cyclopropenyl cation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula . It has attracted attention as the smallest example of an
The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula . It has attracted attention as the smallest example of an

 The parent cation, 3H3sup>+, was reported as its hexachloroantimonate () salt in 1970. It is indefinitely stable at −20 °C.
Trichlorocyclopropenium salts are generated by chloride abstraction from
The parent cation, 3H3sup>+, was reported as its hexachloroantimonate () salt in 1970. It is indefinitely stable at −20 °C.
Trichlorocyclopropenium salts are generated by chloride abstraction from 

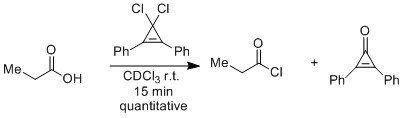 Related cyclopropenium cations are produced in the regeneration of the 1,1-dichlorocyclopropenes from the
Related cyclopropenium cations are produced in the regeneration of the 1,1-dichlorocyclopropenes from the  This method of mildly generating acid chlorides can also be useful for linking alpha-
This method of mildly generating acid chlorides can also be useful for linking alpha- Additionally, some synthetic routes make use of cyclopropenium ring openings yielding an allylcarbene cation. The linear degradation product yields both a nucleophilic and electrophilic carbon centers.
:
Additionally, some synthetic routes make use of cyclopropenium ring openings yielding an allylcarbene cation. The linear degradation product yields both a nucleophilic and electrophilic carbon centers.
:
 Many complexes are known with cyclopropenium ligands. Examples include (C3Ph3)(PPh3)2sup>+ (M = Ni, Pd, Pt) and Co(C3Ph3)(CO)3. Such compounds are prepared by reaction of cyclopropenium salts with low valent
Many complexes are known with cyclopropenium ligands. Examples include (C3Ph3)(PPh3)2sup>+ (M = Ni, Pd, Pt) and Co(C3Ph3)(CO)3. Such compounds are prepared by reaction of cyclopropenium salts with low valent
 The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula . It has attracted attention as the smallest example of an
The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula . It has attracted attention as the smallest example of an aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to satur ...
cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
. Its salts have been isolated, and many derivatives have been characterized by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
. The cation and some simple derivatives have been identified in the atmosphere of the Saturnian moon Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
.
Bonding
With two π electrons, the cyclopropenium cation class obeys Hückel’s rules of aromaticity for electrons since, in this case, ''n'' = 0. Consistent with this prediction, the C3H3 core is planar and the C–C bonds are equivalent. In the case of the cation in 3(SiMe3)3sup>+, the ring C–C distances range from 1.374(2) to 1.392(2) Å.
Syntheses
Salts of many cyclopropenyl cations have been characterized. Their stability varies according to the steric and inductive effects of the substituents. Salts of triphenylcyclopropenium were first reported byRonald Breslow
Ronald Charles David Breslow (March 14, 1931 – October 25, 2017) was an American chemist from Rahway, New Jersey. He was University Professor at Columbia University, where he was based in the Department of Chemistry and affiliated with the De ...
in 1957. The salt was prepared in two steps starting with the reaction of phenyldiazoacetonitrile with diphenylacetylene
Diphenylacetylene is the chemical compound C6H5C≡CC6H5. The molecule consists of two phenyl groups attached to a C2 unit. A colorless solid, it is used as a building block in organic synthesis and as a ligand in organometallic chemistry.
Prepar ...
to yield 1,2,3-triphenyl-2-cyclopropene nitrile. Treatment of this with boron trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula BF3. This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds.
Structure and bond ...
yielded 3Ph3F4.
: The parent cation, 3H3sup>+, was reported as its hexachloroantimonate () salt in 1970. It is indefinitely stable at −20 °C.
Trichlorocyclopropenium salts are generated by chloride abstraction from
The parent cation, 3H3sup>+, was reported as its hexachloroantimonate () salt in 1970. It is indefinitely stable at −20 °C.
Trichlorocyclopropenium salts are generated by chloride abstraction from tetrachlorocyclopropene
Tetrachlorocyclopropene is a chemical compound with the formula C3Cl4. A colorless liquid, the compound is a reagent used to prepare acetylene derivatives and in organic synthesis. It is prepared by addition of dichlorocarbene to trichloroethyle ...
:
:C3Cl4 + AlCl3 → 3Cl3sup>+
Tetrachlorocyclopropene
Tetrachlorocyclopropene is a chemical compound with the formula C3Cl4. A colorless liquid, the compound is a reagent used to prepare acetylene derivatives and in organic synthesis. It is prepared by addition of dichlorocarbene to trichloroethyle ...
can be converted to tris(''tert''-butyldimethylsilyl)cyclopropene. Hydride abstraction with nitrosonium tetrafluoroborate
Nitrosonium tetrafluoroborate, also called nitrosyl tetrafluoroborate, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula NOBF4. This colourless solid is used in organic synthesis as a nitrosating agent.
NOBF4 is the nitrosonium salt of fluorob ...
yields the trisilyl-substituted cyclopropenium cation.
:
Amino
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent ...
-substituted cyclopropenium salts are particularly stable. Calicene
Calicene or triapentafulvalene is a hydrocarbon of the fulvalene class with chemical formula C8H6, composed of a cyclopentadiene ring and a cyclopropene ring linked by a double bond. Its name is derived from the Latin ''calix'' meaning "goblet", ...
is an unusual derivative featuring cyclopropenium linked to a cyclopentadienide
In chemistry, the cyclopentadienyl anion or cyclopentadienide is an aromatic species with a formula of and abbreviated as Cp−. It is formed from the deprotonation of the molecule cyclopentadiene.
Properties
The cyclopentadienyl anion i ...
.
:
Reactions
Organic chemistry
Chloride salts of cyclopropenium esters are intermediates in the use of dichlorocyclopropenes for the conversion ofcarboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxyli ...
s to acid chloride
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group . Their formula is usually written , where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids (). A specific example o ...
s:
: Related cyclopropenium cations are produced in the regeneration of the 1,1-dichlorocyclopropenes from the
Related cyclopropenium cations are produced in the regeneration of the 1,1-dichlorocyclopropenes from the cyclopropenone
Cyclopropenone is an organic compound with molecular formula C3H2O consisting of a cyclopropene carbon framework with a ketone functional group. It is a colorless, volatile liquid that boils near room temperature. Neat cyclopropenone polymerizes u ...
s.
The cyclopropenium chlorides have been applied to peptide bond formation. For example, in the figure below, reacting a boc-protected amino acid with an unprotected amino acid in the presence of the cyclopropenium ion allows the formation of a peptide bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
via acid chloride formation followed by nucleophilic substitution with the unprotected amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
.
: This method of mildly generating acid chlorides can also be useful for linking alpha-
This method of mildly generating acid chlorides can also be useful for linking alpha-anomeric
In carbohydrate chemistry, a pair of anomers () is a pair of near-identical stereoisomers that differ at only the anomeric carbon, the carbon that bears the aldehyde or ketone functional group in the sugar's open-chain form. However, in order fo ...
sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
s. After using the cyclopropenium ion to form the chloride at the anomeric carbon
In carbohydrate chemistry, a pair of anomers () is a pair of near-identical stereoisomers that differ at only the anomeric carbon, the carbon that bears the aldehyde or ketone functional group in the sugar's open-chain form. However, in order for ...
, the compound is iodinated with tetrabutylammonium iodide
Tetrabutylammonium is a quaternary ammonium cation with the formula (C4H9)4sup>+. It is used in the research laboratory to prepare lipophilic salts of inorganic anions. Relative to tetraethylammonium derivatives, tetrabutylammonium salts are more ...
. This iodine can thereafter be substituted by any ROH group to quickly undergo alpha-selective linkage of sugars.
: Additionally, some synthetic routes make use of cyclopropenium ring openings yielding an allylcarbene cation. The linear degradation product yields both a nucleophilic and electrophilic carbon centers.
:
Additionally, some synthetic routes make use of cyclopropenium ring openings yielding an allylcarbene cation. The linear degradation product yields both a nucleophilic and electrophilic carbon centers.
:
Organometallic compounds
 Many complexes are known with cyclopropenium ligands. Examples include (C3Ph3)(PPh3)2sup>+ (M = Ni, Pd, Pt) and Co(C3Ph3)(CO)3. Such compounds are prepared by reaction of cyclopropenium salts with low valent
Many complexes are known with cyclopropenium ligands. Examples include (C3Ph3)(PPh3)2sup>+ (M = Ni, Pd, Pt) and Co(C3Ph3)(CO)3. Such compounds are prepared by reaction of cyclopropenium salts with low valent metal complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many ...
es.
As polyelectrolytes
Because many substituted derivatives are known, cyclopropenium salts have attracted attention as possiblepolyelectrolytes
Polyelectrolytes are polymers whose repeating units bear an electrolyte group. Polycations and polyanions are polyelectrolytes. These groups dissociate in aqueous solutions (water), making the polymers charged. Polyelectrolyte properties are ...
, relevant to technologies such as desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in soil desalination, which is an issue for agriculture. Salt ...
and fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
s. The tris(dialkylamino)cyclopropenium salts have been particularly evaluated because of their high stability.
See also
*Phosphirenium ion
Phosphirenium ions () are a series of organophosphorus compounds containing unsaturated three-membered ring phosphorus (V) Heterocyclic compound, heterocycles and σ*-aromaticity is believed to be present in such molecules. Many of the salts conta ...
References
{{reflist Non-benzenoid aromatic carbocycles Cations Cyclopropenes