County of Holstein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers
Holstein (; ; ; ; ) is the region between the rivers 
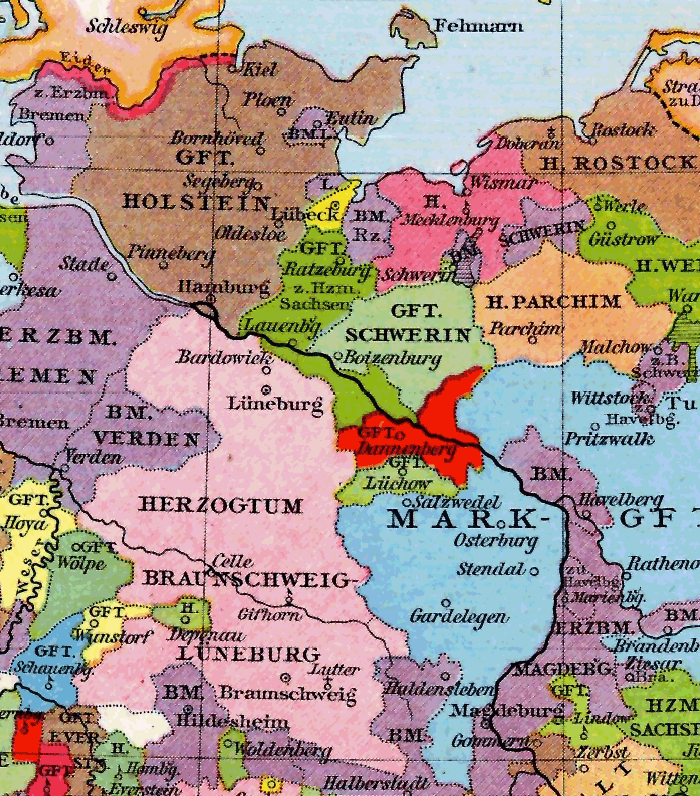 The new county of Holstein was established in 1111; it was first a fief of the
The new county of Holstein was established in 1111; it was first a fief of the

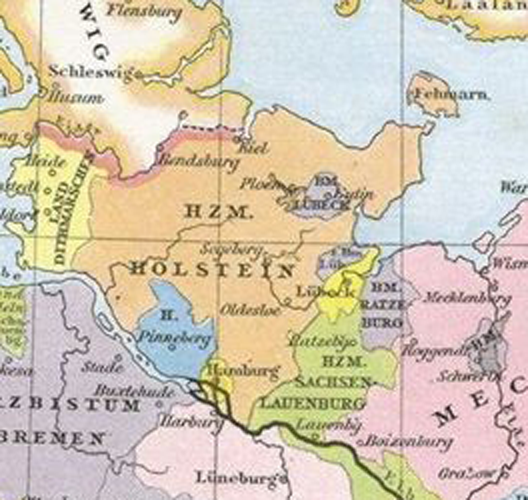 In 1474 Lauenburg's
In 1474 Lauenburg's
Elbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Ge ...
and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; ; ; ; ; occasionally in English ''Sleswick-Holsatia'') is the Northern Germany, northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical Duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of S ...
, the northernmost state of Germany.
Holstein once existed as the German County of Holstein (; 811–1474), the later Duchy of Holstein
The Duchy of Holstein (; ) was the northernmost state of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the present German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It originated when King Christian I of Denmark had his County of Holstein-Rendsburg elevated to a duchy ...
(; 1474–1866), and was the northernmost territory of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. The history of Holstein is closely intertwined with the history of the Danish Duchy of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig (; ; ; ; ; ) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been div ...
(). The capital of Holstein is Kiel
Kiel ( ; ) is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein. With a population of around 250,000, it is Germany's largest city on the Baltic Sea. It is located on the Kieler Förde inlet of the Ba ...
.
Holstein's name comes from the Holcetae, a Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
tribe mentioned by Adam of Bremen as living on the north bank of the Elbe, to the west of Hamburg. The name means "dwellers in the wood" or "hill-sitters" (Northern Low Saxon: ; ).

History
Origins
After theMigration Period
The Migration Period ( 300 to 600 AD), also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories ...
of the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
, Holstein was adjacent to the Obotrites on the coast of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
and the land of the Danes in Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It ...
.
With the conquest of Old Saxony
Old Saxony was the homeland of the Saxons who fought the Frankish empire during the Early Middle Ages, until they conquered it and converted it into a Carolingian stem duchy in the 8th century, the Duchy of Saxony. Contemporary authors such a ...
by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
''circa'' 800, he granted the land north of the Eider River (Schleswig) to the Danes
Danes (, ), or Danish people, are an ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
History
Early history
Denmark ...
by the Treaty of Heiligen signed in 811. The ownership of what would late become eastern Holstein (districts of Plön and Ostholstein) was given to the Obotrites, namely the Wagrians, and the Saxon elite was deported to various areas of the empire. After 814, however, the Saxons were restored to Western Holstein. The Wagrians were pushed out of the Limes Saxoniae - the new border running from the Elbe River near Boizenburg northwards along the Bille River to the mouth of the Schwentine at the Kiel Fjord and the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
. For the following 300 years, Holstein continued to be a part of Saxony.
County of Holstein
 The new county of Holstein was established in 1111; it was first a fief of the
The new county of Holstein was established in 1111; it was first a fief of the Duchy of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony () was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 CE and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 84 ...
. After that, it belonged to the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (, ), was a ''reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296 to 1803 and again from 1814 to 1876 in the extreme southeast region of what is now Schleswig-Holstein. Its territorial centre was in the modern district of Herz ...
, and finally it came into a possession of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck.
With the establishment of the new territorial unit, expansion to the East began and the Wagrians were finally defeated in 1138.
The County of Holstein was ruled by the House of Schaumburg; the first count was Adolf I, Count of Holstein.
Holstein was temporarily occupied by Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
after the Battle of Stellau
The Battle of Stellau took place in the year 1201 near the village of Stellau near Wrist, in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein.
A German army led by Count Adolf III of Holstein fought a Danish army under King Canute VI of Denmark. Du ...
(1201), but was reconquered by the Count of Schauenburg and his allies in the Battle of Bornhöved (1227)
The (second) Battle of Bornhöved took place on 22 July 1227 near Bornhöved in Holstein. Count Adolf IV of Schauenburg and Holstein — leading an army consisting of troops from the cities of Lübeck and Hamburg, Dithmarschen, Holstein, a ...
.
Partitions of the County of Holstein (1111–1474)
TheCounts of Schauenburg and Holstein
The Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein were titles of the Holy Roman Empire. The dynastic family came from the County of Schauenburg near Rinteln (district Schaumburg) on the Weser in Germany. Together with its ancestral possessions in Bückebur ...
partitioned Holstein several times among the inheriting sons into up to six lines, named after their towns of residence:
* Holstein-Itzehoe, branch county between 1261 and 1290, partitioned from Holstein, repartitioned into Holstein-Pinneberg, Holstein-Plön and Holstein-Rendsburg
* Holstein-Kiel
The imperial county of Holstein-Kiel was a line of the counts of Schauenburg and Holstein, House of Schauenburg and Holstein from 1261 to 1390.
History
The County of Holstein was ruled until 1238 by Adolphus IV of Schauenburg and Holstein. When ...
, branch county between 1261 and 1390, partitioned from Holstein, in 1273 Holstein-Segeberg (first) was partitioned from Holstein-Kiel, but reverted in 1308, but then lost to Holstein-Pinneberg, Holstein-Plön and Holstein-Rendsburg in 1316; Holstein-Kiel acquired Holstein-Plön in 1350, and merged itself into Holstein-Rendsburg
* Holstein-Pinneberg, branch county between 1290 and 1640, partitioned from Holstein-Itzehoe, acquired a share of Holstein-Segeberg in 1316, merged into the Duchy of Holstein
* Holstein-Plön, branch county between 1290 and 1390, partitioned from Holstein-Itzehoe, acquired a share of Holstein-Segeberg in 1316, merged into Holstein-Kiel
* Holstein-Rendsburg, branch county between 1290 and 1474, partitioned from Holstein-Itzehoe, acquired a share of Holstein-Segeberg (first) in 1316, and Holstein-Kiel in 1390, in 1381/1384 Holstein-Segeberg (second) was partitioned from Holstein-Rendsburg, but reverted in 1403, elevated to ducal rank in 1474
* Holstein- Segeberg (first), branch county between 1273 and 1308, partitioned from and reverted to Holstein-Kiel, but seized by allied Holstein-Pinneberg, Holstein-Plön, and Holstein-Rendsburg, partitioning Segeberg in three shares, each merged into one of the lines in 1316
* Holstein-Segeberg (second), branch county between 1381/1384 and 1403, partitioned from and reverted to Holstein-Rendsburg
In 1386 King Oluf II of Denmark and his mother, Queen Margaret I, enfeoffed in Nyborg
Nyborg is a city in central Denmark, located in Nyborg Municipality on the island of Funen and with a population of 17,990 (2025). It is the easternmost settlement on Funen. By road, it is located 34 km east of Odense, 35 km north of ...
Gerhard VI, Count of Holstein-Rendsburg and his cognatic successors with the Duchy of Schleswig. He thus became as Gerhard II duke of Schleswig. Until 1390 the Rendsburg branch united by inheritance all branches except of that of Holstein-Pinneberg.
When the Holstein-Rendsburg line of the Schauenburg counts became extinct with the death of Adolf VIII of Holstein-Rendsburg (and in personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
as Adolf I Duke of Schleswig) in 1459, Christian I of Denmark
Christian I ''(Christiern I)'' (February 1426 – 21 May 1481) was a German noble and Scandinavian monarch under the Kalmar Union. He was king of Denmark (1448–1481), King of Norway, Norway (1450–1481) and King of Sweden, Sweden (1457 ...
inherited – from his maternal uncle Adolf I – the Duchy of Schleswig, a Danish fief. Through the Treaty of Ribe (1460) Christian was elected Count of Holstein-Rendsburg, then still a Saxe-Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (, ), was a ''reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296 to 1803 and again from 1814 to 1876 in the extreme southeast region of what is now Schleswig-Holstein. Its territorial centre was in the modern district of Herz ...
ian subfief within the Holy Roman Empire.
Duchy of Holstein

 In 1474 Lauenburg's
In 1474 Lauenburg's liege lord
Homage (/ˈhɒmɪdʒ/ or ) (from Medieval Latin , lit. "pertaining to a man") in the Middle Ages was the ceremony in which a feudal tenant or vassal pledged reverence and submission to his feudal lord, receiving in exchange the symbolic title t ...
, the German Emperor Frederick III, elevated Christian I as Count of Holstein-Rendsburg to Duke of Holstein, thus becoming an immediate imperial ('' reichsunmittelbar'') vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
(see imperial immediacy
In the Holy Roman Empire, imperial immediacy ( or ) was the status of an individual or a territory which was defined as 'immediate' () to Emperor and Empire () and not to any other intermediate authorities, while one that did not possess that stat ...
). The Duchy of Holstein retained that status until the dissolution of the Empire in 1806.
Partitions of the Duchy of Holstein (1474–1866)
In 1490, the Duchy of Holstein was divided into Holstein-Segeberg andHolstein-Gottorp
Holstein-Gottorp () is the historiographical name, as well as contemporary shorthand name, for the parts of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, also known as Ducal Holstein, that were ruled by the dukes of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp, a side ...
. Holstein-Segeberg remained with the Danish king and was also known as Royal Holstein; later it came to be known as Holstein-Glückstadt. Holstein-Gottorp, also known as Ducal Holstein, was given to a cadet branch of the House of Oldenburg
The House of Oldenburg is a Germans, German dynasty whose members rule or have ruled in Danish Realm, Denmark, Kingdom of Iceland, Iceland, Kingdom of Greece, Greece, Norway, Russian Empire, Russia, Sweden, United Kingdom, the United Kingdom, King ...
, to which the kings of Denmark belonged.
Between 1533 and 1544 King Christian III of Denmark
Christian III (12 August 1503 – 1 January 1559) reigned as King of Denmark from 1534 and King of Norway from 1537 until his death in 1559. During his reign, Christian formed close ties between the church and the crown. He established ...
ruled the entire Duchies of Holstein and of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig (; ; ; ; ; ) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been di ...
also in the name of his then still minor half-brothers John the Elder and Adolf. In 1544 they partitioned the Duchies of Holstein (a fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
of the Holy Roman Empire) and of Schleswig (a Danish fief) in an unusual way, following negotiations between the brothers and the Estates of the Realm
The estates of the realm, or three estates, were the broad orders of social hierarchy used in Christendom (Christian Europe) from the Middle Ages to early modern Europe. Different systems for dividing society members into estates developed a ...
of the duchies, which had constituted in 1460 by the Treaty of Ribe and strictly opposed a factual partition. The elder three brothers determined their youngest brother Frederick for a career as Lutheran administrator of an ecclesiastical state within the Holy Roman Empire.
So the revenues of the duchies were divided in three equal shares by assigning the revenues of particular areas and landed estates to each of the elder brothers, while other general revenues, such as taxes from towns and customs dues, were levied together but then shared among the brothers. The estates, whose revenues were assigned to the parties, made Holstein and Schleswig look like patchworks, technically inhibiting the emergence of separate new duchies, as intended by the estates of the duchies. The secular rule in the fiscally divided duchies thus became a condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership regime in which a building (or group of buildings) is divided into multiple units that are either each separately owned, or owned in common with exclusive rights of occupation by individual own ...
of the parties. As dukes of Holstein and Schleswig the rulers of both houses bore the formal title of "Duke of Schleswig, Holstein, Ditmarsh and Stormarn". The three shares are usually called:
* Gottorp ducal share in Holstein and Schleswig, partitioned from ducal Holstein in 1544, acquired half of Haderslev share in 1581 (thus thereafter simply called ducal share), merged into the royal share in 1773 with its ruler receiving in return the prior Danish-held County of Oldenburg
The County of Oldenburg () was a county of the Holy Roman Empire.
In 1448 Christian I of Denmark (of the House of Oldenburg), Count of Oldenburg became King of Denmark, and later King of Norway and King of Sweden. One of his grandsons, Adolf, ...
.
* Haderslev
Haderslev (; ) is a Denmark, Danish town in the Region of Southern Denmark with a population of 22,405 (1 January 2025).Holstein-Glückstadt after its capital  The territory of Holstein was enlarged by the conquest of the independent Republic of Dithmarschen in 1559, which was divided among the three ducal houses. After 1581 the southern part remained to the Danish Crown, the northern part was ruled by the House of Gottorp until 1773.
The territory of Holstein was enlarged by the conquest of the independent Republic of Dithmarschen in 1559, which was divided among the three ducal houses. After 1581 the southern part remained to the Danish Crown, the northern part was ruled by the House of Gottorp until 1773.
 Following the death of King
Following the death of King 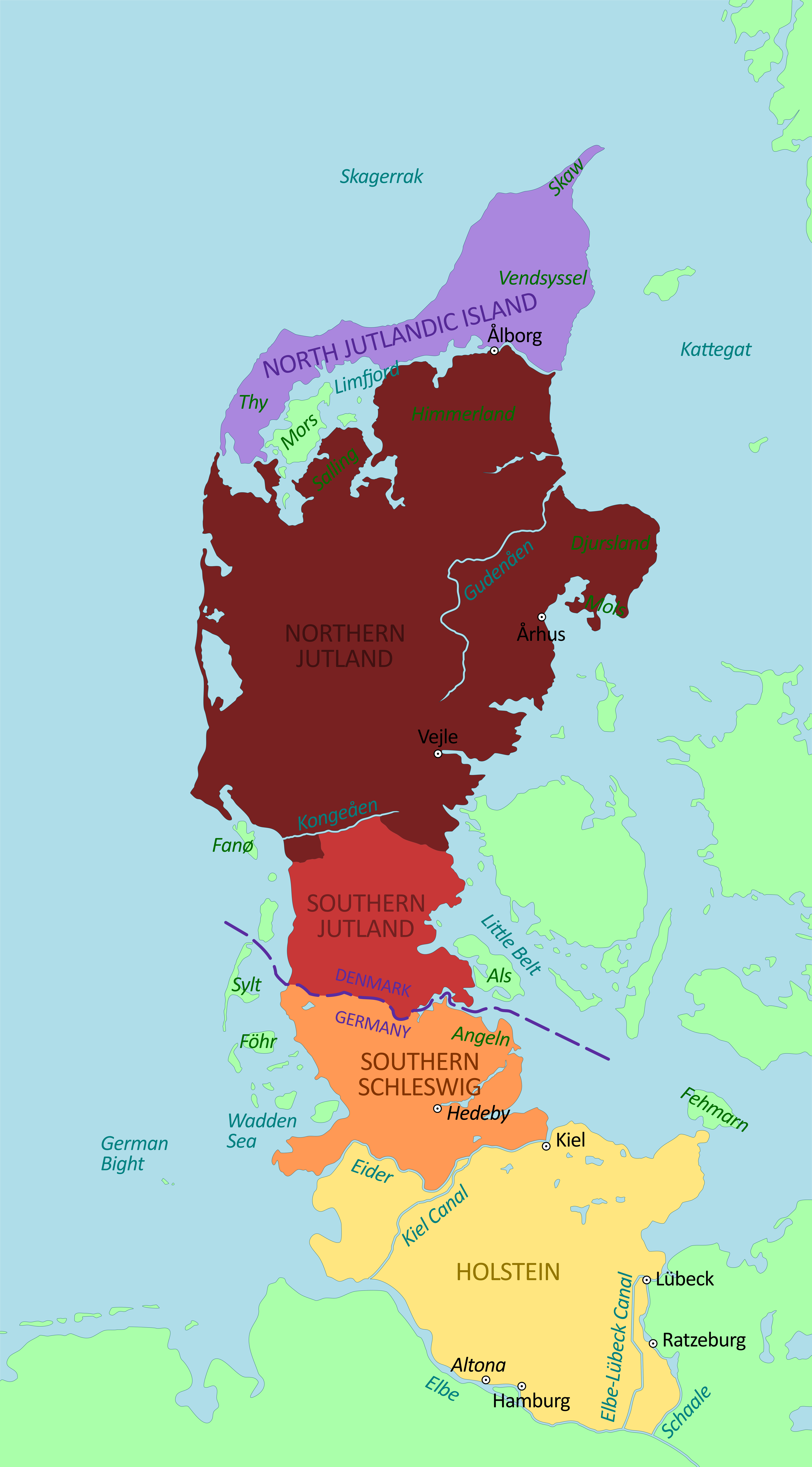 For a list of rulers, see ''
For a list of rulers, see ''
Map of Schleswig-Holstein in 1730
{{Coord, 54.1667, N, 9.66667, E, source:kolossus-nowiki, display=title History of Schleswig-Holstein Counties of the Holy Roman Empire States and territories established in 1474 Regions of Schleswig-Holstein
Glückstadt
Glückstadt (; ) is a town in the Steinburg district of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is located on the right bank of the Lower Elbe at the confluence of the small Rhin river, about northwest of Altona. Glückstadt is part of the Hamburg ...
. Parts of the former County of Holstein-Pinneberg were transformed 1649/50 into the Imperial County of Rantzau, which fell back to the Danish Crown in 1726.
The dynastic name Holstein-Gottorp comes as convenient usage from the technically more correct Duke of Schleswig and Holstein at Gottorp. Adolf, the third son of Duke and King Frederick I and the second youngest half-brother of King Christian III, founded the dynastic branch called House of Holstein-Gottorp, which is a cadet branch of the then royal Danish House of Oldenburg
The House of Oldenburg is a Germans, German dynasty whose members rule or have ruled in Danish Realm, Denmark, Kingdom of Iceland, Iceland, Kingdom of Greece, Greece, Norway, Russian Empire, Russia, Sweden, United Kingdom, the United Kingdom, King ...
. The Danish monarchs and the Dukes of Holstein-Gottorp ruled both duchies together as to general government, however, collected their revenues in their separate estates. John the Elder conveniently called Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Haderslev produced no issue, so no branch emerged from his side.
Similar to the above-mentioned agreement Christian III's youngest son John the Younger gained for him and his heirs a share in Holstein's and Schleswig's revenues in 1564, comprising a third of the royal share, thus a ninth of Holstein and Schleswig as to the fiscal point of view. John the Younger and his heirs, however, had no share in the condominial rule, so they were not ruling but mere titular dukes.
The share of John the Elder, who died in 1581, was halved between Adolf and Frederick II, thus increasing again the royal share by a fiscal sixth of Holstein and Schleswig.Cf. Carsten Porskrog Rasmussen, "Die dänischen Könige als Herzöge von Schleswig und Holstein", Frauke Witte and Marion Hartwig (trls.), in: ''Die Fürsten des Landes: Herzöge und Grafen von Schleswig, Holstein und Lauenburg'' e slevigske hertuger; German Carsten Porskrog Rasmussen (ed.) on behalf of the Gesellschaft für Schleswig-Holsteinische Geschichte, Neumünster: Wachholtz, 2008, pp. 73–109, here pp. 87seq. As an effect the complicated fiscal division of both separate duchies, Holstein and Schleswig, with shares of each party scattered in both duchies, provided them with a condominial government binding both together, partially superseding their legally different affiliation as Holy Roman and Danish fiefs.
The County of Holstein-Pinneberg, which had remained a separately ruled territory in Holstein until its line was extinct in 1640, was merged into the then royal share of the Duchy of Holstein. The Duke of Holstein-Gottorp became emperor of Russia in 1762 as Peter III and was planning an attack on Denmark to recover the Holstein-Gottorp
Holstein-Gottorp () is the historiographical name, as well as contemporary shorthand name, for the parts of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, also known as Ducal Holstein, that were ruled by the dukes of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp, a side ...
lands possessions in Schleswig, which were seized by the Danish king in 1713. Although Peter was soon overthrown by his wife, Catherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
, the Danes determined to rid themselves of this problem. In 1773, they exchanged the County of Oldenburg
The County of Oldenburg () was a county of the Holy Roman Empire.
In 1448 Christian I of Denmark (of the House of Oldenburg), Count of Oldenburg became King of Denmark, and later King of Norway and King of Sweden. One of his grandsons, Adolf, ...
for the Gottorp lands in Holstein, bringing all of Holstein under their control. Thus, Holstein was again united in one state.
 The territory of Holstein was enlarged by the conquest of the independent Republic of Dithmarschen in 1559, which was divided among the three ducal houses. After 1581 the southern part remained to the Danish Crown, the northern part was ruled by the House of Gottorp until 1773.
The territory of Holstein was enlarged by the conquest of the independent Republic of Dithmarschen in 1559, which was divided among the three ducal houses. After 1581 the southern part remained to the Danish Crown, the northern part was ruled by the House of Gottorp until 1773.
United Holstein
With the dissolution of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
in 1806 Holstein's imperial vassal status turned void. It thus became a sovereign state. Because of its personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
with Denmark, the Duchy of Holstein did not come under French occupation during the Napoleonic era
The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France and history of Europe, Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly (French Revoluti ...
(however, the neighboring duchy of Lauenburg was annexed by France in 1811 and became a part of Bouches-de-l'Elbe). From 1815 to 1864 it was a member of the German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
, though still in personal union with Denmark (the King of Denmark being also Duke of Holstein).
 Following the death of King
Following the death of King Frederick VII of Denmark
Frederick VII (Frederik Carl Christian; 6 October 1808 – 15 November 1863) was King of Denmark from 1848 to 1863. He was the last Danish monarch of the older Royal branch of the House of Oldenburg and the last monarch, king of Denmark to r ...
(House of Oldenburg
The House of Oldenburg is a Germans, German dynasty whose members rule or have ruled in Danish Realm, Denmark, Kingdom of Iceland, Iceland, Kingdom of Greece, Greece, Norway, Russian Empire, Russia, Sweden, United Kingdom, the United Kingdom, King ...
) in 1863, the inheritance of Schleswig and Holstein was disputed. The new king, Christian IX ( House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg, a cadet branch of the House of Oldenburg), made his claim to the Danish throne through a female line. The Duke of Augustenborg, a minor scion from another cadet line of the House of Oldenburg, claimed the Duchies, and soon the German Confederation, led by Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
and Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, went to the Second Schleswig War
The Second Schleswig War (; or German Danish War), also sometimes known as the Dano-Prussian War or Prusso-Danish War, was the second military conflict over the Schleswig–Holstein question of the nineteenth century. The war began on 1 Februar ...
with Denmark, quickly defeating it in 1864 and forcing it to cede the duchies.
However, the duchies were not given to the Duke of Augustenborg. In 1865 an arrangement was worked out between Prussia and Austria where the Austrians occupied and administered Holstein, while the Prussians did the same in Schleswig. This arrangement came to an end with the Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War (German: ''Preußisch-Österreichischer Krieg''), also known by many other names,Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Second War of Unification, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), ''Deutsc ...
of 1866, which resulted in Schleswig and Holstein both being incorporated into Prussia as the Province of Schleswig-Holstein
The Province of Schleswig-Holstein ( ) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia (from 1868 to 1918) and the Free State of Prussia (from 1918 to 1946).
History
It was created from the Duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, which had been conquere ...
. Holstein, meanwhile including former Saxe-Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (, ), was a ''reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296 to 1803 and again from 1814 to 1876 in the extreme southeast region of what is now Schleswig-Holstein. Its territorial centre was in the modern district of Herz ...
(as of 1876) and the former Free and Hanseatic City of Lübeck
Free may refer to:
Concept
* Freedom, the ability to act or change without constraint or restriction
* Emancipate, attaining civil and political rights or equality
* Free (''gratis''), free of charge
* Gratis versus libre, the difference betw ...
and Region of Lübeck (both as of 1937) regained statehood, now united with Schleswig, in 1946, when the British occupation government elevated the province to the State of Schleswig-Holstein, followed by the official dissolution of Prussia in 1947.
Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein
The Counts of Schauenburg and Holstein were titles of the Holy Roman Empire. The dynastic family came from the County of Schauenburg near Rinteln (district Schaumburg) on the Weser in Germany. Together with its ancestral possessions in Bückebur ...
'' and '' List of rulers of Schleswig-Holstein''.
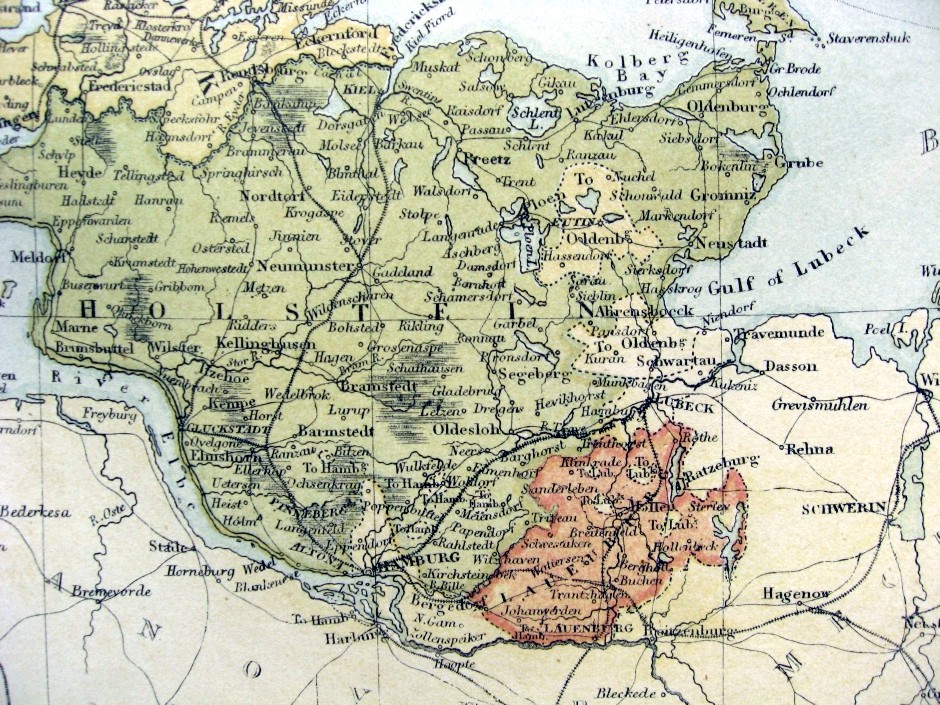
Geography
As of 1864, Holstein borderedDenmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
in the north, the Principality of Lübeck (formerly the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, an exclave of the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg (, also known as Holstein-Oldenburg) was a grand duchy within the German Confederation, North German Confederation and German Empire, that consisted of three widely separated territories: Oldenburg, Eutin and Bir ...
), the Free and Hanseatic City of Lübeck
Free may refer to:
Concept
* Freedom, the ability to act or change without constraint or restriction
* Emancipate, attaining civil and political rights or equality
* Free (''gratis''), free of charge
* Gratis versus libre, the difference betw ...
, and the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg in the east, and the Kingdom of Hanover
The Kingdom of Hanover () was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic Wars, Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Hanover, and j ...
and the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and 7th-largest in the European Union with a population of over 1.9 million. The Hamburg Metropolitan Region has a ...
in the south. It also borders the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
in the west and the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
in the east. Its only major island is Fehmarn, originally a part of the Duchy of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig (; ; ; ; ; ) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been div ...
until 1867.
Cities in Holstein included Kiel
Kiel ( ; ) is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein. With a population of around 250,000, it is Germany's largest city on the Baltic Sea. It is located on the Kieler Förde inlet of the Ba ...
, Altona, Glückstadt
Glückstadt (; ) is a town in the Steinburg district of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is located on the right bank of the Lower Elbe at the confluence of the small Rhin river, about northwest of Altona. Glückstadt is part of the Hamburg ...
, Rendsburg
Rendsburg (, also ''Rensborg'', , also ''Rensborg'') is a town on the Eider (river), River Eider and the Kiel Canal in the central part of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is the capital of the ''Kreis'' (district) of Rendsburg-Eckernfoerde, Rends ...
, Segeberg, Heiligenhafen, Oldenburg in Holstein, and Plön. It had an area of 8,385 km2.
Notes
References
External links
Map of Schleswig-Holstein in 1730
{{Coord, 54.1667, N, 9.66667, E, source:kolossus-nowiki, display=title History of Schleswig-Holstein Counties of the Holy Roman Empire States and territories established in 1474 Regions of Schleswig-Holstein