Criticism of capitalism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Criticism of capitalism ranges from expressing disagreement with the principles of
Criticism of capitalism ranges from expressing disagreement with the principles of
 Early critics of capitalism, such as
Early critics of capitalism, such as
 Criticism of capitalism ranges from expressing disagreement with the principles of
Criticism of capitalism ranges from expressing disagreement with the principles of capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
in its entirety to expressing disagreement with particular outcomes of capitalism.
Criticism of capitalism comes from various political and philosophical approaches, including anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessar ...
, socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
, Marxist
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialecti ...
, religious
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
, and nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Th ...
viewpoints. Some believe that capitalism can only be overcome through revolution while others believe that structural change can come slowly through political reforms. Some critics believe there are merits in capitalism and wish to balance it with some form of social control, typically through government regulation (e.g. the social market
The social market economy (SOME; german: soziale Marktwirtschaft), also called Rhine capitalism, Rhine-Alpine capitalism, the Rhenish model, and social capitalism, is a socioeconomic model combining a free-market capitalist economic system alon ...
movement).
Prominent among critiques of capitalism are accusations that capitalism is inherently exploitative, alienating, unstable, unsustainable, and creates massive economic inequality
There are wide varieties of economic inequality, most notably income inequality measured using the distribution of income (the amount of money people are paid) and wealth inequality measured using the distribution of wealth (the amount of ...
, commodifies people, and is anti-democratic and leads to an erosion of human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
and national sovereignty while it incentivises imperialist
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power ( economic and ...
expansion and war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
.
History
 Early critics of capitalism, such as
Early critics of capitalism, such as Frederick Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ,"Engels"
'' rapid industrialization in Europe created working conditions viewed as unfair, including 14-hour work days,
 Within anarchism, there emerged a critique of wage slavery which refers to a situation perceived as quasi-
Within anarchism, there emerged a critique of wage slavery which refers to a situation perceived as quasi-
Libertarian Left
, ''
"Appendix A: Message from the President of the United States Transmitting Recommendations Relative to the Strengthening and Enforcement of Antitrust Laws"
''
 Critics of capitalism view the system as inherently exploitative. In an economic sense, exploitation is often related to the
Critics of capitalism view the system as inherently exploitative. In an economic sense, exploitation is often related to the
 Critics argue that capitalism is associated with the unfair distribution of wealth and power; a tendency toward market monopoly or oligopoly (and government by oligarchy); imperialism, counter-revolutionary wars and various forms of economic and cultural exploitation; Political repression, repression of workers and
Critics argue that capitalism is associated with the unfair distribution of wealth and power; a tendency toward market monopoly or oligopoly (and government by oligarchy); imperialism, counter-revolutionary wars and various forms of economic and cultural exploitation; Political repression, repression of workers and 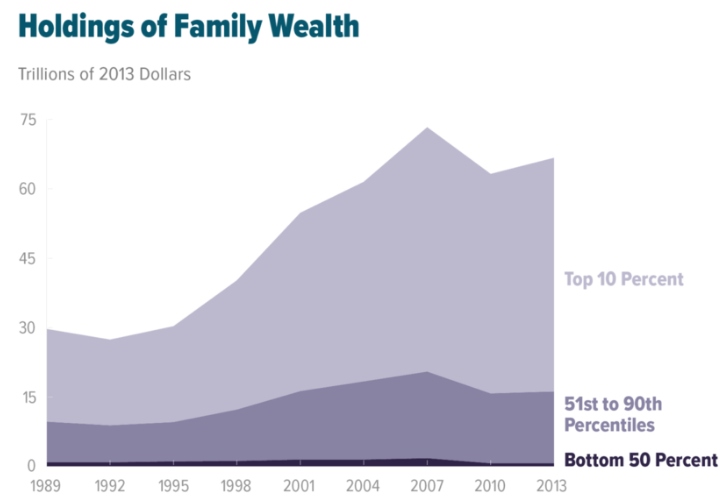 A modern critic of capitalism is Ravi Batra, who focuses on inequality as a source of immiserization but also of system failure. Batra popularised the concept "share of wealth held by richest 1%" as an indicator of inequality and an important determinant of depressions in his best-selling books in the 1980s. The scholars Kristen Ghodsee and Mitchell A. Orenstein suggest that left to its own devices, capitalism will result in a small group of economic elites capturing the majority of wealth and power in society. Dylan Sullivan and Jason Hickel argue that poverty continues to exist in the contemporary global capitalist system in spite of it being highly productive because it is undemocratic and has maintained conditions of extreme inequality where masses of working people, who have no ownership or control over the means of production, have their labor power "appropriated by a ruling class or an external imperial power," and are cut off from common land and resources.
In the United States, the shares of earnings and wealth of the households in the top 1 percent of the corresponding distributions are 21 percent (in 2006) and 37 percent (in 2009), respectively. Critics, such as Ravi Batra, argue that the capitalist system has inherent biases favoring those who already possess greater resources. The inequality may be propagated through inheritance and economic policy. Rich people are in a position to give their children a better education and inherited wealth and that this can create or increase large differences in wealth between people who do not differ in ability or effort. One study shows that in the United States 43.35% of the people in the ''Forbes'' magazine "400 richest individuals" list were already rich enough at birth to qualify. Another study indicated that in the United States wealth, race and schooling are important to the inheritance of economic status, but that IQ is not a major contributor and the genetic transmission of IQ is even less important. Batra has argued that the tax and benefit legislation in the United States since the Presidency of Ronald Reagan, Reagan presidency has contributed greatly to the inequalities and economic problems and should be repealed.
A modern critic of capitalism is Ravi Batra, who focuses on inequality as a source of immiserization but also of system failure. Batra popularised the concept "share of wealth held by richest 1%" as an indicator of inequality and an important determinant of depressions in his best-selling books in the 1980s. The scholars Kristen Ghodsee and Mitchell A. Orenstein suggest that left to its own devices, capitalism will result in a small group of economic elites capturing the majority of wealth and power in society. Dylan Sullivan and Jason Hickel argue that poverty continues to exist in the contemporary global capitalist system in spite of it being highly productive because it is undemocratic and has maintained conditions of extreme inequality where masses of working people, who have no ownership or control over the means of production, have their labor power "appropriated by a ruling class or an external imperial power," and are cut off from common land and resources.
In the United States, the shares of earnings and wealth of the households in the top 1 percent of the corresponding distributions are 21 percent (in 2006) and 37 percent (in 2009), respectively. Critics, such as Ravi Batra, argue that the capitalist system has inherent biases favoring those who already possess greater resources. The inequality may be propagated through inheritance and economic policy. Rich people are in a position to give their children a better education and inherited wealth and that this can create or increase large differences in wealth between people who do not differ in ability or effort. One study shows that in the United States 43.35% of the people in the ''Forbes'' magazine "400 richest individuals" list were already rich enough at birth to qualify. Another study indicated that in the United States wealth, race and schooling are important to the inheritance of economic status, but that IQ is not a major contributor and the genetic transmission of IQ is even less important. Batra has argued that the tax and benefit legislation in the United States since the Presidency of Ronald Reagan, Reagan presidency has contributed greatly to the inequalities and economic problems and should be repealed.
'' rapid industrialization in Europe created working conditions viewed as unfair, including 14-hour work days,
child labor
Child labour refers to the exploitation of children through any form of work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular school, and is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such e ...
and shanty towns. Some modern economists argue that average living standards did not improve, or only very slowly improved, before 1840.
Early socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
thinkers rejected capitalism altogether, attempting to create socialist communities free of the perceived injustices of early capitalism. Among these utopian socialists
Utopian socialism is the term often used to describe the first current of modern socialism and socialist thought as exemplified by the work of Henri de Saint-Simon, Charles Fourier, Étienne Cabet, and Robert Owen. Utopian socialism is often de ...
were Charles Fourier
François Marie Charles Fourier (;; 7 April 1772 – 10 October 1837) was a French philosopher, an influential early socialist thinker and one of the founders of utopian socialism. Some of Fourier's social and moral views, held to be radical ...
and Robert Owen
Robert Owen (; 14 May 1771 – 17 November 1858) was a Welsh people, Welsh textile manufacturer, philanthropist and social reformer, and a founder of utopian socialism and the cooperative movement. He strove to improve factory working conditio ...
. In 1848, Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
and Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ,"Engels"
'' The Communist Manifesto ''The Communist Manifesto'', originally the ''Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (german: Manifest der Kommunistischen Partei), is a political pamphlet written by German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Commissioned by the Commu ...
'', which outlined a political and economic critique of capitalism based on the philosophy of '' The Communist Manifesto ''The Communist Manifesto'', originally the ''Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (german: Manifest der Kommunistischen Partei), is a political pamphlet written by German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Commissioned by the Commu ...
historical materialism
Historical materialism is the term used to describe Karl Marx's theory of history. Marx locates historical change in the rise of class societies and the way humans labor together to make their livelihoods. For Marx and his lifetime collaborat ...
. Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (, , ; 15 January 1809, Besançon – 19 January 1865, Paris) was a French socialist,Landauer, Carl; Landauer, Hilde Stein; Valkenier, Elizabeth Kridl (1979) 959 "The Three Anticapitalistic Movements". ''European Socia ...
, a contemporary of Marx, was another notable critic of capitalism and was one of the first to call himself an anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessar ...
.
By the early 20th century, myriad socialist tendencies (e.g. anarcho-syndicalism
Anarcho-syndicalism is a political philosophy and anarchist school of thought that views revolutionary industrial unionism or syndicalism as a method for workers in capitalist society to gain control of an economy and thus control influence in ...
, social democracy
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote s ...
and Bolshevism
Bolshevism (from Bolshevik) is a revolutionary socialist current of Soviet Marxist–Leninist political thought and political regime associated with the formation of a rigidly centralized, cohesive and disciplined party of social revolution, ...
) had arisen based on different interpretations of current events. Governments also began placing restrictions on market operations and created interventionist programs, attempting to ameliorate perceived market shortcomings (e.g. Keynesian economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output ...
and the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Con ...
). Starting with the 1917 Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
, Communist state
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state that is administered and governed by a communist party guided by Marxism–Leninism. Marxism–Leninism was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, the Comint ...
s increased in number and a Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
started with the developed capitalist nations. Following the Revolutions of 1989
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Natio ...
, many of these Communist states adopted market economies.
Criticism by different schools of thought
Anarchism
French anarchistPierre-Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (, , ; 15 January 1809, Besançon – 19 January 1865, Paris) was a French socialist,Landauer, Carl; Landauer, Hilde Stein; Valkenier, Elizabeth Kridl (1979) 959 "The Three Anticapitalistic Movements". ''European Socia ...
opposed government privilege that protects capitalist, banking and land interests and the accumulation or acquisition of property (and any form of coercion
Coercion () is compelling a party to act in an involuntary manner by the use of threats, including threats to use force against a party. It involves a set of forceful actions which violate the free will of an individual in order to induce a des ...
that led to it) which he believed hampers competition and keeps wealth in the hands of the few. The Spanish individualist anarchist Miguel Giménez Igualada sees "capitalism is an effect of government; the disappearance of government means capitalism falls from its pedestal vertiginously ... That which we call capitalism is not something else but a product of the State, within which the only thing that is being pushed forward is profit, good or badly acquired. And so to fight against capitalism is a pointless task, since be it State capitalism
State capitalism is an economic system in which the state undertakes business and commercial (i.e. for-profit) economic activity and where the means of production are nationalized as state-owned enterprises (including the processes of capital ...
or Enterprise capitalism, as long as Government exists, exploiting capital will exist. The fight, but of consciousness, is against the State".
 Within anarchism, there emerged a critique of wage slavery which refers to a situation perceived as quasi-
Within anarchism, there emerged a critique of wage slavery which refers to a situation perceived as quasi-voluntary slavery
Voluntary slavery, in theory, is the condition of slavery entered into at a point of voluntary consent. It is distinguished from involuntary slavery where an individual is forced to a period of servitude usually as punishment for a crime.
Origi ...
, where a person's livelihood
A person's livelihood (derived from ''life-lode'', "way of life"; cf. OG ''lib-leit'') refers to their "means of securing the basic necessities (food, water, shelter and clothing) of life". Livelihood is defined as a set of activities essential t ...
depends on wage
A wage is payment made by an employer to an employee for work done in a specific period of time. Some examples of wage payments include compensatory payments such as ''minimum wage'', '' prevailing wage'', and ''yearly bonuses,'' and remune ...
s, especially when the dependence is total and immediate. It is a negatively connoted term used to draw an analogy between slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and wage labor
Wage labour (also wage labor in American English), usually referred to as paid work, paid employment, or paid labour, refers to the socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer in which the worker sells their labour power unde ...
by focusing on similarities between owning and renting
Renting, also known as hiring or letting, is an agreement where a payment is made for the temporary use of a good, service or property owned by another. A gross lease is when the tenant pays a flat rental amount and the landlord pays for a ...
a person. The term "wage slavery" has been used to criticize economic exploitation and social stratification
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, race, education, ethnicity, gender, occupation, social status, or derived power (social and politi ...
, with the former seen primarily as unequal bargaining power between labor and capital (particularly when workers are paid comparatively low wages, e.g. in sweatshops) and the latter as a lack of workers' self-management
Workers' self-management, also referred to as labor management and organizational self-management, is a form of organizational management based on self-directed work processes on the part of an organization's workforce. Self-management is a def ...
, fulfilling job choices and leisure in an economy.
Libertarian socialists believe if freedom is valued, then society must work towards a system in which individuals have the power to decide economic issues along with political issues. Libertarian socialists seek to replace unjustified authority with direct democracy
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the electorate decides on policy initiatives without elected representatives as proxies. This differs from the majority of currently established democracies, which are repres ...
, voluntary federation and popular autonomy in all aspects of life, including physical communities and economic enterprises. With the advent of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, thinkers such as Proudhon and Marx elaborated the comparison between wage labor and slavery in the context of a critique of societal property not intended for active personal use, Luddite
The Luddites were a secret oath-based organisation of English textile workers in the 19th century who formed a radical faction which destroyed textile machinery. The group is believed to have taken its name from Ned Ludd, a legendary weaver ...
s emphasized the dehumanization
Dehumanization is the denial of full humanness in others and the cruelty and suffering that accompanies it. A practical definition refers to it as the viewing and treatment of other persons as though they lack the mental capacities that are c ...
brought about by machines while later Emma Goldman
Emma Goldman (June 27, 1869 – May 14, 1940) was a Russian-born anarchist political activist and writer. She played a pivotal role in the development of anarchist political philosophy in North America and Europe in the first half of the ...
famously denounced wage slavery by saying: "The only difference is that you are hired slaves instead of block slaves". American anarchist Emma Goldman believed that the economic system of capitalism was incompatible with human liberty. "The only demand that property recognizes", she wrote in ''Anarchism and Other Essays'', "is its own gluttonous appetite for greater wealth, because wealth means power; the power to subdue, to crush, to exploit, the power to enslave, to outrage, to degrade". She also argued that capitalism dehumanized workers, "turning the producer into a mere particle of a machine, with less will and decision than his master of steel and iron".
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky i ...
contends that there is little moral difference between chattel slavery and renting one's self to an owner or "wage slavery". He feels that it is an attack on personal integrity that undermines individual freedom. He holds that workers should own and control their workplace. Many libertarian socialists argue that large-scale voluntary associations should manage industrial manufacture while workers retain rights to the individual products of their labor. As such, they see a distinction between the concepts of "private property" and " personal possession". Whereas "private property" grants an individual exclusive control over a thing whether it is in use or not and regardless of its productive capacity, "possession" grants no rights to things that are not in use.
In addition to anarchist Benjamin Tucker
Benjamin Ricketson Tucker (; April 17, 1854 – June 22, 1939) was an American individualist anarchist and libertarian socialist.Martin, James J. (1953)''Men Against the State: The Expositers of Individualist Anarchism in America, 1827–1908''< ...
's "big four" monopolies (land, money, tariffs and patents) that have emerged under capitalism, neo- mutualist economist Kevin Carson argues that the state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
has also transferred wealth to the wealthy by subsidizing organizational centralization in the form of transportation and communication subsidies. He believes that Tucker overlooked this issue due to Tucker's focus on individual market transactions, whereas Carson also focuses on organizational issues. The theoretical sections of '' Studies in Mutualist Political Economy'' are presented as an attempt to integrate marginalist
Marginalism is a theory of economics that attempts to explain the discrepancy in the value of goods and services by reference to their secondary, or marginal, utility. It states that the reason why the price of diamonds is higher than that of wa ...
critiques into the labor theory of value
The labor theory of value (LTV) is a theory of value that argues that the economic value of a good or service is determined by the total amount of " socially necessary labor" required to produce it.
The LTV is usually associated with Marxian ...
. Carson has also been highly critical of intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
. The primary focus of his most recent work has been decentralized manufacturing and the informal and household economies. Carson holds that " pitalism, arising as a new class society directly from the old class society of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, was founded on an act of robbery as massive as the earlier feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
conquest of the land. It has been sustained to the present by continual state intervention to protect its system of privilege without which its survival is unimaginable".Richman, SheldonLibertarian Left
, ''
The American Conservative
''The American Conservative'' (''TAC'') is a magazine published by the American Ideas Institute which was founded in 2002. Originally published twice a month, it was reduced to monthly publication in August 2009, and since February 2013, it has ...
'' (March 2011)
Carson coined the pejorative
A pejorative or slur is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or a disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility, or disregard. Sometimes, a ...
term "vulgar libertarianism", a phrase that describes the use of a free market rhetoric in defense of corporate capitalism
In social science and economics, corporate capitalism is a capitalist marketplace characterized by the dominance of hierarchical and bureaucratic corporations.
Overview
A large proportion of the economy of the United States and its labour mark ...
and economic inequality
There are wide varieties of economic inequality, most notably income inequality measured using the distribution of income (the amount of money people are paid) and wealth inequality measured using the distribution of wealth (the amount of ...
. According to Carson, the term is derived from the phrase "vulgar political economy", which Karl Marx described as an economic order that "deliberately becomes increasingly apologetic and makes strenuous attempts to talk out of existence the ideas which contain the contradictions xisting in economic life. Capitalism has been criticized for establishing power in the hands of a minority capitalist class that exists through the exploitation of a working class majority; for prioritizing profit over social good, natural resources and the environment; and for being an engine of inequality and economic instabilities.
Conservatism and traditionalism
Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke (; 12 January NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS">New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">NS/nowiki>_1729_–_9_July_1797)_was_an_NS.html"_;"title="New_Style.html"_;"title="/nowiki>New_Style">N ...
accepted the liberal ideals of private property and the economics of Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——� ...
, but he thought that economics should remain subordinate to the conservative social ethic, that capitalism should be subordinate to the medieval social tradition and that the business class should be subordinate to aristocracy
Aristocracy (, ) is a form of government that places strength in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats. The term derives from the el, αριστοκρατία (), meaning 'rule of the best'.
At the time of the word' ...
.
Distributism
Distributism is an economic theory asserting that the world's productive assets should be widely owned rather than concentrated.
Developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, distributism was based upon Catholic social teaching prin ...
is an economic ideology asserting that the world's productive assets should be widely owned rather than concentrated. It was developed in Europe in the late 19th and early 20th centuries based upon the principles of Catholic social teaching
Catholic social teaching, commonly abbreviated CST, is an area of Catholic doctrine concerning matters of human dignity and the common good in society. The ideas address oppression, the role of the state, subsidiarity, social organizatio ...
, especially the teachings of Pope Leo XIII
Pope Leo XIII ( it, Leone XIII; born Vincenzo Gioacchino Raffaele Luigi Pecci; 2 March 1810 – 20 July 1903) was the head of the Catholic Church from 20 February 1878 to his death in July 1903. Living until the age of 93, he was the second-ol ...
in his encyclical
An encyclical was originally a circular letter sent to all the churches of a particular area in the ancient Roman Church. At that time, the word could be used for a letter sent out by any bishop. The word comes from the Late Latin (originally fr ...
''Rerum novarum
''Rerum novarum'' (from its incipit, with the direct translation of the Latin meaning "of revolutionary change"), or ''Rights and Duties of Capital and Labor'', is an encyclical issued by Pope Leo XIII on 15 May 1891. It is an open letter, pa ...
'' (1891) and Pope Pius XI
Pope Pius XI ( it, Pio XI), born Ambrogio Damiano Achille Ratti (; 31 May 1857 – 10 February 1939), was head of the Catholic Church from 6 February 1922 to his death in February 1939. He was the first sovereign of Vatican City f ...
in '' Quadragesimo anno'' (1931). It views both capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
and socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes th ...
as equally flawed and exploitative, and it favors economic mechanisms such as small-scale cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-contro ...
s and family business
A family business is a commercial organization in which decision-making is influenced by multiple generations of a family, related by blood or marriage or adoption, who has both the ability to influence the vision of the business and the willingn ...
es, and large-scale antitrust regulations.
In ''Conservatives Against Capitalism'', Peter Kolozi relies on Norberto Bobbio
Norberto Bobbio (; 18 October 1909 – 9 January 2004) was an Italian philosopher of law and political sciences and a historian of political thought. He also wrote regularly for the Turin-based daily ''La Stampa''.
Bobbio was a social libe ...
's definition of right and left, dividing the two camps according to their preference for equality or hierarchy. Kolozi argued that capitalism has faced persistent criticism from the right since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. Such critics, while heterogeneous, are united in the belief “that laissez-faire capitalism has undermined an established social hierarchy governed by the virtuous or excellent".
In September 2018, Murtaza Hussain wrote in ''The Intercept
''The Intercept'' is an American left-wing news website founded by Glenn Greenwald, Jeremy Scahill, Laura Poitras and funded by billionaire eBay co-founder Pierre Omidyar. Its current editor is Betsy Reed. The publication initially report ...
'' about "Conservatives Against Capitalism", stating:
For all their differences, there is one key aspect of the intellectual history charted in "Conservatives Against Capitalism" that deals with an issue of shared concern on both the left and the right: the need for community. One of the grim consequences of the Social Darwinian pressures unleashed by free-market capitalism has been the destruction of networks of community, family, and professional associations in developed societies. ... These so-called intermediate institutions have historically played a vital role giving ordinary people a sense of meaning and protecting them from thestructural violence Structural violence is a form of violence wherein some social structure or social institution may harm people by preventing them from meeting their basic needs. The term was coined by Norwegian sociologist Johan Galtung, who introduced it in hi ...of the state and the market. Their loss has led to the creation of a huge class of atomized and lonely people, cut adrift from traditional sources of support and left alone to contend with the power of impersonal economic forces.
Fascism
Fascists opposed bothinternational socialism
Proletarian internationalism, sometimes referred to as international socialism, is the perception of all communist revolutions as being part of a single global class struggle rather than separate localized events. It is based on the theory that ...
and free-market capitalism
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or an ...
, arguing that their views represented a Third Position
The Third Position is a set of neo-fascist political ideologies that were first described in Western Europe following the Second World War. Developed in the context of the Cold War, it developed its name through the claim that it represented a ...
and claiming to provide a realistic economic alternative that was neither ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups ...
'' capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
nor communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
. They favored corporatism
Corporatism is a collectivist political ideology which advocates the organization of society by corporate groups, such as agricultural, labour, military, business, scientific, or guild associations, on the basis of their common interests. The ...
and class collaboration
Class collaboration is a principle of social organization based upon the belief that the division of society into a hierarchy of social classes is a positive and essential aspect of civilization.
Fascist support
Class collaboration is one of th ...
, believing that the existence of inequality and social hierarchy was beneficial (contrary to the views of socialists
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the econ ...
) while also arguing that the state had a role in mediating relations between classes (contrary to the views of economic liberals
Economic liberalism is a political and economic ideology that supports a market economy based on individualism and private property in the means of production. Adam Smith is considered one of the primary initial writers on economic liberalism, ...
).
Liberalism
During theAge of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
, some proponents of liberalism were critics of wage slavery. On the other hand, some modern-day liberals are critical only of ''laissez-faire'' capitalism and support a social market economy
The social market economy (SOME; german: soziale Marktwirtschaft), also called Rhine capitalism, Rhine-Alpine capitalism, the Rhenish model, and social capitalism, is a socioeconomic model combining a free-market capitalist economic system alon ...
while others are critical of the mixed economy
A mixed economy is variously defined as an economic system blending elements of a market economy with elements of a planned economy, markets with state interventionism, or private enterprise with public enterprise. Common to all mixed economie ...
welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equita ...
and advocate either its abolition in favor of ''laissez-faire'' capitalism or a reduction of its role in favor of free-market capitalism
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or an ...
.
Marxian responses
Marx considered capitalism to be a historically specific mode of production (the way in which the productive property is owned and controlled, combined with the correspondingsocial relations
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals ...
between individuals based on their connection with the process of production).
The "capitalistic era" according to Karl Marx dates from 16th-century merchants and small urban workshops. Marx knew that wage labour existed on a modest scale for centuries before capitalist industry. For Marx, the capitalist stage of development or "bourgeois
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. ...
society" represented the most advanced form of social organization to date, but he also thought that the working classes would come to power in a worldwide socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
or communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
transformation of human society as the end of the series of first aristocratic, then capitalist and finally working class rule was reached.
Following Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——� ...
, Marx distinguished the use value of commodities from their exchange value
In political economy and especially Marxian economics, exchange value (German: ''Tauschwert'') refers to one of the four major attributes of a commodity, i.e., an item or service produced for, and sold on the market, the other three attributes ...
in the market. According to Marx, capital is created with the purchase of commodities for the purpose of creating new commodities with an exchange value higher than the sum of the original purchases. For Marx, the use of labor power had itself become a commodity under capitalism and the exchange value of labor power, as reflected in the wage, is less than the value it produces for the capitalist.
This difference in values, he argues, constitutes surplus value
In Marxian economics, surplus value is the difference between the amount raised through a sale of a product and the amount it cost to the owner of that product to manufacture it: i.e. the amount raised through sale of the product minus the cos ...
, which the capitalists extract and accumulate. In his book ''Capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
'', Marx argues that the capitalist mode of production is distinguished by how the owners of capital extract this surplus from workers—all prior class societies had extracted surplus labor, but capitalism was new in doing so via the sale-value of produced commodities. He argues that a core requirement of a capitalist society is that a large portion of the population must not possess sources of self-sustenance that would allow them to be independent and are instead forced to sell their labor for a wage.
In conjunction with his criticism of capitalism was Marx's belief that the working class, due to its relationship to the means of production and numerical superiority under capitalism, would be the driving force behind the socialist revolution. This argument is intertwined with Marx' version of the labor theory of value
The labor theory of value (LTV) is a theory of value that argues that the economic value of a good or service is determined by the total amount of " socially necessary labor" required to produce it.
The LTV is usually associated with Marxian ...
arguing that labor is the source of all value and thus of profit.
In '' Imperialism, the Highest Stage of Capitalism'' (1916), Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
further developed Marxist theory and argued that capitalism necessarily led to monopoly capitalism
''Monopoly Capital: An Essay on the American Economic and Social Order'' is a 1966 book by the Marxian economists Paul Sweezy and Paul A. Baran. It was published by Monthly Review Press. It made a major contribution to Marxian theory by shifti ...
and the export of capital—which he also called "imperialism"—to find new markets and resources, representing the last and highest stage of capitalism. Some 20th-century Marxian economists consider capitalism to be a social formation where capitalist class processes dominate, but are not exclusive.
To these thinkers, capitalist class processes are simply those in which surplus labor takes the form of surplus value, usable as capital; other tendencies for utilization of labor nonetheless exist simultaneously in existing societies where capitalist processes predominate. However, other late Marxian thinkers argue that a social formation as a whole may be classed as capitalist if capitalism is the mode by which a surplus is extracted, even if this surplus is not produced by capitalist activity as when an absolute majority of the population is engaged in non-capitalist economic activity.
In ''Limits to Capital'' (1982), David Harvey
David W. Harvey (born 31 October 1935) is a British-born Marxist economic geographer, podcaster and Distinguished Professor of anthropology and geography at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York (CUNY). He received his P ...
outlines an overdetermined, "spatially restless" capitalism coupled with the spatiality of crisis formation and resolution. Harvey used Marx's theory of crisis to aid his argument that capitalism must have its "fixes", but that we cannot predetermine what fixes will be implemented, nor in what form they will be. His work on contractions of capital accumulation and international movements of capitalist modes of production and money flows has been influential.Lawson, Victoria. ''Making Development Geography (Human Geography in the Making)''. New York: A Hodder Arnold Publication, 2007. Print. According to Harvey, capitalism creates the conditions for volatile and geographically uneven development.
Sociologists such as Ulrich Beck envisioned the society of risk as a new cultural value which saw risk as a commodity to be exchanged in globalized economies. This theory suggested that disasters and capitalist economy were inevitably entwined. Disasters allow the introduction of economic programs which otherwise would be rejected as well as decentralizing the class structure in production.
Religion
Manyorganized religion
Organized religion, also known as institutional religion, is religion in which belief systems and rituals are systematically arranged and formally established. Organized religion is typically characterized by an official doctrine (or dogma), ...
s have criticized or opposed specific elements of capitalism. Traditional Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
, and Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
forbid lending money at interest, although alternative methods of banking have been developed. Some Christians have criticized capitalism for its materialist
Materialism is a form of philosophical monism which holds matter to be the fundamental substance in nature, and all things, including mental states and consciousness, are results of material interactions. According to philosophical materiali ...
aspects and its inability to account for the wellbeing of all people. Many of Jesus' parables deal with economic concerns: farming, shepherding, being in debt, doing hard labor, being excluded from banquets and the houses of the rich and have implications for wealth and power distribution. Catholic scholars and clergy have often criticized capitalism because of its disenfranchisement of the poor, often promoting distributism
Distributism is an economic theory asserting that the world's productive assets should be widely owned rather than concentrated.
Developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, distributism was based upon Catholic social teaching prin ...
as an alternative. In his 84-page apostolic exhortation , Catholic Pope Francis
Francis may refer to:
People
*Pope Francis, the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State and Bishop of Rome
* Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Francis (surname)
Places
*Rural ...
described unfettered capitalism as "a new tyranny" and called on world leaders to fight rising poverty and inequality, stating:
The Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
forbids usury
Usury () is the practice of making unethical or immoral monetary loans that unfairly enrich the lender. The term may be used in a moral sense—condemning taking advantage of others' misfortunes—or in a legal sense, where an interest rate is c ...
. As established by papal encyclicals ''Rerum Novarum
''Rerum novarum'' (from its incipit, with the direct translation of the Latin meaning "of revolutionary change"), or ''Rights and Duties of Capital and Labor'', is an encyclical issued by Pope Leo XIII on 15 May 1891. It is an open letter, pa ...
'' and '' Quadragesimo Anno'', Catholic social teaching
Catholic social teaching, commonly abbreviated CST, is an area of Catholic doctrine concerning matters of human dignity and the common good in society. The ideas address oppression, the role of the state, subsidiarity, social organizatio ...
does not support unrestricted capitalism, primarily because it is considered part of liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostilit ...
and secondly by its nature, which goes against social justice. In 2013, Pope Francis
Pope Francis ( la, Franciscus; it, Francesco; es, link=, Francisco; born Jorge Mario Bergoglio, 17 December 1936) is the head of the Catholic Church. He has been the bishop of Rome and sovereign of the Vatican City State since 13 March 2013 ...
said that more restrictions on the free market were required because the "dictatorship" of the global financial system and the "cult of money" were making people miserable. In his encyclical '' Laudato si''', Pope Francis denounced the role of capitalism in furthering climate change.
Islam forbids lending money at interest (''riba''), the mode of operation of capitalist finance, although Islamic banks
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main ...
have developed alternative methods of making profits in transactions that are traditionally arranged using interest.
Socialism
Socialists argue that the accumulation of capital generates waste throughexternalities
In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either c ...
that require costly corrective regulatory measures. They also point out that this process generates wasteful industries and practices that exist only to generate sufficient demand for products to be sold at a profit (such as high-pressure advertisement), thereby creating rather than satisfying economic demand.
Socialists argue that capitalism consists of irrational activity, such as the purchasing of commodities only to sell at a later time when their price appreciates (known as speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. (It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.)
Many ...
), rather than for consumption. Therefore, a crucial criticism often made by socialists is that making money, or accumulation of capital, does not correspond to the satisfaction of demand (the production of use-values). The fundamental criterion for economic activity in capitalism is the accumulation of capital for reinvestment in production. This spurs the development of new, non-productive industries that do not produce use-value and only exist to keep the accumulation process afloat. An example of a non-productive industry is the financial industry
Financial services are the economic services provided by the finance industry, which encompasses a broad range of businesses that manage money, including credit unions, banks, credit-card companies, insurance companies, accountancy companies, ...
, which contributes to the formation of economic bubbles.
Socialists view private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property and personal property, which is owned by a state entity, and from collective or ...
relations as limiting the potential of productive forces
Productive forces, productive powers, or forces of production (German: ''Produktivkräfte'') is a central idea in Marxism and historical materialism.
In Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels' own critique of political economy, it refers to the combina ...
in the economy. According to socialists, private property becomes obsolete when it concentrates into centralized, socialized institutions based on private appropriation of revenue (but based on cooperative work and internal planning in allocation of inputs) until the role of the capitalist becomes redundant. With no need for capital accumulation
Capital accumulation is the dynamic that motivates the pursuit of profit, involving the investment of money or any financial asset with the goal of increasing the initial monetary value of said asset as a financial return whether in the form ...
and a class of owners, private property of the means of production is perceived as being an outdated form of economic organization that should be replaced by a free association of individuals based on public or common ownership
Common ownership refers to holding the assets of an organization, enterprise or community indivisibly rather than in the names of the individual members or groups of members as common property.
Forms of common ownership exist in every econom ...
of these socialized assets.Marx and Engels Selected Works, Lawrence and Wishart, 1968, p. 40. Capitalist property relations put a "fetter" on the productive forces. Private ownership imposes constraints on planning, leading to uncoordinated economic decisions that result in business fluctuations, unemployment and a tremendous waste of material resources during crisis of overproduction
In economics, overproduction, oversupply, excess of supply or glut refers to excess of supply over demand of products being offered to the market. This leads to lower prices and/or unsold goods along with the possibility of unemployment.
The d ...
.''The Political Economy of Socialism'', by Horvat, Branko. 1982. (p. 197)
Excessive disparities in income distribution lead to social instability and require costly corrective measures in the form of redistributive taxation. This incurs heavy administrative costs while weakening the incentive to work, inviting dishonesty and increasing the likelihood of tax evasion (the corrective measures) while reducing the overall efficiency of the market economy.''The Political Economy of Socialism'', by Horvat, Branko. 1982. (pp. 197–198) These corrective policies limit the market's incentive system by providing things such as minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation by the end of the 20th century. B ...
s, unemployment insurance
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a comp ...
, taxing profits and reducing the reserve army of labor, resulting in reduced incentives for capitalists to invest in more production. In essence, social welfare policies cripple capitalism's incentive system and are thus unsustainable in the long-run.''Market Socialism: The Debate Among Socialists'', 1998. pp. 60–61"
Marxists
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialectical ...
argue that the establishment of a socialist mode of production
The socialist mode of production, sometimes referred to as the communist mode of production, or simply (Marxian) socialism or communism as Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels used the terms ''communism'' and ''socialism'' interchangeably, is a specif ...
is the only way to overcome these deficiencies. Socialists and specifically Marxian socialists, argue that the inherent conflict of interests between the working class and capital prevent optimal use of available human resources and leads to contradictory interest groups (labor and business) striving to influence the state to intervene in the economy at the expense of overall economic efficiency.
Early socialists (utopian socialists
Utopian socialism is the term often used to describe the first current of modern socialism and socialist thought as exemplified by the work of Henri de Saint-Simon, Charles Fourier, Étienne Cabet, and Robert Owen. Utopian socialism is often de ...
and Ricardian socialists) criticized capitalism for concentrating power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
and wealth
Wealth is the abundance of valuable financial assets or physical possessions which can be converted into a form that can be used for transactions. This includes the core meaning as held in the originating Old English word , which is from an I ...
within a small segment of society who do not utilize available technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
and resources to their maximum potential in the interests of the public.
Topics of criticism
Democracy and freedom
EconomistBranko Horvat
Branko Horvat (24 July 1928 – 18 December 2003) was a Croatian economist and politician.
Horvat was born in Petrinja on 24 July 1928. In 1944 during World War II, Horvat and his father Artur Horvat joined the Partisan movement in Croatia. He w ...
stated that " is now well known that capitalist development leads to the concentration of capital, employment and power. It is somewhat less known that it leads to the almost complete destruction of economic freedom".
Critics argue that capitalism leads to a significant loss of political, democratic and economic power
Economic power refers to the ability of countries, businesses or individuals to improve living standards. It increases their ability to make decisions on their own that benefit them. Scholars of international relations also refer to the economic p ...
for the vast majority of the global human population. The reason for this is they believe capitalism creates very large concentrations of money and property in the hands of a relatively small minority of the global human population (the elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (french: élite, from la, eligere, to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. ...
or the power elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (french: élite, from la, eligere, to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. ...
), leading, they say, to very large and increasing wealth and income inequalities between the elite and the majority of the population. "Corporate capitalism" and " inverted totalitarianism" are terms used by the aforementioned activists and critics of capitalism to describe a capitalist marketplace—and society—characterized by the dominance of hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
, bureaucratic
The term bureaucracy () refers to a body of non-elected governing officials as well as to an administrative policy-making group. Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments staffed with non-elected offi ...
, large corporations, which are legally required to pursue profit without concern for social welfare. Corporate capitalism has been criticized for the amount of power and influence corporations and large business interest groups have over government policy, including the policies of regulatory agencies and influencing political campaigns. Many social scientists have criticized corporation
A corporation is an organization—usually a group of people or a company—authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law "born out of statute"; a legal person in legal context) and ...
s for failing to act in the interests of the people; they claim the existence of large corporations seems to circumvent the principles of democracy, which assumes equal power relations between all individuals in a society. As part of the political left
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
, activists against corporate power and influence work towards a decreased income gap and improved economical equity.
The rise of giant multinational corporation
A multinational company (MNC), also referred to as a multinational enterprise (MNE), a transnational enterprise (TNE), a transnational corporation (TNC), an international corporation or a stateless corporation with subtle but contrasting senses, i ...
s has been a topic of concern among the aforementioned scholars, intellectuals and activists, who see the large corporation as leading to deep, structural erosion of such basic human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
and civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life ...
as equitable wealth and income distribution, equitable democratic political and socio-economic power representation and many other human rights and needs. They have pointed out that in their view large corporations create false needs in consumers and—they contend—have had a long history of interference in and distortion of the policies of sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
nation states
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may ...
through high-priced legal lobbying
In politics, lobbying, persuasion or interest representation is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agencies. Lobbying, whic ...
and other almost always legal, powerful forms of influence peddling
Influence peddling is the practice of using one's influence in government or connections with authorities to obtain favours or preferential treatment for another, usually in return for payment. It is also called traffic of influence or trading i ...
. In their view, evidence supporting this belief includes invasive advertising (such as billboards, television ads, adware
Adware, often called advertising-supported software by its developers, is software that generates revenue for its developer by automatically generating online advertisements in the user interface of the software or on a screen presented to the ...
, spam
Spam may refer to:
* Spam (food), a canned pork meat product
* Spamming, unsolicited or undesired electronic messages
** Email spam, unsolicited, undesired, or illegal email messages
** Messaging spam, spam targeting users of instant messaging ...
, telemarketing
Telemarketing (sometimes known as inside sales, or telesales in the UK and Ireland) is a method of direct marketing in which a salesperson solicits prospective customers to buy products or services, either over the phone or through a subsequen ...
, child-targeted advertising and guerrilla marketing), massive open or secret corporate political campaign contributions
Contribution or Contribute may refer to:
* ''Contribution'' (album), by Mica Paris (1990)
** "Contribution" (song), title song from the album
* Contribution (law), an agreement between defendants in a suit to apportion liability
*Contributions, ...
in so-called "democratic" elections, corporatocracy
Corporatocracy (, from corporate and el, -κρατία, translit=-kratía, lit=domination by; short form corpocracy) is an economic, political and judicial system controlled by corporations or corporate interests.
The concept has been used ...
, the revolving door
A revolving door typically consists of three or four doors that hang on a central shaft and rotate around a vertical axis within a cylindrical enclosure. Revolving doors are energy efficient as they, acting as an airlock, prevent drafts, thus de ...
between government and corporations, regulatory capture
In politics, regulatory capture (also agency capture and client politics) is a form of corruption of authority that occurs when a political entity, policymaker, or regulator is co-opted to serve the commercial, ideological, or political interests ...
, "too big to fail
"Too big to fail" (TBTF) and "too big to jail" is a theory in banking and finance that asserts that certain corporations, particularly financial institutions, are so large and so interconnected that their failure would be disastrous to the great ...
" (also known as " too big to jail"), massive taxpayer-provided corporate bailout
A bailout is the provision of financial help to a corporation or country which otherwise would be on the brink of bankruptcy.
A bailout differs from the term ''bail-in'' (coined in 2010) under which the bondholders or depositors of global sys ...
s, socialism/communism for the very rich and brutal, vicious, Darwinian capitalism for everyone else, and—they claim—seemingly endless global news stories about corporate corruption
In criminology, corporate crime refers to crimes committed either by a corporation (i.e., a business entity having a separate legal personality from the natural persons that manage its activities), or by individuals acting on behalf of a corpo ...
(Martha Stewart
Martha Helen Stewart (, ; born August 3, 1941) is an American retail businesswoman, writer, and television personality. As founder of Martha Stewart Living Omnimedia, she gained success through a variety of business ventures, encompassing pu ...
and Enron
Enron Corporation was an American energy, commodities, and services company based in Houston, Texas. It was founded by Kenneth Lay in 1985 as a merger between Lay's Houston Natural Gas and InterNorth, both relatively small regional compani ...
, among other examples). Anti-corporate-activists express the view that large corporations answer only to large shareholders, giving human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
issues, social justice
Social justice is justice in terms of the distribution of wealth, opportunities, and privileges within a society. In Western and Asian cultures, the concept of social justice has often referred to the process of ensuring that individuals ...
issues, environmental issues and other issues of high significance to the bottom 99% of the global human population virtually no consideration. American political philosopher Jodi Dean
Jodi Dean (born April 9, 1962) is an American political theorist and professor in the Political Science department at Hobart and William Smith Colleges in New York state. She held the Donald R. Harter ’39 Professorship of the Humanities and So ...
says that contemporary economic and financial calamities have dispelled the notion that capitalism is a viable economic system, adding that "the fantasy that democracy exerts a force for economic justice has dissolved as the US government funnels trillions of dollars to banks and European central banks rig national governments and cut social programs to keep themselves afloat."
David Schweickart wrote: "Ordinary people n capitalist societiesare deemed competent enough to select their political leaders-but not their bosses. Contemporary capitalism celebrates democracy, yet denies us our democratic rights at precisely the point where they might be utilized most immediately and concretely: at the place where we spend most of the active and alert hours of our adult lives".
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
, one of the founders of the United States, said "I hope we shall crush ... in its birth the aristocracy of our moneyed corporations, which dare already to challenge our government to a trial of strength and bid defiance to the laws of our country". In an 29 April 1938 message to the U. S. Congress, Franklin D. Roosevelt warned that the growth of private power could lead to fascism
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and t ...
, arguing that "the liberty of a democracy is not safe if the people tolerate the growth of private power to a point where it becomes stronger than their democratic state itself. That, in its essence, is fascism—ownership of government by an individual, by a group, or by any other controlling private power.Franklin D. Roosevelt, "Recommendations to the Congress to Curb Monopolies and the Concentration of Economic Power", April 29, 1938, in ''The Public Papers and Addresses of Franklin D. Roosevelt'', ed. Samuel I. Rosenman, vol. 7, (New York, MacMillan: 1941), pp. 305–315.Franklin D. Roosevelt"Appendix A: Message from the President of the United States Transmitting Recommendations Relative to the Strengthening and Enforcement of Antitrust Laws"
''
The American Economic Review
The ''American Economic Review'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal published by the American Economic Association. First published in 1911, it is considered one of the most prestigious and highly distinguished journals in the field of eco ...
'', Vol. 32, No. 2, Part 2, Supplement, Papers Relating to the Temporary National Economic Committee The Temporary National Economic Committee (TNEC) was established by a joint resolution of the United States Congress on June 16, 1938 and operated until its defunding on April 3, 1941. The TNEC's function was to study the concentration of economic p ...
(Jun., 1942), pp. 119–128. Statistics of the Bureau of Internal Revenue reveal the following figures for 1935: "Ownership of corporate assets: Of all corporations reporting from every part of the Nation, one-tenth of 1 percent of them owned 52 percent of the assets of all of them".
U. S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower criticized the notion of the confluence of corporate power and ''de facto'' fascism and in his 1961 Farewell Address to the Nation brought attention to the "conjunction of an immense military establishment and a large arms industry" in the United States and stressed "the need to maintain balance in and among national programs—balance between the private and the public economy, balance between cost and hoped for advantage".
In a 1986 debate on Socialism vs Capitalism with John Judis
John B. Judis is an author and American journalist, an editor-at-large at ''Talking Points Memo'', a former senior writer at the ''National Journal'' and a former senior editor at ''The New Republic''.
Education
Judis was born in Chicago to a ...
vs Harry Binswanger and John Ridpath
John B. Ridpath (; 19 May 1936 – 23 March 2021) was a Canadian intellectual historian. He was an Objectivist and an associate professor of economics and intellectual history at York University in Toronto. He also taught courses at Duke Unive ...
, intellectual Christopher Hitchens
Christopher Eric Hitchens (13 April 1949 – 15 December 2011) was a British-American author and journalist who wrote or edited over 30 books (including five essay collections) on culture, politics, and literature. Born and educated in England, ...
said:
Exploitation of workers
 Critics of capitalism view the system as inherently exploitative. In an economic sense, exploitation is often related to the
Critics of capitalism view the system as inherently exploitative. In an economic sense, exploitation is often related to the expropriation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to p ...
of labor for profit
Profit may refer to:
Business and law
* Profit (accounting), the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market
* Profit (economics), normal profit and economic profit
* Profit (real property), a nonpossessory inter ...
and based on Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
's version of the labor theory of value
The labor theory of value (LTV) is a theory of value that argues that the economic value of a good or service is determined by the total amount of " socially necessary labor" required to produce it.
The LTV is usually associated with Marxian ...
. The labor theory of value was supported by classical economists like David Ricardo
David Ricardo (18 April 1772 – 11 September 1823) was a British political economist. He was one of the most influential of the classical economists along with Thomas Malthus, Adam Smith and James Mill. Ricardo was also a politician, and a ...
and Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——� ...
who believed that "the value of a commodity depends on the relative quantity of labor which is necessary for its production".
In ''Das Kapital
''Das Kapital'', also known as ''Capital: A Critique of Political Economy'' or sometimes simply ''Capital'' (german: Das Kapital. Kritik der politischen Ökonomie, link=no, ; 1867–1883), is a foundational theoretical text in materialist phi ...
'', Marx identified the commodity as the basic unit of capitalist organization. Marx described a "common denominator" between commodities, in particular that commodities are the product of labor and are related to each other by an exchange value
In political economy and especially Marxian economics, exchange value (German: ''Tauschwert'') refers to one of the four major attributes of a commodity, i.e., an item or service produced for, and sold on the market, the other three attributes ...
(i.e. price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the ...
). By using the labor theory of value, Marxists
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialectical ...
see a connection between labor and exchange value, in that commodities are exchanged depending on the socially necessary labor time
Socially necessary labour time in Marx's critique of political economy is what regulates the exchange value of commodities in trade and consequently constrains producers in their attempt to economise on labour. It does not 'guide' them, as it can ...
needed to produce them. However, due to the productive forces of industrial organization, laborers are seen as creating more exchange value during the course of the working day than the cost of their survival (food, shelter, clothing and so on). Marxists argue that capitalists are thus able to pay for this cost of survival while expropriating the excess labor (i.e. surplus value
In Marxian economics, surplus value is the difference between the amount raised through a sale of a product and the amount it cost to the owner of that product to manufacture it: i.e. the amount raised through sale of the product minus the cos ...
).
Marxists further argue that due to economic inequality
There are wide varieties of economic inequality, most notably income inequality measured using the distribution of income (the amount of money people are paid) and wealth inequality measured using the distribution of wealth (the amount of ...
, the purchase of labor cannot occur under "free" conditions. Since capitalists control the means of production
The means of production is a term which describes land, labor and capital that can be used to produce products (such as goods or services); however, the term can also refer to anything that is used to produce products. It can also be used as a ...
(e.g. factories, businesses, machinery and so on) and workers control only their labor, the worker is naturally coerced into allowing their labor to be exploited. Critics argue that exploitation occurs even if the exploited consents, since the definition of exploitation is independent of consent. In essence, workers must allow their labor to be exploited or face starvation. Since some degree of unemployment is typical in modern economies, Marxists argue that wages are naturally driven down in free market systems. Hence, even if a worker contests their wages, capitalists are able to find someone from the reserve army of labor
Reserve army of labour is a concept in Karl Marx's critique of political economy. It refers to the unemployed and underemployed in capitalist society. It is synonymous with "industrial reserve army" or "relative surplus population", except that ...
who is more desperate.
The act (or threat) of striking has historically been an organized action to withhold labor from capitalists, without fear of individual retaliation. Some critics of capitalism, while acknowledging the necessity of trade union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ...
ism, believe that trade unions simply reform an already exploitative system, leaving the system of exploitation intact. Lysander Spooner
Lysander Spooner (January 19, 1808May 14, 1887) was an American individualist anarchist, abolitionist, entrepreneur, essayist, legal theorist, pamphletist, political philosopher, Unitarian and writer.
Spooner was a strong advocate of the labor ...
argued that "almost all fortunes are made out of the capital and labour of other men than those who realize them. Indeed, large fortunes could rarely be made at all by one individual, except by his sponging capital and labour from others".
Some labor historians and scholars have argued that unfree labor—by slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, indentured servants
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensation or debt repayment, ...
, prisoners
A prisoner (also known as an inmate or detainee) is a person who is deprived of liberty against their will. This can be by confinement, captivity, or forcible restraint. The term applies particularly to serving a prison sentence in a prison.
...
, or other coerced persons—is compatible with capitalist relations. Tom Brass
Tom Brass is an academic who has written widely on peasant studies. For many years he was at the University of Cambridge as an affiliated lecturer in their Faculty of Social and Political Sciences and at Queens' College, Cambridge as their Dire ...
argued that unfree labor is acceptable to capital. Historian Greg Grandin
Greg Grandin (born 1962) is a professor of history at Yale University. He previously taught at New York University. He is author of a number of books, including ''Fordlândia: The Rise and Fall of Henry Ford's Forgotten Jungle City'', which wa ...
argues that capitalism has its origins in slavery, saying that " en historians talk about the Atlantic market revolution, they are talking about capitalism. And when they are talking about capitalism, they are talking about slavery." Some historians, including Edward E. Baptist and Sven Beckert, assert that slavery was an integral component in the violent development of American and global capitalism. The Slovenian continental philosopher Slavoj Žižek
Slavoj Žižek (, ; ; born 21 March 1949) is a Slovenian philosopher, cultural theorist and public intellectual. He is international director of the Birkbeck Institute for the Humanities at the University of London, visiting professor at New ...
posits that the new era of global capitalism has ushered in new forms of contemporary slavery, including migrant workers deprived of basic civil rights on the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
, the total control of workers in Asian sweatshops and the use of forced labor in the exploitation of natural resources in Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Co ...
.
Academics such as the Developmental psychology, developmental psychologist Howard Gardner have proposed the adoption of upper limits in individual wealth as "a solution that would make the world a better place". Marxian economics, Marxian economist Richard D. Wolff postulates that capitalist economies prioritize profits and capital accumulation over the social needs of communities, and that capitalist enterprises rarely include the workers in the basic decisions of the enterprise.
Political economist Clara E. Mattei of the New School for Social Research demonstrates that the imposition of fiscal, monetary and industrial austerity policies meant to discipline labor by reinforcing hierarchal wage relations and therefore protect the capitalist system through wage repression and the weakening of collective bargaining power by workers can increase their exploitation while boosting the profits of the ownership class, which she says is one of the primary drivers of the "global inequality trend". As an example, Mattei shows that over the last four decades in the United States the profit share of national output increased while labor's share plummeted, demonstrating a symmetrical relationship between owner profit and worker loss, where the former was taking from the latter. She adds that “an increase in exploitation was also evident, with real wages grossly lagging behind labor productivity.”
Imperialism, political oppression, and genocide
Near the start of the 20th century,Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
wrote that state use of military power to defend capitalist interests abroad was an inevitable corollary of monopoly capitalism. He argued that capitalism needs imperialism to survive. According to Lenin, the export of financial capital superseded the export of commodities; banking and industrial capital merged to form large financial cartels and trusts in which production and distribution are highly centralized; and monopoly capitalism, monopoly capitalists influenced state policy to carve up the world into spheres of interest. These trends led states to defend their capitalist interests abroad through military power.
According to economic anthropologist Jason Hickel, capitalism requires the accumulation of excess wealth in the hands of economic elites for the purpose of large scale investment, continuous growth and expansion, and enormous amounts of cheap labor. As such, there was never and could never have been a gradual or peaceful transition to capitalism, and that "organized violence, mass impoverishment, and the destruction of self-sufficient subsistence economies" ushered in the capitalist era. Its emergence was fueled by Immiseration thesis, immiseration and extreme violence that accompanied enclosure and colonization, with colonized peoples becoming enslaved workers producing products that were then processed by European peasants, dispossessed by enclosure, who filled the factories in desperation as exploited cheap labor. Hickel adds that there was fierce resistance to these developments, as that the period 1500 to the 1800s, "right into the Industrial Revolution, was among the bloodiest, most tumultuous times in world history."
Sociologist David Nibert argues that while capitalism "turned out to be every bit as violent and oppressive as the social systems dominated by the old aristocrats", it also included "an additional and pernicious peril—the necessity for continuous growth and expansion". As an example of this, Nibert points to the mass killing of millions of buffalo on the Great Plains and the subjugation and expulsion of the indigenous population by the U.S. military in the 19th century for the purpose of expanding ranching operations, and rearing livestock for the purpose of profit.
Capitalism and capitalist governments have also been criticized as oligarchic in nature, due to the inevitable inequality.
The military–industrial complex, mentioned in Dwight D. Eisenhower's presidential farewell address, appears to play a significant role in the American capitalist system. It may be one of the driving forces of American militarism and intervention abroad. The United States has used military force and has encouraged and facilitated state terrorism and mass violence to entrench Neoliberalism, neoliberal capitalism in the Global South, protect the interests of U.S. economic elites, and to crush any possible resistance to this entrenchment, especially during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, with significant cases being Military dictatorship in Brazil, Brazil, Military dictatorship of Chile (1973–1990), Chile and Transition to the New Order, Indonesia.
Inefficiency, irrationality, and unpredictability
Some opponents criticize capitalism's inefficiency. They note a shift from pre-industrial reuse and thriftiness before capitalism to a consumer-based economy that pushes "ready-made" materials. It is argued that a sanitation industry arose under capitalism that deemed trash valueless—a significant break from the past when much "waste" was used and reused almost indefinitely. In the process, critics say, capitalism has created a profit driven system based on selling as many products as possible. Critics relate the "ready-made" trend to a growing garbage problem in which, as of 2008, 4.5 pounds of trash are generated per person each day (compared to 2.7 pounds in 1960). Anti-capitalist groups with an emphasis on Conservation movement, conservation include eco-socialists and Social ecology (theory), social ecologists. Planned obsolescence has been criticized as a wasteful practice under capitalism. By designing products to wear out faster than need be, new consumption is generated. This would benefit corporations by increasing sales while at the same time generating excessive waste. A well-known example is the charge that Apple designed its iPod to fail after 18 months. Critics view planned obsolescence as wasteful and an inefficient use of resources. Other authors such as Naomi Klein have criticized brand-based marketing for putting more emphasis on the company's name-brand than on manufacturing products. Some economists, most notably Marxian economists, argue that the system of perpetual capital accumulation leads to irrational outcomes and a mis-allocation of resources as industries and jobs are created for the sake of making money as opposed to satisfying actual demands and needs.Market failure
Market failure is a term used by economists to describe the condition where the allocation of goods and services by a market is not Efficiency (economics), efficient. Keynesian economics, Keynesian economist Paul Krugman views this scenario in which individuals' pursuit of self-interest leads to bad results for society as a whole.Krugman, Paul, Wells, Robin, ''Economics'', Worth Publishers, New York, (2006) John Maynard Keynes preferred economic intervention by government to free markets. Some believe that the lack of perfect information and perfect competition in a free market is grounds for government intervention. Others perceive certain unique problems with a free market including: Monopoly, monopolies, monopsony, monopsonies, insider trading and price gouging.Inequality
trade union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ...
ists and phenomena such as social alienation, economic inequality, unemployment and economic instability. Critics have argued that there is an inherent tendency toward oligopolistic structures when ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups ...
'' is combined with capitalist private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property and personal property, which is owned by a state entity, and from collective or ...
. Capitalism is regarded by many socialists to be irrational in that production and the direction of the economy are unplanned, creating many inconsistencies and internal contradictions and thus should be controlled through competition law, public policy.
In the early 20th century, Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
argued that state use of military power to defend capitalist interests abroad was an inevitable corollary of monopoly capitalism.
In a 1965 letter to Carlos Quijano, editor of ''Marcha (newspaper), Marcha'', a weekly newspaper published in Montevideo, Uruguay, Che Guevara wrote:
The laws of capitalism, which are blind and are invisible to ordinary people, act upon the individual without he or she being aware of it. One sees only the vastness of a seemingly infinite horizon ahead. That is how it is painted by capitalist propagandists who purport to draw a lesson from the example of John D. Rockefeller, Rockefeller—whether or not it is true—about the possibilities of individual success. The amount of poverty and suffering required for a Rockefeller family, Rockefeller to emerge, and the amount of depravity entailed in the accumulation of a fortune of such magnitude, are left out of the picture, and it is not always possible for the popular forces to expose this clearly. ... It is a contest among wolves. One can win only at the cost of the failure of others.GUevara, Che (12 March 1965
"From Algiers, for Marcha: The Cuban Revolution Today"
Retrieved 19 August 2020.
 A modern critic of capitalism is Ravi Batra, who focuses on inequality as a source of immiserization but also of system failure. Batra popularised the concept "share of wealth held by richest 1%" as an indicator of inequality and an important determinant of depressions in his best-selling books in the 1980s. The scholars Kristen Ghodsee and Mitchell A. Orenstein suggest that left to its own devices, capitalism will result in a small group of economic elites capturing the majority of wealth and power in society. Dylan Sullivan and Jason Hickel argue that poverty continues to exist in the contemporary global capitalist system in spite of it being highly productive because it is undemocratic and has maintained conditions of extreme inequality where masses of working people, who have no ownership or control over the means of production, have their labor power "appropriated by a ruling class or an external imperial power," and are cut off from common land and resources.
In the United States, the shares of earnings and wealth of the households in the top 1 percent of the corresponding distributions are 21 percent (in 2006) and 37 percent (in 2009), respectively. Critics, such as Ravi Batra, argue that the capitalist system has inherent biases favoring those who already possess greater resources. The inequality may be propagated through inheritance and economic policy. Rich people are in a position to give their children a better education and inherited wealth and that this can create or increase large differences in wealth between people who do not differ in ability or effort. One study shows that in the United States 43.35% of the people in the ''Forbes'' magazine "400 richest individuals" list were already rich enough at birth to qualify. Another study indicated that in the United States wealth, race and schooling are important to the inheritance of economic status, but that IQ is not a major contributor and the genetic transmission of IQ is even less important. Batra has argued that the tax and benefit legislation in the United States since the Presidency of Ronald Reagan, Reagan presidency has contributed greatly to the inequalities and economic problems and should be repealed.
A modern critic of capitalism is Ravi Batra, who focuses on inequality as a source of immiserization but also of system failure. Batra popularised the concept "share of wealth held by richest 1%" as an indicator of inequality and an important determinant of depressions in his best-selling books in the 1980s. The scholars Kristen Ghodsee and Mitchell A. Orenstein suggest that left to its own devices, capitalism will result in a small group of economic elites capturing the majority of wealth and power in society. Dylan Sullivan and Jason Hickel argue that poverty continues to exist in the contemporary global capitalist system in spite of it being highly productive because it is undemocratic and has maintained conditions of extreme inequality where masses of working people, who have no ownership or control over the means of production, have their labor power "appropriated by a ruling class or an external imperial power," and are cut off from common land and resources.
In the United States, the shares of earnings and wealth of the households in the top 1 percent of the corresponding distributions are 21 percent (in 2006) and 37 percent (in 2009), respectively. Critics, such as Ravi Batra, argue that the capitalist system has inherent biases favoring those who already possess greater resources. The inequality may be propagated through inheritance and economic policy. Rich people are in a position to give their children a better education and inherited wealth and that this can create or increase large differences in wealth between people who do not differ in ability or effort. One study shows that in the United States 43.35% of the people in the ''Forbes'' magazine "400 richest individuals" list were already rich enough at birth to qualify. Another study indicated that in the United States wealth, race and schooling are important to the inheritance of economic status, but that IQ is not a major contributor and the genetic transmission of IQ is even less important. Batra has argued that the tax and benefit legislation in the United States since the Presidency of Ronald Reagan, Reagan presidency has contributed greatly to the inequalities and economic problems and should be repealed.
Market instability
Critics of capitalism, particularly Marxists, identify market instability as a permanent feature of capitalist economy. Marx believed that the unplanned and explosive growth of capitalism does not occur in a smooth manner, but is interrupted by periods of overproduction in which stagnation or decline occur (i.e. recessions). In the view of Marxists, several contradictions in the capitalist mode of production are present, particularly the internal contradiction between anarchy in the sphere of capital (i.e. free market) and socialised production in the sphere of labor (i.e. industrialism). In ''The Communist Manifesto
''The Communist Manifesto'', originally the ''Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (german: Manifest der Kommunistischen Partei), is a political pamphlet written by German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Commissioned by the Commu ...
'', Marx and Engels highlighted what they saw as a uniquely capitalist juxtaposition of overabundance and poverty: "Society suddenly finds itself put back into a state of momentary barbarism. And why? Because there is too much civilization, too much means of subsistence, too much industry, too much commerce".
Some scholars blame the financial crisis of 2007–2008 on the neoliberal capitalist model. Following the banking crisis of 2007, economist and former Chair of the Federal Reserve, Alan Greenspan told the United States Congress on 23 October 2008 that "[t]his modern risk-management paradigm held sway for decades. The whole intellectual edifice, however, collapsed in the summer of last year", and that "I made a mistake in presuming that the self-interests of organizations, specifically banks and others, were such that they were best capable of protecting their own shareholders and their equity in firms ... I was shocked".
Property
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (, , ; 15 January 1809, Besançon – 19 January 1865, Paris) was a French socialist,Landauer, Carl; Landauer, Hilde Stein; Valkenier, Elizabeth Kridl (1979) 959 "The Three Anticapitalistic Movements". ''European Socia ...
and Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ,"Engels"
'' They view capitalist regulations, including the enforcement of
 Many aspects of capitalism have come under attack from the anti-globalization movement, which is primarily opposed to
Many aspects of capitalism have come under attack from the anti-globalization movement, which is primarily opposed to
 Wage labor has long been compared to slavery. As a result, the phrase "Labour economics#Wage slavery, wage slavery" is often utilized as a pejorative for wage labor. Similarly, advocates of slavery looked upon the "comparative evils of Slave Society and of Free Society, of slavery to human Masters and slavery to Capital" and proceeded to argue that wage slavery was actually worse than chattel slavery. Slavery apologists like George Fitzhugh contended that workers only accepted wage labor with the passage of time as they became "familiarised and inattentive to the infected social atmosphere they continually inhale". Scholars have debated the exact relationship between wage labor, slavery, and capitalism at length, especially for the Antebellum South.
With the advent of the
Wage labor has long been compared to slavery. As a result, the phrase "Labour economics#Wage slavery, wage slavery" is often utilized as a pejorative for wage labor. Similarly, advocates of slavery looked upon the "comparative evils of Slave Society and of Free Society, of slavery to human Masters and slavery to Capital" and proceeded to argue that wage slavery was actually worse than chattel slavery. Slavery apologists like George Fitzhugh contended that workers only accepted wage labor with the passage of time as they became "familiarised and inattentive to the infected social atmosphere they continually inhale". Scholars have debated the exact relationship between wage labor, slavery, and capitalism at length, especially for the Antebellum South.
With the advent of the  Some Anti-capitalism, anti-capitalist thinkers claim that the
Some Anti-capitalism, anti-capitalist thinkers claim that the
 At least two assumptions are necessary for the validity of the standard model: first, that supply and demand are independent; and second, that supply is "constrained by a fixed resource". If these conditions do not hold, then the Marshallian surplus, Marshallian model cannot be sustained. Piero Sraffa, Sraffa's critique focused on the inconsistency (except in implausible circumstances) of partial equilibrium analysis and the rationale for the upward slope of the supply curve in a market for a produced consumption good. The notability of Sraffa's critique is also demonstrated by Paul A. Samuelson's comments and engagements with it over many years, stating:
At least two assumptions are necessary for the validity of the standard model: first, that supply and demand are independent; and second, that supply is "constrained by a fixed resource". If these conditions do not hold, then the Marshallian surplus, Marshallian model cannot be sustained. Piero Sraffa, Sraffa's critique focused on the inconsistency (except in implausible circumstances) of partial equilibrium analysis and the rationale for the upward slope of the supply curve in a market for a produced consumption good. The notability of Sraffa's critique is also demonstrated by Paul A. Samuelson's comments and engagements with it over many years, stating:
A Reconsideration of the Theory of Entrepreneurship: a participatory approach
– critique of capitalism
– 1907 anti-capitalist pamphlet by John Wheatley
by Allin F. Cottrell and Paul Cockshott, W. Paul Cockshott
Value, Price and Profit
– Karl Marx on the basic features of capitalism
Crisis of Capitalism
by
Richard Wolff on Curing Capitalism
''Moyers & Company''. 22 March 2013.
Occupy was right: capitalism has failed the world
Andrew Hussey. ''The Guardian''. 12 April 2014 (interview with Thomas Piketty).
Unless It Changes, Capitalism Will Starve Humanity By 2050
''Forbes''. 9 February 2016.
New Zealand's new prime minister calls capitalism a 'blatant failure'
''The Independent''. 22 October 2017.
''The Washington Post''. 20 April 2019
Broken Capitalism
series in ''The Guardian''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Criticism Of Capitalism Criticism of capitalism, Issues in anarchism Marxian economics Social philosophy Socialism
'' They view capitalist regulations, including the enforcement of
private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property and personal property, which is owned by a state entity, and from collective or ...
on land and exclusive rights to natural resources, as unjustly Enclosure, enclosing upon what should be owned by all, forcing those without private property to sell their labor to capitalists and landlords in a market favorable to the latter, thus forcing workers to accept low wages to survive. In his criticism of capitalism, Proudhon believed that the emphasis on private property is the problem. He argued that property is theft, arguing that private property leads to despotism: "Now, property necessarily engenders despotism—the government of caprice, the reign of libidinous pleasure. That is so clearly the essence of property that, to be convinced of it, one need but remember what it is, and observe what happens around him. Property is the right to use and abuse". Many left-wing anarchists, such as anarchist communists, believe in replacing capitalist private property with a system where people can lay claim to things based on personal use and claim that "[private] property is the domination of an individual, or a coalition of individuals, over things; it is not the claim of any person or persons to the use of things" and "this is, usufruct, a very different matter. Property means the monopoly of wealth, the right to prevent others using it, whether the owner needs it or not".
Mutualism (economic theory), Mutualists and some anarchists support markets and private property, but not in their present form. They argue that particular aspects of modern capitalism violate the ability of individuals to trade in the absence of coercion. Mutualists support markets and private property in the product of labor, but only when these markets guarantee that workers worker cooperative, will realize for themselves the value of their labor.
In recent times, most economies have extended private property rights to include such things as patents and copyrights. Critics see these so-called intellectual property
Intellectual property (IP) is a category of property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. There are many types of intellectual property, and some countries recognize more than others. The best-known types are patents, co ...
laws as coercive against those with few prior resources. They argue that such regulations discourage the sharing of ideas and encourage nonproductive rent seeking behavior, both of which enact a deadweight loss on the economy, erecting a prohibitive barrier to entry into the market. Not all pro-capitalists support the concept of copyrights, but those who do argue that compensation to the creator is necessary as an incentive.
Environmental sustainability
 Many aspects of capitalism have come under attack from the anti-globalization movement, which is primarily opposed to
Many aspects of capitalism have come under attack from the anti-globalization movement, which is primarily opposed to corporate capitalism
In social science and economics, corporate capitalism is a capitalist marketplace characterized by the dominance of hierarchical and bureaucratic corporations.
Overview
A large proportion of the economy of the United States and its labour mark ...
. Environmentalists and scholars have argued that capitalism requires continual economic growth and that it will inevitably deplete the finite natural resources of Earth and cause Holocene extinction, mass extinctions of animal and plant life. Such critics argue that while neoliberalism, the ideological backbone of contemporary globalized capitalism, has indeed increased global trade, it has also destroyed traditional ways of life, exacerbated inequality, increased global poverty, and that environmental indicators indicate massive environmental degradation since the late 1970s.
Some scholars argue that the capitalist approach to environmental economics does not take into consideration the preservation of natural resources and that capitalism creates three ecological problems: growth, technology, and consumption. The growth problem results from the nature of capitalism, as it focuses around the accumulation of capital. The innovation of new technologies has an impact on the environmental future as they serve as a capitalist tool in which environmental technologies can result in the expansion of the system. Consumption is focused around the capital accumulation of commodities and neglects the use-value of production.
One of the main modern criticism to the sustainability of capitalism is related to the so-called commodity chains, or production/consumption chains. These terms refer to the network of transfers of materials and commodities that is currently part of the functioning of the global capitalist system. Examples include high tech commodities produced in countries with low average wages by multinational firms and then being sold in distant high income countries; materials and resources being extracted in some countries, turned into finished products in some others and sold as commodities in further ones; and countries exchanging with each other the same kind of commodities for the sake of consumers' choice (e.g. Europe both exporting and importing cars to and from the United States). According to critics, such processes, all of which produce pollution and waste of resources, are an integral part of the functioning of capitalism (i.e. its "metabolism").
Critics note that the statistical methods used in calculating ecological footprint have been criticized and some find the whole concept of counting how much land is used to be flawed, arguing that there is nothing intrinsically negative about using more land to improve living standards (rejection of the Intrinsicism, intrinsic value of nature).
Many environmentalists have long argued that the real dangers are due to the world's current social institutions that claim to promote environmentally irresponsible consumption and production. Under what they call the "grow or die" imperative of capitalism, they say there is little reason to expect hazardous consumption and production practices to change in a timely manner. They also claim that markets and states invariably drag their feet on substantive environmental reform and are notoriously slow to adopt viable sustainable technologies. Immanuel Wallerstein, referring to the externalization of costs as the "dirty secret" of capitalism, claims that there are built-in limits to ecological reform and that the costs of doing business in the world capitalist economy are ratcheting upward because of deruralization and democratization.
A team of Finnish scientists hired by the UN Secretary-General to aid the 2019 Global Sustainable Development Report assert that capitalism as we know it is moribund, primarily because it focuses on short term profits and fails to look after the long term needs of people and the environment which is being subjected to unsustainable exploitation. Their report goes on to link many seemingly disparate contemporary crises to this system, including environmental factors such as global warming and accelerated Holocene extinction, species extinctions and also societal factors such as rising economic inequality
There are wide varieties of economic inequality, most notably income inequality measured using the distribution of income (the amount of money people are paid) and wealth inequality measured using the distribution of wealth (the amount of ...
, unemployment, sluggish economic growth, rising debt levels, and impuissant governments unable to deal with these problems. The scientists say a new economic model, one which focuses on sustainability and efficiency and not profit and growth, will be needed as decades of robust economic growth driven by abundant resources and cheap energy is rapidly coming to a close. Another group of scientists contributing to the 2020 "Scientists warning on affluence" argue that a shift away from paradigms fixating on economic growth and the "profit-driven mechanism of prevailing economic systems" will be necessary to mitigate human impacts on the environment, and suggest a range of ideas from the reformist to the radical, with the latter consisting of degrowth, eco-socialism and eco-anarchism.
Some scientists contend that the rise of capitalism, which itself developed out of European imperialism and colonialism of the 15th and 16th centuries, marks the emergence of the Anthropocene epoch, in which human beings started to have significant and mostly negative impacts on the earth system. Others have warned that contemporary global capitalism "requires fundamental changes" to mitigate the worst environmental impacts, including the "abolition of perpetual economic growth, properly pricing Externality, externalities, a rapid exit from fossil-fuel use, strict regulation of markets and property acquisition, reining in corporate lobbying, and the empowerment of women". Jason Hickel writes that capitalism creates pressures for population growth: "more people means more labour, cheaper labour, and more consumers." He argues that continued population growth makes the challenge of sustainability even more difficult, but adds that even if the population leveled off, capitalism will simply get already existing consumers to increase their consumption, as consumption rates have always outpaced population growth rates.
Profit motive
The majority of criticisms against the profit motive centre on the idea that the profit motive encourages selfishness and greed, rather than serving the public good or necessarily creating an increase in net wealth. Critics of the profit motive contend that companies disregard morals or public safety in the pursuit of profits. Free market economists counter that the profit motive, coupled with competition, actually reduces the final price of an item for consumption, rather than raising it. They argue that businesses profit by selling a good at a lower price and at a greater volume than the competition. Economist Thomas Sowell uses supermarkets as an example to illustrate this point: American economist Milton Friedman has argued that greed and self-interest are Trait theory#List of personality traits, universal human traits. In a 1979 episode of ''The Phil Donahue Show'', Friedman stated: "The world runs on individuals pursuing their separate interests". He continued by explaining that only in capitalist countries, where individuals can pursue their own self-interest, people have been able to escape from "grinding poverty".Comparison to slavery
 Wage labor has long been compared to slavery. As a result, the phrase "Labour economics#Wage slavery, wage slavery" is often utilized as a pejorative for wage labor. Similarly, advocates of slavery looked upon the "comparative evils of Slave Society and of Free Society, of slavery to human Masters and slavery to Capital" and proceeded to argue that wage slavery was actually worse than chattel slavery. Slavery apologists like George Fitzhugh contended that workers only accepted wage labor with the passage of time as they became "familiarised and inattentive to the infected social atmosphere they continually inhale". Scholars have debated the exact relationship between wage labor, slavery, and capitalism at length, especially for the Antebellum South.
With the advent of the
Wage labor has long been compared to slavery. As a result, the phrase "Labour economics#Wage slavery, wage slavery" is often utilized as a pejorative for wage labor. Similarly, advocates of slavery looked upon the "comparative evils of Slave Society and of Free Society, of slavery to human Masters and slavery to Capital" and proceeded to argue that wage slavery was actually worse than chattel slavery. Slavery apologists like George Fitzhugh contended that workers only accepted wage labor with the passage of time as they became "familiarised and inattentive to the infected social atmosphere they continually inhale". Scholars have debated the exact relationship between wage labor, slavery, and capitalism at length, especially for the Antebellum South.
With the advent of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, thinkers such as Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (, , ; 15 January 1809, Besançon – 19 January 1865, Paris) was a French socialist,Landauer, Carl; Landauer, Hilde Stein; Valkenier, Elizabeth Kridl (1979) 959 "The Three Anticapitalistic Movements". ''European Socia ...
and Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
elaborated the comparison between wage labor and slavery in the context of a critique of societal property not intended for active personal use while Luddite
The Luddites were a secret oath-based organisation of English textile workers in the 19th century who formed a radical faction which destroyed textile machinery. The group is believed to have taken its name from Ned Ludd, a legendary weaver ...
s emphasized the dehumanisation brought about by machines. Before the American Civil War, Southern defenders of African American slavery invoked the concept of wage slavery to favorably compare the condition of their slaves to workers in the North. The United States abolished slavery during the Civil War, but labor union activists found the metaphor useful. According to Lawrence B. Glickman, Lawrence Glickman, in the Gilded Age "references abounded in the labor press, and it is hard to find a speech by a labour leader without the phrase".
According to Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky i ...
, analysis of the psychological implications of wage slavery goes back to the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment era. In his 1791 book ''On the Limits of State Action'', liberalism, liberal thinker Wilhelm von Humboldt explained how "whatever does not spring from a man's free choice, or is only the result of instruction and guidance, does not enter into his very nature; he does not perform it with truly human energies, but merely with mechanical exactness" and so when the laborer works under external control, "we may admire what he does, but we despise what he is". Both the Milgram experiment, Milgram and Stanford prison experiment, Stanford experiments have been found useful in the psychological study of wage-based workplace relations. Additionally, as per anthropologist David Graeber, the earliest wage labor contracts we know about were in fact contracts for the rental of chattel slaves (usually the owner would receive a share of the money and the slave another, with which to maintain his or her living expenses). According to Graeber, such arrangements were quite common in New World slavery as well, whether in the United States or Brazil. C. L. R. James argued in ''The Black Jacobins'' that most of the techniques of human organisation employed on factory workers during the Industrial Revolution were first developed on slave plantations.
 Some Anti-capitalism, anti-capitalist thinkers claim that the
Some Anti-capitalism, anti-capitalist thinkers claim that the elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (french: élite, from la, eligere, to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. ...
maintain wage slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and a divided working class through their influence over the media and entertainment industry, educational institutions, unjust laws, nationalist and corporate propaganda, pressures and incentives to internalize values serviceable to the power structure, State (polity), state violence, fear of unemployment and a historical legacy of exploitation and profit accumulation/transfer under prior systems, which shaped the development of economic theory.
Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptized 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the thinking of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as "The Father of Economics"——� ...
noted that employers often conspire together to keep wages low:
Aristotle made the statement that "the citizens must not live a mechanic or a mercantile life (for such a life is ignoble and inimical to virtue), nor yet must those who are to be citizens in the best state be tillers of the soil (for leisure is needed both for the development of virtue and for active participation in politics)", often paraphrased as "all paid jobs absorb and degrade the mind". Cicero wrote in 44 BC that "vulgar are the means of livelihood of all hired workmen whom we pay for mere manual labour, not for artistic skill; for in their case the very wage they receive is a pledge of their slavery". Somewhat similar criticisms have also been expressed by some proponents of liberalism, like Henry George, Silvio Gesell and Thomas Paine as well as the Distributism, Distributist school of thought within the Roman Catholic Church.
To Marxist
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialecti ...
and anarchist thinkers like Mikhail Bakunin and Peter Kropotkin, wage slavery was a class (social), class condition in place due to the existence of private property
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property and personal property, which is owned by a state entity, and from collective or ...
and the state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
. This class situation rested primarily on:
# The existence of property not intended for active use.
# The concentration of ownership in few hands.
# The lack of direct access by workers to the means of production
The means of production is a term which describes land, labor and capital that can be used to produce products (such as goods or services); however, the term can also refer to anything that is used to produce products. It can also be used as a ...
and consumption goods.
# The perpetuation of a Reserve army of labour, reserve army of unemployed workers.
For Marxists, labor as commodity, which is how they regard wage labor, provides a fundamental point of attack against capitalism. "It can be persuasively argued", noted one concerned philosopher, "that the conception of the worker's labour as a commodity confirms Marx's stigmatization of the wage system of private capitalism as 'wage-slavery;' that is, as an instrument of the capitalist's for reducing the worker's condition to that of a slave, if not below it". That this objection is fundamental follows immediately from Marx's conclusion that wage labor is the very foundation of capitalism: "Without a class dependent on wages, the moment individuals confront each other as free persons, there can be no production of surplus value; without the production of surplus-value there can be no capitalist production, and hence no capital and no capitalist!".
Supply and demand
What a cleaned-up version of Sraffa (1926) establishes is how nearly empty are all of Marshall's partial equilibrium boxes. To a logical purist of Wittgenstein and Sraffa class, the Marshallian partial equilibrium box of constant cost is even more empty than the box of increasing cost.Aggregate excess demand in a market is the difference between the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied as a function of price. In the model with an upward-sloping supply curve and downward-sloping demand curve, the aggregate excess demand function only intersects the axis at one point, namely at the point where the supply and demand curves intersect. The Sonnenschein–Mantel–Debreu theorem shows that the standard model cannot be rigorously derived in general from general equilibrium theory. The model of prices being determined by supply and demand assumes perfect competition. However, "economists have no adequate model of how individuals and firms adjust prices in a competitive model. If all participants are price-takers by definition, then the actor who adjusts prices to eliminate excess demand is not specified". Goodwin, Nelson, Ackerman and Weisskopf write:
If we mistakenly confuse Accuracy and precision, precision with accuracy, then we might be misled into thinking that an explanation expressed in precise mathematical or graphical terms is somehow more rigorous or useful than one that takes into account particulars of history, institutions or business strategy. This is not the case. Therefore, it is important not to put too much confidence in the apparent precision of supply and demand graphs. Supply and demand analysis is a useful precisely formulated conceptual tool that clever people have devised to help us gain an abstract understanding of a complex world. It does not—nor should it be expected to—give us in addition an accurate and complete description of any particular real world market.
Surveillance
According to Harvard academic Shoshana Zuboff, a new genus of capitalism, surveillance capitalism monetizes data acquired through surveillance. She states that it was first discovered and consolidated at Google, emerged due to the "coupling of the vast powers of the digital electronics, digital with the radical indifference and intrinsic narcissism of the financial capitalism and its neoliberal vision that have dominated commerce for at least three decades, especially in the Anglo economies" and depends on the global architecture of computer mediation which produces a distributed and largely uncontested new expression of power she calls "Big Other".Racism
According to Immanuel Wallerstein, institutional racism has been "one of the most significant pillars" of the capitalist system and serves as "the ideological justification for the hierarchization of the work-force and its highly unequal distributions of reward".Counter-criticism
Austrian School
Austrian School economists have argued that capitalism can organize itself into a complex system without an external guidance or central planning mechanism. Friedrich Hayek considered the phenomenon of self-organisation as underpinning capitalism. Prices serve as a signal as to the urgent and unfulfilled wants of people and the opportunity to earn profits if successful, or absorb losses if resources are used poorly or left idle, gives entrepreneurs incentive to use their Dispersed knowledge, knowledge and resources to satisfy those wants. Thus the activities of millions of people, each seeking their own interest, are coordinated.Ayn Rand
The novelist Ayn Rand made positive moral defenses of ''laissez-faire'' capitalism, most notably in her 1957 novel ''Atlas Shrugged'' and in her 1966 collection of essays ''Capitalism: The Unknown Ideal''. She argued that capitalism should be supported on moral grounds, not just on the basis of practical benefits. Her ideas have had significant influence over conservative and libertarian supporters of capitalism, especially within the American Tea Party movement. Rand defined capitalism as "a social system based on the recognition of individual rights, including property rights, in which all property is privately owned". According to Rand, the role of government in a capitalist state has three broad categories of proper functions: first, the police "to protect men from criminals"; second, the armed services "to protect men from foreign invaders"; and third, the law courts "to settle disputes among men according to objective laws".Ayn Rand, "Nature of Government", Virtue of selfishness.See also
* Almighty dollar * Anarchism and capitalism * Anti-globalisation * ''Capital in the Twenty-First Century'' * Crisis theory * Criticism of communist party rule * Criticisms of corporations * Criticism of Marxism * Criticism of socialism * Culture of capitalism * Economic calculation problem * Late capitalism * Market fundamentalism * Post-capitalism * Social criticism * Socialism for the rich and capitalism for the poor * * ''The Theory of the Leisure Class'' * ''This Changes Everything (book), This Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. the Climate'' * ''Why Socialism?''References
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * *External links
A Reconsideration of the Theory of Entrepreneurship: a participatory approach
– critique of capitalism
– 1907 anti-capitalist pamphlet by John Wheatley
by Allin F. Cottrell and Paul Cockshott, W. Paul Cockshott
Value, Price and Profit
– Karl Marx on the basic features of capitalism
Crisis of Capitalism
by
David Harvey
David W. Harvey (born 31 October 1935) is a British-born Marxist economic geographer, podcaster and Distinguished Professor of anthropology and geography at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York (CUNY). He received his P ...
. ''Royal Society of Arts''. 28 June 2010.
Richard Wolff on Curing Capitalism
''Moyers & Company''. 22 March 2013.
Occupy was right: capitalism has failed the world
Andrew Hussey. ''The Guardian''. 12 April 2014 (interview with Thomas Piketty).
Unless It Changes, Capitalism Will Starve Humanity By 2050
''Forbes''. 9 February 2016.
New Zealand's new prime minister calls capitalism a 'blatant failure'
''The Independent''. 22 October 2017.
''The Washington Post''. 20 April 2019
Broken Capitalism
series in ''The Guardian''. {{DEFAULTSORT:Criticism Of Capitalism Criticism of capitalism, Issues in anarchism Marxian economics Social philosophy Socialism