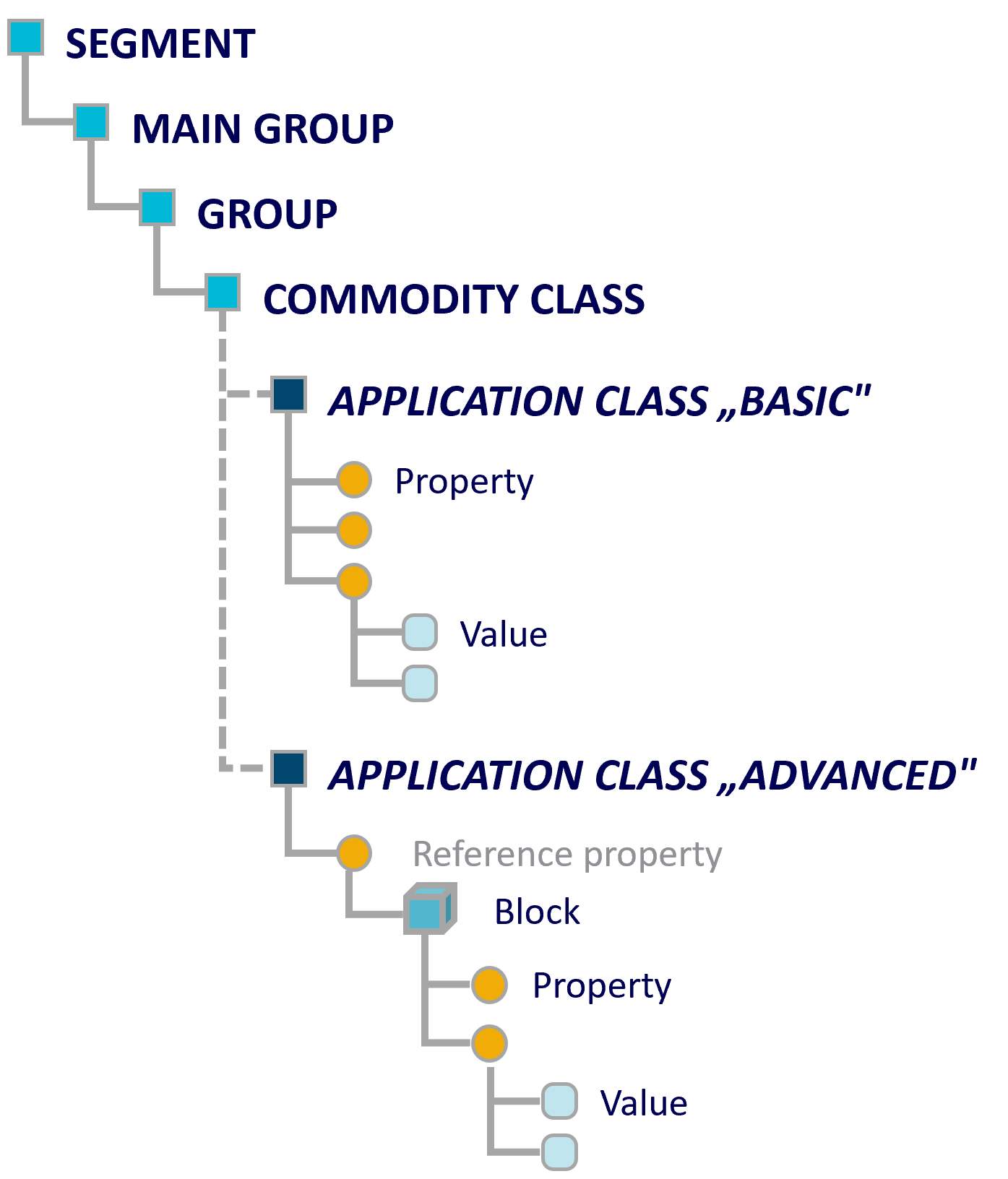 The nodes of the tree structure are collectively referred to as material classes. On the 4th level (subgroup), ECLASS provides so-called property lists. Properties enable the detailed description of products and services in the associated master data and thus enable searching in the various catalogs. The properties are defined by values. Attached keywords and synonyms are used to quickly find the product classes and their property lists.
In summary, the system consists of the following elements:
* Classes - the classes or product groups allow products to be grouped and organized in this way.
* Keywords - keywords assigned to the individual classes simplify and standardize the search for products (e.g. product group "chairs" is also found with search terms such as "seat" or "office chair").
* Properties - Properties are additional product attributes that can only be used meaningfully for products in a specific class, for example the power of light bulbs or the diameter of tubes. The aim is to incorporate these properties into standardization, i.e.
The nodes of the tree structure are collectively referred to as material classes. On the 4th level (subgroup), ECLASS provides so-called property lists. Properties enable the detailed description of products and services in the associated master data and thus enable searching in the various catalogs. The properties are defined by values. Attached keywords and synonyms are used to quickly find the product classes and their property lists.
In summary, the system consists of the following elements:
* Classes - the classes or product groups allow products to be grouped and organized in this way.
* Keywords - keywords assigned to the individual classes simplify and standardize the search for products (e.g. product group "chairs" is also found with search terms such as "seat" or "office chair").
* Properties - Properties are additional product attributes that can only be used meaningfully for products in a specific class, for example the power of light bulbs or the diameter of tubes. The aim is to incorporate these properties into standardization, i.e.

Webpage of ECLASS e.V. association
ECLASS structure
ECLASS Technical Support
classification
Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identif ...
of products and services using standardized ISO-compliant properties. The ECLASS Standard enables the digital exchange of product master data across industries, countries, languages or organizations. Its use as a standardized basis for a product group structure or with product-describing properties of master data is particularly widespread in ERP systems.
As an ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
-compliant and the world's only property-based classification standard, ECLASS also serves as a "language" for Industry 4.0 (IOTS).
The association
Foundation and organization
ECLASS e.V. was founded on November 14, 2000 by 12 major companies in the German economy. As of 2023, the association has around 150 members worldwide from industry, associations and public institutions. A standard for the exchange of information between suppliers and customers is fundamental to the electronic procurement of services - just as it is for material products. ECLASS e.V. is anon-profit organization
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or so ...
that defines, develops and distributes the cross-industry classification and master data standard of the same name internationally.
ECLASS e.V. was founded by the companies Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, building automation, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest engineering company in Europe, and holds the positi ...
, BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Ge ...
, Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. A subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The origins of the compa ...
/ VW, E.ON
E.ON SE is a European multinational electric utility company based in Essen, Germany. It operates as one of the world's largest investor-owned electric utility service providers. The name originates from the Latin word '' aeon'', derived from ...
, SAP
Sap is a fluid transported in the xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a s ...
, Bayer AG
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's ...
, Degussa, Wacker Chemie
Wacker Chemie AG is a German multinational chemical company which was founded in 1914 by Alexander Wacker. The company is controlled by the Wacker family holding more than 50 percent of the shares. The corporation operates more than 25 producti ...
, Infraserv Chemfidence and Solvay. Today, in addition to large industrial companies, its members include many medium-sized companies as well as large public sector organizations such as the state of North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia or North-Rhine/Westphalia, commonly shortened to NRW, is a States of Germany, state () in Old states of Germany, Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the List of German states by population, most ...
and the Austrian Federal Procurement Agency.
Membership
 The association offers the following memberships:
* Ordinary members: Ordinary members can be companies, associations or public bodies or regional authorities.
* Supporting members: The purpose of supporting membership is to give natural persons or companies the opportunity to get to know the work of the association, to support it financially and professionally and to receive suitable information on classification, standardization, etc. on the basis of a reduced membership fee.
In addition to the usual association bodies such as the General Assembly and the Board, the association also has the following bodies:
* A Head Office for the coordination and implementation of ongoing tasks as assigned by the Board: The operational and administrative activities of the association are carried out by a Head Office on behalf of the Board. In addition to the Head Office in Germany (at the German Economic Institute), ECLASS maintains regional offices in China, Austria, Portugal, Spain, South Korea, the USA and Switzerland.
The association offers the following memberships:
* Ordinary members: Ordinary members can be companies, associations or public bodies or regional authorities.
* Supporting members: The purpose of supporting membership is to give natural persons or companies the opportunity to get to know the work of the association, to support it financially and professionally and to receive suitable information on classification, standardization, etc. on the basis of a reduced membership fee.
In addition to the usual association bodies such as the General Assembly and the Board, the association also has the following bodies:
* A Head Office for the coordination and implementation of ongoing tasks as assigned by the Board: The operational and administrative activities of the association are carried out by a Head Office on behalf of the Board. In addition to the Head Office in Germany (at the German Economic Institute), ECLASS maintains regional offices in China, Austria, Portugal, Spain, South Korea, the USA and Switzerland.
Financing
The association is financed by membership fees and income from the distribution of the ECLASS Standard. Each ordinary member pays an annual membership fee according to the size of their company. Supporting members pay a reduced fee. The specific amount of the membership fee is set out in the association's membership fee regulations. The Standard requires a license. The costs for this are staggered according to the size of the company. ECLASS licenses can be purchased via the ECLASS website.The ECLASS Standard
 The ECLASS standard is a hierarchical system, similar to the UNSPSC classification system, for grouping products and services. It consists of four levels of hierarchy (classes): Segment (Level 1), Main Group (Level 2), Group (Level 3) and Subgroup (Level 4). The hierarchy shows that a superordinate class comprises its subordinate classes, i.e. they are logically assigned to it.
The ECLASS standard is a hierarchical system, similar to the UNSPSC classification system, for grouping products and services. It consists of four levels of hierarchy (classes): Segment (Level 1), Main Group (Level 2), Group (Level 3) and Subgroup (Level 4). The hierarchy shows that a superordinate class comprises its subordinate classes, i.e. they are logically assigned to it.
 The nodes of the tree structure are collectively referred to as material classes. On the 4th level (subgroup), ECLASS provides so-called property lists. Properties enable the detailed description of products and services in the associated master data and thus enable searching in the various catalogs. The properties are defined by values. Attached keywords and synonyms are used to quickly find the product classes and their property lists.
In summary, the system consists of the following elements:
* Classes - the classes or product groups allow products to be grouped and organized in this way.
* Keywords - keywords assigned to the individual classes simplify and standardize the search for products (e.g. product group "chairs" is also found with search terms such as "seat" or "office chair").
* Properties - Properties are additional product attributes that can only be used meaningfully for products in a specific class, for example the power of light bulbs or the diameter of tubes. The aim is to incorporate these properties into standardization, i.e.
The nodes of the tree structure are collectively referred to as material classes. On the 4th level (subgroup), ECLASS provides so-called property lists. Properties enable the detailed description of products and services in the associated master data and thus enable searching in the various catalogs. The properties are defined by values. Attached keywords and synonyms are used to quickly find the product classes and their property lists.
In summary, the system consists of the following elements:
* Classes - the classes or product groups allow products to be grouped and organized in this way.
* Keywords - keywords assigned to the individual classes simplify and standardize the search for products (e.g. product group "chairs" is also found with search terms such as "seat" or "office chair").
* Properties - Properties are additional product attributes that can only be used meaningfully for products in a specific class, for example the power of light bulbs or the diameter of tubes. The aim is to incorporate these properties into standardization, i.e. DIN
DIN or Din or din may refer to:
People and language
* Din (name), people with the name
* Dīn, an Arabic word with three general senses: judgment, custom, and religion from which the name originates
* Dinka language (ISO 639 code: din), spoken ...
, EN, ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
, DKE/IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a vast range of ...
.
* Values - values specify the value range for the properties.
* Units - based on DIN and ECE units to specify the unit of the properties.
International Standards
Both the processes for developing the Standard and the export formats and data model principles are based on international standards. * The data model is based on ISO 13584-42 / IEC 61360. * There is aGlobally Unique Identifier
A Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) is a 128-bit label used to uniquely identify objects in computer systems. The term Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) is also used, mostly in Microsoft systems.
When generated according to the standard methods ...
for each element. This IRDI (International Registration Data Identifier) is based on international standards ISO/IEC 11179-6, ISO 29002 and ISO 6523.
The identification consists of a three-character prefix as proof of origin, of the identifier and the version number of the structural element. The ICD (International Code Designer) for ECLASS is 173.
* The Release process is in accordance with ISO 22274.
Versioning
There is a new release every year. This represents an update of the existing standard in a new version. Until 2021, the planning was staggered: "Major Releases", which contain additional structural changes, were alternated with "Minor Releases", which offer new content with an unchanged structure. In order to accelerate the expansion of the ECLASS Standard and meet the dynamic requirements of users even faster, the ECLASS Board decided to publish only Major Releases from ECLASS Release 12.0 (published in November 2021) onwards. Compared to the previous version "ECLASS 14.0", the latest Release with the name "ECLASS 15.0" (published in November 2024) has approx. 490 new classes, approx. 810 new properties and approx. 1,700 new values. 14 new language translations were added. Over 275,000 Change Requests from users and experts were processed for ECLASS 15.0. ECLASS e.V. publishes machine-readable files for each new version. This makes ECLASS the only standard worldwide that enables automatic - since machine-readable - migrations. The current version of the ECLASS Standard is version 15.0. ECLASS 14.0 (published in November 2023) contains more than 48,000 classes, around 23,000 features and approx. 140,000 keywords.
Release development
Standard is based on ISO standards. Participation in the further development is free of charge for everyone. A free online portal, the ContentDevelopmentPlatform, is available for this purpose, where Change Requests can be submitted. There is also the opportunity to actively participate in expert groups.Benefits
Master data management is only possible with standardized master data. The ECLASS Standard offers benefits along the entire value chain: * Reducing costs: With ECLASS, companies can make purchasing, merchandise management and sales more efficient by bundling volumes and streamlining the variety of goods. * Open up international sales markets: Companies can digitally exchange product master data in 17 languages across all borders. ECLASS opens up electronic catalogs and digital marketplaces to users. * Increasing productivity: ECLASS enables continuous processes, automated interfaces and standardized product information. This helps companies improve their ROI and time-to-market. * Ensuring quality: Thanks to ECLASS, engineering and CAx data is exchanged across the board, efficiently and without data loss. * Optimizing processes sustainably: Harmonized data along the entire value chain - from development to production and sales to maintenance - saves companies time and money. * Staying future-proof: ECLASS offers semantic interoperability and is thus the basis for machine-to-machine communication, I4.0 applications and the digital twin.Cooperation with other organizations
Since January 1, 2006, ETIM has been a member of ECLASS and vice versa. ETIM Deutschland e.V. (from German: ElektroTechnisches InformationsModell) is an initiative to standardize the electronic exchange of product data in the field ofelectrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
. Both organizations have set themselves the goal of harmonizing ETIM with the ECLASS Standard and are working together with VDMA
The VDMA e.V. is a German association of 3,600 German and European mechanical and plant engineering companies. 'Industry' refers to innovation, export orientation and Small and medium-sized enterprises, SMEs. The companies employ around 3 milli ...
, ZVEI and DIN
DIN or Din or din may refer to:
People and language
* Din (name), people with the name
* Dīn, an Arabic word with three general senses: judgment, custom, and religion from which the name originates
* Dinka language (ISO 639 code: din), spoken ...
, among others. Prolist International e.V. was merged into ECLASS e.V. on January 1, 2013.
Distribution
Over 4,000 companies worldwide are already successfully using the ECLASS Standard for digital data exchange across all borders. ECLASS is used in industry, commerce, trade and the service sector. The current 40 segments (as of 2023) include, for example, construction, logistics, food, medicine, optics, automotive, laboratory technology and office supplies. In addition to large international companies such as Siemens, SAP, VW-Audi and BASF, the German medical sector, for example, has opted for ECLASS as the classification standard for electronic data exchange. It is also used in public procurement, e.g. by the purchasing department of the federal government and some federal states of Germany. In 2002, the Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Engineering published a survey according to which 34.9% of the 296 companies surveyed used a standard product classification system, of which 32.4% used ECLASS, i.e. 11.3% in absolute terms. This put ECLASS ahead of ETIM (6.6%) and UNSPSC (3.8%) in Germany.Literature
* * *External links
Webpage of ECLASS e.V. association
ECLASS structure
ECLASS Technical Support
References
{{reflist Product classifications