cradle of Humankind on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Cradle of Humankind is a
The Cradle of Humankind is a
 In October 2013, Berger commissioned geologist Pedro Boshoff to investigate cave systems in the Cradle of Humankind for the express purpose of discovering more fossil hominin sites. Cavers Rick Hunter and Steven Tucker discovered hominid fossils in a previously unexplored area of the Rising Star/Westminster Cave System assigned site designation UW-101. In November 2013, Berger led a joint expedition of the University of the Witwatersrand and National Geographic Society to the Rising Star Cave System near Swartkrans. In just three weeks of excavation, the six-woman international team of advance speleological scientists (K. Lindsay Eaves, Marina Elliott,
In October 2013, Berger commissioned geologist Pedro Boshoff to investigate cave systems in the Cradle of Humankind for the express purpose of discovering more fossil hominin sites. Cavers Rick Hunter and Steven Tucker discovered hominid fossils in a previously unexplored area of the Rising Star/Westminster Cave System assigned site designation UW-101. In November 2013, Berger led a joint expedition of the University of the Witwatersrand and National Geographic Society to the Rising Star Cave System near Swartkrans. In just three weeks of excavation, the six-woman international team of advance speleological scientists (K. Lindsay Eaves, Marina Elliott, 

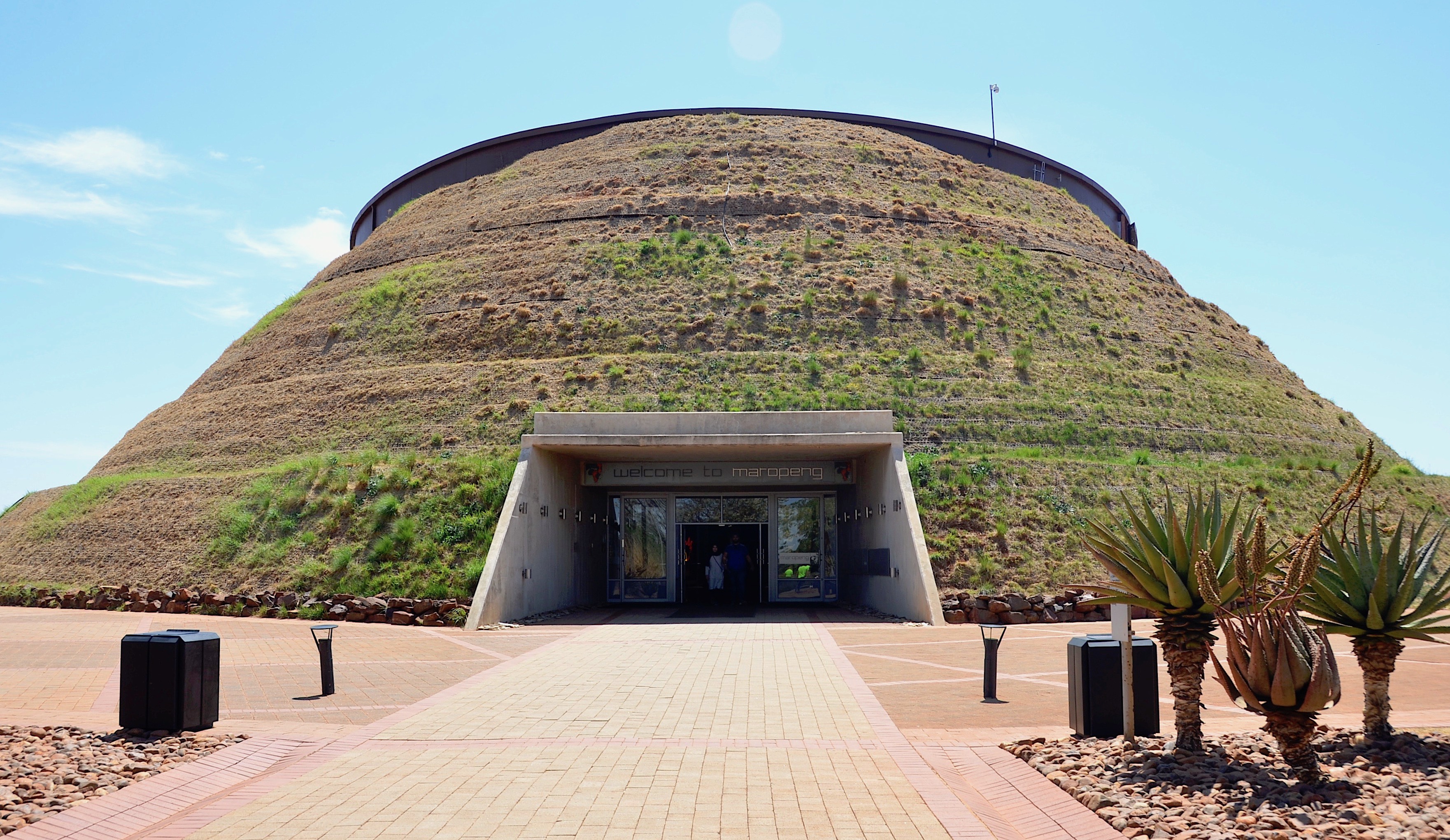
 On 7 December 2005, South African President Thabo Mbeki opened the new Maropeng Visitors Centre at the site. Per the maropeng.co.za website, visitors can see fossils, view stone tools, and learn about the birth of humankind in the visitors centre. The visitors centre additionally offers a tour of the Sterkfontein Caves and the exhibition at Sterkfontein. A light, moveable, steel structure known as the Beetle has been placed over the Malapa site, to allow the paying public to view excavations, once they resume at the site. (Digging has been on hold since 2009, when the remains of four '' A. sediba'' individuals were removed.)
On 7 December 2005, South African President Thabo Mbeki opened the new Maropeng Visitors Centre at the site. Per the maropeng.co.za website, visitors can see fossils, view stone tools, and learn about the birth of humankind in the visitors centre. The visitors centre additionally offers a tour of the Sterkfontein Caves and the exhibition at Sterkfontein. A light, moveable, steel structure known as the Beetle has been placed over the Malapa site, to allow the paying public to view excavations, once they resume at the site. (Digging has been on hold since 2009, when the remains of four '' A. sediba'' individuals were removed.)
BBC, "Richest human fossil site found in South Africa"
28 November 2013
National Geographic, Rising Star ExpeditionSterkfontein and Maropeng visitor attractions websiteMaropeng – The Cradle of Humankind
Official Website
UNESCO – Fossil Hominid Sites of Sterkfontein, Swartkrans, Kromdraai, and EnvironsPalaeo Tours – Scientist-led tours to the "Cradle"Human Timeline (Interactive)
– Smithsonian,
 The Cradle of Humankind is a
The Cradle of Humankind is a paleoanthropological
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinship ...
site and is located about northwest of Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a Megacity#List of megacities, megacity, and is List of urban areas by p ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, in the Gauteng
Gauteng ( ) is one of the nine provinces of South Africa. The name in Sotho-Tswana languages means 'place of gold'.
Situated on the Highveld, Gauteng is the smallest province by land area in South Africa. Although Gauteng accounts for only ...
province. Declared a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
in 1999, the site is home to the largest concentration of human ancestral remains anywhere in the world. The site currently occupies and contains a complex system of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
caves. The registered name of the site in the list of World Heritage Sites is '' Fossil Hominid Sites of South Africa''.
According to the '' South African Journal of Science,'' Bolt's Farm is the place where the earliest primate was discovered. Bolt's Farm was heavily mined for speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, dependi ...
(calcium carbonate from stalagmites, stalactites
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via
''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble ...
and flowstones) in the terminal 19th and early 20th centuries.
The Sterkfontein Caves were the site of the discovery of a 2.3-million-year-old fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
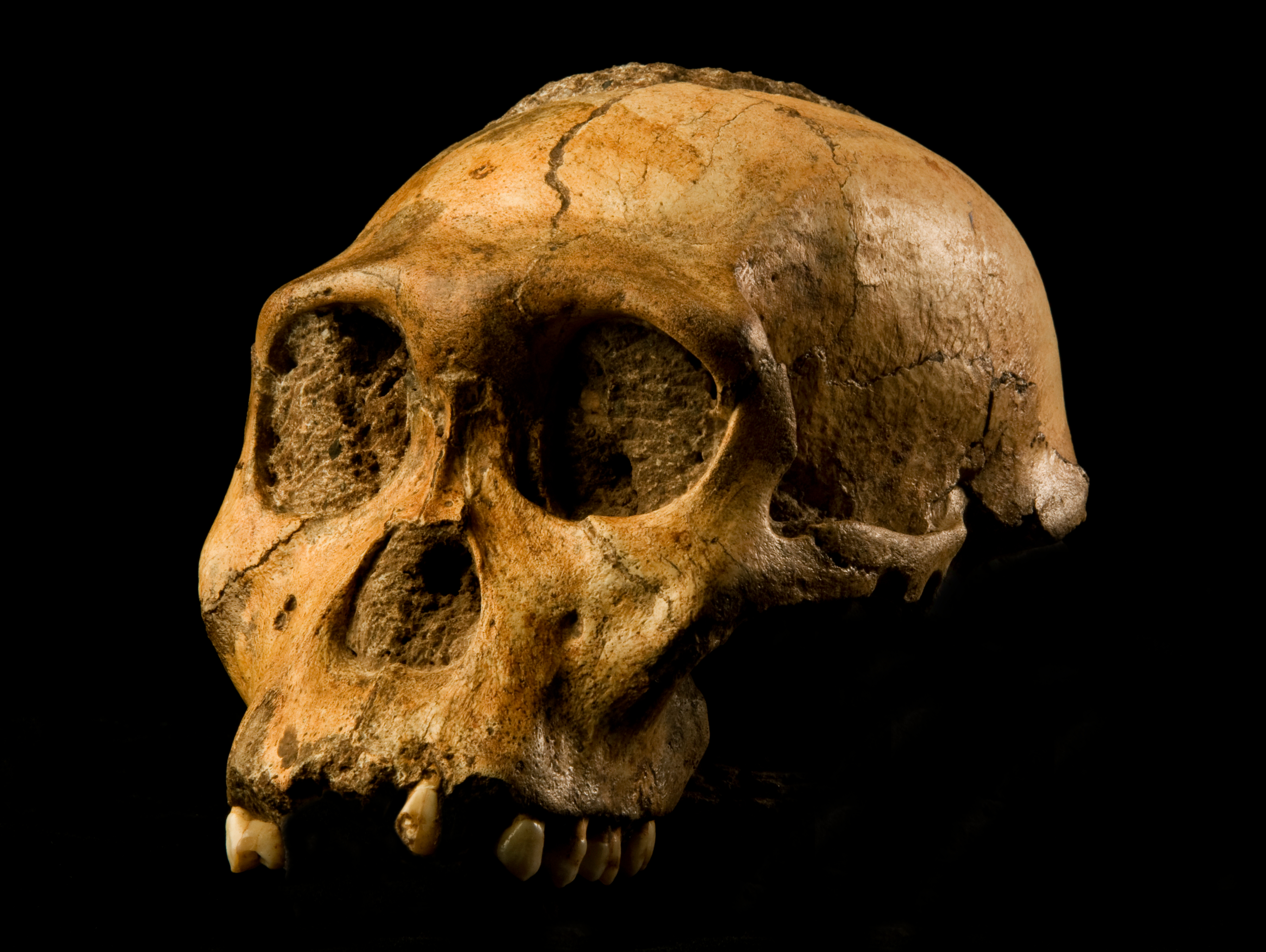
'' Australopithecus africanus'' (nicknamed " Mrs. Ples"), found in 1947 by Robert Broom
Robert Broom FRS FRSE (30 November 1866 6 April 1951) was a British- South African doctor and palaeontologist. He qualified as a medical practitioner in 1895 and received his DSc in 1905 from the University of Glasgow.
From 1903 to 1910, he ...
and John T. Robinson. The find helped corroborate the 1924 discovery of the juvenile ''Australopithecus africanus'' skull known as the " Taung Child", by Raymond Dart, at Taung in the North West Province of South Africa, where excavations still continue.
Nearby, but not in the site, the Rising Star Cave system contains the Dinaledi Chamber (chamber of stars), in which were discovered fifteen fossil skeletons
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure insid ...
of an extinct species
This page features lists of extinct species, organisms that have become Extinction, extinct, either in the wild or completely disappeared from Earth.
In actual theoretical practice, a species not definitely located in the wild in the last fifty ...
of hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
, provisionally named '' Homo naledi''.
Sterkfontein alone has produced more than a third of early hominid fossils ever found prior to 2010. The Dinaledi Chamber contains over 1,500 ''H. naledi'' fossils, the most extensive discovery of a single hominid species ever found in Africa.
Etymology
The name ''Cradle of Humankind'' reflects the fact that the site has produced a substantially large number ofhominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
fossils, some the oldest ever found, dating as far back as 3.5 million years ago.
History of discoveries
In 1935, Robert Broom found the first ape-man fossils at Sterkfontein and began work at this site. In 1938, a young schoolboy, Gert Terrblanche, brought Raymond Dart fragments of a skull from nearby Kromdraai which later were identified as '' Paranthropus robustus''. Also in 1938, a single ape-man tooth was found at the Cooper's site between Kromdraai and Sterkfontein. In 1948, the Camp-Peabody Expedition from the United States worked at Bolts Farm and Gladysvale looking for fossil hominids but failed to find any. Later in 1948, Robert Broom identified the first hominid remains from Swartkrans cave. In 1954, C.K. Brain began working at sites in the Cradle, including Cooper's Cave. He then initiated his three-decade work at Swartkrans cave, which resulted in the recovery of the second-largest sample of hominid remains from the Cradle. The oldest controlled use of fire by Homo erectus was also discovered at Swartkrans and dated to over 1 million years ago. In 1966,Phillip Tobias
Phillip Vallentine Tobias (14 October 1925 – 7 June 2012) was a South African palaeoanthropologist and Professor Emeritus at the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg. He was best known for his work at South Africa's hominid fossil ...
began his excavations of Sterkfontein which are still continuing and are the longest continuously running fossil excavations in the world. In 1991, Lee Berger
Lee Rogers Berger (born December 22, 1965) is an American-born South African paleoanthropologist and National Geographic Explorer-in-Residence. He is best known for his discovery of the ''Australopithecus sediba'' type site, Malapa; his leadersh ...
of the University of the Witwatersrand discovered the first hominid specimens from the Gladysvale site, making this the first new early hominid site to be discovered in South Africa in 48 years. In 1994, Andre Keyser discovered fossil hominids at the site of Drimolen. In 1997, Kevin Kuykendall and Colin Menter of the University of the Witwatersrand found two fossil hominid teeth at the site of Gondolin. Also in 1997, the near-complete ''Australopithecus'' skeleton of " Little Foot", dating to around 3.3 million years ago (although more recent dating suggest it is closer to 2.5 million years ago), was discovered by Ron Clarke
Ronald William Clarke, AO, MBE (21 February 1937 – 17 June 2015) was an Australian athlete, writer, and the Mayor of the Gold Coast from 2004 to 2012. He was one of the best-known middle- and long-distance runners in the 1960s, notable for ...
. In 2001, Steve Churchill of Duke University
Duke University is a private research university in Durham, North Carolina. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1892. In 1924, tobacco and electric power industrialist Jam ...
and Lee Berger found early modern human remains at Plovers Lake. Also in 2001, the first hominid fossils and stone tools were discovered ''in-situ'' at Coopers. In 2008, Lee Berger discovered the partial remains of two hominids ('' Australopithecus sediba'') in the Malapa Fossil Site
Malapa is a fossil-bearing cave located about northeast of the well known South African hominid-bearing sites of Sterkfontein and Swartkrans and about north-northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa. It is situated within the Cradle of Hum ...
that lived between 1.78 and 1.95 million years ago.
 In October 2013, Berger commissioned geologist Pedro Boshoff to investigate cave systems in the Cradle of Humankind for the express purpose of discovering more fossil hominin sites. Cavers Rick Hunter and Steven Tucker discovered hominid fossils in a previously unexplored area of the Rising Star/Westminster Cave System assigned site designation UW-101. In November 2013, Berger led a joint expedition of the University of the Witwatersrand and National Geographic Society to the Rising Star Cave System near Swartkrans. In just three weeks of excavation, the six-woman international team of advance speleological scientists (K. Lindsay Eaves, Marina Elliott,
In October 2013, Berger commissioned geologist Pedro Boshoff to investigate cave systems in the Cradle of Humankind for the express purpose of discovering more fossil hominin sites. Cavers Rick Hunter and Steven Tucker discovered hominid fossils in a previously unexplored area of the Rising Star/Westminster Cave System assigned site designation UW-101. In November 2013, Berger led a joint expedition of the University of the Witwatersrand and National Geographic Society to the Rising Star Cave System near Swartkrans. In just three weeks of excavation, the six-woman international team of advance speleological scientists (K. Lindsay Eaves, Marina Elliott, Elen Feuerriegel
Elen Feuerriegel is an Australian palaeoanthropologist, known for being one of the "underground astronauts" of the Rising Star Expedition. She is a researcher at the University of Washington.
Feuerriegel studied anthropology at the Universit ...
, Alia Gurtov, Hannah Morris, and Becca Peixotto), chosen for their paleoanthropological and caving skills, as well as their small size, recovered over 1,200 specimens of a presently unidentified fossil hominin species. The site is still in the process of being dated. In September 2015, Berger, in collaboration with National Geographic, announced the discovery of a new species of human relative, named ''Homo naledi'', from UW-101. Most remarkably, besides shedding light on the origins and diversity of our genus, ''H. naledi'' also appears to have intentionally deposited bodies of its dead in a remote cave chamber, a behaviour previously thought limited to humans. In the last days of the Rising Star Expedition, cavers Rick Hunter and Steven Tucker discovered additional fossil hominid material in another portion of the cave system. Preliminary excavations at this site, designated UW-102, have begun and yielded complete hominid fossil material of its own. It is unknown what the relationship of sites 101 and 102 is.


Geological context
The hominin remains at the Cradle of Humankind are found indolomitic
Dolomite () is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite. An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic ...
caves, and are often encased in a mixture of limestone and other sediments called breccia
Breccia () is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or rocks cemented together by a fine-grained matrix.
The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of ...
that fossilised over time. Hominids may have lived all over Africa, but their remains are found only at sites where conditions allowed for the formation and preservation of fossils.
Visitor centres
See also
* Wonder Cave * Cradle of civilization *'' Dawn of Humanity'', a 2015 PBS film *Muldersdrift
Muldersdrift, in the Gauteng Province of South Africa, is a picturesque rural area situated 27 km north-west of the CBD of Johannesburg, between Johannesburg and the Magaliesberg mountain range. The area falls under the West Rand District ...
*Recent African origin of modern humans
In paleoanthropology, the recent African origin of modern humans, also called the "Out of Africa" theory (OOA), recent single-origin hypothesis (RSOH), replacement hypothesis, or recent African origin model (RAO), is the dominant model of the ...
* Maropeng Cavemen, South Africa field hockey club
References
Further reading
*L.R. Berger and B. Hilton-Barber, ''Field Guide to the Cradle of Humankind'' (Struik, 2003)External links
BBC, "Richest human fossil site found in South Africa"
28 November 2013
National Geographic, Rising Star Expedition
Official Website
UNESCO – Fossil Hominid Sites of Sterkfontein, Swartkrans, Kromdraai, and Environs
– Smithsonian,
National Museum of Natural History
The National Museum of Natural History is a natural history museum administered by the Smithsonian Institution, located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., United States. It has free admission and is open 364 days a year. In 2021, with 7. ...
(August 2016).
{{Authority control
Geography of Gauteng
Paleoanthropological sites
World Heritage Sites in South Africa
Prehistoric Africa
Tourist attractions in Johannesburg
Fossil parks
Paleontology in South Africa