Currencies of the United States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A currency, "in circulation", from la, currens, -entis, literally meaning "running" or "traversing" is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a
 Originally currency was a form of receipt, representing grain stored in temple granaries in Sumer in ancient Mesopotamia and in Ancient Egypt.
In this first stage of currency, metals were used as symbols to represent value stored in the form of commodities. This formed the basis of trade in the Fertile Crescent for over 1500 years. However, the collapse of the Near Eastern trading system pointed to a flaw: in an era where there was no place that was safe to store value, the value of a circulating medium could only be as sound as the forces that defended that store. A trade could only reach as far as the credibility of that military. By the late
Originally currency was a form of receipt, representing grain stored in temple granaries in Sumer in ancient Mesopotamia and in Ancient Egypt.
In this first stage of currency, metals were used as symbols to represent value stored in the form of commodities. This formed the basis of trade in the Fertile Crescent for over 1500 years. However, the collapse of the Near Eastern trading system pointed to a flaw: in an era where there was no place that was safe to store value, the value of a circulating medium could only be as sound as the forces that defended that store. A trade could only reach as far as the credibility of that military. By the late
 Most major economies using coinage had several tiers of coins of different values, made of copper, silver, and gold. Gold coins were the most valuable and were used for large purchases, payment of the military, and backing of state activities. Units of account were often defined as the value of a particular type of gold coin. Silver coins were used for midsized transactions, and sometimes also defined a unit of account, while coins of copper or silver, or some mixture of them (see debasement), might be used for everyday transactions. This system had been used in ancient India since the time of the
Most major economies using coinage had several tiers of coins of different values, made of copper, silver, and gold. Gold coins were the most valuable and were used for large purchases, payment of the military, and backing of state activities. Units of account were often defined as the value of a particular type of gold coin. Silver coins were used for midsized transactions, and sometimes also defined a unit of account, while coins of copper or silver, or some mixture of them (see debasement), might be used for everyday transactions. This system had been used in ancient India since the time of the
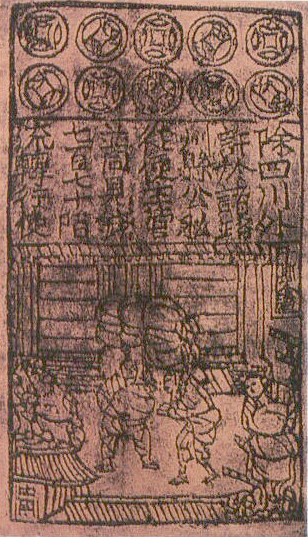 At around the same time in the
At around the same time in the
 The currency used is based on the concept of lex monetae; that a sovereign state decides which currency it shall use. The International Organization for Standardization has introduced a system of three-letter codes (
The currency used is based on the concept of lex monetae; that a sovereign state decides which currency it shall use. The International Organization for Standardization has introduced a system of three-letter codes (

 In most cases, a
In most cases, a
Tracker Monthly reporting and statistics on renminbi(RMB) progress towards becoming an international currency
/ref>
medium of exchange
In economics, a medium of exchange is any item that is widely acceptable in exchange for goods and services. In modern economies, the most commonly used medium of exchange is currency.
The origin of "mediums of exchange" in human societies is as ...
, for example banknote
A banknote—also called a bill ( North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issue ...
s and coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to ...
s.
A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound Sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
(US$)) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all asp ...
s, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance - i.e. legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies.
Other definitions of the term "currency" appear in the respective synonymous articles: banknote
A banknote—also called a bill ( North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issue ...
, coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to ...
, and money. This article uses the definition which focuses on the currency systems of countries.
One can classify currencies into three monetary systems: fiat money
Fiat money (from la, fiat, "let it be done") is a type of currency that is not backed by any commodity such as gold or silver. It is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tender. Throughout history, fiat money was somet ...
, commodity money
Commodity money is money whose value comes from a commodity of which it is made. Commodity money consists of objects having value or use in themselves (intrinsic value) as well as their value in buying goods.
This is in contrast to representati ...
, and representative money
Representative money or receipt money is any medium of exchange, printed or digital, that represents something of value, but has little or no value of its own (intrinsic value). Unlike some forms of fiat money (which may have no commodity backi ...
, depending on what guarantees a currency's value (the economy at large vs. the government's physical metal reserves). Some currencies function as legal tender in certain jurisdictions, or for specific purposes, such as payment to a government ( taxes), or government agencies (fees, fines). Others simply get traded for their economic value.
Digital currency
Digital currency (digital money, electronic money or electronic currency) is any currency, money, or money-like asset that is primarily managed, stored or exchanged on digital computer systems, especially over the internet. Types of digital cu ...
has arisen with the popularity of computers and the Internet. Whether digital notes and coins will be successfully developed remains dubious. Decentralized digital currencies, such as cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it. It i ...
are different as they are not issued by a government monetary authority
In finance and economics, a monetary authority is the entity that manages a country’s currency and money supply, often with the objective of controlling inflation, interest rates, real GDP or unemployment rate. With its monetary tools, a mone ...
. Many warnings issued by various countries note the opportunities that cryptocurrencies create for illegal activities, such as money laundering and terrorism.
In 2014 the United States IRS issued a statement explaining that virtual currency is treated as property for Federal income-tax purposes and providing examples of how longstanding tax principles applicable to transactions involving property apply to virtual currency.
History
Early currency
 Originally currency was a form of receipt, representing grain stored in temple granaries in Sumer in ancient Mesopotamia and in Ancient Egypt.
In this first stage of currency, metals were used as symbols to represent value stored in the form of commodities. This formed the basis of trade in the Fertile Crescent for over 1500 years. However, the collapse of the Near Eastern trading system pointed to a flaw: in an era where there was no place that was safe to store value, the value of a circulating medium could only be as sound as the forces that defended that store. A trade could only reach as far as the credibility of that military. By the late
Originally currency was a form of receipt, representing grain stored in temple granaries in Sumer in ancient Mesopotamia and in Ancient Egypt.
In this first stage of currency, metals were used as symbols to represent value stored in the form of commodities. This formed the basis of trade in the Fertile Crescent for over 1500 years. However, the collapse of the Near Eastern trading system pointed to a flaw: in an era where there was no place that was safe to store value, the value of a circulating medium could only be as sound as the forces that defended that store. A trade could only reach as far as the credibility of that military. By the late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
, however, a series of treaties had established safe passage for merchants around the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to commun ...
, spreading from Minoan Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cypru ...
and Mycenae in the northwest to Elam and Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an a ...
in the southeast. It is not known what was used as a currency for these exchanges, but it is thought that ox-hide shaped ingots of copper, produced in Cyprus, may have functioned as a currency.
It is thought that the increase in piracy and raiding associated with the Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near Eas ...
, possibly produced by the Peoples of the Sea, brought the trading system of oxhide ingots to an end. It was only the recovery of Phoenician trade in the 10th and 9th centuries BC that led to a return to prosperity, and the appearance of real coinage, possibly first in Anatolia with Croesus
Croesus ( ; Lydian: ; Phrygian: ; grc, Κροισος, Kroisos; Latin: ; reigned: c. 585 – c. 546 BC) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC.
Croesus was r ...
of Lydia and subsequently with the Greeks and Persians. In Africa, many forms of value store have been used, including beads, ingots, ivory, various forms of weapons, livestock, the manilla currency, and ochre and other earth oxides. The manilla rings of West Africa were one of the currencies used from the 15th century onwards to sell slaves. African currency is still notable for its variety, and in many places, various forms of barter
In trade, barter (derived from ''baretor'') is a system of exchange in which participants in a transaction directly exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using a medium of exchange, such as money. Economists distingu ...
still apply.
Coinage
The prevalence of metal coins possibly led to the metal itself being the store of value: first copper, then both silver and gold, and at one point also bronze. Today other non-precious metals are used for coins. Metals were mined, weighed, and stamped into coins. This was to assure the individual accepting the coin that he was getting a certain known weight of precious metal. Coins could be counterfeited, but the existence of standard coins also created a new unit of account, which helped lead tobanking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Because ...
. Archimedes' principle
Archimedes' principle (also spelled Archimedes's principle) states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. Archimedes ...
provided the next link: coins could now be easily tested for their fine weight of the metal, and thus the value of a coin could be determined, even if it had been shaved, debased or otherwise tampered with (see Numismatics).
 Most major economies using coinage had several tiers of coins of different values, made of copper, silver, and gold. Gold coins were the most valuable and were used for large purchases, payment of the military, and backing of state activities. Units of account were often defined as the value of a particular type of gold coin. Silver coins were used for midsized transactions, and sometimes also defined a unit of account, while coins of copper or silver, or some mixture of them (see debasement), might be used for everyday transactions. This system had been used in ancient India since the time of the
Most major economies using coinage had several tiers of coins of different values, made of copper, silver, and gold. Gold coins were the most valuable and were used for large purchases, payment of the military, and backing of state activities. Units of account were often defined as the value of a particular type of gold coin. Silver coins were used for midsized transactions, and sometimes also defined a unit of account, while coins of copper or silver, or some mixture of them (see debasement), might be used for everyday transactions. This system had been used in ancient India since the time of the Mahajanapadas
The Mahājanapadas ( sa, great realm, from ''maha'', "great", and '' janapada'' "foothold of a people") were sixteen kingdoms or oligarchic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second ur ...
. The exact ratios between the values of the three metals varied greatly between different eras and places; for example, the opening of silver mines in the Harz mountains of central Europe made silver relatively less valuable, as did the flood of New World silver after the Spanish conquests. However, the rarity of gold consistently made it more valuable than silver, and likewise silver was consistently worth more than copper.
Paper money
Inpremodern
The term premodern refers to the period in human history immediately preceding the modern era, as well as the conceptual framework in the humanities and social sciences relating to the artistic, literary and philosophical practices which precede ...
China, the need for lending and for a medium of exchange that was less physically cumbersome than large numbers of copper coins led to the introduction of paper money, i.e. banknote
A banknote—also called a bill ( North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issue ...
s. Their introduction was a gradual process that lasted from the late Tang dynasty (618–907) into the Song dynasty (960–1279). It began as a means for merchants to exchange heavy coinage for receipt
A receipt (also known as a packing list, packing slip, packaging slip, (delivery) docket, shipping list, delivery list, bill of the parcel, manifest, or customer receipt) is a document acknowledging that a person has received money or proper ...
s of deposit issued as promissory notes by wholesaler
Wholesaling or distributing is the sale of goods or merchandise to retailers; to industrial, commercial, institutional or other professional business users; or to other wholesalers (wholesale businesses) and related subordinated services. In ...
s' shops. These notes were valid for temporary use in a small regional territory. In the 10th century, the Song dynasty government began to circulate these notes amongst the traders in its monopolized salt industry. The Song government granted several shops the right to issue banknotes, and in the early 12th century the government finally took over these shops to produce state-issued currency. Yet the banknotes issued were still only locally and temporarily valid: it was not until the mid 13th century that a standard and uniform government issue of paper money became an acceptable nationwide currency. The already widespread methods of woodblock printing and then Bi Sheng
Bi Sheng (; 972–1051 AD) was a Chinese artisan, engineer, and inventor of the world's first movable type technology, with printing being one of the Four Great Inventions. Bi Sheng's system was made of Chinese porcelain and was invented betwe ...
's movable type printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The e ...
by the 11th century were the impetus for the mass production of paper money in premodern China.
 At around the same time in the
At around the same time in the medieval Islamic world
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
, a vigorous monetary economy
Monetary economics is the branch of economics that studies the different competing theories of money: it provides a framework for analyzing money and considers its functions (such as medium of exchange, store of value and unit of account), and it ...
was created during the 7th–12th centuries on the basis of the expanding levels of circulation of a stable high-value currency (the dinar
The dinar () is the principal currency unit in several countries near the Mediterranean Sea, and its historical use is even more widespread.
The modern dinar's historical antecedents are the gold dinar and the silver dirham, the main coin of ...
). Innovations introduced by Muslim economists, traders and merchants include the earliest uses of credit, cheque
A cheque, or check (American English; see spelling differences) is a document that orders a bank (or credit union) to pay a specific amount of money from a person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued. The per ...
s, promissory notes, savings accounts, transaction accounts, loaning, trusts, exchange rates, the transfer of credit and debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The d ...
, and banking institution
Financial institutions, sometimes called banking institutions, are business entities that provide services as intermediaries for different types of financial monetary transactions. Broadly speaking, there are three major types of financial insti ...
s for loans and deposits
A deposit account is a bank account maintained by a financial institution in which a customer can deposit and withdraw money. Deposit accounts can be savings accounts, current accounts or any of several other types of accounts explained below. ...
.
In Europe, paper currency was first introduced on a regular basis in Sweden in 1661 (although Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories " Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and "The Legen ...
records an earlier emergency use of it, by the Spanish in a siege during the Conquest of Granada
The Granada War ( es, Guerra de Granada) was a series of military campaigns between 1482 and 1491 during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, against the Nasrid dynasty's Emirate of Granada. It e ...
). As Sweden was rich in copper, many copper coins were in circulation, but its relatively low value necessitated extraordinarily big coins, often weighing several kilograms.
The advantages of paper currency were numerous: it reduced the need to transport gold and silver, which was risky; it facilitated loans of gold or silver at interest, since the underlying specie (money in the form of gold or silver coins rather than notes) never left the possession of the lender until someone else redeemed the note; and it allowed a division of currency into credit- and specie-backed forms. It enabled the sale of stock in joint-stock companies
A joint-stock company is a business entity in which shares of the company's stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their shares (certificates of ownership). Shareholders are ...
and the redemption of those shares in a paper.
But there were also disadvantages. First, since a note has no intrinsic value, there was nothing to stop issuing authorities from printing more notes than they had specie to back them with. Second, because this increased the money supply, it increased inflationary pressures, a fact observed by David Hume in the 18th century. Thus paper money would often lead to an inflationary bubble, which could collapse if people began demanding hard money, causing the demand for paper notes to fall to zero. The printing of paper money was also associated with wars, and financing of wars, and therefore regarded as part of maintaining a standing army. For these reasons, paper currency was held in suspicion and hostility in Europe and America. It was also addictive since the speculative profits of trade and capital creation were quite large. Major nations established mints
A mint or breath mint is a food item often consumed as an after-meal refreshment or before business and social engagements to improve breath odor. Mints are commonly believed to soothe the stomach given their association with natural byproducts ...
to print money and mint coins, and branches of their treasury to collect taxes and hold gold and silver stock.
At that time, both silver and gold were considered a legal tender and accepted by governments for taxes. However, the instability in the exchange rate between the two grew over the course of the 19th century, with the increases both in the supply of these metals, particularly silver, and in trade. The parallel use of both metals is called bimetallism
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a monetary standard in which the value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold and silver, creating a fixed rate of exchange betwe ...
, and the attempt to create a bimetallic standard where both gold and silver backed currency remained in circulation occupied the efforts of inflationists. Governments at this point could use currency as an instrument of policy, printing paper currency such as the United States greenback, to pay for military expenditures. They could also set the terms at which they would redeem notes for specie, by limiting the amount of purchase, or the minimum amount that could be redeemed.
By 1900, most of the industrializing nations were on some form of gold standard, with paper notes and silver coins constituting the circulating medium. Private bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Because ...
s and governments across the world followed Gresham's law: keeping the gold and silver they received but paying out in notes. This did not happen all around the world at the same time, but occurred sporadically, generally in times of war or financial crisis, beginning in the early 20th century and continuing across the world until the late 20th century, when the regime of floating fiat currencies came into force. One of the last countries to break away from the gold standard was the United States in 1971, an action which was known as the Nixon shock. No country has an enforceable gold standard or silver standard currency system.
Banknote era
Abanknote
A banknote—also called a bill ( North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issue ...
or bill is a type of currency and is commonly used as legal tender in many jurisdictions. Together with coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to ...
s, banknotes make up the cash
In economics, cash is money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.
In bookkeeping and financial accounting, cash is current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-imm ...
form of a currency. Banknotes were initially mostly paper, but Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency responsible for scientific research.
CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO ...
developed a polymer currency in the 1980s; it went into circulation on the nation's bicentenary in 1988. Polymer banknotes had already been introduced in the Isle of Man in 1983. As of 2016, polymer currency is used in over 20 countries (over 40 if counting commemorative issues), and dramatically increases the life span of banknotes and reduces counterfeiting.
Modern currencies
 The currency used is based on the concept of lex monetae; that a sovereign state decides which currency it shall use. The International Organization for Standardization has introduced a system of three-letter codes (
The currency used is based on the concept of lex monetae; that a sovereign state decides which currency it shall use. The International Organization for Standardization has introduced a system of three-letter codes (ISO 4217
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual cu ...
) to denote currency (as opposed to simple names or currency sign
A currency symbol or currency sign is a graphic symbol used to denote a currency unit. Usually it is defined by the monetary authority, like the national central bank for the currency concerned.
In formatting, the symbol can use various forma ...
s), in order to remove the confusion arising because there are dozens of currencies called the dollar and several called the franc. Even the "pound" is used in nearly a dozen different countries; most of these are tied to the pound sterling, while the remainder has varying values. In general, the three-letter code uses the ISO 3166-1 country code for the first two letters and the first letter of the name of the currency (D for dollar, for example) as the third letter. United States currency, for instance, is globally referred to as USD. Currencies such as the pound sterling have different codes, as the first two letters denote not the exact country name but an alternative name also used to describe the country. The pound's code is GBP where ''GB'' denotes Great Britain instead of the United Kingdom.
The former currencies include the marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks, trademarks owned by an organisation for the benefit of its members
* Marks & Co, the inspiration for the novel '' ...
that were in circulation in Germany and Finland.
The International Monetary Fund uses a different system when referring to national currencies.
Alternative currencies
Distinct from centrally controlled government-issued currencies, private decentralized trust-reduced networks support alternative currencies such asCardano (blockchain platform)
Cardano is a public blockchain platform. It is open-source and decentralized, with consensus achieved using proof of stake. It can facilitate peer-to-peer transactions with its internal cryptocurrency, ADA.
Cardano's development began in 2015 ...
, bitcoin, Ethereum's ether, Litecoin
Litecoin (Abbreviation: LTC; sign: Ł) is a decentralized peer-to-peer cryptocurrency and open-source software project released under the MIT/X11 license. Inspired by Bitcoin, Litecoin was among the earliest altcoins, starting in October 201 ...
, Monero
Monero (; Abbreviation: XMR) is a decentralized cryptocurrency. It uses a public distributed ledger with privacy-enhancing technologies that obfuscate transactions to achieve anonymity and fungibility. Observers cannot decipher addresses tra ...
, Peercoin
Peercoin, also known as Peer-to-Peer Coin, PP Coin, or PPC is a cryptocurrency utilizing both proof-of-stake and proof-of-work systems.
History
Peercoin is based on an August 2012 paper which listed the authors as Scott Nadal and Sunny King. K ...
, or Dogecoin, which are classified as cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it. It i ...
since the transfer of value is assured through cryptographic signatures validated by all users. There are also brand
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create an ...
ed currencies, for example 'obligation' based stores of value, such as quasi-regulated BarterCard, Loyalty Points (Credit Cards, Airlines) or Game-Credits (MMO games) that are based on reputation of commercial products, or highly regulated 'asset-backed' 'alternative currencies' such as mobile-money schemes like MPESA (called E-Money Issuance).● ''TED Video:'' ● ''Corresponding written article:''
The currency may be Internet-based and digital, for instance, bitcoin is not tied to any specific country, or the IMF's SDR that is based on a basket of currencies (and assets held).
Possession and sale of alternative forms of currencies is often outlawed by governments in order to preserve the legitimacy of the constitutional currency for the benefit of all citizens. For example, Article I, section 8, clause 5 of the United States Constitution delegates to Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
the power to coin money and to regulate the value thereof. This power was delegated to Congress in order to establish and preserve a uniform standard of value and to insure a singular monetary system for all purchases and debts in the United States, public and private. Along with the power to coin money, the United States Congress has the concurrent power to restrain the circulation of money which is not issued under its own authority in order to protect and preserve the constitutional currency. It is a violation of federal law for individuals, or organizations to create private coin or currency systems to compete with the official coinage and currency of the United States.
Control and production
 In most cases, a
In most cases, a central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union,
and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central ba ...
has the exclusive power to issue all forms of currency, including coins and banknotes (fiat money
Fiat money (from la, fiat, "let it be done") is a type of currency that is not backed by any commodity such as gold or silver. It is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tender. Throughout history, fiat money was somet ...
), and to restrain the circulation alternative currencies for its own area of circulation (a country or group of countries); it regulates the production of currency by banks ( credit) through monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to control either the interest rate payable for very short-term borrowing (borrowing by banks from each other to meet their short-term needs) or the money supply, often ...
.
An exchange rate is a price at which two currencies can be exchanged against each other. This is used for trade between the two currency zones. Exchange rates can be classified as either floating or fixed. In the former, day-to-day movements in exchange rates are determined by the market; in the latter, governments intervene in the market to buy or sell their currency to balance supply and demand at a static exchange rate.
In cases where a country has control of its own currency, that control is exercised either by a central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union,
and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central ba ...
or by a Ministry of Finance. The institution that has control of monetary policy is referred to as the monetary authority. Monetary authorities have varying degrees of autonomy from the governments that create them. A monetary authority is created and supported by its sponsoring government, so independence can be reduced by the legislative or executive authority that creates it.
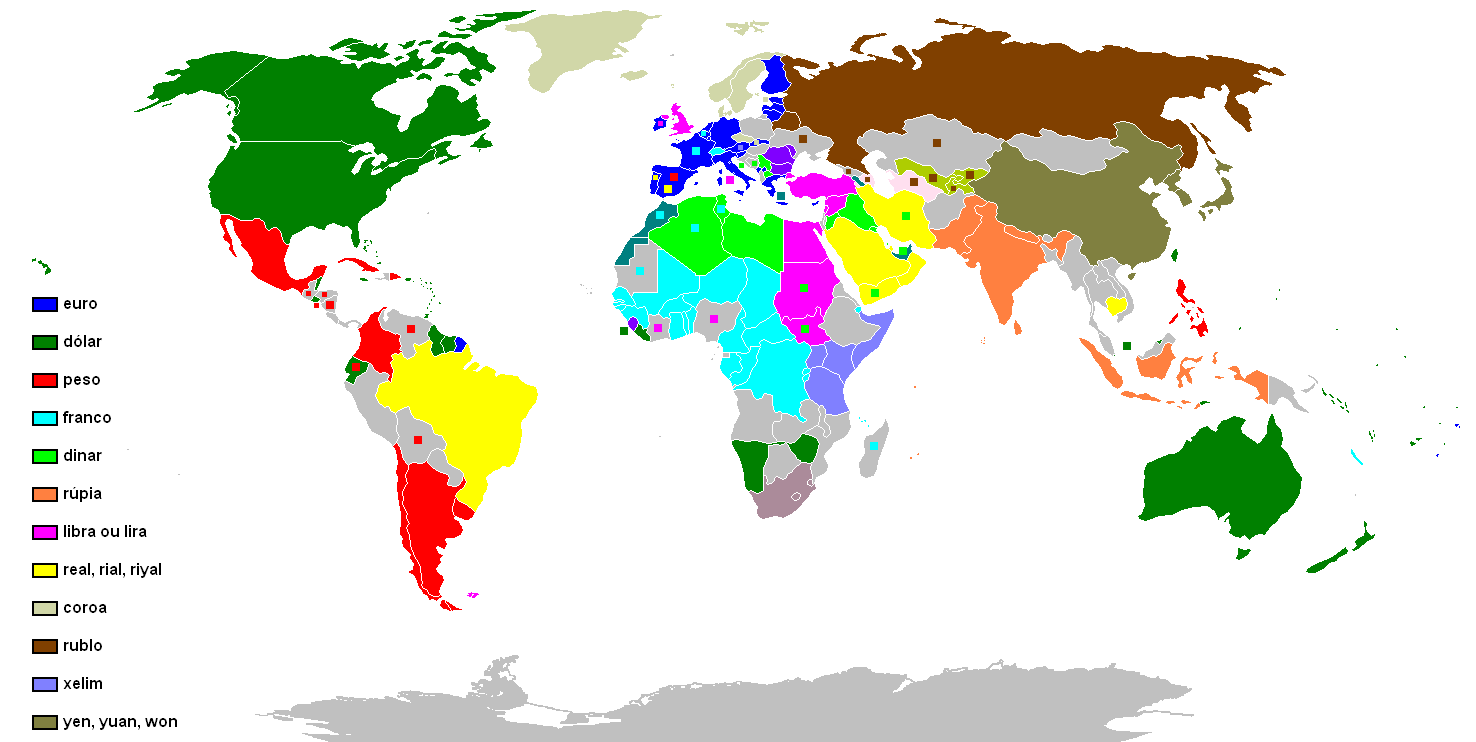
Several countries can use the same name for their own separate currencies (for example, a ''dollar'' in Australia, Canada, and the United States). By contrast, several countries can also use the same currency (for example, the euro or the CFA franc
The CFA franc (french: franc CFA, , Franc of the Financial Community of Africa, originally Franc of the French Colonies in Africa, or colloquially ; abbreviation: F.CFA) is the name of two currencies, the West African CFA franc, used in eight Wes ...
), or one country can declare the currency of another country to be legal tender. For example, Panama and El Salvador have declared US currency to be legal tender, and from 1791 to 1857, Spanish dollars
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight ( es, Real de a ocho, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content ...
were legal tender in the United States. At various times countries have either re-stamped foreign coins or used currency board
In public finance, a currency board is a monetary authority which is required to maintain a fixed exchange rate with a foreign currency. This policy objective requires the conventional objectives of a central bank to be subordinated to the excha ...
s, issuing one note of currency for each note of a foreign government held, as Ecuador currently does.
Each currency typically has a main currency unit (the dollar, for example, or the euro) and a fractional unit, often defined as of the main unit: 100 cents = 1 dollar, 100 centime
Centime (from la, centesimus) is French for " cent", and is used in English as the name of the fraction currency in several Francophone countries (including Switzerland, Algeria, Belgium, Morocco and France).
In France, the usage of ''ce ...
s = 1 franc, 100 pence = 1 pound, although units of or occasionally also occur. Some currencies do not have any smaller units at all, such as the Icelandic króna
The króna or krona (sometimes called Icelandic crown; sign: kr; code: ISK) is the currency of Iceland. Iceland is the second-smallest country by population, after the Seychelles, to have its own currency and monetary policy.
Name
Like the ...
and the Japanese yen.
Mauritania and Madagascar are the only remaining countries that have theoretical fractional units not based on the decimal system; instead, the Mauritanian ouguiya is in theory divided into 5 khoums
The khoums (singular and plural in English; ar, خمس, "fifth") is the subdivisory unit of the Mauritanian monetary system, the ouguiya. Five khoums make an ouguiya, hence one khoums can be expressed as 0.2 ouguiya.
When the ouguiya was adapte ...
, while the Malagasy ariary
The ariary ( sign: Ar; ISO 4217 code MGA) is the currency of Madagascar. It is notionally subdivided into 5 '' iraimbilanja'' and is one of only two non-decimal currencies currently circulating (the other is the '' Mauritanian ouguiya''). The nam ...
is theoretically divided into 5 iraimbilanja
The iraimbilanja (singular and plural) is the divisory currency unit of Madagascar, being equal to one fifth of an ariary.
Etymology
Iraimbilanja means literally "one iron weight" and was the name of an old coin worth of an ariary.
Value
T ...
. In these countries, words like ''dollar'' or ''pound'' "were simply names for given weights of gold". Due to inflation khoums and iraimbilanja have in practice fallen into disuse. (See non-decimal currencies for other historic currencies with non-decimal divisions.)
Currency convertibility
Subject to variation around the world, local currency can be converted to another currency or vice versa with or without central bank/government intervention. Such conversions take place in theforeign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all asp ...
. Based on the above restrictions or free and readily conversion features, currencies are classified as:
; Fully convertible: When there are no restrictions or limitations on the amount of currency that can be traded on the international market, and the government does not artificially impose a fixed value or minimum value on the currency in international trade. The US dollar is one of the main fully convertible currencies.
; Partially convertible: Central banks control international investments flowing into and out of a country. While most domestic transactions are handled without any special requirements, there are significant restrictions on international investing, and special approval is often required in order to convert into other currencies. The Indian rupee and the renminbi are examples of partially convertible currencies.
; Nonconvertible: A government neither participates in the international currency market nor allows the conversion of its currency by individuals or companies. These currencies are also known as ''blocked'', e.g. the North Korean won and the Cuban peso
The Cuban peso (in Spanish , ISO 4217 code: CUP) also known as , is the official currency of Cuba.
The Cuban peso historically circulated at par with the Spanish-American silver dollar from the 16th to 19th centuries, and then at par with the ...
.
According to the three aspects of trade in goods and services
Goods are items that are usually (but not always) tangible, such as pens, physical books, salt, apples, and hats. Services are activities provided by other people, who include architects, suppliers, contractors, technologists, teachers, doc ...
, capital flows and national policies, the supply-demand relationship of different currencies determines the exchange ratio between currencies.
Trade in goods and services
Through cost transfer, goods and services circulating in the country (such as hotels, tourism, catering, advertising, household services) will indirectly affect the trade cost of goods and services and the price of export trade. Therefore, services and goods involved in international trade are not the only reason affecting the exchange rate. The large number of international tourists and overseas students has resulted in the flow of services and goods at home and abroad. It also represents that the competitiveness of global goods and services directly affects the change of international exchange rates.
Capital flows
National currencies will be traded on international markets for investment purposes. Investment opportunities in each country attract other countries into investment programs, so that these foreign currencies become the reserves of the central banks
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union,
and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central ...
of each country. The exchange rate mechanism, in which currencies are quoted continuously between countries, is based on foreign exchange markets in which currencies are invested by individuals and traded or speculated by central banks and investment institutions. In addition, changes in interest rates, capital market fluctuations and changes in investment opportunities will affect the global capital inflows and outflows of countries around the world, and exchange rates will fluctuate accordingly.
National policies
The country's foreign trade, monetary and fiscal policies affect the exchange rate fluctuations. Foreign trade includes policies such as tariffs and import standards for commodity exports. The impact of monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to control either the interest rate payable for very short-term borrowing (borrowing by banks from each other to meet their short-term needs) or the money supply, often ...
on the total amount and yield of money directly determines the changes in the international exchange rate. Fiscal policies, such as transfer payments, taxation ratios, and other factors, dominate the profitability of capital and economic development, and the ratio of national debt issuance to deficit determines the repayment capacity and credit rating of the country. Such policies determine the mechanism of linking domestic and foreign currencies and therefore have a significant impact on the generation of exchange rates.
Currency convertibility is closely linked to economic development and finance. There are strict conditions for countries to achieve currency convertibility, which is a good way for countries to improve their economies. The currencies of some countries or regions in the world are freely convertible, such as the US dollar, Australian dollar and Japanese yen. The requirements for currency convertibility can be roughly divided into four parts:
; Sound microeconomic agency
With a freely convertible currency, domestic firms will have to compete fiercely with their foreign counterparts. The development of competition among them will affect the implementation effect of currency convertibility. In addition, microeconomics is a prerequisite for macroeconomic conditions.
; The macroeconomic situation and policies are stable
Since currency convertibility is the cross-border flow of goods and capital, it will have an impact on the macro economy. This requires that the national economy be in a normal and orderly state, that is, there is no serious inflation and economic overheating. In addition, the government should use macro policies to make mature adjustments to deal with the impact of currency exchange on the economy.
; A reasonable and open economy
The maintainability of international balance of payments is the main performance of reasonable economic structure. Currency convertibility not only causes difficulties in the sustainability of international balance of payments but also affects the government's direct control over international economic transactions. To eliminate the foreign exchange shortage, the government needs adequate international reserves.
; Appropriate exchange rate regime and level
The level of exchange rate is an important factor in maintaining exchange rate stability, both before and after currency convertibility. The exchange rate of freely convertible currency is too high or too low, which can easily trigger speculation and undermine the stability of macroeconomic and financial markets. Therefore, to maintain the level of exchange rate, a proper exchange rate regime is crucial.
Local currency
In economics, a local currency is a currency not backed by a national government and intended to trade only in a small area. Advocates such asJane Jacobs
Jane Jacobs (''née'' Butzner; 4 May 1916 – 25 April 2006) was an American-Canadian journalist, author, theorist, and activist who influenced urban studies, sociology, and economics. Her book ''The Death and Life of Great American Cities'' ...
argue that this enables an economically depressed region to pull itself up, by giving the people living there a medium of exchange that they can use to exchange services and locally produced goods (in a broader sense, this is the original purpose of all money). Opponents of this concept argue that local currency creates a barrier that can interfere with economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables a ...
and comparative advantage and that in some cases they can serve as a means of tax evasion
Tax evasion is an illegal attempt to defeat the imposition of taxes by individuals, corporations, trusts, and others. Tax evasion often entails the deliberate misrepresentation of the taxpayer's affairs to the tax authorities to reduce the taxp ...
.
Local currencies can also come into being when there is economic turmoil involving the national currency. An example of this is the Argentinian economic crisis of 2002 in which IOUs
An IOU (abbreviated from the phrase "I owe you") is usually an informal document acknowledging debt. An IOU differs from a promissory note in that an IOU is not a negotiable instrument and does not specify repayment terms such as the time of rep ...
issued by local governments quickly took on some of the characteristics of local currencies.
One of the best examples of a local currency is the original LETS currency, founded on Vancouver Island in the early 1980s. In 1982, the Canadian Central Bank’s lending rates ran up to 14% which drove chartered bank lending rates as high as 19%. The resulting currency and credit scarcity left island residents with few options other than to create a local currency.
List of major world payment currencies
The following table are estimates of the 20 most frequently used currencies in world payments in November 2022 by SWIFT./ref>
See also
Related concepts *Counterfeit money
Counterfeit money is currency produced without the legal sanction of a state or government, usually in a deliberate attempt to imitate that currency and so as to deceive its recipient. Producing or using counterfeit money is a form of fraud or f ...
* Currency band
A currency band is a range of values for the exchange rate for a country’s currency which the country’s central bank acts to keep the exchange rate within.
The central bank selects a range, or "band", of values at which to set their currency ...
* Currency transaction tax
A currency transaction tax is a tax placed on the use of currency for various types of transactions. The tax is associated with the financial sector and is a type of financial transaction tax, as opposed to a consumption tax paid by consumers, t ...
* Debasement
* Exchange rate
* Fiscal localism
* Foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (Forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all asp ...
* Foreign exchange reserves
* Functional currency Functional currency refers to the main currency used by a business or unit of a business. It is the monetary unit of account of the principal economic environment in which an economic entity operates.
International Accounting Standards (IAS) and U ...
* History of banking
The history of banking began with the first prototype banks, that is, the merchants of the world, who gave grain loans to farmers and traders who carried goods between cities. This was around 2000 BCE in Assyria, India and Sumeria. Later, in an ...
* History of money
The history of money concerns the development throughout time of systems that provide the functions of money. Such systems can be understood as means of trading wealth indirectly; not directly as with bartering. Money is a mechanism that facilit ...
* Mutilated currency
Mutilated currency is a term used by the United States Bureau of Engraving and Printing (BEP) to describe currency which is damaged to the point where it is difficult to determine the value of the currency, or where it is not clear that at least ...
* Optimum currency area In economics, an optimum currency area (OCA) or optimal currency region (OCR) is a geographical region in which it would maximize economic efficiency to have the entire region share a single currency.
The underlying theory describes the optimal ch ...
* Slang terms for money
* Virtual currency
* World currency
Accounting units
* Currency pair
A currency pair is the dyadic quotation of the relative value of a currency unit against the unit of another currency in the foreign exchange market. The currency that is used as the reference is called the counter currency, quote currency, or ...
* Currency symbol
A currency symbol or currency sign is a graphic symbol used to denote a currency unit. Usually it is defined by the monetary authority, like the national central bank for the currency concerned.
In formatting, the symbol can use various forma ...
* Currency strength
Currency strength expresses the value of currency. For economists, it is often calculated as purchasing power, while for financial traders, it can be described as an indicator, reflecting many factors related to the currency; for example, fundament ...
* European Currency Unit
The European Currency Unit (, ; , ECU, or XEU) was a unit of account used by the European Economic Community and composed of a basket of member country currencies. The ECU came in to operation on 13 March 1979 and was assigned the ISO 42 ...
* Fictional currency
A fictional currency is some form of system of money defined, depicted, or alluded to, in works of fiction, such as novels, films or video games. The names of units of such currency are sometimes based on extant or historic currencies (e.g. " ...
* Franc Poincaré
The Franc Poincaré is a unit of account that was used in the international regulation of liability. It is defined as 65.5 milligrams of gold of millesimal fineness .900. Formerly it was identical to the French franc, although it has not been so s ...
* Local currencies
In economics, a local currency is a currency that can be spent in a particular geographical locality at participating organisations. A regional currency is a form of local currency encompassing a larger geographical area, while a community curren ...
* Petrocurrency
Petrocurrency (or petrodollar) is a word used with three distinct meanings, often confused:
#Dollars paid to oil-producing nations (petrodollar recycling)—a term invented in the 1970s meaning trading surpluses of oil-producing nations.
#Currenci ...
* Special drawing rights
Special drawing rights (SDRs, code ) are supplementary foreign exchange reserve assets defined and maintained by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). SDRs are units of account for the IMF, and not a currency ''per se''. They represent a claim ...
Lists
* ISO 4217
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual cu ...
* List of alternative names for currency
This is a list of alternative names for currency. A currency refers to money in any form when in actual use or circulation as a medium of exchange, especially circulating banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''sy ...
* List of currencies
A list of all currencies, current and historic. The local name of the currency is used in this list, with the adjectival form of the country or region.
A
* Afghani – Afghanistan
* Akşa – Tuva
* Angolar – Angola
* Apsar - Abkhazia
* ...
* List of circulating currencies
* List of proposed currencies
This is a list of proposed currencies. Currencies are listed by their latest significant proposal.
19th century
* Perun, planned to be introduced by Petar II Petrović-Njegoš in Montenegro
* Romanat
20th century
* ANCAP
* Bancor, an interna ...
* List of historical currencies
* List of historical exchange rates
Listed below is a table of historical exchange rates relative to the U.S. dollar, at present the most widely traded currency in the world.Financial GuidFX FundamentalsRetrieved on July 6, 2007 An exchange rate represents the value of one currency ...
* List of international trade topics
* List of motifs on banknotes
This is a list of current motifs on the banknotes of different countries. The customary design of banknotes in most countries is a portrait of a notable citizen on the front (or ''obverse'') and a different motif on the back (or ''reverse'') - oft ...
Notes
References
External links
* * * {{Authority control Foreign exchange market