Du Noüy ring method on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 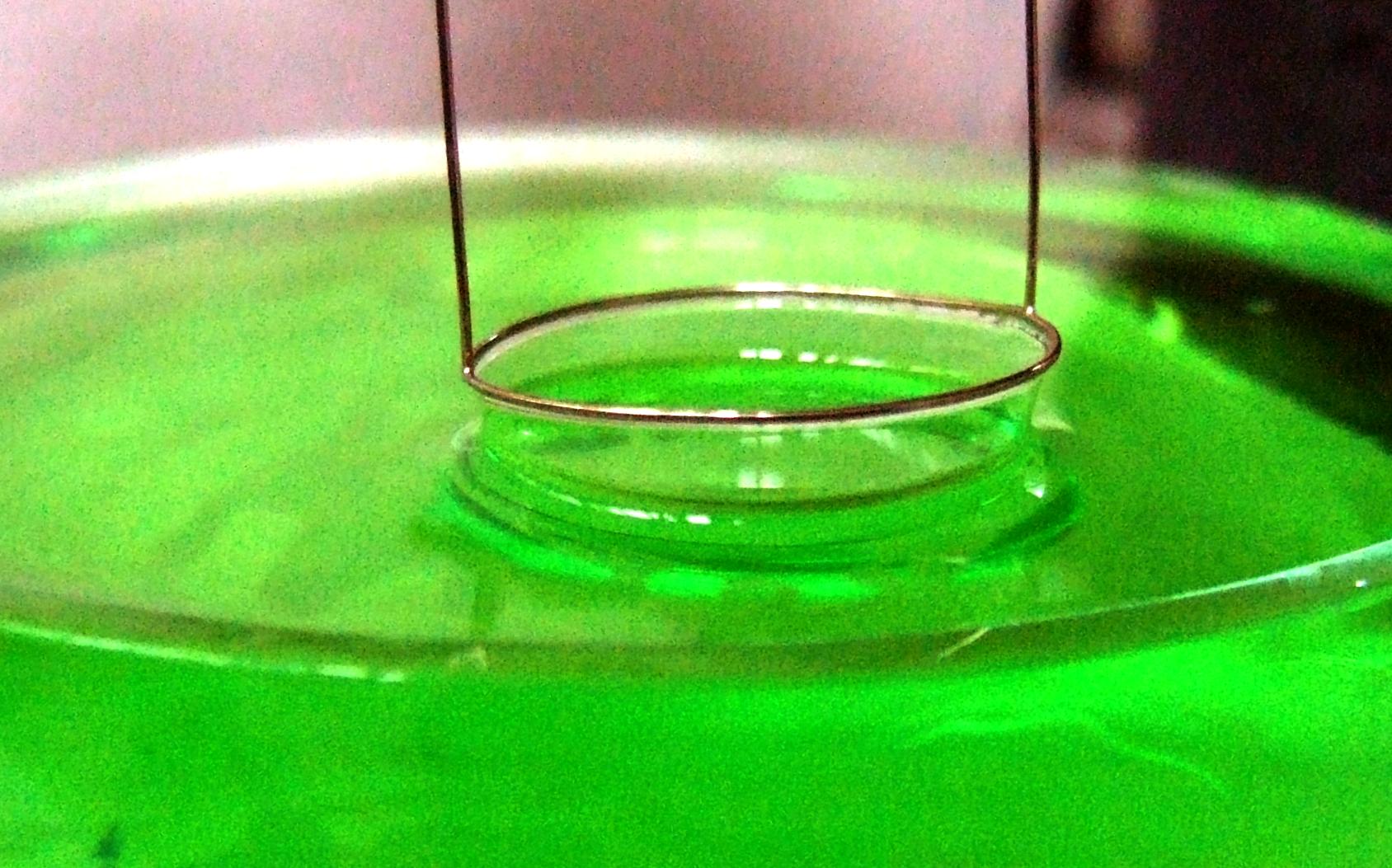 The measurement is performed with a force
The measurement is performed with a force
 *
*
Video showing a classical torsion wire du Noüy tensiometer
Picture of a classical torsion wire du Noüy tensiometer
(National Institutes of Health) {{DEFAULTSORT:Du Nouy ring method Scientific techniques
surface science
Surface science is the study of physical and chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two phases, including solid–liquid interfaces, solid–gas interfaces, solid–vacuum interfaces, and liquid–gas interfaces. It includes the fiel ...
, the du Noüy ring method is a technique for measuring the surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to f ...
of a liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
. The method involves slowly lifting a ring, often made of platinum, from the surface of a liquid. The force, , required to raise the ring from the liquid's surface is measured and related to the liquid's surface tension, :
:
where is the radius of the inner ring of the liquid film pulled and is the radius of the outer ring of the liquid film. is the weight of the ring minus the buoyant force due to the part of the ring below the liquid surface.
When the ring's thickness is much smaller than its diameter, this equation can be simplified to:
:
where is the average of the inner and outer radius of the ring, i.e.
This technique was proposed by the French physicist Pierre Lecomte du Noüy
Pierre Lecomte du Noüy (; 20 December 1883, Paris – 22 September 1947, New York City) was a French biophysicist and philosopher. He is probably best remembered by scientists for his work on the surface tension, and other properties, of liqu ...
(1883–1947) in a paper published in 1925.
 The measurement is performed with a force
The measurement is performed with a force tensiometer
Tensiometer may refer to one of a number of devices. The two most common are:
* Tensiometer (surface tension) an instrument used to measure the surface tension of liquids
*Tensiometer (soil science)
A tensiometer in soil science is a measur ...
, which typically uses an electrobalance to measure the excess force caused by the liquid being pulled up and automatically calculates and displays the surface tension corresponding to the force. Earlier, torsion wire balances were commonly used. The maximum force is used for the calculations, and empirically determined correction factors are required to remove the effect caused by the finite diameter of the ring:
:
with being the correction factor.
The most common correction factors include those by Zuidema and Waters (for liquids with low interfacial tension), Huh and Mason (which covers a wider range than Zuidema-Waters), and Harkins and Jordan (more precise than Huh-Mason while still covering the most widely used liquids).
The surface tension and correction factors are expressed by the following equations:
:
where is surface tension, is the average diameter of the ring, and is correction factor.
* Zuidema and Waters:
** = maximum pull of rings dyn/cm">Dyne.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Dyne">dyn/cm** = density of the lower and upper phases
*
**
** [s2.cm−1]
** = Du Noüy wire radius
** = Du Noüy ring radius
* Huh & Mason: The correction factor is described as a function of and See the references.
* Harkins and Jordan: The correction factor is tabulated as a function of and See the references.
See also
 *
* Sessile drop technique
image:Contact angle.svg, 400px, Fig 1: An illustration of the sessile drop technique with a liquid droplet partially wetting a solid substrate. is the contact angle, and represent the solid–gas, gas–liquid, and liquid–solid interfaces, res ...
* Wilhelmy plate
A Wilhelmy plate is a thin plate that is used to measure equilibrium surface or interfacial tension at an air–liquid or liquid–liquid interface. In this method, the plate is oriented perpendicular to the interface, and the force exerted on ...
References
External links
Video showing a classical torsion wire du Noüy tensiometer
Picture of a classical torsion wire du Noüy tensiometer
(National Institutes of Health) {{DEFAULTSORT:Du Nouy ring method Scientific techniques