Dutch-Americans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dutch Americans () are

 The earliest Dutch settlement was built around 1613; it consisted of a number of small huts built by the crew of the ''Tijger'' (''Tiger''), a Dutch ship under the command of Captain
The earliest Dutch settlement was built around 1613; it consisted of a number of small huts built by the crew of the ''Tijger'' (''Tiger''), a Dutch ship under the command of Captain
 In the hundred years of British rule that followed the change of ownership of New Netherland, Dutch immigration to America came to an almost complete standstill.
While the Netherlands was a small country, the Dutch Empire was quite large so emigrants leaving the mother country had a wide variety of choices. New Amsterdam was not high on their list, especially because of the Native American risk. The major Dutch cities were centers of high culture, but they still sent immigrants. Most new arrivals were farmers from remote villages who, on arrival, in America scattered into widely separated villages with little contact with one another. Even inside a settlement, different Dutch groups had minimal interaction. With very few new arrivals, the result was an increasingly traditional system cut off from the forces for change. The people maintained their popular culture, revolving around their language and their Calvinist religion. The Dutch brought along their own folklore, most famously ''
In the hundred years of British rule that followed the change of ownership of New Netherland, Dutch immigration to America came to an almost complete standstill.
While the Netherlands was a small country, the Dutch Empire was quite large so emigrants leaving the mother country had a wide variety of choices. New Amsterdam was not high on their list, especially because of the Native American risk. The major Dutch cities were centers of high culture, but they still sent immigrants. Most new arrivals were farmers from remote villages who, on arrival, in America scattered into widely separated villages with little contact with one another. Even inside a settlement, different Dutch groups had minimal interaction. With very few new arrivals, the result was an increasingly traditional system cut off from the forces for change. The people maintained their popular culture, revolving around their language and their Calvinist religion. The Dutch brought along their own folklore, most famously ''
 *
*
 Many of the Dutch heritage festivals that take place around the United States coincide with the blooming of tulips in a particular region. The Tulip Time Festival in Holland, Michigan is the largest such festival with other notable gatherings such as the Pella Tulip Time in Pella, Iowa
Many of the Dutch heritage festivals that take place around the United States coincide with the blooming of tulips in a particular region. The Tulip Time Festival in Holland, Michigan is the largest such festival with other notable gatherings such as the Pella Tulip Time in Pella, Iowa
Tulip Festival
in Orange City, Iowa and Albany, New York; Dutch Days in Fulton, Illinois; Let's Go Dutch Days in Baldwin, Wisconsin; Holland Days in Lynden, Washington; Holland Happening in Oak Harbor, Washington; Holland Fest in Cedar Grove, Wisconsin, and the Wooden Shoe Tulip Fest in Woodburn, Oregon. Often Dutch heritage festivals coincide with the blooming of the tulip. See Tulip Festival for additional explanations of some of these festivals. A Dutch Festival is also held at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York; and a Holland Festival in Long Beach, California. A traditional Dutch Kermis Festival is celebrated in October in Little Chute, WI. During late November and early December, a Dutch Winterfest is held in Holland, MI, to coincide with the traditional arrival of
Herbert J. Brinks There is an annual Sinterklass festival held in Rhinebeck, New York, Rhinebeck and Kingston, New York where Sinterklaas crosses the
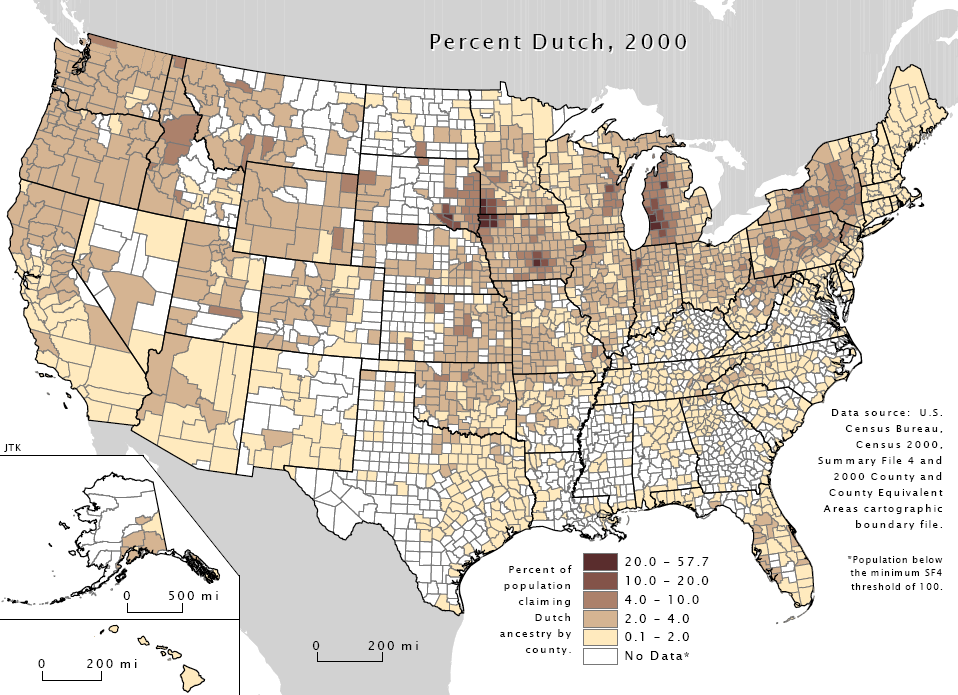 According to the 2000 United States Census, US Census, more than 5 million Americans claimed total or partial
According to the 2000 United States Census, US Census, more than 5 million Americans claimed total or partial
online
*Corwin, S. T. ''History of the Dutch Reformed Church in the United States'' (1895). * De Gerald, F. Jong ''The Dutch in America, 1609-1974''. (Twayne, 1975); short survey * Ganzevoort, Herman, and Mark Boekelman, eds. ''Dutch Immigration to North America''. Toronto: Multicultural History Society of Ontario, 1983. * Goodfriend, Joyce D. Benjamin Schmidt, and Annette Stott, eds. ''Going Dutch: The Dutch Presence in America, 1609-2009'' (2008) * Kirk, Gordon W. ''The Promise of American Life: Social Mobility in a Nineteenth-Century Immigrant Community, Holland, Michigan, 1847-1894.'' Philadelphia: American Philosophical Society, 1978. * Krabbendam, Hans. ''Freedom on the Horizon: Dutch Immigration to America, 1840-1940'' (2009), Emphasis on the Dutch Reformed Church * Kroes, Rob. ''The Persistence of Ethnicity: Dutch Calvinist Pioneers in Amsterdam, Montana.'' University of Illinois Press, 1992. * Kroes, Rob, and Henk-Otto Neuschafer, eds. ''The Dutch in North America: Their Immigration and Cultural Continuity.'' Amsterdam: Free University Press, 1991. * Kromminga, John. ''The Christian Reformed Church: A Study in Orthodoxy.'' Grand Rapids, Mich.: Baker Books, 1949. * Lucas, Henry. ''Netherlanders in America: Dutch Immigration to the United States and Canada, 1789-1950.'' The University of Michigan Press, 1955. * Schreuder, Yda. ''Dutch Catholic Immigrant Settlement in Wisconsin, 1850-1905.'' New York: Garland, 1989. * Swierenga, Robert P. ''The Forerunners: Dutch Jewry in the North American Diaspora.'' Wayne State University Press, 1994. * Swierenga, Robert P. ed. ''The Dutch in America: Immigration, Settlement, and Cultural Change''. Rutgers University Press, 1985. * Swierenga, Robert P., "Faith and Family --Dutch Immigration and Settlement in the United States, 1820–1920" (Ellis Island Series.) New York: Holmes and Meyer. 2000. * Taylor, Lawrence J. ''Dutchmen on the Bay: The Ethnohistory of a Contractual Community.'' The University of Pennsylvania Press, 1983. * Thernstrom, Stephan, ed. ''Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups''. Harvard University Press, 1980. * Van Jacob Hinte. ''Netherlanders in America: A Study of Emigration and Settlement in the Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries in the United States of America.'' Ed. Robert P. Swierenga. Grand Rapids, Mich.: Baker Book House, 1985. translation of a 1928 Dutch-language book *Wabeke, Bertus Harr
''Dutch emigration to North America, 1624-1860''
* Wittke, Carl. ''We Who Built America: The Saga of the Immigrant'' (1939), ch 2, 11
in JSTOR
* Cooke, Jacob Ernest, ed. ''Encyclopedia of the North American colonies'' (3 vol. 1993), highly detailed topical coverage of the Dutch colonists. * Jacobs, Jaap. ''New Netherland: a Dutch colony in seventeenth-century America'' (Brill, 2005
online
* Kenney, Alice P. "Neglected Heritage: Hudson River Valley Dutch Material Culture." ''Winterthur Portfolio'' 20#1 (1985): 49–70
in JSTOR
* Kim, Sung Bok. ''Landlord and Tenant in Colonial New York: Manorial Society, 1664-1775'' (1987) * Leiby; Adrian C. ''The Revolutionary War in the Hackensack Valley: The Jersey Dutch and the Neutral Ground, 1775-1783'' Rutgers University Press. 1962. * Nissenson, S. G. ''The Patroon's Domain'' (1937). * Roeber, A. G. "Dutch colonists cope with English control" in Bernard Bailyn, and Philip D. Morgan, eds. ''Strangers within the realm: cultural margins of the first British Empire'' (1991) pp 222–36. * Scheltema, Gajus and Westerhuijs, Heleen (eds.),''Exploring Historic Dutch New York''. Museum of the City of New York/Dover Publications, New York (2011). *Todt, Kim. "'Women Are as Knowing Therein as the Men': Dutch Women in Early America," in Thomas A. Foster, ed. ''Women in Early America'' (2015) pp 43–6
online
* Van Lieburg, Fred. "Interpreting the Dutch Great Awakening (1749–1755)." ''Church History'' 77#2 (2008): 318–336
in JSTOR
* Wermuth, Thomas S. ''Rip Van Winkle's Neighbors: The Transformation of Rural Society in the Hudson River Valley, 1720-1850'' (2001). * Wermuth, Thomas S. "New York farmers and the market revolution: Economic behavior in the mid-Hudson Valley, 1780-1830." ''Journal of Social History'' (1998): 179–196
in JSTOR
* Wittke, Carl. ''We Who Built America: The Saga of the Immigrant'' (1939), ch 2
* [http://www.focol.org/littlechutehistory/ Little Chute Historical Society, Little Chute, Wisconsin] {{Authority control American people of Dutch descent, Dutch diaspora by country, American European diaspora in the United States
Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Law of the United States, U.S. federal law does not equate nationality with Race (hu ...
of Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
and Flemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
descent whose ancestors came from the Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Bene ...
in the distant past, or from the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
as from 1830 when the Flemish became independent from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed from 1815 to 1839. The United Netherlands was created in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars through the fusion of territories t ...
by creating the Kingdom of Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southe ...
. Dutch settlement in the Americas started in 1613 with New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), fac ...
, which was exchanged with the English for Suriname
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America, also considered as part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a Human Development Index, high level of human development; i ...
at the Treaty of Breda (1667)
The Peace of Breda, or Treaty of Breda was signed in the Dutch city of Breda, on 31 July 1667. It consisted of three separate treaties between England and each of its opponents in the Second Anglo-Dutch War: the Dutch Republic, France, and Denma ...
and renamed New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
. The English split the Dutch colony of New Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
into two pieces and named them New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
and New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
. Further waves of immigration occurred in the 19th and 20th centuries.
According to the 2021 American Community Survey
The American Community Survey (ACS) is an annual demographics survey program conducted by the United States Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the United States census, decennial census ...
, an estimated 3.1 million Americans claim total or partial Dutch heritage, while 884,857 Americans claimed total Dutch heritage. In 2021, 113,634 Dutch Americans were foreign-born (of which 61.5% in Europe). The 2009-2013 survey estimated 141,580 people of 5 years and over to speak Dutch at home, which was equal to 0.0486% of the total population of the United States. In 2021, 95.3% of the total Dutch American population of 5 years and over only spoke English at home.
Prominent (partial) Dutch American political figures include Presidents Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was the eighth president of the United States, serving from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as Attorney General o ...
, Warren G. Harding
Warren Gamaliel Harding (November 2, 1865 – August 2, 1923) was the 29th president of the United States, serving from 1921 until his death in 1923. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he was one of the most ...
, and Theodore Theodore may refer to:
Places
* Theodore, Australian Capital Territory, Australia
* Theodore, Queensland, Australia
* Theodore, Saskatchewan, Canada
* Theodore, Alabama, United States
* Theodore Reservoir, in Saskatchewan
People
* Theodore (gi ...
and Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
and U.S. Senators Philip Schuyler
Philip John Schuyler (; November 20, 1733 - November 18, 1804) was an American general in the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War and a United States Senate, United States Senator from New York (state), New York. He is usually known as ...
, Nicholas Van Dyke, Hamilton Fish
Hamilton Fish (August 3, 1808September 7, 1893) was an American statesman who served as the sixteenth governor of New York from 1849 to 1850, a United States senator from New York from 1851 to 1857, and the 26th U.S. secretary of state from ...
, John C. Ten Eyck, Daniel W. Voorhees
Daniel Wolsey Voorhees (September 26, 1827April 10, 1897) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States Senator from Indiana from 1877 to 1897. He was the leader of the Democratic Party and an anti-war Copperhead during ...
, Arthur Vandenberg
Arthur Hendrick Vandenberg Sr. (March 22, 1884April 18, 1951) was an American politician who served as a United States senator from Michigan from 1928 to 1951. A member of the Republican Party, he participated in the creation of the United Nat ...
, Peter G. Van Winkle
Peter Godwin Van Winkle (September 7, 1808April 15, 1872) was an American lawyer, businessman, and politician. A prominent officer of the Northwestern Virginia Railroad for many years, he became one of the founders of West Virginia and later ...
, Alan Simpson, Fred Thompson
Freddie Dalton Thompson (August 19, 1942 – November 1, 2015) was an American politician, attorney, lobbyist, columnist, actor, and radio personality. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as a Unite ...
, John Hoeven
John Henry Hoeven III ( ; born March 13, 1957) is an American banker and politician serving as the senior U.S. senator from North Dakota, a seat he has held since 2011. A member of the Republican Party, Hoeven served as the 31st governor of N ...
, and Christopher Van Hollen. Two of the Founding Fathers of the United States
The Founding Fathers of the United States, often simply referred to as the Founding Fathers or the Founders, were a group of late-18th-century American Revolution, American revolutionary leaders who United Colonies, united the Thirteen Colon ...
, Egbert Benson
Egbert Benson (June 21, 1746 – August 24, 1833) was an American lawyer, jurist, politician and Founding Father who represented New York State in the Continental Congress, Annapolis Convention, and United States House of Representatives. He ...
and John Jay
John Jay (, 1745 – May 17, 1829) was an American statesman, diplomat, signatory of the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris, and a Founding Father of the United States. He served from 1789 to 1795 as the first chief justice of the United ...
, were also of Dutch descent. Governors John Hickenlooper
John Wright Hickenlooper Jr. ( ; born February 7, 1952) is an American politician, geologist, and businessman serving as the Seniority in the United States Senate, junior United States Senate, United States senator from Colorado since 2021. A mem ...
of Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
, Harold G. Hoffman
Harold Giles Hoffman (February 7, 1896 – June 4, 1954) was an American businessman and Republican Party politician who served as the 41st Governor of New Jersey from 1935 to 1938. His time in office was marked by controversy over his support ...
and Thomas Kean
Thomas Howard Kean ( ; born April 21, 1935) is an American politician, statesman, and academic administrator from the state of New Jersey. A Republican Party (United States), Republican, Kean served two terms as the 48th governor of New Jersey f ...
of New Jersey, William Henry Vanderbilt III
William Henry Vanderbilt III (November 24, 1901April 14, 1981) was an American politician who served as Governor of Rhode Island from 1939 to 1941, and a member of the wealthy and socially prominent Vanderbilt family.
Early life
Vanderbilt was ...
of Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
, George Bell Timmerman Jr. of South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, and Cornelius P. Van Ness of Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Ca ...
were also born to Dutch American families. Today the majority of the Dutch Americans live in Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
, California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, Montana
Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, an ...
, Minnesota
Minnesota ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Upper Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Ontario to the north and east and by the U.S. states of Wisconsin to the east, Iowa to the so ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
, Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
, Colorado, North Dakota
North Dakota ( ) is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota people, Dakota and Sioux peoples. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minneso ...
, South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state, state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Dakota people, Dakota Sioux ...
, Nebraska
Nebraska ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Ka ...
, Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
, Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the s ...
, New York, New Jersey, Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
, Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
, Iowa
Iowa ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the upper Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west; Wisconsin to the northeast, Ill ...
, Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
, West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
, and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
.
Not included among Dutch Americans are the Pennsylvania Dutch
The Pennsylvania Dutch (), also referred to as Pennsylvania Germans, are an ethnic group in Pennsylvania in the United States, Ontario in Canada, and other regions of both nations. They largely originate from the Palatinate (region), Palatina ...
, a group of mainly German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
s who settled in Pennsylvania in the colonial era and whose name is a derivation of the Pennsylvania Dutch endonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
', which means "Pennsylvania Dutch" or "German". Ultimately, the terms Deitsch, Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
, Diets
The Low Countries comprise the coastal Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta region in Western Europe, whose definition usually includes the modern countries of Luxembourg, Belgium, the Netherlands and parts of Northern France. Both Belgium and the ...
and Deutsch
Deutsch ( , ) or Deutsche ( , ) may refer to:
* or : the German language or in particular Standard German, spoken in central European countries and other places
*Old High German language refers to Deutsch as a way to define the primary characteris ...
are all descendants of the Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from ...
word , meaning "popular" or "of the people"; while all Germanic cognates of the term refer to some Germanic people, they more commonly refer to Germans than Netherlanders.
Dutch presence in the present-day territory of the United States
Early exploration
In 1602, the Dutch government chartered theDutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States Ge ...
(''Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie'', VOC). It sent explorers under the command of Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the Northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
, who arrived in 1609 and mapped what is now known as the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
. Their initial goal was to find an alternative route to Asia, but they found good farmland and plenty of wildlife instead.
Oldest Dutch settlement

Adriaen Block
Adriaen Courtsen Block (c. 1567 – 27 April 1627) was a Dutch private trader, privateer, and ship's captain who is best known for exploring the coastal and river valley areas between present-day New Jersey and Massachusetts during four voyages ...
which had caught fire while sailing on the Hudson in the winter of 1613. The ship was lost and Block and his crew established a camp ashore. In the spring, Block and his men did some explorations along the coast of Long Island. Block Island
Block Island is an island of the Outer Lands coastal archipelago in New England, located approximately south of mainland Rhode Island and east of Long Island's Montauk Point. The island is coterminous with the town of New Shoreham, Rhode Isl ...
still bears his name. Finally, they were sighted and rescued by another Dutch ship and the settlement was abandoned.
17th century migration
Dutch trade in the New York area led to the establishment of trade posts as early as 1613. Permanent settlers arrived in 1617 at what is nowAlbany, New York
Albany ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It is located on the west bank of the Hudson River, about south of its confluence with the Mohawk River. Albany is the oldes ...
. New Amsterdam was settled in 1625. In 1629, Dutch officials tried to expand the northern colony through a plan that promised "Liberties and Exemptions" to anyone who would ship fifty colonists to America at his own expense. Anyone who did so would be allowed to buy a stretch of land along the Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
from the Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company () was a Dutch chartered company that was founded in 1621 and went defunct in 1792. Among its founders were Reynier Pauw, Willem Usselincx (1567–1647), and Jessé de Forest (1576–1624). On 3 June 1621, it was gra ...
of about twelve miles, extending as far inland as the owner wanted. The landowners were called patroon
In the United States, a patroon (; from Dutch '' patroon'' ) was a landholder with manorial rights to large tracts of land in the 17th-century Dutch colony of New Netherland on the east coast of North America. Through the Charter of Free ...
s and had complete jurisdiction over their domains as well as extensive trading privileges. They also received these rights in perpetuity. That was a form of feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of struc ...
, which had vanished in the Dutch Republic but was introduced in North America. The Patroonships were not a success; by 1635, the Dutch West India Company had bought back four of the five patroonships originally registered in Amsterdam.
The Native Americans were no longer consulted or offered/asked to sell their lands. The Dutch were confronted with a new phenomenon, Native American raids, since the local tribes had now realized that the Dutch were not simply visitors but people set to settle their land.
The Dutch realized that they had gone with the wrong approach as they offered great privileges to wealthy, not poor, citizens. It was not until 1656 that the Dutch state abandoned its passivity and decided to actively support New Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
. The Dutch state issued a proclamation, which stated that "all mechanics and farmers who can prove their ability to earn a living here shall receive free passage for themselves, their wives and children".
Although the Dutch were in control, only about half the settlers were ethnically Dutch (the other half consisted mainly of Walloons
Walloons ( ; ; ) are a Gallo-Romance languages, Gallo-Romance ethnic group native to Wallonia and the immediate adjacent regions of Flanders, France, Germany, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Walloons primarily speak ''langues d'oïl'' such as B ...
, Germans, and French Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
as well as New England Yankees). Manhattan grew increasingly multicultural. In 1664, the English seized the colony and renamed it New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. The Dutch briefly recaptured the colony in 1673, but during peace talks with the English, they decided to trade it in 1674 for Suriname
Suriname, officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America, also considered as part of the Caribbean and the West Indies. It is a developing country with a Human Development Index, high level of human development; i ...
in South America, which was more profitable.
18th century
 In the hundred years of British rule that followed the change of ownership of New Netherland, Dutch immigration to America came to an almost complete standstill.
While the Netherlands was a small country, the Dutch Empire was quite large so emigrants leaving the mother country had a wide variety of choices. New Amsterdam was not high on their list, especially because of the Native American risk. The major Dutch cities were centers of high culture, but they still sent immigrants. Most new arrivals were farmers from remote villages who, on arrival, in America scattered into widely separated villages with little contact with one another. Even inside a settlement, different Dutch groups had minimal interaction. With very few new arrivals, the result was an increasingly traditional system cut off from the forces for change. The people maintained their popular culture, revolving around their language and their Calvinist religion. The Dutch brought along their own folklore, most famously ''
In the hundred years of British rule that followed the change of ownership of New Netherland, Dutch immigration to America came to an almost complete standstill.
While the Netherlands was a small country, the Dutch Empire was quite large so emigrants leaving the mother country had a wide variety of choices. New Amsterdam was not high on their list, especially because of the Native American risk. The major Dutch cities were centers of high culture, but they still sent immigrants. Most new arrivals were farmers from remote villages who, on arrival, in America scattered into widely separated villages with little contact with one another. Even inside a settlement, different Dutch groups had minimal interaction. With very few new arrivals, the result was an increasingly traditional system cut off from the forces for change. The people maintained their popular culture, revolving around their language and their Calvinist religion. The Dutch brought along their own folklore, most famously ''Sinterklaas
Sinterklaas () or Sint-Nicolaas () is a legendary figure based on Saint Nicholas, patron saint of children. Other Dutch names for the figure include ''De Sint'' ("The Saint"), ''De Goede Sint'' ("The Good Saint") and ''De Goedheiligman'' (derive ...
'' (the foundation of the modern-day Santa Claus
Santa Claus (also known as Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Father Christmas, Kris Kringle or Santa) is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring gifts during the late evening and overnight hours on Chris ...
), and created their own as in ''The Legend of Sleepy Hollow
"The Legend of Sleepy Hollow" is an 1820 short story by American author Washington Irving contained in his collection of 34 essays and short stories titled '' The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon, Gent.'' Irving wrote the story while living in Bi ...
''. They maintained their distinctive clothing, and food preferences and introduced some new foods to America, including beets, endive, spinach, parsley, and cookies.
After the British takeover, the rich Dutch families in Albany and New York City emulated the English elite and purchased English furniture, silverware, crystal, and jewelry. They were proud of their language, which was strongly reinforced by the church, but they were much slower than the Yankees in setting up schools for their children. They finally set up Queens College (now Rutgers University) in New Jersey, but it quickly became anglicized. They never attempted to start newspapers; they published no books and only a handful of religious tracts annually. Pietist leader Theodorus Jacobus Frelinghuysen
Theodorus Jacobus Frelinghuysen (born Theodor Jakob Frelinghaus, – ) was a German-American Dutch Reformed minister, theologian and the progenitor of the Frelinghuysen family in the United States of America. Frelinghuysen is most remember ...
(1691–1747) launched a series of revivals that challenge the mainstream church's emphasis on sacraments. Church buildings increasingly followed English rather than historic Dutch models. Politically, however, there was a strong anti-British sentiment that led most of the Dutch to support the American Revolution. One famous Dutch folk hero was Rip Van Winkle
"Rip Van Winkle" () is a short story by the American author Washington Irving, first published in 1819. It follows a Dutch-American villager in Colonial history of the United States, colonial America named Rip Van Winkle who meets mysterious Du ...
, characterized by being absurdly old-fashioned and out of date, which aimed to instill the establishment of an American culture distinct from British culture. Most farmers focused on providing subsistence for their families; about a third were chiefly oriented to market prices.
Dutch Quakers came to the Philadelphia area in response to the appeal of William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer, religious thinker, and influential Quakers, Quaker who founded the Province of Pennsylvania during the British colonization of the Americas, British colonial era. An advocate of democracy and religi ...
. Penn, himself a Dutch Briton (his mother being from Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , ; ; ) is the second-largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city in the Netherlands after the national capital of Amsterdam. It is in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, part of the North S ...
), had paid three visits to the Netherlands, where he published several pamphlets.
Colonial Dutch American population in 1790
TheCensus Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the U ...
produced estimates of the colonial American population with roots in the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, in collaboration with the American Council of Learned Societies
The American Council of Learned Societies (ACLS) is a private, nonprofit federation of 75 scholarly organizations in the humanities and related social sciences founded in 1919. It is best known for its fellowship competitions which provide a ra ...
, by scholarly classification of the names of all White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
heads of families recorded in the first U.S. census of 1790. The government required accurate estimates of the origins of the colonial stock population as basis for computing National Origins Formula
The National Origins Formula is an umbrella term for a series of quantitative immigration quotas in the United States used from 1921 to 1965, which restricted immigration from the Eastern Hemisphere on the basis of national origin. These restri ...
immigration quotas in the 1920s; for this task scholars estimated the proportion of names in each state determined to be of Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
derivation. The final report estimated about 3.1% of the U.S. population in 1790 was of Dutch origin, heavily concentrated in the Middle Colonies
The Middle Colonies were a subset of the Thirteen Colonies in British America, located between the New England Colonies and the Southern Colonies. Along with the Chesapeake Colonies, this area now roughly makes up the Mid-Atlantic states.
Muc ...
of historic New Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
which became the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
American Colonial
American colonial architecture includes several building design styles associated with the colonial period of the United States, including First Period English (late-medieval), Spanish Colonial, French Colonial, Dutch Colonial, and Georgian. ...
Province of New York
The Province of New York was a British proprietary colony and later a royal colony on the northeast coast of North America from 1664 to 1783. It extended from Long Island on the Atlantic, up the Hudson River and Mohawk River valleys to ...
, Province of New Jersey
The Province of New Jersey was one of the Middle Colonies of Colonial history of the United States, Colonial America and became the U.S. state of New Jersey in 1776. The province had originally been settled by Europeans as part of New Netherla ...
, Province of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn, who received the land through a grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania was derived from ...
, and Delaware Colony
The Delaware Colony, officially known as the three Lower Counties on the Delaware, was a semiautonomous region of the proprietary Province of Pennsylvania and a '' de facto'' British colony in North America. Although not royally sanctioned, ...
—ultimately forming the U.S. states of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, and Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
.
19th century
During the early nineteenth century, large numbers of Dutch farmers, forced by high taxes and low wages, started immigrating to America. They mainly settled down in theMidwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
, especially Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
and Iowa
Iowa ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the upper Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west; Wisconsin to the northeast, Ill ...
. In the 1840s, Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continenta ...
immigrants desiring more religious freedom immigrated. West Michigan
West Michigan and Western Michigan are terms for a region in the U.S. state of Michigan's Lower Peninsula. Generally, it refers to the Grand Rapids- Muskegon-Holland area, and more broadly to most of the region along the Lower Peninsula's Lake ...
in particular has become associated with Dutch American culture, and the highly conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
influence of the Dutch Reformed Church
The Dutch Reformed Church (, , abbreviated NHK ) was the largest Christian denomination in the Netherlands from the onset of the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century until 1930. It was the traditional denomination of the Dutch royal famil ...
, centering on the cities of Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
and (to a lesser extent) Grand Rapids
Grand Rapids is the largest city and county seat of Kent County, Michigan, United States. With a population of 198,917 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census and estimated at 200,117 in 2024, Grand Rapids is the List of municipalities ...
.
Waves of Catholic emigrants, initially encouraged in the 1840s by Father Theodore J. van den Broek
Theodore J. van den Broek (5 November 1783 – 5 November 1851) was a Dutch Dominican missionary to the United States. He was known for his capacity for foreign languages, his community building efforts, and extensive work among several American ...
, emigrated from the southern Netherlands to form communities in Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
, primarily to Little Chute
Little Chute is a village in Outagamie County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 11,619 at the 2020 census. It is immediately east of the city of Appleton, Wisconsin and runs along the Fox River. It is a part of the Appleton, Wisco ...
, Hollandtown, and the outlying farming communities. Whole families and even neighborhoods left for America. Most of these early emigrants were from villages near Uden
Uden () is a town and former municipality in the province of North Brabant, in the Netherlands. Since 2022 it has been part of the new municipality of Maashorst.
History
Uden was first recorded around 1190 as "Uthen". However, earlier settle ...
, including Zeeland
Zeeland (; ), historically known in English by the Endonym and exonym, exonym Zealand, is the westernmost and least populous province of the Netherlands. The province, located in the southwest of the country, borders North Brabant to the east ...
, Boekel
Boekel () is a municipality and a town in the southern Netherlands.
Etymology
Previously it was assumed the name Boekel referred to the forest ("loo" in Dutch) of the lords Boc, similar to places like Boxmeer and Boxtel. The lords Boc were ...
, Mill
Mill may refer to:
Science and technology
* Factory
* Mill (grinding)
* Milling (machining)
* Millwork
* Paper mill
* Steel mill, a factory for the manufacture of steel
* Sugarcane mill
* Textile mill
* List of types of mill
* Mill, the arithmetic ...
, Oploo
Oploo is a village in the Dutch province of North Brabant. It is located in the former municipality of Sint Anthonis. Since 2022 it has been part of the new municipality of Land van Cuijk.
History
Oploo developed in the valley of a brook in t ...
and Gemert
Gemert is a town in the Dutch province of North Brabant. It is located in the municipality of Gemert-Bakel.
Gemert was a separate municipality until 1997, when it merged with Bakel.
The spoken language is Peellands (an East Brabantian dialec ...
. By contrast, many Protestant agrarian emigrants to Michigan and Iowa were drawn from Groningen, Friesland, and Zeeland; areas known for their clay soils.
The Dutch economy of the 1840s was stagnant and much of the motivation to emigrate was economic rather than political or religious. The emigrants were not poor, as the cost of passage, expenses, and land purchase in America would have been substantial. They were not, however, affluent and many would have been risking most of their wealth on the chance of economic improvement. There were also political pressures at the time that favored mass emigrations of Protestants.
20th century migration
A significant number of Dutchmen emigrated to the United States after World War II arrived from Indonesia via the Netherlands. After Indonesia, formerly known as theDutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
, gained independence its Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
(Eurasian) population known as ''Indies Dutchmen'' (Dutch: Indische Nederlanders) repatriated to the Netherlands. Around 60,000 continued their diaspora to the United States. This particular group is also known as ''Dutch-Indonesians'', ''Indonesian-Dutch'', or ''Amerindos''.
"Nine tenths of the so called Europeans (in the Dutch East Indies) are the offspring of whites married to native women. These mixed people are called ''Indo-Europeans''... They have formed the backbone of officialdom. In general they feel the same loyalty to Holland as do the white Netherlanders. They have full rights as Dutch citizens and they are Christians and follow Dutch customs. This group has suffered more than any other during the Japanese occupation." Official U.S. Army publication for the benefit ofThese Dutch Indos mainly entered the United States under legislative refugee measures and were sponsored by Christian organizations such as theG.I. G.I. is an informal term that refers to "a soldier in the United States armed forces, especially the army". It is most deeply associated with World War II, but continues to see use. It was originally an initialism used in U.S. Army paperwork f ...'s, 1944.
Church World Service
Church World Service (CWS) was founded in 1946 and is a cooperative ministry of 37 Christian denominations and communions, providing sustainable self-help, development, disaster relief, and refugee assistance around the world. The CWS mission is ...
and the Catholic Relief Services
Catholic Relief Services (CRS) is the international humanitarian agency of the Catholic community in the United States. Founded in 1943 by the Bishops of the United States, the agency provides assistance to 130 million people in more than 110 ...
. An accurate count of Indo immigrants is not available, as the U.S. Census classified people according to their self-determined ethnic affiliation. The Indos could have therefore been included in overlapping categories of "country of origin", "other Asians," "total foreign", "mixed parentage", "total foreign-born" and "foreign mother tongue". However the Indos that settled in the United States via the legislative refugee measures number at least 25,000 people.
The original post-war refugee legislation of 1948, already adhering to a strict "affidavit of support" policy, was still maintaining a color bar making it difficult for Indos to emigrate to the United States. By 1951 American consulates in the Netherlands registered 33,500 requests and had waiting times of 3 to 5 years. Also the Walter-McCarren Act of 1953 adhered to the traditional American policy of minimizing immigrants from Asia. The yearly quota for Indonesia was limited to a 100 visas, even though Dutch foreign affairs attempted to profile Indos as refugees from the alleged pro-communist Sukarno administration.
The 1953 flood disaster in the Netherlands resulted in the Refugee Relief Act
On August 7, 1953, President Eisenhower signed the Refugee Relief Act of 1953, also known as the Emergency Migration Act, into law to provide relief for certain refugees, orphans, and other purposes. This act was mainly intended for people from ...
including a slot for 15,000 ethnic Dutch that had at least 50% European blood (one year later loosened to Dutch citizens with at least two Dutch grandparents) and an immaculate legal and political track record. In 1954 only 187 visas were actually granted. Partly influenced by the anti-Western rhetoric and policies of the Sukarno administration the anti-communist senator Francis E. Walter pleaded for a second term of the Refugee Relief Act in 1957 and an additional slot of 15,000 visas in 1958.
In 1958, the Pastore–Walter Immigration Act for the relief of certain distressed aliens was passed allowing for a one-off acceptance of 10,000 Dutchmen from Indonesia (excluding the regular annual quota of 3,136 visas). It was hoped however that only 10% of these Dutch refugees would in fact be racially mixed Indos and the American embassy in The Hague was frustrated with the fact that Canada, where ethnic profiling was even stricter, was getting the full-blooded Dutch and the United States was getting Dutch "all rather heavily dark". Still in 1960 senators Pastore and Walter managed to get a second two-year term for their act which was used by a great number of Dutch Indos.
Dutch influence on the United States
*According to tradition, in 1626Peter Minuit
Peter Minuit (French language, French: ''Pierre Minuit'', Dutch language, Dutch: ''Peter Minnewit''; 1580 – August 5, 1638) was a Walloons, Walloon merchant and politician who was the 3rd Director of New Netherland, Director of the Dutch Nort ...
obtained the island of Manhattan from the Native Americans in exchange for goods with a total value of 60 guilder
Guilder is the English translation of the Dutch and German ''gulden'', originally shortened from Middle High German ''guldin pfenninc'' (" gold penny"). This was the term that became current in the southern and western parts of the Holy Rom ...
s ($24); most aspects of the story have been called into question by experts. Minuit, a Walloon, was employed by the Dutch West India Company to manage its colony of New Amsterdam, the future New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. The names of some other settlements that were established still exist today as boroughs and neighborhoods of New York: Brooklyn
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelv ...
(Breukelen
Breukelen () is a town and former municipality in the Netherlands, in the province of Utrecht. It is situated to the northwest of Utrecht, along the river Vecht and close to the lakes of the Loosdrechtse Plassen, an area of natural and tourist i ...
), Wall Street
Wall Street is a street in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs eight city blocks between Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway in the west and South Street (Manhattan), South Str ...
(Wal Straat), Stuyvesant, Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is the southernmost of the boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County and situated at the southernmost point of New York (state), New York. The borough is separated from the ad ...
(named after the Dutch parliament, the ''Staten Generaal
The States General of the Netherlands ( ) is the supreme bicameral legislature of the Netherlands consisting of the Senate () and the House of Representatives (). Both chambers meet at the Binnenhof in The Hague.
The States General originated in ...
''), Harlem
Harlem is a neighborhood in Upper Manhattan, New York City. It is bounded roughly by the Hudson River on the west; the Harlem River and 155th Street on the north; Fifth Avenue on the east; and Central Park North on the south. The greater ...
(Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English language, English) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the Provinces of the Nether ...
), Coney Island
Coney Island is a neighborhood and entertainment area in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The neighborhood is bounded by Brighton Beach to its east, Lower New York Bay to the south and west, and Gravesend to ...
(''Konijnen Eiland'', means "Rabbit Island") and Flushing
Flushing may refer to:
Places
Netherlands
* Flushing, Netherlands, an English name for the city of Vlissingen, Netherlands
United Kingdom
* Flushing, Cornwall, a village in Cornwall, England
* The Flushing, a building in Suffolk, England ...
(''Vlissingen
Vlissingen (; ) is a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality and a city in the southwestern Netherlands on the island of Walcheren. With its strategic location between the Scheldt river and the North Sea, Vlissingen has been an importan ...
'').
*In 1657, the clash between Peter Stuyvesant
Peter Stuyvesant ( – August 1672)Mooney, James E. "Stuyvesant, Peter" in p.1256 was a Dutch colonial administrator who served as the Directors of New Netherland, director-general of New Netherland from 1647 to 1664, when the colony was pro ...
and Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestantism, Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally ...
led by John Bowne
John Bowne (1627–1695), the progenitor of the Bowne family in America, was a Quaker and an English settler residing in the Dutch colony of New Netherland. He is historically significant for his struggle for religious liberty.
Background
Born i ...
resulted in the Flushing Remonstrance
The Flushing Remonstrance was a 1657 petition to Director-General of New Netherland Peter Stuyvesant, in which some thirty residents of the small settlement at Flushing, Queens, Flushing requested an exemption to his ban on Religious Society of ...
which served as the basis for religious freedom
Freedom of religion or religious liberty, also known as freedom of religion or belief (FoRB), is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice ...
in America.
* Dutch settlers and their descendants in the colonies played active roles in the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
and the formation of the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, most especially descendants of the Schuyler family and the Van Cortlandt family. Dutch American signers of the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence included Philip Livingston and Lewis Morris, both from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. Generals for the patriots included Philip Schuyler
Philip John Schuyler (; November 20, 1733 - November 18, 1804) was an American general in the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War and a United States Senate, United States Senator from New York (state), New York. He is usually known as ...
, Peter Gansevoort, and Major General James Morgan Jr. from New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
. On the side working with the British included New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
Mayor David Mathews (a cousin of General Schuyler), Major General Oliver De Lancey (American loyalist), Oliver Delancey and Brigadier General Cortlandt Skinner (both Schuyler family descendants).
* During the American war of Independence the Dutch were active allies of the American revolutionaries. From the island of Sint Eustatius they gave the Thirteen Colonies one of the few opportunities to acquire arms. In 1778, British David Murray, 2nd Earl of Mansfield, Lord Stormont claimed in parliament that "if Sint Eustatius had sunk into the sea three years before, the United Kingdom would already have dealt with George Washington".
* The Dutch were the first to salute the flag and, therefore, the first to acknowledge the independence of the United States on November 16, 1776.
* The American Declaration of Independence is said to have in many ways been influenced by the Dutch "Act of Abjuration, ''Plakkaat van Verlatinghe''" (Act of Abjuration).
Several President of the United States, American Presidents had Dutch ancestry:
 *
* Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was the eighth president of the United States, serving from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as Attorney General o ...
, 8th President. He was a key organizer of the Democratic Party and the first president who was not of English, Irish, Scottish, or Welsh descent. He is also the only president not to have spoken English as his first language, but rather grew up speaking Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
.
* Theodore Roosevelt, 26th President. Roosevelt is most famous for his personality, his energy, his vast range of interests and achievements, his model of masculinity, and his "cowboy" persona. In 1901, he became president after the assassination of President William McKinley. Roosevelt was a Progressive reformer who sought to move the Republican Party into the Progressive camp.
* Warren G. Harding
Warren Gamaliel Harding (November 2, 1865 – August 2, 1923) was the 29th president of the United States, serving from 1921 until his death in 1923. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he was one of the most ...
, 29th President. His mother's ancestors were Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
, including the well known Van Kirk family.
* Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
, 32nd President. Elected to four terms in office, he served from 1933 to 1945, and is the only U.S. president to have served more than two terms. A central figure of the twentieth century, he has consistently been ranked as one of the three greatest U.S. presidents in scholarly surveys.
* George H. W. Bush and George W. Bush, 41st and 43rd Presidents, respectively. They count members of the Schuyler family and the related Beekman family among their ancestors.
Dutch language and Dutch names in North America
The first Dutch settlers lived in small isolated communities, and as a consequence were barely exposed to English. As the Dutch lost their own colonies in North America to the British, the Dutch settlers increasingly were exposed to other immigrants and their languages and the Dutch language gradually started to disappear. The 2009-2013American Community Survey
The American Community Survey (ACS) is an annual demographics survey program conducted by the United States Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the United States census, decennial census ...
estimated 141,580 people of 5 years and over to speak Dutch at home, which was equal to 0.0486% of the population in the United States. In 2021, 95.3% of the total Dutch American population of 5 years and over only spoke English at home.
In 1764, Archibald Laidlie preached the first English sermon to the Dutch Reformed congregation in New York City. Ten years later English was introduced in the schools. In Kingston, Dutch was used in church as late as 1808. A few years before, a traveler had reported that on Long Island and along the North River (Hudson River), North River in Albany, Dutch was still the lingua franca of the elderly.
Francis Adrian van der Kemp, who came to the United States as a refugee in 1788, wrote that his wife was able to converse in Dutch with the wives of Alexander Hamilton and General George Clinton (vice president), George Clinton. In 1847, immigrants from the Netherlands were welcomed in Dutch by the Reverend Isaac Wyckoff upon their arrival in New York. Wyckoff himself was a descendant of one of the first settlers in Rensselaerswyck, who had learned to speak English at school.
Names of Dutch origin
In the first half of the twentieth century, the Dutch language was hardly spoken in North America, with the exception of first generation Dutch immigrants. The marks of the Dutch heritage — in language, in reference to historical Dutch people (for example Peter Stuyvesant, Stuyvesant) and in reference to Dutch places — can still be seen. There are about 35 Dutch restaurants and bakeries in the United States, most of them founded in the 20th century. Anglicisation, Adaptation of Dutch names for places in the United States was common. New York City for example has many originally Dutch street and place names, which date back to the time it was the Dutch colony ofNew Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
. Several landmarks like ''Conyne Eylandt'' (Modern Dutch: ''Konijn eiland'', meaning Rabbit Island) became more suitable to Anglophones (Coney Island
Coney Island is a neighborhood and entertainment area in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The neighborhood is bounded by Brighton Beach to its east, Lower New York Bay to the south and west, and Gravesend to ...
). Additionally, Brooklyn (''Breukelen
Breukelen () is a town and former municipality in the Netherlands, in the province of Utrecht. It is situated to the northwest of Utrecht, along the river Vecht and close to the lakes of the Loosdrechtse Plassen, an area of natural and tourist i ...
''), Harlem (''Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English language, English) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the Provinces of the Nether ...
''), Wall Street (''walstraat'') and Broadway (''brede weg'') are adapted after Dutch names or words. And up the river in New York State Piermont, New York, Piermont, Orangeburg, New York, Orangeburg, Blauvelt, New York, Blauvelt and Haverstraw, New York, Haverstraw, just to name a few places. In the Hudson Valley region there are many places and waterways whose names incorporate the word ''-kill'', Dutch for "stream" or "riverbed", including the Catskill Mountains, Peekskill, and the Kill van Kull. Also, the American state of Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
is a surviving example of Dutch influence in Colonial America. In 1614, was christened as ''Roodt Eylandt'' (''Rood Eiland'' in modern Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
), meaning "Red Island", referring to the red clay found on the island.
English words of Dutch origin
Dutch and English are both part of the West Germanic languages, West Germanic language group and share several aspects, due to the fact that the birthplaces of both languages (Netherlands and the United Kingdom) are only separated by the North Sea. Similarities between Dutch and English are abundant, as an estimated 1% of the English words is of Dutch origin. Examples include the article "the" (''de'' in Dutch), the words "book" (''boek''), "house" (''huis''), "pen" (''pen''), and, "street" (''straat''), among others. There are also some words in American English that are of Dutch origin, like "cookie" (''koekje'') and "boss" (''baas''). And in some American family names a couple of Dutch characteristics still remain. Like (a) the prefix "van" (as inMartin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was the eighth president of the United States, serving from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as Attorney General o ...
), (b) the prefix "de"(/"der"/"des"/"den") (as in Jared DeVries), (c) a combination of the two "van de ..." (as in Robert J. Van de Graaff), or (d) "ter"/"te"("ten") or "ver", which mean respectively (a) "of" (possessive or locative), (b) "the" (definite article), (c) "of the..." and (d) "at the" ("of the"/"in the") (locative).
Creole dialects
Contact between other languages also created various Dutch-based creole languages, creoles with Dutch as the base language. Two examples, Jersey Dutch and Mohawk Dutch, are now extinct. This is possibly due to the ease of transition from Dutch to English, stemming from a shared linguistic genealogy.Newspapers
Little Chute, Wisconsin, Little Chute,Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
, remained a Dutch-speaking community—known locally as "speaking Hollander"—into the twentieth century. As late as 1898, church sermons and event announcements were in Dutch.''Milwaukee Sentinel'', July 15, 1898 Dutch newspapers continued in the area—mainly in De Pere by Catholic clergymen—were published up until World War I. The only remaining publication that is written exclusively in Dutch is Maandblad de Krant, which is published monthly in Penticton, British Columbia, Canada, and mailed to subscribers throughout the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
from Oroville, Washington.
Dutch-American Heritage Day
As of 1990, November 16 is "Dutch-American Heritage Day". On November 16, 1776, a small American warship, the Andrew Doria, sailed into the harbor of the Dutch island of Sint Eustatius in the West Indies. Only four months before, the United States had declared its independence from Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain. The American crew was delighted when the governor of the island ordered that his fort's cannons be fired in a friendly salute. The first ever given by a foreign power to the flag of the United States, it was a risky and courageous act. Indeed, angered by Dutch trading and contraband with the rebellious colonies, the British seized the island a few years later. The Dutch recaptured the island in 1784.Dutch-American Friendship Day
April 19 is Dutch-American Friendship Day, which remembers the day in 1782 when John Adams, later to become the second president of the United States, was received by the States-General of the Netherlands, States General in The Hague and recognized as Minister Plenipotentiary of the United States of America. It was also the day that the house he had purchased at Fluwelen Burgwal 18 in The Hague was to become the first Diplomatic missions of the United States, American Embassy in the world.Dutch Heritage Festivals
 Many of the Dutch heritage festivals that take place around the United States coincide with the blooming of tulips in a particular region. The Tulip Time Festival in Holland, Michigan is the largest such festival with other notable gatherings such as the Pella Tulip Time in Pella, Iowa
Many of the Dutch heritage festivals that take place around the United States coincide with the blooming of tulips in a particular region. The Tulip Time Festival in Holland, Michigan is the largest such festival with other notable gatherings such as the Pella Tulip Time in Pella, IowaTulip Festival
in Orange City, Iowa and Albany, New York; Dutch Days in Fulton, Illinois; Let's Go Dutch Days in Baldwin, Wisconsin; Holland Days in Lynden, Washington; Holland Happening in Oak Harbor, Washington; Holland Fest in Cedar Grove, Wisconsin, and the Wooden Shoe Tulip Fest in Woodburn, Oregon. Often Dutch heritage festivals coincide with the blooming of the tulip. See Tulip Festival for additional explanations of some of these festivals. A Dutch Festival is also held at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York; and a Holland Festival in Long Beach, California. A traditional Dutch Kermis Festival is celebrated in October in Little Chute, WI. During late November and early December, a Dutch Winterfest is held in Holland, MI, to coincide with the traditional arrival of
Sinterklaas
Sinterklaas () or Sint-Nicolaas () is a legendary figure based on Saint Nicholas, patron saint of children. Other Dutch names for the figure include ''De Sint'' ("The Saint"), ''De Goede Sint'' ("The Good Saint") and ''De Goedheiligman'' (derive ...
; the cultural ancestor of the American Santa Claus.""Dutch Americans"Herbert J. Brinks There is an annual Sinterklass festival held in Rhinebeck, New York, Rhinebeck and Kingston, New York where Sinterklaas crosses the
Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the ...
and a parade is held in recognition of the New York metropolitan area, Greater New York Area's Dutch cultural heritage.
Lately, many of the larger cities in the U.S. have a King's Day (Koningsdag) festival that is celebrated in the Netherlands on April 27 to celebrate the birthday of Willem-Alexander of the Netherlands, King Willem Alexander. The Portland Dutch Society started this annual Dutch Holiday celebration in Portland, OR in 2013 and will have one again in 2015 on April 26. It is celebrated by people of Dutch heritage dressed in their Orange clothes and enjoying the sounds of Dutch music and eating typical Dutch foods like kroketten, friet met mayonaise, zoute haring, and other Dutch delicacies.
Dutch-American people of color
Most Dutch-Americans are white, but some are Person of color, people of color, including Black Dutch-Americans. During the 18th and 19th centuries, many enslaved and free Black people spoke Dutch. New York City and New Jersey had notable Dutch-speaking Black populations during the colonial era and into the 1800s, dating back to the Dutch settlement inNew Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), fac ...
.
Religion
The beginnings of the Reformed Church in America date to 1628. By 1740, it had 65 congregations inNew York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
and New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, served by ministers trained in Europe. Schools were few but to obtain their own ministers they formed "Queens College" (now Rutgers University) in 1766. In 1771, there were 34 ministers for over 100 churches. Until 1764, in at least three Dutch churches in New York City, all sermons were in Dutch; Theodore Roosevelt reports his grandfather's church used Dutch as late as 1810. Other churches with roots in Dutch immigration to the United States include the Christian Reformed Church in North America, Christian Reformed Church, the Protestant Reformed Churches in America, Protestant Reformed Churches, the United Reformed Churches in North America, United Reformed Churches, the Netherlands Reformed Congregations, the Heritage Netherlands Reformed Congregations and the Free Reformed Churches of North America, Free Reformed Churches. Along with the Reformed churches, Roman Catholicism is the other major religion of Dutch Americans. Beginning in 1848, a significant number of Roman Catholics from the Dutch provinces of North Brabant, Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg and southern Gelderland went to create many settlements in northeastern Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
. But even today, Dutch Americans remain majority Protestant.
Numbers
Between 1820 and 1900, 340,000 Dutch emigrated from theNetherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
to the United States. In the aftermath of World War II, several tens of thousands of Dutch immigrants joined them, mainly moving to California and Washington (state), Washington. In several counties in Michigan and Iowa, Dutch Americans remain the largest ethnic group. In 2020, most self-reported Dutch Americans live in Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
, followed by California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. While the highest concentration of Dutch Americans are found in South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state, state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Dakota people, Dakota Sioux ...
, Michigan, Iowa
Iowa ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the upper Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west; Wisconsin to the northeast, Ill ...
, and Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
. According to 2021 United States census, US Census data, 3,083,041 Americans self-reported to be of (partial) Dutch ancestry, while 884,857 Americans claimed full Dutch heritage. 2,969,407 Dutch Americans were native born in 2021, while 113,634 Dutch Americans were foreign-born, of which 61.5% was born in Europe and 62,9% entered the United States before 2000.
2000 population of Dutch ancestry
 According to the 2000 United States Census, US Census, more than 5 million Americans claimed total or partial
According to the 2000 United States Census, US Census, more than 5 million Americans claimed total or partial Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
heritage. They were particularly concentrated around Grand Rapids, Michigan; Rock Rapids, Iowa; Sioux City, Iowa; Des Moines, Iowa; Fulton, Illinois, Celeryville, Ohio, and Little Chute, Wisconsin. These areas are surrounded with towns and villages that were founded by Dutch settlers in the 19th century, such as Holland, Michigan and Zeeland, Michigan; Pella, Iowa, and Orange City, Iowa. Other Dutch enclaves include Lynden, Washington, Ripon, California, and places in New Jersey. It is estimated that, by 1927, as many as 40,000 Dutch settlers, primarily from North Brabant and Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg, had immigrated to the United States, with the largest concentrations in the area near Little Chute
Little Chute is a village in Outagamie County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 11,619 at the 2020 census. It is immediately east of the city of Appleton, Wisconsin and runs along the Fox River. It is a part of the Appleton, Wisco ...
, Wisconsin."Nederlanders in Amerika", Van Hinte, Assen, 1928 By the early twentieth century, Little Chute was the largest Catholic Dutch community in the United States."Netherlanders in America" Lucas, 1955 In the Chicago metropolitan area, Chicago suburbs, there are sizable Dutch communities in and around Elmhurst, Illinois, Elmhurst, Wheaton, Illinois, Wheaton, Palos Heights, Illinois, Palos Heights, South Holland, Illinois, South Holland, Lansing, Illinois, Lansing, Dyer, Indiana, Dyer, and other surrounding communities, anchored by Reformed churches and Christian schools.
In California, the San Joaquin County, California, San Joaquin Delta had a major Dutch (incl. Frisians, Frisian) and Belgians, Belgian influence, as settlers from those countries arrived in the 1850s, after California obtained statehood. They drained away swamps and created artificial islands known as polders, constructed dikes to back away the Sacramento and San Joaquin Rivers flowing into the San Francisco Bay, also turned them into fertile farmlands and set up inland ports such as Stockton, California, Stockton. Also their communities like Lathrop, California, Lathrop, Galt, California, Galt, Rio Vista, California, Rio Vista and French Camp, California, French Camp which were named for Belgians from Belgium are of both French (Walloons, Walloon) or Flemish
Flemish may refer to:
* Flemish, adjective for Flanders, Belgium
* Flemish region, one of the three regions of Belgium
*Flemish Community, one of the three constitutionally defined language communities of Belgium
* Flemish dialects, a Dutch dialec ...
origin. There is a Dutch community in Redlands, California, Redlands, Ontario, California, Ontario, Ripon, California, Ripon and Bellflower, California, Bellflower.
2020 population of Dutch ancestry by state
As of 2020, the distribution of self-reported Dutch Americans across the 50 states and DC is as presented in the following table:Notable people
Harmen Jansen Knickerbocker was an early Dutch settler of New York's Hudson River Valley. In art, Willem de Kooning was a leading Abstract Expressionist painter, often depicting the human form in violent brush strokes and daring color juxtapositions. Muralist Anthony Heinsbergen interior designs are still seen today in most of the world's movie theaters. Cowboy artist Earl W. Bascom, a sculptor known as the "cowboy of cowboy artists", is a descendant of the Van Riper family who was early settlers of New York. In business, the Vanderbilt family was once among the richest families in the United States. In education, Stephen Van Rensselaer, Stephen Van Rensselaer III founded Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York, in 1824, which is the oldest technological university in the English-speaking world and the Western Hemisphere. Famous accomplishments of alumni include the Ferris Wheel, Brooklyn Bridge, commercially viable television and radar, and the microprocessor. In literature, Janwillem van de Wetering is renowned for his detective fiction; his most popular creation being that of Grijpstra and de Gier. Edward W. Bok was a Pulitzer Prize-winning autobiographer and magazine editor. He is also credited with coining the term "living room". Greta Van Susteren's father was a Dutch American. Prolific poet Leo Vroman escaped from the Nazi-occupied Netherlands to theDutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
to end up in a harsh concentration camp for Europeans run by the Japanese army when it overran the islands. After the war, he immigrated to the United States. His Indo people, Dutch Indonesian friend, fellow camp survivor, and author Tjalie Robinson also lived in the United States, where he founded several cultural institutions. The author Erik Hazelhoff Roelfzema, writer of the book Soldier of Orange, was a Dutch resistance fighter, spy, and decorated war hero that immigrated to the United States after World War II. Born on Java in the Dutch East Indies, he died in his home in Hawaii.
In entertainment, actor, Television presenter, presenter and entertainer Dick Van Dyke is of Dutch descent, with a career spanning six decades. He is best known for his starring roles in ''Mary Poppins (film), Mary Poppins'', ''Chitty Chitty Bang Bang (film), Chitty Chitty Bang Bang'', ''The Dick Van Dyke Show'' and ''Diagnosis: Murder''. Dick Van Patten and his son Vincent Van Patten, Vincent are of Dutch descent; Dick was famous for the television show ''Eight is Enough''. Three generations of Fondas from Fonda, New York have graced the stage and screen for almost a century, including Henry Fonda, son Peter Fonda, daughter Jane Fonda, granddaughter Bridget Fonda and grandson Troy Garity. The X-Men (film), '' X-Men'' trilogy starred Dutch actress Famke Janssen and Dutch-descended Rebecca Romijn who is perhaps best known for her TV roles in such comedies as ''Ugly Betty''. Anneliese van der Pol, a singer and actress, is a star of Disney's ''That's so Raven''. Iconic star Audrey Hepburn was born in Belgium to a Dutch expatriate. Musicians Eddie van Halen, Eddie and Alex van Halen were the lead guitarist and drummer, respectively, and co-founders of the band Van Halen, born to a Dutch father and Indo people, Dutch-Indonesian mother. Bruce Springsteen's father was of Dutch and Irish heritage, from one of the original families that settled in New Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
. The brothers Ronny, Johnny, and Donnie van Zant, the lead singer of Lynyrd Skynyrd and founder of 38 Special (band), 38 Special have Dutch ancestry. Singer Whitney Houston had Dutch ancestry. Don Van Vliet, the musician with the stage name Captain Beefheart, changed his middle name from Glen to the preposition to 1965 to honor his Dutch heritage. Actor Mark-Paul Gosselaar, known from the series ''Saved by the Bell'', was born to a Dutch father and a Indo people, Dutch-Indonesian mother. Matt Groening, the author of ''The Simpsons'' and ''Futurama'' has Dutch Mennonite ancestors, his family name originating from the Dutch city of Groningen (city), Groningen. Chevy Chase also has deep Dutch roots from colonial New York.
In politics, Peter Stuyvesant
Peter Stuyvesant ( – August 1672)Mooney, James E. "Stuyvesant, Peter" in p.1256 was a Dutch colonial administrator who served as the Directors of New Netherland, director-general of New Netherland from 1647 to 1664, when the colony was pro ...
was the last Director-General of the colony of New Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
. Stuyvesant greatly expanded the settlement of New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), fac ...
, today known as New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. Stuyvesant's administration built the protective wall on Wall Street
Wall Street is a street in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It runs eight city blocks between Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway in the west and South Street (Manhattan), South Str ...
, and the canal that became Broad Street (Manhattan), Broad Street, known today as Broadway (Manhattan), Broadway. The prestigious Stuyvesant High School is named after him. Theodore Roosevelt and Franklin Delano Roosevelt, presidents of the United States, were not only of Dutch descent but cousins. Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was the eighth president of the United States, serving from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as Attorney General o ...
was another president of Dutch descent. Martin Kalbfleisch served as a U.S. Representative for the state of New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. Pete Hoekstra served as congressman for the state of Michigan's 2nd congressional district from 1993 until 2011. On January 10, 2018, he took office as United States Ambassador to the Netherlands. Jacob Aaron Westervelt was a renowned and prolific shipbuilder and Mayors of New York, Mayor of New York (1853–1855).
In science and technology, inventor and businessman Thomas Edison was of Dutch descent. Nicolaas Bloembergen won the Nobel Prize in 1981 for his work in laser spectroscopy. He was also awarded the Lorentz Medal in 1978. Physicists Samuel Abraham Goudsmit and George Eugene Uhlenbeck proposed the concept of electron spin. Goudsmit was also the scientific head of the Operation Alsos mission in the Manhattan Project. Tjalling Koopmans was the recipient of the Nobel Prize in Economics in 1975.
In astronomy, Maarten Schmidt pioneered the research of quasars. Astronomer Gerard Kuiper discovered two new moons in the Solar System and predicted the existence of the Kuiper belt, which is named in his honor. Popular astronomer Bart J. Bok won the Klumpke-Roberts Award in 1982 and the Bruce Medal in 1977. Jan Schilt invented the Schilt photometer.
In sports, National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum, Hall of Fame baseball player and two-time World Series champion Bert Blyleven gained fame for his curveball. Earl W. Bascom, Earl Bascom was a Hall of Fame rodeo champion known as the "father of modern rodeo." Golfer Tiger Woods has Dutch ancestry through his mother.
In religion, Albertus van Raalte was a Reformed Church of America pastor who led the Dutch immigrants who founded the city of Holland, Michigan in 1846. Louis Berkhof, a Reformed tradition, Reformed systematic theologian, is greatly studied today in seminaries and Bible colleges. Herman Hoeksema, a theologian, was instrumental in the series of events that precipitated the creation of the Protestant Reformed Church. Prominent Christians, Christian author Lewis B. Smedes wrote ''Forgive and Forget: Healing the Hurts We Don't Deserve, Forgive and Forget'', an influential work discussing a religious view on Human sexuality, sexuality and forgiveness. Menno Simons (1496 – January 31, 1561) was a former Catholic priest from the Friesland region of the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
who became an influential Anabaptist religious leader. Simons was a contemporary of the Protestant Reformers and it is from his name that his followers became known as Mennonites.
See also
* Dutch Americans in Michigan * Dutch Americans in New York City * Dutch Canadians * Dutch West Indian Americans * ''Dutch, the magazine'' * European Americans * Hyphenated American * Netherlands–United States relations * Surinamese Americans * Van (Dutch)References
Further reading
*Bratt, James D. ''Dutch Calvinism in Modern America: A History of a Conservative Subculture''. (Eerdmans, 1984). * Brinks, Herbert J. "Dutch Americans." in ''Gale Encyclopedia of Multicultural America,'' edited by Thomas Riggs, (3rd ed., vol. 2, Gale, 2014), pp. 35–45online
*Corwin, S. T. ''History of the Dutch Reformed Church in the United States'' (1895). * De Gerald, F. Jong ''The Dutch in America, 1609-1974''. (Twayne, 1975); short survey * Ganzevoort, Herman, and Mark Boekelman, eds. ''Dutch Immigration to North America''. Toronto: Multicultural History Society of Ontario, 1983. * Goodfriend, Joyce D. Benjamin Schmidt, and Annette Stott, eds. ''Going Dutch: The Dutch Presence in America, 1609-2009'' (2008) * Kirk, Gordon W. ''The Promise of American Life: Social Mobility in a Nineteenth-Century Immigrant Community, Holland, Michigan, 1847-1894.'' Philadelphia: American Philosophical Society, 1978. * Krabbendam, Hans. ''Freedom on the Horizon: Dutch Immigration to America, 1840-1940'' (2009), Emphasis on the Dutch Reformed Church * Kroes, Rob. ''The Persistence of Ethnicity: Dutch Calvinist Pioneers in Amsterdam, Montana.'' University of Illinois Press, 1992. * Kroes, Rob, and Henk-Otto Neuschafer, eds. ''The Dutch in North America: Their Immigration and Cultural Continuity.'' Amsterdam: Free University Press, 1991. * Kromminga, John. ''The Christian Reformed Church: A Study in Orthodoxy.'' Grand Rapids, Mich.: Baker Books, 1949. * Lucas, Henry. ''Netherlanders in America: Dutch Immigration to the United States and Canada, 1789-1950.'' The University of Michigan Press, 1955. * Schreuder, Yda. ''Dutch Catholic Immigrant Settlement in Wisconsin, 1850-1905.'' New York: Garland, 1989. * Swierenga, Robert P. ''The Forerunners: Dutch Jewry in the North American Diaspora.'' Wayne State University Press, 1994. * Swierenga, Robert P. ed. ''The Dutch in America: Immigration, Settlement, and Cultural Change''. Rutgers University Press, 1985. * Swierenga, Robert P., "Faith and Family --Dutch Immigration and Settlement in the United States, 1820–1920" (Ellis Island Series.) New York: Holmes and Meyer. 2000. * Taylor, Lawrence J. ''Dutchmen on the Bay: The Ethnohistory of a Contractual Community.'' The University of Pennsylvania Press, 1983. * Thernstrom, Stephan, ed. ''Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups''. Harvard University Press, 1980. * Van Jacob Hinte. ''Netherlanders in America: A Study of Emigration and Settlement in the Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries in the United States of America.'' Ed. Robert P. Swierenga. Grand Rapids, Mich.: Baker Book House, 1985. translation of a 1928 Dutch-language book *Wabeke, Bertus Harr
''Dutch emigration to North America, 1624-1860''
* Wittke, Carl. ''We Who Built America: The Saga of the Immigrant'' (1939), ch 2, 11
Colonial/ New Netherland
* Balmer, Randall. ''A Perfect Babel of Confusion: Dutch Religion and English Culture in the Middle Colonies'' (2002). * * Cohen, David Steven. "How Dutch Were the Dutch of New Netherland?." ''New York History'' 62#1 (1981): 43–60in JSTOR
* Cooke, Jacob Ernest, ed. ''Encyclopedia of the North American colonies'' (3 vol. 1993), highly detailed topical coverage of the Dutch colonists. * Jacobs, Jaap. ''New Netherland: a Dutch colony in seventeenth-century America'' (Brill, 2005
online
* Kenney, Alice P. "Neglected Heritage: Hudson River Valley Dutch Material Culture." ''Winterthur Portfolio'' 20#1 (1985): 49–70
in JSTOR
* Kim, Sung Bok. ''Landlord and Tenant in Colonial New York: Manorial Society, 1664-1775'' (1987) * Leiby; Adrian C. ''The Revolutionary War in the Hackensack Valley: The Jersey Dutch and the Neutral Ground, 1775-1783'' Rutgers University Press. 1962. * Nissenson, S. G. ''The Patroon's Domain'' (1937). * Roeber, A. G. "Dutch colonists cope with English control" in Bernard Bailyn, and Philip D. Morgan, eds. ''Strangers within the realm: cultural margins of the first British Empire'' (1991) pp 222–36. * Scheltema, Gajus and Westerhuijs, Heleen (eds.),''Exploring Historic Dutch New York''. Museum of the City of New York/Dover Publications, New York (2011). *Todt, Kim. "'Women Are as Knowing Therein as the Men': Dutch Women in Early America," in Thomas A. Foster, ed. ''Women in Early America'' (2015) pp 43–6
online
* Van Lieburg, Fred. "Interpreting the Dutch Great Awakening (1749–1755)." ''Church History'' 77#2 (2008): 318–336
in JSTOR
* Wermuth, Thomas S. ''Rip Van Winkle's Neighbors: The Transformation of Rural Society in the Hudson River Valley, 1720-1850'' (2001). * Wermuth, Thomas S. "New York farmers and the market revolution: Economic behavior in the mid-Hudson Valley, 1780-1830." ''Journal of Social History'' (1998): 179–196
in JSTOR
* Wittke, Carl. ''We Who Built America: The Saga of the Immigrant'' (1939), ch 2
Historiography
* Doezema, Linda Pegman. ''Dutch Americans: A Guide to Information Sources''. Gale Research, 1979. BibliographyPrimary sources
*Herbert J. Brinks, ''Dutch American Voices: Letters from the United States, 1850-1930'' (1995) *Lucas, Henry, ed. ''Dutch Immigrant Memoirs and Related Writings''. 2 vols. Assen, Netherlands: Van Gorcum, 1955.External links
* [http://www.focol.org/littlechutehistory/ Little Chute Historical Society, Little Chute, Wisconsin] {{Authority control American people of Dutch descent, Dutch diaspora by country, American European diaspora in the United States