Crates of Mallus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Crates of Mallus ( grc-gre, Κράτης ὁ Μαλλώτης, ''Krátēs ho Mallṓtēs''; century BC) was a Greek
 According to
According to
grammarian
Grammarian may refer to:
* Alexandrine grammarians, philologists and textual scholars in Hellenistic Alexandria in the 3rd and 2nd centuries BCE
* Biblical grammarians, scholars who study the Bible and the Hebrew language
* Grammarian (Greco-Roman ...
and Stoic philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
, leader of the literary school and head of the library of Pergamum. He was described as the Crates from Mallus to distinguish him from other philosophers by the same name. His chief work was a critical and exegetical commentary on Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
. He is also famous for constructing the earliest known globe of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
.
Life
He was born in Mallus inCilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
, and was brought up at Tarsus, and then moved to Pergamon, and there lived under the patronage of Eumenes II, and Attalus II. He was the founder of the Pergamon school of grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes doma ...
, and seems to have been at one time the head of the library of Pergamon. Among his followers were Hermias (Κρατήτειος Ἑρμείας mentioned in sch. Hom. ''Il''. 16.207a), Zenodotus of Mallus and Herodicus of Babylon.
He visited Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
as ambassador of either Eumenes, in 168 BC, or Attalus in 159 BC. Having broken his leg after falling into an open sewer, he was compelled to stay in Rome for some time and delivered lectures which gave the first impulse to the study of grammar and criticism among the Romans.
Works
Crates made a strong distinction betweencriticism
Criticism is the construction of a judgement about the negative qualities of someone or something. Criticism can range from impromptu comments to a written detailed response. , ''"the act of giving your opinion or judgment about the good or bad q ...
and grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes doma ...
, the latter of which he regarded as subordinate to the former. A critic, according to Crates, should investigate everything which could throw light upon literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to ...
; the grammarian was only to apply the rules of language to clear up the meaning of particular passages, and to settle the text, prosody, accentuation, etc. From this part of his system, Crates derived the surname of ''Kritikos''.
Like Aristarchus of Samothrace
Aristarchus of Samothrace ( grc-gre, Ἀρίσταρχος ὁ Σαμόθραξ ''Aristarchos o Samothrax''; c. 220 – c. 143 BC) was an ancient Greek grammarian, noted as the most influential of all scholars of Homeric poetry. He was the h ...
, Crates gave the greatest attention to the works of Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
, from his labours upon which he was also surnamed ''Homerikos''. He wrote a commentary on the Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Ody ...
and Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Iliad'', ...
in nine books. Some fragments of this commentary are preserved by the scholiasts and other ancient writers. His principles were opposed to those of Aristarchus, who was the leader of the Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
n school. Crates was the chief representative of the allegorical theory of exegesis, and maintained that Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
intended to express scientific or philosophical truths in the form of poetry.
Besides his work on Homer, Crates wrote commentaries on the ''Theogony
The ''Theogony'' (, , , i.e. "the genealogy or birth of the gods") is a poem by Hesiod (8th–7th century BC) describing the origins and genealogies of the Greek gods, composed . It is written in the Epic dialect of Ancient Greek and contain ...
'' of Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
, on Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars ...
, on Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; grc, Ἀριστοφάνης, ; c. 446 – c. 386 BC), son of Philippus, of the deme Kydathenaion ( la, Cydathenaeum), was a comic playwright or comedy-writer of ancient Athens and a poet of Old Attic Comedy. Eleven of his ...
, and probably on other ancient authors; a work on the Attic dialect; and works on geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
, natural history, and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
, of which only a few fragments exist.
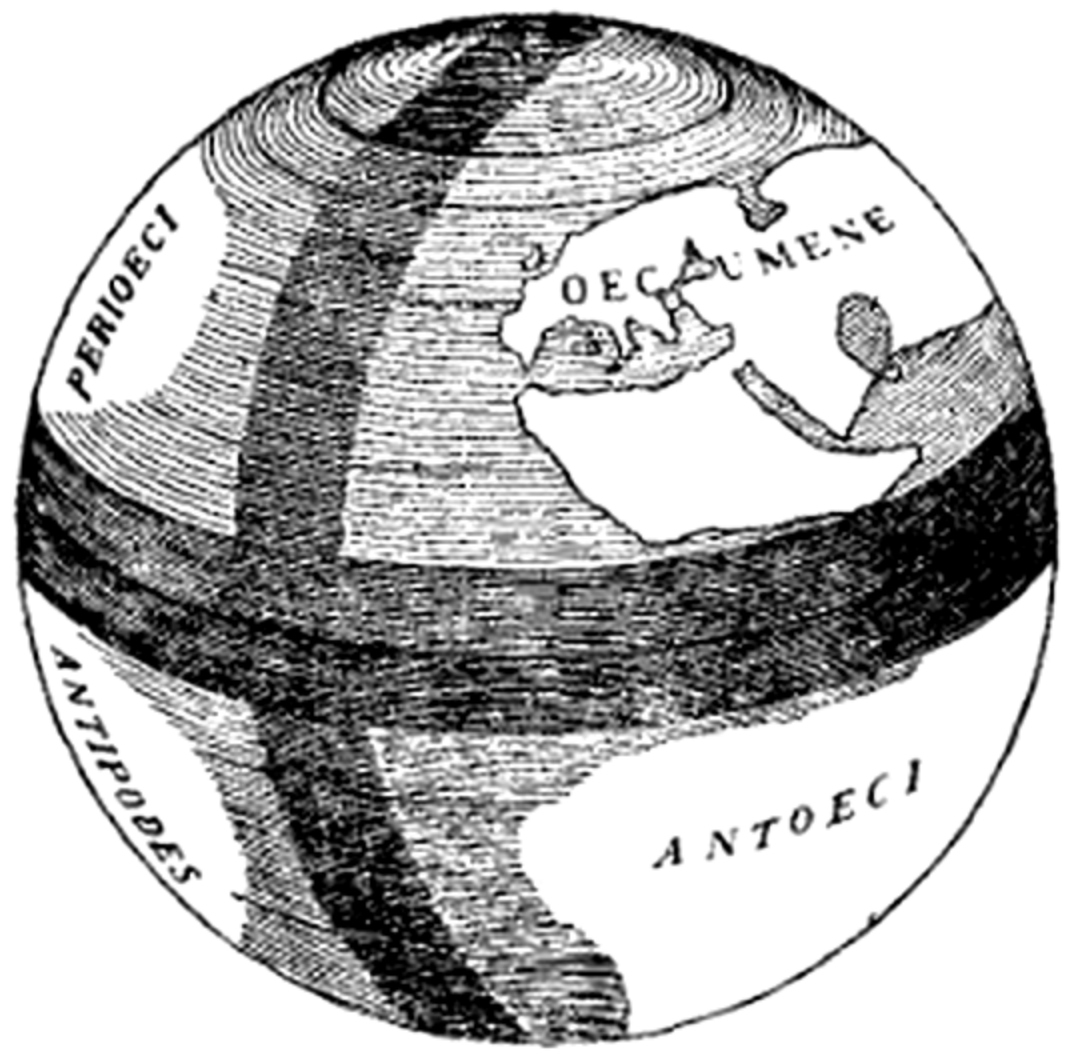
The Globe of Crates
 According to
According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, Crates devised a globe representing the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
, which is thus the earliest known globe representing the Earth:
We have now traced on a spherical surface the area in which we say the inhabited world is situated; and the man who would most closely approximate the truth by constructed figures must necessarily take for the earth a globe like that of Crates, and lay off on it the quadrilateral, and within the quadrilateral put down the map of the inhabited world. But since the need of a large globe, so that the section in question (being a small fraction of the globe) may be large enough to receive distinctly the appropriate parts of the inhabited world and to present the proper appearance to observers, it is better for him to construct a globe of adequate size, if he can do so; and let it be no less than ten feet in diameter.Following the theory of five climatic zones, Crates considered that the torrid zone is occupied by the
Ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wor ...
and that, by analogy, one can imagine people living beyond the torrid zone:
For Crates, following the mere form of mathematical demonstration, says that the torrid zone is "occupied" byThe classic drawing of the sphere displays the known world, or Oecumene (Europe, North Africa, and Asia), with three other continents, labeled the Perioeci, the Antipodes, and the Antioeci. Crates' Perioeci and Antipodes arguably do exist, corresponding roughly toOceanus In Greek mythology, Oceanus (; grc-gre, , Ancient Greek pronunciation: , also Ὠγενός , Ὤγενος , or Ὠγήν ) was a Titan son of Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys, and the father of the river gods and ...and that on both sides of this zone are the temperate zones, the one being on our side, while the other is on the other side of it. Now, just as theseEthiopians Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts o ...on our side of Oceanus, who face the south throughout the whole length of the inhabited land, are called the most remote of the one group of peoples, since they dwell on the shores of Oceanus, so too, Crates thinks, we must conceive that on the other side of Oceanus also there are certain Ethiopians, the most remote of the other group of peoples in the temperate zone, since they dwell on the shores of this same Oceanus; and that they are in two groups and are "sundered in twain" by Oceanus.Strabo
''Geography'', i.2.24
/ref>
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
respectively, but the continent of the Antioeci, Terra Australis, does not, except in fragments (Australasia
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologic ...
and southern Africa). And the earth does in fact have a ring of water around it, but at 60 degrees South latitude, not at the Equator.
Honours
Crates Bay inAntarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
is named after Crates of Mallus.
Notes
References
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Crates Of Mallus Librarians of Pergamon Ancient Greek cartographers Ancient Greek grammarians Hellenistic-era philosophers from Anatolia Stoic philosophers 2nd-century BC Greek people Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown People from Tarsus, Mersin