DMAD on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate (DMAD) is an organic compound with the formula CH3O2CC2CO2CH3. It is a di- ester in which the ester groups are conjugated with a C-C triple bond. As such, the molecule is highly
electrophilic
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carri ...
, and is widely employed as a dienophile in cycloaddition reactions, such as the Diels-Alder reaction. It is also a potent Michael acceptor. This compound exists as a colorless liquid at room temperature. This compound was used in the preparation of nedocromil.
Preparation
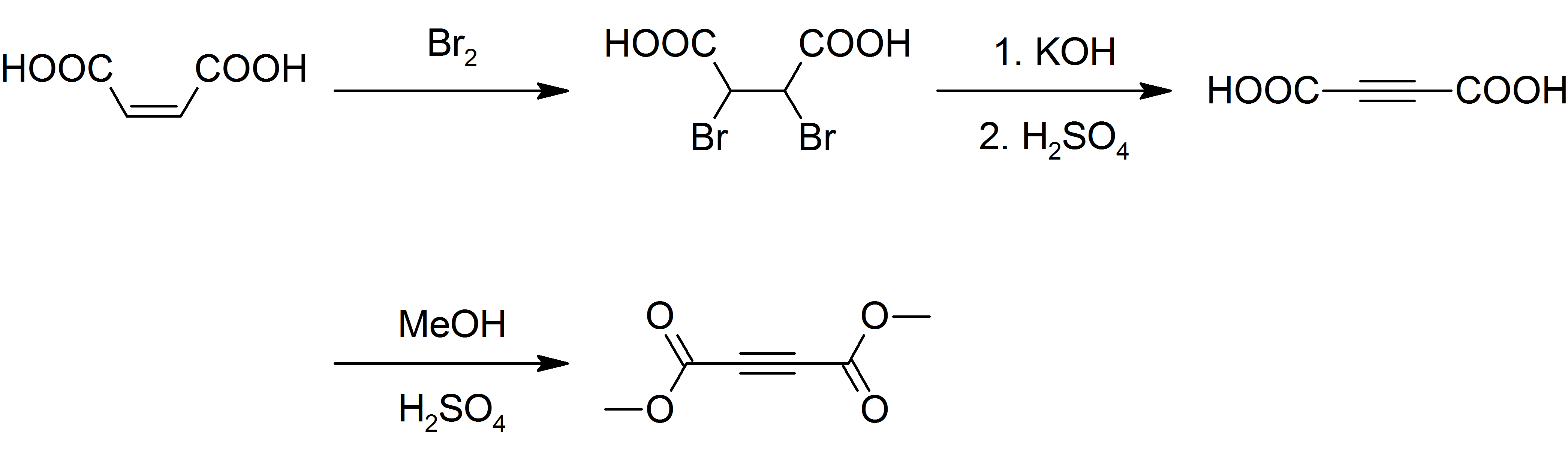
Although inexpensively available, DMAD is prepared today as it was originally. Maleic acid is brominated and the resulting dibromo succinic acid is dehydrohalogenated with potassium hydroxide yieldingacetylenedicarboxylic acid
Acetylenedicarboxylic acid or butynedioic acid is an organic compound (a dicarboxylic acid) with the formula C4H2O4 or . It is a crystalline solid that is soluble in diethyl ether.
The removal of two protons yields the acetylenedicarboxylate dian ...
. The acid is then esterified
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fa ...
with methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a ...
and sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
as a catalyst:
:
Safety
DMAD is a lachrymator and avesicant
A blister agent (or vesicant), is a chemical compound that causes severe skin, eye and mucosal pain and irritation. They are named for their ability to cause severe chemical burns, resulting in painful water blisters on the bodies of those affec ...
.
References
{{Reflist Alkyne derivatives Methyl esters Carboxylate esters