Cryptanalysis of the Enigma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cryptanalysis of the Enigma ciphering system enabled the western Allies in
 The Enigma rotor cipher machine was potentially an excellent system. It generated a polyalphabetic
The Enigma rotor cipher machine was potentially an excellent system. It generated a polyalphabetic
 Later Enigma models included an ''alphabet ring'' like a tyre around the core of each rotor. This could be set in any one of 26 positions in relation to the rotor's core. The ring contained one or more notches that engaged with a pawl that advanced the next rotor to the left.
Later still, the three rotors for the scrambler were selected from a set of five or, in the case of the German Navy, eight rotors. The alphabet rings of rotors VI, VII and VIII contained two notches which, despite shortening the period of the substitution alphabet, made decryption more difficult.
Most military Enigmas also featured a
Later Enigma models included an ''alphabet ring'' like a tyre around the core of each rotor. This could be set in any one of 26 positions in relation to the rotor's core. The ring contained one or more notches that engaged with a pawl that advanced the next rotor to the left.
Later still, the three rotors for the scrambler were selected from a set of five or, in the case of the German Navy, eight rotors. The alphabet rings of rotors VI, VII and VIII contained two notches which, despite shortening the period of the substitution alphabet, made decryption more difficult.
Most military Enigmas also featured a
 In the 1920s the German military began using a 3-rotor Enigma, whose security was increased in 1930 by the addition of a plugboard. The Polish Cipher Bureau sought to break it due to the threat that Poland faced from Germany, but its early attempts did not succeed. Near the beginning of 1929, the Polish Cipher Bureau realized that mathematicians may make good codebreakers; the bureau invited math students at Poznań University to take a class on cryptology. After the class, the Bureau recruited some students to work part-time at a Bureau branch set up in Poznań for the students. The branch operated for some time. On 1 September 1932, 27-year-old Polish mathematician Marian Rejewski and two fellow Poznań University mathematics graduates,
In the 1920s the German military began using a 3-rotor Enigma, whose security was increased in 1930 by the addition of a plugboard. The Polish Cipher Bureau sought to break it due to the threat that Poland faced from Germany, but its early attempts did not succeed. Near the beginning of 1929, the Polish Cipher Bureau realized that mathematicians may make good codebreakers; the bureau invited math students at Poznań University to take a class on cryptology. After the class, the Bureau recruited some students to work part-time at a Bureau branch set up in Poznań for the students. The branch operated for some time. On 1 September 1932, 27-year-old Polish mathematician Marian Rejewski and two fellow Poznań University mathematics graduates,
 Rejewski realised that, although the letters in the cycle groups were changed by the plugboard, the number and lengths of the cycles were unaffected—in the example above, six cycle groups with lengths of 9, 9, 3, 3, 1 and 1. He described this invariant structure as the ''characteristic'' of the indicator setting. There were only 105,456 possible rotor settings. The Poles therefore set about creating a ''card catalog'' of these cycle patterns.
The cycle-length method would avoid using the grill. The card catalog would index the cycle-length for all starting positions (except for turnovers that occurred while enciphering an indicator). The day's traffic would be examined to discover the cycles in the permutations. The card catalog would be consulted to find the possible starting positions. There are roughly 1 million possible cycle-length combinations and only 105,456 starting positions. Having found a starting position, the Poles would use an Enigma double to determine the cycles at that starting position without a plugboard. The Poles would then compare those cycles to the cycles with the (unknown) plugboard and solve for the plugboard permutation (a simple substitution cipher). Then the Poles could find the remaining secret of the ring settings with the ANX method.
The problem was compiling the large card catalog.
Rejewski, in 1934 or 1935, devised a machine to facilitate making the catalog and called it a '' cyclometer''. This "comprised two sets of rotors... connected by wires through which electric current could run. Rotor N in the second set was three letters out of phase with respect to rotor N in the first set, whereas rotors L and M in the second set were always set the same way as rotors L and M in the first set". Preparation of this catalog, using the cyclometer, was, said Rejewski, "laborious and took over a year, but when it was ready, obtaining daily keys was a question of ome fifteenminutes".
However, on 1 November 1937, the Germans changed the Enigma reflector, necessitating the production of a new catalog—"a task which ays Rejewskiconsumed, on account of our greater experience, probably somewhat less than a year's time".
This characteristics method stopped working for German naval Enigma messages on 1 May 1937, when the indicator procedure was changed to one involving special codebooks (see German Navy 3-rotor Enigma below). Worse still, on 15 September 1938 it stopped working for German army and air force messages because operators were then required to choose their own ''Grundstellung'' (initial rotor setting) for each message. Although German army message keys would still be double-enciphered, the day's keys would not be double-enciphered at the same initial setting, so the characteristic could no longer be found or exploited.
Rejewski realised that, although the letters in the cycle groups were changed by the plugboard, the number and lengths of the cycles were unaffected—in the example above, six cycle groups with lengths of 9, 9, 3, 3, 1 and 1. He described this invariant structure as the ''characteristic'' of the indicator setting. There were only 105,456 possible rotor settings. The Poles therefore set about creating a ''card catalog'' of these cycle patterns.
The cycle-length method would avoid using the grill. The card catalog would index the cycle-length for all starting positions (except for turnovers that occurred while enciphering an indicator). The day's traffic would be examined to discover the cycles in the permutations. The card catalog would be consulted to find the possible starting positions. There are roughly 1 million possible cycle-length combinations and only 105,456 starting positions. Having found a starting position, the Poles would use an Enigma double to determine the cycles at that starting position without a plugboard. The Poles would then compare those cycles to the cycles with the (unknown) plugboard and solve for the plugboard permutation (a simple substitution cipher). Then the Poles could find the remaining secret of the ring settings with the ANX method.
The problem was compiling the large card catalog.
Rejewski, in 1934 or 1935, devised a machine to facilitate making the catalog and called it a '' cyclometer''. This "comprised two sets of rotors... connected by wires through which electric current could run. Rotor N in the second set was three letters out of phase with respect to rotor N in the first set, whereas rotors L and M in the second set were always set the same way as rotors L and M in the first set". Preparation of this catalog, using the cyclometer, was, said Rejewski, "laborious and took over a year, but when it was ready, obtaining daily keys was a question of ome fifteenminutes".
However, on 1 November 1937, the Germans changed the Enigma reflector, necessitating the production of a new catalog—"a task which ays Rejewskiconsumed, on account of our greater experience, probably somewhat less than a year's time".
This characteristics method stopped working for German naval Enigma messages on 1 May 1937, when the indicator procedure was changed to one involving special codebooks (see German Navy 3-rotor Enigma below). Worse still, on 15 September 1938 it stopped working for German army and air force messages because operators were then required to choose their own ''Grundstellung'' (initial rotor setting) for each message. Although German army message keys would still be double-enciphered, the day's keys would not be double-enciphered at the same initial setting, so the characteristic could no longer be found or exploited.
 Although the characteristics method no longer worked, the inclusion of the enciphered message key twice gave rise to a phenomenon that the cryptanalyst Henryk Zygalski was able to exploit. Sometimes (about one message in eight) one of the repeated letters in the message key enciphered to the same letter on both occasions. These occurrences were called ''samiczki'' (in English, ''females''—a term later used at Bletchley Park).
Only a limited number of scrambler settings would give rise to females, and these would have been identifiable from the card catalog. If the first six letters of the ciphertext were ''SZVSIK'', this would be termed a 1-4 female; if ''WHOEHS'', a 2-5 female; and if ''ASWCRW'', a 3-6 female. The method was called ''Netz'' (from ''Netzverfahren'', "net method"), or the Zygalski sheet method as it used perforated sheets that he devised, although at Bletchley Park Zygalski's name was not used for security reasons. About ten females from a day's messages were required for success.
There was a set of 26 of these sheets for each of the six possible sequences ''wheel orders''. Each sheet was for the left (slowest-moving) rotor. The 51×51 matrices on the sheets represented the 676 possible starting positions of the middle and right rotors. The sheets contained about 1000 holes in the positions in which a female could occur. The set of sheets for that day's messages would be appropriately positioned on top of each other in the perforated sheets apparatus. Rejewski wrote about how the device was operated:
The holes in the sheets were painstakingly cut with razor blades and in the three months before the next major setback, the sets of sheets for only two of the possible six wheel orders had been produced.
Although the characteristics method no longer worked, the inclusion of the enciphered message key twice gave rise to a phenomenon that the cryptanalyst Henryk Zygalski was able to exploit. Sometimes (about one message in eight) one of the repeated letters in the message key enciphered to the same letter on both occasions. These occurrences were called ''samiczki'' (in English, ''females''—a term later used at Bletchley Park).
Only a limited number of scrambler settings would give rise to females, and these would have been identifiable from the card catalog. If the first six letters of the ciphertext were ''SZVSIK'', this would be termed a 1-4 female; if ''WHOEHS'', a 2-5 female; and if ''ASWCRW'', a 3-6 female. The method was called ''Netz'' (from ''Netzverfahren'', "net method"), or the Zygalski sheet method as it used perforated sheets that he devised, although at Bletchley Park Zygalski's name was not used for security reasons. About ten females from a day's messages were required for success.
There was a set of 26 of these sheets for each of the six possible sequences ''wheel orders''. Each sheet was for the left (slowest-moving) rotor. The 51×51 matrices on the sheets represented the 676 possible starting positions of the middle and right rotors. The sheets contained about 1000 holes in the positions in which a female could occur. The set of sheets for that day's messages would be appropriately positioned on top of each other in the perforated sheets apparatus. Rejewski wrote about how the device was operated:
The holes in the sheets were painstakingly cut with razor blades and in the three months before the next major setback, the sets of sheets for only two of the possible six wheel orders had been produced.
 The demountable drums on the front of the bombe were wired identically to the connections made by Enigma's different rotors. Unlike them, however, the input and output contacts for the left-hand and the right-hand sides were separate, making 104 contacts between each drum and the rest of the machine. This allowed a set of scramblers to be connected in series by means of 26-way cables. Electrical connections between the rotating drums' wiring and the rear plugboard were by means of metal brushes. When the bombe detected a scrambler position with no contradictions, it stopped and the operator would note the position before restarting it.
Although Welchman had been given the task of studying Enigma traffic
The demountable drums on the front of the bombe were wired identically to the connections made by Enigma's different rotors. Unlike them, however, the input and output contacts for the left-hand and the right-hand sides were separate, making 104 contacts between each drum and the rest of the machine. This allowed a set of scramblers to be connected in series by means of 26-way cables. Electrical connections between the rotating drums' wiring and the rear plugboard were by means of metal brushes. When the bombe detected a scrambler position with no contradictions, it stopped and the operator would note the position before restarting it.
Although Welchman had been given the task of studying Enigma traffic
 Dilly Knox's last great cryptanalytical success, before his untimely death in February 1943, was the solving of the '' Abwehr'' Enigma in 1941. Intercepts of traffic which had an 8-letter indicator sequence before the usual 5-letter groups led to the suspicion that a 4-rotor machine was being used. The assumption was correctly made that the indicator consisted of a 4-letter message key enciphered twice. The machine itself was similar to a Model G Enigma, with three conventional rotors, though it did not have a plug board. The principal difference to the model G was that it was equipped with a reflector that was advanced by the stepping mechanism once it had been set by hand to its starting position (in all other variants, the reflector was fixed). Collecting a set of enciphered message keys for a particular day allowed ''cycles'' (or ''boxes'' as Knox called them) to be assembled in a similar way to the method used by the Poles in the 1930s.
Knox was able to derive, using his ''buttoning up'' procedure, some of the wiring of the rotor that had been loaded in the fast position on that day. Progressively he was able to derive the wiring of all three rotors. Once that had been done, he was able to work out the wiring of the reflector. Deriving the indicator setting for that day was achieved using Knox's time-consuming ''rodding'' procedure. This involved a great deal of trial and error, imagination and crossword puzzle-solving skills, but was helped by ''cillies''.
The ''Abwehr'' was the
Dilly Knox's last great cryptanalytical success, before his untimely death in February 1943, was the solving of the '' Abwehr'' Enigma in 1941. Intercepts of traffic which had an 8-letter indicator sequence before the usual 5-letter groups led to the suspicion that a 4-rotor machine was being used. The assumption was correctly made that the indicator consisted of a 4-letter message key enciphered twice. The machine itself was similar to a Model G Enigma, with three conventional rotors, though it did not have a plug board. The principal difference to the model G was that it was equipped with a reflector that was advanced by the stepping mechanism once it had been set by hand to its starting position (in all other variants, the reflector was fixed). Collecting a set of enciphered message keys for a particular day allowed ''cycles'' (or ''boxes'' as Knox called them) to be assembled in a similar way to the method used by the Poles in the 1930s.
Knox was able to derive, using his ''buttoning up'' procedure, some of the wiring of the rotor that had been loaded in the fast position on that day. Progressively he was able to derive the wiring of all three rotors. Once that had been done, he was able to work out the wiring of the reflector. Deriving the indicator setting for that day was achieved using Knox's time-consuming ''rodding'' procedure. This involved a great deal of trial and error, imagination and crossword puzzle-solving skills, but was helped by ''cillies''.
The ''Abwehr'' was the
 On 1 February 1942, the Enigma messages to and from Atlantic U-boats, which Bletchley Park called '"Shark," became significantly different from the rest of the traffic, which they called "Dolphin."
This was because a new Enigma version had been brought into use. It was a development of the 3-rotor Enigma with the reflector replaced by a thin rotor and a thin reflector. Eventually, there were two fourth-position rotors that were called Beta and Gamma and two thin reflectors, Bruno and Caesar which could be used in any combination. These rotors were not advanced by the rotor to their right, in the way that rotors I to VIII were.
The introduction of the fourth rotor did not catch Bletchley Park by surprise, because captured material dated January 1941 had made reference to its development as an adaptation of the 3-rotor machine, with the fourth rotor wheel to be a reflector wheel. Indeed, because of operator errors, the wiring of the new fourth rotor had already been worked out.
This major challenge could not be met by using existing methods and resources for a number of reasons.
# The work on the Shark cipher would have to be independent of the continuing work on messages in the Dolphin cipher.
# Solving Shark keys on 3-rotor bombes would have taken 50 to 100 times as long as an average Air Force or Army job.
# U-boat cribs at this time were extremely poor.
It seemed, therefore, that effective, fast, 4-rotor bombes were the only way forward. This was an immense problem and it gave a great deal of trouble. Work on a high speed machine had been started by Wynn-Williams of the TRE late in 1941 and some nine months later Harold Keen of BTM started work independently. Early in 1942, Bletchley Park were a long way from possessing a high speed machine of any sort.
Eventually, after a long period of being unable to decipher U-boat messages, a source of cribs was found. This was the Kurzsignale (short signals), a code which the German navy used to minimize the duration of transmissions, thereby reducing the risk of being located by
On 1 February 1942, the Enigma messages to and from Atlantic U-boats, which Bletchley Park called '"Shark," became significantly different from the rest of the traffic, which they called "Dolphin."
This was because a new Enigma version had been brought into use. It was a development of the 3-rotor Enigma with the reflector replaced by a thin rotor and a thin reflector. Eventually, there were two fourth-position rotors that were called Beta and Gamma and two thin reflectors, Bruno and Caesar which could be used in any combination. These rotors were not advanced by the rotor to their right, in the way that rotors I to VIII were.
The introduction of the fourth rotor did not catch Bletchley Park by surprise, because captured material dated January 1941 had made reference to its development as an adaptation of the 3-rotor machine, with the fourth rotor wheel to be a reflector wheel. Indeed, because of operator errors, the wiring of the new fourth rotor had already been worked out.
This major challenge could not be met by using existing methods and resources for a number of reasons.
# The work on the Shark cipher would have to be independent of the continuing work on messages in the Dolphin cipher.
# Solving Shark keys on 3-rotor bombes would have taken 50 to 100 times as long as an average Air Force or Army job.
# U-boat cribs at this time were extremely poor.
It seemed, therefore, that effective, fast, 4-rotor bombes were the only way forward. This was an immense problem and it gave a great deal of trouble. Work on a high speed machine had been started by Wynn-Williams of the TRE late in 1941 and some nine months later Harold Keen of BTM started work independently. Early in 1942, Bletchley Park were a long way from possessing a high speed machine of any sort.
Eventually, after a long period of being unable to decipher U-boat messages, a source of cribs was found. This was the Kurzsignale (short signals), a code which the German navy used to minimize the duration of transmissions, thereby reducing the risk of being located by
 Commander Edward Travis, Deputy Director and Frank Birch, Head of the German Naval Section travelled from Bletchley Park to Washington in September 1942. With
Commander Edward Travis, Deputy Director and Frank Birch, Head of the German Naval Section travelled from Bletchley Park to Washington in September 1942. With
Dayton's Code Breakers
* Dayton Codebreakers Web site
DaytonCodebreakers.org
About the Enigma (National Security Agency)
"The Enigma machine and Bletchley Park"
''Cybertwists'' *
* ttp://www.matematiksider.dk/enigma_eng.html "The German cipher machine Enigma" ''Matematik Sider'', 20 September 2014
"The Polish Enigma crackers"
''Deutsche Welle'', 17 February 2015 (an audio report for general audiences)
* Sir Dermot Turing said that his uncle's achievements in cracking German communications encrypted on the Enigma machines were based on work by a group of Polish mathematicians:
Turing cult has obscured role of Polish codebreakers
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cryptanalysis Of The Enigma Bletchley Park Enigma machine History of cryptography Signals intelligence of World War II
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
to read substantial amounts of Morse-coded radio communications of the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
that had been enciphered using Enigma machines. This yielded military intelligence
Military intelligence is a military discipline that uses information collection and analysis approaches to provide guidance and direction to assist commanders in their decisions. This aim is achieved by providing an assessment of data from a ...
which, along with that from other decrypted Axis radio and teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Init ...
transmissions, was given the codename '' Ultra''.
The Enigma machines were a family of portable cipher machines with rotor
Rotor may refer to:
Science and technology
Engineering
* Rotor (electric), the non-stationary part of an alternator or electric motor, operating with a stationary element so called the stator
*Helicopter rotor, the rotary wing(s) of a rotorcraft ...
scramblers. Good operating procedures, properly enforced, would have made the plugboard Enigma machine unbreakable. However, most of the German military forces, secret services, and civilian agencies that used Enigma employed poor operating procedures, and it was these poor procedures that allowed the Enigma machines to be reverse-engineered
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accompli ...
and the ciphers to be read.
The German plugboard-equipped Enigma became Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
's principal crypto-system. In December 1932 it was "broken" by mathematician Marian Rejewski at the Polish General Staff
Polish General Staff, formally known as the General Staff of the Polish Armed Forces ( Polish: ''Sztab Generalny Wojska Polskiego'') is the highest professional body within the Polish Armed Forces. Organizationally, it is an integral part of the M ...
's Cipher Bureau, using mathematical permutation group theory combined with French-supplied intelligence material obtained from a German spy. By 1938 Rejewski had invented a device, the cryptologic bomb, and Henryk Zygalski
Henryk Zygalski (; 15 July 1908 – 30 August 1978) was a Polish mathematician and cryptologist who worked at breaking German Enigma ciphers before and during World War II.
Life
Zygalski was born on 15 July 1908 in Posen, German Empire (now Pozn ...
had devised his sheets
A bed sheet is a rectangular piece of cloth used either singly or in a pair as bedding, which is larger in length and width than a mattress, and which is placed immediately above a mattress or bed, but below blankets and other bedding (such as ...
, to make the cipher-breaking more efficient. Five weeks before the outbreak of World War II, in late July 1939, at a conference just south of Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, the Polish Cipher Bureau shared its Enigma-breaking techniques and technology with the French and British.
During the German invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
, core Polish Cipher Bureau personnel were evacuated via Romania to France, where they established the ''PC Bruno
''PC Bruno'' was a Polish–French–Spanish signals–intelligence station near Paris during World War II, from October 1939 until June 1940. Its function was decryption of cipher messages, most notably German messages enciphered on the Enigma ...
'' signals intelligence station with French facilities support. Successful cooperation among the Poles, the French, and the British at Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes ( Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World War. The mansion was constructed during the years followin ...
continued until June 1940, when France surrendered to the Germans.
From this beginning, the British Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS)
Government Communications Headquarters, commonly known as GCHQ, is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the Uni ...
at Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes ( Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World War. The mansion was constructed during the years followin ...
built up an extensive cryptanalytic capability. Initially the decryption was mainly of ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
'' (German air force) and a few '' Heer'' (German army) messages, as the '' Kriegsmarine'' (German navy) employed much more secure procedures for using Enigma. Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical co ...
, a Cambridge University
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III of England, Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world' ...
mathematician and logician, provided much of the original thinking that led to upgrading of the Polish cryptologic bomb used in decrypting German Enigma ciphers. However, the ''Kriegsmarine'' introduced an Enigma version with a fourth rotor for its U-boats, resulting in a prolonged period when these messages could not be decrypted. With the capture of cipher keys and the use of much faster US Navy bombes, regular, rapid reading of U-boat messages resumed.
General principles
The Enigma machines produced a polyalphabetic substitution cipher. DuringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, inventors in several countries realized that a purely random key sequence, containing no repetitive pattern, would, in principle, make a polyalphabetic substitution cipher unbreakable. This led to the development of rotor cipher machines which alter each character in the plaintext
In cryptography, plaintext usually means unencrypted information pending input into cryptographic algorithms, usually encryption algorithms. This usually refers to data that is transmitted or stored unencrypted.
Overview
With the advent of com ...
to produce the ciphertext, by means of a scrambler comprising a set of ''rotors'' that alter the electrical path from character to character, between the input device and the output device. This constant altering of the electrical pathway produces a very long period before the pattern—the key sequence or substitution alphabet—repeats.
Decrypting enciphered messages involves three stages, defined somewhat differently in that era than in modern cryptography. First, there is the ''identification'' of the system in use, in this case Enigma; second, ''breaking'' the system by establishing exactly how encryption takes place, and third, ''solving'', which involves finding the way that the machine was set up for an individual message, ''i.e.'' the ''message key''. Today, it is often assumed that an attacker knows how the encipherment process works (see Kerckhoffs's principle) and ''breaking'' is often used for ''solving'' a key. Enigma machines, however, had so many potential internal wiring states that reconstructing the machine, independent of particular settings, was a very difficult task.
The Enigma machine
 The Enigma rotor cipher machine was potentially an excellent system. It generated a polyalphabetic
The Enigma rotor cipher machine was potentially an excellent system. It generated a polyalphabetic substitution cipher
In cryptography, a substitution cipher is a method of encrypting in which units of plaintext are replaced with the ciphertext, in a defined manner, with the help of a key; the "units" may be single letters (the most common), pairs of letters, tri ...
, with a period before repetition of the substitution alphabet that was much longer than any message, or set of messages, sent with the same key.
A major weakness of the system, however, was that no letter could be enciphered to itself. This meant that some possible solutions could quickly be eliminated because of the same letter appearing in the same place in both the ciphertext and the putative piece of plaintext. Comparing the possible plaintext ''Keine besonderen Ereignisse'' (literally, "no special occurrences"—perhaps better translated as "nothing to report"; a phrase regularly used by one German outpost in North Africa), with a section of ciphertext, might produce the following:
Structure
The mechanism of the Enigma consisted of a keyboard connected to a battery and a current entry plate or wheel (German: ''Eintrittswalze''), at the right hand end of the scrambler (usually via aplugboard
A plugboard or control panel (the term used depends on the application area) is an array of jacks or sockets (often called hubs) into which patch cords can be inserted to complete an electrical circuit. Control panels are sometimes used to di ...
in the military versions). This contained a set of 26 contacts that made electrical connection with the set of 26 spring-loaded pins on the right hand rotor. The internal wiring of the core of each rotor provided an electrical pathway from the pins on one side to different connection points on the other. The left hand side of each rotor made electrical connection with the rotor to its left. The leftmost rotor then made contact with the reflector (German: ''Umkehrwalze''). The reflector provided a set of thirteen paired connections to return the current back through the scrambler rotors, and eventually to the lampboard where a lamp under a letter was illuminated.
Whenever a key on the keyboard was pressed, the stepping motion was actuated, advancing the rightmost rotor one position. Because it moved with each key pressed it is sometimes called the ''fast rotor''. When a notch on that rotor engaged with a pawl on the middle rotor, that too moved; and similarly with the leftmost ('slow') rotor.
There are a huge number of ways that the connections within each scrambler rotor—and between the entry plate and the keyboard or plugboard or lampboard—could be arranged. For the reflector plate there are fewer, but still a large number of options to its possible wirings.
Each scrambler rotor could be set to any one of its 26 starting positions (any letter of the alphabet). For the Enigma machines with only three rotors, their sequence in the scrambler—which was known as the ''wheel order (WO)'' to Allied cryptanalysts—could be selected from the six that are possible.
 Later Enigma models included an ''alphabet ring'' like a tyre around the core of each rotor. This could be set in any one of 26 positions in relation to the rotor's core. The ring contained one or more notches that engaged with a pawl that advanced the next rotor to the left.
Later still, the three rotors for the scrambler were selected from a set of five or, in the case of the German Navy, eight rotors. The alphabet rings of rotors VI, VII and VIII contained two notches which, despite shortening the period of the substitution alphabet, made decryption more difficult.
Most military Enigmas also featured a
Later Enigma models included an ''alphabet ring'' like a tyre around the core of each rotor. This could be set in any one of 26 positions in relation to the rotor's core. The ring contained one or more notches that engaged with a pawl that advanced the next rotor to the left.
Later still, the three rotors for the scrambler were selected from a set of five or, in the case of the German Navy, eight rotors. The alphabet rings of rotors VI, VII and VIII contained two notches which, despite shortening the period of the substitution alphabet, made decryption more difficult.
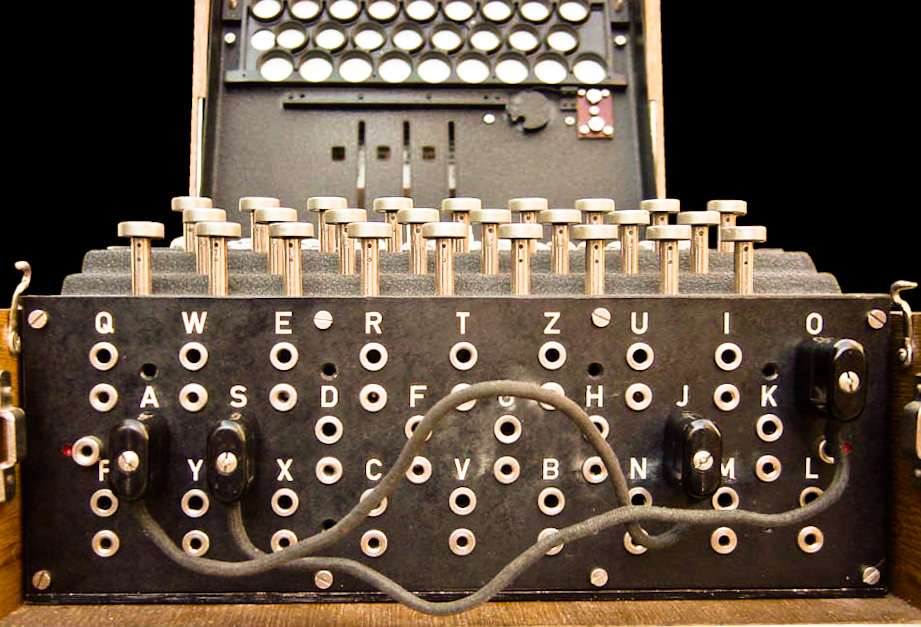
Most military Enigmas also featured a plugboard
A plugboard or control panel (the term used depends on the application area) is an array of jacks or sockets (often called hubs) into which patch cords can be inserted to complete an electrical circuit. Control panels are sometimes used to di ...
(German: ''Steckerbrett''). This altered the electrical pathway between the keyboard and the entry wheel of the scrambler and, in the opposite direction, between the scrambler and the lampboard. It did this by exchanging letters reciprocally, so that if ''A'' was plugged to ''G'' then pressing key ''A'' would lead to current entering the scrambler at the ''G'' position, and if ''G'' was pressed the current would enter at ''A''. The same connections applied for the current on the way out to the lamp panel.
To decipher German military Enigma messages, the following information would need to be known.
Logical structure of the machine (unchanging)
*The wiring between the keyboard (and lampboard) and the entry plate.
*The wiring of each rotor.
*The number and position(s) of turnover notches on the rings of the rotors.
*The wiring of the reflectors.
Internal settings (usually changed less frequently than external settings)
*The selection of rotors in use and their ordering on the spindle (''Walzenlage'' or "wheel order").
*The positions of the alphabet ring in relation to the core of each rotor in use (''Ringstellung'' or "ring settings").
External settings (usually changed more frequently than internal settings)
*The plugboard connections (''Steckerverbindungen'' or "stecker values").
*The rotor positions at the start of enciphering the text of the message.
Discovering the logical structure of the machine may be called "breaking" it, a one-off process except when changes or additions were made to the machines. Finding the internal and external settings for one or more messages may be called "solving" – although breaking is often used for this process as well.
Security properties
The various Enigma models provided different levels of security. The presence of a plugboard (''Steckerbrett'') substantially increased the security of the encipherment. Each pair of letters that were connected together by a plugboard lead were referred to as ''stecker partners'', and the letters that remained unconnected were said to be ''self-steckered''. In general, the unsteckered Enigma was used for commercial and diplomatic traffic and could be broken relatively easily using hand methods, while attacking versions with a plugboard was much more difficult. The British read unsteckered Enigma messages sent during theSpanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
, and also some Italian naval traffic enciphered early in World War II.
The strength of the security of the ciphers that were produced by the Enigma machine was a product of the large numbers associated with the scrambling process.
#It produced a polyalphabetic substitution cipher with a period (16,900) that was many times the length of the longest message.
#The 3-rotor scrambler could be set in 26 × 26 × 26 = 17,576 ways, and the 4-rotor scrambler in 26 × 17,576 = 456,976 ways.
#With ''L'' leads on the plugboard, the number of ways that pairs of letters could be interchanged was
#*With ''L''=6, the number of combinations was 100,391,791,500 (100 billion) and with ten leads, it was 150,738,274,937,250 (151 trillion).
However, the way that Enigma was used by the Germans meant that, if the settings for one day (or whatever period was represented by each row of the setting sheet) were established, the rest of the messages for that network on that day could quickly be deciphered.
The security of Enigma ciphers did have fundamental weaknesses that proved helpful to cryptanalysts.
#A letter could never be encrypt
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can deci ...
ed to itself, a consequence of the reflector. This property was of great help in using '' cribs''—short sections of plaintext thought to be somewhere in the ciphertext—and could be used to eliminate a crib in a particular position. For a possible location, if any letter in the crib matched a letter in the ciphertext at the same position, the location could be ruled out. It was this feature that the British mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems.
Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change.
History
On ...
and logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premise ...
ian Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical co ...
exploited in designing the British bombe
The bombe () was an electro-mechanical device used by British cryptologists to help decipher German Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II. The US Navy and US Army later produced their own machines to the same functi ...
.
#The plugboard connections were reciprocal, so that if A was plugged to N, then N likewise became A. It was this property that led mathematician Gordon Welchman
William Gordon Welchman (15 June 1906 – 8 October 1985) was a British mathematician. During World War II, he worked at Britain's secret codebreaking centre, "Station X" at Bletchley Park, where he was one of the most important contributors. ...
at Bletchley Park to propose that a ''diagonal board'' be introduced into the bombe, substantially reducing the number of incorrect rotor settings that the bombes found.
#The notches in the ''alphabet rings'' of rotors I to V were in different positions, which helped cryptanalysts to work out the ''wheel order'' by observing when the middle rotor was turned over by the right-hand rotor.
#There were substantial weaknesses, in both policies and practice, in the way that Enigma was used (see 'Operating shortcomings' below).
Key setting
Enigma featured the major operational convenience of beingsymmetrical
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definiti ...
(or self-inverse). This meant that decipherment worked in the same way as encipherment
In cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from grc, , translit=kryptós "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or '' -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in ...
, so that when the ciphertext was typed in, the sequence of lamps that lit yielded the plaintext
In cryptography, plaintext usually means unencrypted information pending input into cryptographic algorithms, usually encryption algorithms. This usually refers to data that is transmitted or stored unencrypted.
Overview
With the advent of com ...
.
Identical setting of the machines at the transmitting and receiving ends was achieved by key setting procedures. These varied from time to time and across different networks
Network, networking and networked may refer to:
Science and technology
* Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects
* Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks
Mathematics
...
. They consisted of ''setting sheets'' in a '' codebook''. which were distributed to all users of a network, and were changed regularly. The message key was transmitted in an '' indicator'' as part of the message preamble. The word ''key'' was also used at Bletchley Park to describe the network that used the same Enigma setting sheets. Initially these were recorded using coloured pencils and were given the names ''red'', ''light blue'' etc., and later the names of birds such as ''kestrel''. During World War II the settings for most networks lasted for 24 hours, although towards the end of the war, some were changed more frequently. The sheets had columns specifying, for each day of the month, the rotors to be used and their positions, the ring positions and the plugboard connections. For security, the dates were in reverse chronological order down the page, so that each row could be cut off and destroyed when it was finished with.
Up until 15 September 1938, the transmitting operator indicated to the receiving operator(s) how to set their rotors, by choosing a three letter ''message key'' (the key specific to that message) and enciphering it twice using the specified initial ring positions (the ''Grundstellung''). The resultant 6-letter indicator, was then transmitted before the enciphered text of the message. Suppose that the specified ''Grundstellung'' was ''RAO'', and the chosen 3-letter message key was ''IHL'', the operator would set the rotors to ''RAO'' and encipher ''IHL'' twice. The resultant ciphertext, ''DQYQQT'', would be transmitted, at which point the rotors would be changed to the message key (''IHL'') and then the message itself enciphered. The receiving operator would use the specified ''Grundstellung RAO'' to decipher the first six letters, yielding ''IHLIHL''. The receiving operator, seeing the repeated message key would know that there had been no corruption and use ''IHL'' to decipher the message.
The weakness in this indicator procedure came from two factors. First, use of a global ''Grundstellung'' —this was changed in September 1938 so that the operator selected his initial position to encrypt the message key, and sent the initial position in clear followed by the enciphered message key. The second problem was the repetition of message key within the indicator, which was a serious security flaw. The message setting was encoded twice, resulting in a relation between first and fourth, second and fifth, and third and sixth character. This security problem enabled the Polish Cipher Bureau to break into the pre-war Enigma system as early as 1932. On 1 May 1940 the Germans changed the procedures to encipher the message key only once.
British efforts
In 1927, the UK openly purchased a commercial Enigma. Its operation was analysed and reported. Although a leading British cryptographer,Dilly Knox
Alfred Dillwyn "Dilly" Knox, CMG (23 July 1884 – 27 February 1943) was a British classics scholar and papyrologist at King's College, Cambridge and a codebreaker. As a member of the Room 40 codebreaking unit he helped decrypt the Zimm ...
(a veteran of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the cryptanalytical activities of the Royal Navy's Room 40), worked on decipherment he had only the messages he generated himself to practice with. After Germany supplied modified commercial machines to the Nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
side in the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
, and with the Italian Navy (who were also aiding the Nationalists) using a version of the commercial Enigma that did not have a plugboard, Britain could intercept the radio broadcast messages. In April 1937 Knox made his first decryption of an Enigma encryption using a technique that he called ''buttoning up'' to discover the rotor wirings and another that he called ''rodding'' to solve messages. This relied heavily on cribs and on a crossword-solver's expertise in Italian, as it yielded a limited number of spaced-out letters at a time.
Britain had no ability to read the messages broadcast by Germany, which used the military Enigma machine.
Polish breakthroughs
 In the 1920s the German military began using a 3-rotor Enigma, whose security was increased in 1930 by the addition of a plugboard. The Polish Cipher Bureau sought to break it due to the threat that Poland faced from Germany, but its early attempts did not succeed. Near the beginning of 1929, the Polish Cipher Bureau realized that mathematicians may make good codebreakers; the bureau invited math students at Poznań University to take a class on cryptology. After the class, the Bureau recruited some students to work part-time at a Bureau branch set up in Poznań for the students. The branch operated for some time. On 1 September 1932, 27-year-old Polish mathematician Marian Rejewski and two fellow Poznań University mathematics graduates,
In the 1920s the German military began using a 3-rotor Enigma, whose security was increased in 1930 by the addition of a plugboard. The Polish Cipher Bureau sought to break it due to the threat that Poland faced from Germany, but its early attempts did not succeed. Near the beginning of 1929, the Polish Cipher Bureau realized that mathematicians may make good codebreakers; the bureau invited math students at Poznań University to take a class on cryptology. After the class, the Bureau recruited some students to work part-time at a Bureau branch set up in Poznań for the students. The branch operated for some time. On 1 September 1932, 27-year-old Polish mathematician Marian Rejewski and two fellow Poznań University mathematics graduates, Henryk Zygalski
Henryk Zygalski (; 15 July 1908 – 30 August 1978) was a Polish mathematician and cryptologist who worked at breaking German Enigma ciphers before and during World War II.
Life
Zygalski was born on 15 July 1908 in Posen, German Empire (now Pozn ...
and Jerzy Różycki
Jerzy Witold Różycki (; Vilshana, Ukraine, 24 July 1909 – 9 January 1942, Mediterranean Sea, near the Balearic Islands) was a Polish mathematician and cryptologist who worked at breaking German Enigma-machine ciphers before and during World ...
, joined the Bureau full-time and moved to Warsaw. Their first task was to reconstruct a four-letter German naval cipher.
Near the end of 1932 Rejewski was asked to work a couple of hours a day on breaking the Enigma.
Rejewski's characteristics method
Marian Rejewski quickly spotted the Germans' major procedural weaknesses of specifying a single indicator setting (''Grundstellung'') for all messages on a network for a day, and repeating the operator's chosen ''message key'' in the enciphered 6-letter indicator. Those procedural mistakes allowed Rejewski to decipher the message keys without knowing any of the machine's wirings. In the above example of ''DQYQQT'' being the enciphered indicator, it is known that the first letter ''D'' and the fourth letter ''Q'' represent the same letter, enciphered three positions apart in the scrambler sequence. Similarly with ''Q'' and ''Q'' in the second and fifth positions, and ''Y'' and ''T'' in the third and sixth. Rejewski exploited this fact by collecting a sufficient set of messages enciphered with the same indicator setting, and assembling three tables for the 1,4, the 2,5, and the 3,6 pairings. Each of these tables might look something like the following: A path from one first letter to the corresponding fourth letter, then from that letter as the first letter to its corresponding fourth letter, and so on until the first letter recurs, traces out a cycle group. The following table contains six cycle groups. Rejewski recognized that a cycle group must pair with another group of the same length. Even though Rejewski did not know the rotor wirings or the plugboard permutation, the German mistake allowed him to reduce the number of possible substitution ciphers to a small number. For the 1,4 pairing above, there are only possibilities for the substitution ciphers at positions 1 and 4. Rejewski also exploited cipher clerk laziness. Scores of messages would be enciphered by several cipher clerks, but some of those messages would have the same encrypted indicator. That meant that both clerks happened to choose the same three letter starting position. Such a collision should be rare with randomly selected starting positions, but lazy cipher clerks often chose starting positions such as "AAA", "BBB", or "CCC". Those security mistakes allowed Rejewski to solve each of the six permutations used to encipher the indicator. That solution was an extraordinary feat. Rejewski did it without knowing the plugboard permutation or the rotor wirings. Even after solving for the six permutations, Rejewski did not know how the plugboard was set or the positions of the rotors. Knowing the six permutations also did not allow Rejewski to read any messages.The spy and the rotor wiring
Before Rejewski started work on the Enigma, the French had a spy, Hans-Thilo Schmidt, who worked at Germany's Cipher Office in Berlin and had access to some Enigma documents. Even with the help of those documents, the French did not make progress on breaking the Enigma. The French decided to share the material with their British and Polish allies. In a December 1931 meeting, the French provided Gwido Langer, head of the Polish Cipher Bureau, with copies of some Enigma material. Langer asked the French for more material, andGustave Bertrand
Gustave Bertrand (1896–1976) was a French military intelligence officer who made a vital contribution to the decryption, by Poland's Cipher Bureau, of German Enigma ciphers, beginning in December 1932. This achievement would in turn lead to ...
of French Military Intelligence quickly obliged; Bertrand provided additional material in May and September 1932. The documents included two German manuals and two pages of Enigma daily keys.
In December 1932, the Bureau provided Rejewski with some German manuals and monthly keys. The material enabled Rejewski to achieve "one of the most important breakthroughs in cryptologic history" by using the theory of permutations and groups to work out the Enigma scrambler wiring.
Rejewski could look at a day's cipher traffic and solve for the permutations at the six sequential positions used to encipher the indicator. Since Rejewski had the cipher key for the day, he knew and could factor out the plugboard permutation. He assumed the keyboard permutation was the same as the commercial Enigma, so he factored that out. He knew the rotor order, the ring settings, and the starting position. He developed a set of equations that would allow him to solve for the rightmost rotor wiring assuming the two rotors to the left did not move.
He attempted to solve the equations, but failed with inconsistent results. After some thought, he realized one of his assumptions must be wrong.
Rejewski found that the connections between the military Enigma's keyboard and the entry ring were not, as in the commercial Enigma, in the order of the keys on a German typewriter. He made an inspired correct guess that it was in alphabetical order. Britain's Dilly Knox
Alfred Dillwyn "Dilly" Knox, CMG (23 July 1884 – 27 February 1943) was a British classics scholar and papyrologist at King's College, Cambridge and a codebreaker. As a member of the Room 40 codebreaking unit he helped decrypt the Zimm ...
was astonished when he learned, in July 1939, that the arrangement was so simple.
With the new assumption, Rejewski succeeded in solving the wiring of the rightmost rotor. The next month's cipher traffic used a different rotor in the rightmost position, so Rejewski used the same equations to solve for its wiring. With those rotors known, the remaining third rotor and the reflector wiring were determined. Without capturing a single rotor to reverse engineer, Rejewski had determined the logical structure of the machine.
The Polish Cipher Bureau then had some Enigma machine replicas made; the replicas were called "Enigma doubles".
The grill method
The Poles now had the machine's wiring secrets, but they still needed to determine the daily keys for the cipher traffic. The Poles would examine the Enigma traffic and use the method of characteristics to determine the six permutations used for the indicator. The Poles would then use the grill method to determine the rightmost rotor and its position. That search would be complicated by the plugboard permutation, but that permutation only swapped six pairs of letters — not enough to disrupt the search. The grill method also determined the plugboard wiring. The grill method could also be used to determine the middle and left rotors and their setting (and those tasks were simpler because there was no plugboard), but the Poles eventually compiled a catalog of the possible permutations (reflector and 2 leftmost rotor permutations), so they could just look up the answer. The only remaining secret of the daily key would be the ring settings, and the Poles would attack that problem with brute force. Most messages would start with the three letters "ANX" (''an'' is German for "to" and the "X" character was used as a space). It may take almost trials, but that was doable. Once the ring settings were found, the Poles could read the day's traffic. The Germans made it easy for the Poles in the beginning. The rotor order only changed every quarter, so the Poles would not have to search for the rotor order. Later the Germans changed it every month, but that would not cause much trouble, either. Eventually, the Germans would change the rotor order every day, and late in the war (after Poland had been overrun) the rotor order might be changed during the day. The Poles kept improving their techniques as the Germans kept improving their security measures.Invariant cycle lengths and the card catalog
 Rejewski realised that, although the letters in the cycle groups were changed by the plugboard, the number and lengths of the cycles were unaffected—in the example above, six cycle groups with lengths of 9, 9, 3, 3, 1 and 1. He described this invariant structure as the ''characteristic'' of the indicator setting. There were only 105,456 possible rotor settings. The Poles therefore set about creating a ''card catalog'' of these cycle patterns.
The cycle-length method would avoid using the grill. The card catalog would index the cycle-length for all starting positions (except for turnovers that occurred while enciphering an indicator). The day's traffic would be examined to discover the cycles in the permutations. The card catalog would be consulted to find the possible starting positions. There are roughly 1 million possible cycle-length combinations and only 105,456 starting positions. Having found a starting position, the Poles would use an Enigma double to determine the cycles at that starting position without a plugboard. The Poles would then compare those cycles to the cycles with the (unknown) plugboard and solve for the plugboard permutation (a simple substitution cipher). Then the Poles could find the remaining secret of the ring settings with the ANX method.
The problem was compiling the large card catalog.
Rejewski, in 1934 or 1935, devised a machine to facilitate making the catalog and called it a '' cyclometer''. This "comprised two sets of rotors... connected by wires through which electric current could run. Rotor N in the second set was three letters out of phase with respect to rotor N in the first set, whereas rotors L and M in the second set were always set the same way as rotors L and M in the first set". Preparation of this catalog, using the cyclometer, was, said Rejewski, "laborious and took over a year, but when it was ready, obtaining daily keys was a question of ome fifteenminutes".
However, on 1 November 1937, the Germans changed the Enigma reflector, necessitating the production of a new catalog—"a task which ays Rejewskiconsumed, on account of our greater experience, probably somewhat less than a year's time".
This characteristics method stopped working for German naval Enigma messages on 1 May 1937, when the indicator procedure was changed to one involving special codebooks (see German Navy 3-rotor Enigma below). Worse still, on 15 September 1938 it stopped working for German army and air force messages because operators were then required to choose their own ''Grundstellung'' (initial rotor setting) for each message. Although German army message keys would still be double-enciphered, the day's keys would not be double-enciphered at the same initial setting, so the characteristic could no longer be found or exploited.
Rejewski realised that, although the letters in the cycle groups were changed by the plugboard, the number and lengths of the cycles were unaffected—in the example above, six cycle groups with lengths of 9, 9, 3, 3, 1 and 1. He described this invariant structure as the ''characteristic'' of the indicator setting. There were only 105,456 possible rotor settings. The Poles therefore set about creating a ''card catalog'' of these cycle patterns.
The cycle-length method would avoid using the grill. The card catalog would index the cycle-length for all starting positions (except for turnovers that occurred while enciphering an indicator). The day's traffic would be examined to discover the cycles in the permutations. The card catalog would be consulted to find the possible starting positions. There are roughly 1 million possible cycle-length combinations and only 105,456 starting positions. Having found a starting position, the Poles would use an Enigma double to determine the cycles at that starting position without a plugboard. The Poles would then compare those cycles to the cycles with the (unknown) plugboard and solve for the plugboard permutation (a simple substitution cipher). Then the Poles could find the remaining secret of the ring settings with the ANX method.
The problem was compiling the large card catalog.
Rejewski, in 1934 or 1935, devised a machine to facilitate making the catalog and called it a '' cyclometer''. This "comprised two sets of rotors... connected by wires through which electric current could run. Rotor N in the second set was three letters out of phase with respect to rotor N in the first set, whereas rotors L and M in the second set were always set the same way as rotors L and M in the first set". Preparation of this catalog, using the cyclometer, was, said Rejewski, "laborious and took over a year, but when it was ready, obtaining daily keys was a question of ome fifteenminutes".
However, on 1 November 1937, the Germans changed the Enigma reflector, necessitating the production of a new catalog—"a task which ays Rejewskiconsumed, on account of our greater experience, probably somewhat less than a year's time".
This characteristics method stopped working for German naval Enigma messages on 1 May 1937, when the indicator procedure was changed to one involving special codebooks (see German Navy 3-rotor Enigma below). Worse still, on 15 September 1938 it stopped working for German army and air force messages because operators were then required to choose their own ''Grundstellung'' (initial rotor setting) for each message. Although German army message keys would still be double-enciphered, the day's keys would not be double-enciphered at the same initial setting, so the characteristic could no longer be found or exploited.
Perforated sheets
 Although the characteristics method no longer worked, the inclusion of the enciphered message key twice gave rise to a phenomenon that the cryptanalyst Henryk Zygalski was able to exploit. Sometimes (about one message in eight) one of the repeated letters in the message key enciphered to the same letter on both occasions. These occurrences were called ''samiczki'' (in English, ''females''—a term later used at Bletchley Park).
Only a limited number of scrambler settings would give rise to females, and these would have been identifiable from the card catalog. If the first six letters of the ciphertext were ''SZVSIK'', this would be termed a 1-4 female; if ''WHOEHS'', a 2-5 female; and if ''ASWCRW'', a 3-6 female. The method was called ''Netz'' (from ''Netzverfahren'', "net method"), or the Zygalski sheet method as it used perforated sheets that he devised, although at Bletchley Park Zygalski's name was not used for security reasons. About ten females from a day's messages were required for success.
There was a set of 26 of these sheets for each of the six possible sequences ''wheel orders''. Each sheet was for the left (slowest-moving) rotor. The 51×51 matrices on the sheets represented the 676 possible starting positions of the middle and right rotors. The sheets contained about 1000 holes in the positions in which a female could occur. The set of sheets for that day's messages would be appropriately positioned on top of each other in the perforated sheets apparatus. Rejewski wrote about how the device was operated:
The holes in the sheets were painstakingly cut with razor blades and in the three months before the next major setback, the sets of sheets for only two of the possible six wheel orders had been produced.
Although the characteristics method no longer worked, the inclusion of the enciphered message key twice gave rise to a phenomenon that the cryptanalyst Henryk Zygalski was able to exploit. Sometimes (about one message in eight) one of the repeated letters in the message key enciphered to the same letter on both occasions. These occurrences were called ''samiczki'' (in English, ''females''—a term later used at Bletchley Park).
Only a limited number of scrambler settings would give rise to females, and these would have been identifiable from the card catalog. If the first six letters of the ciphertext were ''SZVSIK'', this would be termed a 1-4 female; if ''WHOEHS'', a 2-5 female; and if ''ASWCRW'', a 3-6 female. The method was called ''Netz'' (from ''Netzverfahren'', "net method"), or the Zygalski sheet method as it used perforated sheets that he devised, although at Bletchley Park Zygalski's name was not used for security reasons. About ten females from a day's messages were required for success.
There was a set of 26 of these sheets for each of the six possible sequences ''wheel orders''. Each sheet was for the left (slowest-moving) rotor. The 51×51 matrices on the sheets represented the 676 possible starting positions of the middle and right rotors. The sheets contained about 1000 holes in the positions in which a female could occur. The set of sheets for that day's messages would be appropriately positioned on top of each other in the perforated sheets apparatus. Rejewski wrote about how the device was operated:
The holes in the sheets were painstakingly cut with razor blades and in the three months before the next major setback, the sets of sheets for only two of the possible six wheel orders had been produced.
Polish ''bomba''
After Rejewski's characteristics method became useless, he invented an electro-mechanical device that was dubbed the ''bomba kryptologiczna'' or ''cryptologic bomb''. Each machine contained six sets of Enigma rotors for the six positions of the repeated three-letter key. Like the Zygalski sheet method, the ''bomba'' relied on the occurrence of ''females'', but required only three instead of about ten for the sheet method. Six ''bomby'' were constructed, one for each of the then possible ''wheel orders''. Each ''bomba'' conducted an exhaustive ( brute-force) analysis of the 17,576 possible message keys. Rejewski has written about the device: The cipher message transmitted the ''Grundstellung'' in the clear, so when a ''bomba'' found a match, it revealed the rotor order, the rotor positions, and the ring settings. The only remaining secret was the plugboard permutation.Major setback
On 15 December 1938, the German Army increased the complexity of Enigma enciphering by introducing two additional rotors (IV and V). This increased the number of possible ''wheel orders'' from 6 to 60. The Poles could then read only the small minority of messages that used neither of the two new rotors. They did not have the resources to commission 54 more bombs or produce 58 sets of Zygalski sheets. Other Enigma users received the two new rotors at the same time. However, until 1 July 1939 the ''Sicherheitsdienst
' (, ''Security Service''), full title ' (Security Service of the '' Reichsführer-SS''), or SD, was the intelligence agency of the SS and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany. Established in 1931, the SD was the first Nazi intelligence organization ...
'' (SD)—the intelligence agency of the SS and the Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
—continued to use its machines in the old way with the same indicator setting for all messages. This allowed Rejewski to reuse his previous method, and by about the turn of the year he had worked out the wirings of the two new rotors. On 1 January 1939, the Germans increased the number of plugboard connections from between five and eight to between seven and ten, which made other methods of decryption even more difficult.
Rejewski wrote, in a 1979 critique of appendix 1, volume 1 (1979), of the official history of British Intelligence in the Second World War:
World War II
Polish disclosures
As the likelihood of war increased in 1939, Britain and France pledged support for Poland in the event of action that threatened its independence. In April, Germany withdrew from the German–Polish Non-Aggression Pact of January 1934. The Polish General Staff, realizing what was likely to happen, decided to share their work on Enigma decryption with their western allies. Marian Rejewski later wrote: At a conference near Warsaw on 26 and 27 July 1939, the Poles revealed to the French and British that they had broken Enigma and pledged to give each a Polish-reconstructed Enigma, along with details of their Enigma-solving techniques and equipment, including Zygalski's perforated sheets and Rejewski's cryptologic bomb. In return, the British pledged to prepare two full sets ofZygalski sheets
The method of Zygalski sheets was a cryptologic technique used by the Polish Cipher Bureau before and during World War II, and during the war also by British cryptologists at Bletchley Park, to decrypt messages enciphered on German Enigma mac ...
for all 60 possible wheel orders. Dilly Knox was a member of the British delegation. He commented on the fragility of the Polish system's reliance on the repetition in the indicator, because it might "at any moment be cancelled". In August two Polish Enigma doubles were sent to Paris, whence Gustave Bertrand
Gustave Bertrand (1896–1976) was a French military intelligence officer who made a vital contribution to the decryption, by Poland's Cipher Bureau, of German Enigma ciphers, beginning in December 1932. This achievement would in turn lead to ...
took one to London, handing it to Stewart Menzies
Major General Sir Stewart Graham Menzies, (; 30 January 1890 – 29 May 1968) was Chief of MI6, the British Secret Intelligence Service (SIS), from 1939 to 1952, during and after the Second World War.
Early life, family
Stewart Graham Menzies wa ...
of Britain's Secret Intelligence Service at Victoria Station.
Gordon Welchman, who became head of Hut 6
Hut 6 was a wartime section of the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park, Buckinghamshire, Britain, tasked with the solution of German Army and Air Force Enigma machine cyphers. Hut 8, by contrast, attacked Naval Enigma. ...
at Bletchley Park, wrote:
Peter Calvocoressi
Peter John Ambrose Calvocoressi (17 November 1912 – 5 February 2010) was a British lawyer, Liberal politician, historian, and publisher. He served as an intelligence officer at Bletchley Park during World War II.
Early years
Calvocoressi w ...
, who became head of the Luftwaffe section in Hut 3, wrote of the Polish contribution:
''PC Bruno''
On 5 September 1939 the Cipher Bureau began preparations to evacuate key personnel and equipment from Warsaw. Soon a special evacuation train, the Echelon F, transported them eastward, then south. By the time the Cipher Bureau was ordered to cross the border into allied Romania on 17 September, they had destroyed all sensitive documents and equipment and were down to a single very crowded truck. The vehicle was confiscated at the border by a Romanian officer, who separated the military from the civilian personnel. Taking advantage of the confusion, the three mathematicians ignored the Romanian's instructions. They anticipated that in an internment camp they might be identified by the Romanian security police, in which the German Abwehr and SD had informers. The mathematicians went to the nearest railroad station, exchanged money, bought tickets, and boarded the first train headed south. After a dozen or so hours, they reached Bucharest, at the other end of Romania. There they went to the British embassy. Told by the British to "come back in a few days", they next tried the French embassy, introducing themselves as "friends of Bolek" (Bertrand's Polish code name) and asking to speak with a French military officer. A French Army colonel telephoned Paris and then issued instructions for the three Poles to be assisted in evacuating to Paris. On 20 October 1939, at ''PC Bruno
''PC Bruno'' was a Polish–French–Spanish signals–intelligence station near Paris during World War II, from October 1939 until June 1940. Its function was decryption of cipher messages, most notably German messages enciphered on the Enigma ...
'' outside Paris, the Polish cryptologists resumed work on German Enigma ciphers, in collaboration with Bletchley Park.
''PC Bruno'' and Bletchley Park worked together closely, communicating via a telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas p ...
line secured by the use of Enigma doubles. In January 1940 Alan Turing spent several days at ''PC Bruno'' conferring with his Polish colleagues. He had brought the Poles a full set of Zygalski sheets that had been punched at Bletchley Park by John Jeffreys using Polish-supplied information, and on 17 January 1940, the Poles made the first break into wartime Enigma traffic—that from 28 October 1939. From that time, until the Fall of France in June 1940, 17 percent of the Enigma keys that were found by the allies, were solved at ''PC Bruno''.
Just before opening their 10 May 1940 offensive against the Low Countries and France, the Germans made the feared change in the indicator procedure, discontinuing the duplication of the enciphered message key. This meant that the Zygalski sheet method no longer worked. Instead, the cryptanalysts had to rely on exploiting the operator weaknesses described below, particularly the cillies and the Herivel tip.
After the June Franco-German armistice, the Polish cryptological team resumed work in France's southern ''Free Zone'', although probably not on Enigma. Marian Rejewski and Henryk Zygalski, after many travails, perilous journeys and Spanish imprisonment, finally made it to Britain, where they were inducted into the Polish Army and put to work breaking German '' SS'' and '' SD'' hand ciphers at a Polish signals facility in Boxmoor
Boxmoor is part of Hemel Hempstead in Hertfordshire. It is within the district of Dacorum and comprises mainly 19th-century housing and meadowland, with transport links from London to the Midlands. At the 2011 Census, the population of Boxmoor wa ...
. Due to their having been in occupied France, it was thought too risky to invite them to work at Bletchley Park.
After the German occupation of Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its te ...
, several of those who had worked at ''PC Bruno'' were captured by the Germans. Despite the dire circumstances in which some of them were held, none betrayed the secret of Enigma's decryption.
Operating shortcomings
Apart from some less-than-ideal inherent characteristics of the Enigma, in practice the system's greatest weakness was the way that it was used. The basic principle of this sort of enciphering machine is that it should deliver a very long stream of transformations that are difficult for a cryptanalyst to predict. Some of the instructions to operators, however, and their sloppy habits, had the opposite effect. Without these operating shortcomings, Enigma would, almost certainly, not have been broken. The set of shortcomings that the Polish cryptanalysts exploited to such great effect included the following: * The production of an early Enigma training manual containing an example of plaintext and its genuine ciphertext, together with the relevant message key. When Rejewski was given this in December 1932, it "made is reconstruction of the Enigma machinesomewhat easier". * Repetition of the message key as described in Rejewski's characteristics method, above. (This helped in Rejewski's solving Enigma's wiring in 1932, and was continued until May 1940.) * Repeatedly using the same stereotypical expressions in messages, an early example of what Bletchley Park would later term cribs. Rejewski wrote that "... we relied on the fact that the greater number of messages began with the letters ''ANX''—German for "to", followed by ''X'' as a spacer". * The use of easily guessed keys such as ''AAA'' or ''BBB'', or sequences that reflected the layout of the Enigma keyboard, such as "three ypingkeys that stand next to each other diagonally rom each other.." At Bletchley Park such occurrences were called ''cillies''. Cillies in the operation of the four-rotor ''Abwehr'' Enigma included four-letter names and German obscenities. Sometimes, with multi-part messages, the operator would not enter a key for a subsequent part of a message, merely leaving the rotors as they were at the end of the previous part, to become the message key for the next part. * Having only three different rotors for the three positions in the scrambler. (This continued until December 1938, when it was increased to five and then eight for naval traffic in 1940.) * Using only six plugboard leads, leaving 14 letters ''unsteckered''. (This continued until January 1939 when the number of leads was increased, leaving only a small number of letters unsteckered.) Other useful shortcomings that were discovered by the British and later the American cryptanalysts included the following, many of which depended on frequent solving of a particular network: * The practice of re-transmitting a message in an identical, or near-identical, form on different cipher networks. If a message was transmitted using both a low-level cipher that Bletchley Park broke by hand, and Enigma, the decrypt provided an excellent crib for Enigma decipherment. * For machines where there was a choice of more rotors than there were slots for them, a rule on some networks stipulated that no rotor should be in the same slot in the scrambler as it had been for the immediately preceding configuration. This reduced the number of wheel orders that had to be tried. * Not allowing a wheel order to be repeated on a monthly setting sheet. This meant that when the keys were being found on a regular basis, economies in excluding possible wheel orders could be made. * The stipulation, for Air Force operators, that no letter should be connected on the plugboard to its neighbour in the alphabet. This reduced the problem of identifying the plugboard connections and was automated in some Bombes with a Consecutive Stecker Knock-Out (CSKO) device. * The sloppy practice that John Herivel anticipated soon after his arrival at Bletchley Park in January 1940. He thought about the practical actions that an Enigma operator would have to make, and the short cuts he might employ. He thought that, after setting the alphabet rings to the prescribed setting, and closing the lid, the operator might not turn the rotors by more than a few places in selecting the first part of the indicator. Initially this did not seem to be the case, but after the changes of May 1940, what became known as the Herivel tip proved to be most useful. * The practice of re-using some of the columns of wheel orders, ring settings or plugboard connections from previous months. The resulting analytical short-cut was christened at Bletchley Park ''Parkerismus'' after Reg Parker, who had, through his meticulous record-keeping, spotted this phenomenon. * The re-use of a permutation in the German Air Force METEO code as the Enigma ''stecker'' permutation for the day. Mavis Lever, a member of Dilly Knox's team, recalled an occasion when there was an extraordinary message. Postwar debriefings of German cryptographic specialists, conducted as part of projectTICOM
TICOM (Target Intelligence Committee) was a secret Allied project formed in World War II to find and seize German intelligence assets, particularly in the field of cryptology and signals intelligence.
It operated alongside other Western Allied ...
, tend to support the view that the Germans were well aware that the un-steckered Enigma was theoretically solvable, but thought that the steckered Enigma had not been solved.
Crib-based decryption
The term '' crib'' was used at Bletchley Park to denote any ''known plaintext
The known-plaintext attack (KPA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis where the attacker has access to both the plaintext (called a crib), and its encrypted version (ciphertext). These can be used to reveal further secret information such as secre ...
'' or ''suspected plaintext'' at some point in an enciphered message.
Britain's Government Code and Cipher School (GC&CS), before its move to Bletchley Park, had realised the value of recruiting mathematicians and logicians to work in codebreaking teams. Alan Turing, a Cambridge University mathematician with an interest in cryptology and in machines for implementing logical operations—and who was regarded by many as a genius—had started work for GC&CS on a part-time basis from about the time of the Munich Crisis
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
in 1938. Gordon Welchman, another Cambridge mathematician, had also received initial training in 1938, and they both reported to Bletchley Park on 4 September 1939, the day after Britain declared war on Germany.
Most of the Polish success had relied on the repetition within the indicator. But as soon as Turing moved to Bletchley Park—where he initially joined Dilly Knox in the research section—he set about seeking methods that did not rely on this weakness, as they correctly anticipated that the German Army and Air Force might follow the German Navy in improving their indicator system.
The Poles had used an early form of crib-based decryption in the days when only six leads were used on the plugboard. The technique became known as the ''Forty Weepy Weepy'' method for the following reason. When a message was a continuation of a previous one, the plaintext would start with ''FORT'' (from ''Fortsetzung'', meaning "continuation") followed by the time of the first message given twice bracketed by the letter ''Y''. At this time numerals were represented by the letters on the top row of the Enigma keyboard. So, "continuation of message sent at 2330" was represented as ''FORTYWEEPYYWEEPY''.
''Cribs'' were fundamental to the British approach to solving Enigma keys, but guessing the plaintext for a message was a highly skilled business. So in 1940 Stuart Milner-Barry
Sir Philip Stuart Milner-Barry (20 September 1906 – 25 March 1995) was a British chess player, chess writer, World War II codebreaker and civil servant. He represented England in chess both before and after World War II. He worked at Bletch ...
set up a special ''Crib Room'' in Hut 8.
Foremost amongst the knowledge needed for identifying cribs was the text of previous decrypts. Bletchley Park maintained detailed indexes of message preambles, of every person, of every ship, of every unit, of every weapon, of every technical term and of repeated phrases such as forms of address and other German military jargon. For each message the traffic analysis
Traffic analysis is the process of intercepting and examining messages in order to deduce information from patterns in communication, it can be performed even when the messages are encrypted. In general, the greater the number of messages observe ...
recorded the radio frequency, the date and time of intercept, and the preamble—which contained the network-identifying discriminant, the time of origin of the message, the callsign of the originating and receiving stations, and the indicator setting. This allowed cross referencing of a new message with a previous one. Thus, as Derek Taunt, another Cambridge mathematician-cryptanalyst wrote, the truism that "nothing succeeds like success" is particularly apposite here.
Stereotypical messages included ''Keine besonderen Ereignisse'' (literally, "no special occurrences"—perhaps better translated as "nothing to report"), ''An die Gruppe'' ("to the group") and a number that came from weather stations such as ''weub null seqs null null'' ("weather survey 0600"). This was actually rendered as ''WEUBYYNULLSEQSNULLNULL''. The word ''WEUB'' being short for ''Wetterübersicht'', ''YY'' was used as a separator and ''SEQS'' was common abbreviation of ''sechs'' (German for "six"). As another example, Field Marshal Erwin Rommel's Quartermaster started all of his messages to his commander with the same formal introduction.
With a combination of probable plaintext fragment and the fact that no letter could be enciphered as itself, a corresponding ciphertext fragment could often be tested by trying every possible alignment of the crib against the ciphertext, a procedure known as ''crib-dragging''. This, however, was only one aspect of the processes of solving a key. Derek Taunt has written that the three cardinal personal qualities that were in demand for cryptanalysis were (1) a creative imagination, (2) a well-developed critical faculty, and (3) a habit of meticulousness. Skill at solving crossword puzzles was famously tested in recruiting some cryptanalysts. This was useful in working out plugboard settings when a possible solution was being examined. For example, if the crib was the word ''WETTER'' (German for "weather") and a possible decrypt before the plugboard settings had been discovered, was ''TEWWER'', it is easy to see that ''T'' with ''W'' are ''stecker partners''. These examples, although illustrative of the principles, greatly over-simplify the cryptanalysts' tasks.
A fruitful source of cribs was re-encipherments of messages that had previously been decrypted either from a lower-level manual cipher or from another Enigma network. This was called a '' kiss'' and happened particularly with German naval messages being sent in the ''dockyard cipher'' and repeated ''verbatim'' in an Enigma cipher. One German agent in Britain, Nathalie Sergueiew, code named ''Treasure'', who had been '' turned'' to work for the Allies, was very verbose in her messages back to Germany, which were then re-transmitted on the ''Abwehr'' Enigma network. She was kept going by MI5
The Security Service, also known as MI5 ( Military Intelligence, Section 5), is the United Kingdom's domestic counter-intelligence and security agency and is part of its intelligence machinery alongside the Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), G ...
because this provided long cribs, not because of her usefulness as an agent to feed incorrect information to the ''Abwehr''.
Occasionally, when there was a particularly urgent need to solve German naval Enigma keys, such as when an Arctic convoy
The Arctic convoys of World War II were oceangoing convoys which sailed from the United Kingdom, Iceland, and North America to northern ports in the Soviet Union – primarily Arkhangelsk (Archangel) and Murmansk in Russia. There were 78 convoys ...
was about to depart, mines would be laid by the RAF
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
in a defined position, whose grid reference in the German naval system did not contain any of the words (such as ''sechs'' or ''sieben'') for which abbreviations or alternatives were sometimes used. The warning message about the mines and then the "all clear" message, would be transmitted both using the ''dockyard cipher'' and the U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
Enigma network. This process of ''planting'' a crib was called '' gardening''.
Although ''cillies'' were not actually cribs, the ''chit-chat'' in clear that Enigma operators indulged in amongst themselves, often gave a clue as to the cillies that they might generate.
When captured German Enigma operators revealed that they had been instructed to encipher numbers by spelling them out rather than using the top row of the keyboard, Alan Turing reviewed decrypted messages and determined that the word ''eins'' ("one") appeared in 90% of messages. Turing automated the crib process, creating the ''Eins Catalogue'', which assumed that ''eins'' was encoded at all positions in the plaintext. The catalogue included every possible rotor position for ''EINS'' with that day's ''wheel order'' and plugboard connections.
British ''bombe''
The British bombe was an electromechanical device designed by Alan Turing soon after he arrived at Bletchley Park in September 1939. Harold "Doc" Keen of theBritish Tabulating Machine Company
__NOTOC__
The British Tabulating Machine Company (BTM) was a firm which manufactured and sold Hollerith unit record equipment and other data-processing equipment. During World War II, BTM constructed some 200 "bombes", machines used at Bletchley ...
(BTM) in Letchworth
Letchworth Garden City, commonly known as Letchworth, is a town in the North Hertfordshire district of Hertfordshire, England. It is noted for being the first garden city. The population at the time of the 2011 census was 33,249.
Letchworth ...
( from Bletchley) was the engineer who turned Turing's ideas into a working machine—under the codename CANTAB. Turing's specification developed the ideas of the Poles' ''bomba kryptologiczna'' but was designed for the much more general crib-based decryption.
The bombe helped to identify the ''wheel order'', the initial positions of the rotor cores, and the ''stecker partner'' of a specified letter. This was achieved by examining all 17,576 possible scrambler positions for a set of ''wheel orders'' on a comparison between a crib and the ciphertext, so as to eliminate possibilities that contradicted the Enigma's known characteristics. In the words of Gordon Welchman "the task of the bombe was simply to reduce the assumptions of ''wheel order'' and scrambler positions that required 'further analysis' to a manageable number."
 The demountable drums on the front of the bombe were wired identically to the connections made by Enigma's different rotors. Unlike them, however, the input and output contacts for the left-hand and the right-hand sides were separate, making 104 contacts between each drum and the rest of the machine. This allowed a set of scramblers to be connected in series by means of 26-way cables. Electrical connections between the rotating drums' wiring and the rear plugboard were by means of metal brushes. When the bombe detected a scrambler position with no contradictions, it stopped and the operator would note the position before restarting it.
Although Welchman had been given the task of studying Enigma traffic
The demountable drums on the front of the bombe were wired identically to the connections made by Enigma's different rotors. Unlike them, however, the input and output contacts for the left-hand and the right-hand sides were separate, making 104 contacts between each drum and the rest of the machine. This allowed a set of scramblers to be connected in series by means of 26-way cables. Electrical connections between the rotating drums' wiring and the rear plugboard were by means of metal brushes. When the bombe detected a scrambler position with no contradictions, it stopped and the operator would note the position before restarting it.
Although Welchman had been given the task of studying Enigma traffic callsigns
In broadcasting and radio communications, a call sign (also known as a call name or call letters—and historically as a call signal—or abbreviated as a call) is a unique identifier for a transmitter station. A call sign can be formally assigne ...
and discriminants, he knew from Turing about the bombe design and early in 1940, before the first pre-production bombe was delivered, he showed him an idea to increase its effectiveness. It exploited the reciprocity in plugboard connections, to reduce considerably the number of scrambler settings that needed to be considered further. This became known as the ''diagonal board'' and was subsequently incorporated to great effect in all the bombes.
A cryptanalyst would prepare a crib for comparison with the ciphertext. This was a complicated and sophisticated task, which later took the Americans some time to master. As well as the crib, a decision as to which of the many possible ''wheel orders'' could be omitted had to be made. Turing's Banburismus
Banburismus was a cryptanalytic process developed by Alan Turing at Bletchley Park in Britain during the Second World War. It was used by Bletchley Park's Hut 8 to help break German ''Kriegsmarine'' (naval) messages enciphered on Enigma machin ...
was used in making this major economy. The cryptanalyst would then compile a ''menu'' which specified the connections of the cables of the patch panels on the back of the machine, and a particular letter whose ''stecker partner'' was sought. The menu reflected the relationships between the letters of the crib and those of the ciphertext. Some of these formed loops (or ''closures'' as Turing called them) in a similar way to the ''cycles'' that the Poles had exploited.
The reciprocal nature of the plugboard meant that no letter could be connected to more than one other letter. When there was a contradiction of two different letters apparently being ''stecker partners'' with the letter in the menu, the bombe would detect this, and move on. If, however, this happened with a letter that was not part of the menu, a false stop could occur. In refining down the set of stops for further examination, the cryptanalyst would eliminate stops that contained such a contradiction. The other plugboard connections and the settings of the alphabet rings would then be worked out before the scrambler positions at the possible true stops were tried out on Typex machines that had been adapted to mimic Enigmas. All the remaining stops would correctly decrypt the crib, but only the true stop would produce the correct plaintext of the whole message.
To avoid wasting scarce bombe time on menus that were likely to yield an excessive number of false stops, Turing performed a lengthy probability analysis (without any electronic aids) of the estimated number of stops per rotor order. It was adopted as standard practice only to use menus that were estimated to produce no more than four stops per ''wheel order''. This allowed an 8-letter crib for a 3-closure menu, an 11-letter crib for a 2-closure menu and a 14-letter crib for a menu with only one closure. If there was no closure, at least 16 letters were required in the crib. The longer the crib, however, the more likely it was that ''turn-over'' of the middle rotor would have occurred.
The production model 3-rotor bombes contained 36 scramblers arranged in three banks of twelve. Each bank was used for a different ''wheel order'' by fitting it with the drums that corresponded to the Enigma rotors being tested. The first bombe was named ''Victory'' and was delivered to Bletchley Park on 18 March 1940. The next one, which included the diagonal board, was delivered on 8 August 1940. It was referred to as a ''spider bombe'' and was named ''Agnus Dei'' which soon became ''Agnes'' and then ''Aggie''. The production of British bombes was relatively slow at first, with only five bombes being in use in June 1941, 15 by the year end, 30 by September 1942, 49 by January 1943 but eventually 210 at the end of the war.
A refinement that was developed for use on messages from those networks that disallowed the plugboard (''Stecker'') connection of adjacent letters, was the ''Consecutive Stecker Knock Out''. This was fitted to 40 bombes and produced a useful reduction in false stops.
Initially the bombes were operated by ex-BTM servicemen, but in March 1941 the first detachment of members of the Women's Royal Naval Service
The Women's Royal Naval Service (WRNS; popularly and officially known as the Wrens) was the women's branch of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. First formed in 1917 for the First World War, it was disbanded in 1919, then revived in 1939 at the ...
(known as ''Wrens'') arrived at Bletchley Park to become bombe operators. By 1945 there were some 2,000 Wrens operating the bombes. Because of the risk of bombing, relatively few of the bombes were located at Bletchley Park. The largest two outstations were at Eastcote
Eastcote is a suburban area in the London Borough of Hillingdon, in northwest London.
In the Middle Ages, Eastcote was one of the three areas that made up the parish of Ruislip, under the name of Ascot. The name came from its position to the e ...
(some 110 bombes and 800 Wrens) and Stanmore (some 50 bombes and 500 Wrens). There were also bombe outstations at Wavendon, Adstock and Gayhurst. Communication with Bletchley Park was by teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Init ...
links.
When the German Navy started using 4-rotor Enigmas, about sixty 4-rotor bombes were produced at Letchworth, some with the assistance of the General Post Office. The NCR-manufactured US Navy 4-rotor bombes were, however, very fast and the most successful. They were extensively used by Bletchley Park over teleprinter links (using the Combined Cipher Machine) to OP-20-G
OP-20-G or "Office of Chief Of Naval Operations (OPNAV), 20th Division of the Office of Naval Communications, G Section / Communications Security", was the U.S. Navy's signals intelligence and cryptanalysis group during World War II. Its mission ...
for both 3-rotor and 4-rotor jobs.
''Luftwaffe'' Enigma
Although the German army, SS, police, and railway all used Enigma with similar procedures, it was the ''Luftwaffe'' (Air Force) that was the first and most fruitful source of Ultra intelligence during the war. The messages were decrypted inHut 6
Hut 6 was a wartime section of the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park, Buckinghamshire, Britain, tasked with the solution of German Army and Air Force Enigma machine cyphers. Hut 8, by contrast, attacked Naval Enigma. ...
at Bletchley Park and turned into intelligence reports in Hut 3
Hut 3 was a section of the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park during World War II. It retained the name for its functions when it moved into Block D. It produced military intelligence codenamed ULTRA from the decrypts ...
. The network code-named 'Red' at Bletchley Park was broken regularly and quickly from 22 May 1940 until the end of hostilities. Indeed, the Air Force section of Hut 3 expected the new day's Enigma settings to have been established in Hut 6 by breakfast time. The relative ease of solving this network's settings was a product of plentiful cribs and frequent German operating mistakes. Luftwaffe chief Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German politician, military leader and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which ruled Germany from 1933 to 1 ...
was known to use it for trivial communications, including informing squadron commanders to make sure the pilots he was going to decorate had been properly deloused. Such messages became known as "Göring funnies" to the staff at Bletchley Park.
''Abwehr'' Enigma
 Dilly Knox's last great cryptanalytical success, before his untimely death in February 1943, was the solving of the '' Abwehr'' Enigma in 1941. Intercepts of traffic which had an 8-letter indicator sequence before the usual 5-letter groups led to the suspicion that a 4-rotor machine was being used. The assumption was correctly made that the indicator consisted of a 4-letter message key enciphered twice. The machine itself was similar to a Model G Enigma, with three conventional rotors, though it did not have a plug board. The principal difference to the model G was that it was equipped with a reflector that was advanced by the stepping mechanism once it had been set by hand to its starting position (in all other variants, the reflector was fixed). Collecting a set of enciphered message keys for a particular day allowed ''cycles'' (or ''boxes'' as Knox called them) to be assembled in a similar way to the method used by the Poles in the 1930s.
Knox was able to derive, using his ''buttoning up'' procedure, some of the wiring of the rotor that had been loaded in the fast position on that day. Progressively he was able to derive the wiring of all three rotors. Once that had been done, he was able to work out the wiring of the reflector. Deriving the indicator setting for that day was achieved using Knox's time-consuming ''rodding'' procedure. This involved a great deal of trial and error, imagination and crossword puzzle-solving skills, but was helped by ''cillies''.
The ''Abwehr'' was the
Dilly Knox's last great cryptanalytical success, before his untimely death in February 1943, was the solving of the '' Abwehr'' Enigma in 1941. Intercepts of traffic which had an 8-letter indicator sequence before the usual 5-letter groups led to the suspicion that a 4-rotor machine was being used. The assumption was correctly made that the indicator consisted of a 4-letter message key enciphered twice. The machine itself was similar to a Model G Enigma, with three conventional rotors, though it did not have a plug board. The principal difference to the model G was that it was equipped with a reflector that was advanced by the stepping mechanism once it had been set by hand to its starting position (in all other variants, the reflector was fixed). Collecting a set of enciphered message keys for a particular day allowed ''cycles'' (or ''boxes'' as Knox called them) to be assembled in a similar way to the method used by the Poles in the 1930s.
Knox was able to derive, using his ''buttoning up'' procedure, some of the wiring of the rotor that had been loaded in the fast position on that day. Progressively he was able to derive the wiring of all three rotors. Once that had been done, he was able to work out the wiring of the reflector. Deriving the indicator setting for that day was achieved using Knox's time-consuming ''rodding'' procedure. This involved a great deal of trial and error, imagination and crossword puzzle-solving skills, but was helped by ''cillies''.
The ''Abwehr'' was the intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be des ...
and counter-espionage
Counterintelligence is an activity aimed at protecting an agency's intelligence program from an opposition's intelligence service. It includes gathering information and conducting activities to prevent espionage, sabotage, assassinations or ot ...
service of the German High Command. The spies that it placed in enemy countries used a lower level cipher (which was broken by Oliver Strachey
Oliver Strachey CBE (3 November 1874 – 14 May 1960), a British civil servant in the Foreign Office, was a cryptographer from World War I to World War II.
Life and work
Strachey was a son of Sir Richard Strachey, colonial administrator and ...
's section at Bletchley Park) for their transmissions. However, the messages were often then re-transmitted word-for-word on the ''Abwehr's'' internal Enigma networks, which gave the best possible crib for deciphering that day's indicator setting. Interception and analysis of ''Abwehr'' transmissions led to the remarkable state of affairs that allowed MI5 to give a categorical assurance that all the German spies in Britain were controlled as double agents working for the Allies under the Double Cross System.
German Army Enigma
In the summer of 1940 following the Franco-German armistice, most Army Enigma traffic was travelling by land lines rather than radio and so was not available to Bletchley Park. The airBattle of Britain
The Battle of Britain, also known as the Air Battle for England (german: die Luftschlacht um England), was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defende ...
was crucial, so it was not surprising that the concentration of scarce resources was on ''Luftwaffe'' and ''Abwehr'' traffic. It was not until early in 1941 that the first breaks were made into German Army Enigma traffic, and it was the spring of 1942 before it was broken reliably, albeit often with some delay. It is unclear whether the German Army Enigma operators made deciphering more difficult by making fewer operating mistakes.
German Naval Enigma
The German Navy used Enigma in the same way as the German Army and Air Force until 1 May 1937 when they changed to a substantially different system. This used the same sort of setting sheet but, importantly, it included the ground key for a period of two, sometimes three days. The message setting was concealed in the indicator by selecting a trigram from a book (the '' Kenngruppenbuch'', or K-Book) and performing a bigram substitution on it. This defeated the Poles, although they suspected some sort of bigram substitution. The procedure for the naval sending operator was as follows. First they selected a trigram from the K-Book, say YLA. They then looked in the appropriate columns of the K-Book and selected another trigram, say YVT, and wrote it in the boxes at the top of the message form: They then filled in the "dots" with any letters, giving say: Finally they looked up the vertical pairs of letters in the Bigram Tables and wrote down the resultant pairs, UB, LK, RS and PW which were transmitted as two four letter groups at the start and end of the enciphered message. The receiving operator performed the converse procedure to obtain the message key for setting his Enigma rotors. As well as these ''Kriegsmarine'' procedures being much more secure than those of the German Army and Air Force, the German Navy Enigma introduced three more rotors (VI, VII and VIII), early in 1940. The choice of three rotors from eight meant that there were a total of 336 possible permutations of rotors and their positions. Alan Turing decided to take responsibility for German naval Enigma because "no one else was doing anything about it and I could have it to myself". He establishedHut 8
Hut 8 was a section in the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park (the British World War II codebreaking station, located in Buckinghamshire) tasked with solving German naval ( Kriegsmarine) Enigma messages. The section was ...
with Peter Twinn
Peter Frank George Twinn (9 January 1916 – 29 October 2004Dan van der Vat, "Obituary: Peter Twinn", ''The Guardian'', 20 November 2004) was a British mathematician, Second World War Cryptanalysis, codebreaker and entomologist. The first prof ...
and two "girls". Turing used the indicators and message settings for traffic from 1–8 May 1937 that the Poles had worked out, and some very elegant deductions to diagnose the complete indicator system. After the messages were deciphered they were translated for transmission to the Admiralty in Hut 4.
German Navy 3-rotor Enigma
The first break of wartime traffic was in December 1939, into signals that had been intercepted in November 1938, when only three rotors and six plugboard leads had been in use. It used "Forty Weepy Weepy" cribs. A captured German ''Funkmaat'' ("radio operator") named Meyer had revealed that numerals were now spelt out as words. EINS, the German for "one", was present in about 90% of genuine German Navy messages. An EINS catalogue was compiled consisting of the encipherment of EINS at all 105,456 rotor settings. These were compared with the ciphertext, and when matches were found, about a quarter of them yielded the correct plaintext. Later this process was automated in Mr Freeborn's section using Hollerith equipment. When the ground key was known, this EINS-ing procedure could yield three bigrams for the tables that were then gradually assembled. Further progress required more information from German Enigma users. This was achieved through a succession of ''pinches'', the capture of Enigma parts and codebooks. The first of these was on 12 February 1940, when rotors VI and VII, whose wiring was at that time unknown, were captured from the , by minesweeper . On 26 April 1940, the Narvik-bound German patrol boat ''VP2623'', disguised as a Dutch trawler named ''Polares'', was captured by . This yielded an instruction manual, codebook sheets and a record of some transmissions, which provided complete cribs. This confirmed that Turing's deductions about the trigram/bigram process were correct and allowed a total of six days' messages to be broken, the last of these using the first of the bombes. However, the numerous possible rotor sequences, together with a paucity of usable cribs, made the methods used against the Army and Air Force Enigma messages of very limited value with respect to the Navy messages. At the end of 1939, Turing extended the clock method invented by the Polish cryptanalystJerzy Różycki
Jerzy Witold Różycki (; Vilshana, Ukraine, 24 July 1909 – 9 January 1942, Mediterranean Sea, near the Balearic Islands) was a Polish mathematician and cryptologist who worked at breaking German Enigma-machine ciphers before and during World ...
. Turing's method became known as "Banburismus
Banburismus was a cryptanalytic process developed by Alan Turing at Bletchley Park in Britain during the Second World War. It was used by Bletchley Park's Hut 8 to help break German ''Kriegsmarine'' (naval) messages enciphered on Enigma machin ...
". Turing said that at that stage "I was not sure that it would work in practice, and was not in fact sure until some days had actually broken." Banburismus used large cards printed in Banbury (hence the Banburismus name) to discover correlations and a statistical scoring system to determine likely rotor orders (''Walzenlage'') to be tried on the bombes. The practice conserved scarce bombe time and allowed more messages to be attacked. In practice, the 336 possible rotor orders could be reduced to perhaps 18 to be run on the bombes. Knowledge of the bigrams was essential for Banburismus, and building up the tables took a long time. This lack of visible progress led to Frank Birch, head of the Naval Section, to write on 21 August 1940 to Edward Travis
Sir Edward Wilfred Harry Travis (24 September 1888 – 23 April 1956) was a British cryptographer and intelligence officer, becoming the operational head of Bletchley Park during World War II, and later the head of GCHQ.
Career
Educated loc ...
, Deputy Director of Bletchley Park:
Schemes for capturing Enigma material were conceived including, in September 1940, Operation Ruthless by Lieutenant Commander Ian Fleming (author of the James Bond
The ''James Bond'' series focuses on a fictional British Secret Service agent created in 1953 by writer Ian Fleming, who featured him in twelve novels and two short-story collections. Since Fleming's death in 1964, eight other authors have ...
novels). When this was cancelled, Birch told Fleming that "Turing and Twinn came to me like undertakers cheated of a nice corpse..."
A major advance came through Operation Claymore
Operation Claymore was a British commando raid on the Norwegian Lofoten Islands during the Second World War. The Lofoten Islands were an important centre for the production of fish oil and glycerine, used in the German war economy. The landing ...
, a commando
Royal Marines from 40 Commando on patrol in the Sangin">40_Commando.html" ;"title="Royal Marines from 40 Commando">Royal Marines from 40 Commando on patrol in the Sangin area of Afghanistan are pictured
A commando is a combatant, or operativ ...
raid on the Lofoten Islands on 4 March 1941. The German armed trawler
Naval trawlers are vessels built along the lines of a fishing trawler but fitted out for naval purposes; they were widely used during the First and Second World Wars. Some—known in the Royal Navy as "Admiralty trawlers"— were purpose-built t ...
''Krebs'' was captured, including the complete Enigma keys for February, but no bigram tables or K-book. However, the material was sufficient to reconstruct the bigram tables by "EINS-ing", and by late March they were almost complete.
Banburismus then started to become extremely useful. Hut 8 was expanded and moved to 24-hour working, and a crib room was established. The story of Banburismus for the next two years was one of improving methods, of struggling to get sufficient staff, and of a steady growth in the relative and absolute importance of cribbing as the increasing numbers of bombes made the running of cribs ever faster. Of value in this period were further "pinches" such as those from the German weather ships ''München'' and ''Lauenburg'' and the submarines and .
Despite the introduction of the 4-rotor Enigma for Atlantic U-boats, the analysis of traffic enciphered with the 3-rotor Enigma proved of immense value to the Allied navies. Banburismus was used until July 1943, when it became more efficient to use the many more bombes that had become available.
M4 (German Navy 4-rotor Enigma)
high-frequency direction finding
High-frequency direction finding, usually known by its abbreviation HF/DF or nickname huff-duff, is a type of radio direction finder (RDF) introduced in World War II. High frequency (HF) refers to a radio band that can effectively communicate over ...
techniques. The messages were only 22 characters long and were used to report sightings of possible Allied targets. A copy of the code book had been captured from on 9 May 1941. A similar coding system was used for weather reports from U-boats, the ''Wetterkurzschlüssel'', (Weather Short Code Book). A copy of this had been captured from on 29 or 30 October 1942. These short signals had been used for deciphering 3-rotor Enigma messages and it was discovered that the new rotor had a neutral position at which it, and its matching reflector, behaved just like a 3-rotor Enigma reflector. This allowed messages enciphered at this neutral position to be deciphered by a 3-rotor machine, and hence deciphered by a standard bombe. Deciphered Short Signals provided good material for bombe menus for Shark. Regular deciphering of U-boat traffic restarted in December 1942.
Italian naval Enigma
In 1940 Dilly Knox wanted to establish whether the Italian Navy were still using the same system that he had cracked during the Spanish Civil War; he instructed his assistants to use rodding to see whether the crib ''PERX'' (''per'' being Italian for "for" and ''X'' being used to indicate a space between words) worked for the first part of the message. After three months there was no success, but Mavis Lever, a 19-year-old student, found that rodding produced ''PERS'' for the first four letters of one message. She then (against orders) tried beyond this and obtained ''PERSONALE'' (Italian for "personal"). This confirmed that the Italians were indeed using the same machines and procedures. The subsequent breaking of Italian naval Enigma ciphers led to substantial Allied successes. The cipher-breaking was disguised by sending a reconnaissance aircraft to the known location of a warship before attacking it, so that the Italians assumed that this was how they had been discovered. The Royal Navy's victory at theBattle of Cape Matapan
The Battle of Cape Matapan ( el, Ναυμαχία του Ταινάρου) was a naval battle during the Second World War between the Allies, represented by the navies of the United Kingdom and Australia, and the Royal Italian navy, from 27 t ...
in March 1941 was considerably helped by Ultra intelligence obtained from Italian naval Enigma signals.
American ''bombes''
Unlike the situation at Bletchley Park, the United States armed services did not share a combined cryptanalytical service. Before the US joined the war, there was collaboration with Britain, albeit with a considerable amount of caution on Britain's side because of the extreme importance of Germany and her allies not learning that its codes were being broken. Despite some worthwhile collaboration amongst the cryptanalysts, their superiors took some time to achieve a trusting relationship in which both British and American bombes were used to mutual benefit. In February 1941, Captain Abraham Sinkov and Lieutenant Leo Rosen of the US Army, and Lieutenants Robert Weeks and Prescott Currier of the US Navy, arrived at Bletchley Park, bringing, amongst other things, a replica of the 'Purple' cipher machine for Bletchley Park's Japanese section in Hut 7. The four returned to America after ten weeks, with a naval radio direction finding unit and many documents, including a "paper Enigma". The main American response to the 4-rotor Enigma was the US Navy bombe, which was manufactured in much less constrained facilities than were available in wartime Britain. Colonel John Tiltman, who later became Deputy Director at Bletchley Park, visited the US Navy cryptanalysis office (OP-20-G) in April 1942 and recognised America's vital interest in deciphering U-boat traffic. The urgent need, doubts about the British engineering workload and slow progress prompted the US to start investigating designs for a Navy bombe, based on the fullblueprint
A blueprint is a reproduction of a technical drawing or engineering drawing using a contact print process on light-sensitive sheets. Introduced by Sir John Herschel in 1842, the process allowed rapid and accurate production of an unlimited number ...
s and wiring diagrams received by US Navy Lieutenants Robert Ely and Joseph Eachus at Bletchley Park in July 1942. Funding for a full, $2 million, Navy development effort was requested on 3 September 1942 and approved the following day.
 Commander Edward Travis, Deputy Director and Frank Birch, Head of the German Naval Section travelled from Bletchley Park to Washington in September 1942. With
Commander Edward Travis, Deputy Director and Frank Birch, Head of the German Naval Section travelled from Bletchley Park to Washington in September 1942. With Carl Frederick Holden
Carl Frederick Holden (May 25, 1895May 18, 1953) was a decorated officer in the United States Navy who reached the rank of Vice Admiral. A veteran of both World Wars, he became an expert in Naval communications, graduating with Master's degree ...
, US Director of Naval Communications they established, on 2 October 1942, a UK:US accord which may have "a stronger claim than BRUSA to being the forerunner of the UKUSA Agreement
The United Kingdom – United States of America Agreement (UKUSA, ) is a multilateral agreement for cooperation in signals intelligence between Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The alliance of intellig ...
," being the first agreement "to establish the special Sigint
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of '' signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication ...
relationship between the two countries," and "it set the pattern for UKUSA, in that the United States was very much the senior partner in the alliance." It established a relationship of "full collaboration" between Bletchley Park and OP-20-G.
An all electronic solution to the problem of a fast bombe was considered, but rejected for pragmatic reasons, and a contract was let with the National Cash Register Corporation (NCR) in Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is the sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County. The 2020 U.S. census estimate put the city population at 137,644, while Greater D ...
. This established the United States Naval Computing Machine Laboratory. Engineering development was led by NCR's Joseph Desch, a brilliant inventor and engineer. He had already been working on electronic counting devices.
Alan Turing, who had written a memorandum to OP-20-G (probably in 1941), was seconded to the British Joint Staff Mission in Washington in December 1942, because of his exceptionally wide knowledge about the bombes and the methods of their use. He was asked to look at the bombes that were being built by NCR and at the security of certain speech cipher equipment under development at Bell Labs. He visited OP-20-G, and went to NCR in Dayton on 21 December. He was able to show that it was not necessary to build 336 Bombes, one for each possible rotor order, by utilising techniques such as Banburismus
Banburismus was a cryptanalytic process developed by Alan Turing at Bletchley Park in Britain during the Second World War. It was used by Bletchley Park's Hut 8 to help break German ''Kriegsmarine'' (naval) messages enciphered on Enigma machin ...
. The initial order was scaled down to 96 machines.
The US Navy bombes used drums for the Enigma rotors in much the same way as the British bombes, but were very much faster. The first machine was completed and tested on 3 May 1943. Soon, these bombes were more available than the British bombes at Bletchley Park and its outstations, and as a consequence they were put to use for Hut 6 as well as Hut 8 work. A total of 121 Navy bombes were produced. In Alexander's "Cryptographic History of Work on German Naval Enigma", he wrote as follows.
The US Army also produced a version of a bombe. It was physically very different from the British and US Navy bombes. A contract was signed with Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial Research and development, research and scientific developm ...
on 30 September 1942. The machine was designed to analyse 3-rotor, not 4-rotor traffic. It did not use drums to represent the Enigma rotors, using instead telephone-type relays. It could, however, handle one problem that the bombes with drums could not. The set of ten bombes consisted of a total of 144 Enigma-equivalents, each mounted on a rack approximately long high and wide. There were 12 control stations which could allocate any of the Enigma-equivalents into the desired configuration by means of plugboards. Rotor order changes did not require the mechanical process of changing drums, but was achieved in about half a minute by means of push buttons. A 3-rotor run took about 10 minutes.
German suspicions
The German navy was concerned that Enigma could be compromised. Key schedules were printed in water-soluble inks so they could not be salvaged. The navy policed what its operators did and disciplined them when errors that could compromise the cipher were made. The navy minimized its exposure. For example, Enigma machines were not carried by ships that might be captured or run aground. When ships were lost in circumstances where they might be salvaged, the Germans investigated. After investigating some losses in 1940, Germany changed some message indicators. In April 1940, the British sank eight German destroyers in Norway. The Germans concluded that it was unlikely that the British were reading Enigma. In May 1941, the British deciphered some messages that gave the location of some supply ships for the battleship ''Bismarck'' and the cruiser ''Prinz Eugen''. As part of the '' Operation Rheinübung'' commerce raid, the Germans had assigned five tankers, two supply ships, and two scouts to support the warships. After the ''Bismarck'' was sunk, the British directed its forces to sink the supporting ships ''Belchen'', ''Esso Hamburg'', ''Egerland'', and some others. The Admiralty specifically did not target the tanker ''Gedania'' and the scout ''Gonzenheim'', figuring that sinking so many ships within one week would indicate to Germany that Britain was reading Enigma. However, by chance, British forces found those two ships and sank them. The Germans investigated, but concluded Enigma had not been breached by either seizures or brute force cryptanalysis. Nevertheless, the Germans took some steps to make Enigma more secure. Grid locations (an encoded latitude and longitude) were further disguised using digraph tables and a numeric offset. The U-boats were given their own network, ''Triton'', to minimize the chance of a cryptanalytic attack. In August 1941, the British captured . The Germans concluded the crew would have destroyed the important documents, so the cipher was safe. Even if the British had captured the materials intact and could read Enigma, the British would lose that ability when the keys changed on 1 November. Although Germany realized that convoys were avoiding its wolfpacks, it did not attribute that ability to reading Enigma traffic. Instead, Dönitz thought that Britain was using radar and direction finding. The ''Kriegsmarine'' continued to increase the number of networks to avoid superimposition attacks on Enigma. At the beginning of 1943, the ''Kriegsmarine'' had 13 networks. The ''Kriegsmarine'' also improved the Enigma. On 1 February 1942, it started using the four-rotor Enigma. The improved security meant that convoys no longer had as much information about the whereabouts of wolfpacks, and were therefore less able to avoid areas where they would be attacked. The increased success of wolfpack attacks following the strengthening of the encryption might have given the Germans a clue that the previous Enigma codes had been broken. However, that recognition did not happen because other things changed at the same time, the United States had entered the war and Dönitz had sent U-boats to raid the US East Coast where there were many easy targets. In early 1943, Dönitz was worried that the Allies were reading Enigma. Germany's own cryptanalysis of Allied communications showed surprising accuracy in its estimates of wolfpack sizes. It was concluded, however, that Allied direction finding was the source. The Germans also recovered acavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and currently in microwave ovens and linear particle accelerators. It generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field whi ...
from a downed British bomber. The conclusion was that the Enigma was secure. The Germans were still suspicious, so each submarine got its own key net in June 1944.
By 1945, almost all German Enigma traffic (Wehrmacht military; comprising the Heer, Kriegsmarine and Luftwaffe; and German intelligence and security services like the Abwehr, SD, etc.) could be decrypted within a day or two, yet the Germans remained confident of its security. They openly discussed their plans and movements, handing the Allies huge amounts of information, not all of which was used effectively. For example, Rommel's actions at Kasserine Pass were clearly foreshadowed in decrypted Enigma traffic, but the information was not properly appreciated by the Americans.
After the war, Allied TICOM
TICOM (Target Intelligence Committee) was a secret Allied project formed in World War II to find and seize German intelligence assets, particularly in the field of cryptology and signals intelligence.
It operated alongside other Western Allied ...
project teams found and detained a considerable number of German cryptographic personnel. Among the things learned was that German cryptographers, at least, understood very well that Enigma messages might be read; they knew Enigma was not unbreakable. They just found it impossible to imagine anyone going to the immense effort required. When Abwehr personnel who had worked on Fish cryptography and Russian traffic were interned at Rosenheim around May 1945, they were not at all surprised that Enigma had been broken, only that someone had mustered all the resources in time to actually do it. Admiral Dönitz had been advised that a cryptanalytic attack was the least likely of all security problems.
After World War II
Modern computers can be used to solve Enigma, using a variety of techniques. There have been projects to decrypt some remaining messages usingdistributed computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer sci ...
. Stefan Krah led an effort in Germany to decrypt three messages intercepted in 1942 by ; the messages were published by Ralph Erskine in a 1995 letter to ''Cryptologia''. Two of these messages were cracked in 2006, and the final one was decrypted in 2013. As of January 2018, the Enigma@home project is working on Enigma M4 message P1030680, which was sent from U-534 on 1 May 1945.
On 8 May 2020, to mark the 75th anniversary of VE Day
Victory in Europe Day is the day celebrating the formal acceptance by the Allies of World War II of Germany's unconditional surrender of its armed forces on Tuesday, 8 May 1945, marking the official end of World War II in Europe in the Easter ...
, GCHQ
Government Communications Headquarters, commonly known as GCHQ, is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the Uni ...
released the last Enigma message to be decrypted by codebreakers at Bletchley Park. The message was sent at 07:35 on 7 May 1945 by a German radio operator in Cuxhaven and read: "British troops entered Cuxhaven at 14:00 on 6 May 1945 - all radio broadcast will cease with immediate effect - I wish you all again the best of luck." It was immediately followed by another message: "Closing down forever - all the best - goodbye."
See also
*Cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher
Cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher was the process that enabled the British to read high-level German army messages during World War II. The British Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park decrypted many communications betwee ...
* I.J. Good
*Good–Turing frequency estimation
Good–Turing frequency estimation is a statistical technique for estimating the probability of encountering an object of a hitherto unseen species, given a set of past observations of objects from different species. In drawing balls from an urn, t ...
* Gisbert Hasenjaeger – responsible for Enigma security
*John Herivel
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second ...
* Erhard Maertens – investigated Enigma security
* Tadeusz Pełczyński
* Kiss (cryptanalysis)
*''The Imitation Game
''The Imitation Game'' is a 2014 American historical drama film directed by Morten Tyldum and written by Graham Moore, based on the 1983 biography '' Alan Turing: The Enigma'' by Andrew Hodges. The film's title quotes the name of the game c ...
''
* SIGABA, U.S. WWII rotor machine designed to overcome Enigma's weaknesses
* Typex, British WWII rotor machine with increased security
References and notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * This paper was written at the request ofTICOM
TICOM (Target Intelligence Committee) was a secret Allied project formed in World War II to find and seize German intelligence assets, particularly in the field of cryptology and signals intelligence.
It operated alongside other Western Allied ...
to show how the various German cipher machines could be solved. The authors assume Kerckhoffs's principle and do not address the breaking of the machines, only the solving of keys.
*
*
*
*
* A revised and augmented translation of ''W kręgu enigmy'', Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, Książka i Wiedza, 1979, supplemented with appendices by Marian Rejewski
* Largely an abridgment of , minus Rejewski's appendices, which have been replaced with appendices of varying quality by other authors
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Manuscript written at Uzès
Uzès (; ) is a commune in the Gard department in the Occitanie region of Southern France. In 2017, it had a population of 8,454. Uzès lies about north-northeast of Nîmes, west of Avignon and south-east of Alès.
History
Originally ''Uc ...
, France
* Manuscript
*
*
* Appendix B of
* Appendix C of
* Appendix D of
* Appendix E of
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* An early publication containing several misapprehensions that are corrected in an ''addendum'' in the 1997 edition.
* New edition updated with an ''addendum'' consisting of a 1986 paper written by Welchman that corrects his misapprehensions in the 1982 edition.
* This is reproduced as an ''addendum'' in the 1997 edition of Welchman's 'The Hut Six Story'.
*
* (also National Archives and Records Administration Record Group 457, File 35701.)
* ASIN: B0006RLRA4
*
External links
* Dayton Daily NewsDayton's Code Breakers
* Dayton Codebreakers Web site
DaytonCodebreakers.org
About the Enigma (National Security Agency)
"The Enigma machine and Bletchley Park"
''Cybertwists'' *
* ttp://www.matematiksider.dk/enigma_eng.html "The German cipher machine Enigma" ''Matematik Sider'', 20 September 2014
"The Polish Enigma crackers"
''Deutsche Welle'', 17 February 2015 (an audio report for general audiences)
* Sir Dermot Turing said that his uncle's achievements in cracking German communications encrypted on the Enigma machines were based on work by a group of Polish mathematicians:
Turing cult has obscured role of Polish codebreakers
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cryptanalysis Of The Enigma Bletchley Park Enigma machine History of cryptography Signals intelligence of World War II