Diffraction spike on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
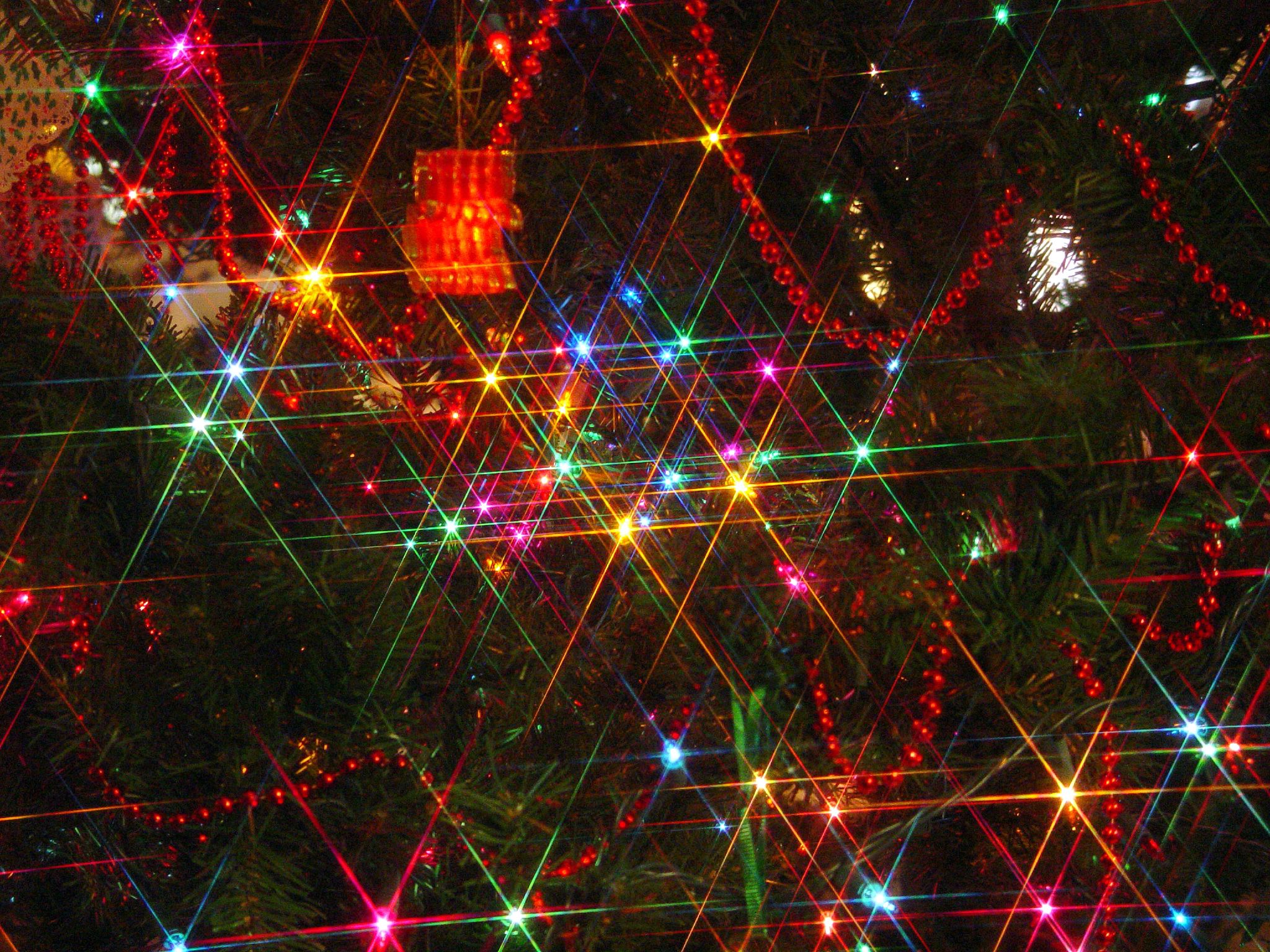
 Diffraction spikes are lines radiating from bright light sources, causing what is known as the starburst effect or sunstars in photographs and in vision. They are artifacts caused by light diffracting around the support vanes of the secondary mirror in
Diffraction spikes are lines radiating from bright light sources, causing what is known as the starburst effect or sunstars in photographs and in vision. They are artifacts caused by light diffracting around the support vanes of the secondary mirror in
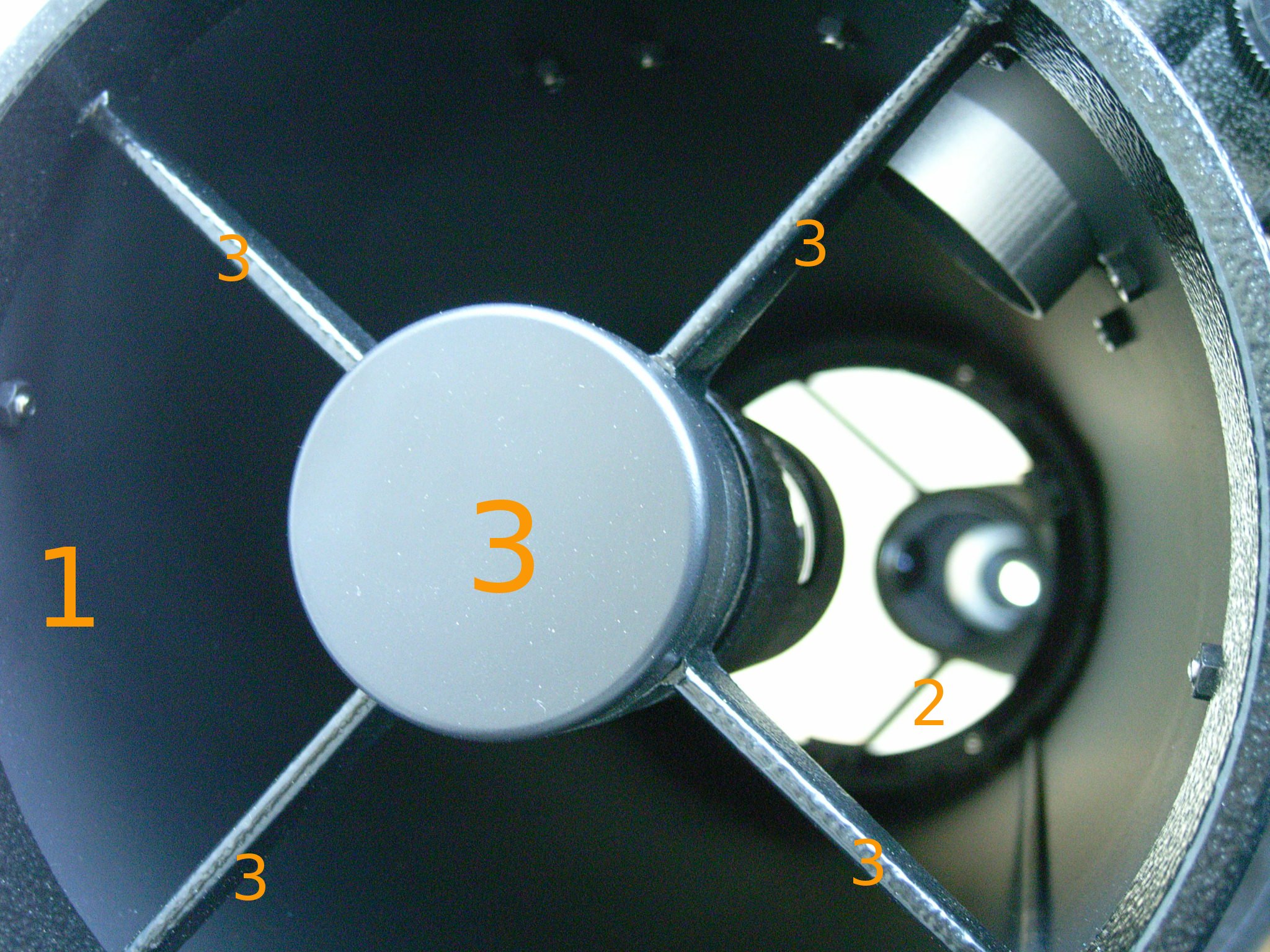 In the vast majority of
In the vast majority of
 Iris diaphragms with moving blades are used in most modern camera lenses to restrict the light received by the film or sensor. While manufacturers attempt to make the
Iris diaphragms with moving blades are used in most modern camera lenses to restrict the light received by the film or sensor. While manufacturers attempt to make the
File:Path near floating restaurant, with moon, Infosys Mysore.JPG, 5 blades giving 10 spikes
File:Night London Panorama with Full Moon.jpg, 6 blades giving 6 spikes
File:US Navy 061220-N-4965F-001 The Pearl Harbor Memorial fountain illuminates the night as holiday lights shine from the Ticonderoga-class guided-missile cruiser USS Lake Erie (CG 70).jpg, 7 blades giving 14 spikes
File:Sydneyoperahouse at night.jpg, 8 blades giving 8 spikes
File:US Army 52253 Best Warrior At Night.jpg, 9 blades giving 18 spikes
File:Speyer - Altstadt - Gedächtniskirche der Protestation - Gewölbe der Vierung quer.jpg, 10 blades giving 10 spikes
File:Squarelens.jpg, 4 blades giving 4 spikes
Webb's_First_Deep_Field.jpg, The first JWST deep field with diffraction spikes
JWST_diffraction_spikes.svg, Edges of the JWST primary mirror segments and spider colour-coded with their corresponding diffraction spikes
 An improperly cleaned lens or cover glass, or one with a fingerprint may have parallel lines which diffract light similarly to support vanes. They can be distinguished from spikes due to non-circular aperture as they form a prominent smear in a single direction, and from CCD bloom by their oblique angle.
An improperly cleaned lens or cover glass, or one with a fingerprint may have parallel lines which diffract light similarly to support vanes. They can be distinguished from spikes due to non-circular aperture as they form a prominent smear in a single direction, and from CCD bloom by their oblique angle.
 A cross screen filter, also known as a star filter, creates a star pattern using a very fine
A cross screen filter, also known as a star filter, creates a star pattern using a very fine
 In amateur astrophotography, a Bahtinov mask can be used to focus small astronomical telescopes accurately. Light from a bright point such as an isolated bright star reaching different quadrants of the primary mirror or lens is first passed through grilles at three different orientations. Half of the mask generates a narrow "X" shape from four diffraction spikes (blue and green in the illustration); the other half generates a straight line from two spikes (red). Changing the focus causes the shapes to move with respect to each other. When the line passes exactly through the middle of the "X", the telescope is in focus and the mask can be removed.
In amateur astrophotography, a Bahtinov mask can be used to focus small astronomical telescopes accurately. Light from a bright point such as an isolated bright star reaching different quadrants of the primary mirror or lens is first passed through grilles at three different orientations. Half of the mask generates a narrow "X" shape from four diffraction spikes (blue and green in the illustration); the other half generates a straight line from two spikes (red). Changing the focus causes the shapes to move with respect to each other. When the line passes exactly through the middle of the "X", the telescope is in focus and the mask can be removed.
Diffraction spikes explained
by
 Diffraction spikes are lines radiating from bright light sources, causing what is known as the starburst effect or sunstars in photographs and in vision. They are artifacts caused by light diffracting around the support vanes of the secondary mirror in
Diffraction spikes are lines radiating from bright light sources, causing what is known as the starburst effect or sunstars in photographs and in vision. They are artifacts caused by light diffracting around the support vanes of the secondary mirror in reflecting telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternat ...
s, or edges of non-circular camera aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane.
An op ...
s, and around eyelashes and eyelids in the eye.
Diffraction spikes due to support vanes
reflecting telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternat ...
designs, the secondary mirror has to be positioned at the central axis of the telescope and so has to be held by struts within the telescopes tube. No matter how fine these support rods are they diffract the incoming light from a subject star and this appears as diffraction spikes which are the Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed ...
of the support struts. The spikes represent a loss of light that could have been used to image the star.
Although diffraction spikes can obscure parts of a photograph and are undesired in professional contexts, some amateur astronomers
Amateur astronomy is a hobby where participants enjoy observing or imaging celestial objects in the sky using the unaided eye, binoculars, or telescopes. Even though scientific research may not be their primary goal, some amateur astronomers ...
like the visual effect they give to bright stars – the "Star of Bethlehem
The Star of Bethlehem, or Christmas Star, appears in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew chapter 2 where "wise men from the East" (Magi) are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There, they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask hi ...
" appearance – and even modify their refractors to exhibit the same effect, or to assist with focusing when using a CCD.
A small number of reflecting telescopes designs avoid diffraction spikes by placing the secondary mirror off-axis. Early off-axis designs such as the Herschelian and the Schiefspiegler telescopes have serious limitations such as astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at nig ...
and long focal ratios, which make them useless for research. The brachymedial design by Ludwig Schupmann
Ludwig Ignaz Schupmann (23 January 1851 in Geseke (Westphalia), Germany – 2 October 1920 also in Geseke) was a German professor of architecture and an optical designer. He is principally remembered today for his Medial and Brachymedial telescopes ...
, which uses a combination of mirrors and lenses, is able to correct chromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion and spherochromatism, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the lens elements varies with the wa ...
perfectly over a small area and designs based on the Schupmann brachymedial are currently used for research of double star
In observational astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear close to each other as viewed from Earth, especially with the aid of optical telescopes.
This occurs because the pair either forms a binary star (i.e. ...
s.
There are also a small number of off-axis unobstructed all-reflecting anastigmat
An anastigmat or anastigmatic lens is a photographic lens completely corrected for the three main optical aberrations: spherical aberration, coma, and astigmatism. Early lenses often included the word ''Anastigmat'' in their name to advertise thi ...
s which give optically perfect images.
Refracting telescope
A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens as its objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope design was originally used in spyglasses and ...
s and their photographic images do not have the same problem as their lenses are not supported with spider vanes.
Diffraction spikes due to non-circular aperture
 Iris diaphragms with moving blades are used in most modern camera lenses to restrict the light received by the film or sensor. While manufacturers attempt to make the
Iris diaphragms with moving blades are used in most modern camera lenses to restrict the light received by the film or sensor. While manufacturers attempt to make the aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane.
An op ...
circular for a pleasing bokeh
In photography, bokeh ( or ; ) is the aesthetic quality of the blur produced in out-of-focus parts of an image. Bokeh has also been defined as "the way the lens renders out-of-focus points of light". Differences in lens aberrations an ...
, when stopped down to high f-number
In optics, the f-number of an optical system such as a camera lens is the ratio of the system's focal length to the diameter of the entrance pupil ("clear aperture").Smith, Warren ''Modern Optical Engineering'', 4th Ed., 2007 McGraw-Hill P ...
s (small apertures), its shape tends towards a polygon with the same number of sides as blades. Diffraction spreads out light waves passing through the aperture perpendicular to the roughly-straight edge, each edge yielding two spikes 180° apart. As the blades are uniformly distributed around the circle, on a diaphragm with an even number of blades, the diffraction spikes from blades on opposite sides overlap. Consequently, a diaphragm with ''n'' blades yields ''n'' spikes if ''n'' is even, and 2''n'' spikes if ''n'' is odd.
Diffraction spikes due to segmented mirrors
Images fromtelescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obs ...
s with segmented mirror
A segmented mirror is an array of smaller mirrors designed to act as segments of a single large curved mirror. The segments can be either spherical or asymmetric (if they are part of a larger parabolic reflector). They are used as objectives ...
s also exhibit diffraction spikes due to diffraction from the mirrors' edges. As before, two spikes are perpendicular to each edge orientation, resulting in six spikes (plus two fainter ones due to the spider supporting the secondary mirror) in photographs taken by the James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble S ...
.
Diffraction spikes due to dirty optics
 An improperly cleaned lens or cover glass, or one with a fingerprint may have parallel lines which diffract light similarly to support vanes. They can be distinguished from spikes due to non-circular aperture as they form a prominent smear in a single direction, and from CCD bloom by their oblique angle.
An improperly cleaned lens or cover glass, or one with a fingerprint may have parallel lines which diffract light similarly to support vanes. They can be distinguished from spikes due to non-circular aperture as they form a prominent smear in a single direction, and from CCD bloom by their oblique angle.
In vision
In normal vision, diffraction through eyelashes – and due to the edges of the eyelids if one is squinting – produce many diffractions spikes. If it is windy, then the motion of the eyelashes cause spikes that move around and scintillate. After a blink, the eyelashes may come back in a different position and cause the diffraction spikes to jump around. This is classified as anentoptic phenomenon
Entoptic phenomena () are visual effects whose source is within the human eye itself. (Occasionally, these are called entopic phenomena, which is probably a typographical mistake.)
In Helmholtz's words: "Under suitable conditions light falling ...
.
Other uses of diffraction spikes
Special effects
 A cross screen filter, also known as a star filter, creates a star pattern using a very fine
A cross screen filter, also known as a star filter, creates a star pattern using a very fine diffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure that diffraction, diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions (i.e., different diffraction angles). The emerging coloration is a form ...
embedded in the filter, or sometimes by the use of prisms in the filter. The number of stars varies by the construction of the filter, as does the number of points each star has.
A similar effect is achieved by photographing bright lights through a window screen with vertical and horizontal wires. The angles of the bars of the cross depend on the orientation of the screen relative to the camera.
Bahtinov mask
References
External links
Diffraction spikes explained
by
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) is a website provided by NASA and Michigan Technological University (MTU). According to the website, "Each day a different image or photograph of our universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written ...
.
*
* {{cite web, last=Kratzke, first=Bastian, title=Best lenses for Sunstars, url=https://phillipreeve.net/blog/best-lenses-for-sunstars/, work=phillipreeve.net, date=15 July 2020
Astrophotography
Science of photography
Diffraction