Depreciation (economics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
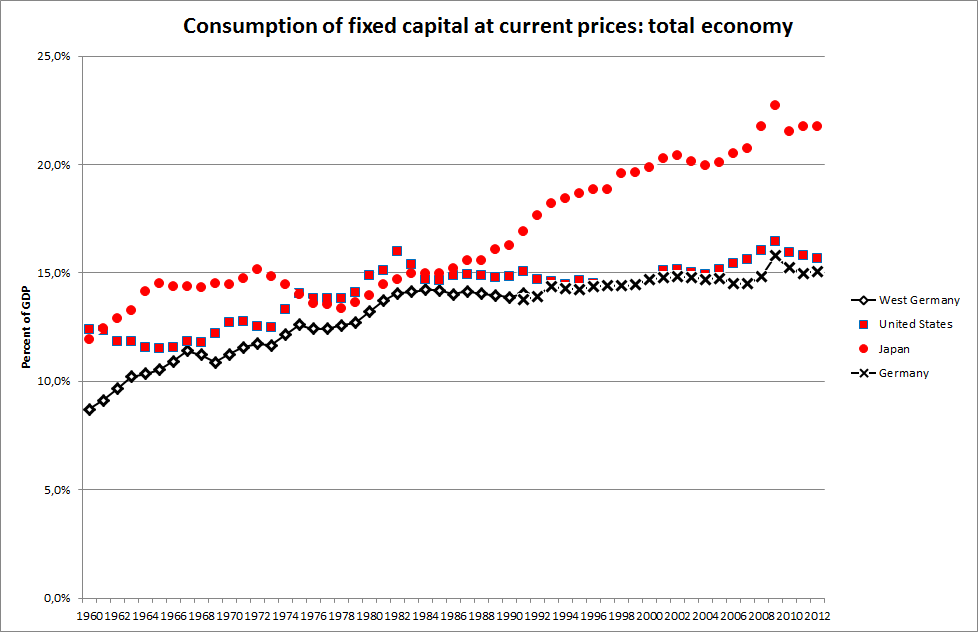 In
In
Depreciation Accounting Simplified
{{Authority control Valuation (finance) Capital management
economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
, depreciation is the gradual decrease in the economic value of the capital stock
In economics, capital goods or capital are "those durable produced goods that are in turn used as productive inputs for further production" of goods and services. A typical example is the machinery used in a factory. At the macroeconomic level, ...
of a firm, nation or other entity, either through physical depreciation, obsolescence or changes in the demand for the services of the capital in question. If the capital stock is in one period , gross (total) investment spending on newly produced capital is and depreciation is , the capital stock in the next period, , is . The net increment to the capital stock is the difference between gross investment and depreciation, and is called net investment
In economics, net investment is spending which increases the availability of fixed capital goods or means of production and goods inventories. It is the total spending on newly produced physical capital (fixed investment) and on inventories (inven ...
.
Models
In economics, the value of a capital asset may be modeled as thepresent value
In economics and finance, present value (PV), also known as present discounted value (PDV), is the value of an expected income stream determined as of the date of valuation. The present value is usually less than the future value because money ha ...
of the flow of services the asset will generate in future, appropriately adjusted for uncertainty. Economic depreciation over a given period is the reduction in the remaining value of future goods and services.
Under certain circumstances, such as an unanticipated increase in the price of the services generated by an asset or a reduction in the discount rate, its value may increase rather than decline. Depreciation is then negative.
Depreciation can alternatively be measured as the change in the ''market'' value of capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
over a given period: the market price of the capital at the beginning of the period minus its market price at the end of the period.
Such a method in calculating depreciation differs from other methods, such as straight-line depreciation in that it is included in the calculation of implicit cost
In economics, an implicit cost, also called an imputed cost, implied cost, or notional cost, is the opportunity cost equal to what a firm must give up in order to use a factor of production for which it already owns and thus does not pay rent. It i ...
, and thus economic profit
In economics, profit is the difference between revenue that an economic entity has received from its outputs and total costs of its inputs, also known as surplus value. It is equal to total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit an ...
.
Modeling depreciation of a durable as delivering the same services from purchase until failure, with zero scrap value (rather than slowing degrading and retaining residual value
Residual value also known as salvage value describes the future value of a good in terms of absolute value in monetary terms after depreciation, and it is sometimes abbreviated into a percentage of the initial price when the item was new. It is one ...
), is referred to as the light bulb model of depreciation, or more colorfully as the one-hoss shay model, after a poem by Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr.
Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. (; August 29, 1809 – October 7, 1894) was an American physician, poet, and polymath based in Boston. Grouped among the fireside poets, he was acclaimed by his peers as one of the best writers of the day. His most ...
, about a carriage which worked perfectly for exactly one hundred years, then fell completely apart in an instant.
National accounts
 In
In national accounts
National accounts or national account systems (NAS) are the implementation of complete and consistent accounting Scientific technique, techniques for measuring the economic activity of a nation. These include detailed underlying measures that ...
the decline in the aggregate capital stock
In economics, capital goods or capital are "those durable produced goods that are in turn used as productive inputs for further production" of goods and services. A typical example is the machinery used in a factory. At the macroeconomic level, ...
arising from the use of fixed assets in production is referred to as consumption of fixed capital
Consumption of fixed capital (CFC) is a term used in business accounts, tax assessments and national accounts for depreciation of fixed assets. CFC is used in preference to "depreciation" to emphasize that fixed capital is used up in the process ...
(CFC). Hence, CFC is equal to the difference between aggregate gross fixed capital formation
Gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) is a component of the expenditure on gross domestic product (GDP) that indicates how much of the new value added in an economy is invested rather than consumed. It measures the value of acquisitions of new or ...
( gross investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broade ...
) and net fixed capital formation (net investment
In economics, net investment is spending which increases the availability of fixed capital goods or means of production and goods inventories. It is the total spending on newly produced physical capital (fixed investment) and on inventories (inven ...
) or between Gross National Product
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total amount of factor incomes earned by the residents of a country. It is equal to gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes received from n ...
and Net National Product Net national product (NNP) is gross national product (GNP), i.e. the total market value of all final goods and services produced by the factors of production of a country or other polity during a given time period, minus depreciation. Similarly, n ...
. Unlike depreciation in business accounting, CFC in national accounts is, in principle, not a method of allocating the costs of past expenditures on fixed assets over subsequent accounting periods. Rather, fixed assets at a given moment in time are valued according to the remaining benefits to be derived from their use.
References
Depreciation Accounting Simplified
{{Authority control Valuation (finance) Capital management
economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...