Data modeling on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Data modeling in
Data modeling in
 Data models provide a framework for
Data models provide a framework for
Developing High Quality Data Models
. The European Process Industries STEP Technical Liaison Executive (EPISTLE). Some common problems found in data models are: * Business rules, specific to how things are done in a particular place, are often fixed in the structure of a data model. This means that small changes in the way business is conducted lead to large changes in computer systems and interfaces. So, business rules need to be implemented in a flexible way that does not result in complicated dependencies, rather the data model should be flexible enough so that changes in the business can be implemented within the data model in a relatively quick and efficient way. * Entity types are often not identified, or are identified incorrectly. This can lead to replication of data, data structure and functionality, together with the attendant costs of that duplication in development and maintenance. Therefore, data definitions should be made as explicit and easy to understand as possible to minimize misinterpretation and duplication. * Data models for different systems are arbitrarily different. The result of this is that complex interfaces are required between systems that share data. These interfaces can account for between 25 and 70% of the cost of current systems. Required interfaces should be considered inherently while designing a data model, as a data model on its own would not be usable without interfaces within different systems. * Data cannot be shared electronically with customers and suppliers, because the structure and meaning of data have not been standardised. To obtain optimal value from an implemented data model, it is very important to define standards that will ensure that data models will both meet business needs and be consistent.
 In 1975
In 1975
 In the context of business process integration (see figure), data modeling complements business process modeling, and ultimately results in database generation.
The process of designing a database involves producing the previously described three types of schemas – conceptual, logical, and physical. The database design documented in these schemas is converted through a Data Definition Language, which can then be used to generate a database. A fully attributed data model contains detailed attributes (descriptions) for every entity within it. The term "database design" can describe many different parts of the design of an overall database system. Principally, and most correctly, it can be thought of as the logical design of the base data structures used to store the data. In the
In the context of business process integration (see figure), data modeling complements business process modeling, and ultimately results in database generation.
The process of designing a database involves producing the previously described three types of schemas – conceptual, logical, and physical. The database design documented in these schemas is converted through a Data Definition Language, which can then be used to generate a database. A fully attributed data model contains detailed attributes (descriptions) for every entity within it. The term "database design" can describe many different parts of the design of an overall database system. Principally, and most correctly, it can be thought of as the logical design of the base data structures used to store the data. In the
Van Scott on tdan.com
Accessed November 1, 2008. only two modeling methodologies stand out, top-down and bottom-up: * Bottom-up models or View Integration models are often the result of a reengineering effort. They usually start with existing data structures forms, fields on application screens, or reports. These models are usually physical, application-specific, and incomplete from an enterprise perspective. They may not promote data sharing, especially if they are built without reference to other parts of the organization. * Top-down logical data models, on the other hand, are created in an abstract way by getting information from people who know the subject area. A system may not implement all the entities in a logical model, but the model serves as a reference point or template. Sometimes models are created in a mixture of the two methods: by considering the data needs and structure of an application and by consistently referencing a subject-area model. In many environments, the distinction between a logical data model and a physical data model is blurred. In addition, some CASE tools don't make a distinction between logical and
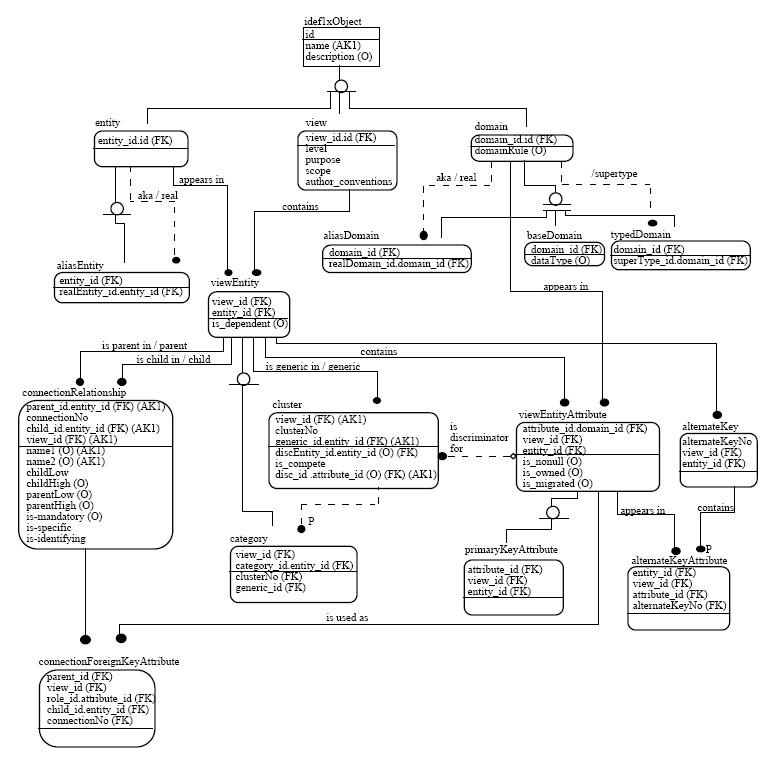 There are several notations for data modeling. The actual model is frequently called "entity–relationship model", because it depicts data in terms of the entities and relationships described in the
There are several notations for data modeling. The actual model is frequently called "entity–relationship model", because it depicts data in terms of the entities and relationships described in the
 Generic data models are generalizations of conventional data models. They define standardized general relation types, together with the kinds of things that may be related by such a relation type.
The definition of the generic data model is similar to the definition of a natural language. For example, a generic data model may define relation types such as a 'classification relation', being a
Generic data models are generalizations of conventional data models. They define standardized general relation types, together with the kinds of things that may be related by such a relation type.
The definition of the generic data model is similar to the definition of a natural language. For example, a generic data model may define relation types such as a 'classification relation', being a
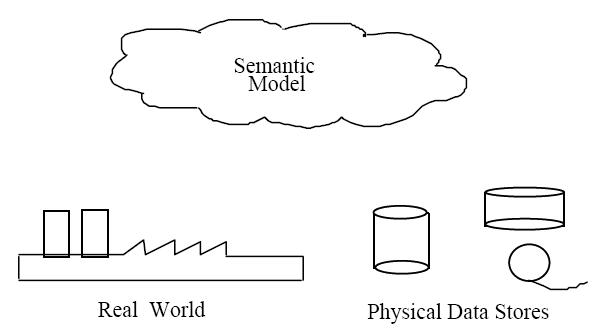 Therefore, the need to define data from a conceptual view has led to the development of semantic data modeling techniques. That is, techniques to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. As illustrated in the figure the real world, in terms of resources, ideas, events, etc., is symbolically defined by its description within physical data stores. A semantic data model is an
Therefore, the need to define data from a conceptual view has led to the development of semantic data modeling techniques. That is, techniques to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. As illustrated in the figure the real world, in terms of resources, ideas, events, etc., is symbolically defined by its description within physical data stores. A semantic data model is an
Agile/Evolutionary Data Modeling
Data modeling articles
Database Modelling in UML
Notes on by Tony Drewry
Request For Proposal - Information Management Metamodel (IMM)
of the Object Management Group
Data Modeling is NOT just for DBMS's Part 1
Chris Bradley
Data Modeling is NOT just for DBMS's Part 2
Chris Bradley {{DEFAULTSORT:Data Modeling
software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
is the process of creating a data model for an information system
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, Information Processing and Management, store, and information distribution, distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, info ...
by applying certain formal techniques. It may be applied as part of broader Model-driven engineering (MDE) concept.
Overview
Data modeling is aprocess
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
* Business process, activities that produce a specific s ...
used to define and analyze data requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a condition that must be satisfied for the output of a work effort to be acceptable. It is an explicit, objective, clear and often quantitative description of a condition to be satisfied by a material, design, pro ...
s needed to support the business process
A business process, business method, or business function is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks performed by people or equipment in which a specific sequence produces a service or product (that serves a particular business g ...
es within the scope of corresponding information systems in organizations. Therefore, the process of data modeling involves professional data modelers working closely with business stakeholders, as well as potential users of the information system.
There are three different types of data models produced while progressing from requirements to the actual database to be used for the information system.Simison, Graeme. C. & Witt, Graham. C. (2005). ''Data Modeling Essentials''. 3rd Edition. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers. The data requirements are initially recorded as a conceptual data model which is essentially a set of technology independent specifications about the data and is used to discuss initial requirements with the business stakeholders. The conceptual model
The term conceptual model refers to any model that is formed after a wikt:concept#Noun, conceptualization or generalization process. Conceptual models are often abstractions of things in the real world, whether physical or social. Semantics, Semant ...
is then translated into a logical data model, which documents structures of the data that can be implemented in databases. Implementation of one conceptual data model may require multiple logical data models. The last step in data modeling is transforming the logical data model to a physical data model
A physical data model (or database design) is a representation of a data design as implemented, or intended to be implemented, in a database management system. In the Project lifecycle, lifecycle of a project it typically derives from a logical ...
that organizes the data into tables, and accounts for access, performance and storage details. Data modeling defines not just data elements, but also their structures and the relationships between them.
Data modeling techniques and methodologies are used to model data in a standard, consistent, predictable manner in order to manage it as a resource. The use of data modeling standards is strongly recommended for all projects requiring a standard means of defining and analyzing data within an organization, e.g., using data modeling:
* to assist business analysts, programmers, testers, manual writers, IT package selectors, engineers, managers, related organizations and clients to understand and use an agreed-upon semi-formal model that encompasses the concepts of the organization and how they relate to one another
* to manage data as a resource
* to integrate information systems
* to design databases/data warehouse
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for Business intelligence, reporting and data analysis and is a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central Re ...
s (aka data repositories)
Data modelling may be performed during various types of projects and in multiple phases of projects. Data models are progressive; there is no such thing as the final data model for a business or application. Instead, a data model should be considered a living document that will change in response to a changing business. The data models should ideally be stored in a repository so that they can be retrieved, expanded, and edited over time. Whitten et al. (2004) determined two types of data modelling:
* Strategic data modelling: This is part of the creation of an information systems strategy, which defines an overall vision and architecture for information systems. Information technology engineering
Data engineering is a software engineering approach to the building of data systems, to enable the collection and usage of data. This data is usually used to enable subsequent data analytics, analysis and data science, which often involves machin ...
is a methodology that embraces this approach.
* Data modelling during systems analysis: In systems analysis logical data models are created as part of the development of new databases.
Data modelling is also used as a technique for detailing business requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a condition that must be satisfied for the output of a work effort to be acceptable. It is an explicit, objective, clear and often quantitative description of a condition to be satisfied by a material, design, pro ...
s for specific database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
s. It is sometimes called ''database modelling'' because a data model is eventually implemented in a database. Whitten, Jeffrey L.; Lonnie D. Bentley, Kevin C. Dittman. (2005). ''Systems Analysis and Design Methods''. 6th edition. .
Topics
Data models
data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
to be used within information system
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, Information Processing and Management, store, and information distribution, distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, info ...
s by providing specific definitions and formats. If a data model is used consistently across systems then compatibility of data can be achieved. If the same data structures are used to store and access data then different applications can share data seamlessly. The results of this are indicated in the diagram. However, systems and interfaces are often expensive to build, operate, and maintain. They may also constrain the business rather than support it. This may occur when the quality of the data models implemented in systems and interfaces is poor.Matthew West and Julian Fowler (1999)Developing High Quality Data Models
. The European Process Industries STEP Technical Liaison Executive (EPISTLE). Some common problems found in data models are: * Business rules, specific to how things are done in a particular place, are often fixed in the structure of a data model. This means that small changes in the way business is conducted lead to large changes in computer systems and interfaces. So, business rules need to be implemented in a flexible way that does not result in complicated dependencies, rather the data model should be flexible enough so that changes in the business can be implemented within the data model in a relatively quick and efficient way. * Entity types are often not identified, or are identified incorrectly. This can lead to replication of data, data structure and functionality, together with the attendant costs of that duplication in development and maintenance. Therefore, data definitions should be made as explicit and easy to understand as possible to minimize misinterpretation and duplication. * Data models for different systems are arbitrarily different. The result of this is that complex interfaces are required between systems that share data. These interfaces can account for between 25 and 70% of the cost of current systems. Required interfaces should be considered inherently while designing a data model, as a data model on its own would not be usable without interfaces within different systems. * Data cannot be shared electronically with customers and suppliers, because the structure and meaning of data have not been standardised. To obtain optimal value from an implemented data model, it is very important to define standards that will ensure that data models will both meet business needs and be consistent.
Conceptual, logical and physical schemas
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
described three kinds of data-model ''instance'':
* Conceptual schema: describes the semantics of a domain (the scope of the model). For example, it may be a model of the interest area of an organization or of an industry. This consists of entity classes, representing kinds of things of significance in the domain, and relationship assertions about associations between pairs of entity classes. A conceptual schema specifies the kinds of facts or propositions that can be expressed using the model. In that sense, it defines the allowed expressions in an artificial "language" with a scope that is limited by the scope of the model. Simply described, a conceptual schema is the first step in organizing the data requirements.
* Logical schema A logical data model or logical schema is a data model of a specific problem domain expressed independently of a particular database management product or storage technology ( physical data model) but in terms of data structures such as relational ...
: describes the structure of some domain of information. This consists of descriptions of (for example) tables, columns, object-oriented classes, and XML tags. The logical schema and conceptual schema are sometimes implemented as one and the same.
* Physical schema: describes the physical means used to store data. This is concerned with partitions, CPUs, tablespaces, and the like.
According to ANSI, this approach allows the three perspectives to be relatively independent of each other. Storage technology can change without affecting either the logical or the conceptual schema. The table/column structure can change without (necessarily) affecting the conceptual schema. In each case, of course, the structures must remain consistent across all schemas of the same data model.
Data modelling process
relational model
The relational model (RM) is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by English computer scientist Edgar F. Codd, where all data are represented in terms of t ...
these are the tables and views. In an object database the entities and relationships map directly to object classes and named relationships. However, the term "database design" could also be used to apply to the overall process of designing, not just the base data structures, but also the forms and queries used as part of the overall database application within the Database Management System
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and an ...
or DBMS.
In the process, system interfaces account for 25% to 70% of the development and support costs of current systems. The primary reason for this cost is that these systems do not share a common data model. If data models are developed on a system by system basis, then not only is the same analysis repeated in overlapping areas, but further analysis must be performed to create the interfaces between them. Most systems within an organization contain the same basic data, redeveloped for a specific purpose. Therefore, an efficiently designed basic data model can minimize rework with minimal modifications for the purposes of different systems within the organization
Modeling methodologies
Data models represent information areas of interest. While there are many ways to create data models, according to Len Silverston (1997)Len Silverston, W.H.Inmon, Kent Graziano (2007). ''The Data Model Resource Book''. Wiley, 1997. . Reviewed bVan Scott on tdan.com
Accessed November 1, 2008. only two modeling methodologies stand out, top-down and bottom-up: * Bottom-up models or View Integration models are often the result of a reengineering effort. They usually start with existing data structures forms, fields on application screens, or reports. These models are usually physical, application-specific, and incomplete from an enterprise perspective. They may not promote data sharing, especially if they are built without reference to other parts of the organization. * Top-down logical data models, on the other hand, are created in an abstract way by getting information from people who know the subject area. A system may not implement all the entities in a logical model, but the model serves as a reference point or template. Sometimes models are created in a mixture of the two methods: by considering the data needs and structure of an application and by consistently referencing a subject-area model. In many environments, the distinction between a logical data model and a physical data model is blurred. In addition, some CASE tools don't make a distinction between logical and
physical data model
A physical data model (or database design) is a representation of a data design as implemented, or intended to be implemented, in a database management system. In the Project lifecycle, lifecycle of a project it typically derives from a logical ...
s.
Entity–relationship diagrams
 There are several notations for data modeling. The actual model is frequently called "entity–relationship model", because it depicts data in terms of the entities and relationships described in the
There are several notations for data modeling. The actual model is frequently called "entity–relationship model", because it depicts data in terms of the entities and relationships described in the data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
. An entity–relationship model (ERM) is an abstract conceptual representation of structured data. Entity–relationship modeling is a relational schema database model
A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database. It fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized and manipulated. The most popular example of a database model is the relatio ...
ing method, used in software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
to produce a type of conceptual data model (or semantic data model) of a system, often a relational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
, and its requirements in a top-down fashion.
These models are being used in the first stage of information system
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, Information Processing and Management, store, and information distribution, distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, info ...
design during the requirements analysis to describe information needs or the type of information
Information is an Abstraction, abstract concept that refers to something which has the power Communication, to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the Interpretation (philosophy), interpretation (perhaps Interpretation (log ...
that is to be stored in a database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
. The data modeling technique can be used to describe any ontology
Ontology is the philosophical study of existence, being. It is traditionally understood as the subdiscipline of metaphysics focused on the most general features of reality. As one of the most fundamental concepts, being encompasses all of realit ...
(i.e. an overview and classifications of used terms and their relationships) for a certain universe of discourse
In the formal sciences, the domain of discourse or universe of discourse (borrowing from the mathematical concept of ''universe'') is the set of entities over which certain variables of interest in some formal treatment may range.
It is also ...
i.e. the area of interest.
Several techniques have been developed for the design of data models. While these methodologies guide data modelers in their work, two different people using the same methodology will often come up with very different results. Most notable are:
* Bachman diagrams
* Barker's notation
* Chen's notation
* Data Vault Modeling
* Extended Backus–Naur form
Extension, extend or extended may refer to:
Mathematics
Logic or set theory
* Axiom of extensionality
* Extensible cardinal
* Extension (model theory)
* Extension (proof theory)
* Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values ...
* IDEF1X
* Object-relational mapping
* Object-Role Modeling and Fully Communication Oriented Information Modeling
* Relational Model
The relational model (RM) is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by English computer scientist Edgar F. Codd, where all data are represented in terms of t ...
* Relational Model/Tasmania
Generic data modeling
 Generic data models are generalizations of conventional data models. They define standardized general relation types, together with the kinds of things that may be related by such a relation type.
The definition of the generic data model is similar to the definition of a natural language. For example, a generic data model may define relation types such as a 'classification relation', being a
Generic data models are generalizations of conventional data models. They define standardized general relation types, together with the kinds of things that may be related by such a relation type.
The definition of the generic data model is similar to the definition of a natural language. For example, a generic data model may define relation types such as a 'classification relation', being a binary relation
In mathematics, a binary relation associates some elements of one Set (mathematics), set called the ''domain'' with some elements of another set called the ''codomain''. Precisely, a binary relation over sets X and Y is a set of ordered pairs ...
between an individual thing and a kind of thing (a class) and a 'part-whole relation', being a binary relation between two things, one with the role of part, the other with the role of whole, regardless the kind of things that are related.
Given an extensible list of classes, this allows the classification of any individual thing and to specification of part-whole relations for any individual object. By standardization of an extensible list of relation types, a generic data model enables the expression of an unlimited number of kinds of facts and will approach the capabilities of natural languages. Conventional data models, on the other hand, have a fixed and limited domain scope, because the instantiation (usage) of such a model only allows expressions of kinds of facts that are predefined in the model.
Semantic data modeling
The logical data structure of a DBMS, whether hierarchical, network, or relational, cannot totally satisfy the requirements for a conceptual definition of data because it is limited in scope and biased toward the implementation strategy employed by the DBMS. That is unless the semantic data model is implemented in the database on purpose, a choice which may slightly impact performance but generally vastly improves productivity. Therefore, the need to define data from a conceptual view has led to the development of semantic data modeling techniques. That is, techniques to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. As illustrated in the figure the real world, in terms of resources, ideas, events, etc., is symbolically defined by its description within physical data stores. A semantic data model is an
Therefore, the need to define data from a conceptual view has led to the development of semantic data modeling techniques. That is, techniques to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. As illustrated in the figure the real world, in terms of resources, ideas, events, etc., is symbolically defined by its description within physical data stores. A semantic data model is an abstraction
Abstraction is a process where general rules and concepts are derived from the use and classifying of specific examples, literal (reality, real or Abstract and concrete, concrete) signifiers, first principles, or other methods.
"An abstraction" ...
which defines how the stored symbols relate to the real world. Thus, the model must be a true representation of the real world.
The purpose of semantic data modeling is to create a structural model of a piece of the real world, called "universe of discourse". For this, three fundamental structural relations are considered:
* Classification/instantiation: Objects with some structural similarity are described as instances of classes
* Aggregation/decomposition: Composed objects are obtained by joining their parts
* Generalization/specialization: Distinct classes with some common properties are reconsidered in a more generic class with the common attributes
A semantic data model can be used to serve many purposes, such as:
* Planning of data resources
* Building of shareable databases
* Evaluation of vendor software
* Integration of existing databases
The overall goal of semantic data models is to capture more meaning of data by integrating relational concepts with more powerful abstraction
Abstraction is a process where general rules and concepts are derived from the use and classifying of specific examples, literal (reality, real or Abstract and concrete, concrete) signifiers, first principles, or other methods.
"An abstraction" ...
concepts known from the artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
field. The idea is to provide high-level modeling primitives as integral parts of a data model in order to facilitate the representation of real-world situations."Semantic data modeling" In: ''Metaclasses and Their Application''. Book Series Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Publisher Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. Volume Volume 943/1995.
See also
* Architectural pattern * Comparison of data modeling tools *Data (computer science)
''In computer science, data (treated as singular, plural, or as a mass noun) is any sequence of one or more symbols; datum is a single symbol of data. Data requires interpretation to become information. Digital data is data that is represen ...
* Data dictionary
A data dictionary, or metadata repository, as defined in the ''IBM Dictionary of Computing'', is a "centralized repository of information about data such as meaning, relationships to other data, origin, usage, and format". ''Oracle Corporation, ...
* Document modeling
* Enterprise data modelling
* Entity Data Model
* Information management
Information management (IM) is the appropriate and optimized capture, storage, retrieval, and use of information. It may be personal information management or organizational. Information management for organizations concerns a cycle of organiz ...
* Information model
An information model in software engineering is a representation of concepts and the relationships, constraints, rules, and Operation (mathematics), operations to specify Semantic data model, data semantics for a chosen domain of discourse. Typica ...
* Building information modeling
Building information modeling (BIM) is an approach involving the generation and management of digital representations of the physical and functional characteristics of buildings or other physical assets and facilities. BIM is supported by vario ...
* Metadata modeling
* Three-schema approach
* Zachman Framework
References
*Further reading
* * John Vincent Carlis, Joseph D. Maguire (2001). ''Mastering Data Modeling: A User-driven Approach''. * Alan Chmura, J. Mark Heumann (2005). ''Logical Data Modeling: What it is and how to Do it''. * Martin E. Modell (1992). ''Data Analysis, Data Modeling, and Classification''. * M. Papazoglou, Stefano Spaccapietra, Zahir Tari (2000). ''Advances in Object-oriented Data Modeling''. * G. Lawrence Sanders (1995). ''Data Modeling'' * Graeme C. Simsion, Graham C. Witt (2005). ''Data Modeling Essentials * Matthew West (2011) ''Developing High Quality Data Models''External links
Agile/Evolutionary Data Modeling
Data modeling articles
Database Modelling in UML
Notes on by Tony Drewry
Request For Proposal - Information Management Metamodel (IMM)
of the Object Management Group
Data Modeling is NOT just for DBMS's Part 1
Chris Bradley
Data Modeling is NOT just for DBMS's Part 2
Chris Bradley {{DEFAULTSORT:Data Modeling