Dead Sea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by
 The Dead Sea is an
The Dead Sea is an
 With 34.2% salinity (in 2011), it is one of the world's saltiest bodies of water, though
With 34.2% salinity (in 2011), it is one of the world's saltiest bodies of water, though  The mineral content of the Dead Sea is very different from that of ocean water. The exact composition of the Dead Sea water varies mainly with season, depth and temperature. In the early 1980s, the concentration of ionic species (in g/kg) of Dead Sea surface water was Cl− (181.4), Br− (4.2), SO42− (0.4), HCO3− (0.2), Ca2+ (14.1), Na+ (32.5), K+ (6.2) and Mg2+ (35.2). The total salinity was 276 g/kg. These results show that the composition of the salt, as anhydrous chlorides on a weight percentage basis, was
The mineral content of the Dead Sea is very different from that of ocean water. The exact composition of the Dead Sea water varies mainly with season, depth and temperature. In the early 1980s, the concentration of ionic species (in g/kg) of Dead Sea surface water was Cl− (181.4), Br− (4.2), SO42− (0.4), HCO3− (0.2), Ca2+ (14.1), Na+ (32.5), K+ (6.2) and Mg2+ (35.2). The total salinity was 276 g/kg. These results show that the composition of the salt, as anhydrous chlorides on a weight percentage basis, was  The salt concentration of the Dead Sea fluctuates around 31.5%. This is unusually high and results in a nominal density of 1.24 kg/L. Anyone can easily float in the Dead Sea because of natural
The salt concentration of the Dead Sea fluctuates around 31.5%. This is unusually high and results in a nominal density of 1.24 kg/L. Anyone can easily float in the Dead Sea because of natural

 Dwelling in caves near the Dead Sea is recorded in the
Dwelling in caves near the Dead Sea is recorded in the
 The Dead Sea was an important trade route with ships carrying salt, asphalt and agricultural produce. Multiple anchorages existed on both sides of the sea, including in
The Dead Sea was an important trade route with ships carrying salt, asphalt and agricultural produce. Multiple anchorages existed on both sides of the sea, including in
 Explorers and scientists arrived in the area to analyze the minerals and research the unique climate.
After the find of the " Moabite Stone" in 1868 on the plateau east of the Dead Sea, Moses Wilhelm Shapira and his partner Salim al-Khouri forged and sold a whole range of presumed "Moabite" antiquities, and in 1883 Shapira presented what is now known as the "Shapira Strips", a supposedly ancient scroll written on leather strips which he claimed had been found near the Dead Sea. The strips were declared to be forgeries and Shapira took his own life in disgrace.
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, hundreds of religious documents dated between 150 BCE and 70 CE were found in caves near the ancient settlement of
Explorers and scientists arrived in the area to analyze the minerals and research the unique climate.
After the find of the " Moabite Stone" in 1868 on the plateau east of the Dead Sea, Moses Wilhelm Shapira and his partner Salim al-Khouri forged and sold a whole range of presumed "Moabite" antiquities, and in 1883 Shapira presented what is now known as the "Shapira Strips", a supposedly ancient scroll written on leather strips which he claimed had been found near the Dead Sea. The strips were declared to be forgeries and Shapira took his own life in disgrace.
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, hundreds of religious documents dated between 150 BCE and 70 CE were found in caves near the ancient settlement of

 On the Jordanian side, nine international franchises have opened
On the Jordanian side, nine international franchises have opened

Area C and the Future of the Palestinian Economy
October 2, 2013


 In May 2009 at the
In May 2009 at the
Jordan Red Sea Project Description
retrieved on May 11, 2011 At a regional conference in July 2009, officials expressed concern about the declining water levels. Some suggested industrial activities around the Dead Sea might need to be reduced. Others advised environmental measures to restore conditions such as increasing the volume of flow from the Jordan River to replenish the Dead Sea. Currently, only sewage and effluent from fish ponds run in the river's channel. Experts also stressed the need for strict conservation efforts. They said agriculture should not be expanded, sustainable support capabilities should be incorporated into the area and pollution sources should be reduced. In October 2009, the Jordanians accelerated plans to extract around of water per year from the Red Sea, desalinate it for use as fresh water and send the waste water to the Dead Sea by tunnel, despite concerns about inadequate time to assess the potential environmental impact. According to Jordan's minister for water, General Maysoun Zu'bi, this project could be considered as the first phase of the Red Sea–Dead Sea Water Conveyance. In December 2013, Israel, Jordan and the Palestinian Authority signed an agreement for laying a water pipeline to link the Red Sea with the Dead Sea. The pipeline would be long and is estimated to take up to five years to complete. In January 2015 it was reported that the level of water was dropping by a year. On 27 November 2016, the Jordanian government shortlisted five consortia to implement the project. Jordan's ministry of Water and Irrigation said that the $100 million first phase of the project would begin construction in the first quarter of 2018, and would be completed by 2021. The project was officially abandoned in June 2021, having never broken ground.
"The Red Sea - Dead Sea Water Conveyance Study Program"
and source of basic data on the Dead Sea. *Yehouda Enzel, et al., eds (2006) ''New Frontiers in Dead Sea Paleoenvironmental Research'', Geological Society of America, *Niemi, Tina M., Ben-Avraham, Z., and Gat, J., eds., 1997, The Dead Sea: The Lake and Its Setting: N.Y.,
Area C and the Future of the Palestinian Economy
October 2, 2013
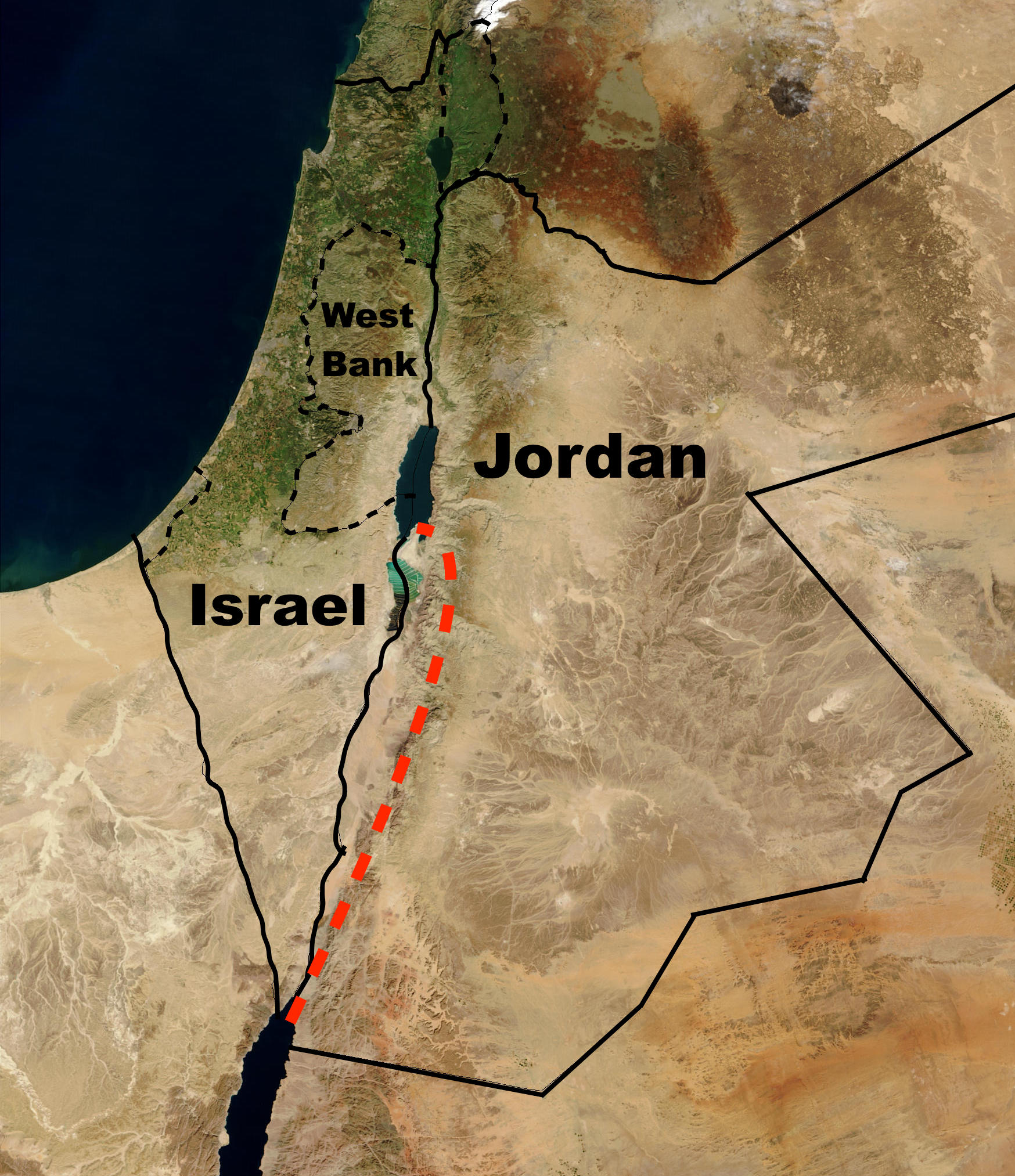
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
to the east and Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
and the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
to the west. It lies in the Jordan Rift Valley
The Jordan Rift Valley, also Jordan Valley ''Bīrʿāt haYardēn'', ar, الغور Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr),, date=November 2022 also called the Syro-African Depression, is an elongated depression located in modern-day Israel, and Jordan. This g ...
, and its main tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drai ...
is the Jordan River.
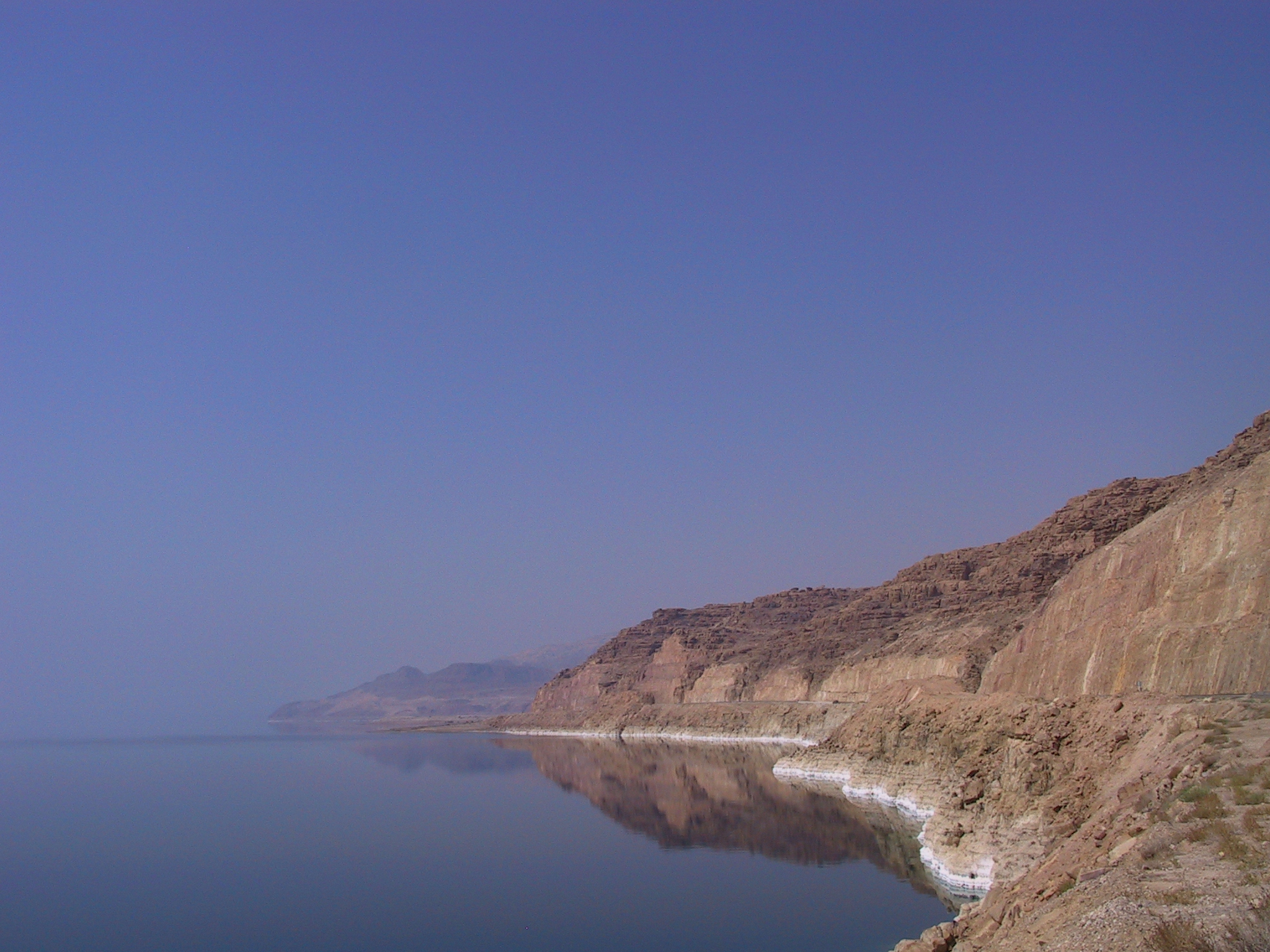
As of 2019, the lake's surface is below sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
, making its shores the lowest land-based elevation on Earth. It is deep, the deepest hypersaline lake
A hypersaline lake is a landlocked body of water that contains significant concentrations of sodium chloride, brines, and other salts, with saline levels surpassing that of ocean water (3.5%, i.e. ).
Specific microbial species can thrive in hi ...
in the world. With a salinity of 342 g/kg, or 34.2% (in 2011), it is one of the world's saltiest bodies of water – 9.6 times as salty as the ocean – and has a density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ...
of 1.24 kg/litre, which makes swimming similar to floating. This salinity makes for a harsh environment in which plants and animals cannot flourish, hence its name. The Dead Sea's main, northern basin is long and wide at its widest point.
The Dead Sea has attracted visitors from around the Mediterranean Basin for thousands of years. It was one of the world's first health resort
A destination spa or health resort is a resort centered on a spa, such as a mineral spa. Historically, many such spas were developed at the location of natural hot springs or mineral springs; in the era before modern biochemical knowledge and ...
s (for Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renova ...
), and it has been the supplier of a wide variety of products, from asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
for Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
mummification
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
to potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
for fertiliser
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s. Today, tourists visit the sea on its Israeli, Jordanian and West Bank coastlines. The Palestinian tourism industry has been met with setbacks in developing along the West Bank coast.
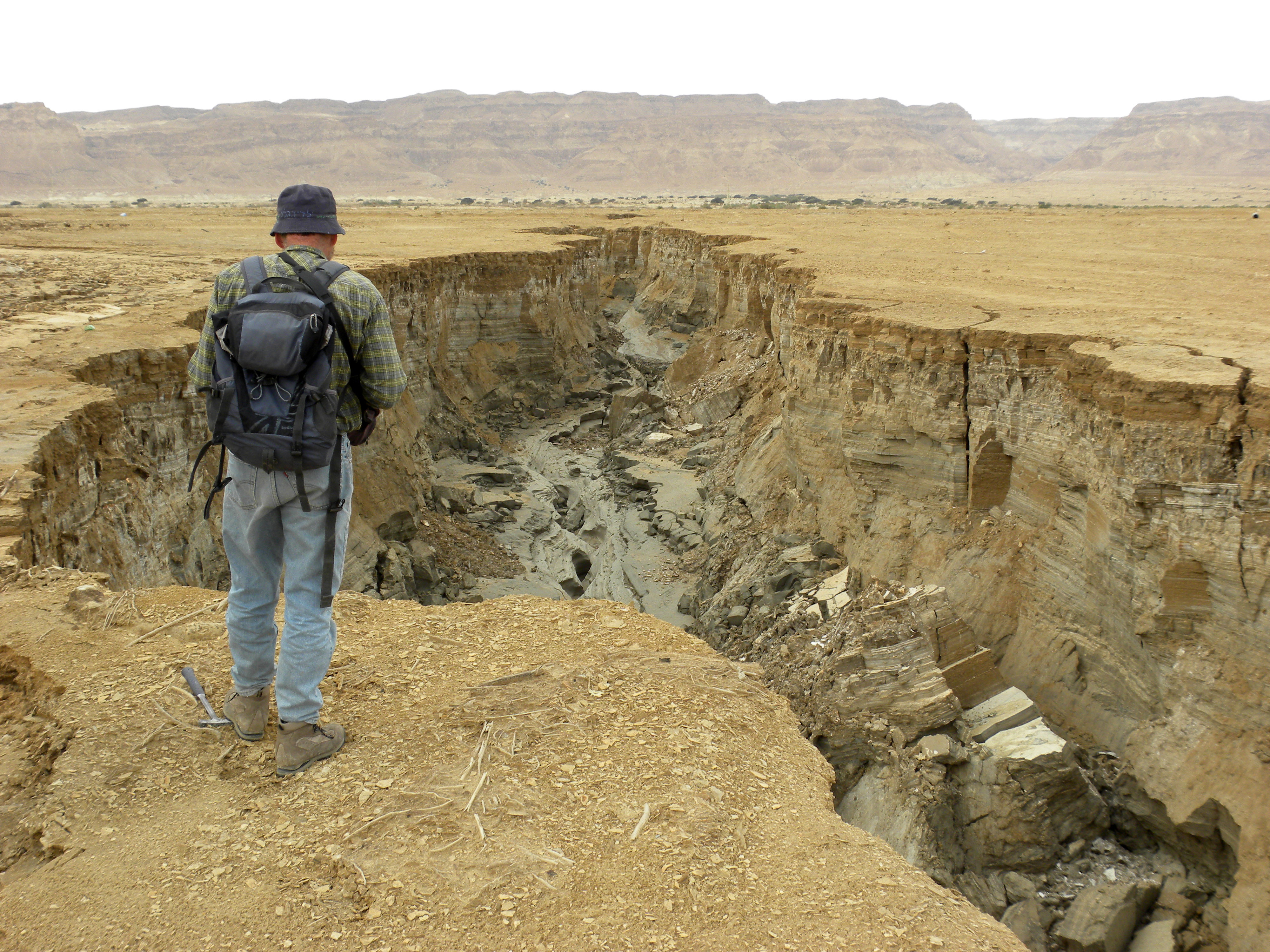
The Dead Sea is receding at a swift rate; its surface area today is , having been in 1930. Multiple canal and pipeline proposals, such as the scrapped Red Sea–Dead Sea Water Conveyance project, have been made to reduce its recession.
Names
TheEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
name "Dead Sea" is a calque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language w ...
of the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
name ''Bahr'' or (),The first article ''al-'' is unnecessary and usually not used. itself a calque of earlier Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(, ''Nekrá Thálassa'') and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
names () in reference to the scarcity of aquatic life caused by the lake's extreme salinity. The name also occasionally appears in Hebrew literature as ''Yām HaMāvet'' (), "Sea of Death".
The usual biblical and modern Hebrew name for the lake is the (, '). Other Hebrew names for the lake also mentioned in the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
are the (, ''Yām Ha‘Ărāvâ'') and the (, ''HaYām HaKadmoni''). In Arabic, it is also known as the (, ''Buhayrat'', ''Bahret'', or ''Birket Lut'') from the nephew of Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
whose wife was said to have turned into a pillar of salt during the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah. Less often, it has been known in Arabic as the from a formerly important city along its shores.
Historical English names include the , from the biblical account of its destruction and from Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
. Because of the large volume of ancient trade in the lake's naturally occurring free-floating bitumen, its usual names in ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
and Roman geography were some form of ( grc-gre, Ἀσφαλτίτης or , ''Asphaltítēs'' or ''Asphaltítis Límnē''; la, Lacus Asphaltites) or Sea (, ''Asphaltítēs Thálassa'').
Geography
 The Dead Sea is an
The Dead Sea is an endorheic lake
An endorheic lake (also called a sink lake or terminal lake) is a collection of water within an endorheic basin, or sink, with no evident outlet. Endorheic lakes are generally saline as a result of being unable to get rid of solutes left in the l ...
located in the Jordan Rift Valley
The Jordan Rift Valley, also Jordan Valley ''Bīrʿāt haYardēn'', ar, الغور Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr),, date=November 2022 also called the Syro-African Depression, is an elongated depression located in modern-day Israel, and Jordan. This g ...
, a geographic feature formed by the Dead Sea Transform
The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system, also sometimes referred to as the Dead Sea Rift, is a series of faults that run from the Maras Triple Junction (a junction with the East Anatolian Fault in southeastern Turkey) to the northern end of the ...
(DST). This left lateral-moving transform fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduct ...
lies along the tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents ...
plate boundary
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
between the African Plate
The African Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes much of the continent of Africa (except for its easternmost part) and the adjacent oceanic crust to the west and south. It is bounded by the North American Plate and South American Plate ...
and the Arabian Plate
The Arabian Plate is a minor tectonic plate in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres.
It is one of the three continental plates (along with the African and the Indian Plates) that have been moving northward in geological history and colliding ...
. It runs between the East Anatolian Fault
The East Anatolian Fault ( tr, Doğu Anadolu Fay Hattı) is a major strike-slip fault zone in eastern Turkey. It forms the transform type tectonic boundary between the Anatolian Plate and the northward-moving Arabian Plate. The difference in t ...
zone in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
and the northern end of the Red Sea Rift
The Red Sea Rift is a spreading center between two tectonic plates, the African Plate and the Arabian Plate. It extends from the Dead Sea Transform fault system, and ends at an intersection with the Aden Ridge and the East African Rift, forming ...
offshore of the southern tip of Sinai. It is here that the Upper Jordan River/Sea of Galilee/Lower Jordan River water system comes to an end.
The Jordan River is the only major water source flowing into the Dead Sea, although there are small perennial springs under and around the Dead Sea, forming pools and quicksand
Quicksand is a colloid consisting of fine granular material (such as sand, silt or clay) and water. It forms in saturated loose sand when the sand is suddenly agitated. When water in the sand cannot escape, it creates a liquefied soil that los ...
pits along the edges. There are no outlet streams.
The Mujib River, biblical Arnon, is one of the larger water sources of the Dead Sea other than the Jordan. The Wadi Mujib
Wadi Mujib ( ar, وادي الموجب, ''Wadi el-Mujib''), also known as Arnon Stream (Hebrew: נַחַל ארנון), is a river in Jordan. The river empties into the Dead Sea circa below sea level. Today, Wadi Mujib is fed by seven tributa ...
valley, 420 m below the sea level in the southern part of the Jordan valley, is a biosphere reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
, with an area of . Other more substantial sources are Wadi Darajeh (Arabic)/Nahal Dragot (Hebrew), and that ends at Ein Gedi
Ein Gedi ( he, עֵין גֶּדִי, ), also spelled En Gedi, meaning "spring of the goat, kid", is an oasis, an Archaeological site, archeological site and a nature reserve in Israel, located west of the Dead Sea, near Masada and the Qu ...
. Wadi Hasa (biblical Zered) is another wadi
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water ...
flowing into the Dead Sea.
Rainfall is scarcely per year in the northern part of the Dead Sea and barely in the southern part. The Dead Sea zone's aridity is due to the rainshadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
effect of the Judaean Mountains
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills ( he, הרי יהודה, translit=Harei Yehuda) or the Hebron Mountains ( ar, تلال الخليل, translit=Tilal al-Khalīl, links=, lit=Hebron Mountains), is a mountain range in Palestine and Israel wh ...
. The highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
*Sou ...
east of the Dead Sea receive more rainfall than the Dead Sea itself.
To the west of the Dead Sea, the Judaean mountains rise less steeply and are much lower than the mountains to the east. Along the southwestern side of the lake is a tall halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, p ...
mineral formation called Mount Sodom
Mount Sodom ( he, הר סדום, ''Har Sedom'') is a hill along the southwestern part of the Dead Sea in Israel; it is part of the Judaean Desert Nature Reserve. It takes its name from the legendary city of Sodom, whose destruction is the subje ...
.
Geology

Formation theories
There are two contending hypotheses about the origin of the low elevation of the Dead Sea. The older hypothesis is that the Dead Sea lies in a true rift zone, an extension of theRed Sea Rift
The Red Sea Rift is a spreading center between two tectonic plates, the African Plate and the Arabian Plate. It extends from the Dead Sea Transform fault system, and ends at an intersection with the Aden Ridge and the East African Rift, forming ...
, or even of the Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it ...
of eastern Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
. A more recent hypothesis is that the Dead Sea basin is a consequence of a "step-over" discontinuity along the Dead Sea Transform, creating an extension of the crust with consequent subsidence.
Sedom Lagoon
During the latePliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
, around 3.7 million years ago, what is now the valley of the Jordan River, Dead Sea, and the northern Wadi Arabah
The Arabah, Araba or Aravah ( he, הָעֲרָבָה, ''hāʿĂrāḇā''; ar, وادي عربة, ''Wādī ʿAraba''; lit. "desolate and dry area") is a loosely defined geographic area south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the bord ...
was repeatedly inundated by waters from the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
. The waters formed in a narrow, crooked bay that is called by geologists the Sedom Lagoon, which was connected to the sea through what is now the Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the he, עמק יזרעאל, translit. ''ʿĒmeq Yīzrəʿēʿl''), or Marj Ibn Amir ( ar, مرج ابن عامر), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern Distr ...
. The floods of the valley came and went depending on long-scale changes in the tectonic and climatic conditions.
The Sedom Lagoon extended at its maximum from the Sea of Galilee in the north to somewhere around south of the current southern end of the Dead Sea, and the subsequent lakes never surpassed this expanse. The Hula Depression was never part of any of these water bodies due to its higher elevation and the high threshold of the Korazim block separating it from the Sea of Galilee basin.
Salt deposits
The Sedom Lagoon depositedevaporites
An evaporite () is a water-soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean ...
mainly consisting of rock salt
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pi ...
, which eventually reached a thickness of on the old basin floor in the area of today's Mount Sedom
Mount Sodom ( he, הר סדום, ''Har Sedom'') is a hill along the southwestern part of the Dead Sea in Israel; it is part of the Judaean Desert Nature Reserve. It takes its name from the legendary city of Sodom, whose destruction is the subje ...
.
Lake formation
Approximately two million years ago, the land between theRift Valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear d ...
and the Mediterranean Sea rose to such an extent that the ocean could no longer flood the area. Thus, the long lagoon became a landlocked lake.
The first prehistoric lake to follow the Sedom Lagoon is named Lake Amora (which possibly appeared in the early Pleistocene; its sediments developed into the Amora (Samra) Formation, dated to over 200-80 kyr BP), followed by Lake Lisan
Lake Lisan was a prehistoric lake that existed between 70,000 and 12,000 BP in the Jordan Rift Valley in the Near East. It is sometimes referred to as a Pleistocene lake.
Lisan means ''tongue'' in Arabic relating to the shape of the Lisan Penin ...
(c. 70-14 kyr) and finally by the Dead Sea.
Lake salinity
The water levels and salinity of the successive lakes (Amora, Lisan, Dead Sea) have either risen or fallen as an effect of the tectonic dropping of the valley bottom, and due to climate variation. As the climate became more arid, Lake Lisan finally shrank and became saltier, leaving the Dead Sea as its last remainder. From 70,000 to 12,000 years ago, Lake Lisan's level was to higher than its current level, possibly due to lower evaporation than in the present. Its level fluctuated dramatically, rising to its highest level around 26,000 years ago, indicating a very wet climate in the Near East. Around 10,000 years ago, the lake's level dropped dramatically, probably even lower than today. During the last several thousand years, the lake has fluctuated approximately , with some significant drops and rises. Current theories as to the cause of this dramatic drop in levels rule outvolcanic activity
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a ...
; therefore, it may have been a seismic event.
Salt mounts formation
In prehistoric times, great amounts of sediment collected on the floor of Lake Amora. The sediment was heavier than the salt deposits and squeezed the salt deposits upwards into what are now the Lisan Peninsula andMount Sodom
Mount Sodom ( he, הר סדום, ''Har Sedom'') is a hill along the southwestern part of the Dead Sea in Israel; it is part of the Judaean Desert Nature Reserve. It takes its name from the legendary city of Sodom, whose destruction is the subje ...
(on the southwest side of the lake). Geologists explain the effect in terms of a bucket of mud into which a large flat stone is placed, forcing the mud to creep up the sides of the bucket. When the floor of the Dead Sea dropped further due to tectonic forces, the salt mounts of Lisan and Mount Sodom stayed in place as high cliffs (see salt dome
A salt dome is a type of structural dome formed when salt (or other evaporite minerals) intrudes into overlying rocks in a process known as diapirism. Salt domes can have unique surface and subsurface structures, and they can be discovered usin ...
).
Climate
The Dead Sea has ahot desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
BWh), with year-round sunny skies and dry air. It has less than mean annual rainfall and a summer average temperature between . Winter average temperatures range between . The region has weaker ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
, particularly the UVB (erythrogenic rays). Given the higher atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, ...
, the air has a slightly higher oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
content (3.3% in summer to 4.8% in winter) as compared to oxygen concentration at sea level. Barometric pressures at the Dead Sea were measured between 1061 and 1065 hPa and clinically compared with health effects at higher altitude. (This barometric measure is about 5% higher than sea level standard atmospheric pressure of 1013.25 hPa, which is the global ocean mean or ATM.) The Dead Sea affects temperatures nearby because of the moderating effect a large body of water has on climate. During the winter, sea temperatures tend to be higher than land temperatures, and vice versa during the summer months. This is the result of the water's mass and specific heat capacity
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat t ...
. On average, there are 192 days above annually.
Chemistry
 With 34.2% salinity (in 2011), it is one of the world's saltiest bodies of water, though
With 34.2% salinity (in 2011), it is one of the world's saltiest bodies of water, though Lake Vanda
Lake Vanda is a lake in Wright Valley, Victoria Land, Ross Dependency, Antarctica. The lake is long and has a maximum depth of . On its shore, New Zealand maintained Vanda Station from 1968 to 1995. Lake Vanda is a hypersaline lake with a salin ...
in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
(35%), Lake Assal in Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
(34.8%), Lagoon Garabogazköl in the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
(up to 35%) and some hypersaline ponds and lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys
The McMurdo Dry Valleys are a row of largely snow-free valleys in Antarctica, located within Victoria Land west of McMurdo Sound. The Dry Valleys experience extremely low humidity and surrounding mountains prevent the flow of ice from nearby ...
in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
(such as Don Juan Pond (44%)) have reported higher salinities.
In the 19th century and the early 20th century, the surface layers of the Dead Sea were less salty than today, which resulted in an average density in the range of 1.15-1.17 g/cm3 instead of the present value of around 1.25 g/cm3. A sample tested by Bernays in the 19th century had a salinity of 19%. By the year 1926, the salinity had increased (although it was also suspected that the salinity varies seasonally and depends on the distance from the mouth of the Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
).
Until the winter of 1978–79, when a major mixing event took place, the Dead Sea was composed of two stratified layers of water that differed in temperature, density, age, and salinity. The topmost or so of the Dead Sea had an average salinity of about 30%, and a temperature that swung between and . Underneath a zone of transition, the lowest level of the Dead Sea had waters of a consistent temperature, salinity of over 34%, and complete saturation
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to:
Chemistry
* Saturation, a property of organic compounds referring to carbon-carbon bonds
**Saturated and unsaturated compounds
** Degree of unsaturation
**Saturated fat or fatty aci ...
of sodium chloride (NaCl). Since the water near the bottom is saturated with NaCl, that salt precipitates out of solution onto the sea floor.
Beginning in the 1960s, water inflow to the Dead Sea from the Jordan River was reduced as a result of large-scale irrigation and generally low rainfall. By 1975, the upper water layer was saltier than the lower layer. Nevertheless, the upper layer remained suspended above the lower layer because its waters were warmer and thus less dense. When the upper layer cooled so its density was greater than the lower layer, the waters mixed (1978–79). For the first time in centuries, the lake was a homogeneous body of water. Since then, stratification
Stratification may refer to:
Mathematics
* Stratification (mathematics), any consistent assignment of numbers to predicate symbols
* Data stratification in statistics
Earth sciences
* Stable and unstable stratification
* Stratification, or st ...
has begun to redevelop.calcium chloride
Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a salt with the chemical formula . It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and it is highly soluble in water. It can be created by neutralising hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide.
Ca ...
(CaCl2) 14.4%, potassium chloride (KCl) 4.4%, magnesium chloride
Magnesium chloride is the family of inorganic compounds with the formula , where x can range from 0 to 12. These salts are colorless or white solids that are highly soluble in water. These compounds and their solutions, both of which occur in natu ...
(MgCl2) 50.8% and sodium chloride (NaCl) 30.4%. In comparison, the salt in the water of most ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s and seas is approximately 85% sodium chloride. The concentration of sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
ions (SO42−) is very low, and the concentration of bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant ...
ions (Br−) is the highest of all waters on Earth.buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the ...
. In this respect the Dead Sea is similar to the Great Salt Lake in Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
in the United States.
An unusual feature of the Dead Sea is its discharge of asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
. From deep seeps, the Dead Sea constantly spits up small pebbles and blocks of the black substance. Asphalt-coated figurines and bitumen-coated Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
skulls from archaeological sites have been found. Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
mummification
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
processes used asphalt imported from the Dead Sea region.
Putative therapies
The Dead Sea area has become a location forhealth
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World Health Organiza ...
research
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness ...
and potential treatment for several reasons. The mineral content of the water, the low content of pollens and other allergen
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies.
In technical terms ...
s in the atmosphere, the reduced ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
component of solar radiation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre ( ...
, and the higher atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, ...
at this great depth each may have specific health effects. For example, persons experiencing reduced respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gre ...
function from disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
s such as cystic fibrosis seem to benefit from the increased atmospheric pressure.
The region's climate and low elevation have made it a popular center for assessment of putative therapies:
* Climatotherapy: Treatment which exploits local climatic features such as temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
, humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
, sunshine, barometric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
and special atmospheric constituents
* Heliotherapy: Treatment that exploits the biological effects of the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
's radiation
*Thalassotherapy
Thalassotherapy (from the Greek word ''thalassa'', meaning " sea") is the use of seawater as a form of therapy. Note: Thalasso therapy is a sub-definition under the listing for Thalasso. It also includes the systematic use of sea products and shor ...
: Treatment that exploits bathing in Dead Sea water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
Climatotherapy at the Dead Sea may be a therapy for psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete ...
by sunbathing for long periods in the area due to its position below sea level and subsequent result that UV rays
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
are partially blocked by the increased thickness of the atmosphere over the Dead Sea.
Rhinosinusitis
Rhinosinusitis is a simultaneous infection of the nasal mucosa (rhinitis) and an infection of the mucosa of the paranasal sinuses ( sinusitis). A distinction is made between acute rhinosinusitis and chronic rhinosinusitis.
Background
Because sin ...
patients receiving Dead Sea saline nasal irrigation
Nasal irrigation (also called nasal lavage, nasal toilet, or nasal douche) is a personal hygiene practice in which the nasal cavity is washed to flush out mucus and debris from the nose and sinuses, in order to enhance nasal breathing. Nasal i ...
exhibited improved symptom relief compared to standard hypertonic saline spray in one study.
Dead Sea mud pack therapy has been suggested to temporarily relieve pain in patients with osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the w ...
of the knees. According to researchers of the Ben Gurion University of the Negev
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) ( he, אוניברסיטת בן-גוריון בנגב, ''Universitat Ben-Guriyon baNegev'') is a public research university in Beersheba, Israel. Ben-Gurion University of the Negev has five campuses: the ...
, treatment with mineral-rich mud compresses can be used to augment conventional medical therapy.
Life forms

In the water
The sea is called "dead" because its high salinity prevents macroscopic aquatic organisms, such as fish and aquatic plants, from living in it, though minuscule quantities of bacteria and microbial fungi are present. In times of flood, the salt content of the Dead Sea can drop from its usual 35% to 30% or lower. The Dead Sea temporarily comes to life in the wake of rainy winters. In 1980, after one such rainy winter, the normally dark blue Dead Sea turned red. Researchers from Hebrew University of Jerusalem found the Dead Sea to be teeming with analga
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
called ''Dunaliella
''Dunaliella'' is a single-celled, photosynthetic green alga, that is characteristic for its ability to outcompete other organisms and thrive in hypersaline environments. It is mostly a marine organism, though there are a few freshwater species ...
''. ''Dunaliella'' in turn nourished carotenoid-containing (red-pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compou ...
ed) halobacteria
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of ...
, whose presence caused the color change. Since 1980, the Dead Sea basin has been dry and the algae and the bacteria have not returned in measurable numbers.
In 2011 a group of scientists from Be'er Sheva, Israel and Germany discovered fissures in the floor of the Dead Sea by scuba diving and observing the surface. These fissures allow fresh and brackish water to enter the Dead Sea. They sampled biofilms surrounding the fissures and discovered numerous species of bacteria and archaea.
Fauna and flora around the lake
Many animal species live in the mountains surrounding the Dead Sea. Hikers can seeibex
An ibex (plural ibex, ibexes or ibices) is any of several species of wild goat (genus ''Capra''), distinguished by the male's large recurved horns, which are transversely ridged in front. Ibex are found in Eurasia, North Africa and East Africa ...
, hares, hyraxes, jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed ...
s, foxes, and even leopards. Hundreds of bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
species inhabit the zone as well. Both Jordan and Israel have established nature reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or ...
s around the Dead Sea.
History
The delta of the Jordan River was formerly ajungle
A jungle is land covered with dense forest and tangled vegetation, usually in tropical climates. Application of the term has varied greatly during the past recent century.
Etymology
The word ''jungle'' originates from the Sanskrit word ''ja� ...
of papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a ...
and palm tree
The Arecaceae is a family of perennial flowering plants in the monocot order Arecales. Their growth form can be climbers, shrubs, tree-like and stemless plants, all commonly known as palms. Those having a tree-like form are called palm ...
s. The Jewish historian Flavius Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
described Jericho as "the most fertile spot in Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous sou ...
". In Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
times, sugarcane, henna, and sycamore fig
''Ficus sycomorus'', called the sycamore fig or the fig-mulberry (because the leaves resemble those of the mulberry), sycamore, or sycomore, is a fig species that has been cultivated since ancient times.
The term '' sycamore'' spelled with an A ...
all made the lower Jordan valley wealthy. One of the most valuable products produced by Jericho was the sap
Sap is a fluid transported in xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a separ ...
of the balsam
Balsam is the resinous exudate (or sap) which forms on certain kinds of trees and shrubs. Balsam (from Latin balsamum "gum of the balsam tree", ultimately from Semitic, Aramaic ''busma'', Arabic ''balsam'' and Hebrew ''basam'', "spice", "perfume ...
tree, which could be made into perfume
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. Th ...
. By the 19th century, Jericho's fertility had disappeared.
Human settlement
There are several small communities near the Dead Sea. These includeEin Gedi
Ein Gedi ( he, עֵין גֶּדִי, ), also spelled En Gedi, meaning "spring of the goat, kid", is an oasis, an Archaeological site, archeological site and a nature reserve in Israel, located west of the Dead Sea, near Masada and the Qu ...
, Neve Zohar
Neve Zohar ( he, נְוֵה זֹהַר) is a community settlement in southern Israel. Located on the junction of Highway 31 and Highway 90 (Zohar Junction), on the shores of the Dead Sea and 23 km from Arad by road, it falls under the jurisd ...
and the Israeli settlements in the Megilot Regional Council
Megilot Regional Council ( he, מועצה אזורית מגילות, ''Mo'atza Azorit Megilot''), also Megilot Dead Sea Regional Council, is a regional council in the Judean Desert of the West Bank, near the western shores of the Dead Sea. It cov ...
: Kalya
Kalya ( he, קַלְיָה) is an Israeli settlement organized as a kibbutz in the West Bank. It was originally established in 1929 but was occupied and destroyed by the Jordanians in 1948; it was later rebuilt in 1968 after the Six-Day War. L ...
, Mitzpe Shalem
Mitzpe Shalem ( he, מִצְפֵּה שָׁלֵם, , Shalem Lookout) is an Israeli settlement and former kibbutz in the eastern West Bank. Located near Highway 90 about north of Ein Gedi and north of the Green Line about 1 km from the wes ...
and Avnat. There is a nature preserve at Ein Gedi, and several Dead Sea hotels are located on the southwest end at Ein Bokek
Ein Bokek ( he, עֵין בּוֹקֵק) is a hotel and resort district on the Israeli shore of the Dead Sea, near Neve Zohar. It is under the jurisdiction of the Tamar Regional Council.
History
Archaeological findings at Ein Bokek include th ...
near Neve Zohar. Highway 90 runs north–south on the Israeli side for a total distance of from Metula
Metula ( he, מְטֻלָּה) is a town in the Northern District of Israel. Metula is located next to the northern border with Lebanon. In it had a population of . Metula is the northernmost town in Israel.
History Bronze and Iron Age
Metu ...
on the Lebanese border in the north to its southern terminus at the Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
ian border near the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
port of Eilat.
Potash City is a small community on the Jordanian side of the Dead Sea, and others including Suweima. Highway 65 runs north–south on the Jordanian side from near Jordan's northern tip down past the Dead Sea to the port of Aqaba
Aqaba (, also ; ar, العقبة, al-ʿAqaba, al-ʿAgaba, ) is the only coastal city in Jordan and the largest and most populous city on the Gulf of Aqaba. Situated in southernmost Jordan, Aqaba is the administrative centre of the Aqaba Govern ...
.
Human history
Biblical period
 Dwelling in caves near the Dead Sea is recorded in the
Dwelling in caves near the Dead Sea is recorded in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Israelites The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan. The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
came to '' Israelites The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan. The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
, and extensively at the time of King David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
.
Just northwest of the Dead Sea is Jericho. Somewhere, perhaps on the southeastern shore, would be the cities mentioned in the Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
which were said to have been destroyed in the time of Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
: Sodom and Gomorrah (Genesis 18) and the three other "Cities of the Plain", Admah, Zeboim and Zoar (Deuteronomy 29:23). Zoar escaped destruction when Abraham's nephew Lot escaped to Zoar from Sodom (Genesis 19:21–22). Before the destruction, the Dead Sea was a valley full of natural tar pit
Tar pits, sometimes referred to as asphalt pits, are large asphalt deposits. They form in the presence of oil, which is created when decayed organic matter is subjected to pressure underground. If this crude oil seeps upward via fractures, co ...
s, which was called the vale of Siddim. King David was said to have hidden from Saul
Saul (; he, , ; , ; ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the first monarch of the United Kingdom of Israel. His reign, traditionally placed in the late 11th century BCE, supposedly marked the transition of Israel and Judah from a scattered t ...
at Ein Gedi nearby.
In Ezekiel 47:8–9 there is a specific prophecy that the sea will "be healed and made fresh", becoming a normal lake capable of supporting marine life. A similar prophecy is stated in Zechariah 14:8, which says that "living waters will go out from Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, half of them to the eastern sea ikely the Dead Seaand half to the western sea Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
]."
Greek and Roman period
Aristotle wrote about the remarkable waters. The Nabataeans, Nabateans and others discovered the value of the globs of naturalasphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
that constantly floated to the surface where they could be harvested with nets. The Egyptians were steady customers, as they used asphalt in the embalming
Embalming is the art and science of preserving human remains by treating them (in its modern form with chemicals) to forestall decomposition. This is usually done to make the deceased suitable for public or private viewing as part of the funeral ...
process that created mummies
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
. The Ancient Romans
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 ...
knew the Dead Sea as "''Palus Asphaltites''" (Asphalt Lake).
 The Dead Sea was an important trade route with ships carrying salt, asphalt and agricultural produce. Multiple anchorages existed on both sides of the sea, including in
The Dead Sea was an important trade route with ships carrying salt, asphalt and agricultural produce. Multiple anchorages existed on both sides of the sea, including in Ein Gedi
Ein Gedi ( he, עֵין גֶּדִי, ), also spelled En Gedi, meaning "spring of the goat, kid", is an oasis, an Archaeological site, archeological site and a nature reserve in Israel, located west of the Dead Sea, near Masada and the Qu ...
, Khirbet Mazin (where the ruins of a Hasmonean-era dry dock are located), Numeira
Numeira (also an-Numayra) is an archaeological site in Jordan near the southern Dead Sea. The site has substantial Early Bronze Age remains.
The site is 280 m below sea level, on the shore of the Dead Sea.
Numeira is also the name given to ...
and near Masada
Masada ( he, מְצָדָה ', "fortress") is an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel situated on top of an isolated rock plateau, akin to a mesa. It is located on the eastern edge of the Judaean Desert, overlooking the D ...
.
King Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renova ...
built or rebuilt several fortresses and palaces on the western bank of the Dead Sea. The most famous was Masada
Masada ( he, מְצָדָה ', "fortress") is an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel situated on top of an isolated rock plateau, akin to a mesa. It is located on the eastern edge of the Judaean Desert, overlooking the D ...
, where in 70 CE a small group of Jewish zealots
The Zealots were a political movement in 1st-century Second Temple Judaism which sought to incite the people of Judea Province to rebel against the Roman Empire and expel it from the Holy Land by force of arms, most notably during the First Jew ...
fled after the fall of the destruction of the Second Temple. The zealots survived until 73 CE, when a siege by the X Legion ended in the deaths by suicide of its 960 inhabitants. Another historically important fortress was Machaerus
Machaerus (Μαχαιροῦς, from grc, μάχαιρα, , makhaira sword he, מכוור; ar, قلعة مكاور, translit=Qala'at Mukawir, lit=Mukawir Castle) was a Hasmonean hilltop palace and desert fortress, now in ruins, located in ...
(מכוור), on the eastern bank, where, according to Josephus, John the Baptist
John the Baptist or , , or , ;Wetterau, Bruce. ''World history''. New York: Henry Holt and Company. 1994. syc, ܝܘܿܚܲܢܵܢ ܡܲܥܡܕ݂ܵܢܵܐ, Yoḥanān Maʿmḏānā; he, יוחנן המטביל, Yohanān HaMatbil; la, Ioannes Bapti ...
was imprisoned by Herod Antipas and died.
Also in Roman times, some Essenes
The Essenes (; Hebrew: , ''Isiyim''; Greek: Ἐσσηνοί, Ἐσσαῖοι, or Ὀσσαῖοι, ''Essenoi, Essaioi, Ossaioi'') were a mystic Jewish sect during the Second Temple period that flourished from the 2nd century BCE to the 1st ce ...
settled on the Dead Sea's western shore; Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
identifies their location with the words, "on the west side of the Dead Sea, away from the coast ... bove Bove is a surname. Notable people with the name include:
* Carol Bove (born 1971), American artist
* Davide Bove (born 1998), Italian footballer
* Edward Bove, American surgeon
* Linda Bove (born 1945), deaf American actress
* Raphael Bove
Ra ...
the town of Engeda" (''Natural History'', Bk 5.73); and it is therefore a hugely popular but contested hypothesis today, that same Essenes are identical with the settlers at Qumran
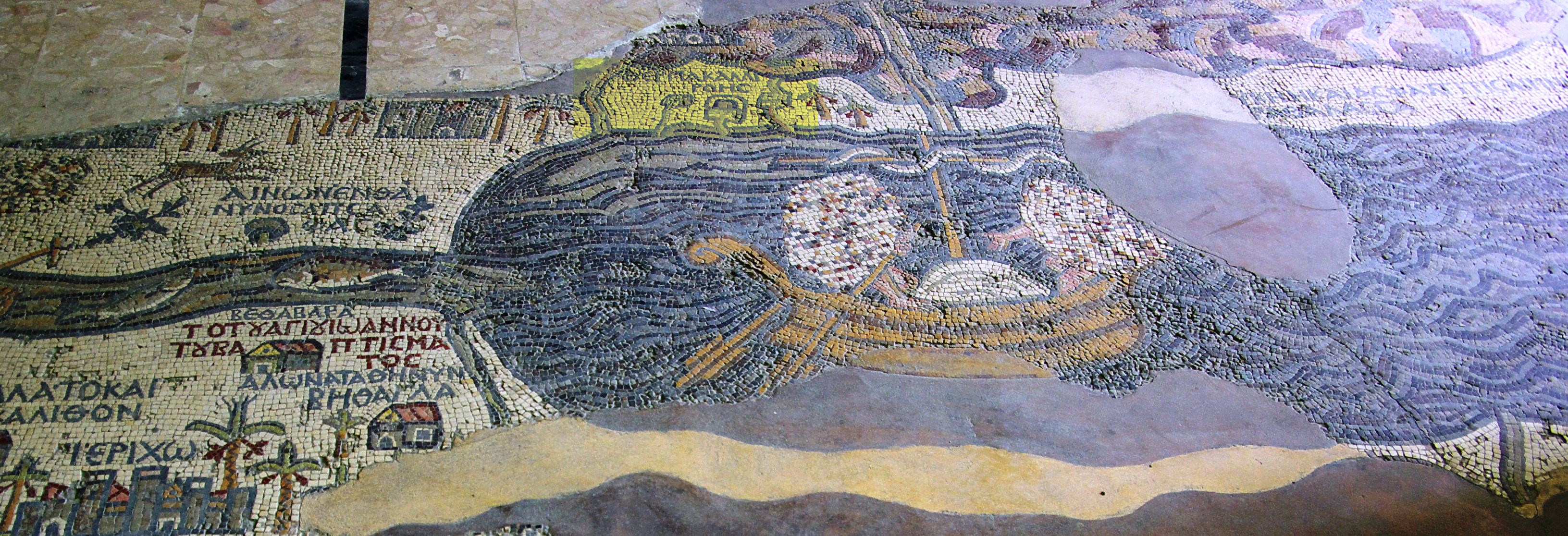
Qumran ( he, קומראן; ar, خربة قمران ') is an archaeological site in the West Bank managed by Israel's Qumran National Park. It is located on a dry marl plateau about from the northwestern shore of the Dead Sea, near the Israeli ...
and that "the Dead Sea Scrolls
The Dead Sea Scrolls (also the Qumran Caves Scrolls) are ancient Jewish and Hebrew religious manuscripts discovered between 1946 and 1956 at the Qumran Caves in what was then Mandatory Palestine, near Ein Feshkha in the West Bank, on the ...
" discovered during the 20th century in the nearby caves had been their own library.
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
identified the Dead Sea in geographic proximity to the ancient Biblical city of Sodom. However, he referred to the lake by its Greek name, Asphaltites.
Various sects of Jews settled in caves overlooking the Dead Sea. The best known of these are the Essenes
The Essenes (; Hebrew: , ''Isiyim''; Greek: Ἐσσηνοί, Ἐσσαῖοι, or Ὀσσαῖοι, ''Essenoi, Essaioi, Ossaioi'') were a mystic Jewish sect during the Second Temple period that flourished from the 2nd century BCE to the 1st ce ...
of Qumran
Qumran ( he, קומראן; ar, خربة قمران ') is an archaeological site in the West Bank managed by Israel's Qumran National Park. It is located on a dry marl plateau about from the northwestern shore of the Dead Sea, near the Israeli ...
, who left an extensive library known as the Dead Sea Scrolls
The Dead Sea Scrolls (also the Qumran Caves Scrolls) are ancient Jewish and Hebrew religious manuscripts discovered between 1946 and 1956 at the Qumran Caves in what was then Mandatory Palestine, near Ein Feshkha in the West Bank, on the ...
. The town of Ein Gedi
Ein Gedi ( he, עֵין גֶּדִי, ), also spelled En Gedi, meaning "spring of the goat, kid", is an oasis, an Archaeological site, archeological site and a nature reserve in Israel, located west of the Dead Sea, near Masada and the Qu ...
, mentioned many times in the Mishna
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah ...
, produced persimmon
The persimmon is the edible fruit of a number of species of trees in the genus '' Diospyros''. The most widely cultivated of these is the Oriental persimmon, ''Diospyros kaki'' ''Diospyros'' is in the family Ebenaceae, and a number of non-per ...
for the temple's fragrance and for export, using a secret recipe. "Sodomite salt" was an essential mineral for the temple's holy incense, but was said to be dangerous for home use and could cause blindness. The Roman camps surrounding Masada
Masada ( he, מְצָדָה ', "fortress") is an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel situated on top of an isolated rock plateau, akin to a mesa. It is located on the eastern edge of the Judaean Desert, overlooking the D ...
were built by Jewish slaves receiving water from the towns around the lake. These towns had drinking water from the Ein Feshcha springs and other sweetwater springs in the vicinity.
Byzantine period
Intimately connected with the Judean wilderness to its northwest and west, the Dead Sea was a place of escape and refuge. The remoteness of the region attractedGreek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
s since the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
era. Their monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
, such as Saint George
Saint George (Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
in Wadi Kelt and Mar Saba in the Judaean Desert
The Judaean Desert or Judean Desert ( he, מִדְבַּר יְהוּדָה, Midbar Yehuda}, both ''Desert of Judah'' or ''Judaean Desert''; ar, صحراء يهودا, Sahraa' Yahuda) is a desert in Palestine and Israel that lies east of Jerusa ...
, are places of pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
.
Modern times
In the 19th century the River Jordan and the Dead Sea were explored by boat primarily by Christopher Costigan in 1835, Thomas Howard Molyneux in 1847,William Francis Lynch
Captain William Francis Lynch (1 April 1801 – 17 October 1865) was a naval officer who served first in the United States Navy and later in the Confederate States Navy.
Personal life
William F. Lynch was born in Virginia. On 2 June 1828, on ...
in 1848, and John MacGregor in 1869. The full text of W. F. Lynch's 1949 book '' Narrative of the United States' Expedition to the River Jordan and the Dead Sea'' is available online. Charles Leonard Irby and James Mangles travelled along the shores of the Dead Sea already in 1817–18, but didn't navigate on its waters.
 Explorers and scientists arrived in the area to analyze the minerals and research the unique climate.
After the find of the " Moabite Stone" in 1868 on the plateau east of the Dead Sea, Moses Wilhelm Shapira and his partner Salim al-Khouri forged and sold a whole range of presumed "Moabite" antiquities, and in 1883 Shapira presented what is now known as the "Shapira Strips", a supposedly ancient scroll written on leather strips which he claimed had been found near the Dead Sea. The strips were declared to be forgeries and Shapira took his own life in disgrace.
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, hundreds of religious documents dated between 150 BCE and 70 CE were found in caves near the ancient settlement of
Explorers and scientists arrived in the area to analyze the minerals and research the unique climate.
After the find of the " Moabite Stone" in 1868 on the plateau east of the Dead Sea, Moses Wilhelm Shapira and his partner Salim al-Khouri forged and sold a whole range of presumed "Moabite" antiquities, and in 1883 Shapira presented what is now known as the "Shapira Strips", a supposedly ancient scroll written on leather strips which he claimed had been found near the Dead Sea. The strips were declared to be forgeries and Shapira took his own life in disgrace.
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, hundreds of religious documents dated between 150 BCE and 70 CE were found in caves near the ancient settlement of Qumran
Qumran ( he, קומראן; ar, خربة قمران ') is an archaeological site in the West Bank managed by Israel's Qumran National Park. It is located on a dry marl plateau about from the northwestern shore of the Dead Sea, near the Israeli ...
, about inland from the northwestern shore of the Dead Sea (presently in the West Bank). They became known and famous as the Dead Sea Scrolls
The Dead Sea Scrolls (also the Qumran Caves Scrolls) are ancient Jewish and Hebrew religious manuscripts discovered between 1946 and 1956 at the Qumran Caves in what was then Mandatory Palestine, near Ein Feshkha in the West Bank, on the ...
.
The world's lowest roads, Highway 90, run along the Israeli and West Bank shores of the Dead Sea, along with Highway 65 on the Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
ian side, at below sea level.
Tourism and leisure

British Mandate period
Agolf course
A golf course is the grounds on which the sport of golf is played. It consists of a series of holes, each consisting of a tee box, a fairway, the rough and other hazards, and a green with a cylindrical hole in the ground, known as a "cup". ...
named for Sodom and Gomorrah was built by the British at Kalia on the northern shore.
Israel
The first major Israeli hotels were built in nearby Arad, and since the 1960s at theEin Bokek
Ein Bokek ( he, עֵין בּוֹקֵק) is a hotel and resort district on the Israeli shore of the Dead Sea, near Neve Zohar. It is under the jurisdiction of the Tamar Regional Council.
History
Archaeological findings at Ein Bokek include th ...
resort complex.
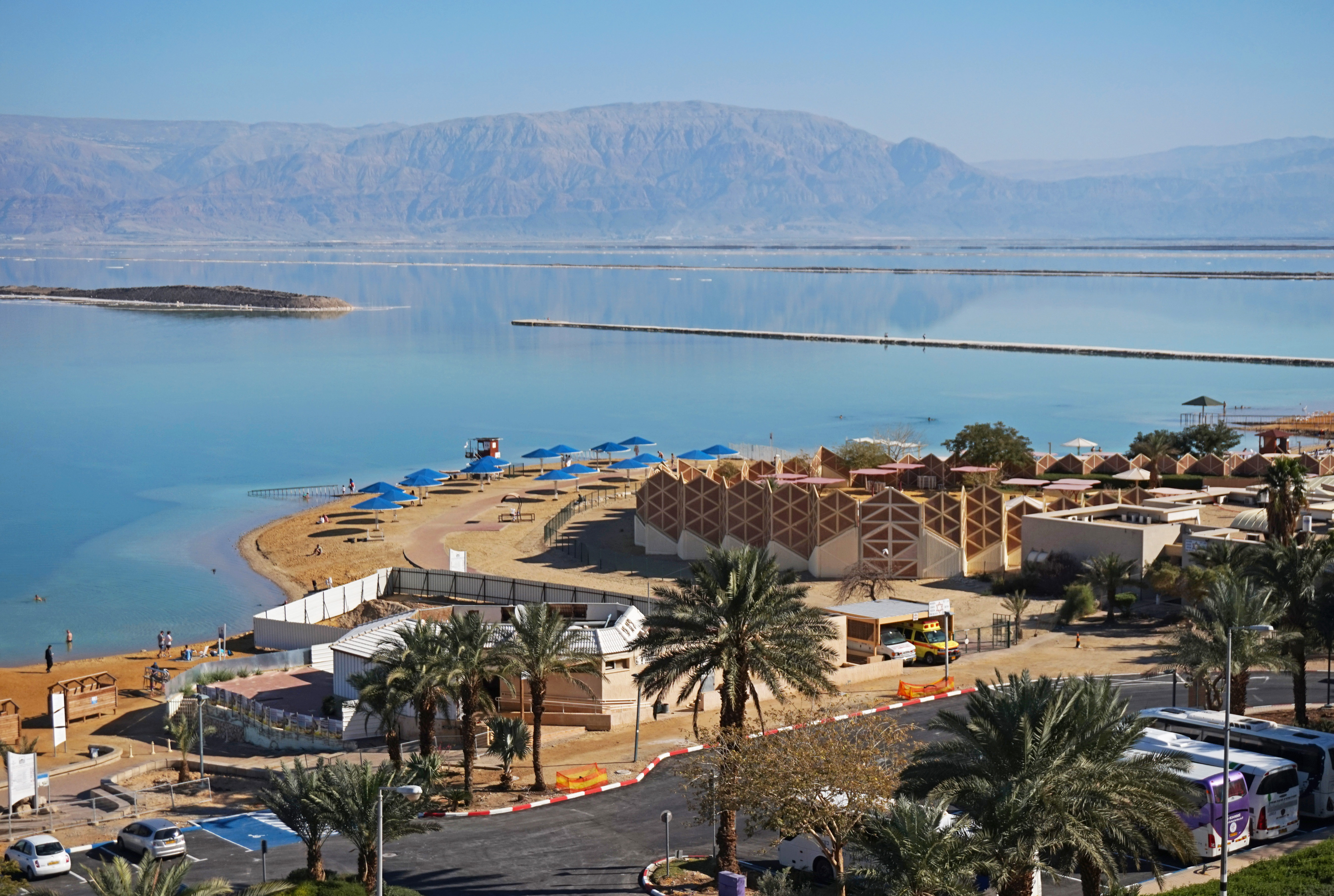
Israel has 15 hotels along the Dead Sea shore, generating total revenues of $291 million in 2012. Most Israeli hotels and resorts on the Dead Sea are on a stretch of the southern shore.
Jordan
 On the Jordanian side, nine international franchises have opened
On the Jordanian side, nine international franchises have opened seaside resort
A seaside resort is a town, village, or hotel that serves as a vacation resort and is located on a coast. Sometimes the concept includes an aspect of official accreditation based on the satisfaction of certain requirements, such as in the Germ ...
hotels near the King Hussein Bin Talal Convention Center, along with resort apartments, on the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The 9 hotels have boosted the Jordanian side's capacity to 2,800 rooms.
On November 22, 2015, the Dead Sea panorama road was included along with 40 archaeological locations in Jordan, to become live on Google Street View
Google Street View is a technology featured in Google Maps and Google Earth that provides interactive panoramas from positions along many streets in the world. It was launched in 2007 in several cities in the United States, and has since expan ...
.
West Bank
The portion of Dead Sea coast which Palestinians could possibly eventually manage is about long. The World Bank estimates that such Dead Sea tourism industry could generate $290 million of revenues per year and 2,900 jobs. However, Palestinians have been unable to obtain construction permits for tourism-related investments on the Dead Sea. According to the World Bank, officials in the Palestinian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities state that the only way to apply for such permits is through the Joint Committees established under the Oslo Agreement, but the relevant committee has not met with any degree of regularity since 2000.Chemical industry

British Mandate period
In the early part of the 20th century, the Dead Sea began to attract interest from chemists who deduced the sea was a natural deposit ofpotash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
(potassium chloride) and bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
. A concession was granted by the British Mandatory government to the newly formed Palestine Potash Company in 1929. Its founder, Siberian Jewish engineer and pioneer of Lake Baikal exploitation, Moses Novomeysky, had worked for the charter for over ten years having first visited the area in 1911. The first plant, on the north shore of the Dead Sea at Kalya
Kalya ( he, קַלְיָה) is an Israeli settlement organized as a kibbutz in the West Bank. It was originally established in 1929 but was occupied and destroyed by the Jordanians in 1948; it was later rebuilt in 1968 after the Six-Day War. L ...
, commenced production in 1931 and produced potash by solar evaporation of the brine. Employing Arabs and Jews, it was an island of peace in turbulent times. The company quickly grew into the largest industrial site in the Middle East, and in 1934 built a second plant on the southwest shore, in the Mount Sodom
Mount Sodom ( he, הר סדום, ''Har Sedom'') is a hill along the southwestern part of the Dead Sea in Israel; it is part of the Judaean Desert Nature Reserve. It takes its name from the legendary city of Sodom, whose destruction is the subje ...
area, south of the 'Lashon' region of the Dead Sea. Palestine Potash Company supplied half of Britain's potash during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Both plants were destroyed by the Jordanians in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War.
Israel
TheDead Sea Works
The Dead Sea Works ( he, מפעלי ים המלח, ''Mif'alei Yam HaMelakh'') is an Israeli potash plant in Sdom, on the Dead Sea coast of Israel.
History
Under the British administration, concessions from the Mandatory government were given ...
was founded in 1952 as a state-owned enterprise based on the remnants of the Palestine Potash Company. In 1995, the company was privatized and it is now owned by Israel Chemicals
ICL Group Ltd. (Hebrew: איי.סי. אל. גרופ בע"מ) (formerly Israel Chemicals Ltd., ICL) is a multi-national manufacturing concern that develops, produces and markets fertilizers, metals and other special-purpose chemical products. I ...
. From the Dead Sea brine, Israel produces (2001) 1.77 million ton
Ton is the name of any one of several units of measure. It has a long history and has acquired several meanings and uses.
Mainly it describes units of weight. Confusion can arise because ''ton'' can mean
* the long ton, which is 2,240 pounds
...
s potash, 206,000 tons elemental bromine, 44,900 tons caustic soda
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and alkali ...
, 25,000 tons magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
metal, and sodium chloride. Israeli companies generate around US$3 billion annually from the sale of Dead Sea minerals (primarily potash and bromine), and from other products that are derived from Dead Sea Minerals.World Bank, Poverty Reduction and Economic Management DepartmentArea C and the Future of the Palestinian Economy
October 2, 2013
Jordan
On the Jordanian side of the Dead Sea, Arab Potash (APC), formed in 1956, produces 2.0 million tons of potash annually, as well as sodium chloride and bromine. The plant is located at Safi, South Aghwar Department, in theKarak Governorate
Karak ( ar, الكرك) is one of the governorates of Jordan, located south-west of Amman, Jordan's capital. Its capital is Al-Karak. It s bordered by Madaba and the Capital governorates to the north, Ma'an Governorate to the east, Tafilah Governor ...
.
Jordanian Dead Sea mineral industries generate about $1.2 billion in sales (equivalent to 4 percent of Jordan's GDP).
West Bank
The Palestinian Dead Sea Coast is about long. The Palestinian economy is unable to benefit from Dead Sea chemicals due to restricted access, permit issues and the uncertainties of the investment climate. The World Bank estimates that a Palestinian Dead Sea chemicals industry could generate $918M incremental value added per year, "almost equivalent to the contribution of the entire manufacturing sector of Palestinian territories today".Extraction
Both companies, Dead Sea Works Ltd. and Arab Potash, use extensive salt evaporation pans that have essentially diked the entire southern end of the Dead Sea for the purpose of producingcarnallite
Carnallite (also carnalite) is an evaporite mineral, a hydrated potassium magnesium chloride with formula KMgCl3·6(H2O). It is variably colored yellow to white, reddish, and sometimes colorless or blue. It is usually massive to fibrous with rare ...
, potassium magnesium chloride, which is then processed further to produce potassium chloride. The ponds
A pond is an area filled with water, either natural or artificial, that is smaller than a lake. Defining them to be less than in area, less than deep, and with less than 30% emergent vegetation helps in distinguishing their ecology from t ...
are separated by a central dike that runs roughly north–south along the international border. The power plant
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an el ...
on the Israeli side allows production of magnesium metal (by a subsidiary, Dead Sea Magnesium Ltd.).
Due to the popularity of the sea's therapeutic and healing properties, several companies have also shown interest in the manufacturing and supplying of Dead Sea salts as raw materials for body and skin care products.
Recession and environmental concerns
Receding shoreline
Since 1930, when its surface was and its level was below sea level, the Dead Sea has been monitored continuously. The Dead Sea has been rapidly shrinking since the 1960s because of diversion of incoming water from the Jordan River to the north as part of theNational Water Carrier
National Water Carrier of Israel
The National Water Carrier of Israel ( he, המוביל הארצי, ''HaMovil HaArtzi'') is the largest water project in Israel, completed in 1964. Its main purpose is to transfer water from the Sea of Galilee ...
scheme, completed in 1964. The southern end is fed by a canal maintained by the Dead Sea Works
The Dead Sea Works ( he, מפעלי ים המלח, ''Mif'alei Yam HaMelakh'') is an Israeli potash plant in Sdom, on the Dead Sea coast of Israel.
History
Under the British administration, concessions from the Mandatory government were given ...
, a company that converts the sea's raw materials. From a water surface of below sea level in 1970 it fell to below sea level in 2006, reaching a drop rate of per year. As the water level decreases, the characteristics of the Sea and surrounding region may substantially change.
The Dead Sea level drop has been followed by a groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated ...
level drop, causing brines that used to occupy underground layers near the shoreline to be flushed out by freshwater. This is believed to be the cause of the recent appearance of large sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
s along the western shore—incoming freshwater dissolves salt layers, rapidly creating subsurface cavities that subsequently collapse to form these sinkholes. Ein Gedi
Ein Gedi ( he, עֵין גֶּדִי, ), also spelled En Gedi, meaning "spring of the goat, kid", is an oasis, an Archaeological site, archeological site and a nature reserve in Israel, located west of the Dead Sea, near Masada and the Qu ...
, on the western coast, has been subject to a large number of sinkholes appearing in the area, attributed to the decline in the water level of the Dead Sea.
, the surface of the Sea has shrunk by about 33 percent since the 1960s, which is partly attributed to the much-reduced flow of the Jordan River since the construction of the National Water Carrier project, and the amount of water from the rains reaching the Dead Sea has diminished even further since flash floods started pouring into the sinkholes. The EcoPeace Middle East, a joint Israeli-Palestinian-Jordanian environmental group, has estimated that the annual flow into the Dead Sea from the Jordan is less than of water, compared with former flows of between and .
Sources: Israel Oceanographic and Limnological Research, '' Haaretz'', Jordan Valley Authority.

Link to the Red Sea
 In May 2009 at the
In May 2009 at the World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an international non-governmental and lobbying organisation based in Cologny, canton of Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded on 24 January 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab. The foundation, ...
, Jordan introduced plans for a " Jordan National Red Sea Development Project" (JRSP). This is a plan to convey seawater from the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
near Aqaba to the Dead Sea. Water would be desalinated along the route to provide fresh water to Jordan, with the brine discharge sent to the Dead Sea for replenishment. Israel has expressed its support and will likely benefit from some of the water delivery to its Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its sout ...
region.Jordan Red Sea Project: OriginalJordan Red Sea Project Description
retrieved on May 11, 2011 At a regional conference in July 2009, officials expressed concern about the declining water levels. Some suggested industrial activities around the Dead Sea might need to be reduced. Others advised environmental measures to restore conditions such as increasing the volume of flow from the Jordan River to replenish the Dead Sea. Currently, only sewage and effluent from fish ponds run in the river's channel. Experts also stressed the need for strict conservation efforts. They said agriculture should not be expanded, sustainable support capabilities should be incorporated into the area and pollution sources should be reduced. In October 2009, the Jordanians accelerated plans to extract around of water per year from the Red Sea, desalinate it for use as fresh water and send the waste water to the Dead Sea by tunnel, despite concerns about inadequate time to assess the potential environmental impact. According to Jordan's minister for water, General Maysoun Zu'bi, this project could be considered as the first phase of the Red Sea–Dead Sea Water Conveyance. In December 2013, Israel, Jordan and the Palestinian Authority signed an agreement for laying a water pipeline to link the Red Sea with the Dead Sea. The pipeline would be long and is estimated to take up to five years to complete. In January 2015 it was reported that the level of water was dropping by a year. On 27 November 2016, the Jordanian government shortlisted five consortia to implement the project. Jordan's ministry of Water and Irrigation said that the $100 million first phase of the project would begin construction in the first quarter of 2018, and would be completed by 2021. The project was officially abandoned in June 2021, having never broken ground.
See also
* Aral Sea *List of drying lakes
A number of natural lakes throughout the world are drying or completely dry due to irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, a ...
*List of places on land with elevations below sea level
This is a list of places on land below mean sea level.
Places artificially created such as tunnels, mines, basements, and dug holes, or places under water, or existing temporarily as a result of ebbing of sea tide etc., are not included. Places ...
* Mediterranean–Dead Sea Canal
* Benjamin Elazari Volcani
*PEF rock
Ein Feshkha ( ar, عين فشخة, also Ain Al-Fashka) or Einot Tzukim ( he, עינות צוקים, lit=cliff springs) is a 2,500 ha nature reserve and archaeological site on the north-western shore of the Dead Sea, about 3 km south of ...
with the Dead Sea level reference line used between 1900 and 1913
References
Further reading
*The World Bank, 2013"The Red Sea - Dead Sea Water Conveyance Study Program"
and source of basic data on the Dead Sea. *Yehouda Enzel, et al., eds (2006) ''New Frontiers in Dead Sea Paleoenvironmental Research'', Geological Society of America, *Niemi, Tina M., Ben-Avraham, Z., and Gat, J., eds., 1997, The Dead Sea: The Lake and Its Setting: N.Y.,
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
, 286 p.
* World Bank, Poverty Reduction and Economic Management DepartmentArea C and the Future of the Palestinian Economy
October 2, 2013
External links
* * ( Israeli and West Bank part and Jordanian part) * {{Authority control Endorheic lakes of Asia Extreme points of Earth Lowest points Bodies of water of Jordan Lakes of Israel Catholic pilgrimage sites Sacred lakes Shrunken lakes Hebrew Bible geography Lakes of the West Bank Saline lakes of Asia Israel–Jordan border Borders of the West Bank International lakes of Asia Articles containing video clips