DRAKON on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
DRAKON () is a
/ref> The goal was to replace specialized languages used in the Buran project with one universal
 DRAKON (; meaning "
DRAKON (; meaning "
 With DRAKON, the reader of the algorithm can visually trace all possible paths in the decision tree.
With DRAKON, the reader of the algorithm can visually trace all possible paths in the decision tree.
 The ''noProjectile'' function handles the specific situation when there is no falling projectile. If there is a filled row, that row is removed from the grid. Otherwise, the game tries to insert a new projectile. If there is no space for the projectile, the game is lost.
The ''noProjectile'' function handles the specific situation when there is no falling projectile. If there is a filled row, that row is removed from the grid. Otherwise, the game tries to insert a new projectile. If there is no space for the projectile, the game is lost.
 The ''clearRow'' function scans all rows bottom-up until it hits a row with no gaps. In such case the row is removed from the grid, the score is increased, and the game's tempo goes up.
The ''clearRow'' function scans all rows bottom-up until it hits a row with no gaps. In such case the row is removed from the grid, the score is increased, and the game's tempo goes up.

Example of medical program for reducing body fat (in Russian)
/ref>
Как улучшить работу ума. Алгоритмы без программистов - это очень просто! М.: Дело, 2001. - 360с.
* S. Mitkin
DRAKON: The Human Revolution in Understanding Programs
About the DRAKON language in English
DRAKON Editor
at
free and open source
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term encompassing free ...
algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
ic visual programming
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create programs by manipulating prog ...
and modeling language
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express data, information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in ...
developed as part of the defunct Soviet Union Buran space program in 1986 following the need in increase of software development productivity. The visual language provides a uniform way to represent processes in flowchart
A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task.
The flowchart shows the steps as boxes of v ...
s.
There are various implementation of the language specification that may be used to draw and export actual flowcharts. Notable examples include free and open source DRAKON Editor (September 2011).
History
The development of DRAKON started in 1986 to address the emerging risk of misunderstandings - and subsequent errors - between users of different programming languages in the Russian space program. Its development was directed by Vladimir Parondzhanov with the participation of theRussian Federal Space Agency
The State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos (), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research.
Originating from ...
( Academician Pilyugin Center, Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
) and Russian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such ...
( Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics).
The language was constructed by formalization, ergonomization and nonclassical structurization of flowchart
A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task.
The flowchart shows the steps as boxes of v ...
s described in the ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
5807-85 standard and Russian standard «Гост 19.701-90».Окулова Л. П. Проектирование образовательного процесса в соответствии с требованиями педагогической эргономики // Вестник. Наука и практика. Материалы конференции «Инновации и научные исследования, а также их применение на практике \ Innowacje i badania naukowe, jak rowniez ich zastosowanie w praktyce. — 29.05.2012- 31.05.2012. Варшава \ Warszaw»./ref> The goal was to replace specialized languages used in the Buran project with one universal
programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs.
Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ...
. Namely PROL2 (ПРОЛ2), used for developing inflight systems software for the computer system Biser-4 (Бисер-4),Штурманы ракет / Под общей редакцией Е. Л. Межирицкого. — М.: БЛОК-Информ-Экспресс, 2008. — 384 с. — C. 192. — DIPOL (ДИПОЛЬ), used for developing software for the ground maintenance computer systems) and LAKS (ЛАКС), used for modelling.
The work was finished in 1996 (3 years after the Buran project was officially closed), when an automated CASE
Case or CASE may refer to:
Instances
* Instantiation (disambiguation), a realization of a concept, theme, or design
* Special case, an instance that differs in a certain way from others of the type
Containers
* Case (goods), a package of relate ...
programming system called "Grafit-Floks" was developed.
This CASE is used since 1996 in: an international project Sea Launch
Sea Launch was a multinational—Norway, Russia, Ukraine, United States—spacecraft launch company founded in 1995 that provided orbital launch services from 1999 to 2014. The company used a mobile maritime launch platform for equatorial l ...
, Russian orbit insertion upper stage Fregat
Fregat () is an upper stage developed by NPO Lavochkin for universal compatibility with a wide range of medium- and heavy-lift launch vehicles. Fregat has been used primarily with Soyuz and Zenit rockets, and entered operational service in ...
(Russian: Фрегат, frigate) for onboard control systems and tests, upgraded heavy launch vehicle
A launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload (a crewed spacecraft or satellites) from Earth's surface or lower atmosphere to outer space. The most common form is the ballistic missile-shaped multistage ...
(carrier rocket) Proton-M
The Proton-M, (Протон-М) GRAU index 8K82M or , is an Expendable launch system, expendable Russian heavy-lift launch vehicle derived from the Soviet Union, Soviet-developed Proton (rocket family), Proton. It is built by Khrunichev State R ...
.
Overview
The name DRAKON is the Russian acronym for "Дружелюбный Русский Алгоритмический �зык Который Обеспечивает Наглядность", which translates to "Friendly Russian Algorithmic anguagethat illustrates (or provides clarity)". The word "наглядность" (pronounced approximately as "na-GLYA-dnost") refers to a concept or idea being easy to imagine and understand, and may be translated as "clarity". Unlike UML's philosophy, DRAKON's language philosophy is based on being augmented if needed, by using a hybrid language, which can be illustrated as "incrustating code snippets from text language used into shape DRAKON requires". This way, DRAKON always remains a simple visual language that can be used as an augmentation for a programmer who is interested in making their own project code easier to support or other long-term needs for example improving the ergonomics of the coding process or to making code easier to review and understand. The DRAKON language can be used both as a modelling/"markup" language (which is considered a standalone "pure DRAKON" program) and as a programming language (as part of a hybrid language). Integration of a stricter, "academic", variant of a markup language into programming, such as provided by DRAKON, addssyntactic sugar
In computer science, syntactic sugar is syntax within a programming language that is designed to make things easier to read or to express. It makes the language "sweeter" for human use: things can be expressed more clearly, more concisely, or in an ...
allowing users of different programming languages to comprehend each other's contributions to the overall project and even provide commentary if needed.
Family of DRAKON languages
dragon
A dragon is a Magic (supernatural), magical legendary creature that appears in the folklore of multiple cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but European dragon, dragons in Western cultures since the Hi ...
" in English) is designed with the intent of allowing for easy understanding and legibility, as usage of multiple languages in a single project can lead to confusion.
DRAKON is a family of hybrid languages, such as DRAKON-C, DRAKON-ASM, DRAKON-Java, etc. All languages of the DRAKON-family share a uniform, graphical syntax based on flowcharts. The standard graphical syntax provides similarity of drakon-charts for different hybrid languages. The text language uses its own syntax.
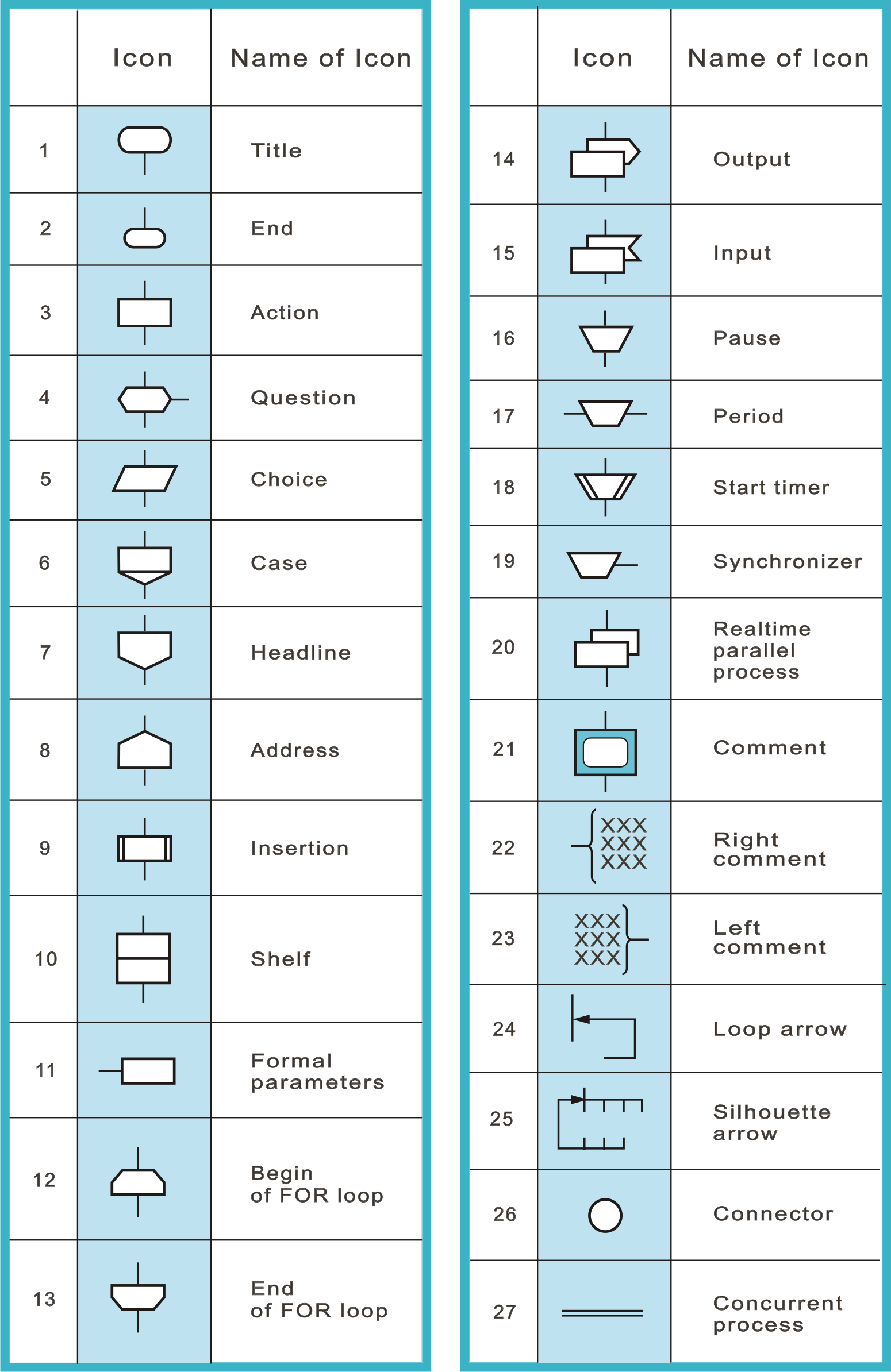
The basis of the graphical syntax is a graphical alphabet. Graphical elements ("letters") of the DRAKON alphabet are called ''icons'' (not symbols). DRAKON also has ''macroicons''. Macroicons are the graphical words of the DRAKON language; they consist of icons. There are 27 icons and 21 macroicons in the DRAKON language.
Drakon-charts are constructed out of icons and macroicons.
The important parts of maсroiсons are valence points (in the illustration depicted as black circles). Into these points, icons or microicons can be successively entered and arranged by the drakon-editor into columns.
Design
DRAKON was created as an easy to learn visual language to aid the comprehension of computer programs written in different programming languages for illustrative, planning and strategy purposes. DRAKON uses drakon-chart, which is a formalization of traditional flowcharts to depict the overall structure of the program. Code snippets of a programming language are added to the DRAKON icons. The combination of visual elements with code helps with the creation and maintenance of readable flowcharts alongside the development of the program in question. DRAKON rules for creating diagrams are cognitively optimized for easy comprehension, making it a tool for intelligence augmentation. вузов". ''Учись писать, читать и понимать алгоритмы. Алгоритмы для правильного мышления. Основы алгоритмизации''. М.: ДМК Пресс. p. 520. . Drakon-charts of big multi-purpose programs can be complex and hard to comprehend. A set of smaller programs, that together serve the same purpose, are often easier to understand when depicted as drakon-charts. A similar problem exists in maintaining code of large programs. This problem is occasionally referred to as "rule of 30 ines of code among programmers.Visual syntax
The full-text article containing description of the visual syntax of the DRAKON language in English, 12 pages, free to download, pdf.Examples
Tetris example
Simple example of a program in the DRAKON language These examples are real code from an implementation of theTetris
''Tetris'' () is a puzzle video game created in 1985 by Alexey Pajitnov, a Soviet software engineer. In ''Tetris'', falling tetromino shapes must be neatly sorted into a pile; once a horizontal line of the game board is filled in, it disa ...
game. The examples are in DRAKON-JavaScript language. The icons (visual primitives) of the DRAKON language define the overall structure of the algorithms. The code snippets inside the icons (primitives) are in JavaScript.
advanceStep
The ''advanceStep'' function implements the core logic of the game. ''advanceStep'' is astate machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number o ...
represented as a decision tree
A decision tree is a decision support system, decision support recursive partitioning structure that uses a Tree (graph theory), tree-like Causal model, model of decisions and their possible consequences, including probability, chance event ou ...
. The game engine calls ''advanceStep'' periodically. This state machine has three states "playing", "dropping", and "finished". The game takes different actions depending on the current state. For example, in the "playing" state, when there is a falling projectile and the projectile can move down, it is moved down one step.
 With DRAKON, the reader of the algorithm can visually trace all possible paths in the decision tree.
With DRAKON, the reader of the algorithm can visually trace all possible paths in the decision tree.
noProjectile
 The ''noProjectile'' function handles the specific situation when there is no falling projectile. If there is a filled row, that row is removed from the grid. Otherwise, the game tries to insert a new projectile. If there is no space for the projectile, the game is lost.
The ''noProjectile'' function handles the specific situation when there is no falling projectile. If there is a filled row, that row is removed from the grid. Otherwise, the game tries to insert a new projectile. If there is no space for the projectile, the game is lost.
clearRow
 The ''clearRow'' function scans all rows bottom-up until it hits a row with no gaps. In such case the row is removed from the grid, the score is increased, and the game's tempo goes up.
The ''clearRow'' function scans all rows bottom-up until it hits a row with no gaps. In such case the row is removed from the grid, the score is increased, and the game's tempo goes up.
DRAKON execution animation
The picture below illustrated the execution of the silhouette DRAKON algorithm. The algorithm execution is animated by highlighting diagram elements in the running order. The 'Fishing' silhouette consists of four trees: * Preparing for fishing. * Waiting for a bite. * Fishing work. * Way back. The main path of each tree is shown by highlighting thick vertical line which is called a ''skewer.'' The flow graph always has a path from the Headline icon to each vertex (node) of the control flow graph. Consequently, a silhouette can't have unreachable code in any conditions.
Modern usage
DRAKON in the German Aerospace Center
DRAKON language is used in theGerman Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (, abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany, founded in 1969. It is headquartered in Cologne with 3 ...
for implementation of some critical functions dictated by the safety regulations of the flight tests, where automation is important because of maximum distance to the ground station and the process needs quick automatic execution.
The DRAKON Editor software was used to graphically program flowcharts which were specially checked. C-code was generated from the drakon-charts, for instance, for a DRAKON representation of code for launch detection.
Business processes modelling
The DRAKON language may be used as the language to model and visualize business processes. "The DRAKON language was applied as the basic language for constructing models of business processes, which makes it possible to obtain a prototype of a finite-state machine when building models of business processes. The visualization of business processes in the state space allows the decision maker to improve the efficiency of the decision-making".Uses outside of programming
While DRAKON is primarily designed as a tool for comprehending computer programs, drakon-charts can also be used to illustrate processes in fields not related to computing. In the DRAKON editor pictures can be added to the DRAKON icons. This ability is used in some fields to easily create "flowchart like"infographics
Infographics (a clipped compound of "information" and "graphics") are graphic visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly.Doug Newsom and Jim Haynes (2004). ''Public Relations Wri ...
. In Russia the DRAKON editor is known for being used in the medical field as a tool for making 'instructional' charts for patients or medical personnel./ref>
See also
* ERILReferences
Sources
* V. Parondzhanov. ''How to improve the work of your mind. Algorithms without programmers - it's very simple!''Как улучшить работу ума. Алгоритмы без программистов - это очень просто! М.: Дело, 2001. - 360с.
* S. Mitkin
DRAKON: The Human Revolution in Understanding Programs
External links
{{commons categoryAbout the DRAKON language in English
DRAKON Editor
at
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug trackin ...
Visual programming languages
Buran program
Computing in the Soviet Union
Diagramming software
Modeling languages