Design-based learning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Design-based learning (DBL), also known as design-based instruction, is an inquiry-based form of learning, or pedagogy, that is based on integration of
Retrieved 2016-03-15 Design-based
. Retrieved 2016-03-15 DBL, as well as
Retrieved 2016-03-15 Deeper learning is supported when students design and create an artifact that requires understanding and application of knowledge. DBL activity supports iteration as students create, assess, and redesign their projects. The work's complexity often requires collaboration and specialized roles, providing students with the opportunity to become "experts" in a particular area. Design projects require students to establish goals and constraints, generate ideas, and create prototypes through
Retrieved 2016-03-15 *investigate context *identify needs *develop criteria *generate alternatives *select alternative *prototype/test *produce *evaluate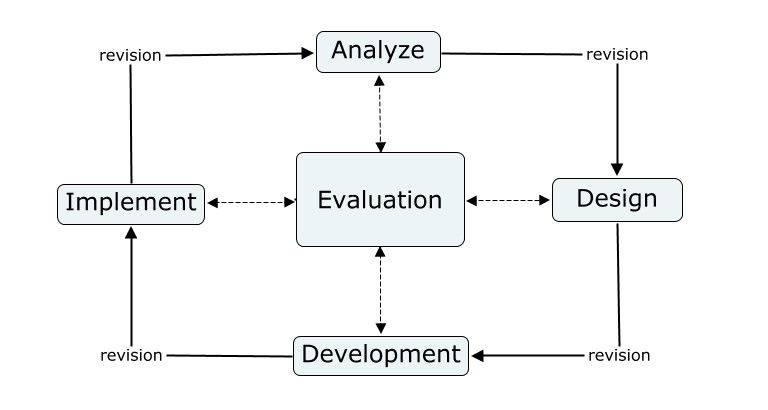 A similar approach is the ADDIE Model of instructional design, a framework of generic processes used by instructional designers and training developers. It represents a descriptive guideline with five distinct phases:
* Analysis
* Design
* Development
* Implementation
* Evaluation
A similar approach is the ADDIE Model of instructional design, a framework of generic processes used by instructional designers and training developers. It represents a descriptive guideline with five distinct phases:
* Analysis
* Design
* Development
* Implementation
* Evaluation
''Engagement and Achievements: A Case Study of Design-Based Learning in a Science Context,'' Doppelt, Mehalik, Schunn, Silk, Krysinski
. Retrieved 2016-03-15 Significant benefits of implementing DBL has been observed in the areas of math and science (Darling-Hammond et al., 2008). Research has found that students who participate in learning by design projects have a more systematic understanding of a system's parts and functions that control groups (Hmelo, Holton, & Kolodner, 2000). A 2000 study (Hmelo, Holton, and Kolodner) found that the design project led to better learning outcomes and included deeper learning than the traditional learning approach. The researchers also noted that the students developed greater understanding of complex systems. The study found that in using DBL, both higher-achieving and lower-achieving students showed strong evidence of progress in learning the targeted concepts, students were able to apply key concepts in their work, and there were positive effects on motivation and sense of ownership over work product by both groups and individual students.
Design Based Learning
* ttps://www.cpp.edu/~dnelson/intro.html ''About Design-Based Learning,'' Cal Poly Pomona Applied learning Inquiry Pedagogy Educational practices
design thinking
Design thinking refers to the set of cognitive, strategic and practical procedures used by designers in the process of designing, and to the body of knowledge that has been developed about how people reason when engaging with design problems.
Desi ...
and the design process into the classroom at the K-12 and post-secondary levels.Powerful Learning: Studies Show Deep Understanding Derives from Collaborative Methods, By Brigid Barron, Linda Darling-Hammond, in Edutopia, October 8, 2008Retrieved 2016-03-15 Design-based
learning environment
The term learning environment can refer to an educational approach, cultural context, or physical setting in which teaching and learning occur. The term is commonly used as a more definitive alternative to "classroom", but it typically refers to ...
s can be found across many disciplines, including those traditionally associated with design (e.g. art, architecture, engineering, interior design, graphic design), as well as others not normally considered to be design-related (science, technology, business, humanities).''Teaching for meaningful learning,'' Edutopia. Retrieved 2016-03-15 DBL, as well as
project-based learning
Project-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered pedagogy that involves a dynamic classroom approach in which it is believed that students acquire a deeper knowledge through active exploration of real-world challenges and problems. Students l ...
and problem-based learning, is used to teach 21st century skills
21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions that have been identified as being required for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. Th ...
such as communication and collaboration
Collaboration (from Latin ''com-'' "with" + ''laborare'' "to labor", "to work") is the process of two or more people, entities or organizations working together to complete a task or achieve a goal. Collaboration is similar to cooperation. Most ...
and foster deeper learning. ''21st Century Skills - for Students and Teachers'', Research and Evaluation, August 2010, Kamehameha SchoolsRetrieved 2016-03-15 Deeper learning is supported when students design and create an artifact that requires understanding and application of knowledge. DBL activity supports iteration as students create, assess, and redesign their projects. The work's complexity often requires collaboration and specialized roles, providing students with the opportunity to become "experts" in a particular area. Design projects require students to establish goals and constraints, generate ideas, and create prototypes through
storyboarding
A storyboard is a graphic organizer that consists of illustrations or images displayed in sequence for the purpose of pre-visualizing a motion picture, animation, motion graphic or interactive media sequence. The storyboarding process, in t ...
or other representational practices. Robotics competitions in schools are popular design-based learning activities, wherein student teams design, build and then pilot their robots in competitive challenges.
Design-based learning was developed in the 1980s by Doreen Nelson, a professor at California State Polytechnic University, Pomona and the Art Center College of Design
Art Center College of Design (stylized as ArtCenter College of Design) is a private art college in Pasadena, California.
History
ArtCenter College of Design was founded in 1930 in downtown Los Angeles as the Art Center School.
In 1935, Fred ...
. Her findings suggested that kinesthetic problem-solving helps students acquire, retain, and synthesize information in practical ways.
Design process
The design process is an iterative process that has a variety of sequential steps:''Middle-School Science Through Design- Based Learning versus Scripted Inquiry: Better Overall Science Concept Learning and Equity Gap Reduction'', Mehalik, Doppelt, Schunn. Journal of Engineering Education, January 2008Retrieved 2016-03-15 *investigate context *identify needs *develop criteria *generate alternatives *select alternative *prototype/test *produce *evaluate
 A similar approach is the ADDIE Model of instructional design, a framework of generic processes used by instructional designers and training developers. It represents a descriptive guideline with five distinct phases:
* Analysis
* Design
* Development
* Implementation
* Evaluation
A similar approach is the ADDIE Model of instructional design, a framework of generic processes used by instructional designers and training developers. It represents a descriptive guideline with five distinct phases:
* Analysis
* Design
* Development
* Implementation
* Evaluation
Results
Positive benefits of the design-based learning approach have been observed, including student-based learning where students (often) identify their project's needs, develop their own ideas, and engage in a larger range of thinking than with the traditional scripted inquiry model. The results from the 2008 study by Mehalik et al. found significant improvement in student performance using the DBL model compared to the scripted model. A 1998 study (Fraser, Fraser & Tobin, 1991) suggest that DBL has the potential to increase students' desire to learn, enhance success in science class, and increase interest in science topics. Students were observed to be engaged in DBL and the lower-achieving students were able to explain concepts at higher levels than previously observed by their teacher. In-depth experience in design activities and creation of meaningful outcomes in technology were observed in terms of the finished product, documentation, and reflection.. Retrieved 2016-03-15 Significant benefits of implementing DBL has been observed in the areas of math and science (Darling-Hammond et al., 2008). Research has found that students who participate in learning by design projects have a more systematic understanding of a system's parts and functions that control groups (Hmelo, Holton, & Kolodner, 2000). A 2000 study (Hmelo, Holton, and Kolodner) found that the design project led to better learning outcomes and included deeper learning than the traditional learning approach. The researchers also noted that the students developed greater understanding of complex systems. The study found that in using DBL, both higher-achieving and lower-achieving students showed strong evidence of progress in learning the targeted concepts, students were able to apply key concepts in their work, and there were positive effects on motivation and sense of ownership over work product by both groups and individual students.
Implementation
The teaching of21st century skills
21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions that have been identified as being required for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. Th ...
is more effective when teachers gain expertise in both the practice and the teaching of these skills, in effect becoming successful 21st century learners in the areas of: communication and collaboration amongst teachers and with students; being flexible with new classroom dynamics; fostering independent student learning; adapting teaching and learning styles to new pedagogical approaches.
Challenges to implementing DBL include developing the skills of the instructors:
* teachers' ability to select topics and activities that support, and benefit from, differing viewpoints and students' real-world experiences
* selecting students who will work well together
* setting of effective ground rules to ensure equal opportunities to participate,
* encouraging multiple strategies to foster full participation for all members of a group of team.
See also
* * * * *Organizational learning
Organizational learning is the process of creating, retaining, and transferring knowledge within an organization. An organization improves over time as it gains experience. From this experience, it is able to create knowledge. This knowledge is bro ...
*
References
{{Reflist, 30em * Fraser, B. J., & Tobin, K.: Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in classroom environment research. In B. J. Fraser & H. J. Walberg (Eds.), Educational environments: Evaluation, antecedents, and consequences (pp. 271–290). Oxford, UK: Pergamon Press. 1991.External links
Design Based Learning
* ttps://www.cpp.edu/~dnelson/intro.html ''About Design-Based Learning,'' Cal Poly Pomona Applied learning Inquiry Pedagogy Educational practices