Dobruja on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the



 Except for the Danube Delta, a marshy region located in its northeastern corner, Dobruja is hilly, with an average altitude of about 200–300 metres. The highest point is the Țuțuiatu (Greci) Peak in the Măcin Mountains, having a height of 467 m. The Dobruja Plateau covers most of the Romanian part of Dobruja. The
Except for the Danube Delta, a marshy region located in its northeastern corner, Dobruja is hilly, with an average altitude of about 200–300 metres. The highest point is the Țuțuiatu (Greci) Peak in the Măcin Mountains, having a height of 467 m. The Dobruja Plateau covers most of the Romanian part of Dobruja. The
 During the early
During the early  In 313 BC and again in 310–309 BC, the Greek colonies led by Callatis, supported by Antigonus I Monophthalmus, revolted against Macedonian rule. The revolts were suppressed by Lysimachus, the diadochus of
In 313 BC and again in 310–309 BC, the Greek colonies led by Callatis, supported by Antigonus I Monophthalmus, revolted against Macedonian rule. The revolts were suppressed by Lysimachus, the diadochus of
 In 15 AD the Roman province of Moesia was created, but Dobruja, under the name ''Ripa Thraciae'', remained part of the Odrysian kingdom. The Greek cities on the coast formed a '' praefectura orae maritimae''. In 46 AD
In 15 AD the Roman province of Moesia was created, but Dobruja, under the name ''Ripa Thraciae'', remained part of the Odrysian kingdom. The Greek cities on the coast formed a '' praefectura orae maritimae''. In 46 AD
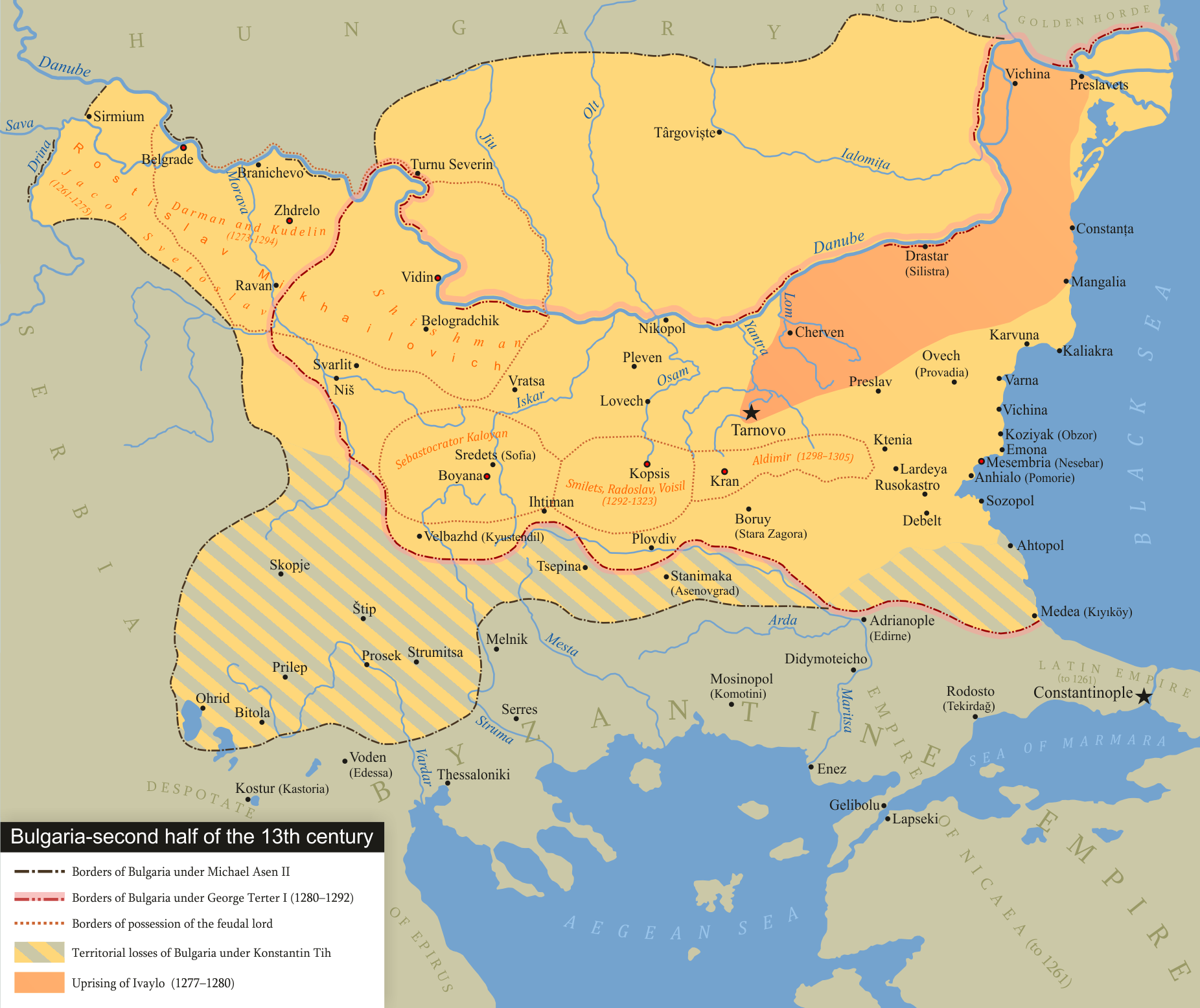 In 1187 the Byzantines lost control of Dobruja to the restored Bulgarian Empire. In 1241, the first Tatar groups, under
In 1187 the Byzantines lost control of Dobruja to the restored Bulgarian Empire. In 1241, the first Tatar groups, under 
 Between 1352 and 1359, with the collapse of Golden Horde rule in Northern Dobruja, a new state appeared. It was controlled by Tatar prince
Between 1352 and 1359, with the collapse of Golden Horde rule in Northern Dobruja, a new state appeared. It was controlled by Tatar prince
 Ottoman Sultan
Ottoman Sultan
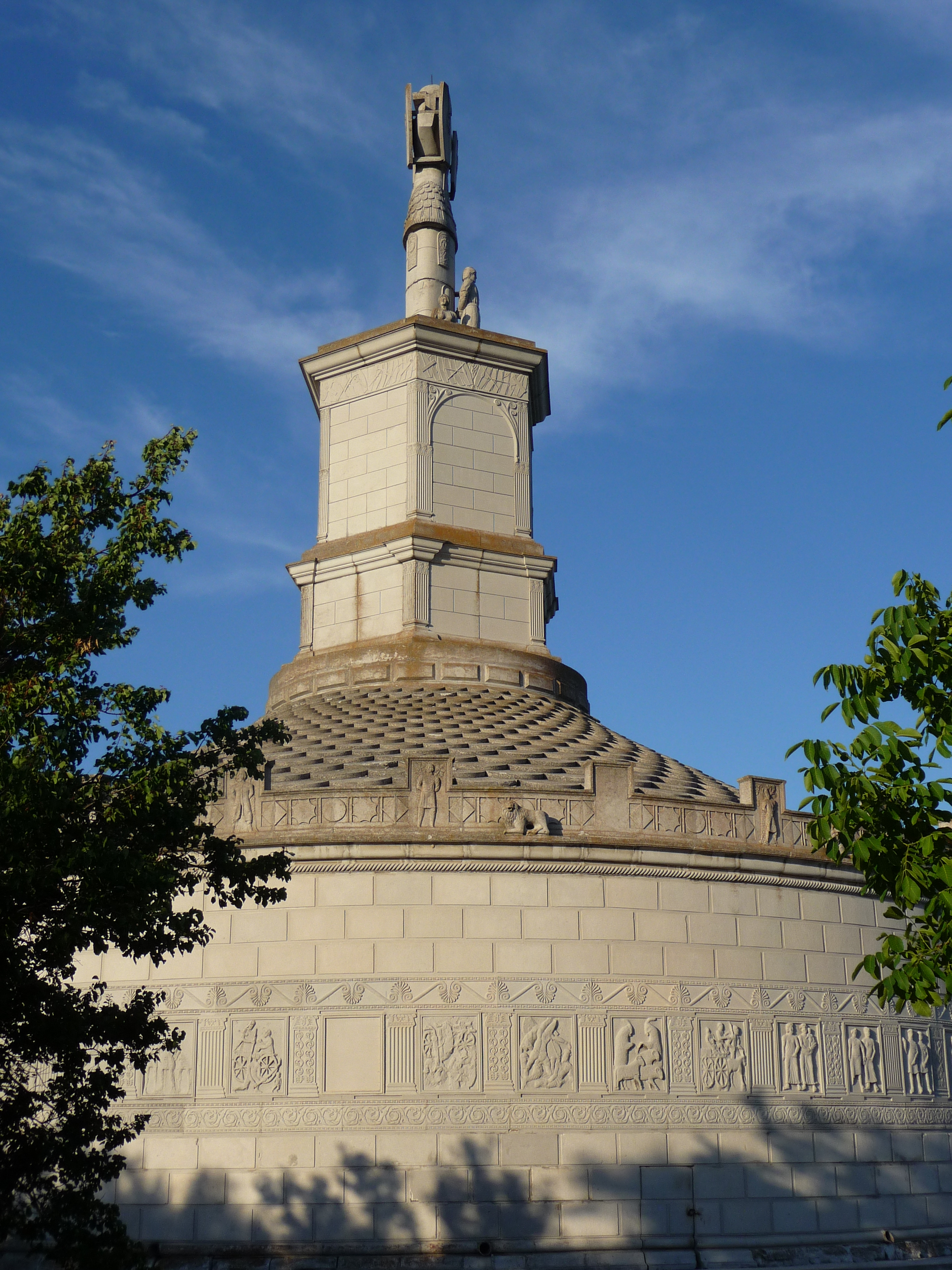
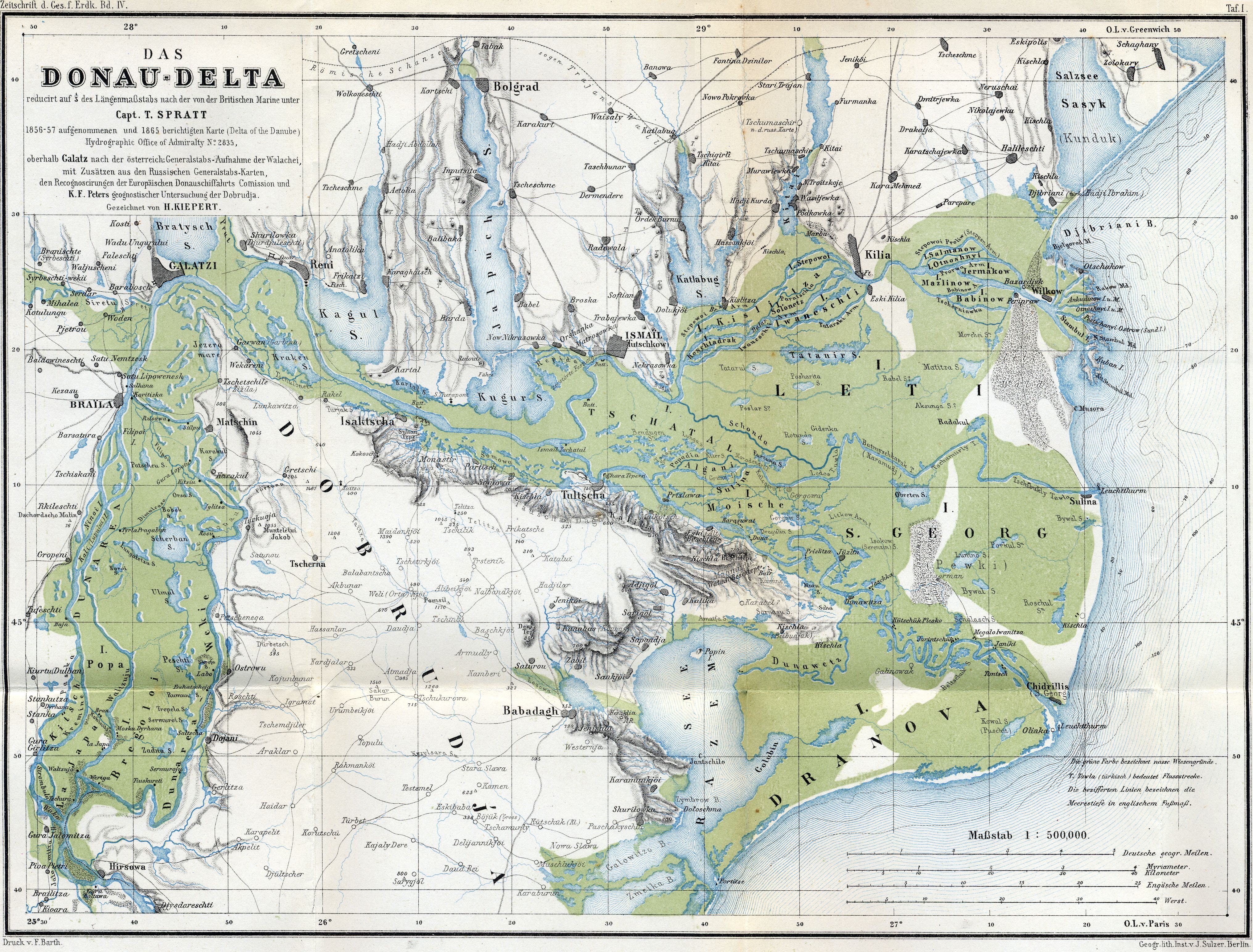 Occupied by the Turks in 1420, the region remained under Ottoman control until the late 19th century. Initially, it was organised as an ''udj'' (border province), included in the sanjak of Silistra, part of the Eyalet of Rumelia. Later, under
Occupied by the Turks in 1420, the region remained under Ottoman control until the late 19th century. Initially, it was organised as an ''udj'' (border province), included in the sanjak of Silistra, part of the Eyalet of Rumelia. Later, under  According to Bulgarian historian
According to Bulgarian historian
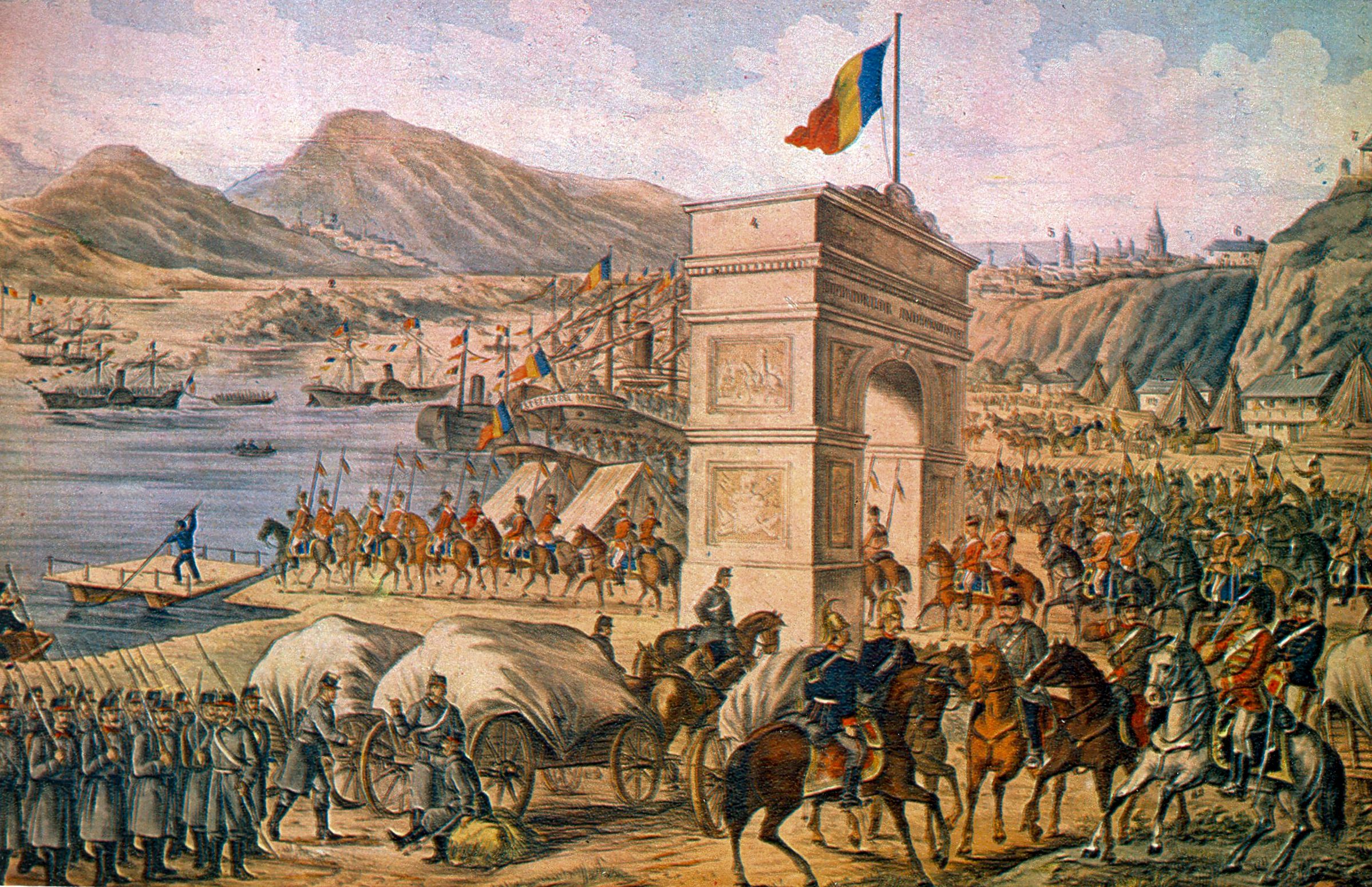

 After the 1878 war, the
After the 1878 war, the 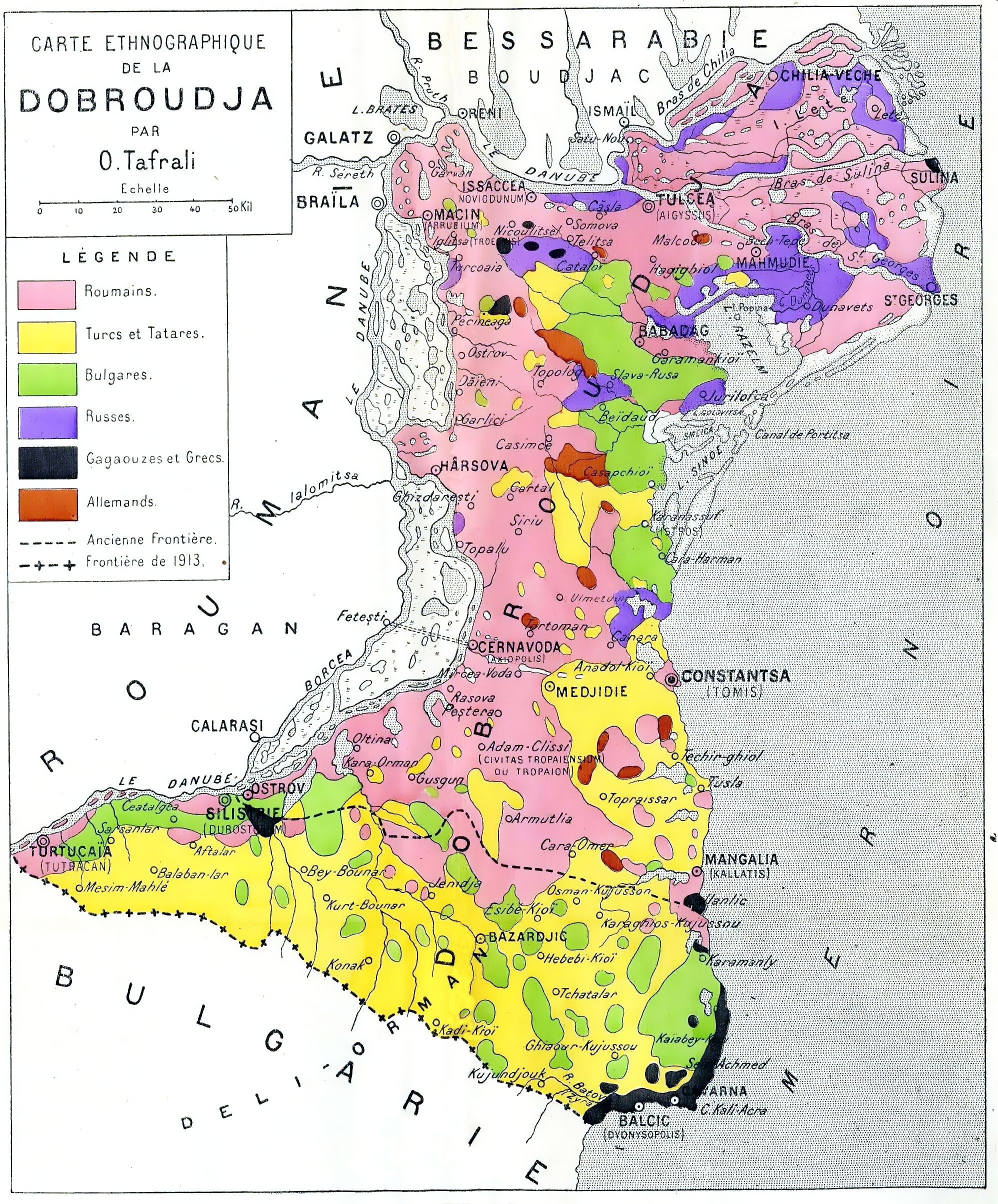 At the beginning of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, most of Dobruja's population was composed of ethnic Tatars, Turks, Romanians, and Bulgarians. During the war, a large part of the Muslim population was evacuated to Bulgaria and Turkey. After 1878, the Romanian government encouraged Romanians from other regions to settle in Northern Dobruja and accepted the return of some Muslim population displaced by the war.
According to Bulgarian historians, after 1878 the Romanian church authorities took control over all local churches, with the exception of two in the towns of Tulcea and Constanţa, which managed to retain use of their Bulgarian Slavonic liturgy. Between 1879 and 1900, Bulgarians built 15 new churches in Northern Dobruja. After 1880,
At the beginning of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, most of Dobruja's population was composed of ethnic Tatars, Turks, Romanians, and Bulgarians. During the war, a large part of the Muslim population was evacuated to Bulgaria and Turkey. After 1878, the Romanian government encouraged Romanians from other regions to settle in Northern Dobruja and accepted the return of some Muslim population displaced by the war.
According to Bulgarian historians, after 1878 the Romanian church authorities took control over all local churches, with the exception of two in the towns of Tulcea and Constanţa, which managed to retain use of their Bulgarian Slavonic liturgy. Between 1879 and 1900, Bulgarians built 15 new churches in Northern Dobruja. After 1880,
File:Cazinoul din Constanta vedere laterala.jpg, Constanța
File:Administrația Pescăriei Statului.jpg,
"The California of the Romanians": The Integration of Northern Dobrogea into Romania, 1878-1913''
in ''Nation-Building and Contested Identities Romanian & Hungarian Case Studies'' * * {{Coord, 44, 27, N, 28, 20, E, display=t Divided regions Historical regions in Bulgaria Historical regions in Romania
Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
. It is situated between the lower Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
River and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
, and includes the Danube Delta, Romanian coast, and the northernmost part of the Bulgarian coast. The territory of Dobruja is made up of Northern Dobruja, which is part of Romania, and Southern Dobruja, which is part of Bulgaria.
The territory of the Romanian region Dobrogea is organised as the counties of Constanța and Tulcea
Tulcea (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in Northern Dobruja, Romania. It is the administrative center of Tulcea County, and had a population of 73,707 . One village, Tudor Vladimirescu, is administered by the city.
Names
The ...
, with a combined area of and a population of slightly less than 900,000. Its main cities are Constanța, Tulcea
Tulcea (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in Northern Dobruja, Romania. It is the administrative center of Tulcea County, and had a population of 73,707 . One village, Tudor Vladimirescu, is administered by the city.
Names
The ...
, Medgidia and Mangalia. Dobrogea is represented by dolphins in the coat of arms of Romania
The coat of arms of Romania was adopted in the Romanian Parliament on 10 September 1992 as a representative coat of arms for Romania. It is based on the Lesser Coat of Arms of the Kingdom of Romania (used between 1922 and 1947), redesigned by Vi ...
.
The Bulgarian region Dobrudzha is divided among the administrative regions of Dobrich and Silistra; the following villages of Razgrad Province: Konevo, Rainino, Terter and Madrevo; and the village General Kantardzhievo ( Varna). This section has a total area of , with a combined population of some 310,000 people, the main towns being Dobrich and Silistra (regional seats).
Geography


 Except for the Danube Delta, a marshy region located in its northeastern corner, Dobruja is hilly, with an average altitude of about 200–300 metres. The highest point is the Țuțuiatu (Greci) Peak in the Măcin Mountains, having a height of 467 m. The Dobruja Plateau covers most of the Romanian part of Dobruja. The
Except for the Danube Delta, a marshy region located in its northeastern corner, Dobruja is hilly, with an average altitude of about 200–300 metres. The highest point is the Țuțuiatu (Greci) Peak in the Măcin Mountains, having a height of 467 m. The Dobruja Plateau covers most of the Romanian part of Dobruja. The Ludogorie Plateau
The Ludogorie ( bg, Лудогорие, usually used with a definite article, Лудогорието, ''Ludogorieto'') or Deliorman (''Делиорман'', tr, Deli Orman, lit=mad forest and Bulgarian: lud - "mad", "crazy" and gora - "forest"), ...
is found in Bulgaria. Lake Razelm is one of the most important lakes in Northern Dobruja.
Dobruja lies in the temperate continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continent, the major landmasses of Earth
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' ( ...
climatic area; the local climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
is determined by the influx of oceanic air from the northwest and northeast and continental air from the East European Plain
The East European Plain (also called the Russian Plain, "Extending from eastern Poland through the entire European Russia to the Ural Mountaina, the ''East European Plain'' encompasses all of the Baltic states and Belarus, nearly all of Ukraine, an ...
. Dobruja's relatively level terrain and its bare location facilitate the influx of humid, warm air in the spring, summer, and autumn from the northwest, as well as that of northern and northeastern polar air in the winter. The Black Sea also exerts an influence over the region's climate, particularly within 40–60 kilometres from the coast. The average annual temperatures range from 11 °C inland and along the Danube, to 11.8 °C on the coast and less than 10 °C in the higher parts of the plateau. The coastal region of Southern Dobruja is the aridest part of Bulgaria, with an annual precipitation of 450 millimetres.
Dobruja is a windy region once known for its windmill
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called sails or blades, specifically to mill grain (gristmills), but the term is also extended to windpumps, wind turbines, and other applications, in some ...
s. There is wind during about 85–90% of all days; it usually comes from the north or northeast. The average wind speed is about twice higher than the average in Bulgaria. Due to the limited precipitation and the proximity to the sea, rivers in Dobruja are usually short and with low discharge. The region has several shallow seaside lakes with brackish water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
.
Etymology
The most widespread opinion among scholars is that the origin of the term ''Dobruja'' is to be found in the Turkish rendition of the name of a 14th‑century Bulgarian ruler, despot Dobrotitsa. It was common for the Turks to name countries after one of their early rulers (for example, nearby Moldavia was known as ''Bogdan Iflak'' by the Turks, named after Bogdan I). Other etymologies have been considered, but never gained widespread acceptance. Abdolonyme Ubicini believed the name meant "good lands", derived from Slavic ''dobro'' ("good"), an opinion that was adopted by several 19th‑century scholars. This derivation appears to contrast with the usual 19th‑century description of Dobruja as a dry barren land; it has been explained as expressing the point of view of Ruthenes, who considered the Danube delta in the northern Dobruja as a significant improvement over thesteppes
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grassland ...
to the North. I. A. Nazarettean combines the Slavic word with the Tatar ''budjak'' ("corner"), thus proposing the etymology "good corner".
A version matching contemporaneous descriptions was suggested by Kanitz, who associated the name with the Bulgarian ''dobrice'' ("rocky and unproductive terrain"). According to Gheorghe I. Brătianu
Gheorghe (George) I. Brătianu (January 28 1898 – April 23–27, 1953) was a Romanian politician and historian. A member of the Brătianu family and initially affiliated with the National Liberal Party (Romania, 1875), National Liberal Par ...
, the name is a Slavic derivation from the Turkic word ''Bordjan'' or ''Brudjars'', which referred to the Turkic Proto-Bulgarians; this term was also used by Arabic writers.
One of the earliest documented uses of the name can be found in the Turkish ''Oghuz-name'' narrative, dated to the 15th century, where it appears as ''Dobruja-éli''. The possessive suffix
In linguistics, a possessive affix (from la, affixum possessivum) is an affix (usually suffix or prefix) attached to a noun to indicate its possessor, much in the manner of possessive adjectives.
Possessive affixes are found in many languages o ...
''el-i'' indicated that the land was considered as belonging to Dobrotitsa ("" in the original Ottoman Turkish). The loss of the final particle is not unusual in the Turkish world, a similar evolution being observed in the name of Aydın, originally ''Aydın-éli''. Another early use is in the 16th‑century Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
translation of Laonicus Chalcondyles' ''Histories'', where the term ''Dobroditia'' is used for the original Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
"Dobrotitsa's country" (). In the 17th century, the region was referred to in more accounts, with renditions such as ''Dobrucia'', ''Dobrutcha'', ''Dobrus'', ''Dobruccia'', ''Dobroudja'', ''Dobrudscha'', and others being used by foreign authors.
Initially, the name meant just the steppe of the southern region, between the forests around Babadag in the north and the Silistra– Dobrich–Balchik
Balchik ( bg, Балчик ; ro, Balcic) is a Black Sea coastal town and seaside resort in the Southern Dobruja area of northeastern Bulgaria. It is in Dobrich Province, 35 km southeast of Dobrich and 42 km northeast of Varna. It spr ...
line in the south. Eventually, the term was extended to include the northern part and the Danube Delta. In the 19th century, some authors used the name to refer just to the territory between the southernmost branch of the Danube (St. George) in the north and the Karasu Valley (nowadays the Danube-Black Sea Canal) in the south.
History
Prehistory
The territory of Dobruja has been inhabited by humans since Middle and Upper Palaeolithic, as the remains at Babadag, Slava Rusă and Enisala demonstrate. Paleolithic people made tools of silex and ate fruits, fish, and other hunted animals. In this period fire was discovered, and at its end, the bow with arrows and the boat sculpted from a trunk tree was invented. There were found tools in caves, inclusive Gura Dobrogei. In theNeolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
, the territory was occupied by members of the Hamangia culture (named after a village on the Dobrujan coast), Boian culture, and Karanovo V culture. At the end of the fifth millennium BC, under the influence of some Aegeo-Mediterranean tribes and cultures, the Gumelniţa culture appeared in the region. In the Eneolithic
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often v ...
, populations migrating from the north of the Black Sea, of the Kurgan
A kurgan is a type of tumulus constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central As ...
culture, mixed with the previous population, creating the Cernavodă I culture. Under Kurgan II influence, the Cernavodă II culture emerged. Through the combination of the Cernavodă I and Ezero culture
The Ezero culture, 3300—2700 BC, was a Bronze Age archaeological culture occupying most of present-day Bulgaria. It takes its name from the Tell-settlement of Ezero.
Ezero follows the copper age cultures of the area ( Karanovo VI culture, ...
, the Cernavodă III culture developed. The region had commercial contact with the Mediterranean world since the 14th century BC, as proven by a Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; grc, Μυκῆναι or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos; and south of Corinth. ...
a sword discovered at Medgidia, but under the reserve demanded by lack of hard evidence in what concerns the provenience/manufacturer of such armours.
Mikra Skythia
Ancient history
 During the early
During the early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
(8th–6th centuries BC), there was increased differentiation of the local Getic tribes from the Thracian mass. In the second part of the 8th century BC, the first signs of commercial relations between the indigenous population and the Greeks appeared on the shore of the Halmyris Gulf (now the Sinoe Lake).
In 657/656 BC ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
colonists from Miletus founded a colony in the region: Histria. In the 7th and 6th centuries BC, more Greek colonies were founded on the Dobrujan coast ( Callatis, Tomis, Mesembria, Dionysopolis, Parthenopolis, Aphrodisias, Eumenia etc.). In the 5th century BC these colonies were under the influence of the Delian League, passing in this period from oligarchy
Oligarchy (; ) is a conceptual form of power structure in which power rests with a small number of people. These people may or may not be distinguished by one or several characteristics, such as nobility, fame, wealth, education, or corporate, r ...
to democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which people, the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation ("direct democracy"), or to choo ...
. In the 6th century BC, the first Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
groups began to enter the region. Two Getic tribes, the ''Crobyzi'' and ''Terizi'', and the town of Orgame ( Argamum) were mentioned on the territory of present Dobruja by Hekataios of Miletus (540–470 BC).
In 514/512 BC King Darius I of Persia subdued the Getae living in the region during his expedition against Scythians living north of the Danube. At about 430 BC, the Odrysian kingdom
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria an ...
under Sitalkes extended its rule to the mouths of the Danube. In 429 BC, Getae from the region participated in an Odrysian campaign in Macedonia. In the 4th century BC, the Scythians brought Dobruja under their sway. In 341–339 BC, one of their kings, Atheas, fought against Histria, which was supported by a ''Histrianorum rex'' (probably a local Getic ruler). In 339 BC, King Atheas was defeated by the Macedonians under King Philip II Philip II may refer to:
* Philip II of Macedon (382–336 BC)
* Philip II (emperor) (238–249), Roman emperor
* Philip II, Prince of Taranto (1329–1374)
* Philip II, Duke of Burgundy (1342–1404)
* Philip II, Duke of Savoy (1438-1497)
* Philip ...
, who afterwards extended his rule over Dobruja.
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, who also began a military expedition against Dromichaetes, the ruler of the Getae north of the Danube, in 300 BC. In the 3rd century BC, colonies on the Dobrujan coast paid tribute to the basilei Zalmodegikos and Moskon
Moskon was a Getic king who ruled in the 3rd century BC the northern parts of Dobruja, probably being the head of a local tribal union, which had close relations with the local Greek colonies and adopted the Greek style of administration.
His exi ...
, who probably also ruled northern Dobruja. In the same century, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
settled in the north of the region. In 260 BC, Byzantion
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
lost the war with Callatis and Histria for the control of Tomis. At the end of the 3rd century BC and the beginning of the 2nd century BC, the Bastarnae
The Bastarnae ( Latin variants: ''Bastarni'', or ''Basternae''; grc, Βαστάρναι or Βαστέρναι) and Peucini ( grc, Πευκῖνοι) were two ancient peoples who between 200 BC and 300 AD inhabited areas north of the Roman front ...
settled in the area of the Danube Delta. Around 200 BC, the Thracian king Zoltes invaded the province several times, but was defeated by Rhemaxos, who became the protector of the Greek colonies.
Early Greek scholars such as Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
appear to have regarded the region as the south-western extension of Scythia – a practice also followed in a 2nd-century BC inscription, recording a decree made in Histria, which refers to the region surrounding the Greek city as ''Scythia''. However, the toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
Μικρά Σκυθία (''Mikra Skythia''), usually translated as Scythia Minor
Scythia Minor or Lesser Scythia (Greek: , ) was a Roman province in late antiquity, corresponding to the lands between the Danube and the Black Sea, today's Dobruja divided between Romania and Bulgaria. It was detached from Moesia Inferior by th ...
or Lesser Scythia appears to have become the name for the specific region later known as Dobruja. The earliest known usage of the name "Scythia Minor" (''Mikra Skythia'') is found in Strabo's early ''Geography'' (1st century AD). The Greeks thus apparently distinguished it from ''Scythia Major'', which lay north of the Danube delta.
Around 100 BC King Mithridates VI of Pontus extended his authority over the Greek cities in Dobruja. However, in 72–71 BC, during the Third Mithridatic War, these cities were occupied by the forces of Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus
Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus (116 – soon after 56 BC), younger brother of the more famous Lucius Licinius Lucullus, was a supporter of Lucius Cornelius Sulla and consul of ancient Rome in 73 BC. As proconsul of Macedonia in 72 BC, he defea ...
, the Roman proconsul
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority.
In the Roman Republic, military command, or ...
of Macedonia. A foedus
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign stat ...
was signed between the Greek colonies and the Roman Republic, but in 62–61 BC the colonies revolted. Gaius Antonius Hybrida intervened, but was defeated by Getae and Bastarnae near Histria. After 55 BC the Dacian Kingdom
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It t ...
under King Burebista conquered Dobruja and all the Greek colonies on the coast. Their rule ended in 44 BC.
Roman rule
In 28/29 BCRholes Rholes or Roles (Ancient Greek Ῥώλης) was a Getae chieftain in Scythia Minor (modern Dobruja) mentioned by Cassius Dio in his ''Roman History''. According to Dio, he helped Roman general Marcus Licinius Crassus defeat the Bastarnae, and when ...
, a Getic ruler from Southern Dobruja, supported the proconsul of Macedonia, Marcus Licinius Crassus, in his action against the Bastarnae. Declared ''friend and ally of the Roman people'' by Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, Rholes helped Crassus in conquering the states of Dapyx Dapyx was a 1st-century BC chieftain of a Getae tribe or a tribe union in Scythia Minor (nowadays in Dobruja). Cassius Dio talks about him in the campaigns of Marcus Licinius Crassus on the Lower Danube region, being said to be a king on the region ...
(in central Dobruja) and Zyraxes (in the north of the region). Dobruja became part of the client kingdom
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
of the Odrysians, while the Greek cities on the coast came under direct rule of the governor of Macedonia. In 12 AD and 15 AD, Getic armies succeeded in conquering the cities of Aegyssus and Troesmis for a short time, but Odrysian king Rhoemetalces I
Rhoemetalces I (Sapaean) ( grc, Ῥοιμητάλκης) was king of the Sapaean kingdom of Thrace from 15 BC to 12 AD. He was king of Odrysian kingdom of Thrace in succession to his nephew Rhescuporis II (Astaean).
Rhoemetalces I was a loya ...
defeated them with the help of the Roman army.
 In 15 AD the Roman province of Moesia was created, but Dobruja, under the name ''Ripa Thraciae'', remained part of the Odrysian kingdom. The Greek cities on the coast formed a '' praefectura orae maritimae''. In 46 AD
In 15 AD the Roman province of Moesia was created, but Dobruja, under the name ''Ripa Thraciae'', remained part of the Odrysian kingdom. The Greek cities on the coast formed a '' praefectura orae maritimae''. In 46 AD Thracia
Thracia or Thrace ( ''Thrakē'') is the ancient name given to the southeastern Balkan region, the land inhabited by the Thracians. Thrace was ruled by the Odrysian kingdom during the Classical and Hellenistic eras, and briefly by the Greek D ...
became a Roman province and the territories of present Dobruja were absorbed into the province of Moesia. The Geto–Dacians invaded the region several times in the 1st century AD, especially between 62 and 70. In the same period, the base of the Roman Danube fleet (''classis Flavia Moesica'') was moved to Noviodunum {{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
Noviodunum is a name of Celtic origin, meaning "new fort": It comes from '' nowyo'', Celtic for "new", and '' dun'', the Celtic for "hillfort" or "fortified settlement", cognate of English ''town''.
Several places ...
. The ''praefectura'' was annexed to Moesia in 86 AD. In the same year Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
divided Moesia, Dobruja being included in the eastern part, '' Moesia Inferior''.
In the winter of 101–102 the Dacian king Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invas ...
led a coalition of Dacians, Carpians, Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
and Burs in an attack against Moesia Inferior. The invading army was defeated by the Roman legions under Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
on the Yantra river
The Yantra ( bg, Янтра ) is a river in northern Bulgaria, a right tributary of the Danube. It is long (the third longest Bulgarian tributary of the Danube, after Iskar and Osam), and has a watershed of . Its average discharge at the mouth ...
. (Later Nicopolis ad Istrum
Nicopolis ad Istrum ( el, Νικόπολις ἡ πρὸς Ἴστρον) or Nicopolis ad Iatrum was a Roman and Early Byzantine town.
Its ruins are located at the village of Nikyup, 20 km north of Veliko Tarnovo in northern Bulgaria. The ...
was founded there to commemorate the victory.) The invaders were also defeated near the modern village of Adamclisi
Adamclisi () is a commune in Constanța County, in the Dobrogea region of Romania.
History
In ancient times, a Roman castrum named Civitas Tropaensium was settled here and in 109 AD a monument named Tropaeum Traiani was built to commemorate th ...
, in the southern part of Dobruja. The latter victory was commemorated by the a monument, built in 109 at the site, and the founding of the city of Tropaeum. After 105, Legio XI Claudia
Legio XI Claudia ("Claudius' Eleventh Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. The legion was levied by Julius Caesar for his campaign against the Nervii. XI ''Claudia'' dates back to the two legions (the other was the XIIth) recruit ...
and Legio V Macedonica were moved to Dobruja, at Durostorum and Troesmis, respectively.
In 118 Hadrian intervened in the region to calm a Sarmatian rebellion. In 170 Costoboci invaded Dobruja, attacking Libida, Ulmetum and Tropaeum
''Tropaeum'' is an extinct genus of ammonites found throughout the oceans of the world during the Early Cretaceous. As with many other members of the family Ancyloceratidae, there was a trend among species within this genus to uncoil somewhat, ...
. The province was generally stable and prosperous until the crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis (AD 235–284), was a period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed. The crisis ended due to the military victories of Aurelian and with the ascensio ...
, which led to the weakening of defences and numerous barbarian invasions. In 248 a coalition of Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, Carpians, Taifali
The Taifals or Tayfals ( la, Taifali, Taifalae or ''Theifali''; french: Taïfales) were a people group of Germanic or Sarmatian origin, first documented north of the lower Danube in the mid third century AD. They experienced an unsettled and fra ...
, Bastarnae and Hasdingi, led by Argaithus and Guntheric, devastated Dobruja. During the reign of Trajan Decius
Gaius Messius Quintus Traianus Decius ( 201 ADJune 251 AD), sometimes translated as Trajan Decius or Decius, was the emperor of the Roman Empire from 249 to 251.
A distinguished politician during the reign of Philip the Arab, Decius was procla ...
the province suffered greatly from the attack of Goths under King Cniva
Cniva ( mid-3rd century AD) was a Gothic king who invaded the Roman Empire. He successfully captured the city of Philippopolis (Plovdiv in Bulgaria) in 250 and killed Emperor Decius and his son Herennius Etruscus at the Battle of Abritus as he ...
. Barbarian attacks followed in 258, 263 and 267. In 269 a fleet of allied Goths, Heruli
The Heruli (or Herules) were an early Germanic people. Possibly originating in Scandinavia, the Heruli are first mentioned by Roman authors as one of several " Scythian" groups raiding Roman provinces in the Balkans and the Aegean Sea, attacking ...
, Bastarnae
The Bastarnae ( Latin variants: ''Bastarni'', or ''Basternae''; grc, Βαστάρναι or Βαστέρναι) and Peucini ( grc, Πευκῖνοι) were two ancient peoples who between 200 BC and 300 AD inhabited areas north of the Roman front ...
and Sarmatians attacked the cities on the coast, including Tomis. In 272 Aurelian defeated the Carpians north of the Danube and settled a part of them near Carsium. The same emperor put an end to the crisis in the Roman Empire, thus helping the reconstruction of the province.
During the reign of Diocletian, Dobruja was organized administratively as a separate province, called Scythia, part of the Diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associa ...
of Thracia. Its capital city was Tomis. Diocletian transferred Legio II Herculia to Troesmis and Legio I Iovia to Noviodunum. In 331–332 Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
defeated the Goths who attacked the province. But Dobruja was devastated again by Ostrogoths in 384–386. Under the Roman emperors Licinius, Julian the Apostate, and Valens
Valens ( grc-gre, Ουάλης, Ouálēs; 328 – 9 August 378) was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the eastern half of ...
, the cities of the region were repaired or rebuilt.
Byzantine rule
After the division of theRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
, Dobruja was absorbed into the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
. Between 513 and 520, the region participated in a revolt against Anastasius I. Its leader, Vitalian, native of Zaldapa in Southern Dobruja, defeated the Byzantine general Hypatius near Kaliakra
Kaliakra ( bg, Калиакра; ro, Caliacra) is a cape in the Southern Dobruja region of the northern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, which ends with a long and narrow headland east of Kavarna, northeast of Varna and southwest of Mangalia. Th ...
. During Justin I's rule, Antes and Slavs invaded the region, but Germanus Justinus
Germanus ( el, Γερμανός; died 550) was an East Roman (Byzantine) general, one of the leading commanders of Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565). Germanus was Emperor Justinian's cousin, and a member of the ruling dynasty. He held commands i ...
defeated them. In 529, the Gepid
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
commander Mundus repelled a new invasion by Bulgars and Antes. Kutrigurs and Avars invaded the region several times, until 561–562, when the Avars under Bayan I
Bayan I reigned as the first khagan of the Avar Khaganate between 562 and 602.
As the Göktürk Empire expanded westwards on the Eurasian Steppe during the 6th century, peoples such as the Avars (also known as the ''Pseudo-Avars'', ''Obri'', ...
were settled south of the Danube as foederati. During the rule of Mauricius Tiberius, the Slavs devastated Dobruja, destroying the cities of Dorostolon, Zaldapa, and Tropaeum. In 591/593, Byzantine general Priscus tried to stop invasions, attacking and defeating the Slavs under Ardagast in the north of the province. In 602 during the mutiny of the Byzantine army in the Balkans under Phocas, a large mass of Slavs crossed the Danube, settling south of the Danube. Dobruja remained under loose Byzantine control, and was reorganised during the reign of Constantine IV
Constantine IV ( la, Constantinus; grc-gre, Κωνσταντῖνος, Kōnstantînos; 650–685), called the Younger ( la, iunior; grc-gre, ὁ νέος, ho néos) and sometimes incorrectly the Bearded ( la, Pogonatus; grc-gre, Πωγων ...
as '' Thema Scythia''.
First Bulgarian Empire rule
The results of archaeological research indicate that the Byzantine presence on Dobruja's mainland and the banks of the Danube were reduced at the end of the 6th century, under the pressure of the Migration Period. In the coastal fortifications on the southern bank of the Danube, the latest Byzantine coin found dates from the time of the emperorsTiberius II Constantine
Tiberius II Constantine ( grc-gre, Τιβέριος Κωνσταντῖνος, Tiberios Konstantinos; died 14 August 582) was Eastern Roman emperor from 574 to 582. Tiberius rose to power in 574 when Justin II, prior to a mental breakdown, proc ...
(574–582) and Heraclius (610–641). After that period, all inland Byzantine cities were demolished by the invaders and abandoned.
Some of the earliest Slavic settlements to the south of Danube have been discovered in Dobruja, near the villages of Popina, Garvăn and Nova Cherna. They have been dated to the end of the 6th and the beginning of the 7th centuries. These lands became the main zone of compact Bulgar
Bulgar may refer to:
*Bulgars, extinct people of Central Asia
*Bulgar language, the extinct language of the Bulgars
* Oghur languages
Bulgar may also refer to:
*Bolghar, the capital city of Volga Bulgaria
*Bulgur, a wheat product
* Bulgar, an Ash ...
settlement in the end of the 7th century.
According to the peace treaty of 681, signed after the Bulgarian victory over Byzantines in the Battle of Ongala, Dobruja became part of the First Bulgarian Empire. Shortly after, the Bulgar founded the city of Pliska
Pliska ( , cu, Пльсковъ, translit=Plĭskovŭ) was the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire during the Middle Ages and is now a small town in Shumen Province, on the Ludogorie plateau of the Danubian Plain, 20 km northeast o ...
, which became the first Bulgarian capital, near the southern border of Dobruja. They rebuilt Madara as a major Bulgar pagan religious centre. According to the '' Bulgarian Apocryphal Chronicle'', from the 11th century, Bulgarian Tsar Ispor "accepted the Bulgarian tsardom", created "great cities, Drastar on the Danube", a "great wall from Danube to the sea", "the city of Pliska
Pliska ( , cu, Пльсковъ, translit=Plĭskovŭ) was the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire during the Middle Ages and is now a small town in Shumen Province, on the Ludogorie plateau of the Danubian Plain, 20 km northeast o ...
" and "populated the lands of Karvuna".
According to Bulgarian historians, during the 7th–10th centuries, the region was fortified by construction of a large network of earthen and wooden strongholds and ramparts. Around the end of the 8th century, widespread building of new stone fortresses and defensive walls began. Romanian historians dispute attributing these walls to the Bulgarians, based on their interpretation of the construction system and archaeological evidence. The Bulgarians also reconstructed some of the ruined Byzantine fortresses (Kaliakra and Silistra in the 8th century, Madara and Varna in the 9th). According to Barnea, among other historians, during the following three centuries of Bulgarian domination, Byzantines still controlled the Black Sea coast and the mouths of Danube, and for short periods, even some cities. But Bulgarian archaeologists note that the last Byzantine coins found, which are considered a proof of Byzantine presence, date in Kaliakra
Kaliakra ( bg, Калиакра; ro, Caliacra) is a cape in the Southern Dobruja region of the northern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, which ends with a long and narrow headland east of Kavarna, northeast of Varna and southwest of Mangalia. Th ...
from the time of Emperor Justin II
Justin II ( la, Iustinus; grc-gre, Ἰουστῖνος, Ioustînos; died 5 October 578) or Justin the Younger ( la, Iustinus minor) was Eastern Roman Emperor from 565 until 578. He was the nephew of Justinian I and the husband of Sophia, the ...
(565–578), in Varna from the time of Emperor Heraclius (610–641), and in Tomis from Constantine IV
Constantine IV ( la, Constantinus; grc-gre, Κωνσταντῖνος, Kōnstantînos; 650–685), called the Younger ( la, iunior; grc-gre, ὁ νέος, ho néos) and sometimes incorrectly the Bearded ( la, Pogonatus; grc-gre, Πωγων ...
's rule (668–685).
At the beginning of the 8th century, Justinian II
Justinian II ( la, Iustinianus; gr, Ἰουστινιανός, Ioustinianós; 668/69 – 4 November 711), nicknamed "the Slit-Nosed" ( la, Rhinotmetus; gr, ὁ Ῥινότμητος, ho Rhinótmētos), was the last Eastern Roman emperor of the ...
visited Dobruja to ask Bulgarian Khan Tervel
Khan Tervel ( bg, Тервел) also called ''Tarvel'', or ''Terval'', or ''Terbelis'' in some Byzantine sources, was the khan of Bulgaria during the First Bulgarian Empire at the beginning of the 8th century. In 705 Emperor Justinian II named ...
for military help. Khan Omurtag
Omurtag (or Omortag) ( bg, Омуртаг; original gr, Μορτάγων and Ομουρτάγ', Inscription No.64. Retrieved 10 April 2012.) was a Great Khan ('' Kanasubigi'') of Bulgaria from 814 to 831. He is known as "the Builder".
In the v ...
(815–831) built a "glorious home on the Danube" and erected a mound in the middle of the distance between Pliska and his new building, according to his inscription kept in SS. Forty Martyrs Church in Veliko Tarnovo. The location of this edifice is unclear; the main theories place it at Silistra or at Păcuiul lui Soare. Many early medieval Bulgar stone inscriptions were found in Dobruja, including historical narratives, inventories of armament or buildings, and commemorative texts. During this period Silistra became an important Bulgarian ecclesiastical centre—an episcopate after 865 and seat of the Bulgarian Patriarch at the end of the 10th century. In 895, Magyar tribes from Budjak invaded Dobruja and northeastern Bulgaria. An old Slavic inscription, found at Mircea Vodă, mentions Zhupan Dimitri (Дѣимитрѣ жѹпанѣ), a local feudal landlord prominent in the south of the region in 943.
Return of Byzantine rule and late migrations
With financial encouragement from the Byzantine emperor, Nikephoros II Phocas, Sviatoslav I of Kiev agreed to assist the Byzantines in their war with the Bulgarians. Sviatoslav defeated the Bulgarians (led by Boris II) and proceeded to occupy the whole of northern Bulgaria. He occupied Dobruja in 968 and moved the capital of Kievan Rus' toPereyaslavets
Pereyaslavets ( East Slavic: ) or Preslavets ( bg, Преславец) was a trade city located near mouths of the Danube. The city's name is derived from that of the Bulgarian capital of the time, Preslav, and means Little Preslav (). In Greek ...
, in the north of the region. Sviatoslav refused to turn his Balkan conquests over to the Byzantines, and the parties fell out as a result. So the Byzantines under John I Tzimisces
John I Tzimiskes (; 925 – 10 January 976) was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general, he strengthened the Empire and expanded its borders during his short reign.
Background
John I Tzimiskes ...
reconquered Dobruja in 971 and included it in the theme 'Mesopotamia of the West' (Μεσοποταμια της Δυσεον).
According to some historians, soon after 976 or in 986, the southern part of Dobruja was included in the Bulgarian state then ruled by Samuel. The northern part remained under Byzantine rule, being reorganised in an autonomous ''klimata''. Other historians are of the view that Northern Dobruja was reconquered by Bulgarians as well. In 1000, a Byzantine army commanded by Theodorokanos reconquered the whole of Dobruja, organizing the region as the Strategia of Dorostolon and, after 1020, as '' Paristrion'' (Paradounavon).
To prevent mounted attacks from the north, the Byzantines constructed three ramparts from the Black Sea down to the Danube, in the 10th–11th centuries. According to Bulgarian archaeologists and historians, these fortifications may have been built much earlier and were erected by the First Bulgarian Empire in response to the threat of Khazars' raids.
From the 10th century, Byzantines accepted small groups of Pechenegs settling in Dobruja. In the spring of 1036, an invasion of the Pecheneg devastated large parts of the region, destroying the forts at Capidava and Dervent, and burning the settlement of Dinogeţia. In 1046 the Byzantines accepted the Pecheneg under Kegen settling in Paristrion as foederati. The Pecheneg dominated the region until 1059, when Isaac I Komnenos reconquered Dobruja.
In 1064, an invasion by the Oghuz Turks affected the region. During 1072 to 1074, when Nestor (the new strategos of Paristrion) was in Dristra, he found that the Pecheneg ruler, Tatrys, was leading a rebellion. In 1091, three autonomous, probably Pecheneg, rulers were mentioned in the Alexiad: Tatos (''Τατοῦ'') or Chalis (''χαλῆ''), in the area of Dristra (probably the same person as Tatrys), and Sesthlav (''Σεσθλάβου'') and Satza (''Σατζά'') in the area of Vicina. The Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
moved into Dobruja in 1094 and were influential in the region until the advent of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
.
Second Bulgarian Empire and Mongol domination
 In 1187 the Byzantines lost control of Dobruja to the restored Bulgarian Empire. In 1241, the first Tatar groups, under
In 1187 the Byzantines lost control of Dobruja to the restored Bulgarian Empire. In 1241, the first Tatar groups, under Kadan
Kadan (also Qadan) was the son of the second Great Khan of the Mongols Ögedei and a concubine. He was the grandson of Genghis Khan and the brother of Güyük Khan. During the Mongol invasion of Europe, Kadan, along with Baidar (son of Chaga ...
, invaded Dobruja starting a century long history of turmoil in the region.A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, ''Istoria Dobrogei'', p. 194 Around 1263–64, Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaeologus gave permission to Sultan Kaykaus II to settle in the area with a group of Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
from Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
. A missionary Turkish mystic, Sarı Saltuk, was the spiritual leader of this group. His tomb in Babadag (which was named after him) is still a place of pilgrimage for Muslims.
Arab chronicles of the 13th century mentioned Dobrogea under the name "Şakji" and the Vlachs inhabitants under the names "al-Awalak" and "ulaqut".
In 1265, the Bulgarian Emperor Constantine Tikh Asen hired 20,000 Tatars to cross the Danube and attack Byzantine Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
. On their way back, the Tatars forced most of the Seljuk Turks, including their chief Sarı Saltuk, to resettle in Kipchak (Cumania).
In the second part of the 13th century, the Turco–Mongolian Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragme ...
Empire continuously raided and plundered Dobruja. The inability of the Bulgarian authorities to cope with the numerous raids became the main reason for the uprising, led by Ivailo (1277–1280), that broke out in eastern Bulgaria. Ivailo's army defeated the Tatars, who were forced to leave the Bulgarian territory; he next outed Constantine Tikh's army, and Ivailo has crowned Emperor of Bulgaria.
The war with the Tatars continued. In 1278, after a new Tatar invasion in Dobruja, Ivailo was forced to retreat to the strong fortress of Silistra, where he withstood a three-month siege. In 1280 the Bulgarian nobility, which feared the growing influence of the peasant emperor, organised a coup. Ivailo had to flee to his enemy the Tatar Nogai Khan, who later killed him. In 1300 Toqta, the new Khan of the Golden Horde, ceded Bessarabia to Emperor Theodore Svetoslav
Theodore Svetoslav ( bg, Тодор Светослав, ''Todor Svetoslav'' and also Теодор Светослав, ''Teodor Svetoslav'') ruled as emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria from 1300 to 1322. The date of his birth is unknown. He expanded the ter ...
.

Autonomous Dobruja
In 1325, the Ecumenical Patriarch nominated Methodius as Metropolitan of Varna and Carvona. After this date, Balik/Balica is mentioned as a local ruler in Southern Dobruja. In 1346, he supported John V Palaeologus in his dispute for the Byzantine throne withJohn VI Cantacuzenus
John VI Kantakouzenos or Cantacuzene ( el, , ''Iōánnēs Ángelos Palaiológos Kantakouzēnós''; la, Johannes Cantacuzenus; – 15 June 1383) was a Byzantine Greek nobleman, statesman, and general. He served as grand domestic under And ...
. He sent an army corps under his son Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici and his brother, Theodore, to help the mother of John Palaeologus, Anna of Savoy. For his bravery, Dobrotitsa received the title of ''strategos'' and married the daughter of megadux Apokaukos. After the reconciliation of the two pretenders, a territorial dispute broke out between the Dobrujan polity and the Byzantine Empire for the port of Midia
''Midia'' is a monotypic taxon, monotypic genus of Linyphiidae, dwarf spiders containing the single species, ''Midia midas''. It was first described by Michael Saaristo, Michael I. Saaristo & J. Wunderlich in 1995.
See also
* List of Linyphiida ...
. In 1347, at John V Palaeologus' request, Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
Bahud-din Umur, Bey of Aydın, led a naval expedition against Balik, destroying Dobruja's seaports. Balik and Theodore died during the confrontation, and Dobrotitsa became the new ruler.
 Between 1352 and 1359, with the collapse of Golden Horde rule in Northern Dobruja, a new state appeared. It was controlled by Tatar prince
Between 1352 and 1359, with the collapse of Golden Horde rule in Northern Dobruja, a new state appeared. It was controlled by Tatar prince Demetrius
Demetrius is the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, Dimitris, Dmytro, Dimitri, Dimitrie, Dimitar, Dumi ...
, who claimed to be the protector of the river mouths of the Danube.I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, ''Bizantini, romani și bulgari la Dunărea de Jos'', p. 351
In 1357 Dobrotitsa was mentioned as a '' despot'' ruling over a large territory, including the fortresses of Varna, Kozeakos (near Obzor), and Emona
Emona (early gkm, Ἤμονα) or Aemona (short for ) was a Roman castrum, located in the area where the navigable Ljubljanica river came closest to Castle Hill,
. In 1366, John V Palaeologus visited Rome and Buda, trying to gather military support for his campaigns. On his return, he was captured at Vidin by Ivan Alexander, Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
of Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
, who believed that the new alliances were directed against his realm. An anti-Ottoman crusade under Amadeus VI of Savoy, supported by the republics of Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
and Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
, was diverted to free the Byzantine emperor. Dobrotitsa collaborated with the crusaders, and after the allies conquered several Bulgarian forts on the Black Sea, Ivan Alexander freed John and negotiated a peace agreement. Dobrotitsa's role in this conflict brought him numerous political advantages: his daughter married one of John V's sons, Michael, and his principality extended its control over some of the forts lost by the Bulgarians ( Anchialos and Mesembria).
In 1368, after the death of prince Demetrius, Dobrotitsa was recognised as ruler by Pangalia and other cities on the right bank of the Danube. In 1369, together with Vladislav I of Wallachia
Vladislav I or Vladimareïo/ Vila·Dumas of the Basarab dynasty, also known as Vlaicu or Vlaicu-Vodă, was the Voivode of Wallachia between 1364 and 1377. He was the son of Nicholas Alexander of Wallachia and Clara Dobokai.
In February 136 ...
, Dobrotitsa helped Prince Stratsimir to win back the throne of Vidin
Vidin ( bg, Видин, ; Old Romanian: Diiu) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as ...
.
Between 1370 and 1375, allied with Venice, Dobritsia challenged Genoese power in the Black Sea. In 1376, he tried to impose his son-in-law, Michael, as Emperor of Trebizond, but was unsuccessful. Dobrotitsa supported John V Palaeologus against his son Andronicus IV Palaeologus. In 1379, the Dobrujan fleet participated in the blockade of Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, fighting with the Genoese fleet.
In 1386, Dobrotitsa died and was succeeded by Ivanko/Ioankos. That same year he accepted a peace agreement with Murad I
Murad I ( ota, مراد اول; tr, I. Murad, Murad-ı Hüdavendigâr (nicknamed ''Hüdavendigâr'', from fa, خداوندگار, translit=Khodāvandgār, lit=the devotee of God – meaning "sovereign" in this context); 29 June 1326 – 15 Jun ...
and in 1387 signed a commercial treaty with Genoa. Ivanko was killed in 1388 during the expedition of Ottoman Grand Vizier Çandarli Ali Pasha against Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
and Dristra. The expedition brought most of the Dobrujan forts under Turkish rule.
Wallachian rule
In 1388/1389 Dobruja (''Terrae Dobrodicii''—as mentioned in a document from 1390) and Dristra (''Dârstor'') came under the control ofMircea the Elder
Mircea the Elder ( ro, Mircea cel Bătrân, ; c. 1355 – 31 January 1418) was the Voivode of Wallachia from 1386 until his death in 1418. He was the son of Radu I of Wallachia and brother of Dan I of Wallachia, after whose death he inherited t ...
, ruler of Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
, who defeated the Ottoman Grand Vizier.
 Ottoman Sultan
Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I
Bayezid I ( ota, بايزيد اول, tr, I. Bayezid), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt ( ota, link=no, یلدیرم بايزيد, tr, Yıldırım Bayezid, link=no; – 8 March 1403) was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted ...
conquered the southern part of the territory in 1393, attacking Mircea one year later, but without success. In the spring of 1395 Mircea regained the lost Dobrujan territories, with the help of his Hungarian allies.
The Ottomans recaptured Dobruja in 1397 and ruled it to 1404, although in 1401 Mircea strongly defeated an Ottoman army.
The defeat of Sultan Beyezid I by Tamerlane
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
at Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, maki ...
in 1402 opened a period of anarchy in the Ottoman Empire. Mircea took advantage of it to organise a new anti-Ottoman campaign: in 1403, he occupied the Genoese fort of Kilia at the mouths of the Danube. Thus in 1404, he could impose his authority on Dobruja. In 1416, Mircea supported the revolt against Sultan Mehmed I
Mehmed I ( 1386 – 26 May 1421), also known as Mehmed Çelebi ( ota, چلبی محمد, "the noble-born") or Kirişçi ( el, Κυριτζής, Kyritzis, "lord's son"), was the Ottoman sultan from 1413 to 1421. The fourth son of Sultan Bayezid ...
, led by Sheikh Bedreddin
Sheikh Bedreddin (1359–1420) ( ota, شیخ بدرالدین), full name Sheikh Bedreddin Mahmud bin Israel bin Abdulaziz was an influential mystic, scholar, theologian, and revolutionary. He is best known for his role in a 1416 revolt against t ...
in the area of Deliorman, in Southern Dobruja.
After Mircea died in 1418, his son Mihail I fought against the amplified Ottoman attacks, eventually being killed in a battle in 1420. That year, Sultan Mehmed I conducted the definitive conquest of Dobruja by the Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
. Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
kept only the mouths of the Danube, but not for a long duration.
In the late 14th century, German traveller Johann Schiltberger described these lands as follows:
Ottoman rule
Murad II
Murad II ( ota, مراد ثانى, Murād-ı sānī, tr, II. Murad, 16 June 1404 – 3 February 1451) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1421 to 1444 and again from 1446 to 1451.
Murad II's reign was a period of important economic deve ...
or Suleiman I, the sanjak of Silistra and surrounding territories were organised as a separate eyalet. In 1555, a revolt led by the "false" (''düzme'') Mustafa, a pretender to the Turkish throne, broke out against Ottoman administration in Rumelia and rapidly spread to Dobruja, but was repressed by the beylerbey of Nigbolu.
In 1603 and 1612, the region suffered from the forays of Cossacks, who burnt down Isaķči and plundered Küstendje. The Russian Empire occupied Dobruja several times during the Russo-Turkish wars
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
— in 1771–1774, 1790–1791, 1809–1810, 1829, and 1853. The most violent invasion was that of 1829, which resulted in the depopulation of numerous villages and towns. The Treaty of Adrianople of 1829 ceded the Danube Delta to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. However, Russia was forced to return it to the Ottomans in 1856, after the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
. In 1864 Dobruja was included in the Vilayet of Danube.
On account of the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774), one of the greatest migration events of the region occurred where an estimated 200,000 Tatars emigrated to the Dobruja region between 1770 and 1784. Whereas, a large group of Christians (likely Greeks and Slavs) moved the other direction into the Tatar's recently-loss region of Azov
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Population:
History
Early settlements in the vicinity
The mout ...
in 1778.
During Ottoman rule, groups of Turk, Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Muslim Romani people and Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
settled in the region, the latter, especially between 1512 and 1514. During the reign of Peter I of Russia and Catherine the Great, Lipovans immigrated to the region of the Danube Delta. After the destruction of Zaporozhian Sich in 1775, Cossacks were settled in the area north of Lake Razim by the Turkish authorities (where they founded the Danubian Sich
The Danubian Sich ( uk, Задунайська Сiч, translit=Zadunaiska Sich) was an organization of the part of former Zaporozhian Cossacks who settled in the territory of the Ottoman Empire (the Danube Delta, hence the name) after their pre ...
). They were forced to leave Dobruja in 1828.
In the second part of the nineteenth century, Ruthenians from the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
also settled in the Danube Delta. After the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
, a large number of Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
were forcibly driven away from in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
, immigrating to then-Ottoman Dobruja and settling mainly in the Karasu Valley in the centre of the region and around Bābā Dāgh. In 1864, Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
fleeing from the Russian invasion and genocide of the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
were settled in the wooded region near Babadag, forming a community there. Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
from Bessarabia also founded colonies in Dobruja between 1840 and 1892.
Lyubomir Miletich
Lyubomir Miletich ( bg, Любомир Милетич) (14 January 1863 – 1 June 1937) was a leading Bulgarian linguist, ethnographer, dialectologist and historian, as well as the chairman of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences from 1926 to ...
, most Bulgarians living in Dobruja in 1900 were nineteenth-century settlers or their descendants. In 1850, the scholar Ion Ionescu de la Brad
Ion Ionescu de la Brad (June 24, 1818 – December 16, 1891), born Ion Isăcescu, was a Moldavian, later Romanian revolutionary, agronomist, statistician, scholar, and writer.
Born in Roman, Romania, Roman, he was the son of a Moldavian Romani ...
, wrote in a study on Dobruja, ordered by the Ottoman government, that Bulgarians came to the region "in the last twenty years or so". According to his study, there were 2,285 Bulgarian families (out of 8,194 Christian families) in the region, 1,194 of them in Northern Dobruja. Lyubomir Miletich puts the number of Bulgarian families in Northern Dobruja in the same year at 2,097. According to the statistics of the Bulgarian Exarchate, before 1877 there were 9,324 Bulgarian families out of a total 12,364 Christian families in the Northern Dobruja. According to Russian knyaz Vladimir Cherkassky, chief of the Provisional Russian government in Bulgaria in 1877–1878, the Bulgarian population in Dobruja was larger than the Romanian one. However, count Shuvalov, the Russian representative to the Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at th ...
, stated that Romania deserved Dobruja "more than anybody else, because of its population". In 1878, the statistics of the Russian governor of Dobruja, Bieloserkovitsch, showed a number of 4,750 Bulgarian "family chiefs" (out of 14,612 Christian family chiefs) in the northern half of the region.
The Christian religious organisation of the region was put under the authority of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church by a firman of the Sultan, promulgated on February 28, 1870. However, the ethnic Greeks and most Romanians in Northern Dobruja remained under the authority of the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
Archdiocese of Tulça (founded in 1829).
After 1878

 After the 1878 war, the
After the 1878 war, the Treaty of San Stefano
The 1878 Treaty of San Stefano (russian: Сан-Стефанский мир; Peace of San-Stefano, ; Peace treaty of San-Stefano, or ) was a treaty between the Russian and Ottoman empires at the conclusion of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877-18 ...
awarded Dobruja to Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
and the newly established Principality of Bulgaria. The northern portion, held by Russia, was ceded to Romania in exchange for Russia obtaining territories in Southern Bessarabia
Southern Bessarabia or South Bessarabia is a territory of Bessarabia which, as a result of the Crimean War, was returned to the Moldavian Principality in 1856. As a result of the unification of the latter with Wallachia, these lands became part ...
, thereby securing direct access to the mouths of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
. In Northern Dobruja, Romanians were the plurality. The population included a Bulgarian ethnic enclave in the northeast (around Babadag), as well as an important Muslim community (mostly Turks and Tatars) scattered around the region.
The southern portion, held by Bulgaria, was reduced the same year by the Treaty of Berlin. At the advice of the French envoy, a strip of land extended inland from the port of Mangalia (shown orange on the map) was ceded to Romania, since its southwestern corner contained a compact area of ethnic Romanians. The town of Silistra, located at the area's most southwestern point, remained Bulgarian due to its large Bulgarian population. Romania subsequently tried to occupy the town as well, but in 1879 a new international commission allowed Romania to occupy only the fort ''Arab Tabia'', which overlooked Silistra, but not the town itself.
Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
from Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
and Veneto
it, Veneto (man) it, Veneta (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 = ...
settled in Greci, Cataloi and Măcin in Northern Dobruja. Most of them worked in the granite quarries in the Măcin Mountains, while some became farmers. The Bulgarian authorities encouraged the settling of ethnic Bulgarians in the territory of Southern Dobruja.
In May 1913, the Great Powers awarded Silistra and the area in a 3 km radius around it to Romania, at the Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
Conference. In August 1913, after the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria lost Southern Dobruja (''Cadrilater'') to Romania (See Treaty of Bucharest, 1913). With Romania's entry in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
on the side of France and Russia, the Central Powers occupied all of Dobruja and gave the Cadrilater, as well as the southern portion of Northern Dobruja, to Bulgaria in the Treaty of Bucharest of 1918. This situation lasted for a short period. As the Allied Powers emerged victorious at the end of the war, Romania regained the lost territories in the Treaty of Neuilly
The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine (french: Traité de Neuilly-sur-Seine) required Bulgaria to cede various territories, after Bulgaria had been one of the Central Powers defeated in World War I. The treaty was signed on 27 November 1919 at Neuilly ...
of 1919. Between 1926 and 1938, about 30,000 Aromanians from Bulgaria, Macedonia, and Greece, were resettled in Southern Dobruja. Some Megleno-Romanians also emigrated to the region.
In 1923 the Internal Dobrujan Revolutionary Organisation
The Internal Dobrujan Revolutionary Organisation ( bg, Вътрешна добруджанска революционна организация; ro, Organizația Revoluționară Internă Dobrogeană) or IDRO was a Bulgarian nationalist and revol ...
(IDRO), a Bulgarian nationalist organisation, was established. Active in Southern Dobruja under different forms until 1940, the IDRO detachments fought against the widespread brigandage in the region, as well as the Romanian administration. Thus, while considered "a terrorist organisation" by the Romanian authorities, the IDRO was regarded by ethnic Bulgarians as a liberation movement. In 1925, part of the Bulgarian revolutionary committees formed the Dobrujan Revolutionary Organisation (DRO), which later became subordinated to the Communist Party of Romania
The Romanian Communist Party ( ro, Partidul Comunist Român, , PCR) was a communist party in Romania. The successor to the pro-Bolshevik wing of the Socialist Party of Romania, it gave ideological endorsement to a communist revolution that woul ...
. In contrast with the IDRO, which fought for the inclusion of the region in the Bulgarian state, the DRO requested the independence of Dobruja and its inclusion in a projected Federative Republic of the Balkans. The means used by DRO to attain its goals were also more peaceful.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Bulgaria regained Southern Dobruja in the September 1940 Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
-sponsored Treaty of Craiova
The Treaty of Craiova ( bg, Крайовска спогодба, Krayovska spogodba; ro, Tratatul de la Craiova) was signed on 7 September 1940 and ratified on 13 September 1940 by the Kingdom of Bulgaria and the Kingdom of Romania. Under its te ...
, despite Romanian negotiators' insistence that Balchik
Balchik ( bg, Балчик ; ro, Balcic) is a Black Sea coastal town and seaside resort in the Southern Dobruja area of northeastern Bulgaria. It is in Dobrich Province, 35 km southeast of Dobrich and 42 km northeast of Varna. It spr ...
and other towns should remain in Romania. As part of the treaty, the Romanian inhabitants (Aromanian and Megleno-Romanian refugee- settlers, settlers from other regions of Romania, and the Romanians indigenous to the region) were forced to leave the regained territory, while the Bulgarian minority in the north was expelled to go to Bulgaria in a population exchange
Population transfer or resettlement is a type of mass migration, often imposed by state policy or international authority and most frequently on the basis of ethnicity or religion but also due to economic development. Banishment or exile is a ...
. The post-war Paris Peace Treaties of 1947 reaffirmed the 1940 border.
In 1948 and again in 1961–1962, Bulgaria proposed a border rectification in the area of Silistra, consisting mainly of the transfer of a Romanian territory containing the water source of that city. Romania made an alternative proposal that did not involve a territorial change and, ultimately, no rectification took place.
In Romania, 14 November is a holiday observed as the Dobruja Day.
Demographic history
In 1913, Dobruja was all made part of Romania in the aftermath of the 1913 Treaty of Bucharest which ended the Second Balkan War. Romania acquired Southern Dobruja from Bulgaria, a territory with a population of 300,000 from which only 6,000 (2%) were Romanians. In 1913, Romanian-held Northern Dobruja had a population of 380,430, from which 216,425 (56.8%) were Romanians. Thus, when Dobruja was unified within Romania in 1913, there were over 222,000 Romanians in the region out of a total population of 680,000, or nearly 33% of the population. By 1930, the Romanian population within Dobruja had increased to 44.2%.Lucian Boia, Central European University Press, 2001, ''History and Myth in Romanian Consciousness'', p. 182Northern Dobruja
:1According to the 1926–1938 Romanian administrative division (counties of Constanța andTulcea
Tulcea (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in Northern Dobruja, Romania. It is the administrative center of Tulcea County, and had a population of 73,707 . One village, Tudor Vladimirescu, is administered by the city.
Names
The ...
), which excluded a part of today's Romania (chiefly the communes of Ostrov and Lipnița, now part of Constanța County
Constanța () is a county (județ) of Romania on the border with Bulgaria, in the Dobruja region. Its capital city is also named Constanța.
Demographics
In 2011, it had a population of 684,082 and the population density was 96/km2. The degr ...
) and included a part of today's Bulgaria (parts of General Toshevo
General Toshevo ( bg, Генерал Тошево ; ro, Casim) is a town in northeastern Bulgaria, part of Dobrich Province. Located in the historic region of Southern Dobruja, it is the administrative centre of the homonymous municipality and ...
and Krushari
Krushari ( bg, Крушари, ) is a village in northeastern Bulgaria, part of Dobrich Province. It is the administrative centre of Krushari Municipality, which lies in the northwestern part of the province. Krushari is located 32 kilometres fro ...
municipalities)
:2Only Russians. (Russians and Lipovans counted separately)
Southern Dobruja
:1According to the 1926–1938 Romanian administrative division (counties of Durostor and Caliacra), which included a part of today's Romania (chiefly the communes of Ostrov and Lipnița, now part ofConstanța County
Constanța () is a county (județ) of Romania on the border with Bulgaria, in the Dobruja region. Its capital city is also named Constanța.
Demographics
In 2011, it had a population of 684,082 and the population density was 96/km2. The degr ...
) and excluded a part of today's Bulgaria (parts of General Toshevo
General Toshevo ( bg, Генерал Тошево ; ro, Casim) is a town in northeastern Bulgaria, part of Dobrich Province. Located in the historic region of Southern Dobruja, it is the administrative centre of the homonymous municipality and ...
and Krushari
Krushari ( bg, Крушари, ) is a village in northeastern Bulgaria, part of Dobrich Province. It is the administrative centre of Krushari Municipality, which lies in the northwestern part of the province. Krushari is located 32 kilometres fro ...
municipalities)
:2Including persons counted as Vlachs
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other E ...
in Bulgarian Census
:3Only includes persons who answered the optional question on ethnic identity. The total population was 309,151.
Area, population and cities
The entire region of Dobruja has an area of around and a population of around 1.2 million, of which just over two-thirds of the former and nearly three-quarters of the latter lie in the Romanian part. Major cities are Constanța,Tulcea
Tulcea (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in Northern Dobruja, Romania. It is the administrative center of Tulcea County, and had a population of 73,707 . One village, Tudor Vladimirescu, is administered by the city.
Names
The ...
, Medgidia and Mangalia in Romania, and Dobrich and Silistra in Bulgaria.
Tulcea
Tulcea (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in Northern Dobruja, Romania. It is the administrative center of Tulcea County, and had a population of 73,707 . One village, Tudor Vladimirescu, is administered by the city.
Names
The ...
File:Medgidia station.jpg, Medgidia
File:Portul Turistic Masngalia - panoramio - Andrei Dan Suciu (3).jpg, Mangalia
File:Dobrich - 1.jpg, Dobrich
File:Silistra-art-gallery-Svik.jpg, Silistra
See also
* Bulgaria during World War I *Romania during World War I
The Kingdom of Romania was neutral for the first two years of World War I, entering on the side of the Allied powers from 27 August 1916 until Central Power occupation led to the Treaty of Bucharest in May 1918, before reentering the war on 10 ...
Notes
References
* * * . Subscription needed for online access. * * * * * *Further reading
* * * Iordachi, Constantin (2001)"The California of the Romanians": The Integration of Northern Dobrogea into Romania, 1878-1913''
in ''Nation-Building and Contested Identities Romanian & Hungarian Case Studies'' * * {{Coord, 44, 27, N, 28, 20, E, display=t Divided regions Historical regions in Bulgaria Historical regions in Romania