Digital Signal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents 
 In
In
 In digital signal processing, a digital signal is a representation of a physical signal that is sampled and quantized. A digital signal is an abstraction that is discrete in time and amplitude. The signal's value only exists at regular time intervals, since only the values of the corresponding physical signal at those sampled moments are significant for further digital processing. The digital signal is a sequence of codes drawn from a finite set of values. The digital signal may be stored, processed or transmitted physically as a
In digital signal processing, a digital signal is a representation of a physical signal that is sampled and quantized. A digital signal is an abstraction that is discrete in time and amplitude. The signal's value only exists at regular time intervals, since only the values of the corresponding physical signal at those sampled moments are significant for further digital processing. The digital signal is a sequence of codes drawn from a finite set of values. The digital signal may be stored, processed or transmitted physically as a
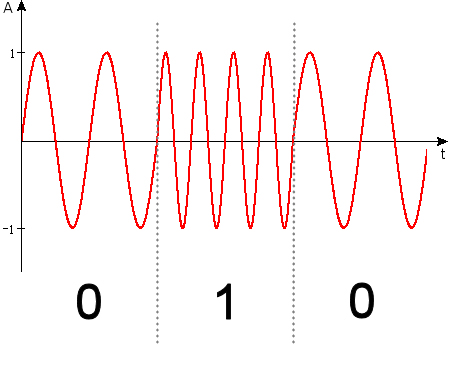 In digital communications, a digital signal is a continuous-time physical signal, alternating between a discrete number of waveforms, Analogue and Digital Communication Techniques
In digital communications, a digital signal is a continuous-time physical signal, alternating between a discrete number of waveforms, Analogue and Digital Communication Techniques
: "A digital signal is a complex waveform and can be defined as a discrete waveform having a finite set of levels" representing a
Computer Networking and the Internet
"In order to transmit a digital signal over an analog subscriber line, modulated transmission must be used; thas is the electrical signal that represents the binary bit stream of the source (digital) output must first be converted to an analog signal that is compatible with a (telephony) speech signal." In communications, sources of interference are usually present, and noise is frequently a significant problem. The effects of interference are typically minimized by filtering off interfering signals as much as possible and by using data redundancy. The main advantages of digital signals for communications are often considered to be noise immunity, and the ability, in many cases such as with audio and video data, to use data compression to greatly decrease the bandwidth that is required on the communication media.
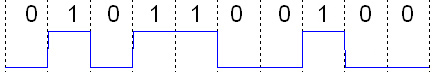
 A waveform that switches representing the two states of a Boolean value (0 and 1, or low and high, or false and true) is referred to as a ''digital signal'' or ''logic signal'' or ''binary signal'' when it is interpreted in terms of only two possible digits.
The two states are usually represented by some measurement of an electrical property: Voltage is the most common, but current is used in some logic families. Two ranges of voltages are typically defined for each logic family, which are frequently not directly adjacent. The signal is low when in the low range and high when in the high range, and in between the two ranges the behaviour can vary between different types of gates.
The clock signal is a special digital signal that is used to
A waveform that switches representing the two states of a Boolean value (0 and 1, or low and high, or false and true) is referred to as a ''digital signal'' or ''logic signal'' or ''binary signal'' when it is interpreted in terms of only two possible digits.
The two states are usually represented by some measurement of an electrical property: Voltage is the most common, but current is used in some logic families. Two ranges of voltages are typically defined for each logic family, which are frequently not directly adjacent. The signal is low when in the low range and high when in the high range, and in between the two ranges the behaviour can vary between different types of gates.
The clock signal is a special digital signal that is used to
 Digital signals may be ''sampled'' by a clock signal at regular intervals by passing the signal through a flip-flop. When this is done, the input is measured at the clock edge, and the signal from that time. The signal is then held steady until the next clock. This process is the basis of synchronous logic.
Asynchronous logic also exists, which uses no single clock, and generally operates more quickly, and may use less power, but is significantly harder to design.
Digital signals may be ''sampled'' by a clock signal at regular intervals by passing the signal through a flip-flop. When this is done, the input is measured at the clock edge, and the signal from that time. The signal is then held steady until the next clock. This process is the basis of synchronous logic.
Asynchronous logic also exists, which uses no single clock, and generally operates more quickly, and may use less power, but is significantly harder to design.
CodSim 2.0: Open source Virtual Laboratory for Digital Data Communications Model
Department of Computer Architecture, University of Malaga. Simulates Digital line encodings and Digital Modulations. Written in HTML for any web browser. {{Telecommunications Telecommunications
 A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous
Continuity or continuous may refer to:
Mathematics
* Continuity (mathematics), the opposing concept to discreteness; common examples include
** Continuous probability distribution or random variable in probability and statistics
** Continuous g ...
values; at any given time it represents a real number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every ...
within a continuous range of values.
Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of analog levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state
In information technology and computer science, a system is described as stateful if it is designed to remember preceding events or user interactions; the remembered information is called the state of the system.
The set of states a system can o ...
. In most digital circuits
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
Digital electronic circuits are usual ...
, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values "zero" and "one" (or "false" and "true") of the Boolean domain, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit (bit). Because of this discretization, relatively small changes to the analog signal levels do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry. As a result, digital signals have noise immunity; electronic noise, provided it is not too great, will not affect digital circuits, whereas noise always degrades the operation of analog signals to some degree.
Digital signals having more than two states are occasionally used; circuitry using such signals is called multivalued logic
Many-valued logic (also multi- or multiple-valued logic) refers to a propositional calculus in which there are more than two truth values. Traditionally, in Aristotle's logical calculus, there were only two possible values (i.e., "true" and "fals ...
. For example, signals that can assume three possible states are called three-valued logic
In logic, a three-valued logic (also trinary logic, trivalent, ternary, or trilean, sometimes abbreviated 3VL) is any of several many-valued logic systems in which there are three truth values indicating ''true'', ''false'' and some indetermina ...
.
In a digital signal, the physical quantity representing the information may be a variable electric current or voltage, the intensity, phase or polarization of an optical or other electromagnetic field, acoustic pressure, the magnetization of a magnetic storage media, etcetera. Digital signals are used in all digital electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
Digital electronic circuits are usu ...
, notably computing equipment and data transmission
Data transmission and data reception or, more broadly, data communication or digital communications is the transfer and reception of data in the form of a digital bitstream or a digitized analog signal transmitted over a point-to-point or ...
.
Definitions
The term ''digital signal'' has related definitions in different contexts.In digital electronics
 In
In digital electronics
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
Digital electronic circuits are usu ...
, a digital signal is a pulse train (a pulse amplitude modulated signal), i.e. a sequence of fixed-width square wave electrical pulses or light pulses, each occupying one of a discrete number of levels of amplitude. A special case is a ''logic signal'' or a ''binary signal'', which varies between a low and a high signal level.
The pulse trains in digital circuits
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
Digital electronic circuits are usual ...
are typically generated by metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) devices, due to their rapid on–off electronic switching speed and large-scale integration (LSI) capability. In contrast, BJT transistors more slowly generate analog signals resembling sine waves.
In signal processing
pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the ...
(PCM) signal.
In communications
 In digital communications, a digital signal is a continuous-time physical signal, alternating between a discrete number of waveforms, Analogue and Digital Communication Techniques
In digital communications, a digital signal is a continuous-time physical signal, alternating between a discrete number of waveforms, Analogue and Digital Communication Techniques: "A digital signal is a complex waveform and can be defined as a discrete waveform having a finite set of levels" representing a
bitstream
A bitstream (or bit stream), also known as binary sequence, is a sequence of bits.
A bytestream is a sequence of bytes. Typically, each byte is an 8-bit quantity, and so the term octet stream is sometimes used interchangeably. An octet may ...
. The shape of the waveform depends the transmission scheme, which may be either a line coding scheme allowing baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is the range of frequencies occupied by a signal that has not been modulated to higher frequencies. Baseband signals typically originate from transducers, converting some other variable i ...
transmission; or a digital modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the '' carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains informa ...
scheme, allowing passband transmission over long wires or over a limited radio frequency band. Such a carrier-modulated sine wave is considered a digital signal in literature on digital communications and data transmission, but considered as a bit stream converted to an analog signal in electronics and computer networking.Fred HalsallComputer Networking and the Internet
"In order to transmit a digital signal over an analog subscriber line, modulated transmission must be used; thas is the electrical signal that represents the binary bit stream of the source (digital) output must first be converted to an analog signal that is compatible with a (telephony) speech signal." In communications, sources of interference are usually present, and noise is frequently a significant problem. The effects of interference are typically minimized by filtering off interfering signals as much as possible and by using data redundancy. The main advantages of digital signals for communications are often considered to be noise immunity, and the ability, in many cases such as with audio and video data, to use data compression to greatly decrease the bandwidth that is required on the communication media.
Logic voltage levels
synchronize
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchrono ...
many digital circuits. The image shown can be considered the waveform of a clock signal. Logic changes are triggered either by the rising edge or the falling edge. The rising edge is the transition from a low voltage (level 1 in the diagram) to a high voltage (level 2). The falling edge is the transition from a high voltage to a low one.
Although in a highly simplified and idealized model of a digital circuit, we may wish for these transitions to occur instantaneously, no real world circuit is purely resistive and therefore no circuit can instantly change voltage levels. This means that during a short, finite transition time the output may not properly reflect the input, and will not correspond to either a logically high or low voltage.
Modulation
To create a digital signal, an analog signal must be modulated with a control signal to produce it. The simplest modulation, a type ofunipolar encoding
Unipolar encoding is a line code. A positive voltage represents a binary 1, and zero volts indicates a binary 0. It is the simplest line code, directly encoding the bitstream, and is analogous to on-off keying in modulation.
Its drawbacks are th ...
, is simply to switch on and off a DC signal so that high voltages represent a '1' and low voltages are '0'.
In digital radio schemes one or more carrier waves are amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
, frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
or phase modulated by the control signal to produce a digital signal suitable for transmission.
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) over telephone wires, does not primarily use binary logic; the digital signals for individual carriers are modulated with different valued logics, depending on the Shannon capacity of the individual channel.
Clocking
See also
*Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference (ISI) is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have a similar effect as noise, thus making ...
References
External links
*CodSim 2.0: Open source Virtual Laboratory for Digital Data Communications Model
Department of Computer Architecture, University of Malaga. Simulates Digital line encodings and Digital Modulations. Written in HTML for any web browser. {{Telecommunications Telecommunications